Kingdom Of France on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of
 For most of the reign of Louis XIV (1643–1715), ("The Sun King"), France was the dominant power in Europe, aided by the diplomacy of Cardinal Richelieu's successor as the King's chief minister, (1642–61) Cardinal Jules Mazarin, (1602–61). Cardinal Mazarin oversaw the creation of a French Royal Navy that rivalled England's, expanding it from 25 ships to almost 200. The size of the Army was also considerably increased. Renewed wars (the War of Devolution, 1667–68 and the Franco-Dutch War, 1672–78) brought further territorial gains (
For most of the reign of Louis XIV (1643–1715), ("The Sun King"), France was the dominant power in Europe, aided by the diplomacy of Cardinal Richelieu's successor as the King's chief minister, (1642–61) Cardinal Jules Mazarin, (1602–61). Cardinal Mazarin oversaw the creation of a French Royal Navy that rivalled England's, expanding it from 25 ships to almost 200. The size of the Army was also considerably increased. Renewed wars (the War of Devolution, 1667–68 and the Franco-Dutch War, 1672–78) brought further territorial gains (
 The reign (1715–74) of Louis XV saw an initial return to peace and prosperity under the regency (1715–23) of Philippe II, Duke of Orléans, whose policies were largely continued (1726–1743) by
The reign (1715–74) of Louis XV saw an initial return to peace and prosperity under the regency (1715–23) of Philippe II, Duke of Orléans, whose policies were largely continued (1726–1743) by


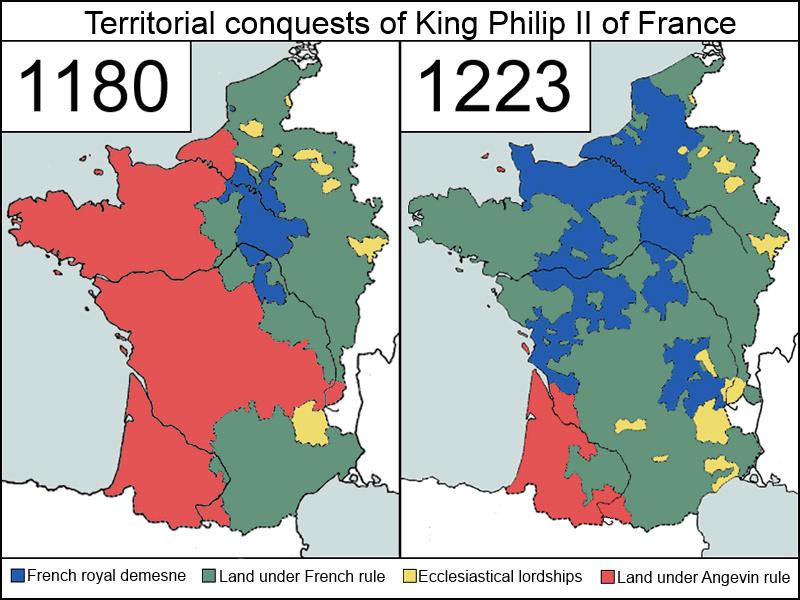 Before the 13th century, only a small part of what is now France was under control of the Frankish king; in the north there were Viking incursions leading to the formation of the
Before the 13th century, only a small part of what is now France was under control of the Frankish king; in the north there were Viking incursions leading to the formation of the
 Prior to the
Prior to the
excerpt and text search
* Caron, François. ''An Economic History of Modern France'' (1979
online edition
* Doyle, William. ''Old Regime France: 1648–1788'' (2001
excerpt and text search
* Duby, Georges. ''France in the Middle Ages 987–1460: From Hugh Capet to Joan of Arc'' (1993), survey by a leader of the Annales Schoo
excerpt and text search
* Fierro, Alfred. ''Historical Dictionary of Paris'' (1998) 392pp, an abridged translation of his ''Histoire et dictionnaire de Paris'' (1996), 1580pp * Goubert, Pierre. ''The Course of French History'' (1991), standard French textboo
excerpt and text search
als
complete text online
* Goubert, Pierre. ''Louis XIV and Twenty Million Frenchmen'' (1972), social history from Annales School * Haine, W. Scott. ''The History of France'' (2000), 280 pp. textbook
and text search
als
online edition
* * Holt, Mack P. ''Renaissance and Reformation France: 1500–1648'' (2002
excerpt and text search
* Jones, Colin, and Emmanuel Le Roy Ladurie. ''The Cambridge Illustrated History of France'' (1999
excerpt and text search
* Jones, Colin. ''The Great Nation: France from Louis XV to Napoleon'' (2002
excerpt and text search
* Jones, Colin. ''Paris: Biography of a City'' (2004), 592pp; comprehensive history by a leading British schola
excerpt and text search
* Le Roy Ladurie, Emmanuel. ''The Ancien Régime: A History of France 1610–1774'' (1999), survey by leader of the Annales Schoo
excerpt and text search
* Potter, David. ''France in the Later Middle Ages 1200–1500,'' (2003
excerpt and text search
* Potter, David. ''A History of France, 1460–1560: The Emergence of a Nation-State'' (1995) * Price, Roger. ''A Concise History of France'' (1993
excerpt and text search
* Raymond, Gino. ''Historical Dictionary of France'' (2nd ed. 2008) 528pp * Roche, Daniel. ''France in the Enlightenment'' (1998), wide-ranging history 1700–178
excerpt and text search
* Wolf, John B. ''Louis XIV'' (1968), the standard scholarly biograph
online edition
excerpt and text search vol 2 excerptsvol 3 excerpts
* Pinkney, David H. "Two Thousand Years of Paris," ''Journal of Modern History'' (1951) 23#3 pp. 262–26
in JSTOR
* Revel, Jacques, and Lynn Hunt, eds. ''Histories: French Constructions of the Past'' (1995). 654pp, 64 essays; emphasis on Annales School * Symes, Carol. "The Middle Ages between Nationalism and Colonialism," ''French Historical Studies'' (Winter 2011) 34#1 pp 37–46 * Thébaud, Françoise. "Writing Women's and Gender History in France: A National Narrative?" ''Journal of Women's History'' (2007) 19#1 pp. 167–172 in Project MUSE
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD 150 ...
. It was also an early colonial power
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their relig ...
, with possessions around the world.
France originated as West Francia (''Francia Occidentalis''), the western half of the Carolingian Empire, with the Treaty of Verdun (843). A branch of the Carolingian dynasty continued to rule until 987, when Hugh Capet
Hugh Capet (; french: Hugues Capet ; c. 939 – 14 October 996) was the King of the Franks from 987 to 996. He is the founder and first king from the House of Capet. The son of the powerful duke Hugh the Great and his wife Hedwige of Saxony, ...
was elected king and founded the Capetian dynasty. The territory remained known as ''Francia'' and its ruler as ''rex Francorum'' ("king of the Franks") well into the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD 150 ...
