James Scott, 1st Duke Of Monmouth on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
James Scott, 1st Duke of Monmouth, 1st Duke of Buccleuch, KG, PC (9 April 1649 – 15 July 1685) was a Dutch-born English nobleman and military officer. Originally called James Crofts or James Fitzroy, he was born in
 Charles, Prince of Wales (later becoming King Charles II), moved to
Charles, Prince of Wales (later becoming King Charles II), moved to
 On 14 February 1663, almost 14 years old, shortly after having been brought to England, James was created Duke of Monmouth, with the subsidiary titles of
On 14 February 1663, almost 14 years old, shortly after having been brought to England, James was created Duke of Monmouth, with the subsidiary titles of
 In 1678, Monmouth was the commander of the Anglo-Dutch brigade, now fighting for the United Provinces against the French, and he distinguished himself at the Battle of Saint-Denis in August that year during the
In 1678, Monmouth was the commander of the Anglo-Dutch brigade, now fighting for the United Provinces against the French, and he distinguished himself at the Battle of Saint-Denis in August that year during the
 From Woodyates Inn the Duke had gone to Shag's Heath, in the middle of which was a cluster of small farms, called the "Island". Amy Farrant gave information that the fugitives were concealed within the Island. The Duke, accompanied by Busse and Brandenburgher, remained concealed all day, with soldiers surrounding the area and threatening to set fire to the woodland. Brandenburgher deserted him at 1 am, and was later captured and interrogated, and is believed to have given away the Duke's hiding place. The spot was at the north-eastern extremity of the Island, now known as Monmouth's Close, in the manor of Woodlands, the property of the Earl of Shaftesbury. At about 7 am Henry Parkin, a militia soldier and servant of Samuel Rolle, discovered the brown skirt of Monmouth's coat as he lay hidden in a ditch covered with fern and brambles under an ash tree, and called for help. The Duke was seized. Bystanders shouted out "Shoot him! shoot him!", but Sir William Portman happening to be near the spot, immediately rode up, and laid hands on him as his prisoner. Monmouth was then "in the last extremity of hunger and fatigue, with no sustenance but a few raw peas in his pocket. He could not stand, and his appearance was much changed. Since landing in England, the Duke had not had a good night's rest, or eaten one meal in quiet, being perpetually agitated with the cares that attend unfortunate ambition". He had "received no other sustenance than the brook and the field afforded".
The Duke was taken to Holt Lodge, in the parish of Wimborne, about away, the residence of Anthony Etterick, a magistrate who asked the Duke what he would do if released, to which he answered: "that if his horse and arms were but restored to him at the same time, he needed only to ride through the army; and he defied them to take him again". The magistrate ordered him taken to London.
From Woodyates Inn the Duke had gone to Shag's Heath, in the middle of which was a cluster of small farms, called the "Island". Amy Farrant gave information that the fugitives were concealed within the Island. The Duke, accompanied by Busse and Brandenburgher, remained concealed all day, with soldiers surrounding the area and threatening to set fire to the woodland. Brandenburgher deserted him at 1 am, and was later captured and interrogated, and is believed to have given away the Duke's hiding place. The spot was at the north-eastern extremity of the Island, now known as Monmouth's Close, in the manor of Woodlands, the property of the Earl of Shaftesbury. At about 7 am Henry Parkin, a militia soldier and servant of Samuel Rolle, discovered the brown skirt of Monmouth's coat as he lay hidden in a ditch covered with fern and brambles under an ash tree, and called for help. The Duke was seized. Bystanders shouted out "Shoot him! shoot him!", but Sir William Portman happening to be near the spot, immediately rode up, and laid hands on him as his prisoner. Monmouth was then "in the last extremity of hunger and fatigue, with no sustenance but a few raw peas in his pocket. He could not stand, and his appearance was much changed. Since landing in England, the Duke had not had a good night's rest, or eaten one meal in quiet, being perpetually agitated with the cares that attend unfortunate ambition". He had "received no other sustenance than the brook and the field afforded".
The Duke was taken to Holt Lodge, in the parish of Wimborne, about away, the residence of Anthony Etterick, a magistrate who asked the Duke what he would do if released, to which he answered: "that if his horse and arms were but restored to him at the same time, he needed only to ride through the army; and he defied them to take him again". The magistrate ordered him taken to London.
