Jat on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Jat people ((), ()) are a traditionally
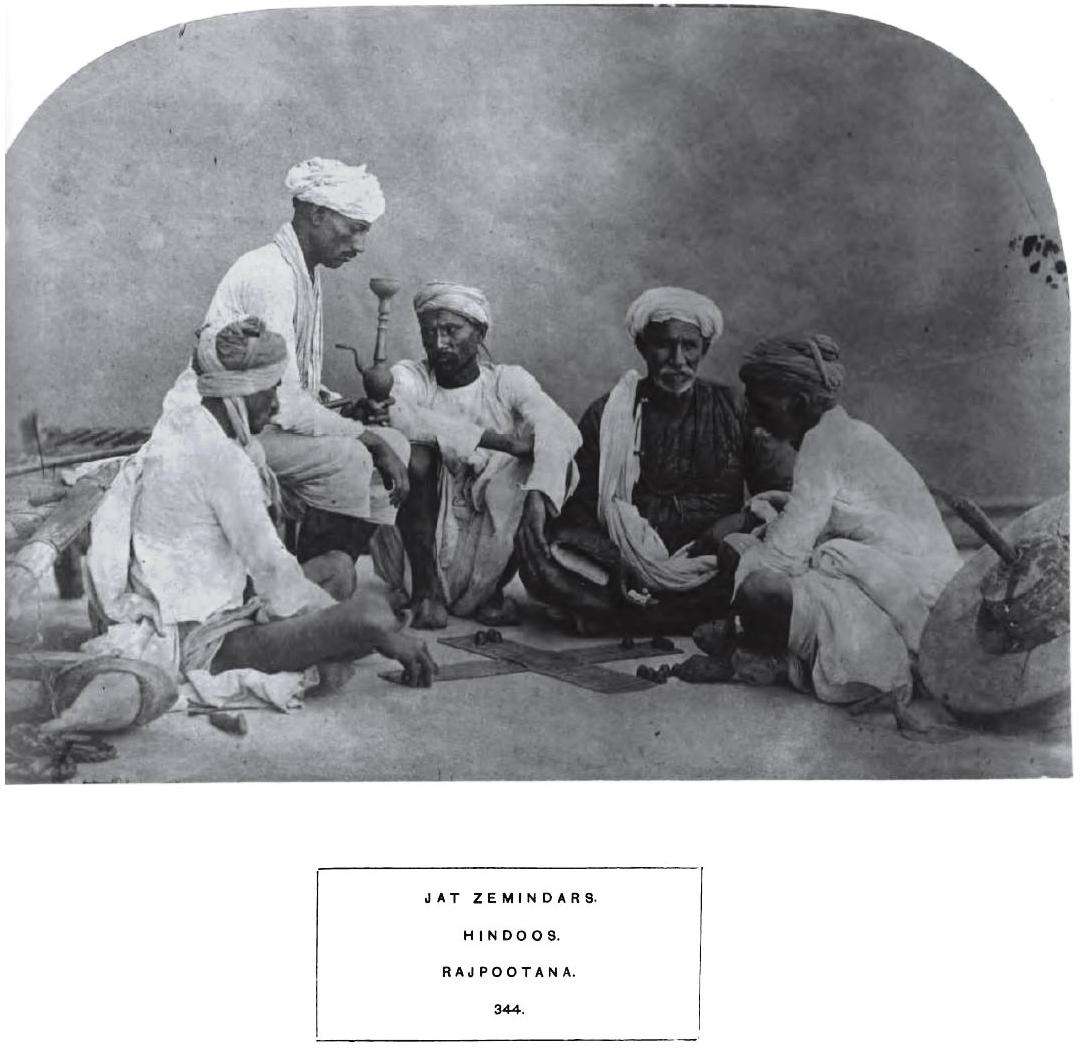 The Jats are a paradigmatic example of community- and identity-formation in early modern
The Jats are a paradigmatic example of community- and identity-formation in early modern  As the Mughal empire faltered, there were a series of rural rebellions in North India. Although these had sometimes been characterized as "peasant rebellions", others, such as
As the Mughal empire faltered, there were a series of rural rebellions in North India. Although these had sometimes been characterized as "peasant rebellions", others, such as
 In 1669, the Hindu Jats, under the leadership of
In 1669, the Hindu Jats, under the leadership of
 When
When
 While followers important to Sikh tradition like
While followers important to Sikh tradition like
 Many Jat people serve in the
Many Jat people serve in the
agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
community in Northern India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central ...
and Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
. Originally pastoralist
Pastoralist may refer to:
* Pastoralism, raising livestock on natural pastures
* Pastoral farming, settled farmers who grow crops to feed their livestock
* People who keep or raise sheep, sheep farming
Sheep farming or sheep husbandry is the ra ...
s in the lower Indus river
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir ...
-valley of Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
, Jats migrated north into the Punjab region
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprisin ...
in late medieval
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Renai ...
times, and subsequently into the Delhi Territory
The Delhi Territory was an administrative region in British India which comprised present-day Delhi plus Bhiwani, Faridabad, Fatehabad, Gurgaon, Hisar, Jhajjar, Karnal, Nuh, Palwal, Panipat, Rewari, Rohtak, Sirsa, Sonipat and Yamunanaga ...
, northeastern Rajputana
Rājputana, meaning "Land of the Rajputs", was a region in the Indian subcontinent that included mainly the present-day States of India, Indian state of Rajasthan, as well as parts of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, and some adjoining areas of Sin ...