. The first king calling himself ''rex Francie'' ("King of France") was Philip II Philip II may refer to:
* Philip II of Macedon (382–336 BC)
* Philip II (emperor) (238–249), Roman emperor
* Philip II, Prince of Taranto (1329–1374)
* Philip II, Duke of Burgundy (1342–1404)
* Philip II, Duke of Savoy (1438-1497)
* Philip ...
, in 1190, and officially from 1204. From then, France was continuously ruled by the Capetians and their cadet lines—the Valois and Bourbon—until the monarchy was abolished in 1792 during the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
. The Kingdom of France was also ruled in personal union with the Kingdom of Navarre over two time periods, 1284–1328 and 1572–1620, after which the institutions of Navarre were abolished and it was fully annexed by France (though the King of France continued to use the title "King of Navarre" through the end of the monarchy).
France in the Middle Ages was a de-centralised, feudal monarchy. In Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period ...
and Catalonia (now a part of Spain), as well as Aquitaine
Aquitaine ( , , ; oc, Aquitània ; eu, Akitania; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne ( oc, Guiana), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former administrative region of the country. Since 1 Janu ...
, the authority of the French king was barely felt. Lorraine
Lorraine , also , , ; Lorrain: ''Louréne''; Lorraine Franconian: ''Lottringe''; german: Lothringen ; lb, Loutrengen; nl, Lotharingen is a cultural and historical region in Northeastern France, now located in the administrative region of Gra ...
and Provence were states of the Holy Roman Empire and not yet a part of France. Initially, West Frankish kings were elected by the secular and ecclesiastic magnates, but the regular coronation of the eldest son of the reigning king during his father's lifetime established the principle of male primogeniture, which became codified in the Salic law. During the Late Middle Ages, rivalry between the Capetian Dynasty, rulers of the Kingdom of France and their vassals the House of Plantagenet, who also ruled the Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, ...
as part of their so-called competing Angevin Empire
The Angevin Empire (; french: Empire Plantagenêt) describes the possessions of the House of Plantagenet during the 12th and 13th centuries, when they ruled over an area covering roughly half of France, all of England, and parts of Ireland and W ...
, resulted in many armed struggles. The most notorious of them all are the series of conflicts known as the Hundred Years' War (1337–1453) in which the kings of England
This list of kings and reigning queens of the Kingdom of England begins with Alfred the Great, who initially ruled Wessex, one of the seven Anglo-Saxon kingdoms which later made up modern England. Alfred styled himself King of the Anglo-Sax ...
laid claim to the French throne. Emerging victorious from said conflicts, France subsequently sought to extend its influence into Italy, but was defeated by Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and the Holy Roman Empire in the ensuing Italian Wars (1494–1559).
France in the early modern era was increasingly centralised; the French language began to displace other languages from official use, and the monarch expanded his absolute power, albeit in an administrative system (the '' Ancien Régime'') complicated by historic and regional irregularities in taxation, legal, judicial, and ecclesiastic divisions, and local prerogatives. Religiously France became divided between the Catholic majority and a Protestant minority, the Huguenots, which led to a series of civil wars, the Wars of Religion (1562–1598). The Wars of Religion crippled France, but triumph over Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and the Habsburg monarchy in the Thirty Years' War made France the most powerful nation on the continent once more. The kingdom became Europe's dominant cultural, political and military power in the 17th century under Louis XIV. In parallel, France developed its first colonial empire in Asia, Africa, and in the Americas. From the 16th to the 17th centuries, the First French colonial empire stretched from a total area at its peak in 1680 to over 10,000,000 square kilometres (3,900,000 sq mi), the second largest empire in the world at the time behind only the Spanish Empire. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It i ...
led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. French intervention in the American Revolutionary War helped secure the independence of the new United States of America but was costly and achieved little for France.
The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic. The monarchy was restored by the other great powers in 1814 and lasted (except for the Hundred Days in 1815) until the French Revolution of 1848.
Political history
West Francia
During the later years of the elderly Charlemagne's rule, the Vikings made advances along the northern and western perimeters of theKingdom of the Franks
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks duri ...
. After Charlemagne's death in 814 his heirs were incapable of maintaining political unity and the empire began to crumble. The Treaty of Verdun of 843 divided the Carolingian Empire into three parts, with Charles the Bald ruling over West Francia, the nucleus of what would develop into the kingdom of France.
Charles the Bald was also crowned King of Lotharingia
The rulers of Lorraine have held different posts under different governments over different regions, since its creation as the kingdom of Lotharingia by the Treaty of Prüm, in 855. The first rulers of the newly established region were kings of ...
after the death of Lothair II in 869, but in the Treaty of Meerssen
The Treaty of Mersen or Meerssen, concluded on 8 August 870, was a treaty to partition the realm of Lothair II, known as Lotharingia, by his uncles Louis the German of East Francia and Charles the Bald of West Francia, the two surviving sons of ...
(870) was forced to cede much of Lotharingia to his brothers, retaining the Rhone and Meuse basins (including Verdun
Verdun (, , , ; official name before 1970 ''Verdun-sur-Meuse'') is a large city in the Meuse department in Grand Est, northeastern France. It is an arrondissement of the department.
Verdun is the biggest city in Meuse, although the capital ...
, Vienne and Besançon
Besançon (, , , ; archaic german: Bisanz; la, Vesontio) is the prefecture of the department of Doubs in the region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté. The city is located in Eastern France, close to the Jura Mountains and the border with Switzer ...
) but leaving the Rhineland with Aachen, Metz
Metz ( , , lat, Divodurum Mediomatricorum, then ) is a city in northeast France located at the confluence of the Moselle and the Seille rivers. Metz is the prefecture of the Moselle department and the seat of the parliament of the Grand ...
, and Trier in East Francia.
Viking incursions up the Loire, the Seine, and other inland waterways increased. During the reign of Charles the Simple
Charles III (17 September 879 – 7 October 929), called the Simple or the Straightforward (from the Latin ''Carolus Simplex''), was the king of West Francia from 898 until 922 and the king of Lotharingia from 911 until 919–923. He was a mem ...
(898–922), Normans under Rollo
Rollo ( nrf, Rou, ''Rolloun''; non, Hrólfr; french: Rollon; died between 928 and 933) was a Viking who became the first ruler of Normandy, today a region in northern France. He emerged as the outstanding warrior among the Norsemen who had se ...
from Scandinavia settled along the Seine, downstream from Paris, in a region that came to be known as Normandy.
