Killarney National Park on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Killarney National Park ( ga, Páirc Náisiúnta Chill Airne), near the town of
 Killarney National Park is one of the very few places in Ireland that has been continuously covered by woodland since the end of the most recent
Killarney National Park is one of the very few places in Ireland that has been continuously covered by woodland since the end of the most recent 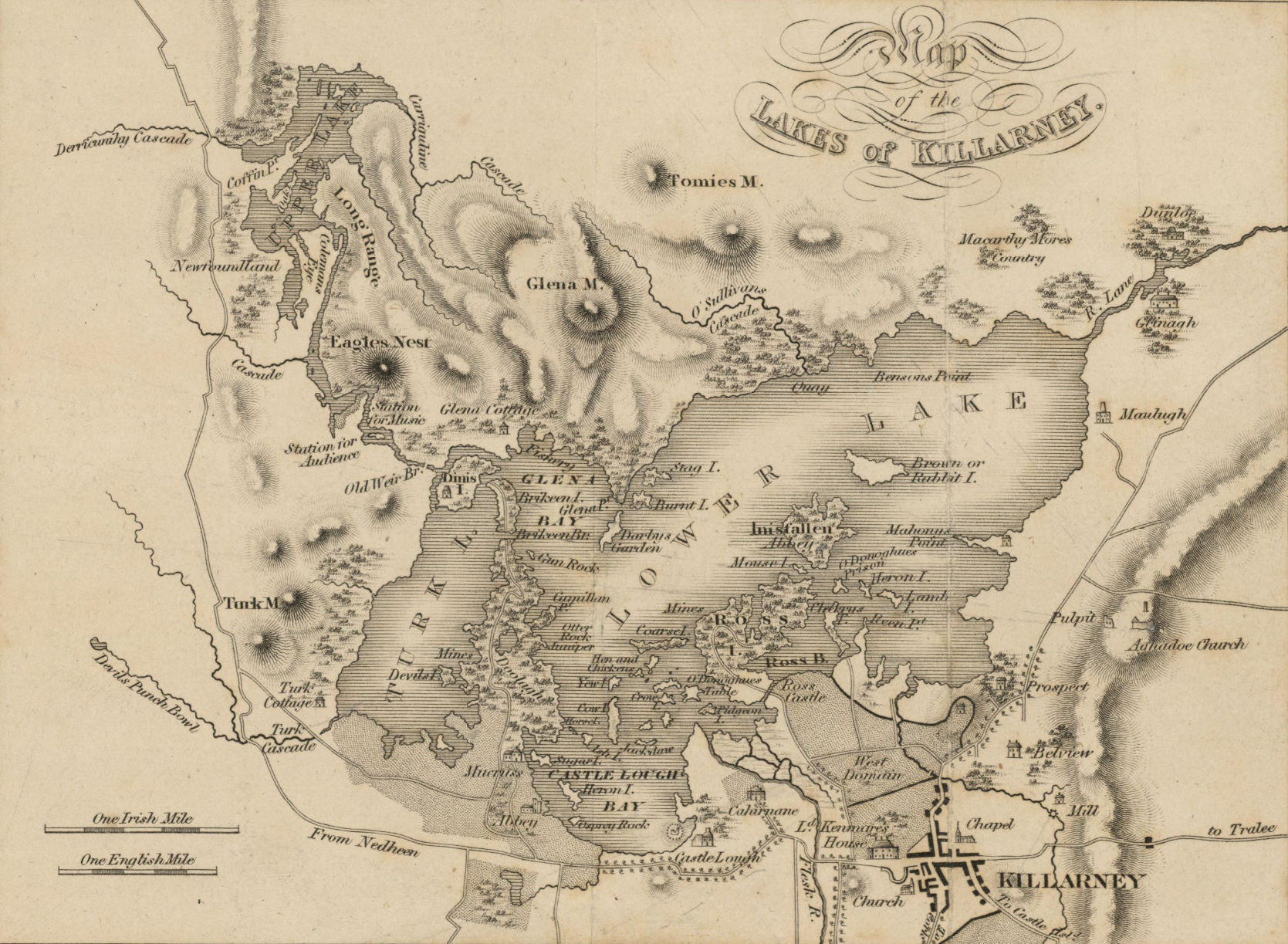 Some of the most impressive archaeological remains in the park are from the early Christian period. The most important of these features is Inisfallen Abbey, the ruins of a
Some of the most impressive archaeological remains in the park are from the early Christian period. The most important of these features is Inisfallen Abbey, the ruins of a  After the Norman invasion of Ireland, the land around the lakes was owned by the McCarthys and
After the Norman invasion of Ireland, the land around the lakes was owned by the McCarthys and
 Maud Vincent died from pneumonia in 1929. In 1932, Arthur Vincent and his parents-in-law donated Muckross Estate to the Irish state in her memory. The estate was renamed as the Bourn Vincent Memorial Park. The Irish government created the national park by passing the Bourn Vincent Memorial Park Act in 1932. The Act required the Commissioners of Public Works to "maintain and manage the Park as a National Park for the purpose of the recreation and enjoyment of the public." The memorial park is the core of today's enlarged national park.
Initially the
Maud Vincent died from pneumonia in 1929. In 1932, Arthur Vincent and his parents-in-law donated Muckross Estate to the Irish state in her memory. The estate was renamed as the Bourn Vincent Memorial Park. The Irish government created the national park by passing the Bourn Vincent Memorial Park Act in 1932. The Act required the Commissioners of Public Works to "maintain and manage the Park as a National Park for the purpose of the recreation and enjoyment of the public." The memorial park is the core of today's enlarged national park.
Initially the

 The Lakes of Killarney are Lough Leane (the lower lake),
The Lakes of Killarney are Lough Leane (the lower lake),
 The
The
 The park has Ireland's only remaining wild herd of native deer (''Cervus elaphus''), comprising approximately 900 individuals. an increase from less than 100 individuals in 1970. They are found in upland areas of the park, mostly on Mangerton and Torc mountains. This herd has been continuously in Ireland for 4,000 years, since the return of red deer to the island, possibly aided by humans, after the last ice age, approximately 10,500 years ago. They were protected in the past by the Kenmare and Muckross estates. The herd is not completely pure because stags were introduced to the herd to improve antler quality in the 19th century.
Pregnant hinds from the lowland areas frequently go to the mountains to give birth in early June. The National Park staff tags the calves. Although red deer and sika deer are capable of interbreeding, no cases of crossbreeding have been recorded in the park. High priority is given to maintaining the genetic purity of the native red deer herd. Red deer are fully protected by law, and their hunting is not permitted.
Sika deer (''Cervus nippon'') were introduced to the park from Japan in 1865. Their population has increased considerably since then. It is estimated there is also up to 1000 Sika deer in Killarney National Park. Within the park they are found both on open upland areas and woodlands.
The park has Ireland's only remaining wild herd of native deer (''Cervus elaphus''), comprising approximately 900 individuals. an increase from less than 100 individuals in 1970. They are found in upland areas of the park, mostly on Mangerton and Torc mountains. This herd has been continuously in Ireland for 4,000 years, since the return of red deer to the island, possibly aided by humans, after the last ice age, approximately 10,500 years ago. They were protected in the past by the Kenmare and Muckross estates. The herd is not completely pure because stags were introduced to the herd to improve antler quality in the 19th century.
Pregnant hinds from the lowland areas frequently go to the mountains to give birth in early June. The National Park staff tags the calves. Although red deer and sika deer are capable of interbreeding, no cases of crossbreeding have been recorded in the park. High priority is given to maintaining the genetic purity of the native red deer herd. Red deer are fully protected by law, and their hunting is not permitted.
Sika deer (''Cervus nippon'') were introduced to the park from Japan in 1865. Their population has increased considerably since then. It is estimated there is also up to 1000 Sika deer in Killarney National Park. Within the park they are found both on open upland areas and woodlands.

 The park has a number of conservation and management challenges. One of these is the park's proximity to Killarney town, one of Ireland's best known tourist destinations. Killarney has hundreds of thousands of visitors every year. Most of these visitors spend time in the park. Careful management is needed to ensure minimal conflict between conservation and recreation.
The past introduction of several exotic species to the park is an additional human influence on the area. These species have damaged the natural ecosystems of Killarney. The most notable of these species are the common rhododendron (''Rhododendron ponticum''), which has infested large areas of the National Park, and sika deer, which overgraze the woodland floor and pose a potential threat to the genetic integrity of the native red deer. Both rhododendron and sika deer can have an adverse effect on the native flora by inhibiting regeneration. A more recent, accidental, introduction is the
The park has a number of conservation and management challenges. One of these is the park's proximity to Killarney town, one of Ireland's best known tourist destinations. Killarney has hundreds of thousands of visitors every year. Most of these visitors spend time in the park. Careful management is needed to ensure minimal conflict between conservation and recreation.
