Kingdom of Bohemia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kingdom of Bohemia (), sometimes referenced in English literature as the Czech Kingdom, was a
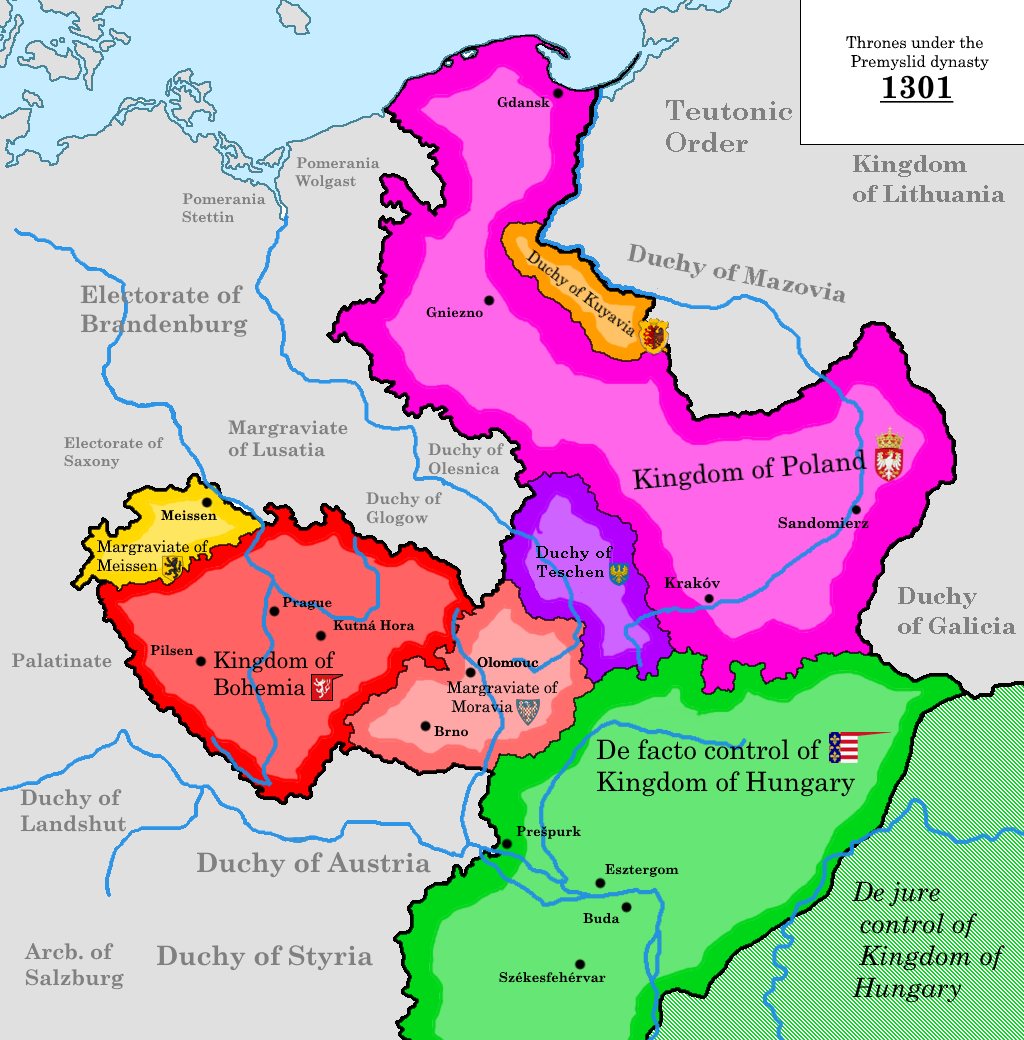 The 14th century – particularly the reign of Charles IV (1342–78) – is considered the Golden Age of Czech history. In 1306, the Přemyslid line died out and, after a series of dynastic wars, John, Count of Luxembourg, was elected Bohemian king. He married Elisabeth, the daughter of Wenceslaus II. He was succeeded as king in 1346 by his son, Charles IV, the second king from the House of Luxembourg. Charles was raised at the French court and was cosmopolitan in attitude.
Charles IV strengthened the power and prestige of the Bohemian kingdom. In 1344 he elevated the bishopric of
The 14th century – particularly the reign of Charles IV (1342–78) – is considered the Golden Age of Czech history. In 1306, the Přemyslid line died out and, after a series of dynastic wars, John, Count of Luxembourg, was elected Bohemian king. He married Elisabeth, the daughter of Wenceslaus II. He was succeeded as king in 1346 by his son, Charles IV, the second king from the House of Luxembourg. Charles was raised at the French court and was cosmopolitan in attitude.