, and the western Gangetic Plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain encompassing northern regions of the Indian subcontinent, including most of northern and eastern India, around half of Pakistan, virtually all of Bangla ...
in the 17th and 18th centuries. Quote: "Hiuen Tsang gave the following account of a numerous pastoral-nomadic population in seventh-century Sin-ti (Sind): 'By the side of the river.. f Sind along the flat marshy lowlands for some thousand li, there are several hundreds of thousands very great manyfamilies ..hich
Ij ( fa, ايج, also Romanized as Īj; also known as Hich and Īch) is a village in Golabar Rural District, in the Central District of Ijrud County, Zanjan Province, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also ...
give themselves exclusively to tending cattle and from this derive their livelihood. They have no masters, and whether men or women, have neither rich nor poor.' While they were left unnamed by the Chinese pilgrim, these same people of lower Sind were called Jats' or 'Jats of the wastes' by the Arab geographers. The Jats, as 'dromedary men.' were one of the chief pastoral-nomadic divisions at that time, with numerous subdivisions, .... Quote: "In Sind, the breeding and grazing of sheep and buffaloes was the regular occupations of pastoral nomads in the lower country of the south, while the breeding of goats and camels was the dominant activity in the regions immediately to the east of the Kirthar range and between Multan and Mansura. The jats were one of the chief pastoral-nomadic divisions here in early-medieval times, and although some of these migrated as far as Iraq, they generally did not move over very long distances on a regular basis. Many jats migrated to the north, into the Panjab, and here, between the eleventh and sixteenth centuries, the once largely pastoral-nomadic Jat population was transformed into sedentary peasants. Some Jats continued to live in the thinly populated ''barr'' country between the five rivers of the Panjab, adopting a kind of transhumance
Transhumance is a type of pastoralism or nomadism, a seasonal movement of livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures. In montane regions (''vertical transhumance''), it implies movement between higher pastures in summer and lower vall ...
, based on the herding of goats and camels. It seems that what happened to the jats is paradigmatic of most other pastoral and pastoral-nomadic populations in India in the sense that they became ever more closed in by an expanding sedentary-agricultural realm." Of Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
, Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraha ...
and Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism (Sikhi), a monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ...
faiths, they are now found mostly in the Indian states of Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprisin ...
, Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ar ...
, Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 195 ...
and Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern si ...
and the Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
i provinces of Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
and Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprisin ...
.
The Jats took up arms against the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
during the late 17th and early 18th centuries. Gokula
Gokula Singh (also known as Veer Gokula, or Gokal or Gokul Singh Jat; died on 1 January 1670 AD) was a Jat zamindar of Tilpat, belonging to Haga(Agre/Agha) gotra, in what is now the state of Haryana, India. The second of four sons born to Mad ...
, a Hindu Jat landlord was among the earliest rebel leaders against the Mughal rule during Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
's era. The Hindu Jat kingdom reached its zenith under Maharaja Suraj Mal
Suraj Mal (13 February 1707 – 25 December 1763) was a Jat ruler of Bharatpur in present-day state of Rajasthan. Under him, the Jat rule covered the present-day districts of Agra, Aligarh, Bharatpur, Dholpur, Etawa, Hathras, Mainpuri, ...
(1707–1763). The community played an important role in the development of the martial Khalsa
Khalsa ( pa, ਖ਼ਾਲਸਾ, , ) refers to both a community that considers Sikhism as its faith,Kha ...
''panth Panth (also panthan, meaning "path" in Sanskrit) is the term used for several religious traditions in India. A panth is founded by a guru or an acharya, and is often led by scholars or senior practitioners of the tradition.
Some of the major pant ...
'' of Sikhism. By the 20th century, the landowning Jats became an influential group in several parts of North India, including Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprisin ...
, Western Uttar Pradesh
Western Uttar Pradesh is a region in India that comprises the western districts of Uttar Pradesh state, including the areas of Rohilkhand and those where Khariboli, Braj and Kannauji are spoken. The region has some demographic, economic and cul ...
, Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern si ...
, Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ar ...
and Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
. Over the years, several Jats abandoned agriculture in favour of urban jobs, and used their dominant economic and political status to claim higher social status.
History
 The Jats are a paradigmatic example of community- and identity-formation in early modern
The Jats are a paradigmatic example of community- and identity-formation in early modern Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India ...
. "Jat" is an elastic label applied to a wide-ranging community from simple landowning peasants to wealthy and influential Zamindars.
By the time of Muhammad bin Qasim
Muḥammad ibn al-Qāsim al-Thaqāfī ( ar, محمد بن القاسم الثقفي; –) was an Arab military commander in service of the Umayyad Caliphate who led the Muslim conquest of Sindh (part of modern Pakistan), inaugurating the Umayya ...
's conquest of Sind in the eighth century, Arab writers described agglomerations of Jats in the arid, the wet, and the mountainous regions of the conquered land of Sindh. The Arab rulers, though professing a theologically egalitarian religion, maintained the position of Jats and the discriminatory practices against them that had been put in place in the long period of Hindu rule in Sind. Quote: "... Nor can the liberation that the Muslim conquerors offered to those who sought to escape from the caste system be taken for granted. … a caliphal governor of Sind in the late 830s is said to have … (continued the previous Hindu requirement that) … the Jats, when walking out of doors in future, to be accompanied by a dog. The fact that the dog is an unclean animal to both Hindu and Muslim made it easy for the Muslim conquerors to retain the ''status quo'' regarding a low-caste tribe. In other words, the new regime in the eighth and ninth centuries did not abrogate discriminatory regulations dating from a period of Hindu sovereignty; rather, it maintained them. (page 15)" Between the eleventh and the sixteenth centuries, Jat herders at the Sind migrated up along the river valleys, Quote: "... the most numerous of the agricultural tribes (in the Punjab) were the Jats. They had come from Sindh and Rajasthan along the river valleys, moving up, displacing the Gujjars and the Rajputs to occupy culturable lands. (page 5)" into the Punjab, which may have been largely uncultivated in the first millennium. Quote: "The flatlands in the upper Punjab doabs do not seem to have been heavily farmed in the first millennium. … Early-medieval dry farming developed in Sindh, around Multan, and in Rajasthan… From here, Jat farmers seem to have moved into the upper Punjab doabs and into the western Ganga basin in the first half of the second millennium. (page 117)" Many took up tilling in regions such as western Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprisin ...