The past introduction of several exotic species to the park is an additional human influence on the area. These species have damaged the natural ecosystems of Killarney. The most notable of these species are the common rhododendron (''Rhododendron ponticum''), which has infested large areas of the National Park, and sika deer, which overgraze the woodland floor and pose a potential threat to the genetic integrity of the native red deer. Both rhododendron and sika deer can have an adverse effect on the native flora by inhibiting regeneration. A more recent, accidental, introduction is the

 The park is open for tourism year-round. There is a visitor and education centre at Killarney House. Visitor attractions in the park include Dinis Cottage, Knockreer Demesne, Inisfallen Island, Ladies View, the Meeting of the Waters and the Old Weir Bridge, Muckross Abbey, Muckross House, the Muckross Peninsula, the Old Kenmare Road, O'Sullivan's Cascade, Ross Castle and Ross Island, Tomies Oakwood, and Torc Waterfall. There is a network of surfaced paths in the Knockreer, Muckross, and Ross Island areas that can be used by cyclists and walkers. The Old Kenmare Road and the track around Tomies Oakwood have views over Lough Leane and Killarney. Boat trips on the lakes are available.
Muckross House is a Victorian mansion, close to Muckross Lake's eastern shore, beneath the backdrop of Mangerton and Torc mountains. The house has now been restored and attracts more than 250,000 visitors a year. Muckross Gardens are famous for their collection of rhododendrons, hybrids and azaleas, and exotic trees. Muckross Traditional Farms is a working farm project that recreates Irish rural life in the 1930s, prior to electrification. Knockreer House is used as the National Park Education Centre.
The park is open for tourism year-round. There is a visitor and education centre at Killarney House. Visitor attractions in the park include Dinis Cottage, Knockreer Demesne, Inisfallen Island, Ladies View, the Meeting of the Waters and the Old Weir Bridge, Muckross Abbey, Muckross House, the Muckross Peninsula, the Old Kenmare Road, O'Sullivan's Cascade, Ross Castle and Ross Island, Tomies Oakwood, and Torc Waterfall. There is a network of surfaced paths in the Knockreer, Muckross, and Ross Island areas that can be used by cyclists and walkers. The Old Kenmare Road and the track around Tomies Oakwood have views over Lough Leane and Killarney. Boat trips on the lakes are available.
Muckross House is a Victorian mansion, close to Muckross Lake's eastern shore, beneath the backdrop of Mangerton and Torc mountains. The house has now been restored and attracts more than 250,000 visitors a year. Muckross Gardens are famous for their collection of rhododendrons, hybrids and azaleas, and exotic trees. Muckross Traditional Farms is a working farm project that recreates Irish rural life in the 1930s, prior to electrification. Knockreer House is used as the National Park Education Centre.
National Parks of Ireland
{{Authority control 1932 establishments in Ireland Biosphere reserves of the Republic of Ireland Forests and woodlands of the Republic of Ireland Geography of County Kerry Killarney National parks of the Republic of Ireland Parks in County Kerry Protected areas established in 1932 Special Areas of Conservation in the Republic of Ireland
Killarney
Killarney ( ; ga, Cill Airne , meaning 'church of sloes') is a town in County Kerry, southwestern Ireland. The town is on the northeastern shore of Lough Leane, part of Killarney National Park, and is home to St Mary's Cathedral, Ross Cast ...
, County Kerry
County Kerry ( gle, Contae Chiarraí) is a county in Ireland. It is located in the South-West Region and forms part of the province of Munster. It is named after the Ciarraige who lived in part of the present county. The population of the co ...
, was the first national park in Ireland, created when the Muckross Estate was donated to the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between the ...
in 1932. The park has since been substantially expanded and encompasses over 102.89 km2 (25,425 acres) of diverse ecology, including the Lakes of Killarney, oak and yew
Yew is a common name given to various species of trees.
It is most prominently given to any of various coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Taxus'':
* European yew or common yew (''Taxus baccata'')
* Pacific yew or western yew (''Taxus br ...
woodlands of international importance, and mountain peaks. It has the only red deer herd on mainland Ireland and the most extensive covering of native forest
An old-growth forestalso termed primary forest, virgin forest, late seral forest, primeval forest, or first-growth forestis a forest that has attained great age without significant disturbance, and thereby exhibits unique ecological featur ...
remaining in Ireland. The park is of high ecological value because of the quality, diversity, and extensiveness of many of its habitats and the wide variety of species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of ...
that they accommodate, some of which are rare. The park was designated a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or o ...
in 1981.
The park forms part of a Special Area of Conservation
A Special Area of Conservation (SAC) is defined in the European Union's Habitats Directive (92/43/EEC), also known as the ''Directive on the Conservation of Natural Habitats and of Wild Fauna and Flora''. They are to protect the 220 habitats and ap ...
and a Special Protection Area.
The National Parks and Wildlife Service is responsible for the management and administration of the park. Nature conservation
Nature conservation is the moral philosophy and conservation movement focused on protecting species from extinction, maintaining and restoring habitats, enhancing ecosystem services, and protecting biological diversity. A range of values under ...
is the main objective of the park, and ecosystems in their natural state are highly valued. The park is known for its scenery,
and recreation and tourism amenities are provided for.
Climate and geography
Killarney National Park is in southwest Ireland close to the island's most westerly point. The Lakes of Killarney and the Mangerton,Torc
A torc, also spelled torq or torque, is a large rigid or stiff neck ring in metal, made either as a single piece or from strands twisted together. The great majority are open at the front, although some had hook and ring closures and a few had ...
, Shehy and Purple Mountains are in the park. Altitudes in the park range from to . A major geological boundary between Devonian Old Red Sandstone
The Old Red Sandstone is an assemblage of rocks in the North Atlantic region largely of Devonian age. It extends in the east across Great Britain, Ireland and Norway, and in the west along the northeastern seaboard of North America. It also exte ...
and Carboniferous limestone
Carboniferous Limestone is a collective term for the succession of limestones occurring widely throughout Great Britain and Ireland that were deposited during the Dinantian Epoch of the Carboniferous Period. These rocks formed between 363 and 3 ...
lies in the park. The underlying geology of the majority of the park is sandstone, with the limestone pavement
A limestone pavement is a natural karst landform consisting of a flat, incised surface of exposed limestone that resembles an artificial pavement. The term is mainly used in the UK and Ireland, where many of these landforms have developed dist ...
s occurring on the low eastern shore of Lough Leane.
Lough Leane is the largest of the Killarney lakes and contains over 30 islands. Some visitors avail of boat trips to Innisfallen, one of the larger islands on Lough Leane.
The park has an oceanic climate, heavily influenced by the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the Unit ...
. It experiences mild winters ( February average) and cool summers ( July average). Mean daily temperatures range from a low of in January to a high of in July. The park experiences high rainfall and changeable fronts, with light showery rainfall being frequent throughout the year. The mean rainfall is per year, 223 days per annum typically having more than precipitation. The mean number of frost days is 40.
The geological boundary, the park's wide range of altitudes, and the climatic influence of the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the Unit ...
combine to give the park a varied ecology. These ecosystems include bogs, lakes, moorland
Moorland or moor is a type of habitat found in upland areas in temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands and montane grasslands and shrublands biomes, characterised by low-growing vegetation on acidic soils. Moorland, nowadays, generall ...
, mountains, waterways, woodland, parks and gardens. Outcropping rock, cliffs and crags are features of the park. Above , the mountainous sandstone areas support large areas of blanket bog
Blanket bog or blanket mire, also known as featherbed bog, is an area of peatland, forming where there is a climate of high rainfall and a low level of evapotranspiration, allowing peat to develop not only in wet hollows but over large expanses o ...
and heath.
History
Early history
 Killarney National Park is one of the very few places in Ireland that has been continuously covered by woodland since the end of the most recent
Killarney National Park is one of the very few places in Ireland that has been continuously covered by woodland since the end of the most recent glacial period
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betw ...
, approximately 10,000 years ago. Humans have lived in the area since at least the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
, approximately 4,000 years ago. Archaeologists
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes ...
have found evidence that copper mining
Copper extraction refers to the methods used to obtain copper from its ores. The conversion of copper consists of a series of physical and electrochemical processes. Methods have evolved and vary with country depending on the ore source, loc ...
took place in the Ross Island
Ross Island is an island formed by four volcanoes in the Ross Sea near the continent of Antarctica, off the coast of Victoria Land in McMurdo Sound. Ross Island lies within the boundaries of Ross Dependency, an area of Antarctica claimed by New ...
area during this period, which suggests that the area was of considerable importance to Bronze Age people. The park has many archaeological features, including a well preserved stone circle at Lissivigeen. The woods in the park have been disturbed and cleared at different periods since the Iron Age. This has caused a gradual decline in the diversity
Diversity, diversify, or diverse may refer to:
Business
*Diversity (business), the inclusion of people of different identities (ethnicity, gender, age) in the workforce
* Diversity marketing, marketing communication targeting diverse customers
...
of tree species in the park.