 Monmouth was
Monmouth was
In summer hot and dry,
In eager argument were met
About priority.
Says the fly to the grasshopper:
"From mighty race I spring,
Bright Phoebus was my dad 'tis known,
And I eat and drink with a king."
Says the grasshopper to the fly:
"Such rogues are still preferr'd;
Your father might be of high degree,
But your mother was but a turd."
So, rebel Jemmy Scott,
That did to the empire soar,
His father might be the Lord knows what,
But his mother we knew a whore".

 His marriage to Anne Scott, 1st Duchess of Buccleuch resulted in the birth of six children:
* Charles Scott, Earl of Doncaster (24 August 1672 – 9 February 1673/1674)
*
His marriage to Anne Scott, 1st Duchess of Buccleuch resulted in the birth of six children:
* Charles Scott, Earl of Doncaster (24 August 1672 – 9 February 1673/1674)
*
Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Rotte (river), Rotte'') is the second largest List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Netherlands. It is in the Prov ...
in the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, the eldest illegitimate son of Charles II of England
Charles II (29 May 1630 – 6 February 1685) was King of Scotland from 1649 until 1651, and King of England, Scotland and Ireland from the 1660 Restoration of the monarchy until his death in 1685.
Charles II was the eldest surviving child o ...
, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, and Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
with his mistress Lucy Walter.
The Duke of Monmouth served in the Second Anglo-Dutch War and commanded English troops taking part in the Third Anglo-Dutch War before commanding the Anglo-Dutch brigade fighting in the Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War (french: Guerre de Hollande; nl, Hollandse Oorlog), was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Nor ...
. He led the unsuccessful Monmouth Rebellion
The Monmouth Rebellion, also known as the Pitchfork Rebellion, the Revolt of the West or the West Country rebellion, was an attempt to depose James II, who in February 1685 succeeded his brother Charles II as king of England, Scotland and Ir ...
in 1685, an attempt to depose his uncle King James II and VII
James VII and II (14 October 1633 16 September 1701) was King of England and King of Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II of England, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was depo ...
. After one of his officers declared Monmouth the legitimate king in the town of Taunton
Taunton () is the county town of Somerset, England, with a 2011 population of 69,570. Its thousand-year history includes a 10th-century monastic foundation, Taunton Castle, which later became a priory. The Normans built a castle owned by the ...
in Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lor ...
, Monmouth attempted to capitalise on his Protestantism
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
and his position as the son of Charles II, in opposition to James, who had become a Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
. The rebellion failed, and Monmouth was beheaded
Decapitation or beheading is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and most other animals, since it deprives the brain of oxygenated blood, while all other organs are deprived of the au ...
for treason on 15 July 1685.
Biography
Parentage and early life
The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital o ...
in 1648, during the Second English Civil War
The Second English Civil War took place between February to August 1648 in England and Wales. It forms part of the series of conflicts known collectively as the 1639-1651 Wars of the Three Kingdoms, which include the 1641–1653 Irish Confed ...
, where his sister Mary and his brother-in-law William II, Prince of Orange, were based. The French relatives of Charles' mother, Queen Henrietta Maria
Henrietta Maria (french: link=no, Henriette Marie; 25 November 1609 – 10 September 1669) was Queen of England, Scotland, and Ireland from her marriage to King Charles I on 13 June 1625 until Charles was executed on 30 January 1649. She wa ...
, had invited Charles to wait out the war in France with the Queen, but he opted for the Netherlands, as he believed there was more support to be gained for the cause of his father, King Charles I, in the Netherlands than in France. During the summer of 1648, the Prince of Wales became captivated by Lucy Walter, who was in The Hague for a short visit. The lovers were only eighteen, and she is often spoken of as his first mistress, though he may have begun having affairs as early as 1646. Their son James was born in Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Rotte (river), Rotte'') is the second largest List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Netherlands. It is in the Prov ...
in the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
on 9 April 1649, and spent his early years in Schiedam
Schiedam () is a city and municipality in the west of the Netherlands. It is located in the Rotterdam–The Hague metropolitan area, west of Rotterdam, east of Vlaardingen, and south of Delft. In the south the city is connected with the villa ...
.