, where the sakia
A sāqiyah or saqiya ( ar, ساقية), also spelled sakia or saqia) is a mechanical water lifting device. It is also called a Persian wheel, tablia, rehat, and in Latin tympanum. It is similar in function to a scoop wheel, which uses buckets, ...
(water wheel) had been recently introduced. Quote: "Between the eleventh and sixteenth centuries, groups of nomadic pastoralists known as Jats, having worked their way northwards from Sind, settled in the Panjab as peasant agriculturalists and, largely on account of the introduction of the Persian wheel, transformed much of western Panjab into a rich producer of food crops. (page 27)" By early Mughal times, in the Punjab, the term "Jat" had become loosely synonymous with "peasant", and some Jats had come to own land and exert local influence. The Jats had their origins in pastoralism
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as "livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands (pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The animal ...
in the Indus valley
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmi ...
, and gradually became agriculturalist farmers. Around 1595, Jat Zamindars controlled a little over 32% of the Zamindar
A zamindar ( Hindustani: Devanagari: , ; Persian: , ) in the Indian subcontinent was an autonomous or semiautonomous ruler of a province. The term itself came into use during the reign of Mughals and later the British had begun using it as ...
is in the Punjab region.
According to historians Catherine Asher and Cynthia Talbot, Over time the Jats became primarily Muslim in the western Punjab, Sikh in the eastern Punjab, and Hindu in the areas between Delhi Territory
The Delhi Territory was an administrative region in British India which comprised present-day Delhi plus Bhiwani, Faridabad, Fatehabad, Gurgaon, Hisar, Jhajjar, Karnal, Nuh, Palwal, Panipat, Rewari, Rohtak, Sirsa, Sonipat and Yamunanaga ...
and Agra, with the divisions by faith reflecting the geographical strengths of these religions.
During the decline of Mughal rule in the early 18th century, the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India ...
's hinterland dwellers, many of whom were armed and nomadic, increasingly interacted with settled townspeople and agriculturists. Many new rulers of the 18th century came from such martial and nomadic backgrounds. The effect of this interaction on India's social organization lasted well into the colonial period. During much of this time, non-elite tillers and pastoralists, such as the Jats or Ahir
Ahir or Aheer are a community of traditionally non-elite pastoralists in India, most members of which identify as being of the Indian Yadav community because they consider the two terms to be synonymous. The Ahirs are variously described as a ...
s, were part of a social spectrum that blended only indistinctly into the elite landowning classes at one end, and the menial or ritually polluting classes at the other. During the heyday of Mughal rule, Jats had recognized rights. According to Barbara D. Metcalf
Barbara Daly Metcalf (born September 13, 1941) is a professor emeritus of history at the University of California, Davis. She is a specialist in the history of South Asia, especially the colonial period, and the history of the Muslim population ...
and Thomas R. Metcalf
Thomas R. Metcalf (born May 31, 1934) is a historian of South Asia, especially colonial India, and of the British Empire. Metcalf is the Emeritus Sarah Kailath Professor of India Studies and Professor of History at the University of California, B ...
:
 As the Mughal empire faltered, there were a series of rural rebellions in North India. Although these had sometimes been characterized as "peasant rebellions", others, such as
As the Mughal empire faltered, there were a series of rural rebellions in North India. Although these had sometimes been characterized as "peasant rebellions", others, such as Muzaffar Alam
Muzaffar Alam (born 3 February 1947) is the George V. Bobrinskoy Professor in South Asian Languages and Civilizations at the University of Chicago.
Biography
Muzaffar Alam is a historian trained at Jamia Millia Islamia (New Delhi), Aligarh Mu ...
, have pointed out that small local landholders, or '' zemindars'', often led these uprisings. The Sikh and Jat rebellions were led by such small local zemindars, who had close association and family connections with each other and with the peasants under them, and who were often armed.
These communities of rising peasant-warriors were not well-established Indian castes, but rather quite new, without fixed status categories, and with the ability to absorb older peasant castes, sundry warlords, and nomadic groups on the fringes of settled agriculture. The Mughal Empire, even at the zenith of its power, functioned by devolving authority and never had direct control over its rural grandees. It was these zemindars who gained most from these rebellions, increasing the land under their control. The triumphant even attained the ranks of minor princes, such as the Jat ruler Badan Singh of the princely state
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to ...
of Bharatpur.
Hindu Jats
 In 1669, the Hindu Jats, under the leadership of
In 1669, the Hindu Jats, under the leadership of Gokula
Gokula Singh (also known as Veer Gokula, or Gokal or Gokul Singh Jat; died on 1 January 1670 AD) was a Jat zamindar of Tilpat, belonging to Haga(Agre/Agha) gotra, in what is now the state of Haryana, India. The second of four sons born to Mad ...
, rebelled against the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
in Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the to ...
. The community came to predominate south and east of Delhi after 1710. According to historian Christopher Bayly
Sir Christopher Alan Bayly, FBA, FRSL (18 May 1945 – 18 April 2015) was a British historian specialising in British Imperial, Indian and global history. From 1992 to 2013, he was Vere Harmsworth Professor of Imperial and Naval History at ...