 Some of the most impressive archaeological remains in the park are from the early Christian period. The most important of these features is Inisfallen Abbey, the ruins of a
Some of the most impressive archaeological remains in the park are from the early Christian period. The most important of these features is Inisfallen Abbey, the ruins of a monastic settlement Monastic settlements are areas built up in and around the development of monasteries with the spread of Christianity. To understand Christian monastic settlements, we must understand a brief history of Christian monasticism. Monasticism was a moveme ...
on Inisfallen Island in Lough Leane. It was founded in the 7th century CE by St. Finian the Leper and was occupied until the 14th century. The ''Annals of Inisfallen
Annals ( la, annāles, from , "year") are a concise historical record in which events are arranged chronologically, year by year, although the term is also used loosely for any historical record.
Scope
The nature of the distinction between anna ...
'', a record of the early history of Ireland as it was known by the monks, was written in the monastery from the 11th to 13th centuries. It is thought that the monastery gave rise to the name Lough Leane, which means "Lake of Learning".
Muckross Abbey was founded in 1448 by Observantine Franciscans and is also still standing, despite having been damaged and reconstructed several times when its inhabitants were raided. "Friars Glen" on Mangerton Mountain is customarily said to have been one of the places the monks would flee to when the monastery was attacked. The central feature of Muckross Abbey is a central courtyard that contains a huge yew tree surrounded by a vaulted cloister
A cloister (from Latin ''claustrum'', "enclosure") is a covered walk, open gallery, or open arcade running along the walls of buildings and forming a quadrangle or garth. The attachment of a cloister to a cathedral or church, commonly against a ...
. It is traditionally said that this tree is as old as Muckross Abbey itself. The abbey was the burial place of local chieftains. In the 17th and 18th centuries the Kerry poets Seafraidh O'Donoghue, Aogán Ó Rathaille
Aodhagán Ó RathailleVariant Irish spellings of his name include ''Aogán'' and ''Ua Rathaille'' or Egan O'Rahilly (c.1670–1726), was an Irish language poet. He is credited with creating the first fully developed Aisling.
Early life
It is tho ...
, and Eoghan Rua Ó Súilleabháin
Eoghan Rua Ó Súilleabháin (174829 June 1784), anglicized as Owen Roe O'Sullivan ("Red Owen"), was an Irish poet. He is known as one of the last great Gaelic poets. A recent anthology of Irish-language poetry speaks of his "extremely musical" p ...
were buried there.
 After the Norman invasion of Ireland, the land around the lakes was owned by the McCarthys and
After the Norman invasion of Ireland, the land around the lakes was owned by the McCarthys and O'Donoghue
Donoghue or O'Donoghue is an anglicized form of the Irish language surname Ó Donnchadha or Ó Donnchú.
Etymology
The name means "descendant of Donnchadh", a personal name composed of the elements ''donn'' "brown-haired an and ''cath'' "battle" ...
s. Ross Castle is a 15th-century tower house on the shore of Lough Leane. It was once the residence of the chieftain O'Donoghue Mór. The castle was extended in the 17th century. It has been restored and is open to the public. A 1580s Elizabethan
The Elizabethan era is the epoch in the Tudor period of the history of England during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I (1558–1603). Historians often depict it as the golden age in English history. The symbol of Britannia (a female personific ...
military record describes the Killarney area as a meagrely inhabited wilderness of forest and mountains.
From the 18th century the land in today's park were divided between two great estates, the Herberts of Muckross and the Brownes (Earls of Kenmare
The title of Earl of Kenmare was created in the Peerage of Ireland in 1801. It became extinct upon the death of the 7th Earl in 1952.
All of the Earls bore the subsidiary titles of Viscount Castlerosse (1801), Viscount Kenmare (1798), and Baron ...
). During the 17th and 18th centuries the woods were extensively utilised for local industries including charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, cal ...
production, cooperage and tanning. Pressure on the woods intensified in the later part of the 18th century. The biggest cause of oakwood destruction in Killarney in the 18th century was the production of charcoal to fire smelters
Smelting is a process of applying heat to ore, to extract a base metal. It is a form of extractive metallurgy. It is used to extract many metals from their ores, including silver, iron, copper, and other base metals. Smelting uses heat and a ch ...
used in the local iron industry. Approximately 25 ton
Ton is the name of any one of several units of measure. It has a long history and has acquired several meanings and uses.
Mainly it describes units of weight. Confusion can arise because ''ton'' can mean
* the long ton, which is 2,240 pounds
...
s of oak was needed to produce one ton of cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impuriti ...
. In 1780 Young famously described Derrycunihy wood as "a great sweep of mountain, covered partly in wood, hanging in a very noble manner, but part cut down, much of it mangled, and the rest inhabited by coopers, boat-builders, carpenters and turners..."
Woodland exploitation again increased during the Napoleonic era in the early 19th century, probably because of the high prices that oak was commanding at this time. Replanting and management of the oak forests was promoted at this time. There was a large-scale felling of oak trees at Ross Island in 1803, Glena in around 1804 and Tomies in 1805. Tomies was then replanted with three-year-old oak and Glena was coppiced
Coppicing is a traditional method of woodland management which exploits the capacity of many species of trees to put out new shoots from their stump or roots if cut down. In a coppiced wood, which is called a copse, young tree stems are repeate ...
. These activities have increased the relative abundance of oak in the park in the past 200 years. As most of the oak trees in the woods today are around 200 years old, it is likely that the majority of them were planted, and the oakwoods that have never been disturbed by humans are restricted to a few isolated pockets in remote areas such as mountain valleys.
The Herbert family owned the land on the Muckross Peninsula from 1770 onwards. They became very wealthy from copper mines on this land. Henry Arthur Herbert and his wife—the water colourist Mary Balfour Herbert—finished building Muckross House in 1843. The Herbert's financial situation became precarious in the late 19th century, and the Muckross estate was purchased by Lord Ardilaun
Arthur Edward Guinness, 1st Baron Ardilaun, 2nd Baronet (1 November 1840 – 20 January 1915), known as Sir Arthur Guinness, Bt, between 1868 and 1880, was an Irish businessman, politician, and philanthropist, best known for giving St Stephen's ...
of the Guinness brewing family in 1899.
Creation of the park
In 1910, the American William Bowers Bourn bought Muckross Estate as a wedding present for his daughter Maud on her marriage to Arthur Vincent. They spent £110,000 improving the estate between 1911 and 1932, building the Sunken Garden, the Stream Garden, and arock garden
A rock garden, also known as a rockery and formerly as a rockwork, is a garden, or more often a part of a garden, with a landscaping framework of rocks, stones, and gravel, with planting appropriate to this setting. Usually these are small ...
on an outcrop of limestone.
 Maud Vincent died from pneumonia in 1929. In 1932, Arthur Vincent and his parents-in-law donated Muckross Estate to the Irish state in her memory. The estate was renamed as the Bourn Vincent Memorial Park. The Irish government created the national park by passing the Bourn Vincent Memorial Park Act in 1932. The Act required the Commissioners of Public Works to "maintain and manage the Park as a National Park for the purpose of the recreation and enjoyment of the public." The memorial park is the core of today's enlarged national park.
Initially the
Maud Vincent died from pneumonia in 1929. In 1932, Arthur Vincent and his parents-in-law donated Muckross Estate to the Irish state in her memory. The estate was renamed as the Bourn Vincent Memorial Park. The Irish government created the national park by passing the Bourn Vincent Memorial Park Act in 1932. The Act required the Commissioners of Public Works to "maintain and manage the Park as a National Park for the purpose of the recreation and enjoyment of the public." The memorial park is the core of today's enlarged national park.
Initially the Irish Government
The Government of Ireland ( ga, Rialtas na hÉireann) is the cabinet that exercises executive authority in Ireland.
The Constitution of Ireland vests executive authority in a government which is headed by the , the head of government. The gover ...
was unable to provide much financial support to the park, so it operated primarily as a working farm that was open to the public. Muckross House was closed to the public until 1964.
Around 1970 there was public disquiet about threats to the Bourn Vincent Memorial Park. The Irish authorities looked at international practices in classifying and managing of national parks. It was decided to expand and re-designate the park as a national park that corresponded broadly to IUCN Category II
IUCN protected area categories, or IUCN protected area management categories, are categories used to classify protected areas in a system developed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
The enlisting of such areas is part ...
. A decision was also made to establish other national parks in Ireland. Almost has been added to the original park, including the three lakes, Knockreer Estate, Ross Island, Innisfallen, and the townlands of Glena, Ullauns, and Poulagower. The park is now more than double the size it was in 1932. As the Irish economy became wealthier and the perception of the role of national parks changed, much more money was made available to the park.
Lakes of Killarney
 The Lakes of Killarney are Lough Leane (the lower lake),
The Lakes of Killarney are Lough Leane (the lower lake), Muckross Lake
Muckross Lake (), also called Middle Lake or The Torc, is a lake in Killarney National Park, County Kerry, Ireland. It is one of the three famous Lakes of Killarney, along with Lough Leane and Upper Lake. It is Ireland's deepest lake, reaching ...
