Kulindadromeus Elements on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Kulindadromeus'' is a
 In 2014, the
In 2014, the
/ref> and hundreds of disarticulated skeletons found in two
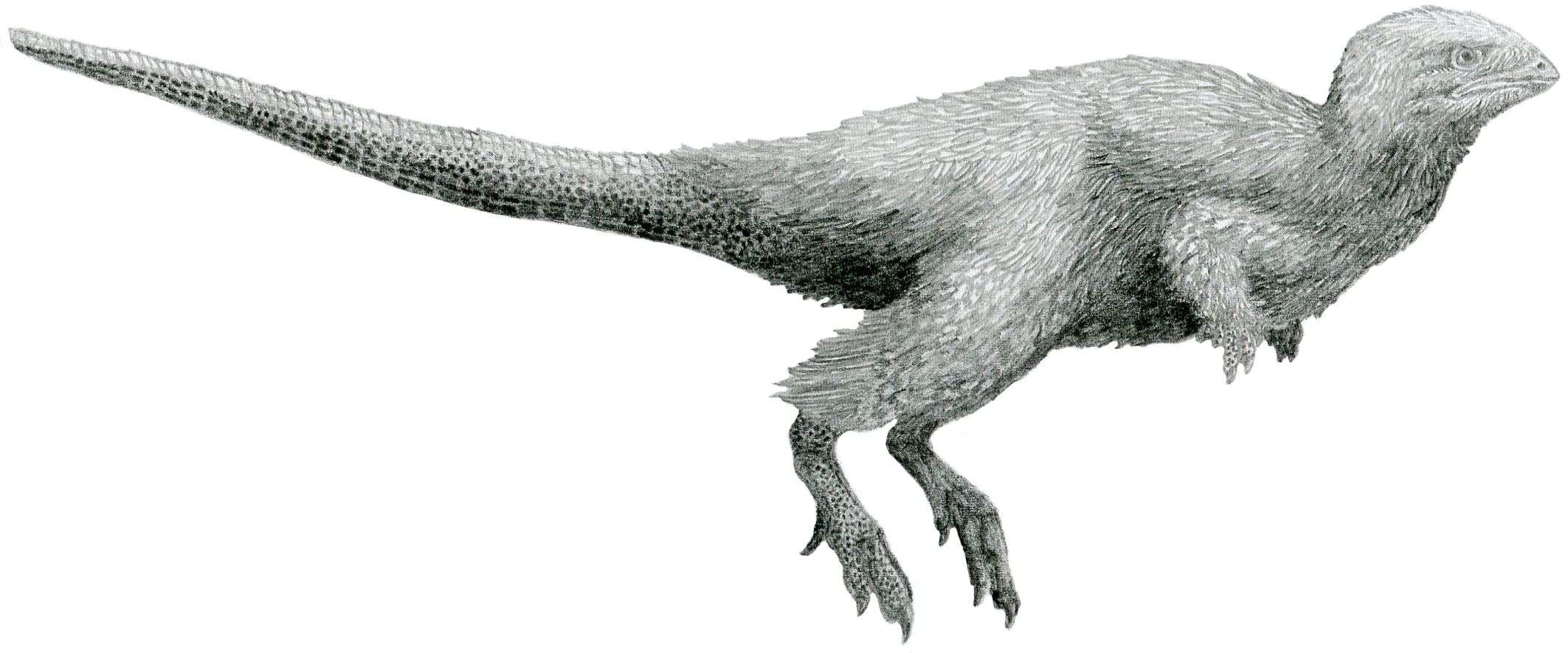 ''Kulindadromeus'' was a small ornithischian, measuring long and weighing . Like other early neornithischians, ''Kulindadromeus'' was a bipedal runner, with a short head, short forelimbs, long hindlimbs and a long tail.
The describers of ''Kulindadromeus'' established some distinguishing traits. The front ascending branch of the
''Kulindadromeus'' was a small ornithischian, measuring long and weighing . Like other early neornithischians, ''Kulindadromeus'' was a bipedal runner, with a short head, short forelimbs, long hindlimbs and a long tail.