High Middle Ages
The Carolingians were to share the fate of their predecessors: after an intermittent power struggle between the two dynasties, the accession in 987 ofHugh Capet
Hugh Capet (; french: Hugues Capet ; c. 939 – 14 October 996) was the King of the Franks from 987 to 996. He is the founder and first king from the House of Capet. The son of the powerful duke Hugh the Great and his wife Hedwige of Saxony, ...
, Duke of France and Count of Paris, established the Capetian dynasty on the throne. With its offshoots, the houses of Valois and Bourbon, it was to rule France for more than 800 years.
The old order left the new dynasty in immediate control of little beyond the middle Seine and adjacent territories, while powerful territorial lords such as the 10th- and 11th-century counts of Blois accumulated large domains of their own through marriage and through private arrangements with lesser nobles for protection and support.
The area around the lower Seine became a source of particular concern when Duke William
''Duke William'' was a ship which served as a troop transport at the Siege of Louisbourg and as a deportation ship in the Île Saint-Jean Campaign of the Expulsion of the Acadians during the Seven Years' War. While ''Duke William'' was transport ...
took possession of the kingdom of England by the Norman Conquest of 1066, making himself and his heirs the King's equal outside France (where he was still nominally subject to the Crown).
Henry II inherited the Duchy of Normandy and the County of Anjou, and married France's newly single ex-queen, Eleanor of Aquitaine, who ruled much of southwest France, in 1152. After defeating a revolt led by Eleanor and three of their four sons, Henry had Eleanor imprisoned, made the Duke of Brittany
This is a list of rulers of the Duchy of Brittany. In different epochs the sovereigns of Brittany were kings, princes, and dukes. The Breton ruler was sometimes elected, sometimes attained the position by conquest or intrigue, or by hereditary r ...
his vassal, and in effect ruled the western half of France as a greater power than the French throne. However, disputes among Henry's descendants over the division of his French territories, coupled with John of England's lengthy quarrel with Philip II, allowed Philip II Philip II may refer to:
* Philip II of Macedon (382–336 BC)
* Philip II (emperor) (238–249), Roman emperor
* Philip II, Prince of Taranto (1329–1374)
* Philip II, Duke of Burgundy (1342–1404)
* Philip II, Duke of Savoy (1438-1497)
* Philip ...
to recover influence over most of this territory. After the French victory at the Battle of Bouvines in 1214, the English monarchs maintained power only in southwestern Duchy of Guyenne
Guyenne or Guienne (, ; oc, Guiana ) was an old French province which corresponded roughly to the Roman province of '' Aquitania Secunda'' and the archdiocese of Bordeaux.
The name "Guyenne" comes from ''Aguyenne'', a popular transformation o ...
.
Late Middle Ages and the Hundred Years' War
The death ofCharles IV of France
Charles IV (18/19 June 1294 – 1 February 1328), called the Fair (''le Bel'') in France and the Bald (''el Calvo'') in Navarre, was last king of the direct line of the House of Capet, King of France and King of Navarre (as Charles I) from 132 ...
in 1328 without male heirs ended the main Capetian line. Under Salic law the crown could not pass through a woman (Philip IV's daughter was Isabella, whose son was Edward III of England), so the throne passed to Philip VI, son of Charles of Valois
Charles of Valois (12 March 1270 – 16 December 1325), the fourth son of King Philip III of France and Isabella of Aragon, was a member of the House of Capet and founder of the House of Valois, whose rule over France would start in 1 ...
. This, in addition to a long-standing dispute over the rights to Gascony in the south of France, and the relationship between England and the Flemish cloth towns, led to the Hundred Years' War of 1337–1453. The following century was to see devastating warfare, peasant revolts (the English peasants' revolt of 1381 and the ''Jacquerie
The Jacquerie () was a popular revolt by peasants that took place in northern France in the early summer of 1358 during the Hundred Years' War. The revolt was centred in the valley of the Oise north of Paris and was suppressed after a few week ...
'' of 1358 in France) and the growth of nationalism in both countries.
The losses of the century of war were enormous, particularly owing to the plague (the Black Death, usually considered an outbreak of bubonic plague), which arrived from Italy in 1348, spreading rapidly up the Rhone valley and thence across most of the country: it is estimated that a population of some 18–20 million in modern-day France at the time of the 1328 hearth tax returns had been reduced 150 years later by 50 percent or more.
Renaissance and Reformation
The Renaissance era was noted for the emergence of powerful centralized institutions, as well as a flourishing culture (much of it imported from Italy). The kings built a strong fiscal system, which heightened the power of the king to raise armies that overawed the local nobility. In Paris especially there emerged strong traditions in literature, art and music. The prevailing style was classical. The Ordinance of Villers-Cotterêts was signed into law by Francis I in 1539. Largely the work of Chancellor Guillaume Poyet, it dealt with a number of government, judicial and ecclesiastical matters. Articles 110 and 111, the most famous, called for the use of the French language in all legal acts, notarised contracts and official legislation.Italian Wars
After the Hundred Years' War, Charles VIII of France signed three additional treaties with Henry VII of England, Maximilian I of Habsburg, and Ferdinand II of Aragon respectively at Étaples (1492), Senlis (1493) and in Barcelona (1493). These three treaties cleared the way for France to undertake the long Italian Wars (1494–1559), which marked the beginning of early modern France. French efforts to gain dominance resulted only in the increased power of the Habsburg house.Wars of Religion
Barely were the Italian Wars over, when France was plunged into a domestic crisis with far-reaching consequences. Despite the conclusion of a Concordat between France and the Papacy (1516), granting the crown unrivalled power in senior ecclesiastical appointments, France was deeply affected by theProtestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and ...
's attempt to break the hegemony of Catholic Europe. A growing urban-based Protestant minority (later dubbed '' Huguenots'') faced ever harsher repression under the rule of Francis I's son King Henry II. After Henry II's death in a joust, the country was ruled by his widow Catherine de' Medici and her sons Francis II, Charles IX and Henry III. Renewed Catholic reaction headed by the powerful dukes of Guise culminated in a massacre of Huguenots (1562), starting the first of the French Wars of Religion, during which English, German, and Spanish forces intervened on the side of rival Protestant and Catholic forces. Opposed to absolute monarchy, the Huguenot Monarchomachs
The Monarchomachs (french: Monarchomaques) were originally Early Modern France, French Huguenot political theory, theorists who opposed monarchism, monarchy at the end of the 16th century, known in particular for having theoretically justified tyra ...
theorized during this time the right of rebellion
In political philosophy, the right of revolution (or right of rebellion) is the right or duty of a people to "alter or abolish" a government that acts against their common interests or threatens the safety of the people without cause. Stated throu ...
and the legitimacy of tyrannicide.