Research by Hugh Noel Williams suggests that Charles had not arrived in The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital o ...
until the middle of September 1648 – seven months before the child's birth, and that he had only met Lucy in July. It was later rumoured that in the summer of 1648 Lucy had been the mistress
Mistress is the feminine form of the English word "master" (''master'' + ''-ess'') and may refer to:
Romance and relationships
* Mistress (lover), a term for a woman who is in a sexual and romantic relationship with a man who is married to a d ...
of Colonel Robert Sidney, a younger son of the Earl of Leicester
Earl of Leicester is a title that has been created seven times. The first title was granted during the 12th century in the Peerage of England. The current title is in the Peerage of the United Kingdom and was created in 1837.
Early creatio ...
. As Charles had no legitimate surviving children, his younger brother James, Duke of York
James VII and II (14 October 1633 16 September 1701) was King of England and King of Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was deposed in the Glorious ...
, was next in line to the throne. When the boy grew up, those loyal to the Duke of York spread rumours about the young James' resemblance to Sidney. These voices may have been encouraged by the Duke of York himself, who wished to prevent any of the fourteen royal bastards his brother acknowledged from gaining support in the succession. In 2012, a DNA test
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or ...
of Monmouth's patrilineal descendant the 10th Duke of Buccleuch showed that he shared the same Y chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or abs ...
as a distant Stuart cousin; this is evidence that Charles II was indeed Monmouth's father.
James had a younger sister or half-sister, Mary Crofts, whose father may have been Lord Taaffe. Mary later married the Irishman William Sarsfield, thus becoming the sister-in-law of the Jacobite general Patrick Sarsfield.
As an illegitimate son, James was ineligible to succeed to the English or Scottish thrones, unless he could prove rumours that his parents had married secretly. He came to maintain that his parents were married and that he possessed evidence of their marriage, but he never produced it. King Charles II testified in writing to his Privy Council
A privy council is a body that advises the head of state of a state, typically, but not always, in the context of a monarchic government. The word "privy" means "private" or "secret"; thus, a privy council was originally a committee of the mo ...
that he had never been married to anyone except his queen consort, Catherine of Braganza.
In March 1658, young James was kidnapped by one of the King's men, sent to Paris, and placed in the care of William Crofts, 1st Baron Crofts, whose surname he took. He briefly attended a school in Familly.
Officer and commander
 On 14 February 1663, almost 14 years old, shortly after having been brought to England, James was created Duke of Monmouth, with the subsidiary titles of
On 14 February 1663, almost 14 years old, shortly after having been brought to England, James was created Duke of Monmouth, with the subsidiary titles of Earl of Doncaster
Earl () is a rank of the nobility in the United Kingdom. The title originates in the Old English word ''eorl'', meaning "a man of noble birth or rank". The word is cognate with the Scandinavian form ''jarl'', and meant "chieftain", particular ...
and Baron Scott of Tynedale, all three in the Peerage of England
The Peerage of England comprises all peerages created in the Kingdom of England before the Act of Union in 1707. In that year, the Peerages of England and Scotland were replaced by one Peerage of Great Britain. There are five peerages in th ...
, and, on 28 March 1663, he was appointed a Knight of the Garter.
On 20 April 1663, just days after his 14th birthday, the Duke of Monmouth was married to the heiress Anne Scott, 4th Countess of Buccleuch. He took his wife's surname upon marriage. The day after his marriage, the couple were made Duke and Duchess of Buccleuch, Earl and Countess of Dalkeith, and Lord and Lady Scott of Whitchester and Eskdale in the Peerage of Scotland
The Peerage of Scotland ( gd, Moraireachd na h-Alba, sco, Peerage o Scotland) is one of the five divisions of peerages in the United Kingdom and for those peers created by the King of Scots before 1707. Following that year's Treaty of Unio ...
. The Duke of Monmouth was popular, particularly for his Protestantism
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
. The King's official heir presumptive
An heir presumptive is the person entitled to inherit a throne, peerage, or other hereditary honour, but whose position can be displaced by the birth of an heir apparent or a new heir presumptive with a better claim to the position in question. ...
, James, Duke of York, had openly converted to Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
.