Charles IV strengthened the power and prestige of the Bohemian kingdom. In 1344 he elevated the bishopric of
 Hus's death sparked the
Hus's death sparked the  When Sigismund died in 1437, the Bohemian estates elected Albert of Austria as his successor. Albert died and his son,
When Sigismund died in 1437, the Bohemian estates elected Albert of Austria as his successor. Albert died and his son,
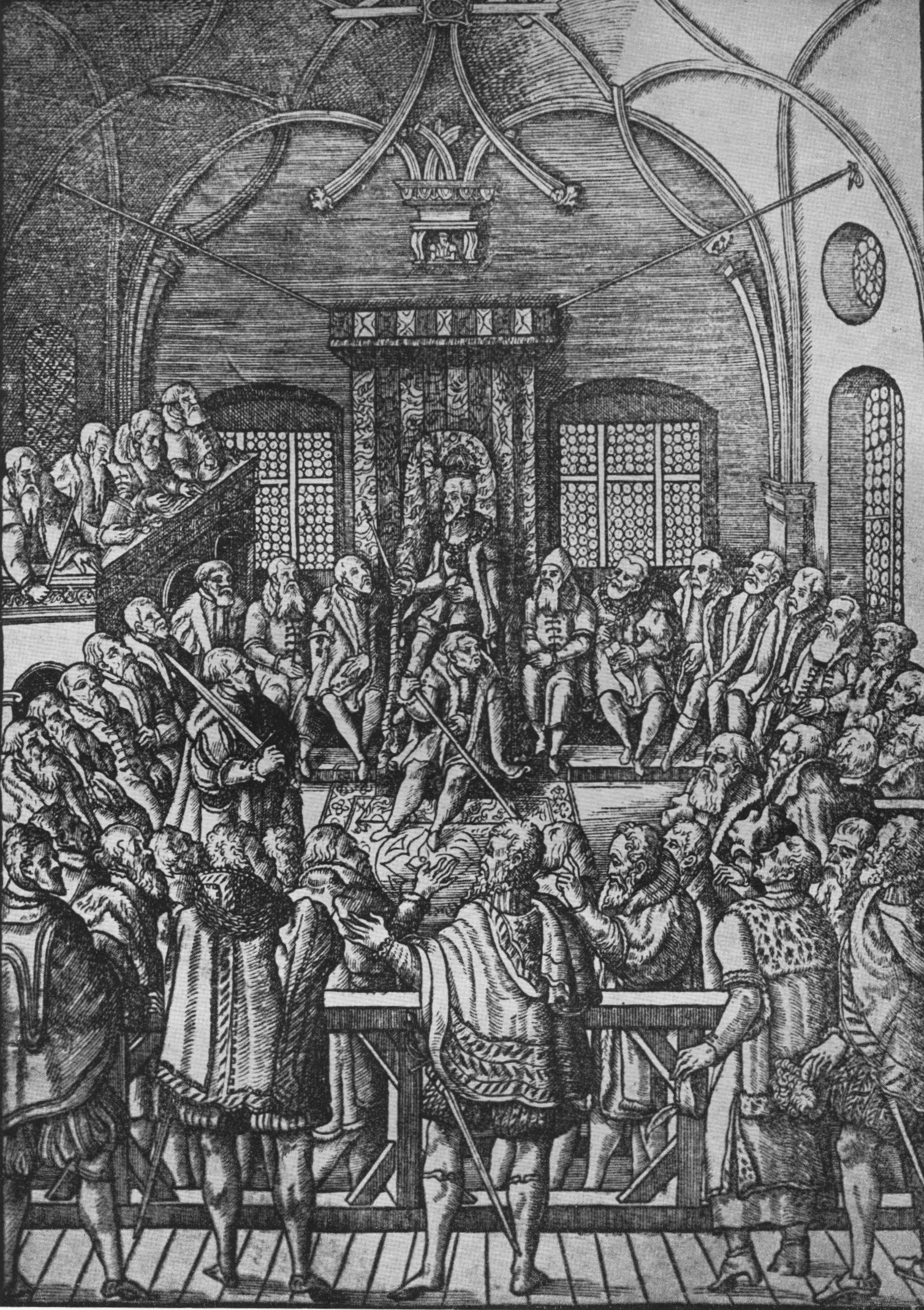 Upon the death of the Hussite king, George of Poděbrady, the Bohemian Diet elected the Polish prince Vladislaus of the Jagiellonian dynasty as king. In 1479, Mattias and Vladislaus made the Peace of Olomouc, which ceded some of Bohemia's territory to Hungary ended the Bohemian–Hungarian War. After Matthias died in 1490, the Diet of Hungary elected Vladislaus as king of Hungary as well, holding both Bohemia and the
Upon the death of the Hussite king, George of Poděbrady, the Bohemian Diet elected the Polish prince Vladislaus of the Jagiellonian dynasty as king. In 1479, Mattias and Vladislaus made the Peace of Olomouc, which ceded some of Bohemia's territory to Hungary ended the Bohemian–Hungarian War. After Matthias died in 1490, the Diet of Hungary elected Vladislaus as king of Hungary as well, holding both Bohemia and the
 Bohemia was among the first countries in Europe to become industrialized. Mining of tin and silver began in
Bohemia was among the first countries in Europe to become industrialized. Mining of tin and silver began in
medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
and early modern
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
monarchy in Central Europe. It was the predecessor state of the modern Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the south ...
.
The Kingdom of Bohemia was an Imperial State
An Imperial Estate (; , plural: ') was an entity or an individual of the Holy Roman Empire with representation and the right to vote in the Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire), Imperial Diet ('). Rulers of these Estates were able to exercise signi ...
in the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
. The Bohemian king was a prince-elector of the empire. The kings of Bohemia, besides the region of Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
itself, also ruled other lands belonging to the Bohemian Crown, which at various times included Moravia
Moravia ( ; ) is a historical region in the eastern Czech Republic, roughly encompassing its territory within the Danube River's drainage basin. It is one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The medieval and early ...
, Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
, Lusatia, and parts of Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
, Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
, and Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
.
The kingdom was established by the Přemyslid dynasty
The Přemyslid dynasty or House of Přemysl (, , ) was a Bohemian royal dynasty that reigned in the Duchy of Bohemia and later Kingdom of Bohemia and Margraviate of Moravia (9th century–1306), as well as in parts of Poland (including Silesia ...
in the 12th century by the Duchy of Bohemia, later ruled by the House of Luxembourg, the Jagiellonian dynasty, and from 1526 the House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful Dynasty, dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout ...
and its successor, the House of Habsburg-Lorraine
The House of Habsburg-Lorraine () originated from the marriage in 1736 of Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor, Francis III, Duke of Lorraine and Bar, and Maria Theresa of Habsburg monarchy, Austria, later successively List of Bohemian monarchs, Queen ...
. Numerous kings of Bohemia were also elected Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans (disambiguation), Emperor of the Romans (; ) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period (; ), was the ruler and h ...
s, and the capital, Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
, was the imperial seat in the late 14th century, and again at the end of the 16th and the beginning of the 17th centuries.