The Wars of Religion culminated in the War of the Three Henrys in which Henry III assassinated Henry de Guise, leader of the Spanish-backed Catholic league, and the king was murdered in return. After the assassination of both Henry of Guise (1588) and Henry III (1589), the conflict was ended by the accession of the Protestant king of Navarre as Henry IV (first king of the Bourbon dynasty) and his subsequent abandonment of Protestantism (Expedient of 1592) effective in 1593, his acceptance by most of the Catholic establishment (1594) and by the Pope (1595), and his issue of the toleration decree known as the Edict of Nantes (1598), which guaranteed freedom of private worship and civil equality.
Early Modern period
Colonial France
France's pacification under Henry IV laid much of the ground for the beginnings of France's rise to European hegemony. France was expansive during all but the end of the seventeenth century: the French began trading in India and Madagascar, founded Quebec and penetrated the North American Great Lakes and Mississippi, established plantation economies in the West Indies and extended their trade contacts in the Levant and enlarged their merchant marine.Thirty Years' War
Henry IV's son Louis XIII and his minister (1624–1642) Cardinal Richelieu, elaborated a policy against Spain and the Holy Roman Empire during the Thirty Years' War (1618–48) which had broken out in Germany. After the death of both king and cardinal, the Peace of Westphalia (1648) secured universal acceptance of Germany's political and religious fragmentation, but the Regency of Anne of Austria and her ministerCardinal Mazarin
Cardinal Jules Mazarin (, also , , ; 14 July 1602 – 9 March 1661), born Giulio Raimondo Mazzarino () or Mazarini, was an Italian cardinal, diplomat and politician who served as the chief minister to the Kings of France Louis XIII and Louis X ...
experienced a civil uprising known as the Fronde
The Fronde () was a series of civil wars in France between 1648 and 1653, occurring in the midst of the Franco-Spanish War, which had begun in 1635. King Louis XIV confronted the combined opposition of the princes, the nobility, the law cour ...
(1648–1653) which expanded into a Franco-Spanish War (1653–59). The Treaty of the Pyrenees (1659) formalised France's seizure (1642) of the Spanish territory of Roussillon after the crushing of the ephemeral Catalan Republic and ushered a short period of peace.
Administrative structures
The ''Ancien Régime'', a French term rendered in English as "Old Rule", or simply "Former Regime", refers primarily to the aristocratic, social and political system of early modern France under the late Valois and Bourbon dynasties. The administrative and social structures of the Ancien Régime were the result of years of state-building, legislative acts (like the Ordinance of Villers-Cotterêts), internal conflicts and civil wars, but they remained a confusing patchwork of local privilege and historic differences until theFrench Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
brought about a radical suppression of administrative incoherence.
Louis XIV, the Sun King
 For most of the reign of Louis XIV (1643–1715), ("The Sun King"), France was the dominant power in Europe, aided by the diplomacy of Cardinal Richelieu's successor as the King's chief minister, (1642–61) Cardinal Jules Mazarin, (1602–61). Cardinal Mazarin oversaw the creation of a French Royal Navy that rivalled England's, expanding it from 25 ships to almost 200. The size of the Army was also considerably increased. Renewed wars (the War of Devolution, 1667–68 and the Franco-Dutch War, 1672–78) brought further territorial gains (
For most of the reign of Louis XIV (1643–1715), ("The Sun King"), France was the dominant power in Europe, aided by the diplomacy of Cardinal Richelieu's successor as the King's chief minister, (1642–61) Cardinal Jules Mazarin, (1602–61). Cardinal Mazarin oversaw the creation of a French Royal Navy that rivalled England's, expanding it from 25 ships to almost 200. The size of the Army was also considerably increased. Renewed wars (the War of Devolution, 1667–68 and the Franco-Dutch War, 1672–78) brought further territorial gains (Artois
Artois ( ; ; nl, Artesië; English adjective: ''Artesian'') is a region of northern France. Its territory covers an area of about 4,000 km2 and it has a population of about one million. Its principal cities are Arras (Dutch: ''Atrecht'') ...
and western Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
and the free county of Burgundy
The Free County of Burgundy or Franche-Comté (french: Franche Comté de Bourgogne; german: Freigrafschaft Burgund) was a medieval county (from 982 to 1678) of the Holy Roman Empire, predecessor to the modern region of Franche-Comté. The name ' ...
, previously left to the Empire in 1482), but at the cost of the increasingly concerted opposition of rival royal powers, and a legacy of an increasingly enormous national debt. An adherent of the theory of the "Divine Right of Kings", which advocates the divine origin of temporal power and any lack of earthly restraint of monarchical rule, Louis XIV continued his predecessors' work of creating a centralized state governed from the capital of Paris. He sought to eliminate the remnants of feudalism still persisting in parts of France and, by compelling the noble elite to regularly inhabit his lavish Palace of Versailles, built on the outskirts of Paris, succeeded in pacifying the aristocracy, many members of which had participated in the earlier "Fronde
The Fronde () was a series of civil wars in France between 1648 and 1653, occurring in the midst of the Franco-Spanish War, which had begun in 1635. King Louis XIV confronted the combined opposition of the princes, the nobility, the law cour ...
" rebellion during Louis' minority youth. By these means he consolidated a system of absolute monarchy in France that endured 150 years until the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
. McCabe says critics used fiction to portray the degraded Turkish Court, using "the harem, the Sultan court, oriental despotism, luxury, gems and spices, carpets, and silk cushions" as an unfavorable analogy to the corruption of the French royal court.
The king sought to impose total religious uniformity on the country, repealing the " Edict of Nantes" in 1685. It is estimated that anywhere between 150,000 and 300,000 Protestants fled France during the wave of persecution that followed the repeal, (following " Huguenots" beginning a hundred and fifty years earlier until the end of the 18th century) costing the country a great many intellectuals, artisans, and other valuable people. Persecution extended to unorthodox Roman Catholics like the Jansenists
Jansenism was an Early modern period, early modern Christian theology, theological movement within Catholicism, primarily active in the Kingdom of France, that emphasized original sin, human Total depravity, depravity, the necessity of divine g ...
, a group that denied free will and had already been condemned by the popes. In this, he garnered the friendship of the papacy, which had previously been hostile to France because of its policy of putting all church property in the country under the jurisdiction of the state rather than that of Rome.
In November 1700, the Spanish king Charles II died, ending the Habsburg line in that country. Louis had long waited for this moment, and now planned to put a Bourbon relative, Philip, Duke of Anjou, (1683–1746), on the throne. Essentially, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
was to become a perpetual ally and even obedient satellite of France, ruled by a king who would carry out orders from Versailles. Realizing how this would upset the balance of power, the other European rulers were outraged. However, most of the alternatives were equally undesirable. For example, putting another Habsburg on the throne would end up recreating the grand multi-national empire of Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infa ...