The describers of ''Kulindadromeus'' established some distinguishing traits. The front ascending branch of the
 According to a
According to a
 ''Kulindadromeus'' is featured on the
''Kulindadromeus'' is featured on the
genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
of basal neornithischia
Neornithischia ("new ornithischians") is a clade of the dinosaur order Ornithischia. It is the sister group of the Thyreophora within the clade Genasauria. Neornithischians are united by having a thicker layer of asymmetrical enamel on the insi ...
n dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
that lived during the Middle Jurassic
The Middle Jurassic is the second Epoch (geology), epoch of the Jurassic Period (geology), Period. It lasted from about 174.1 to 161.5 million years ago. Fossils of land-dwelling animals, such as dinosaurs, from the Middle Jurassic are relativel ...
. The first ''Kulindadromeus'' fossil was found in Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
. Its feather
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and an exa ...
-like integument
In biology, an integument is the tissue surrounding an organism's body or an organ within, such as skin, a husk, Exoskeleton, shell, germ or Peel (fruit), rind.
Etymology
The term is derived from ''integumentum'', which is Latin for "a coverin ...
is evidence for protofeathers being basal to Ornithischia
Ornithischia () is an extinct clade of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek ...
and possibly Dinosauria as a whole, rather than just to Coelurosauria
Coelurosauria (; from Greek, meaning "hollow-tailed lizards") is the clade containing all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds than to carnosaurs.
Coelurosauria is a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs that includes compsognathids, tyra ...
, as previously suspected.
Discovery and naming
 In 2014, the
In 2014, the type species
In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the spe ...
''Kulindadromeus zabaikalicus'' was named and described by Pascal Godefroit, Sofia Sinitsa, Danielle Dhouailly, Yuri Bolotsky, Alexander Sizov, Maria McNamara, Michael Benton
Michael James Benton (born 8 April 1956) is a British palaeontologist, and professor of vertebrate paleontology, vertebrate palaeontology in the School of Earth Sciences at the University of Bristol. His published work has mostly concentrated on ...
, and Paul Spagna. The generic name is derived from the Kulinda sites and Classical Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archa ...
δρομεύς, ''dromeus'', "runner". The specific name Specific name may refer to:
* in Database management systems, a system-assigned name that is unique within a particular database
In taxonomy, either of these two meanings, each with its own set of rules:
* Specific name (botany), the two-part (bino ...
refers to the Zabaykalsky Krai
Zabaykalsky Krai is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (a krai), located in the Russian Far East. Its administrative center is Chita, Zabaykalsky Krai, Chita. As of the Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census, the population was ...
.
The holotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of s ...
, INREC K3/109, was found in a layer of the Ukureyskaya Formation dating from the Middle to Late Jurassic, Bajocian
In the geologic timescale, the Bajocian is an age and stage in the Middle Jurassic. It lasted from approximately 170.9 ±0.8 Ma to around 168.2 ±1.2 Ma (million years ago). The Bajocian Age succeeds the Aalenian Age and precedes the Bathonia ...
-Tithonian
In the geological timescale, the Tithonian is the latest age (geology), age of the Late Jurassic Epoch and the uppermost stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Upper Jurassic Series. It spans the time between 149.2 ±0.7 annum, Ma and 143.1 ±0.6 (mi ...
, with the specific bed likely dating to the Bathonian
In the geologic timescale the Bathonian is an age (geology), age and stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Middle Jurassic. It lasted from approximately 168.2 ±1.2 annum, Ma to around 165.3 ±1.1 Ma (million years ago). The Bathonian Age succeeds ...
stage of the Middle Jurassic, between 168 and 166 million years ago. It consists of a partial skull with lower jaws. The volcanic ash layers of the formation form a '' Konservat-Lagerstätte'' with an exceptional preservation. Since 2010, the area has brought forth considerable amounts of additional fossil material, including subadult and juvenile individuals. In 2014, based on fossils from this material, the genera ''Kulindapteryx'' and ''Daurosaurus'' were named. (in Russian; English translation published in ) According to Godefroit, this publication was based on stolen specimens, and should be ignored. The material consists of six skulls,Dan Vergano, 2014, "Siberian Discovery Suggests Almost All Dinosaurs Were Feathered", National Geographic Daily New/ref> and hundreds of disarticulated skeletons found in two
bone bed
A bone bed is any Geology, geological stratum or deposition (geology), deposit that contains bones of whatever kind. Inevitably, such deposits are Sedimentary rock, sedimentary in nature. Not a formal term, it tends to be used more to describe esp ...
s. Each skeletal element shows a single morphotype and Godefroit et al. concluded, contrary to the earlier publication, that the bone beds are
monospecific, containing but a single species.