Shortly before the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, the kingdom became part of the newly proclaimed Habsburg Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
, and subsequently the Austro-Hungarian Empire from 1867. Bohemia retained its name and formal status as a separate Kingdom of Bohemia until 1918, known as a crown land within the Austro-Hungarian Empire, and its capital Prague was one of the empire's leading cities. The Czech language (called the Bohemian language in English usage until the 19th century) was the main language of the Diet and the nobility until 1627 (after the Bohemian Revolt was suppressed). German was then formally made equal with Czech and eventually prevailed as the language of the Diet until the Czech National Revival in the 19th century. German was also widely used as the language of administration in many towns after the Germans immigrated and populated some areas of the country in the 13th century. The royal court used the Czech, Latin, and German languages, depending on the ruler and period.
Following the defeat of the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,; ; , ; were one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914–1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulga ...
in World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, both the Kingdom and Empire were dissolved. Bohemia became the core part of the newly formed Czechoslovak Republic.
History
13th century (growth)
Although some former rulers of Bohemia had enjoyed a non-hereditary royal title during the 11th and 12th centuries ( Vratislaus II, Vladislaus II), the kingdom was formally established (by elevating Duchy of Bohemia) in 1198 by Přemysl Ottokar I, who had his status acknowledged by Philip of Swabia, electedKing of the Romans
King of the Romans (; ) was the title used by the king of East Francia following his election by the princes from the reign of Henry II (1002–1024) onward.
The title originally referred to any German king between his election and coronatio ...
, in return for his support against the rival Emperor Otto IV. In 1204 Ottokar's royal status was accepted by Otto IV as well as by Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III (; born Lotario dei Conti di Segni; 22 February 1161 – 16 July 1216) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 until his death on 16 July 1216.
Pope Innocent was one of the most power ...
. It was officially recognized in 1212 by the Golden Bull of Sicily issued by Emperor Frederick II, elevating the Duchy of Bohemia to Kingdom status and proclaiming its independence which was also later bolstered by future king of Bohemia and emperor Charles IV, with his golden bull in 1356.
Under these terms, the Czech king was to be exempt from all future obligations to the Holy Roman Empire except for participation in the imperial councils. The imperial prerogative to ratify each Bohemian ruler and to appoint the bishop of Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
was revoked. The king's successor was his son Wenceslaus I, from his second marriage.
Wenceslaus I's sister Agnes, later canonized, refused to marry the Holy Roman Emperor and instead devoted her life to spiritual works. Corresponding with the Pope, she established the Knights of the Cross with the Red Star in 1233, the first military order in the Kingdom of Bohemia. Four other military orders were present in Bohemia: the Order of St. John of Jerusalem from ; the Order of Saint Lazarus from the late 12th century; the Teutonic Order
The Teutonic Order is a religious order (Catholic), Catholic religious institution founded as a military order (religious society), military society in Acre, Israel, Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Sa ...
from c. 1200–1421; and the Knights Templar
The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon, mainly known as the Knights Templar, was a Military order (religious society), military order of the Catholic Church, Catholic faith, and one of the most important military ord ...
from 1232 to 1312.
The 13th century was the most dynamic period of the Přemyslid reign over Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
. German Emperor Frederick II's preoccupation with Mediterranean affairs and the dynastic struggles known as the Great Interregnum (1254–73) weakened imperial authority in Central Europe, thus providing opportunities for Přemyslid assertiveness. At the same time, the Mongol invasions (1220–42) absorbed the attention of Bohemia's eastern neighbors, Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
.
Přemysl Ottokar II (1253–78) married a German princess, Margaret of Babenberg, and became duke of Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
. He thereby acquired Upper Austria
Upper Austria ( ; ; ) is one of the nine States of Austria, states of Austria. Its capital is Linz. Upper Austria borders Germany and the Czech Republic, as well as the other Austrian states of Lower Austria, Styria, and Salzburg (state), Salzbur ...
, Lower Austria
Lower Austria ( , , abbreviated LA or NÖ) is one of the nine states of Austria, located in the northeastern corner of the country. Major cities are Amstetten, Lower Austria, Amstetten, Krems an der Donau, Wiener Neustadt and Sankt Pölten, which ...
, and part of Styria
Styria ( ; ; ; ) is an Austrian Federal states of Austria, state in the southeast of the country. With an area of approximately , Styria is Austria's second largest state, after Lower Austria. It is bordered to the south by Slovenia, and cloc ...
. He conquered the rest of Styria, most of Carinthia, and parts of Carniola. He was called "the king of iron and gold" (iron because of his conquests, gold because of his wealth). He campaigned as far as Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
, where he defeated the pagan natives and in 1256, founded a city he named Královec in Czech, which later became Königsberg
Königsberg (; ; ; ; ; ; , ) is the historic Germany, German and Prussian name of the city now called Kaliningrad, Russia. The city was founded in 1255 on the site of the small Old Prussians, Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teuton ...
(now Kaliningrad).
In 1260, Ottokar defeated Béla IV, king of Hungary in the Battle of Kressenbrunn near the Morava river, where more than 200,000 men clashed. He ruled an area from Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
to the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Se ...
. From 1273, however, Habsburg king Rudolf began to reassert imperial authority, checking Ottokar's power. He also had problems with rebellious nobility in Bohemia. All of Ottokar's German possessions were lost in 1276, and in 1278 he was abandoned by part of the Czech nobility and died in the Battle on the Marchfeld
The Battle on the Marchfeld (''i.e. Morava (river), Morava Field''; ; ; ); at Dürnkrut, Austria, Dürnkrut and Jedenspeigen took place on 26 August 1278 and was a decisive event for the history of Central Europe for the following centuries. T ...
against Rudolf.
Ottokar was succeeded by his son King Wenceslaus II, who was crowned King of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
in 1300. Wenceslaus II's son Wenceslaus III was crowned King of Hungary a year later. At this time, the Kings of Bohemia ruled from Hungary to the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
.