(1500–58), of the Holy Roman Empire (German First Reich), Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, and the Two Sicilies
The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies ( it, Regno delle Due Sicilie) was a kingdom in Southern Italy from 1816 to 1860. The kingdom was the largest sovereign state by population and size in Italy before Italian unification, comprising Sicily and all ...
which would also grossly upset the power balance. After nine years of exhausting war, the last thing Louis wanted was another conflict. However, the rest of Europe would not stand for his ambitions in Spain, and so the long War of the Spanish Succession began (1701–14), a mere three years after the War of the Grand Alliance
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between Kingdom of France, France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by t ...
, (1688–97, aka "War of the League of Augsburg") had just concluded.Daniel Roche, France in the Enlightenment (1998)
Dissent and revolution
 The reign (1715–74) of Louis XV saw an initial return to peace and prosperity under the regency (1715–23) of Philippe II, Duke of Orléans, whose policies were largely continued (1726–1743) by
The reign (1715–74) of Louis XV saw an initial return to peace and prosperity under the regency (1715–23) of Philippe II, Duke of Orléans, whose policies were largely continued (1726–1743) by Cardinal Fleury
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**''Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**'' Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, th ...
, prime minister in all but name. The exhaustion of Europe after two major wars resulted in a long period of peace, only interrupted by minor conflicts like the War of the Polish Succession from 1733 to 1735. Large-scale warfare resumed with the War of the Austrian Succession (1740–48). But alliance with the traditional Habsburg enemy (the "Diplomatic Revolution
The Diplomatic Revolution of 1756 was the reversal of longstanding alliances in Europe between the War of the Austrian Succession and the Seven Years' War. Austria went from an ally of Britain to an ally of France, the Dutch Republic, a long sta ...
" of 1756) against the rising power of Britain and Prussia led to costly failure in the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (175 ...
(1756–63) and the loss of France's North American colonies.
On the whole, the 18th century saw growing discontent with the monarchy and the established order. Louis XV was a highly unpopular king for his sexual excesses, overall weakness, and for losing Canada to the British. A strong ruler like Louis XIV could enhance the position of the monarchy, while Louis XV weakened it. The writings of the philosophes
The ''philosophes'' () were the intellectuals of the 18th-century Enlightenment.Kishlansky, Mark, ''et al.'' ''A Brief History of Western Civilization: The Unfinished Legacy, volume II: Since 1555.'' (5th ed. 2007). Few were primarily philosophe ...
such as Voltaire were a clear sign of discontent, but the king chose to ignore them. He died of smallpox in 1774, and the French people shed few tears at his passing. While France had not yet experienced the Industrial Revolution that was beginning in Britain, the rising middle class of the cities felt increasingly frustrated with a system and rulers that seemed silly, frivolous, aloof, and antiquated, even if true feudalism no longer existed in France.
Upon Louis XV's death, his grandson Louis XVI became king. Initially popular, he too came to be widely detested by the 1780s. He was married to an Austrian archduchess, Marie Antoinette. French intervention in the American War of Independence was also very expensive.
With the country deeply in debt, Louis XVI permitted the radical reforms of Turgot and Malesherbes, but noble disaffection led to Turgot's dismissal and Malesherbes' resignation in 1776. They were replaced by Jacques Necker. Necker had resigned in 1781 to be replaced by Calonne and Brienne, before being restored in 1788. A harsh winter that year led to widespread food shortages, and by then France was a powder keg ready to explode. On the eve of the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
of July 1789, France was in a profound institutional and financial crisis, but the ideas of the Enlightenment had begun to permeate the educated classes of society.
Limited monarchy
On September 3, 1791, the absolute monarchy which had governed France for 948 years was forced to limit its power and become a provisional constitutional monarchy. However, this too would not last very long and on September 21, 1792, the French monarchy was effectively abolished by the proclamation of the French First Republic. The role of the King in France was finally ended with the execution of Louis XVI byguillotine
A guillotine is an apparatus designed for efficiently carrying out executions by beheading. The device consists of a tall, upright frame with a weighted and angled blade suspended at the top. The condemned person is secured with stocks at t ...
on Monday, January 21, 1793, followed by the " Reign of Terror", mass executions and the provisional " Directory" form of republican government, and the eventual beginnings of twenty-five years of reform, upheaval, dictatorship, wars and renewal, with the various Napoleonic Wars.
Restoration
Following theFrench Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
(1789–99) and the First French Empire
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental E ...
under Napoleon (1804–1814), the monarchy was restored when a coalition of European powers restored by arms the monarchy to the House of Bourbon in 1814. However the deposed Emperor Napoleon I
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
returned triumphantly to Paris from his exile in Elba
Elba ( it, isola d'Elba, ; la, Ilva) is a Mediterranean island in Tuscany, Italy, from the coastal town of Piombino on the Italian mainland, and the largest island of the Tuscan Archipelago. It is also part of the Arcipelago Toscano Nationa ...
and ruled France for a short period known as the Hundred Days.
When a Seventh European Coalition again deposed Napoleon after the Battle of Waterloo in 1815, the Bourbon monarchy was once again restored.
The Count of Provence
The land of Provence has a history quite separate from that of any of the larger nations of Europe. Its independent existence has its origins in the frontier nature of the dukedom in Merovingian Gaul. In this position, influenced and affected by ...
- brother of Louis XVI, who was guillotined in 1793 - was crowned as Louis XVIII, nicknamed "The Desired". Louis XVIII tried to conciliate the legacies of the Revolution and the Ancien Régime, by permitting the formation of a Parliament and a constitutional Charter, usually known as the "''Charte octroyée''" ("Granted Charter"). His reign was characterized by disagreements between the Doctrinaires, liberal thinkers who supported the Charter and the rising bourgeoisie, and the Ultra-royalists, aristocrats and clergymen who totally refused the Revolution's heritage. Peace was maintained by statesmen like Talleyrand and the Duke of Richelieu, as well as the King's moderation and prudent intervention. In 1823, the liberal agitations in Spain led to a French intervention
This is a list of wars involving France and its predecessor states. It is an incomplete list of French and proto-French wars and battles from the foundation of Frankish Kingdom, Francia by Clovis I, the Merovingian dynasty, Merovingian king who uni ...
on the royalists' side, which permitted King Ferdinand VII of Spain
, house = Bourbon-Anjou
, father = Charles IV of Spain
, mother = Maria Luisa of Parma
, birth_date = 14 October 1784
, birth_place = El Escorial, Spain
, death_date =
, death_place = Madrid, Spain
, burial_p ...
to abolish the Constitution of 1812
The Political Constitution of the Spanish Monarchy ( es, link=no, Constitución Política de la Monarquía Española), also known as the Constitution of Cádiz ( es, link=no, Constitución de Cádiz) and as ''La Pepa'', was the first Constituti ...
