Kebaran culture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Kebaran culture, also known as the Early Near East Epipalaeolithic, was an
The Kebaran culture, also known as the Early Near East Epipalaeolithic, was an
 Material was adapted from this source, which is available under
Material was adapted from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
The engravings found in Ein Qashish South involve symbolic conceptualization. They suggest that the figurative and non-figurative images comprise a coherent assemblage of symbols that might have been applied in order to store, share and transmit information related to the social activities and the subsistence of mobile bands. They also suggest a level of social complexity in pre-Natufian foragers in the Levant. The apparent similarity in graphics throughout the Material was adapted from this source, which is available under
Material was adapted from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
File:Kebaran Culture Flint Knife.jpg, Flint knife, Kebaran culture, 22000-18000 BP
File:Kebaran culture microliths 22000-18000 BP.jpg, Kebaran culture microliths, 22000-18000 BP
File:Microlith productions, Kebaran culture, 22,000-18,000 BP, Israel (detail).jpg, Microlith productions, Kebaran culture, 22,000-18,000 BP
File:Microlith tools from Ein Qashish South, Jezreel Valley, Israel, Kebaran and Geometric Kebaran deposits (ca. 23ka and ca. 16.5ka BP).jpg, Microlith tools from Ein Qashish South, Jezreel Valley, Israel, Kebaran and Geometric Kebaran deposits (ca. 23ka and ca. 16.5ka BP)
File:Associations of wild cereals and other wild grasses in northern Israel.jpg, Associations of wild cereals and other wild grasses in northern Israel
 The Kebaran culture, also known as the Early Near East Epipalaeolithic, was an
The Kebaran culture, also known as the Early Near East Epipalaeolithic, was an archaeological culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of types of artifacts, buildings and monuments from a specific period and region that may constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between thes ...
in the Eastern Mediterranean
Eastern Mediterranean is a loose definition of the eastern approximate half, or third, of the Mediterranean Sea, often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea.
It typically embraces all of that sea's coastal zones, referring to commun ...
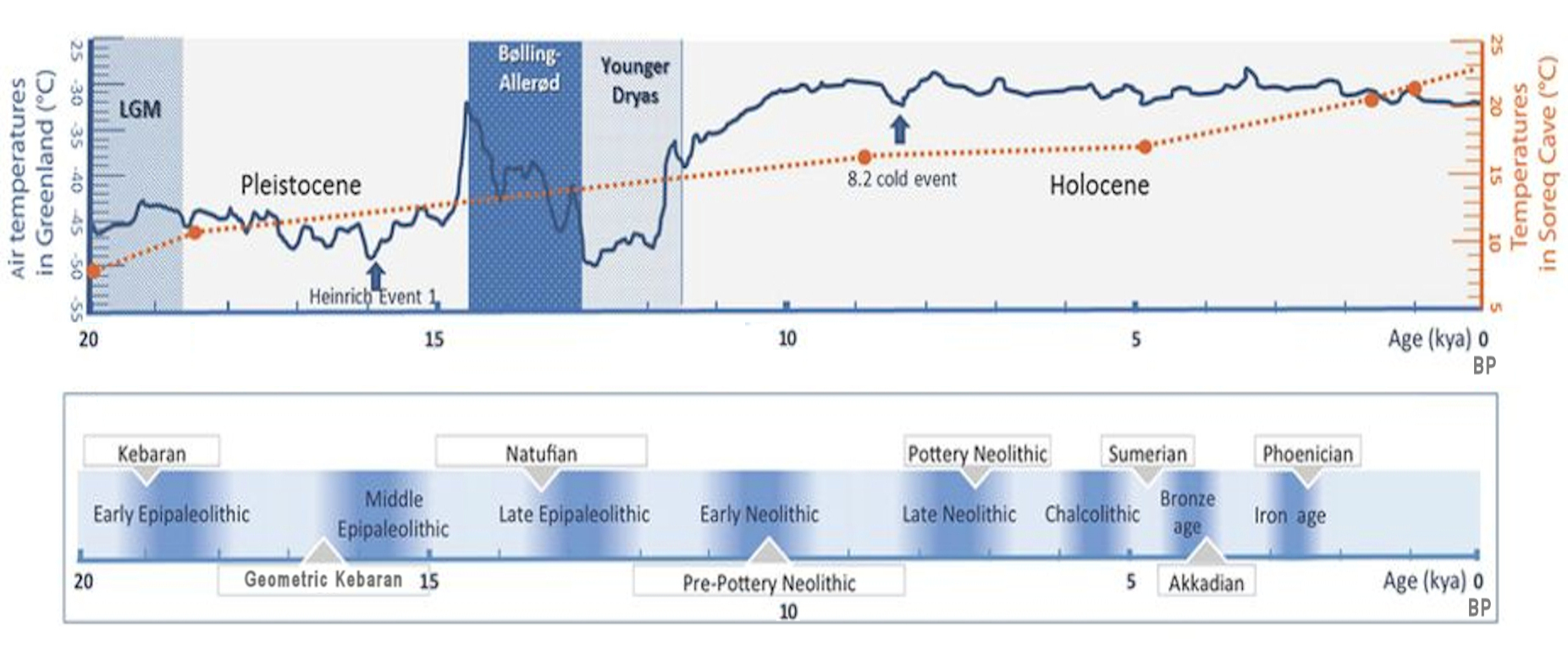
area (c. 23,000 to 15,000 BP), named after its type site, Kebara Cave
Kebara Cave ( he, מערת כבארה, Me'arat Kebbara, ar, مغارة الكبارة, Mugharat al-Kabara) is a limestone cave locality in Wadi Kebara, situated at above sea level on the western escarpment of the Carmel Range, in the Ramat HaN ...
south of Haifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropol ...