The 13th century was also a period of large-scale German immigration, during the , often encouraged by the Přemyslid kings. The Germans populated towns and mining districts on the Bohemian periphery and in some cases formed German colonies in the interior of the Czech lands. Stříbro, Kutná Hora, Německý Brod (present-day Havlíčkův Brod), and Jihlava were important German settlements. The Germans brought their own code of law – the ' – which formed the basis of the later commercial law of Bohemia and Moravia
Moravia ( ; ) is a historical region in the eastern Czech Republic, roughly encompassing its territory within the Danube River's drainage basin. It is one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The medieval and early ...
. Marriages between Czech nobles and Germans soon became commonplace.
14th century ("Golden Age")
 The 14th century – particularly the reign of Charles IV (1342–78) – is considered the Golden Age of Czech history. In 1306, the Přemyslid line died out and, after a series of dynastic wars, John, Count of Luxembourg, was elected Bohemian king. He married Elisabeth, the daughter of Wenceslaus II. He was succeeded as king in 1346 by his son, Charles IV, the second king from the House of Luxembourg. Charles was raised at the French court and was cosmopolitan in attitude.
Charles IV strengthened the power and prestige of the Bohemian kingdom. In 1344 he elevated the bishopric of
The 14th century – particularly the reign of Charles IV (1342–78) – is considered the Golden Age of Czech history. In 1306, the Přemyslid line died out and, after a series of dynastic wars, John, Count of Luxembourg, was elected Bohemian king. He married Elisabeth, the daughter of Wenceslaus II. He was succeeded as king in 1346 by his son, Charles IV, the second king from the House of Luxembourg. Charles was raised at the French court and was cosmopolitan in attitude.
Charles IV strengthened the power and prestige of the Bohemian kingdom. In 1344 he elevated the bishopric of Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
, making it an archbishopric and freeing it from the jurisdiction of Mainz
Mainz (; #Names and etymology, see below) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, and with around 223,000 inhabitants, it is List of cities in Germany by population, Germany's 35th-largest city. It lies in ...
, and the archbishop was given the right to crown Bohemian kings. Charles curbed the Bohemian, Moravian, and Silesian nobility, and rationalized the provincial administration of Bohemia and Moravia. He created the Crown of Bohemia, incorporating Moravia, Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
and Lusatia.
In 1355 Charles was crowned Holy Roman Emperor. The next year he issued the Golden Bull of 1356, defining and codifying the process of election to the Imperial throne, with the Bohemian king among the seven electors. Issuance of the Golden Bull together with the ensuing acquisition of the Brandenburg Electorate gave the Luxemburgs two votes in the electoral college. Charles also made Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
into an Imperial capital.
Extensive building projects undertaken by the king included the founding of the New Town southeast of the old city. The royal castle, Hradčany, was rebuilt. Of particular significance was the founding of Charles University in Prague in 1348. Charles intended to make Prague into an international center of learning, and the university was divided into Czech, Polish, Saxon, and Bavarian "nations", each with one controlling vote. Charles University, however, would become the nucleus of intense Czech particularism.
Charles died in 1378, and the Bohemian crown went to his son, Wenceslas IV. He had also been elected King of the Romans
King of the Romans (; ) was the title used by the king of East Francia following his election by the princes from the reign of Henry II (1002–1024) onward.
The title originally referred to any German king between his election and coronatio ...
in 1376, in the first election since his father's Golden Bull. He was deposed from the Imperial throne in 1400, however, having never been crowned Emperor. His half-brother, Sigismund, was eventually crowned Emperor in Rome in 1433, ruling until 1437, and he was the last male member of the House of Luxemburg.
15th century (Hussite movement)
TheHussite
file:Hussitenkriege.tif, upright=1.2, Battle between Hussites (left) and Crusades#Campaigns against heretics and schismatics, Catholic crusaders in the 15th century
file:The Bohemian Realm during the Hussite Wars.png, upright=1.2, The Lands of the ...
movement (1402–85) was primarily a religious, as well as national, manifestation. As a religious reform movement (the so-called Bohemian Reformation
The Bohemian Reformation (also known as the Czech Reformation or Hussite Reformation), preceding the Reformation of the 16th century, was a Christian movement in the late medieval and early modern Kingdom of Bohemia, Kingdom and Lands of the Bo ...
), it represented a challenge to papal authority and an assertion of national autonomy in ecclesiastical affairs. The Hussites defeated four crusades from the Holy Roman Empire, and the movement is viewed by many as a part of the (worldwide) Protestant Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the papacy and ...
. Because many of warriors of the crusades were Germans, although many were also Hungarians and Catholic Czechs, the Hussite movement is seen as a Czech national movement. In modern times it acquired anti-imperial and anti-German associations and has sometimes been identified as a manifestation of a long-term ethnic Czech–German conflict.
Hussitism began during the long reign of Wenceslaus IV (1378–1419), a period of papal schism and concomitant anarchy in the Holy Roman Empire. It was precipitated by a controversy at Charles University in Prague. In 1403 Jan Hus
Jan Hus (; ; 1369 – 6 July 1415), sometimes anglicized as John Hus or John Huss, and referred to in historical texts as ''Iohannes Hus'' or ''Johannes Huss'', was a Czechs, Czech theologian and philosopher who became a Church reformer and t ...
became rector of the university. A reformist preacher, Hus espoused the anti-papal and anti-hierarchical teachings of John Wycliffe
John Wycliffe (; also spelled Wyclif, Wickliffe, and other variants; 1328 – 31 December 1384) was an English scholastic philosopher, Christianity, Christian reformer, Catholic priest, and a theology professor at the University of Oxfor ...
of England, often referred to as the "Morning Star of the Reformation". Hus' teaching was distinguished by its rejection of what he saw as the wealth, corruption, and hierarchical tendencies of the Catholic Church. He advocated the Wycliffe doctrine of clerical purity and poverty, and insisted on the laity receiving communion under both kinds, bread and wine. (The Catholic Church in practice reserved the cup, or wine, for the clergy.) The more moderate followers of Hus, the Utraquists, took their name from the Latin ', meaning "under each kind". The Taborites, a more radical sect, soon formed, taking their name from the town of Tábor
Tábor (; ) is a town in the South Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 34,000 inhabitants, making it the second most populated town in the region. The town was founded by the Hussites in 1420. The historic town centre is well pres ...