.
However, the work of Louis XVIII was frustrated when, after his death on 16 September 1824, his brother the Count of Artois
The count of Artois (French: Comtes d'Artois, Dutch: Graven van Artesië) was the ruler over the County of Artois from the 9th century until the abolition of the countship by the French revolutionaries in 1790.
House of Artois
*Odalric (c. 850 ...
became king under the name of Charles X
Charles X (born Charles Philippe, Count of Artois; 9 October 1757 – 6 November 1836) was King of France from 16 September 1824 until 2 August 1830. An uncle of the uncrowned Louis XVII and younger brother to reigning kings Louis XVI and Lou ...
. Charles X was a strong reactionary who supported the ultra-royalists and the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. Under his reign, the censorship of newspapers was reinforced, the Anti-Sacrilege Act passed, and compensations to Émigrés were increased. However, the reign also witnessed the French intervention
This is a list of wars involving France and its predecessor states. It is an incomplete list of French and proto-French wars and battles from the foundation of Frankish Kingdom, Francia by Clovis I, the Merovingian dynasty, Merovingian king who uni ...
in the Greek Revolution
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. The Greeks were later assisted b ...
in favour of the Greek rebels, and the first phase of the conquest of Algeria.
The absolutist tendencies of the King were disliked by the Doctrinaire majority in the Chamber of Deputies, that on 18 March 1830 sent an address to the King, upholding the rights of the Chamber and in effect supporting a transition to a full parliamentary system. Charles X received this address as a veiled threat, and in 25 July of the same year, he issued the St. Cloud Ordinances, in an attempt to reduce Parliament's powers and re-establish absolute rule. The opposition reacted with riots in Parliament and barricades in Paris, that resulted in the July Revolution. The King abdicated, as did his son the Prince Louis Antoine, in favour to his grandson Count of Chambord, nominating his cousin the Duke of Orléans as regent. However, it was too late, and the liberal opposition won out over the monarchy.
Aftermath and July Monarchy
On 9 August 1830, the Chamber of Deputies elected Louis Philippe, Duke of Orléans as "King of the French": for the first time since French Revolution, the King was designated as the ruler of the French people and not the country. The Bourbon white flag was substituted with the French tricolour, and a new Charter was introduced in August 1830. The conquest of Algeria continued, and new settlements were established in the Gulf of Guinea,Gabon
Gabon (; ; snq, Ngabu), officially the Gabonese Republic (french: République gabonaise), is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. Located on the equator, it is bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the nort ...
, Madagascar, and Mayotte, while Tahiti was placed under protectorate.
However, despite the initial reforms, Louis Philippe was little different from his predecessors. The old nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The character ...
was replaced by urban bourgeoisie, and the working class was excluded from voting. Louis Philippe appointed notable bourgeois as Prime Minister, like banker Casimir Périer, academic François Guizot, general Jean-de-Dieu Soult
Marshal General Jean-de-Dieu Soult, 1st Duke of Dalmatia, (; 29 March 1769 – 26 November 1851) was a French general and statesman, named Marshal of the Empire in 1804 and often called Marshal Soult. Soult was one of only six officers in Frenc ...
, and thus obtained the nickname of "Citizen King" (''Roi-Citoyen''). The July Monarchy was beset by corruption scandals and financial crisis. The opposition of the King was composed of Legitimists, supporting the Count of Chambord, Bourbon claimant to the throne, and of Bonapartist
Bonapartism (french: Bonapartisme) is the political ideology supervening from Napoleon Bonaparte and his followers and successors. The term was used to refer to people who hoped to restore the House of Bonaparte and its style of government. In thi ...
s and Republicans, who fought against royalty and supported the principles of democracy.
The King tried to suppress the opposition with censorship, but when the '' Campagne des banquets'' ("Banquets' Campaign") was repressed in February 1848, riots and seditions erupted in Paris and later all France, resulting in the February Revolution. The National Guard
National Guard is the name used by a wide variety of current and historical uniformed organizations in different countries. The original National Guard was formed during the French Revolution around a cadre of defectors from the French Guards.
Nat ...
refused to repress the rebellion, resulting in Louis Philippe abdicating and fleeing to England. On 24 February 1848, the monarchy was abolished and the Second Republic was proclaimed. Despite later attempts to re-establish the Kingdom in the 1870s, during the Third Republic, the French monarchy has not returned.
Territories and provinces
 Before the 13th century, only a small part of what is now France was under control of the Frankish king; in the north there were Viking incursions leading to the formation of the
Before the 13th century, only a small part of what is now France was under control of the Frankish king; in the north there were Viking incursions leading to the formation of the Duchy of Normandy
The Duchy of Normandy grew out of the 911 Treaty of Saint-Clair-sur-Epte between King Charles III of West Francia and the Viking leader Rollo. The duchy was named for its inhabitants, the Normans.
From 1066 until 1204, as a result of the Norman c ...
; in the west, the counts of Anjou
The Count of Anjou was the ruler of the County of Anjou, first granted by Charles the Bald in the 9th century to Robert the Strong. Ingelger and his son, Fulk the Red, were viscounts until Fulk assumed the title of Count of Anjou. The Robertians ...
established themselves as powerful rivals of the king, by the late 11th century ruling over the "Angevin Empire
The Angevin Empire (; french: Empire Plantagenêt) describes the possessions of the House of Plantagenet during the 12th and 13th centuries, when they ruled over an area covering roughly half of France, all of England, and parts of Ireland and W ...
", which included the kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, ...
.
It was only with Philip II of France
Philip II (21 August 1165 – 14 July 1223), byname Philip Augustus (french: Philippe Auguste), was King of France from 1180 to 1223. His predecessors had been known as kings of the Franks, but from 1190 onward, Philip became the first French m ...
that the bulk of the territory of Western Francia came under the rule of the Frankish kings, and Philip was consequently the first king to call himself "king of France" (1190).
The division of France between the Angevin (Plantagenet) kings of England and the Capetian kings of France would lead to the Hundred Years' War, and France would regain control over these territories only by the mid 15th century.
What is now eastern France (Lorraine, Arelat) was not part of Western Francia to begin with and was only incorporated into the kingdom during the early modern period.
Territories inherited from Western Francia:
:Domain of the Frankish king (royal domain or '' demesne'', see Crown lands of France
The crown lands, crown estate, royal domain or (in French) ''domaine royal'' (from demesne) of France were the lands, fiefs and rights directly possessed by the kings of France. While the term eventually came to refer to a territorial unit, the ...
)
:* Ile de France
Ile may refer to:
* iLe, a Puerto Rican singer
* Ile District (disambiguation), multiple places
* Ilé-Ifẹ̀, an ancient Yoruba city in south-western Nigeria
* Interlingue (ISO 639:ile), a planned language
* Isoleucine, an amino acid
* Another ...