(the middle lake), and the Upper Lake. These lakes are interlinked and together make up almost a quarter of the park's area. Despite being interlinked, each lake has a unique ecosystem. The lakes join at the Meeting of the Waters, a popular tourist area. Sport angling on the lakes has been a pastime in the area for some time, in particular of the lakes' brown trout
The brown trout (''Salmo trutta'') is a European species of salmonid fish that has been widely introduced into suitable environments globally. It includes purely freshwater populations, referred to as the riverine ecotype, ''Salmo trutta'' morp ...
and salmon populations.
Lough Leane is approximately in size and is by far the largest of the three lakes. It is also the largest body of fresh water in the region.
It is also the lake richest in nutrients. It has become eutrophic as a result of phosphates from agricultural and domestic pollution entering Lough Leane Reedbed, an important habitat on the edge of Lough Leane. This nutrient enrichment has caused several algal bloom
An algal bloom or algae bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in freshwater or marine water systems. It is often recognized by the discoloration in the water from the algae's pigments. The term ''algae'' encompass ...
s in recent years. The blooms have not yet had a severe effect on the lake's ecosystem. To prevent further pollution causing a permanent change in the lake's ecosystem, a review of land use in the catchment
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
area is being carried out. Water quality in the lake appears to have improved since phosphates were removed from sewage in 1985. As of August 2007, several large hotels and businesses have stated their intention to stop using phosphate detergents, in an effort to preserve the quality of the lake water.
Muckross Lake
Muckross Lake (), also called Middle Lake or The Torc, is a lake in Killarney National Park, County Kerry, Ireland. It is one of the three famous Lakes of Killarney, along with Lough Leane and Upper Lake. It is Ireland's deepest lake, reaching ...
is the deepest of the three lakes. It has a maximum depth of , close to where the steeply sloping side of Torc Mountain enters the lake. The lake lies on the geological boundary between the sandstone mountains to the south and west and the limestone to the north.
Lough Leane and Muckross Lake lie across the geological boundary. The presence of limestone causes both of the lakes to be slightly richer in nutrients than the Upper Lake. There are many caves in the limestone at lake level, created by wave action combined with the dissolution
Dissolution may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Books
* ''Dissolution'' (''Forgotten Realms'' novel), a 2002 fantasy novel by Richard Lee Byers
* ''Dissolution'' (Sansom novel), a 2003 historical novel by C. J. Sansom Music
* Dissolution, in mu ...
effect of the lakes' acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
ic water on the exposed rock. These caves are largest on the northern shore of Muckross Lake.
From the Meeting of the Waters a narrow channel called the Long Range leads to the Upper Lake, the smallest of the three lakes. This lake is located in rugged mountain scenery in the upper Killarney/Black Valley area. The fast run-off in its catchment area can cause the level of the lake to rise by up to a meter in a few hours during heavy rain.
Muckross Lake and the Upper Lake are high quality oligotrophic systems, with water that is slightly acidic and low in nutrients. This is caused by run-off from the upland sandstones and blanket bogs in their catchment areas. They have diverse aquatic vegetation
Aquatic plants are plants that have adapted to living in aquatic environments (saltwater or freshwater). They are also referred to as hydrophytes or macrophytes to distinguish them from algae and other microphytes. A macrophyte is a plant that g ...
, including quillwort
''Isoetes'', commonly known as the quillworts, is the only extant genus of plants in the family Isoetaceae, which is in the class of lycopods. There are currently 192 recognized species, with a cosmopolitan distribution but with the individual s ...
(''Isoetes lacustris''), shoreweed (''Littorella uniflora''), and water lobelia (''Lobelia dortmanna'').
All three lakes are very acid sensitive and therefore vulnerable to afforestation
Afforestation is the establishment of a forest or stand of trees (forestation) in an area where there was no previous tree cover. Many government and non-governmental organizations directly engage in afforestation programs to create forests a ...
within their catchment areas.
Woodlands
Killarney possesses the most extensive area (approximately ) of semi-natural native woodland (woodland dominated byindigenous species
In biogeography, a native species is indigenous to a given region or ecosystem if its presence in that region is the result of only local natural evolution (though often popularised as "with no human intervention") during history. The term is equi ...
) remaining in Ireland. Most of this woodland is encompassed by the national park. There are three main types of woodland in the park: acidophilous oak woodland (''Quercus petraea-Ilex aquifolium'') on Devonian sandstone; moss-rich yew woodland (''Taxus baccata'') on Carboniferous limestone outcrops; and wet woodland (also called carr) dominated by alder
Alders are trees comprising the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus comprises about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few spe ...
on low-lying swampy limestone soils on the lake edges. The woods in the park fall naturally into two sectors, along the geologic divide. The oak and yew woodlands are of international importance.
Mixed woodland
Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest is a temperate climate terrestrial habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature, with broadleaf tree ecoregions, and with conifer and broadleaf tree mixed coniferous forest ecoregions.
These fo ...
and conifer plantations also occur in the park. The mixed woodland on Ross Island has one of the richest herb layers in the park's woods.
Grazing and rhododendron
''Rhododendron'' (; from Ancient Greek ''rhódon'' "rose" and ''déndron'' "tree") is a very large genus of about 1,024 species of woody plants in the heath family (Ericaceae). They can be either evergreen or deciduous. Most species are nat ...
invasion threaten the park's woodlands. Rhododendrons affect approximately two-thirds of the oak woodlands. A rhododendron removal programme is under way in the park. The yew woodlands have been negatively affected by heavy grazing for many years.
Oak woodlands
The park is perhaps most famous for its oak woodlands, which are about in size. They form the largest area of native woodland remaining in Ireland and are a remnant of the woodland that once covered much of Ireland. Derrycunihy Wood is perhaps the most natural sessile oak (''Quercus petraea'') wood in Ireland. Most of the oak woodlands are located on the lower slopes of the Shehy and Tomy mountains, adjacent to Lough Leane. They are typically dominated by sessile oak, which favours the acidic soils of the sandstone mountains. The woods have Annex I status in theEU Habitats Directive
The Habitats Directive (more formally known as Council Directive 92/43/EEC on the Conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora) is a directive adopted by the European Community in 1992 as a response to the Berne Convention. The E ...
because of their diverse and rich flora, most notably their bryophyte
The Bryophyta s.l. are a proposed taxonomic division containing three groups of non-vascular land plants (embryophytes): the liverworts, hornworts and mosses. Bryophyta s.s. consists of the mosses only. They are characteristically limited in s ...
s ( mosses and liverwort
The Marchantiophyta () are a division of non-vascular land plants commonly referred to as hepatics or liverworts. Like mosses and hornworts, they have a gametophyte-dominant life cycle, in which cells of the plant carry only a single set of ge ...
s).
The oak woodlands typically have an understory of holly
''Ilex'' (), or holly, is a genus of over 570 species of flowering plants in the family Aquifoliaceae, and the only living genus in that family. ''Ilex'' has the most species of any woody dioecious angiosperm genus. The species are evergreen o ...
(''Ilex aquifolium''). Strawberry trees (''Arbutus unedo'') are a notable part of these woods. There are also scattered yews. The field layer includes bilberry
Bilberries (), or sometimes European blueberries, are a primarily Eurasian species of low-growing shrubs in the genus '' Vaccinium'' (family Ericaceae), bearing edible, dark blue berries. The species most often referred to is ''Vaccinium myrti ...
and woodrush. The herb layer is not rich in species.
Bryophytes, lichens and filmy ferns (''Hymenophyllaceae''), thrive in the humid oceanic climate. Species with restricted Atlantic distributions grow in the woods. The bryophytes in these woods are perhaps the best-developed Atlantic bryophyte
The Bryophyta s.l. are a proposed taxonomic division containing three groups of non-vascular land plants (embryophytes): the liverworts, hornworts and mosses. Bryophyta s.s. consists of the mosses only. They are characteristically limited in s ...
community in Europe. The remote Glaism na Marbh valley has a particularly rich flora of bryophytes, some of which are scarce or absent in other parts of the woods. Mosses, ferns and liverworts frequently occur as epiphytes, attached to the trunks and branches of oak trees. Rare species growing in the woods include '' Cyclodictyon laetevirens'', '' Daltonia splachnoides'', ''Lejeunea flava
''Lejeunea'' is a genus of leafy liverworts in the Lejeuneaceae family. The GBIF lists up to 592 species (as of October 2022), along with a worldwide distribution.
The genus was circumscribed by Marie-Anne Libert in Ann. Gen. Sci. Phys. vol.6 on ...
'', '' Radula carringtonii'', and '' Sematophyllum demissum''.
Bird species that reside in the oak woods include blue tit
The Eurasian blue tit (''Cyanistes caeruleus'') is a small passerine bird in the tit family, Paridae. It is easily recognisable by its blue and yellow plumage and small size.
Eurasian blue tits, usually resident and non-migratory birds, a ...
, common chaffinch
The common chaffinch or simply the chaffinch (''Fringilla coelebs'') is a common and widespread small passerine bird in the finch family. The male is brightly coloured with a blue-grey cap and rust-red underparts. The female is more subdued in ...