, their stronghold in southern Bohemia. They rejected church doctrine and upheld the Bible as the sole authority in all matters of belief.
Soon after Hus assumed office, German professors of theology demanded the condemnation of Wycliffe's writings. Hus protested, receiving the support of the Czech element at the university. Having only one vote in policy decisions against three for the Germans, the Czechs were outvoted, and the orthodox position was maintained. In subsequent years, the Czechs demanded a revision of the university charter, granting more adequate representation to the native Czech faculty. The university controversy was intensified by the vacillating position of the Bohemian king Wenceslas. His favoring of Germans in appointments to councillor and other administrative positions had aroused the nationalist sentiments of the Czech nobility and rallied them to Hus' defense. The German faculties had the support of Zbyněk Zajíc, Archbishop of Prague, and the German clergy. For political reasons, Wenceslas switched his support from the Germans to Hus and allied with the reformers. On 18 January 1409, Wenceslas issued the Decree of Kutná Hora: (as was the case at other major universities in Europe) the Czechs would have three votes; the others, a single vote. In consequence, German faculty and students left Charles University en masse in the thousands, and many ended up founding the University of Leipzig
Leipzig University (), in Leipzig in Saxony, Germany, is one of the world's oldest universities and the second-oldest university (by consecutive years of existence) in Germany. The university was founded on 2 December 1409 by Frederick I, Electo ...
.
Hus' victory was short-lived. He preached against the sale of indulgence
In the teaching of the Catholic Church, an indulgence (, from , 'permit') is "a way to reduce the amount of punishment one has to undergo for (forgiven) sins". The ''Catechism of the Catholic Church'' describes an indulgence as "a remission bef ...
s, which lost him the support of the king, who had received a percentage of such sales. In 1412 Hus and his followers were suspended from the university and expelled from Prague. For two years the reformers served as itinerant preachers throughout Bohemia. In 1414, Hus was summoned to the Council of Constance to defend his views. Imprisoned when he arrived, he was allowed no legal advocate for his defense; the council condemned him as a heretic and relinquished him to an imperial secular court, which decreed he be burned at the stake in 1415.
 Hus's death sparked the
Hus's death sparked the Hussite Wars
The Hussite Wars, also called the Bohemian Wars or the Hussite Revolution, were a series of civil wars fought between the Hussites and the combined Catholic forces of Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund, the Papacy, a ...
, decades of religious warfare. Sigismund, the pro-papal king of Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
and successor to the Bohemian throne after the death of Wenceslas in 1419, failed repeatedly to gain control of the kingdom despite aid by Hungarian and German armies. Riots broke out in Prague. Led by a Czech yeoman, Jan Žižka, the Taborites streamed into the capital. Religious strife pervaded the entire kingdom and was particularly intense in the German-dominated towns. Hussite Czechs and Catholic Germans turned on each other; many were massacred, and many German survivors fled or were exiled to the rest of the Holy Roman Empire. Emperor Sigismund led or instigated various crusades against Bohemia with the support of Hungarians and Bohemian Catholics.
The Hussite Wars followed a pattern. When a crusade was launched against Bohemia, moderate and radical Hussites would unite and defeat it. Once the threat was over, the Hussite armies would focus on raiding the land of Catholic sympathizers. Many historians have painted the Hussites as religious fanatics; they fought in part for a nationalist purpose: to protect their land from a King and a Pope who did not recognize the right of the Hussites to exist. Žižka led armies to storm castles, monasteries, churches, and villages, expelling the Catholic clergy, expropriating ecclesiastical lands, or accepting conversions.
During the struggle against Sigismund, Taborite armies penetrated into areas of modern-day Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
as well. Czech refugees from the religious wars in Bohemia settled there, and from 1438 to 1453 a Czech noble, John Jiskra of Brandýs, controlled most of southern Slovakia from the centers of Zólyom (today Zvolen) and Kassa (today Košice
Košice is the largest city in eastern Slovakia. It is situated on the river Hornád at the eastern reaches of the Slovak Ore Mountains, near the border with Hungary. With a population of approximately 230,000, Košice is the second-largest cit ...
). Thus Hussite doctrines and the Czech Bible were disseminated among the Slovaks, providing the basis for a future link between the Czechs and their Slovak neighbors.
 When Sigismund died in 1437, the Bohemian estates elected Albert of Austria as his successor. Albert died and his son,
When Sigismund died in 1437, the Bohemian estates elected Albert of Austria as his successor. Albert died and his son, Ladislaus the Posthumous
Ladislaus V, more commonly known as Ladislaus the Posthumous (; ; ; ; 22 February 144023 November 1457), was Duke of Austria and King of Hungary, King of Croatia, Croatia and King of Bohemia, Bohemia. He was the posthumous birth, posthumous son ...
– so called because he was born after his father's death – was acknowledged as king. During Ladislaus' minority, Bohemia was ruled by a regency composed of moderate reform nobles who were Utraquists. Internal dissension among the Czechs provided the primary challenge to the regency. A part of the Czech nobility remained Catholic and loyal to the pope. A Utraquist delegation to the Council of Basel in 1433 had negotiated a seeming reconciliation with the Catholic Church. The Compacts of Basel accepted the basic tenets of Hussitism expressed in the Four Articles of Prague: communion under both kinds; free preaching of the Gospels; expropriation of church land; and exposure and punishment of public sinners. The pope, however, rejected the compact, thus preventing the reconciliation of Czech Catholics with the Utraquists.
George of Poděbrady, later to become the "national" king of Bohemia, emerged as leader of the Utraquist regency. George installed another Utraquist, John of Rokycany, as archbishop of Prague and succeeded in uniting the more radical Taborites with the Czech Reformed Church. The Catholic party was driven out of Prague. After Ladislaus died of leukemia in 1457, the following year the Bohemian estates elected George of Poděbrady as king. Although George was noble-born, he was not a successor of royal dynasty; his election to the monarchy was not recognised by the Pope, or any other European monarchs.