In 1665, at the age of 16, Monmouth served in the English fleet under his uncle, the Duke of York, in the Second Anglo-Dutch War. In June 1666, he returned to England to become captain of a troop of cavalry. On 16 September 1668 he was made colonel of the His Majesty's Own Troop of Horse Guards. He acquired Moor Park in Hertfordshire in April 1670. Following the death in 1670, without a male heir, of Josceline Percy, 11th Earl of Northumberland, the earl's estates reverted to the Crown. King Charles II awarded the estates to Monmouth. The Countess of Northumberland successfully sued for the estates to be returned to the late Earl's only daughter and sole heiress, Lady Elizabeth Percy (1667–1722).
At the outbreak of the Third Anglo-Dutch War in 1672, a brigade of 6,000 English and Scottish troops was sent to serve as part of the French army (in return for money paid to King Charles), with Monmouth as its commander. He became Lord Lieutenant of the East Riding of Yorkshire and Governor of Kingston-upon-Hull in April 1673. In the campaign of 1673 and in particular at the Siege of Maastricht that June, Monmouth gained a considerable reputation as one of Britain's finest soldiers. He was reported to be replacing Marshal Schomberg
Friedrich Hermann von Schönberg, 1st Duke of Schomberg, 1st Count of Mertola, (french: Frédéric-Armand; pt, Armando Frederico; 6 December 1615 – 1 July 1690) was a Marshal of France and a General in the English and Portuguese Army. He was ...
as commander of England's Zealand Expedition, but this did not happen.
In 1674, Monmouth became Chancellor of Cambridge University and Master of the Horse, and King Charles II directed that all military orders should be brought first to Monmouth for examination, thus giving him effective command of the forces; his responsibilities included the movement of troops and the suppression of riots. In March 1677, he also became Lord Lieutenant of Staffordshire.
Claim to the Crown
 In 1678, Monmouth was the commander of the Anglo-Dutch brigade, now fighting for the United Provinces against the French, and he distinguished himself at the Battle of Saint-Denis in August that year during the
In 1678, Monmouth was the commander of the Anglo-Dutch brigade, now fighting for the United Provinces against the French, and he distinguished himself at the Battle of Saint-Denis in August that year during the Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War (french: Guerre de Hollande; nl, Hollandse Oorlog), was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Nor ...
, further increasing his reputation. The following year, after his return to Britain, he commanded the small army raised to put down the rebellion of the Scottish Covenanter
Covenanters ( gd, Cùmhnantaich) were members of a 17th-century Scottish religious and political movement, who supported a Presbyterian Church of Scotland, and the primacy of its leaders in religious affairs. The name is derived from '' Covena ...
s and despite being heavily outnumbered, he decisively defeated the (admittedly poorly equipped) Covenanter rebels at the Battle of Bothwell Bridge on 22 June 1679.
Rebellion
As his popularity with the masses increased, Monmouth was obliged to go into exile in the Dutch United Provinces in September 1679. Following the discovery of the so-calledRye House Plot
The Rye House Plot of 1683 was a plan to assassinate King Charles II of England and his brother (and heir to the throne) James, Duke of York. The royal party went from Westminster to Newmarket to see horse races and were expected to make the ...
in 1683, which aimed to assassinate both Charles II and his brother James, Monmouth, who had been encouraged by his supporters to assert his right to the throne, was identified as a conspirator. On King Charles II's death in February 1685, Monmouth led the Monmouth Rebellion, landing with three ships at Lyme Regis
Lyme Regis is a town in west Dorset, England, west of Dorchester and east of Exeter. Sometimes dubbed the "Pearl of Dorset", it lies by the English Channel at the Dorset– Devon border. It has noted fossils in cliffs and beaches on the He ...
in Dorset in early June 1685, in an attempt to take the throne from his uncle, James II and VII
James VII and II (14 October 1633 16 September 1701) was King of England and King of Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II of England, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was depo ...
. He published a "Declaration for the defence and vindication of the protestant religion and of the laws, rights and privileges of England from the invasion made upon them, and for delivering the Kingdom from the usurpation and tyranny of us by the name of James, Duke of York": King James II and VII
James VII and II (14 October 1633 16 September 1701) was King of England and King of Ireland as James II, and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II of England, Charles II, on 6 February 1685. He was depo ...
responded to this by issuing an order for the publishers and distributors of the paper to be arrested.
Monmouth declared himself as the rightful King at various places along the route including Axminster, Chard
Chard or Swiss chard (; '' Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris'', Cicla Group and Flavescens Group) is a green leafy vegetable. In the cultivars of the Flavescens Group, the leaf stalks are large and often prepared separately from the leaf bl ...