The Jats had moved into the Gangetic Plain in two large migrations, in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries respectively. They were not a caste in the usual Hindu sense, for example, in which Bhumihar
Bhumihars, also called Babhan, are a Hindu caste mainly found in Bihar (including the Mithila region), the Purvanchal region of Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, the Bundelkhand region of Madhya Pradesh, and Nepal.
The Bhumihars claim Brahmin statu ...
s of the eastern Gangetic plain were; rather they were an umbrella group of peasant-warriors. According to Christopher Bayly:
By the mid-eighteenth century, the ruler of the recently established Jat kingdom of Bharatpur, Raja Surajmal, felt sanguine enough about durability to build a garden palace at nearby Deeg
Deeg is a historical town and a municipality in Bharatpur district in the state of Rajasthan, India. It is situated north of Bharatpur and northwest of Agra.
In Hindu mythology, Deeg was situated along the ''parikrama'' path of Krishna, whic ...
. According to historian, Eric Stokes,
Muslim Jats
 When
When Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, No ...
entered Sindh and other Southern regions of current Pakistan in the seventh century, the chief tribal groupings they found were the Jats and the Med people The Med are an ethnic community found in the coastal areas of Balochistan, Pakistan, mainly in the regions of Makran and Las Bela, and the Makran region of Sistan and Baluchestan Province of Iran.
Origin
There are different theories as to the o ...
. These Jats are often referred as ''Zatts'' in early Arab writings. The Muslim conquest chronicles further point at the important concentrations of Jats in towns and fortresses of Lower and Central Sindh. Today, Muslim Jats are found in Pakistan and India.
Sikh Jats
 While followers important to Sikh tradition like
While followers important to Sikh tradition like Baba Buddha
Baba Buddha (Gurmukhi: ਬਾਬਾ ਬੁੱਢਾ; ''bābā buḍhā''; lit. meaning "wise old man") (6 October 1506 – 8 September 1631) was a prime figure in early Sikhism. He was born in 1506 in the village of Kathu Nangal, in Amritsar i ...
were among the earliest significant historical Sikh figures, and significant numbers of conversions occurred as early as the time of Guru Angad
Guru Angad (31 March 1504 – 29 March 1552; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਅੰਗਦ, pronunciation: ) was the second of the ten Sikh gurus of Sikhism. After meeting Guru Nanak, the founder of Sikhism, becoming a Sikh, and serving and working with ...
(1504–1552), the first large-scale conversions of Jats is commonly held to have begun during the time of Guru Arjan
Guru Arjan (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਅਰਜਨ, pronunciation: ; 15 April 1563 – 30 May 1606) was the first of the two Gurus martyred in the Sikh faith and the fifth of the ten total Sikh Gurus. He compiled the first official edition of th ...
(1563–1606). While touring the countryside of eastern Punjab, he founded several important towns like Tarn Taran Sahib
Tarn Taran Sahib is a city in the Majha region of the state of Punjab, in northern India. It is the district headquarters and hosts the municipal council of Tarn Taran district. Gurdwara Sri Tarn Taran Sahib, a prominent Sikh shrine is locate ...
, Kartarpur, and Hargobindpur which functioned as social and economic hubs, and together with the community-funded completion of the Darbar Sahib to house the Guru Granth Sahib
The Guru Granth Sahib ( pa, ਗੁਰੂ ਗ੍ਰੰਥ ਸਾਹਿਬ, ) is the central holy religious scripture of Sikhism, regarded by Sikhs as the final, sovereign and eternal Guru following the lineage of the ten human gurus of the rel ...
and serve as a rallying point and center for Sikh activity, established the beginnings of a self-contained Sikh community, which was especially swelled with the region's Jat peasantry. They formed the vanguard of Sikh resistance against the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
from the 18th century onwards.
It has been postulated, though inconclusively, that the increased militarization of the Sikh panth following the martyrdom of Guru Arjan
Guru Arjan (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਅਰਜਨ, pronunciation: ; 15 April 1563 – 30 May 1606) was the first of the two Gurus martyred in the Sikh faith and the fifth of the ten total Sikh Gurus. He compiled the first official edition of th ...
(beginning during the era of Guru Hargobind
Gurū Hargobind (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਹਰਿਗੋਬਿੰਦ, pronunciation: l 19 June 1595 – 28 February 1644), revered as the ''sixth Nānak'', was the sixth of ten Gurus of the Sikh religion. He had become Guru at the young age of ...
and continuing after) and its large Jat presence may have reciprocally influenced each other.
At least eight of the 12 Sikh ''Misl
The Misls (derived from an Arabic word مِثْل meaning 'equal') were the twelve sovereign states of the Sikh Confederacy, which rose during the 18th century in the Punjab region in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent and is cit ...
s'' (Sikh confederacies) were led by Jat Sikhs, who would form the vast majority of Sikh chiefs.
According to censuses in gazetteers published during the colonial period in the early 20th century, further waves of Jat conversions, from Hinduism to Sikhism, continued during the preceding decades. Writing about the Jats of Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprisin ...
, the Sikh author, Khushwant Singh
Khushwant Singh (born Khushal Singh, 2 February 1915 – 20 March 2014) was an Indian author, lawyer, diplomat, journalist and politician. His experience in the 1947 Partition of India inspired him to write '' Train to Pakistan'' in 1956 (made ...
opined that their attitude never allowed themselves to be absorbed in the Brahminic fold :
In Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprisin ...