George sought to establish a "Charter of a Universal Peace Union". He believed that all monarchs should work for a sustainable peace on the principle of national sovereignty of states, principles of non-interference, and solving problems and disputes before an International Tribunal. Also, Europe should unite to fight the Turks. States would have one vote each, with a leading role for France. George did not see a specific role for Papal authority.
Czech Catholic nobles joined in the League of Zelená Hora in 1465, challenging the authority of George of Poděbrady; the next year, Pope Paul II excommunicated George. The Bohemian War (1468-1478) pitted Bohemia against Matthias Corvinus
Matthias Corvinus (; ; ; ; ; ) was King of Hungary and King of Croatia, Croatia from 1458 to 1490, as Matthias I. He is often given the epithet "the Just". After conducting several military campaigns, he was elected King of Bohemia in 1469 and ...
and Frederick III of Habsburg, and the Hungarian forces occupied most of Moravia. George of Poděbrady died in 1471.
After 1471: Jagiellonian and Habsburg rule
 Upon the death of the Hussite king, George of Poděbrady, the Bohemian Diet elected the Polish prince Vladislaus of the Jagiellonian dynasty as king. In 1479, Mattias and Vladislaus made the Peace of Olomouc, which ceded some of Bohemia's territory to Hungary ended the Bohemian–Hungarian War. After Matthias died in 1490, the Diet of Hungary elected Vladislaus as king of Hungary as well, holding both Bohemia and the
Upon the death of the Hussite king, George of Poděbrady, the Bohemian Diet elected the Polish prince Vladislaus of the Jagiellonian dynasty as king. In 1479, Mattias and Vladislaus made the Peace of Olomouc, which ceded some of Bohemia's territory to Hungary ended the Bohemian–Hungarian War. After Matthias died in 1490, the Diet of Hungary elected Vladislaus as king of Hungary as well, holding both Bohemia and the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
in personal union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent in ...
.
The Jagiellonian dynasty governed Bohemia as absentee monarchs because the Hungarian nobility insisted on them putting their capital into Hungary; their influence in the kingdom was minimal, and effective government fell to the regional nobility. Czech Catholics accepted the Compacts of Basel in 1485 and were reconciled with the Utraquist Hussites. The Bohemian estrangement from the Empire continued; not considered an Imperial State
An Imperial Estate (; , plural: ') was an entity or an individual of the Holy Roman Empire with representation and the right to vote in the Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire), Imperial Diet ('). Rulers of these Estates were able to exercise signi ...
, the Lands of the Bohemian Crown were not part of the Imperial Circles established by the 1500 Imperial Reform.
In 1526, Vladislaus's son, King Louis II of Hungary
Louis II (; ; ; ; 1 July 1506 – 29 August 1526) was King of Hungary, King of Croatia, Croatia and King of Bohemia, Bohemia from 1516 to 1526. He died during the Battle of Mohács fighting the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans, whose victory led to the Ot ...
, was killed at the Battle of Mohács, fighting the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
. Louis' death ended the Jagiellonian dynasty in Bohemia and Hungary; Louis' lands were partitioned between the Ottoman Empire, the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
, and the newly formed Eastern Hungarian Kingdom
The Eastern Hungarian Kingdom ( ) is a modern term coined by some historians to designate the realm of John Zápolya and his son John Sigismund Zápolya, who contested the claims of the House of Habsburg to rule the Kingdom of Hungary from 1526 ...
. The Bohemian Diet elected Louis' brother-in-law, Archduke Ferdinand
Ferdinand is a Germanic name composed of the elements "journey, travel", Proto-Germanic , abstract noun from root "to fare, travel" (PIE , "to lead, pass over"), and "courage" or "ready, prepared" related to Old High German "to risk, ventu ...
, as the new king of Boehmia, beginning almost four centuries of Habsburg rule for both Bohemia and Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
.
From 1599 to 1711, Moravia (a Land of the Bohemian Crown) was frequently subjected to raids by the Ottoman Empire and its vassals (especially the Tatars
Tatars ( )Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
and in the Collins English Dictionary are a group of Turkic peoples across Eas ...
Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
). Overall, hundreds of thousands were enslaved whilst tens of thousands were killed.
The incorporation of Bohemia into the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
against the resistance of the local Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
nobility sparked the 1618 Defenestration of Prague, the brief reign of the Winter King, and the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
. Their defeat at the Battle of White Mountain in 1620 put an end to the Bohemian autonomy movement. In 1624, Emperor Ferdinand II issued a patent that allowed only the Catholic religion in Bohemia.
Defeat and dissolution
In 1740 the Prussian Army conquered BohemianSilesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
in the Silesian Wars and forced Maria Theresa in 1742 to cede the majority of Silesia, except the southernmost area with the duchies of Cieszyn, Krnov and Opava, to Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
. In 1756 Prussian King Frederick II faced an enemy coalition led by Austria, when Maria Theresa was preparing for war with Prussia to reclaim Silesia. The Prussian army conquered Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
and in 1757 invaded Bohemia. In the Battle of Prague (1757) Battle of Prague may refer to:
* Battle of White Mountain (1620), an early battle in the Thirty Years' War
* Battle of Prague (1648), the last action of the Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Prague (1742), a siege during the War of the Austrian Successi ...
they defeated the Habsburgs and subsequently occupied Prague. More than one quarter of Prague was destroyed and the St. Vitus Cathedral suffered heavy damage. In the Battle of Kolín, however, Frederick lost and had to vacate Prague and retreat from Bohemia.
With the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, the Bohemian kingdom was incorporated into the now two years old Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
and the royal title retained alongside the title of Austrian Emperor. In the course of the 1867 Austro-Hungarian Compromise the provinces of Bohemia, Moravia and Austrian Silesia became '' k. k.'' crown lands of Cisleithania. The Bohemian Kingdom officially ceased to exist in 1918 by transformation into the Czechoslovak Republic.