:* Reims
:* Bourges
:* Orléans
:Direct vassals of the French king in the 10th to 12th centuries:
:*County of Champagne
The County of Champagne ( la, Comitatus Campaniensis; fro, Conté de Champaigne), or County of Champagne and Brie (region), Brie, was a historic territory and Feudalism, feudal principality in France descended from the early medieval kingdom of ...
(to the royal domain in 1316)
:* County of Blois
The County of Blois was a feudal principality centred on Blois, south of Paris, France. It was created just after king Clovis I conquered Roman Gaul around AD 500. Between the 8th and the 13th centuries, it was amongst the most powerful vassal ...
(to the royal domain in 1391)
:* Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy (; la, Ducatus Burgundiae; french: Duché de Bourgogne, ) emerged in the 9th century as one of the successors of the ancient Kingdom of the Burgundians, which after its conquest in 532 had formed a constituent part of the ...
(until 1477, then divided between France and the Habsburgs)
:* County of Flanders (to Burgundy in 1369)
:* Duchy of Bourbon (1327–1523)
Acquisitions during the 13th to 14th centuries:
* Duchy of Normandy
The Duchy of Normandy grew out of the 911 Treaty of Saint-Clair-sur-Epte between King Charles III of West Francia and the Viking leader Rollo. The duchy was named for its inhabitants, the Normans.
From 1066 until 1204, as a result of the Norman c ...
(1204)
* County of Tourain During the early Middle Ages, the count of Tours was the ruler of the old Roman ''pagus Turonicus'': the city of Tours and its hinterland, the Touraine.
Under the Merovingians, counts at Tours were appointed local representatives of the king, such ...
(1204)
* County of Anjou (1225)
* County of Maine
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
(1225)
* County of Auvergne
The history of the Auvergne dates back to the early Middle Ages, when it was a historic province in south central France. It was originally the feudal domain of the Counts of Auvergne.
History
Auvergne was a province of France deriving its name ...
(1271)
* County of Toulouse (1271), including:
**County of Quercy
Quercy (; oc, Carcin , locally ) is a former province of France located in the country's southwest, bounded on the north by Limousin, on the west by Périgord and Agenais, on the south by Gascony and Languedoc, and on the east by Rouergue and ...
**County of Rouergue
*** County of Rodez
**County of Gevaudan
**Viscounty of Albi
** Marquisat of Gothia
* County of Champagne
The County of Champagne ( la, Comitatus Campaniensis; fro, Conté de Champaigne), or County of Champagne and Brie (region), Brie, was a historic territory and Feudalism, feudal principality in France descended from the early medieval kingdom of ...
(to the royal domain in 1316)
* Dauphiné
The Dauphiné (, ) is a former province in Southeastern France, whose area roughly corresponded to that of the present departments of Isère, Drôme and Hautes-Alpes. The Dauphiné was originally the Dauphiné of Viennois.
In the 12th centu ...
(1349), hereditary possession of the kings of France, to be held by the heir apparent
An heir apparent, often shortened to heir, is a person who is first in an order of succession and cannot be displaced from inheriting by the birth of another person; a person who is first in the order of succession but can be displaced by the b ...
, but technically not part of the kingdom of France because it remained nominally part of the Holy Roman Empire.
* County of Blois
The County of Blois was a feudal principality centred on Blois, south of Paris, France. It was created just after king Clovis I conquered Roman Gaul around AD 500. Between the 8th and the 13th centuries, it was amongst the most powerful vassal ...
(to the royal domain in 1391)
Acquisitions from the Plantagenet kings of England with the French victory in the Hundred Years' War 1453
* Duchy of Aquitaine (Guyenne
Guyenne or Guienne (, ; oc, Guiana ) was an old French province which corresponded roughly to the Roman province of '' Aquitania Secunda'' and the archdiocese of Bordeaux.
The name "Guyenne" comes from ''Aguyenne'', a popular transformation o ...
), including:
** County of Poitou The County of Poitou (Latin ''comitatus Pictavensis'') was a historical region of France, consisting of the three sub-regions of Vendée, Deux-Sèvres and Vienne. Its name is derived from the ancient Gaul tribe of Pictones. The county was bounded ...
** County of La Marche
** County of Angoulême
** County of Périgord
***County of Velay
Velay () is a historical area of France situated in east Haute-Loire ''département'' and south east of Massif central.
History
Julius Caesar mentioned the vellavi as subordinate of the arverni. Strabon suggested that they might have made ...
** County of Saintonge
** Viscounty of Limousin
** Lordship of Issoudun
Issoudun () is a commune in the Indre department, administrative region of Centre-Val de Loire, France. It is also referred to as ''Issoundun'', which is the ancient name.
Geography Location
Issoudun is a sub-prefecture, located in the east ...
**Lordship of Déols
** Duchy of Gascogne ( Gascony)
***County of Agenais
* Duchy of Bretagne (disputed since the War of the Breton Succession
The War of the Breton Succession (, ) was a conflict between the Counts of Blois and the Montforts of Brittany for control of the Sovereign Duchy of Brittany, then a fief of the Kingdom of France. It was fought between 1341 and 12 April 1 ...
, to France in 1453, to the royal demesne in 1547)
Acquisitions after the end of the Hundred Years' War:
* Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy (; la, Ducatus Burgundiae; french: Duché de Bourgogne, ) emerged in the 9th century as one of the successors of the ancient Kingdom of the Burgundians, which after its conquest in 532 had formed a constituent part of the ...
(1477)
* Pale of Calais
The Pale of Calais was a territory in Northern France ruled by the monarchs of England for more than two hundred years from 1347 to 1558. The area, which was taken following the Battle of Crécy in 1346 and the subsequent siege of Calais, was ...
(1558)
* Kingdom of Navarre (1620)
* Alsace: Peace of Westphalia (1648), Treaty of Nijmegen, Truce of Ratisbon
The Truce of Ratisbon, or Truce of Regensburg, concluded the War of the Reunions, fought by France against Spain and the Holy Roman Empire. The Truce was signed on 15 August 1684 at the Dominican convent in Ratisbon (now in Bavaria) between Louis ...
(1684)
* County of Artois
The County of Artois (, ) was a historic province of the Kingdom of France, held by the Dukes of Burgundy from 1384 until 1477/82, and a state of the Holy Roman Empire from 1493 until 1659.
Present Artois lies in northern France, on the border ...
(1659)
* Roussillon and Perpignan, Montmédy and other parts of Luxembourg, parts of Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
, including Arras, Béthune
Béthune ( ; archaic and ''Bethwyn'' historically in English) is a city in northern France, sub-prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department.