, the states of Patiala
Patiala () is a city in southeastern Punjab, northwestern India. It is the fourth largest city in the state and is the administrative capital of Patiala district. Patiala is located around the ''Qila Mubarak'' (the 'Fortunate Castle') construct ...
, Faridkot, Jind
Jind is one of the largest and oldest city in Jind district in the Indian state of Haryana. It is administrative headquarter of Jind district. Rani Talab is the main destination for tourists while Pandu-Pindara and Ramrai are the main relig ...
, and Nabha
Nabha is a city and municipal council in the Patiala district in the south-west of the Indian state of Punjab. It was the capital of the former Nabha State. Nabha is also a sub-division city which comes under Patiala district.
Geography
Nabha ...
were ruled by the Sikh Jats.
Demographics
According to anthropologist Sunil K. Khanna, Jat population is estimated to be around 30 million (or 3crore
A crore (; abbreviated cr) denotes ten million (10,000,000 or 107 in scientific notation) and is equal to 100 lakh in the Indian numbering system. It is written as 1,00,00,000 with the local 2,2,3 style of digit group separators (one lakh is ...
) in South Asia in 2010. This estimation is based on statistics of the last caste census and the population growth of the region. The last caste census was conducted in 1931, which estimated Jats to be 8 million, mostly concentrated in India and Pakistan. Deryck O. Lodrick estimates Jat population to be over 33 million (around 12 million and over 21 million in India and Pakistan, respectively) in South Asia in 2009 while noting the unavailability of precise statistics in this regard. His estimation is based on a late 1980s population projection of Jats and the population growth of India and Pakistan. He also notes that some estimates put their total population in South Asia at approximately 43 million in 2009.
Republic of India
In India, multiple 21st-century estimates put Jats' population share at 20–25% inHaryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ar ...
state and at 20–35% in Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprisin ...
state. In Rajasthan, Delhi, and Uttar Pradesh, they constitute around 9%, 5%, and 1.2% respectively of the total population.
In the 20th century and more recently, Jats have dominated as the political class in Haryana and Punjab. Some Jat people have become notable political leaders, including the sixth Prime Minister of India, Charan Singh
Chaudhary Charan Singh (23 December 1902 – 29 May 1987) served as the 5th Prime Minister of India between 28 July 1979 to 14 January 1980. Historians and people alike frequently refer to him as the 'champion of India's peasants.'
Charan Si ...
and the sixth Deputy Prime Minister of India, Chaudhary Devi Lal
Chaudhary Devi Lal (born Devi Dayal; 25 September 1915 – 6 April 2001) was an Indian statesman who served as 6th Deputy Prime Minister of India from 1989 to 1991 in the governments of V. P. Singh and Chandra Shekhar. Also popularly known as ...
.
Consolidation of economic gains and participation in the electoral process are two visible outcomes of the post-independence situation. Through this participation they have been able to significantly influence the politics of North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central ...
. Economic differentiation, migration and mobility could be clearly noticed amongst the Jat people.
Jats are classified as Other Backward Class
The Other Backward Class is a collective term used by the Government of India to classify castes which are educationally or socially backward. It is one of several official classifications of the population of India, along with Forward caste, Gen ...
(OBC) in seven of India's thirty-six States and UTs, namely Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern si ...
, Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several peaks ...
, Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
, Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand ( , or ; , ), also known as Uttaranchal ( ; the official name until 2007), is a state in the northern part of India. It is often referred to as the "Devbhumi" (literally 'Land of the Gods') due to its religious significance and ...
, Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 195 ...
, Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the second l ...
and Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (, ) is a landlocked state in Central India. It is the ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states – Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Prades ...
. However, only the Jats of Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern si ...
– excluding those of Bharatpur district
Bharatpur District is a district in Rajasthan state in western India. The town of Bharatpur is the District Headquarters, Division Headquarters and Headquarters of Bharatpur Police Range of Rajasthan Police. Bharatpur District is a part of ...
and Dholpur district
Dholpur District is a district of Rajasthan state in Northern India. The town of Dholpur is the district headquarters. Dholpur District is a part of Bharatpur Divisional Commissionerate. It was carved out from the erstwhile Bharatpur District ...
– are entitled to reservation of central government jobs under the OBC reservation. In 2016, the Jats of Haryana organized massive protests demanding to be classified as OBC in order to obtain such affirmative action benefits.
Pakistan
Many Jat Muslim people live in Pakistan and have dominant roles in public life in thePakistani Punjab
Punjab (; , ) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in central-eastern region of the country, Punjab is the second-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the largest province by population. It shares land borders with the ...
and Pakistan in general. Jat communities also exist in Pakistani-administered Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompass ...
, in Sindh, particularly the Indus delta
The Indus River Delta ( ur, سندھ ڈیلٹا, sd, سنڌو ٽِڪور), forms where the Indus River flows into the Arabian Sea, mostly in the southern Sindh province of Pakistan with a small portion in the Kutch Region of India. The delta co ...
and among Seraiki-speaking communities in southern Pakistani Punjab, the Kachhi region of Balochistan and the Dera Ismail Khan District
Dera Ismail Khan District ( ps, ډېره اسماعیل خان ولسوالي, bal, ڈیرہ عِسمائیل خان, ur, , skr, ; often abbreviated as D.I. Khan) is a district in Dera Ismail Khan Division of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province in P ...
of the North West Frontier Province
The North-West Frontier Province (NWFP; ps, شمال لویدیځ سرحدي ولایت, ) was a Chief Commissioner's Province of British India, established on 9 November 1901 from the north-western districts of the Punjab Province. Followin ...
.