, goldcrest
The goldcrest (''Regulus regulus'') is a very small passerine bird in the kinglet family. Its colourful golden crest feathers, as well as being called the "king of the birds" in European folklore, gives rise to its English and scientific n ...
, European robin
The European robin (''Erithacus rubecula''), known simply as the robin or robin redbreast in Great Britain & Ireland, is a small insectivorous passerine bird that belongs to the chat subfamily of the Old World flycatcher family. About in len ...
, and wren. Mammals include badger
Badgers are short-legged omnivores in the family Mustelidae (which also includes the otters, wolverines, martens, minks, polecats, weasels, and ferrets). Badgers are a polyphyletic rather than a natural taxonomic grouping, being united by ...
, fox, pine marten
The European pine marten (''Martes martes''), also known as the pine marten, is a mustelid native to and widespread in most of Europe, Asia Minor, the Caucasus and parts of Iran, Iraq and Syria. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List ...
, red deer, sika deer
The sika deer (''Cervus nippon''), also known as the Northern spotted deer or the Japanese deer, is a species of deer native to much of East Asia and introduced to other parts of the world. Previously found from northern Vietnam in the south to ...
, and red squirrel. Insects include many species of the parasitic gall wasp
Gall wasps, also incorrectly called gallflies, are hymenopterans of the family Cynipidae in the wasp superfamily Cynipoidea. Their common name comes from the galls they induce on plants for larval development. About 1,300 species of this gener ...
and the purple hairstreak
The purple hairstreak (''Favonius quercus'') is a butterfly in the family Lycaenidae distributed throughout much of Europe, North Africa, Anatolia, Caucasia, and Transcaucasia.
The larva feeds on ''Quercus robur'', ''Quercus petraea'', ''Quer ...
butterfly, whose caterpillar is entirely dependent upon oak trees.
The introduced common rhododendron is a large threat to certain areas of the oak woods. For example, it is widespread throughout Camillan Wood despite ongoing attempts to control it.
Yew woodlands
 The
The yew
Yew is a common name given to various species of trees.
It is most prominently given to any of various coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Taxus'':
* European yew or common yew (''Taxus baccata'')
* Pacific yew or western yew (''Taxus br ...
woodland in the park is known as Reenadinna Wood. It is about in size and is located on low-lying karst
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathering-resistant ...
limestone pavement between Muckross Lake and Lough Leane on Muckross Peninsula. Yew woodland is the rarest habitat type in the park. Yew woodlands are one of the rarest types of woodland in Europe, mostly restricted to western Ireland and southern England. It has priority habitat status under Annex I of the EU Habitats Directive. Reenadinna Wood is also one of the largest woods that are dominated by common yew (''Taxus baccata'' L.) in the UK and Ireland. It is the only significant area of yew woodland in Ireland and is one of just three pure yew woodlands in Europe. It is of considerable ecological and conservation interest, as yew is rarely a woodland dominant. The western limit of the wood lies along the geological boundary with Devonian Old Red Sandstone. The wood is bounded to the east by parkland where the limestone no longer outcrops. Muckross bog, a raised bog in area, is in the southern part of the wood. There are hollows between the limestone outcrops. Deep rendzina
Rendzina (or ''rendsina'') is a soil type recognized in various soil classification systems, including those of Britain and Germany as well as some obsolete systems. They are humus-rich shallow soils that are usually formed from carbonate- or oc ...
soils have developed in some of the hollows. It is estimated that the wood developed 3,000–5,000 years ago.
Yew is a native evergreen tree that grows best in the high humidity of mild oceanic climates, which makes Killarney a very suitable location. The soil in the wood is mostly thin and in many places the trees are rooted to fissures in the bare limestone. Yew has an extensive horizontal root system. In the Killarney woods, the roots spread out over the rock surface and penetrate deeply into fissures in the limestone. The wood has a low canopy of 6–14 m (20–46 ft). Yew's extreme tolerance of the dense shade its canopy creates has allowed it to outcompete other species to create the pure yew woodland present today. This dense shade prevents flowering plants from establishing themselves in these woods and prevents the herb layer from developing. Bryophytes are, however, abundant and thrive in humid and cool conditions. In some parts of the wood, there are continuous dense blankets of moss that can be up to deep. The moss species present are primarily '' Thamnium alopecurum'' with '' Eurhynchium striatum'' and ''Thuidium tamariscinum
''Thuidium tamariscinum'' is a species of moss belonging to the family Thuidiaceae. It has an almost cosmopolitan distribution
In biogeography, cosmopolitan distribution is the term for the range of a taxon that extends across all or most of ...
''.
Some of the trees in Re-enadinna wood are two hundred years old. There has been little regeneration of the yew trees in the wood. Overgrazing of the woodland floor by sika deer may be part of the reason for this, but small areas of the wood that have been fenced off since 1969 have experienced very little yew regeneration. The dense canopy created by the yew trees that lets very little sunlight through to the woodland floor may also prevent the growth of yew seedlings.
Despite its poisonous properties, yew is very susceptible to browsing and bark stripping by deer, rabbits, hare, and domestic animals. It is one of the most grazing sensitive trees in the Killarney woodlands. sika deer have killed yews by scoring the trees with their antlers.
Wet woodlands
Wet woodland (also called carr) on the low-lying swampy limestone areas within Lough Leane's floodplain is about in size. This is one of the most extensive areas of this woodland type in Ireland. The dominant canopy species here arealder
Alders are trees comprising the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus comprises about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few spe ...
(''Alnus glutinosa''), ash
Ash or ashes are the solid remnants of fires. Specifically, ''ash'' refers to all non-aqueous, non-gaseous residues that remain after something burns. In analytical chemistry, to analyse the mineral and metal content of chemical samples, ash ...
(''Fraxinus excelsior''), downy birch
''Betula pubescens'' (syn. ''Betula alba''), commonly known as downy birch and also as moor birch, white birch, European white birch or hairy birch, is a species of deciduous tree, native and abundant throughout northern Europe and northern Asi ...
(''Betula pubescens''), and willow (''Salix'' spp.). The areas that are periodically covered by water are rich in species including grasses, rushes, sedges, and flowers such as marsh bedstraw, meadow sweet, and water mint.
Red deer and sika deer heavily use the wetland woods as cover, and bare muddy "deer wallows" are a characteristic feature. Rhododendrons are the greatest threat to these woodlands. They are invading the woodlands, using raised areas such as tussocks or tree bases where the floor is too wet for seedlings to become established. Although some clearance has occurred reinvasion continues.
Bogland
While the lower slopes of the mountains are dominated by sessile oak (''Quercus petraea''), above the mountains are virtually treeless and are dominated byblanket bog
Blanket bog or blanket mire, also known as featherbed bog, is an area of peatland, forming where there is a climate of high rainfall and a low level of evapotranspiration, allowing peat to develop not only in wet hollows but over large expanses o ...
and wet heath. The bogs in the park mostly have a characteristic flora that includes heather (''Calluna vulgaris''), bell heather
''Erica cinerea'', the bell heather, is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae, native to western and central Europe.
The plant provides a great deal of nectar for pollinators. It was rated in the top 5 for most nectar produc ...
(''Erica cinerea'') and western gorse (''Ulex gallii''), with occasional bilberry
Bilberries (), or sometimes European blueberries, are a primarily Eurasian species of low-growing shrubs in the genus '' Vaccinium'' (family Ericaceae), bearing edible, dark blue berries. The species most often referred to is ''Vaccinium myrti ...
(''Vaccinium myrtillus''). Large-flowered butterwort
''Pinguicula'', commonly known as the butterworts, is a genus of carnivorous flowering plants in the family Lentibulariaceae. They use sticky, glandular leaves to lure, trap, and digest insects in order to supplement the poor mineral nutrition ...
(''Pinguicula grandiflora'') is common. The bogs also support a number of notable species, including mosses (''Sphagnum pulchrum'', ''S. fuscum'', ''S. platyphyllum'', ''S. strictum'', ''S. contortum'' and ''Calliergon stramineum''), liverworts (''Cladopodiella francisci'' and ''Calypogeia azurea'') and lichens (''Cladonia mediterranea'', ''C. macilenta'', ''C. rangiferina'', ''C. arbuscula'' and ''Cetraria islandica'').
The remoteness of some of the upland areas aids the survival of Ireland's only remaining wild herd of native red deer. The bogs are threatened by grazing, turbary
Turbary is the ancient right to cut turf, or peat, for fuel on a particular area of bog. The word may also be used to describe the associated piece of bog or peatland and, by extension, the material extracted from the turbary. Turbary rights, whic ...
, burning and afforestation.
Flora
A large number of plant and animal species of interest occur within the site, including most of the native Irish mammal species, several important fish species includingArctic char
The Arctic char or Arctic charr (''Salvelinus alpinus'') is a cold-water fish in the family Salmonidae, native to alpine lakes and arctic and subarctic coastal waters. Its distribution is Circumpolar North. It spawns in freshwater and populati ...
, and a range of rare or scarce plant species. Several of the animal and plant species in the park have a hiberno-lusitanean distribution, meaning that they only occur in southwest Ireland, northern Spain, and Portugal. The main reason for this is the effect of the Gulf Stream on southwest Ireland's climate. The park has been designated a biosphere reserve because of the presence of such rare species.