Description
 ''Kulindadromeus'' was a small ornithischian, measuring long and weighing . Like other early neornithischians, ''Kulindadromeus'' was a bipedal runner, with a short head, short forelimbs, long hindlimbs and a long tail.
The describers of ''Kulindadromeus'' established some distinguishing traits. The front ascending branch of the
''Kulindadromeus'' was a small ornithischian, measuring long and weighing . Like other early neornithischians, ''Kulindadromeus'' was a bipedal runner, with a short head, short forelimbs, long hindlimbs and a long tail.
The describers of ''Kulindadromeus'' established some distinguishing traits. The front ascending branch of the maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxil ...
is much lower than the rear ascending branch. The ''fenestra maxillaris'' is larger than the antorbital fenestra
An antorbital fenestra (plural: fenestrae) is an opening in the skull that is in front of the eye sockets. This skull character is largely associated with Archosauriformes, archosauriforms, first appearing during the Triassic Period. Among Extant ...
, the usually more extensive skull opening in the snout side. The branch of the jugal towards the postorbital is notched. The postorbital has a rear branch that is vertically expanded. The rear blade of the ilium is slender in side view. The second, third and fourth metatarsals have deep grooves for the tendons of the extensor muscles.
Various specimens of ''Kulindadromeus'' show large parts of its integument
In biology, an integument is the tissue surrounding an organism's body or an organ within, such as skin, a husk, Exoskeleton, shell, germ or Peel (fruit), rind.
Etymology
The term is derived from ''integumentum'', which is Latin for "a coverin ...
. This includes imbricated rows of scales on top of its tail and also a covering of scales branching into feather-like structures, which until its discovery were thought to be exclusive to the Theropoda
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek iktionary:θηρίον, , (''therion'') "wild beast"; wiktionary:πούς, , wiktionary:ποδός, (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (Clade, clades) of Dinosaur, dinosaurs, alon ...
, of the saurischia
Saurischia ( , meaning "reptile-hipped" from the Greek ' () meaning 'lizard' and ' () meaning 'hip joint') is one of the two basic divisions of dinosaurs (the other being Ornithischia), classified by their hip structure. Saurischia and Ornithi ...
n line. The feather remains discovered are of three types, adding a level of complexity to the evolution of feathers in dinosaurs. The first type consists of hair-like filaments covering the trunk, neck and head. These are up to three centimetres long and resemble the stage 1 "dino-fuzz" already known from theropods like ''Sinosauropteryx
''Sinosauropteryx'' (meaning "Chinese reptilian wing") is an extinct genus of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs. Described in 1996, it was the first dinosaur taxon outside of Avialae (birds and their immediate relatives) to be found with eviden ...
''. The second type is represented by groups of six or seven downwards-projecting filaments up to 1.5 centimetres long, originating from a base plate. These are present on the upper arm and thigh. They resemble the type 3 feathers of theropods. The base plates are ordered in a hexagonal pattern but do not touch each other. The third type is unique. It was found on the upper lower legs and consists of bundles of six or seven ribbon-like structures, up to two centimetres long. Each ribbon is constructed from about ten parallel filaments up to 0.1 millimetres wide.