, Ilminster and Taunton
Taunton () is the county town of Somerset, England, with a 2011 population of 69,570. Its thousand-year history includes a 10th-century monastic foundation, Taunton Castle, which later became a priory. The Normans built a castle owned by the ...
. The two armies met at the Battle of Sedgemoor
The Battle of Sedgemoor was the last and decisive engagement between the Kingdom of England and rebels led by the Duke of Monmouth during the Monmouth rebellion, fought on 6 July 1685, and took place at Westonzoyland near Bridgwater in Somerset, ...
on 6 July 1685, the last clear-cut pitched battle on open ground between two military forces fought on English soil: Monmouth's makeshift force could not compete with the regular army, and was soundly defeated.
Capture
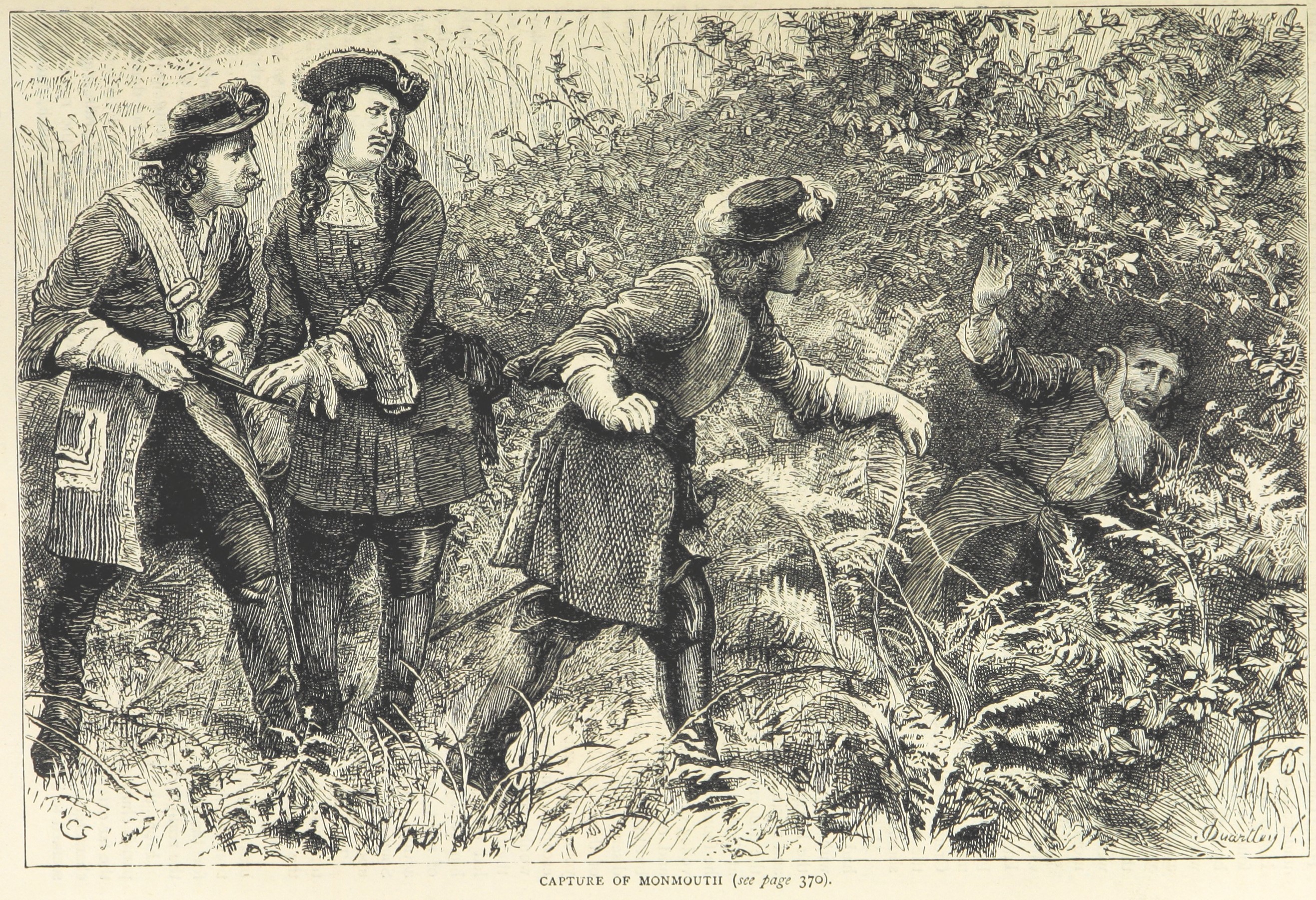
Following the battle a reward of £5,000 was offered for his capture.Roberts, p. 109 On 8 July 1685, Monmouth was captured and arrested near Ringwood in Hampshire, by tradition "in a field of peas". The events surrounding his capture are described by George Roberts in '' Tait's Edinburgh Magazine''. When the Duke had left his horse at Woodyates Inn, he exchanged clothes with a shepherd, who was soon discovered by local loyalists and interrogated. Dogs were then put onto the Duke's scent. Monmouth dropped his gold snuff box, full of gold pieces, in a pea field, where it was afterwards found. From Woodyates Inn the Duke had gone to Shag's Heath, in the middle of which was a cluster of small farms, called the "Island". Amy Farrant gave information that the fugitives were concealed within the Island. The Duke, accompanied by Busse and Brandenburgher, remained concealed all day, with soldiers surrounding the area and threatening to set fire to the woodland. Brandenburgher deserted him at 1 am, and was later captured and interrogated, and is believed to have given away the Duke's hiding place. The spot was at the north-eastern extremity of the Island, now known as Monmouth's Close, in the manor of Woodlands, the property of the Earl of Shaftesbury. At about 7 am Henry Parkin, a militia soldier and servant of Samuel Rolle, discovered the brown skirt of Monmouth's coat as he lay hidden in a ditch covered with fern and brambles under an ash tree, and called for help. The Duke was seized. Bystanders shouted out "Shoot him! shoot him!", but Sir William Portman happening to be near the spot, immediately rode up, and laid hands on him as his prisoner. Monmouth was then "in the last extremity of hunger and fatigue, with no sustenance but a few raw peas in his pocket. He could not stand, and his appearance was much changed. Since landing in England, the Duke had not had a good night's rest, or eaten one meal in quiet, being perpetually agitated with the cares that attend unfortunate ambition". He had "received no other sustenance than the brook and the field afforded".