Significant amounts of plant species found in the park have unusual geographic distributions and are of localised occurrence within Ireland. These plant species are grouped within four main categories: arctic-alpine plants, Atlantic species, North American species and very rare species. Atlantic species are species which are otherwise found mostly in southern and south-western Europe, for example arbutus
''Arbutus'' is a genus of 12 accepted speciesAct. Bot. Mex no.99 Pátzcuaro abr. 2012.''Arbutus bicolor''/ref> of flowering plants in the family Ericaceae, native to warm temperate regions of the Mediterranean, western Europe, the Canary Isla ...
, St Patrick's cabbage and greater butterwort. North American species include blue-eyed grass
''Sisyrinchium'' is a large genus of annual to perennial flowering plant in the family Iridaceae. Native to the New World, the species are known as blue-eyed grasses and, though not true grasses and in varieties with flower colors other than ...
and pipewort.
Bryophytes
Bryophytes (mosses and liverworts) flourish in the park, due partly to the area's mild oceanic climate. The park is internationally significant for bryophytes. Many of the bryophytes found in the park are not found anywhere else in Ireland. Mosses, ferns such as filmy ferns, and liverworts grow luxuriantly. Many of them live as epiphytes, growing on the branches and trunks of trees.Other plant species
The Killarney fern ('' Trichomanes speciosum'') is probably the most rare plant species in the park. It is a filmy fern that grows in the splash zone of waterfalls and other damp places. Although it was once quite common, it was picked almost to extinction when pickers collected it to be sold to tourists. The few sites where this fern remain tend to be in isolated mountainous locations where pickers never found it. Although the strawberry tree (''Arbutus unedo'') is relatively common in the park, it is one of Ireland's rarest native tree species and is found in very few locations outside Killarney. In the park it is found on cliff tops and the edges of the woodlands around the lake. Killarneywhitebeam
The whitebeams are members of the family Rosaceae, comprising subgenus ''Aria'' (or, according to some authorities, its own genus) of genus ''Sorbus'', and hybrids involving species of this subgenus and members of subgenera ''Sorbus'', ''Torminar ...
(''Sorbus anglica'') is a shrub or small tree that grows on rocks close to lakeshores. It is found only in Killarney. The more common Irish whitebeam (''Sorbus hibernica'') is also found in the park.
The greater butterwort (''Pinguicula grandiflora'') (also known as the Kerry violet) is a carnivorous plant
Carnivorous plants are plants that derive some or most of their nutrients from trapping and consuming animals or protozoans, typically insects and other arthropods. Carnivorous plants still generate some of their energy from photosynthesis. Car ...
found in bogs. It digests insects to supplement the poor supply of nutrients (especially nitrogen) available from the bog. Its purple flowers bloom in late May and early June.
Irish spurge
''Euphorbia'' is a very large and diverse genus of flowering plants, commonly called spurge, in the family Euphorbiaceae. "Euphorbia" is sometimes used in ordinary English to collectively refer to all members of Euphorbiaceae (in deference to t ...
(''Euphorbia hyberna'') is an Atlantic species that in Ireland is only found in the southwest. In the past the milky sap
Sap is a fluid transported in xylem cells (vessel elements or tracheids) or phloem sieve tube elements of a plant. These cells transport water and nutrients throughout the plant.
Sap is distinct from latex, resin, or cell sap; it is a separ ...
from its stem was used to cure warts. Fishermen used it to capture fish, utilising compounds in the sap that prevent fish gills from functioning properly and so suffocate the fish.
A number of rare species of myxomycete fungus have been recorded in the park. These are ''Collaria arcyrionema'', ''Craterium muscorum'', ''Cribraria microcarpa'' (the only known location in Ireland), ''C. rufa'', ''C. violacea'', ''Diderma chondrioderma'', ''D. lucidum'', ''D. ochraceum'', ''Fuligo muscorum'', and ''Licea marginata''. The park has a highly diverse lichen flora.
Fauna
Mammals
Most mammals native to Ireland and long established introduced species are found in the park. Thebank vole
The bank vole (''Myodes glareolus'') is a small vole with red-brown fur and some grey patches, with a tail about half as long as its body. A rodent, it lives in woodland areas and is around in length. The bank vole is found in much of Europe an ...
was first identified in 1964 in northwest Kerry. Its range has now expanded and now includes the park. Pine marten
The European pine marten (''Martes martes''), also known as the pine marten, is a mustelid native to and widespread in most of Europe, Asia Minor, the Caucasus and parts of Iran, Iraq and Syria. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List ...
is another notable species in the park.
Deer
 The park has Ireland's only remaining wild herd of native deer (''Cervus elaphus''), comprising approximately 900 individuals. an increase from less than 100 individuals in 1970. They are found in upland areas of the park, mostly on Mangerton and Torc mountains. This herd has been continuously in Ireland for 4,000 years, since the return of red deer to the island, possibly aided by humans, after the last ice age, approximately 10,500 years ago. They were protected in the past by the Kenmare and Muckross estates. The herd is not completely pure because stags were introduced to the herd to improve antler quality in the 19th century.
Pregnant hinds from the lowland areas frequently go to the mountains to give birth in early June. The National Park staff tags the calves. Although red deer and sika deer are capable of interbreeding, no cases of crossbreeding have been recorded in the park. High priority is given to maintaining the genetic purity of the native red deer herd. Red deer are fully protected by law, and their hunting is not permitted.
Sika deer (''Cervus nippon'') were introduced to the park from Japan in 1865. Their population has increased considerably since then. It is estimated there is also up to 1000 Sika deer in Killarney National Park. Within the park they are found both on open upland areas and woodlands.
The park has Ireland's only remaining wild herd of native deer (''Cervus elaphus''), comprising approximately 900 individuals. an increase from less than 100 individuals in 1970. They are found in upland areas of the park, mostly on Mangerton and Torc mountains. This herd has been continuously in Ireland for 4,000 years, since the return of red deer to the island, possibly aided by humans, after the last ice age, approximately 10,500 years ago. They were protected in the past by the Kenmare and Muckross estates. The herd is not completely pure because stags were introduced to the herd to improve antler quality in the 19th century.
Pregnant hinds from the lowland areas frequently go to the mountains to give birth in early June. The National Park staff tags the calves. Although red deer and sika deer are capable of interbreeding, no cases of crossbreeding have been recorded in the park. High priority is given to maintaining the genetic purity of the native red deer herd. Red deer are fully protected by law, and their hunting is not permitted.
Sika deer (''Cervus nippon'') were introduced to the park from Japan in 1865. Their population has increased considerably since then. It is estimated there is also up to 1000 Sika deer in Killarney National Park. Within the park they are found both on open upland areas and woodlands.
Bird species
The Park boasts a wealth of bird life, and is of ornithological importance because it supports a diverse range of birds. 141 bird species have been recorded in the park, including upland, woodland and wintering waterfowl species. Several species which are otherwise rare in Ireland are present, notably the woodland speciesredstart {{Hatnote, For the ship, see USS Redstart (AM-378)
Redstart is a name used for a number of songbirds that are not closely related to each other:
Old world flycatcher family (Muscicapidae)
* ''Phoenicurus'', 14 species found in Africa, Asia and E ...
(1–2 pairs), wood warbler
The wood warbler (''Phylloscopus sibilatrix'') is a common and widespread leaf warbler which breeds throughout northern and temperate Europe, and just into the extreme west of Asian Russia in the southern Ural Mountains.
This warbler is stro ...
(1–2 pairs), and garden warbler
The garden warbler (''Sylvia borin'') is a common and widespread small bird that breeds in most of Europe and in the Palearctic to western Siberia. It is a plain, long-winged and long-tailed typical warbler with brown upperparts and dull white ...
(possibly up to 10 pairs). The red grouse and ring ouzel
The ring ouzel (''Turdus torquatus'') is a mainly European member of the thrush family Turdidae. It is a medium-sized thrush, in length and weighing . The male is predominantly black with a conspicuous white crescent across its breast. Females ...
are on the IUCN Red List of species of high conservation concern (1–2 pairs each). The Greenland white-fronted goose, merlin, and peregrine are listed on Annex I of the EU Birds Directive. Other noteworthy species found in the park are the chough
There are two species of passerine birds commonly called chough ( ) that constitute the genus ''Pyrrhocorax'' of the Corvidae (crow) family of birds. These are the red-billed chough (''Pyrrhocorax pyrrhocorax''), and the Alpine chough (or yell ...
, nightjar
Nightjars are medium-sized nocturnal or crepuscular birds in the family Caprimulgidae and order Caprimulgiformes, characterised by long wings, short legs, and very short bills. They are sometimes called goatsuckers, due to the ancient folk ta ...
, and osprey
The osprey (''Pandion haliaetus''), , also called sea hawk, river hawk, and fish hawk, is a diurnal, fish-eating bird of prey with a cosmopolitan range. It is a large raptor reaching more than in length and across the wings. It is brown o ...