In Pakistan also, Jat people have become notable political leaders, like Hina Rabbani Khar
Hina Rabbani Khar (Urdu: ; born 19 November 1977) is a Pakistani politician, who is serving as the Minister of State for Foreign Affairs since 19 April 2022. She was previously appointed in July 2011 as the Foreign Minister of Pakistan at the ...
.
Culture and society
Military
 Many Jat people serve in the
Many Jat people serve in the Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is a four- ...
, including the Jat Regiment
The Jat Regiment is an infantry regiment of the Indian Army, of which it is one of the longest-serving regiments.Sikh Regiment
The Sikh Regiment is an infantry regiment of the Indian Army. Sikh regiment is the highest decorated regiment of the Indian Army and in 1979, the 1st battalion was the Commonwealth's most decorated battalion with 245 pre-independence and 82 ...
, Rajputana Rifles
The Rajputana Rifles is the oldest rifle regiment of the Indian Army. It was originally a part of the British Indian Army, when six previously existing regiments were amalgamated to form six battalions of the 6th Rajputana Rifles. In 1945, the ...
and the Grenadiers
A grenadier ( , ; derived from the word ''grenade'') was originally a specialist soldier who threw hand grenades in battle. The distinct combat function of the grenadier was established in the mid-17th century, when grenadiers were recruited from ...
, where they have won many of the highest military awards for gallantry and bravery. Jat people also serve in the Pakistan Army especially in the Punjab Regiment Punjab Regiment may refer to the following existing units:
*Punjab Regiment (India)
*Punjab Regiment (Pakistan)
From 1922 to 1947, the British Indian Army included 6 numbered Punjab Regiments:
*1st Punjab Regiment
*2nd Punjab Regiment
* 8th Punj ...
.
The Jat people were designated by officials of the British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was himsel ...
as a "martial race
Martial race was a designation which was created by army officials in British India after the Indian Rebellion of 1857, in which they classified each caste as belonging to one of two categories, the 'martial' caste and the 'non-martial' caste. T ...
", which meant that they were one of the groups whom the British favoured for recruitment to the British Indian Army
The British Indian Army, commonly referred to as the Indian Army, was the main military of the British Raj before its dissolution in 1947. It was responsible for the defence of the British Indian Empire, including the princely states, which cou ...
. This was a designation created by administrators that classified each ethnic group as either "martial" or "non-martial": a "martial race" was typically considered brave and well built for fighting, whilst the remainder were those whom the British believed to be unfit for battle because of their sedentary lifestyles. However, the martial races were also considered politically subservient, intellectually inferior, lacking the initiative or leadership qualities to command large military formations. The British had a policy of recruiting the martial Indians from those who has less access to education as they were easier to control. According to modern historian Jeffrey Greenhunt on military history, "The Martial Race theory had an elegant symmetry. Indians who were intelligent and educated were defined as cowards, while those defined as brave were uneducated and backward". According to Amiya Samanta, the martial race was chosen from people of mercenary spirit (a soldier who fights for any group or country that will pay him/her), as these groups lacked nationalism as a trait. The Jats participated in both World War I and World War II, as a part of the British Indian Army. In the period subsequent to 1881, when the British reversed their prior anti-Sikh policies, it was necessary to profess Sikhism in order to be recruited to the army because the administration believed Hindus to be inferior for military purposes.
The Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is a four- ...
admitted in 2013 that the 150-strong Presidential Bodyguard comprises only people who are Hindu Jats, Jat Sikhs and Hindu Rajputs. Refuting claims of discrimination, it said that this was for "functional" reasons rather than selection based on caste or religion.
Religious beliefs
Deryck O. Lodrick estimates religion-wise break-up of Jats as follows: 47% Hindus, 33% Muslims, and 20% Sikhs. Jats pray to their dead ancestors, a practice which is called ''Jathera.''Varna status
There are conflicting scholarly views regarding the varna status of Jats in Hinduism. Some sources state that Jats are regarded asKshatriya
Kshatriya ( hi, क्षत्रिय) (from Sanskrit ''kṣatra'', "rule, authority") is one of the four varna (social orders) of Hindu society, associated with warrior aristocracy. The Sanskrit term ''kṣatriyaḥ'' is used in the cont ...
s, while others assign Vaishya
Vaishya (Sanskrit: वैश्य, ''vaiśya'') is one of the four varnas of the Hindu social order in India. Vaishyas are classed third in the order of caste hierarchy.
The occupation of Vaishyas consists mainly of agriculture, taking care ...
or Shudra
Shudra or ''Shoodra'' (Sanskrit: ') is one of the four '' varnas'' of the Hindu caste system and social order in ancient India. Various sources translate it into English as a caste, or alternatively as a social class. Theoretically, class ser ...
varna to them.
According to the political scientist Shailendra Sharma, cultivating castes such as Jat and the Bhumihar
Bhumihars, also called Babhan, are a Hindu caste mainly found in Bihar (including the Mithila region), the Purvanchal region of Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, the Bundelkhand region of Madhya Pradesh, and Nepal.
The Bhumihars claim Brahmin statu ...
in Uttar Pradesh and Haryana are of "upper shudra status".
According to the Indian Anthropologist Indera Paul Singh, Brahmins demoted the varna status of Jats from Kshatriya to ''Sat Shudra'' (clean Shudra) in the Vedic period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, betwe ...
for challenging the authority of Brahmins. According to Irfan Habib
Irfan Habib (born August 10, 1931) is an Indian historian of ancient and medieval India, following the methodology of Marxist historiography in his contributions to economic history. He identifies as a Marxist and is well known for his strong ...