The Duke was taken to Holt Lodge, in the parish of Wimborne, about away, the residence of Anthony Etterick, a magistrate who asked the Duke what he would do if released, to which he answered: "that if his horse and arms were but restored to him at the same time, he needed only to ride through the army; and he defied them to take him again". The magistrate ordered him taken to London.
From Woodyates Inn the Duke had gone to Shag's Heath, in the middle of which was a cluster of small farms, called the "Island". Amy Farrant gave information that the fugitives were concealed within the Island. The Duke, accompanied by Busse and Brandenburgher, remained concealed all day, with soldiers surrounding the area and threatening to set fire to the woodland. Brandenburgher deserted him at 1 am, and was later captured and interrogated, and is believed to have given away the Duke's hiding place. The spot was at the north-eastern extremity of the Island, now known as Monmouth's Close, in the manor of Woodlands, the property of the Earl of Shaftesbury. At about 7 am Henry Parkin, a militia soldier and servant of Samuel Rolle, discovered the brown skirt of Monmouth's coat as he lay hidden in a ditch covered with fern and brambles under an ash tree, and called for help. The Duke was seized. Bystanders shouted out "Shoot him! shoot him!", but Sir William Portman happening to be near the spot, immediately rode up, and laid hands on him as his prisoner. Monmouth was then "in the last extremity of hunger and fatigue, with no sustenance but a few raw peas in his pocket. He could not stand, and his appearance was much changed. Since landing in England, the Duke had not had a good night's rest, or eaten one meal in quiet, being perpetually agitated with the cares that attend unfortunate ambition". He had "received no other sustenance than the brook and the field afforded".
The Duke was taken to Holt Lodge, in the parish of Wimborne, about away, the residence of Anthony Etterick, a magistrate who asked the Duke what he would do if released, to which he answered: "that if his horse and arms were but restored to him at the same time, he needed only to ride through the army; and he defied them to take him again". The magistrate ordered him taken to London.