. The osprey sometimes passes through the park as it migrates between northern Africa and Scandinavia. Historical accounts and place names suggest that the osprey bred in the area in the past. Golden eagle
The golden eagle (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known birds ...
s once nested in the park, but were extirpated around 1900 as a result of disturbance, nest robbing, and persecution.
The most common bird species in upland areas are meadow pipit
The meadow pipit (''Anthus pratensis'') is a small passerine bird, which breeds in much of the Palearctic, from southeastern Greenland and Iceland east to just east of the Ural Mountains in Russia, and south to central France and Romania; an isol ...
s, raven
A raven is any of several larger-bodied bird species of the genus ''Corvus''. These species do not form a single taxonomic group within the genus. There is no consistent distinction between "crows" and "ravens", common names which are assigned t ...
s and European stonechat
The European stonechat (''Saxicola rubicola'') is a small passerine bird that was formerly classed as a subspecies of the common stonechat. Long considered a member of the thrush family, Turdidae, genetic evidence has placed it and its relat ...
s. Rare species are merlins (up to five pairs) and peregrine falcon
The peregrine falcon (''Falco peregrinus''), also known as the peregrine, and historically as the duck hawk in North America, is a cosmopolitan bird of prey ( raptor) in the family Falconidae. A large, crow-sized falcon, it has a blue-grey ba ...
s (at least one pair).
Chaffinches and robins are the most common species in the woodlands. Other species that breed there include blackcap
The Eurasian blackcap (''Sylvia atricapilla''), usually known simply as the blackcap, is a common and widespread typical warbler. It has mainly olive-grey upperparts and pale grey underparts, and differences between the five subspecies are sma ...
s and garden warbler
The garden warbler (''Sylvia borin'') is a common and widespread small bird that breeds in most of Europe and in the Palearctic to western Siberia. It is a plain, long-winged and long-tailed typical warbler with brown upperparts and dull white ...
s. The rare redstart and wood warbler
The wood warbler (''Phylloscopus sibilatrix'') is a common and widespread leaf warbler which breeds throughout northern and temperate Europe, and just into the extreme west of Asian Russia in the southern Ural Mountains.
This warbler is stro ...
are thought to have a few breeding pairs in the park's woodlands.
Grey herons, little grebe
The little grebe (''Tachybaptus ruficollis''), also known as dabchick, is a member of the grebe family of water birds. The genus name is from Ancient Greek ''takhus'' "fast" and ''bapto'' "to sink under". The specific ''ruficollis'' is from Lat ...
s, mallard
The mallard () or wild duck (''Anas platyrhynchos'') is a dabbling duck that breeds throughout the temperate and subtropical Americas, Eurasia, and North Africa, and has been introduced to New Zealand, Australia, Peru, Brazil, Uruguay, Argen ...
s, water rail
The water rail (''Rallus aquaticus'') is a bird of the rail family which breeds in well-vegetated wetlands across Europe, Asia and North Africa. Northern and eastern populations are migratory, but this species is a permanent resident in the war ...
s, dipper
Dippers are members of the genus ''Cinclus'' in the bird family Cinclidae, so-called because of their bobbing or dipping movements. They are unique among passerines for their ability to dive and swim underwater.
Taxonomy
The genus ''Cinclus'' ...
s and common kingfisher
The common kingfisher (''Alcedo atthis''), also known as the Eurasian kingfisher and river kingfisher, is a small kingfisher with seven subspecies recognized within its wide distribution across Eurasia and North Africa. It is resident in much of ...
s live on the park's water bodies.
Lough Leane, and the other lakes to a lesser extent, support wintering birds that travel south from higher latitudes. These species include redwing, fieldfare, golden plover and waterfowl such as teal, goldeneye, wigeon, pochard and whooper swan. The park's native bird populations are augmented by migrant species in both winter and summer. A small flock of Greenland white-fronted geese (''Anser albifrons flavirostris'') from the world population of approximately 12,000 migrates to winter on boglands in the Killarney Valley within the park. The numbers of this bird that stay in the park are currently low, at less than twenty individuals. This population is important because it is the most southerly in Ireland and one of the few remaining populations remaining that feed entirely on bogland, and whose habitat almost entirely lies within a protected area.
Other wintering waterfowls are coot
Coots are medium-sized water birds that are members of the rail family, Rallidae. They constitute the genus ''Fulica'', the name being the Latin term for "coot". Coots have predominantly black plumage, and—unlike many rails—they are usually ...
, cormorant
Phalacrocoracidae is a family of approximately 40 species of aquatic birds commonly known as cormorants and shags. Several different classifications of the family have been proposed, but in 2021 the IOC adopted a consensus taxonomy of seven gen ...
, goldeneye, mallard, pochard
Pochard is a common name used for several species of diving ducks:
*Four species in the genus ''Aythya'':
** Common pochard, ''Aythya ferina''
** Baer's pochard, ''Aythya baeri''
** Ferruginous pochard, ''Aythya nyroca''
** Madagascar pochard, '' ...
, teal
alt=American teal duck (male), Green-winged teal (male)
Teal is a greenish-blue colour. Its name comes from that of a bird — the Eurasian teal (''Anas crecca'') — which presents a similarly coloured stripe on its head. The word is ofte ...
, and tufted duck. Other species that live on the lakes are the black-headed gull
The black-headed gull (''Chroicocephalus ridibundus'') is a small gull that breeds in much of the Palearctic including Europe and also in coastal eastern Canada. Most of the population is migratory and winters further south, but some birds re ...
, little grebe
The little grebe (''Tachybaptus ruficollis''), also known as dabchick, is a member of the grebe family of water birds. The genus name is from Ancient Greek ''takhus'' "fast" and ''bapto'' "to sink under". The specific ''ruficollis'' is from Lat ...
, and mute swan
The mute swan (''Cygnus olor'') is a species of swan and a member of the waterfowl family Anatidae. It is native to much of Eurosiberia, and (as a rare winter visitor) the far north of Africa. It is an introduced species in North America, home ...
.
Species that migrate from Africa in the summer include cuckoo
Cuckoos are birds in the Cuculidae family, the sole taxon in the order Cuculiformes . The cuckoo family includes the common or European cuckoo, roadrunners, koels, malkohas, couas, coucals and anis. The coucals and anis are sometimes sepa ...
s, swallows, and swifts
Swift or SWIFT most commonly refers to:
* SWIFT, an international organization facilitating transactions between banks
** SWIFT code
* Swift (programming language)
* Swift (bird), a family of birds
It may also refer to:
Organizations
* SWIFT, a ...
. Some species are vagrants that appear sporadically, for example when there is stormy weather or an unusually cold spell on the European continent.
The park is also the site for a project to reintroduce white-tailed eagle
The white-tailed eagle (''Haliaeetus albicilla'') is a very large species of sea eagle widely distributed across temperate Eurasia. Like all eagles, it is a member of the family Accipitridae (or accipitrids) which includes other diurnal raptor ...
s, which began in 2007 with the release of fifteen birds. The project will last a number of years with many more eagles being released. The species had become extinct in Ireland in the 19th century after persecution from landowners. Fifteen chicks will then be brought in annually for the following five years. Despite a poisoning incident in 2009, the program is continuing and birds introduced to the area have now been tracked to Wicklow and Donegal.
Fish species
The Lakes of Killarney contain many brown trout and an annual run of salmon. Rare species found in the lakes are Arctic char and Killarney shad. The lakes have natural stocks ofbrown trout
The brown trout (''Salmo trutta'') is a European species of salmonid fish that has been widely introduced into suitable environments globally. It includes purely freshwater populations, referred to as the riverine ecotype, ''Salmo trutta'' morp ...
and salmon that can be fished, subject only to usual Irish salmon license regulations.
The lakes contain Arctic char
The Arctic char or Arctic charr (''Salvelinus alpinus'') is a cold-water fish in the family Salmonidae, native to alpine lakes and arctic and subarctic coastal waters. Its distribution is Circumpolar North. It spawns in freshwater and populati ...
(''Salvelinus alpinus'' L.), which is usually found much further north in sub-Arctic lakes. It's a relict species left behind in the area after the last Ice Age, and are consequently indicative of pristine environmental conditions. Although they were once widespread, they now are confined to isolated populations in inland freshwater lakes that have a suitable habitat. They are isolated in their respective lakes since the last Ice age. They are extremely sensitive to environmental changes when they are as far south as Ireland, where they are at the southern edge of their species range. The greatest threats to their survival in Ireland are introduced fish species, eutrophication, acidification and climate change. The rate of extinction of entire populations in Ireland has increased in recent decades.
The Killarney shad (or goureen) (''Alosa fallax killarnensis'') is a land-locked lake-dwelling subspecies of twaite shad, a mostly marine species. It is unique to the Lakes of Killarney. It is rarely seen because it feeds mainly on plankton and thus is rarely caught by fishers. It is listed in the Irish "Red Data Book" of threatened species. It is listed in Annex II of the EU Habitats Directive.