. The Kebaran were a highly mobile nomadic population, composed of hunters and gatherers in the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
and Sinai areas who used microlithic tools.
Overview
The Kebaran is the last Upper Paleolithic phase of theLevant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
. Kebaran stone tool
A stone tool is, in the most general sense, any tool made either partially or entirely out of stone. Although stone tool-dependent societies and cultures still exist today, most stone tools are associated with prehistoric (particularly Stone A ...
assemblages are characterized by small, geometric microliths, and are thought to have lacked the specialized grinders and pounders found in later Near Eastern cultures. Small stone tools called microlith
A microlith is a small stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 35,000 to 3,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia. Th ...
s and retouched bladelets can be found for the first time. The microliths of this culture period differ greatly from the Aurignacian artifacts.
The Kebaran is preceded by the Athlitian phase of the Upper Paleolithic Levantine Aurignacian
The Levantine Aurignacian (35,000-29,000 BP, calibrated, 32,000-26,000 BP, non-calibrated) is an Upper Paleolithic culture of the Near-Eastern Levant that evolved from the Emiran culture. It was named so because of the similarity of stone tools ...
(formerly called Antelian
The Levantine Aurignacian (35,000-29,000 BP, calibrated, 32,000-26,000 BP, non-calibrated) is an Upper Paleolithic culture of the Near-Eastern Levant that evolved from the Emiran culture. It was named so because of the similarity of stone tools w ...
) and followed by the proto-agrarian Natufian culture
The Natufian culture () is a Late Epipaleolithic archaeological culture of the Levant, dating to around 15,000 to 11,500 years ago. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentary or semi-sedentary population even before the introduct ...
of the Epipalaeolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are som ...
. The appearance of the Kebaran
The Kebaran culture, also known as the Early Near East Epipalaeolithic, was an archaeological culture in the Eastern Mediterranean area (c. 23,000 to 15,000 BP), named after its type site, Kebara Cave south of Haifa. The Kebaran were a highly mo ...
culture, of microlith
A microlith is a small stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 35,000 to 3,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia. Th ...
ic type implies a significant rupture in the cultural continuity of Levantine Upper Paleolithic. The Kebaran culture, with its use of microliths, is associated with the use of the bow and arrow and the domestication of the dog. The Kebaran is also characterised by the earliest collecting of wild cereals, known due to the uncovering of grain grinding tools. It was the first step towards the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an inc ...
. The Kebaran people are believed to have practiced dispersal to upland environments in the summer, and aggregation in caves and rockshelters near lowland lakes in the winter. This diversity of environments may be the reason for the variety of tools found in their kits.
Situated in the Terminal Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
, the Kebaran is classified as an Epipalaeolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are som ...
society. They are generally thought to have been ancestral to the later Natufian
The Natufian culture () is a Late Epipaleolithic archaeological culture of the Levant, dating to around 15,000 to 11,500 years ago. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentary or semi-sedentary population even before the introducti ...
culture that occupied much of the same range, Mellaart, James (1976), ''Neolithic of the Near East'' (Macmillan Publishers
Macmillan Publishers (occasionally known as the Macmillan Group; formally Macmillan Publishers Ltd and Macmillan Publishing Group, LLC) is a British publishing company traditionally considered to be one of the 'Big Five' English language publi ...
) who advanced the use of wild grains, building on the Kebaran traits to acquire some symptoms of permanent settlements, agriculture, and hints of civilization.
Artistic expression
Evidence for symbolic behavior of Late Pleistocene foragers in the Levant has been found in engraved limestone plaquettes from the Epipaleolithic open-air site Ein Qashish South in the Jezreel Valley, Israel. The engravings were uncovered in Kebaran and Geometric Kebaran deposits (ca. 23,000 and ca. 16,500 BP), and include the image of a bird, the first figurative representation known so far from a pre-Natufian Epipaleolithic site, together with geometric motifs such as chevrons, cross-hatchings and ladders. Some of the engravings closely resemble roughly contemporary European finds, and may be interpreted as "systems of notations" or "artificial memory systems" related to the timing of seasonal resources and related important events for nomadic groups. Similar looking signs and patterns are well known from the context of the localNatufian
The Natufian culture () is a Late Epipaleolithic archaeological culture of the Levant, dating to around 15,000 to 11,500 years ago. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentary or semi-sedentary population even before the introducti ...
, a final Epipaleolithic period when sedentary or semi-sedentary foragers started practicing agriculture.Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
The engravings found in Ein Qashish South involve symbolic conceptualization. They suggest that the figurative and non-figurative images comprise a coherent assemblage of symbols that might have been applied in order to store, share and transmit information related to the social activities and the subsistence of mobile bands. They also suggest a level of social complexity in pre-Natufian foragers in the Levant. The apparent similarity in graphics throughout the
Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as Upper Pleistocene from a stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division of the Pleistocene Epoch withi ...
world and the mode of their application support the possibility that symbolic behavior has a common and much earlier origin.Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Artifacts
References
Further reading
*M. H. Alimen and M. J. Steve, ''Historia Universal siglo XXI. Prehistoria''. Siglo XXI Editores, 1970 (reviewed and corrected in 1994) (original German edition, 1966, titled ''Vorgeschichte''). *University of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh ( sco, University o Edinburgh, gd, Oilthigh Dhùn Èideann; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in post-nominals) is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Granted a royal charter by King James VI in 1 ...
, Archaeology 1 Lectures, "From Foraging to Farming", 2008
{{Epipalaeolithic Southwest Asia
Upper Paleolithic cultures of Asia
Archaeological cultures of the Near East
Ancient peoples of the Near East
Prehistory of the Middle East
Epipalaeolithic cultures