Geography
Béthune is located in the former province of Artois. It is situated south-east of Calais, ...
, Gravelines and Thionville
Thionville (; ; german: Diedenhofen ) is a city in the northeastern French department of Moselle. The city is located on the left bank of the river Moselle, opposite its suburb Yutz.
History
Thionville was settled as early as the time of th ...
( Treaty of the Pyrenees 1659)
* Free County of Burgundy (1668, 1679)
* French Hainaut (1679)
* Principality of Orange
The Principality of Orange (french: la Principauté d'Orange; oc, Principat d'Aurenja) was, from 1163 to 1713, a feudal state in Provence, in the south of modern-day France, on the east bank of the river Rhone, north of the city of Avignon, an ...
(1713)
* Duchy of Lorraine
The Duchy of Lorraine (french: Lorraine ; german: Lothringen ), originally Upper Lorraine, was a duchy now included in the larger present-day region of Lorraine in northeastern France. Its capital was Nancy.
It was founded in 959 following th ...
(1766)
* French conquest of Corsica (1769)
* Comtat Venaissin (1791)
Religion
 Prior to the
Prior to the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
, the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
was the official state religion of the Kingdom of France. France was traditionally considered the Church's eldest daughter (French: ''Fille aînée de l'Église''), and the King of France always maintained close links to the Pope. However, the French monarchy maintained a significant degree of autonomy, namely through its policy of "Gallicanism
Gallicanism is the belief that popular civil authority—often represented by the monarch's or the state's authority—over the Catholic Church is comparable to that of the Pope. Gallicanism is a rejection of ultramontanism; it has so ...
", whereby the king selected bishops rather than the papacy.
During the Protestant Reformation of the mid 16th century, France developed a large and influential Protestant population, primarily of Reformed confession; after French theologian and pastor John Calvin introduced the Reformation in France, the number of French Protestants ( Huguenots) steadily swelled to 10 percent of the population, or roughly 1.8 million people. The ensuring French Wars of Religion, and particularly the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre, decimated the Huguenot community;Hans J. Hillerbrand, ''Encyclopedia of Protestantism: 4-volume Set'', paragraphs "France" and "Huguenots"; The Huguenot Population of France, 1600-1685: The Demographic Fate and Customs of a Religious Minority by Philip Benedict; American Philosophical Society, 1991 - 164 Protestants declined to seven to eight percent of the kingdom's population by the end of the 16th century. The Edict of Nantes brought decades of respite until its revocation
Revocation is the act of recall or annulment. It is the cancelling of an act, the recalling of a grant or privilege, or the making void of some deed previously existing. A temporary revocation of a grant or privilege is called a suspension.
Con ...
in the late 17th century by Louis XIV. The resulting exodus of Huguenots from the Kingdom of France created a brain drain, as many of them had occupied important places in society.''Encyclopædia Britannica'', 11th ed, Frank Puaux, "Huguenot"
Jews have a documented presence in France since at least the early Middle Ages. The Kingdom of France was a center of Jewish learning in the Middle Ages, producing influential Jewish scholars such as Rashi and even hosting theological debates between Jews and Christians. Widespread persecution began in the 11th century and increased intermittently throughout the Middle Ages, with multiple expulsions and returns.
See also
* Economic history of France * Family tree of French monarchs ** Family tree of French monarchs (simplified)References
Further reading
* Beik, William. ''A Social and Cultural History of Early Modern France'' (2009excerpt and text search
* Caron, François. ''An Economic History of Modern France'' (1979
online edition
* Doyle, William. ''Old Regime France: 1648–1788'' (2001
excerpt and text search
* Duby, Georges. ''France in the Middle Ages 987–1460: From Hugh Capet to Joan of Arc'' (1993), survey by a leader of the Annales Schoo
excerpt and text search
* Fierro, Alfred. ''Historical Dictionary of Paris'' (1998) 392pp, an abridged translation of his ''Histoire et dictionnaire de Paris'' (1996), 1580pp * Goubert, Pierre. ''The Course of French History'' (1991), standard French textboo
excerpt and text search
als
complete text online
* Goubert, Pierre. ''Louis XIV and Twenty Million Frenchmen'' (1972), social history from Annales School * Haine, W. Scott. ''The History of France'' (2000), 280 pp. textbook
and text search
als
online edition
* * Holt, Mack P. ''Renaissance and Reformation France: 1500–1648'' (2002
excerpt and text search
* Jones, Colin, and Emmanuel Le Roy Ladurie. ''The Cambridge Illustrated History of France'' (1999
excerpt and text search
* Jones, Colin. ''The Great Nation: France from Louis XV to Napoleon'' (2002
excerpt and text search
* Jones, Colin. ''Paris: Biography of a City'' (2004), 592pp; comprehensive history by a leading British schola
excerpt and text search
* Le Roy Ladurie, Emmanuel. ''The Ancien Régime: A History of France 1610–1774'' (1999), survey by leader of the Annales Schoo
excerpt and text search
* Potter, David. ''France in the Later Middle Ages 1200–1500,'' (2003
excerpt and text search
* Potter, David. ''A History of France, 1460–1560: The Emergence of a Nation-State'' (1995) * Price, Roger. ''A Concise History of France'' (1993
excerpt and text search
* Raymond, Gino. ''Historical Dictionary of France'' (2nd ed. 2008) 528pp * Roche, Daniel. ''France in the Enlightenment'' (1998), wide-ranging history 1700–178
excerpt and text search
* Wolf, John B. ''Louis XIV'' (1968), the standard scholarly biograph
online edition
Historiography
* Gildea, Robert. ''The Past in French History'' (1996) * Nora, Pierre, ed. ''Realms of Memory: Rethinking the French Past'' (3 vol, 1996), essays by scholarsexcerpt and text search
* Pinkney, David H. "Two Thousand Years of Paris," ''Journal of Modern History'' (1951) 23#3 pp. 262–26
in JSTOR
* Revel, Jacques, and Lynn Hunt, eds. ''Histories: French Constructions of the Past'' (1995). 654pp, 64 essays; emphasis on Annales School * Symes, Carol. "The Middle Ages between Nationalism and Colonialism," ''French Historical Studies'' (Winter 2011) 34#1 pp 37–46 * Thébaud, Françoise. "Writing Women's and Gender History in France: A National Narrative?" ''Journal of Women's History'' (2007) 19#1 pp. 167–172 in Project MUSE
External links
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Kingdom of France * 1st millennium in France 2nd millennium in France 843 establishments 9th-century establishments in FranceFrance
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
Early Modern France
Former countries in French history
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
Medieval France
States and territories disestablished in 1792
States and territories disestablished in 1815
States and territories disestablished in 1848
States and territories established in 1814
States and territories established in 1815
States and territories established in the 980s