Invertebrates
Several unusual invertebrate species can be found in the Killarney valley. Some of these species, including the northern emerald dragonfly (''Somatochlora arctica'') and severalcaddisfly
The caddisflies, or order Trichoptera, are a group of insects with aquatic larvae and terrestrial adults. There are approximately 14,500 described species, most of which can be divided into the suborders Integripalpia and Annulipalpia on the b ...
and stonefly
Plecoptera is an order of insects, commonly known as stoneflies. Some 3,500 species are described worldwide, with new species still being discovered. Stoneflies are found worldwide, except Antarctica. Stoneflies are believed to be one of the mos ...
species are usually found much further north in Europe. They are thought to be relict species that were left behind in Killarney after the last retreat of ice. The northern or moorland emerald dragonfly
A dragonfly is a flying insect belonging to the infraorder Anisoptera below the order Odonata. About 3,000 extant species of true dragonfly are known. Most are tropical, with fewer species in temperate regions. Loss of wetland habitat threat ...
, the rarest Irish dragonfly, is confined to the park. It breeds in shallow pools in bogs.
The oak woods in the remote Glaism na Marbh valley are a stronghold for ''Formica lugubris
''Formica lugubris'', also known as the hairy wood ant is commonly found in wooded upland areas across northern Eurasia. Colonies construct large thatched mound nests occupied by thousands of workers, and one or more queens. Workers look similar ...
Zett.'', a wood ant
The ''Formica rufa'' group is a subgeneric group within the genus ''Formica'', first proposed by William Morton Wheeler. This group contains the mound-building species of ''Formica'' commonly termed "wood ants" or "thatch-mound ants", which build ...
species that is rare both in the Killarney woods and in Ireland as a whole.
The Kerry Slug
The Kerry slug or Kerry spotted slug (''Geomalacus maculosus'') is a species of terrestrial, pulmonate, gastropod mollusc. It is a medium-to-large sized, air-breathing land slug in the family of roundback slugs, Arionidae.
Adult Kerry slugs g ...
(''Geomalacus maculosus'') is a hiberno-lusitanean species. It emerges in Killarney's frequent wet weather to graze on lichens on rocks and tree trunks. It is reputedly the only slug capable of rolling itself into a ball. It is on both Annex II and Annex IV of the EU Habitats Directive.
Conservation threats

 The park has a number of conservation and management challenges. One of these is the park's proximity to Killarney town, one of Ireland's best known tourist destinations. Killarney has hundreds of thousands of visitors every year. Most of these visitors spend time in the park. Careful management is needed to ensure minimal conflict between conservation and recreation.
The past introduction of several exotic species to the park is an additional human influence on the area. These species have damaged the natural ecosystems of Killarney. The most notable of these species are the common rhododendron (''Rhododendron ponticum''), which has infested large areas of the National Park, and sika deer, which overgraze the woodland floor and pose a potential threat to the genetic integrity of the native red deer. Both rhododendron and sika deer can have an adverse effect on the native flora by inhibiting regeneration. A more recent, accidental, introduction is the
The park has a number of conservation and management challenges. One of these is the park's proximity to Killarney town, one of Ireland's best known tourist destinations. Killarney has hundreds of thousands of visitors every year. Most of these visitors spend time in the park. Careful management is needed to ensure minimal conflict between conservation and recreation.
The past introduction of several exotic species to the park is an additional human influence on the area. These species have damaged the natural ecosystems of Killarney. The most notable of these species are the common rhododendron (''Rhododendron ponticum''), which has infested large areas of the National Park, and sika deer, which overgraze the woodland floor and pose a potential threat to the genetic integrity of the native red deer. Both rhododendron and sika deer can have an adverse effect on the native flora by inhibiting regeneration. A more recent, accidental, introduction is the American mink
The American mink (''Neogale vison'') is a semiaquatic species of mustelid native to North America, though human intervention has expanded its range to many parts of Europe, Asia and South America. Because of range expansion, the American mink ...
, which is now firmly established in the park alongside the native otter. Extinctions caused by humans include the wolf (''Canis lupus L.'') and the golden eagle
The golden eagle (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known birds ...
(''Aquila chrysaetos L.'').
Fires caused by human activity occur with some frequency in the park. Despite the wet climate, they can spread quite rapidly to cover large areas. These fires rarely penetrate areas covered by dense woodlands, but they do burn readily through stands of open woodland.
The park was damaged extensively by fires in April 2021.
The main land use within the site is grazing by sheep. Deer grazing is also common. The woods in the park are currently severely overgrazed by sika deer. Grazing has caused damage to many terrestrial habitats, causing heath and blanket bogs to degrade and preventing woodland regeneration. In the upland areas erosion caused by grazing is exacerbated by the exposed nature of the terrain. Pressures from native grazers like red deer and Irish hare have increased since their main natural predators, the wolf and golden eagle, became extinct. Grazing and disturbance of vegetation greatly aids the spread of rhododendron.
The common rhododendron is perhaps the greatest threat to the ecology of the park. It is an evergreen shrub with a natural distribution in the Mediterranean and Black Sea areas. Rhododendrons died out in Ireland because of climate change thousands of years ago. It was introduced to the Killarney area during the 19th century, and rapidly took hold. It has spread through its large numbers of very small easily dispersed seeds. It shades the ground flora and so prevents the regeneration of native woody species. More than of the park are now completely infested. They have had a devastating effect in certain parts of the park. As light cannot penetrate the dense thickets of rhododendrons, very few plants can live beneath it. The park's oak woods are in long-term danger because they cannot regenerate. There is a policy of control and eradication of rhododendrons in the park.
Tourism
 The park is open for tourism year-round. There is a visitor and education centre at Killarney House. Visitor attractions in the park include Dinis Cottage, Knockreer Demesne, Inisfallen Island, Ladies View, the Meeting of the Waters and the Old Weir Bridge, Muckross Abbey, Muckross House, the Muckross Peninsula, the Old Kenmare Road, O'Sullivan's Cascade, Ross Castle and Ross Island, Tomies Oakwood, and Torc Waterfall. There is a network of surfaced paths in the Knockreer, Muckross, and Ross Island areas that can be used by cyclists and walkers. The Old Kenmare Road and the track around Tomies Oakwood have views over Lough Leane and Killarney. Boat trips on the lakes are available.
Muckross House is a Victorian mansion, close to Muckross Lake's eastern shore, beneath the backdrop of Mangerton and Torc mountains. The house has now been restored and attracts more than 250,000 visitors a year. Muckross Gardens are famous for their collection of rhododendrons, hybrids and azaleas, and exotic trees. Muckross Traditional Farms is a working farm project that recreates Irish rural life in the 1930s, prior to electrification. Knockreer House is used as the National Park Education Centre.
The park is open for tourism year-round. There is a visitor and education centre at Killarney House. Visitor attractions in the park include Dinis Cottage, Knockreer Demesne, Inisfallen Island, Ladies View, the Meeting of the Waters and the Old Weir Bridge, Muckross Abbey, Muckross House, the Muckross Peninsula, the Old Kenmare Road, O'Sullivan's Cascade, Ross Castle and Ross Island, Tomies Oakwood, and Torc Waterfall. There is a network of surfaced paths in the Knockreer, Muckross, and Ross Island areas that can be used by cyclists and walkers. The Old Kenmare Road and the track around Tomies Oakwood have views over Lough Leane and Killarney. Boat trips on the lakes are available.
Muckross House is a Victorian mansion, close to Muckross Lake's eastern shore, beneath the backdrop of Mangerton and Torc mountains. The house has now been restored and attracts more than 250,000 visitors a year. Muckross Gardens are famous for their collection of rhododendrons, hybrids and azaleas, and exotic trees. Muckross Traditional Farms is a working farm project that recreates Irish rural life in the 1930s, prior to electrification. Knockreer House is used as the National Park Education Centre.
See also
*List of national parks of the Republic of Ireland
This is a list of national parks of Ireland.
The chart below shows the national parks in Ireland. The first park established in Ireland was Killarney National Park located in County Kerry in 1932. Since then a further five national parks have be ...
* Muckross House
* Ross Castle
* Lakes of Killarney
*Killarney
Killarney ( ; ga, Cill Airne , meaning 'church of sloes') is a town in County Kerry, southwestern Ireland. The town is on the northeastern shore of Lough Leane, part of Killarney National Park, and is home to St Mary's Cathedral, Ross Cast ...
* Purple Mountains
* Mountains of East Kerry
* Muckross Abbey
*Aghadoe
Aghadoe ( Irish: ''Achadh an Dá Eó'') is a large townland overlooking the town and lakes of Killarney in Ireland. Officially it is also a parish, although the parish is larger than the area normally associated with the name. The area is famous ...
* Killarney House
* Kenmare House
References
External links
*National Parks of Ireland
{{Authority control 1932 establishments in Ireland Biosphere reserves of the Republic of Ireland Forests and woodlands of the Republic of Ireland Geography of County Kerry Killarney National parks of the Republic of Ireland Parks in County Kerry Protected areas established in 1932 Special Areas of Conservation in the Republic of Ireland