, Jats were a "pastoral Chandala-like tribe" in Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
during the eighth century. Their 11th-century status of Shudra varna changed to Vaishya varna by the 17th century, with some of them aspiring to improve it further after their 17th-century rebellion against the Mughals.
The Rajputs refused to accept Jat claims to Kshatriya status during the later years of the British Raj and this disagreement frequently resulted in violent incidents between the two communities. The claim at that time of Kshatriya status was being made by the Arya Samaj
Arya Samaj ( hi, आर्य समाज, lit=Noble Society, ) is a monotheistic Indian Hindu reform movement that promotes values and practices based on the belief in the infallible authority of the Vedas. The samaj was founded by the sann ...
, which was popular in the Jat community. The Arya Samaj saw it as a means to counter the colonial belief that the Jats were not of Aryan descent but of Indo-Scythian
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centur ...
origin.
Female infanticide & status of woman in society
During colonial period, many communities including Hindu Jats were found to be practicing female infanticide in different regions of Northern India. In Jat society, it has been observed that differential treatment is given to woman in comparison to man, birth of a male child in a family is celebrated and is considered as auspicious over the birth of a girl child where the family affair is subdued. In villages, female members are supposed to get married at a younger age and they are expected to work in fields as subordinate to the male members. There is general bias against education for the girl child in the society though the trends to it are changing with urbanisation. Purdah system is practiced by women in Jat villages which act as hindrance to their overall emancipation. The village Jat councils which are male-dominated mostly don't allow female members to head their councils as the common opinion on it is that women are inferior, incapable and less intelligent to men.Clan system
The Jat people are subdivided into numerous clans, some of which overlap with other groups. Hindu and Sikh Jats practice clan exogamy.List of clans
*Ahlawat Ahlawat is a Jat clan and Indian surname.
Notable people bearing the name include:
* Jaideep Ahlawat (born 1980), Indian actor
* Mohit Ahlawat (actor) (born 1962), Indian actor
* Mohit Ahlawat (cricketer) (born 1995), Indian sportsman
* Mukesh K ...
* Anjana Chaudhari
* Aulakh
Aulakh is a Jat clan in the Punjab region of India and Pakistan. They are mainly concentrated in the tehsil of Ajnala in the Amritsar district of Punjab, India, with significant presence in the Shahbazpur of Tarn Taran district in the Majha regio ...
* Bagri
* Bajwa
Bajwa ( pa, ਬਾਜਵਾ ; ) is a Jat surname and tribe name commonly found among the Sikhs, Hindus and Muslims of the Punjab region in India and Pakistan.
Notable people bearing the Bajwa name, who may or may not be affiliated with the cl ...
* Bargoti (Uttar Pradesh)
* Beniwal
* Bhalothia (Rajasthan, Haryana)
* Bharwana
* Brar
* Buttar
* Cheema
* Chhina (Punjab)
* Chilka (Rajasthan)
* Dabas
* Dahiya Dahiya, or variants, may refer to:
* Dahiya (surname), an Indian surname
* Dahia (title), derived from Dey
* Dahieh, a suburb of Beirut, Lebanon
* Dihya, or Kahina, a Berber warrior queen
* Dahije, or Dahijas, renegade Janissary officers who too ...
* Dara (Rajasthan)
* Dharan
Dharan ( ne, धरान) a sub-metropolitan city in Sunsari District of Province No. 1, Nepal, which was established as a fourth municipality in the Kingdom in 1958. It is the third most populous city in Eastern Nepal after Biratnagar and ...
* Dhaliwal Dhaliwal may refer to;
Villages in Punjab, India
* Dhaliwal, Nakodar, Jalandhar district
* Dhaliwal Bet, Kapurthala district
* Dhaliwal Dona, Kapurthala district
* Mand Dhaliwal, Kapurthala district
Other uses
* Dhaliwal (surname)
{{dab, geo ...
* Dhaulya (Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu)
* Dhillon
Dhillon ( pronunciation: �i˨llõː is a tribe of Jats found in the Punjab region.
Notable people who bear the name, who may or may not be affiliated with the tribe, include:
* Amritpal Singh Dhillon, an Indian-born Canadian singer, rapper, ...
* Gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are ...
* Goriya (Haryana, Uttar Pradesh)
* Grewal
Grewal or Garewal is a family name historically used in India and Pakistan as a gotra of Jat people.
Notable people
* Alexi Grewal, an Olympic Gold medalist and cyclist;
*Gippy Grewal, a singer, actor, and producer;
*Gurbir Grewal, the current ...
* Jats of Azad Kashmir
The Jats are one of the largest communities found in Azad Kashmir, making up the majority of the population of Mirpur District, and forming a large part of the populations of Bhimber and Kotli districts.
Language
The Kotli, Dadyal and Chaks ...
* Jats of Kutch
* Jewlia (Rajasthan)
* Jhajharia (Haryana, Punjab, Rajasthan)
* Jhanjhar (Rajasthan)
* Johiya
Johiya (also Joiya, Joyia or Joria) is a clan found among the Rajputs of India and Pakistan.
Origin
The Johiya may be modern-day descendants of the ancient Yaudheya warrior tribe that ruled in some areas of northern India until the period of th ...
* Kalwania (Rajasthan, Haryana)
* Kasaniya (Rajasthan)
* Katewa
* Khakh
* Khangura
* Kharal
The Kharal also spelled ''Kharral'' or ''Kharl'' is a very large tribe centered in Punjab Region that was traditionally semi-pastoral and is classed as Jat or Rajput. Modern Indian and Pakistani census reports mention Kharals as Rajputs.
The ...