There are also three types of scales. Overlapping hexagonal scales, up to 3.5 millimetres in diameter, are present on the lower shins. Small round non-overlapping scales, less than one millimetre in cross-section, cover the hands, ankles and feet. The top of the tail is covered by five longitudinal rows of arched rectangular scales, measuring up to one by two centimetres. With these scales the trailing edge of each scale slightly overlaps the front edge of the scale behind it. In the middle, to the contrary, a small spur projects forward, covering the trailing edge of the preceding scale. This way an imbricated row is formed. The scale surface is smooth and the thickness is limited, less than 0.1 millimetres. The authors considered it unlikely these structures were ossified scute
A scute () or scutum (Latin: ''scutum''; plural: ''scuta'' "Scutum (shield), shield") is a bony external plate or scale overlaid with horn, as on the shell of a turtle, the skin of crocodilians, and the feet of Bird anatomy#Scales, birds. The ter ...
s or osteoderm
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinct amph ...
s. Towards the rear of the tail, the scales become smaller and more rounded; they then no longer overlap each other.
The specimens assigned to ''Daurosaurus'' and ''Kulindapteryx'' also include preserved integument on the humerus: "oval platy scales" and bristles. The latter reportedly has longer bristles.
Classification
 According to a
According to a cladistic
Cladistics ( ; from Ancient Greek 'branch') is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is ...
analysis performed by the describing authors, ''Kulindadromeus'' is a basal member of the Neornithischia
Neornithischia ("new ornithischians") is a clade of the dinosaur order Ornithischia. It is the sister group of the Thyreophora within the clade Genasauria. Neornithischians are united by having a thicker layer of asymmetrical enamel on the insi ...
, placed just above '' Hexinlusaurus'' in the evolutionary tree. It is the sister species
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
of the Cerapoda
Neornithischia ("new ornithischians") is a clade of the dinosaur order Ornithischia. It is the sister group of the Thyreophora within the clade Genasauria. Neornithischians are united by having a thicker layer of asymmetrical enamel on the ins ...
.
Implications
Godefroit ''et al.'' concluded that the filaments earlier reported inOrnithischia
Ornithischia () is an extinct clade of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek ...
, with ''Psittacosaurus
''Psittacosaurus'' ( ; "parrot lizard") is a genus of extinct ceratopsian dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of what is now Asia, existing between 125 and 105 million years ago. It is notable for being the most species-rich non-avian dinosaur ...
'' and ''Tianyulong
''Tianyulong'' ( Chinese: 天宇龍; Pinyin: ''tiānyǔlóng''; named for the Shandong Tianyu Museum of Nature where the holotype fossil is housed) is an extinct genus of heterodontosaurid ornithischian dinosaur. The only species is ''T. confuc ...
'', could be homologous to the "protofeathers" found in non-avian theropods. With known feather-like structures in pterosaurs, there is evidence for it being basal to Ornithodira
Avemetatarsalia (meaning "bird metatarsals") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all archosaurs more closely related to birds than to crocodilians. The two most successful groups of avemetatarsalians were the dinosaurs and pterosaurs. Di ...
. An attempt to reconstruct the likely ancestral state of dinosaurs found it to be likely that both Ornithodira and Dinosauria were ancestrally scaly, however, this result was only obtained when assuming that early pterosaurs were scaly.
A comment on Godefroit ''et al.'' argues that the filamentous structures described at ''Kulindadromeus'' do not resemble protofeathers, rather they suggest it to be degraded collagen fibers. Pascal Godefroit and colleagues reply, “If, according to Lingham-Soliar’s hypothesis, those filaments represent collagen fibers or fiber bundles, it is surprising that they are not preserved in the numerous (more than 20) partial or whole tails of ''Kulindadromeus'', given that the tail should have contained particularly high amounts of collagen for structural support. Moreover, Lingham-Soliar fails to explain how scales should be selectively degraded and/or dislocated around the humerus and femur but never around the distal tibia and tail.” Further, they state that the described morphology of the integument are not consistent with degraded collagen fibers, as the filaments are widely spaced.
In culture
 ''Kulindadromeus'' is featured on the
''Kulindadromeus'' is featured on the flag
A flag is a piece of textile, fabric (most often rectangular) with distinctive colours and design. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and fla ...
and coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the last two being outer garments), originating in Europe. The coat of arms on an escutcheon f ...
of Russia's Chernyshevsky District, where it was discovered.
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q17414109 Neornithischia Feathered dinosaurs Fossil taxa described in 2014 Taxa named by Pascal Godefroit Dinosaur genera Bathonian dinosaurs