The current Czech Republic consisting of Bohemia, Moravia and Czech Silesia still uses most of the symbols of the Kingdom of Bohemia: a two-tailed lion in its coat-of-arms, red-white stripes in the state flag and the royal castle as the president's office.
Economy
 Bohemia was among the first countries in Europe to become industrialized. Mining of tin and silver began in
Bohemia was among the first countries in Europe to become industrialized. Mining of tin and silver began in Ore mountains
The Ore Mountains (, or ; ) lie along the Czech–German border, separating the historical regions of Bohemia in the Czech Republic and Saxony in Germany. The highest peaks are the Klínovec in the Czech Republic (German: ''Keilberg'') at ab ...
in early 12th century. The German hospes had a major role in the industrial development of the Czech Kingdom. In the late 12th and in the 13th century the Přemyslid rulers promoted the colonisation of certain areas of their lands by German settlers from the adjacent lands of Bavaria, Franconia, Upper Saxony and Austria during the migration. The new settlers not only brought their customs and language with them, but also new technical skills and equipment that were adapted within a few decades, especially in agriculture and crafts.
In Silesia it had doubled (16% of the total area) by the beginning of the 11th century, 30% in the 16th century and the highest increase rates in the 14th century, the total area of arable land increased seven – to twentyfold in many Silesian regions during the . They settled mostly the hills and mountains and started the mine works and high qualities industry such as metal works, weapon industry and beer making. Forest glass production was a common industry for German Bohemians.
Lands of the Bohemian Crown
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
proper () with the County of Kladsko () was the main area of the Kingdom of Bohemia. The Egerland () was ultimately obtained by King Wenceslaus II between 1291 and 1305; given in pawn to Bohemia by King Louis IV of Germany in 1322 and subsequently joined in personal union with Bohemia proper. In 1348 Charles IV created the Crown of Bohemia (), together with the incorporated provinces:
* the Margraviate of Moravia (), acquired by Přemyslid and Slavník Bohemian rulers after the 955 Battle of Lechfeld, lost in 999 to Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
and reconquered by Duke Bretislaus I in 1019/1029 (uncertain dating);
* Upper Lusatia
Upper Lusatia (, ; , ; ; or ''Milsko''; ) is a historical region in Germany and Poland. Along with Lower Lusatia to the north, it makes up the region of Lusatia, named after the Polabian Slavs, Slavic ''Lusici'' tribe. Both parts of Lusatia a ...
(), incorporated by Charles' father King John of Bohemia
John of Bohemia, also called the Blind or of Luxembourg (; ; ; 10 August 1296 – 26 August 1346), was the Count of Luxembourg from 1313 and King of Bohemia from 1310 and titular King of Poland. He is well known for having died while fighting ...
in 1319 ( Bautzen Land) and 1329 (Görlitz
Görlitz (; ; ; ; ; Lusatian dialects, East Lusatian: , , ) is a town in the Germany, German state of Saxony. It is on the river Lusatian Neisse and is the largest town in Upper Lusatia, the second-largest town in the region of Lusatia after ...
), and Lower Lusatia
Lower Lusatia (; ; ; ; ) is a historical region in Central Europe, stretching from the southeast of the Germany, German state of Brandenburg to the southwest of Lubusz Voivodeship in Poland. Like adjacent Upper Lusatia in the south, Lower Lusa ...
(, former March of Lusatia), acquired by Charles IV from the Wittelsbach duke Otto V of Bavaria in 1367. The Habsburg emperor Ferdinand II ceded the Lusatias to the Electorate of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony, also known as Electoral Saxony ( or ), was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire from 1356 to 1806 initially centred on Wittenberg that came to include areas around the cities of Dresden, Leipzig and Chemnitz. It was a ...
by the 1635 Peace of Prague;
* the Duchies of Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
(), acquired by the 1335 Treaty of Trentschin between King John of Bohemia and King Casimir III of Poland. Queen Maria Theresa lost Silesia in 1742 to the Prussian king Frederick the Great by the Treaty of Breslau, with the exception of Austrian Silesia.
* the northern part of the Upper Palatinate (" Bohemian Palatinate") at Sulzbach, incorporated into the Bohemian crown by Charles IV in 1355. Charles exchanged parts of this territory for Brandenburg in 1373, while his son Wenceslaus lost the rest in 1400 to the Electorate of the Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate was a Imperial State, constituent state of the Holy Roman Empire until it was annexed by the Electorate of Baden in 1803. From the end of the 13th century, its ruler was one of the Prince-electors who elected the Holy ...
under King Rupert of Germany;
* the Brandenburg Electorate, acquired in 1373 by Charles IV from the Wittelsbach duke Otto V of Bavaria. Charles' son Emperor Sigismund granted Brandenburg to Frederick I of Hohenzollern in 1415.
at times were incorporated into the Kingdom of Bohemia these provinces:
* the Duchy of Austria in 1251, the Duchy of Styria
The Duchy of Styria (; ; ) was a duchy located in modern-day southern Austria and northern Slovenia. It was a part of the Holy Roman Empire until its dissolution in 1806 and a Cisleithanian crown land of Austria-Hungary until its dissolution i ...
in 1261, the Egerland in 1266, the Duchy of Carinthia with the March of Carniola
March is the third month of the year in both the Julian and Gregorian calendars. Its length is 31 days. In the Northern Hemisphere, the meteorological beginning of spring occurs on the first day of March. The March equinox on the 20 or 21 ...
and the Windic March in 1269, and the March of Friuli
Friuli (; ; or ; ; ) is a historical region of northeast Italy. The region is marked by its separate regional and ethnic identity predominantly tied to the Friulians, who speak the Friulian language. It comprises the major part of the autono ...
in 1272, all acquired by the Přemyslid king Ottokar II of Bohemia but lost to Rudolph of Habsburg in the 1278 Battle on the Marchfeld
The Battle on the Marchfeld (''i.e. Morava (river), Morava Field''; ; ; ); at Dürnkrut, Austria, Dürnkrut and Jedenspeigen took place on 26 August 1278 and was a decisive event for the history of Central Europe for the following centuries. T ...