* Khatkar (Punjab, Haryana)
* Lashari
The Lashari () is a baloch tribe. According to baloch folklore the tribe was founded by Lashar Khan, one of Mir Jalal Khan's four sons. Lasharis led by Mir Gwahram Khan Lashari, are believed to have engaged in a 30-year war against the Rind, ...
* Malhi Malhi may refer to:
People
* Ali Asjad Malhi, Pakistani politician of Punjabi ancestry
* Naseer Ahmad Malhi, Pakistani politician of Punjabi ancestry
* Harinder Malhi, Canadian politician of Punjabi ancestry
* Gobind Malhi, Indian writer of ...
* Malik
Malik, Mallik, Melik, Malka, Malek, Maleek, Malick, Mallick, or Melekh ( phn, 𐤌𐤋𐤊; ar, ملك; he, מֶלֶךְ) is the Semitic term translating to "king", recorded in East Semitic and Arabic, and as mlk in Northwest Semitic duri ...
* Marhal
* Maulaheri
* Mirdha
* Muley
* Naich
* Panwar
The Panwar is a Rajput
Rajput (from Sanskrit ''raja-putra'' 'son of a king') is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating from the Indi ...
* Pediwal (Rajasthan)
* Poonia
* Rahal
* Rahar
* Randhawa
* Ranjha
* Rath
* Rawn (Punjab)
* Rehvar The Rehvar are a clan found in the state of Gujarat in India.
Origin
The Rehvar Rajput are originally Parmar who came from Ujjain and settled in Chundravati. They then migrated to Tharparkar in Sindh, and then moved to Banaskantha. The Rehvar wer ...
* Sandhawalia
* Sandhila (Sindh, Punjab)
* Sandhu
Sandhu or Sindhu is a clan or family name found among the Punjabi Jatts in India and Pakistan. It is Punjab's second largest Jatt clan. The etymology is connected to the word ''Sindhu'', the native name for the Indus river.
Notable people with ...
* Sangwan
* Sarai (Punjab)
* Sekhon
* Sial
In geology, the term sial refers to the composition of the upper layer of Earth's crust, namely rocks rich in aluminium silicate minerals. It is sometimes equated with the continental crust because it is absent in the wide oceanic basins, but ...
* Sidhu
Sidhu () is a Punjabi Jat clan found in Punjab.Tarar
*
Teotia
Teotia "Tewatia" "Tiwathia" is a royal gotra (clan) of Jat people in India which were the rulers & founders of Ballabhgarh kingdom. It is mainly found in Haryana, Rajasthan and Western Uttar Pradesh
Western Uttar Pradesh is a region in India t ...
* Thaheem
* Tomar
* Virk
* Warraich
In popular culture
Jats are part of Punjabi andHaryanvi
Haryanvi ( ' or '), also known as Bangru, is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the state of Haryana in India, and to a lesser extent in Delhi. Haryanvi is considered to be part of the dialect group of Western Hindi, which also includes Kharibo ...
culture and are often portrayed in Indian and Pakistani films and songs.
*''Maula Jatt
''Maula Jatt'' ( pnb, ), is a 1979 Pakistani Punjabi language action, musical film directed by Younis Malik and produced by ''Sarwar Bhatti''. The film is an unofficial sequel to the 1975's ''Wehshi Jatt'', starring Sultan Rahi as Maula Jatt ...
''
*'' The Legend of Maula Jatt''
*''A Flying Jatt
''A Flying Jatt'' is a 2016 Indian superhero film co-written and directed by Remo D'Souza and produced under the banner of Balaji Motion Pictures. It features Tiger Shroff, Jacqueline Fernandez and Nathan Jones in the lead roles. ''A Flying Jatt ...
''
*'' Jatt & Juliet''
*''Jatt & Juliet 2
''Jatt & Juliet 2'' ( pa, ਜੱਟ ਐਂਡ ਜੂਲੀਅਟ 2) is a 2013 Indian Punjabi romance comedy film directed by Anurag Singh. The film is a sequel to the 2012 blockbuster '' Jatt & Juliet'', however not directly or story-wise. Acto ...
''
*'' Jatt James Bond''
*''Badla Jatti Da''
*'' Jatts In Golmaal''
* ''Jaattan ka Chhora''
Notable people
See also
*Jat Regiment
The Jat Regiment is an infantry regiment of the Indian Army, of which it is one of the longest-serving regiments.Jat reservation agitation
The Jat reservation agitation was a series of violent protests in February 2016 by the Jat people of North India, especially those in the state of Haryana, which "paralysed" the state for 10 days. The protestors sought inclusion of their caste i ...
* World Jat Aryan Foundation
World Jat Aryan Foundation is an organization of the Jats that aims to serve the Jat community around the world, in various aspects. It was founded in 2001, having Hoshiar Singh as its first president.
The foundation is presided by Navjot Singh ...
* List of Jat dynasties and states
* List of Jat people
* Jat Sikh
Jat Sikh (also known by the more conventional endonym Jatt Sikh) is a sub-group of the Jat people and the Sikh religious group from the Indian subcontinent. They are one of the dominant communities in the Punjab owing to their large land holdin ...
* Jāti
''Jāti'' is the term traditionally used to describe a cohesive group of people in the Indian subcontinent, like a tribe, community, clan, sub-clan, or a religious sect. Each Jāti typically has an association with an occupation, geography or t ...
Footnotes
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* {{Authority control * Ethnic groups in India Ethnic groups in Pakistan Agricultural castes Social groups of India Social groups of Pakistan Social groups of Sindh Social groups of Punjab, India Social groups of Haryana Social groups of Punjab, Pakistan Social groups of Uttar Pradesh Social groups of Rajasthan Hindu communities Social groups of Gujarat