;
The modern Czech Republic (Czechia) is the legal successor of the Crown of Bohemia, as stated in the preamble to its Constitution.
Administrative division
Kraje/Kreise of Bohemia (pre-1833)
Prior to 1833, Bohemia was divided into seven to sixteen district units, known in Czech as ( ) and in German as ( ). These included the following in different time periods: * at Bechyně () * atMladá Boleslav
Mladá Boleslav (; ) is a city in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 47,000 inhabitants. It lies on the left bank of the Jizera (river), Jizera River.
Mladá Boleslav is the second most populated city in the region. I ...
()
* at Čáslav ()
* at Chrudim
* at Hradec Králové ()
*the County of Kladsko at Kladsko (); lost to Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
following the First Silesian War (1740–42)
* at Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
(, ); named for Kouřim ()
* at Litoměřice ()
* at Loket
Loket (; ) is a town in Sokolov District in the Karlovy Vary Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 3,100 inhabitants. The town is known for the Loket Castle, a 12th-century Gothic castle. The historic town centre is well preserved and is pr ...
()
* at Plzeň
Plzeň (), also known in English and German as Pilsen (), is a city in the Czech Republic. It is the Statutory city (Czech Republic), fourth most populous city in the Czech Republic with about 188,000 inhabitants. It is located about west of P ...
()
* or at Beroun ()
* Prácheňsko or Prácheňský kraj at Písek (; named after )
* at Rakovník ()
* at Slaný ()
* at Vltava
The Vltava ( , ; ) is the longest river in the Czech Republic, a left tributary of the Elbe River. It runs southeast along the Bohemian Forest and then north across Bohemia, through Český Krumlov, České Budějovice, and Prague. It is com ...
()
* at Žatec ()
Kraje/Kreise 1833–1849
According to Johann Gottfried Sommer Bohemia was divided into 16 district units between 1833 and 1849: *Berounský kraj (German: ) *Bydžovský kraj at Nový Bydžov (German: ) *Budějovický kraj atČeské Budějovice
České Budějovice (; ) is a city in the South Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 97,000 inhabitants. The city is located in the valley of the Vltava River, at its confluence with the Malše.
České Budějovice is the largest ...
(German: )
*Boleslavský kraj (German: )
*Čáslavský kraj (German: )
*Chrudimský kraj (German: )
*Loketský kraj (German: )
*Kouřimský kraj (German: )
* at Klatovy (German: )
*Hradecký kraj (German: )
*Litoměřický kraj (German: )
*Plzeňský kraj (German: )
*Prácheňský kraj at Písek (German: ); named after Prácheň castle)
*Rakovnický kraj (German: )
* (German: )
*Žatecký kraj (German: )
Okresy/Bezirke 1849–1854
In 1849 the number of / was reduced to seven. They were then subdivided into political districts (German: or ('district captaincy'), ; Czech: ), which took over most of the political functions of the /. Prague became a statutory city, administered directly by the kingdom. A total of 79 districts existed during this period.Kraje/Kreise 1854–1868
In 1854 the political districts were abolished and the previous more centralised administrative structure largely restored. However, 13 new / were established in place of the old ones. These / were subdivided into between twelve and 20 (207 in total, plus the capital city of Prague); these acted merely as administrative units of the / rather than taking on powers of their own. Prague remained a statutory city, as well acting as the administrative centre of the /. The city of Reichenberg was a (city district) subordinate to the , as well as the seat of ; the two were counted together as a single .Gesetz vom 9. October 1854, RGBl. 274/1854: 11 of the / had a single district court (). These were located in the administrative centre of the /, except for the /, whose district court was located at Kutná Hora/Kuttenberg. The and ( and ) each had two district courts: Jung-Bunzlau and Reichenberg for the ; Leitmeritz and Böhmisch-Leipa for the .Okresy/Bezirke 1868–1954
In 1868 the / system was abolished and the political districts re-established. In 1868 Bohemia was divided into 89 political districts, each of which was constituted from between one and four of the 1854 administrative districts.Gesetz vom 10. Juli 1868, RGBl. 101/1868: This would grow to 104 districts by 1913. 1868 districts: * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * * * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * * (dissolved in 1884; Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * Prague (statutory city; German: '; Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (statutory city and seat of the '; Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: '; district seat: Prague) * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') * (Czech: ') Districts established after 1868: * (after 1908; Czech: ') * (after 1896; Czech: ') * (before 1913 part of the Falkenau district;Kundmachung vom 24. Oktober 1913, RGBl. 226/1913: Czech: ') * (from 1910; Czech: ') * (from 1905; Czech: ') * (from 1893) * (from 1884; Czech: ') * (before 1913 part of the Schlan district; Czech: ') * (from 1903; Czech: ') * (from 1902; Czech: ') * (before 1899 part of the ''Neustadt an der Mettau'' district; Czech: ') * (from 1910; Czech: ') * (from 1902; Czech: ') * (from 1896; Czech: ') * (from 1908; Czech: ') * (from 1898)Demographics
1910 census
Language distribution by district (1910)
See also
*List of Bohemian monarchs
The Duchy of Bohemia was established in 870 and raised to the Kingdom of Bohemia in Golden Bull of Sicily, 1198. Several Bohemian monarchs ruled as non-hereditary kings and first gained the title in 1085. From 1004 to 1806, Bohemia was part of th ...
* Crown of Saint Wenceslas
* History of the Czech lands
* Kingdom Come: Deliverance
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * *External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Kingdom Of Bohemia History of BohemiaBohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
Medieval Kingdom of Bohemia
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
Boh
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
States and territories established in 1198
States and territories disestablished in 1918
1198 establishments in Europe
1190s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire
1918 disestablishments in Austria-Hungary
2nd millennium in Bohemia
Lands of the Bohemian Crown