Attainder and execution
Following Monmouth's capture,Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
passed an Act of Attainder, ''1 Ja. II c. 2'':
The King took the unusual step of allowing his nephew an audience, despite having no intention of extending a pardon to him, thus breaking with a longstanding tradition that the King would give an audience only when he intended to show clemency. The prisoner unsuccessfully implored his mercy and even offered to convert to Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, but to no avail. The King, disgusted by his abject behaviour, coldly told him to prepare to die, and later remarked that Monmouth "did not behave as well as I expected". Numerous pleas for mercy were addressed to the King, but he ignored them all, even that of his sister-in-law, the Dowager Queen Catherine.
 Monmouth was
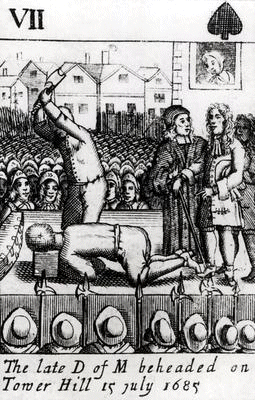
Monmouth was beheaded
Decapitation or beheading is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and most other animals, since it deprives the brain of oxygenated blood, while all other organs are deprived of the au ...
by Jack Ketch on 15 July 1685, on Tower Hill
Tower Hill is the area surrounding the Tower of London in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. It is infamous for the public execution of high status prisoners from the late 14th to the mid 18th century. The execution site on the higher gro ...
. Shortly beforehand, Bishops Turner of Ely and Ken of Bath and Wells
The Diocese of Bath and Wells is a diocese in the Church of England Province of Canterbury in England.
The diocese covers the county of Somerset and a small area of Dorset. The Episcopal seat of the Bishop of Bath and Wells is located in ...
visited the Duke to prepare him for eternity, but withheld the Eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was institu ...
, for the condemned man refused to acknowledge that either his rebellion or his relationship with Lady Wentworth had been sinful. It is said that before laying his head on the block, Monmouth specifically bade Ketch finish him at one blow, saying he had mauled others before. Disconcerted, Ketch did indeed inflict multiple blows with his axe, the prisoner rising up reproachfully the while – a ghastly sight that shocked the witnesses, drawing forth execrations and groans. Some say a knife was at last employed to sever the head from the twitching body. Sources vary; some claim eight blows, the official Tower of London
The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, which is sep ...
fact sheet says it took five blows, while Charles Spencer, in his book ''Blenheim'', puts it at seven. His execution was alluded to in the film '' Kind Hearts and Coronets'', where the executioner says "The last execution of a duke in this country was very badly bungled", but added that that was in the days of the axe.
Monmouth was buried in the Church of St Peter ad Vincula
The Chapel Royal of St Peter ad Vincula ("St Peter in chains") is the former parish church of the Tower of London. It is situated within the Tower's Inner Ward, and the current building dates from 1520, although the church was established seve ...
in the Tower of London. His Dukedom was forfeited, but his subsidiary titles, Earl of Doncaster
Earl () is a rank of the nobility in the United Kingdom. The title originates in the Old English word ''eorl'', meaning "a man of noble birth or rank". The word is cognate with the Scandinavian form ''jarl'', and meant "chieftain", particular ...
and Baron Scott of Tindale
Duke of Buccleuch (pronounced ), formerly also spelt Duke of Buccleugh, is a title in the Peerage of Scotland created twice on 20 April 1663, first for James Scott, 1st Duke of Monmouth and second suo jure for his wife Anne Scott, 4th Count ...
, were restored by King George II on 23 March 1743 to his grandson Francis Scott, 2nd Duke of Buccleuch (1695–1751).
Popular legends
According to legend, a portrait was painted of Monmouth after his execution: the tradition states that it was realised after the execution that there was no officialportrait
A portrait is a painting, photograph, sculpture, or other artistic representation of a person, in which the face and its expressions are predominant. The intent is to display the likeness, personality, and even the mood of the person. For this ...
of the Duke, so his body was exhumed, the head stitched back on, and it was sat for its portrait to be painted. However, there are at least two formal portraits of Monmouth tentatively dated to before his death currently in the National Portrait Gallery in London, and another painting once identified with Monmouth that shows a sleeping or dead man that could have given rise to the story.
One of the many theories about the identity of The Man in the Iron Mask is that he was Monmouth: the theory is that someone else was executed in his place, and James II arranged for Monmouth to be taken to France and put in the custody of his cousin Louis XIV of France
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of ...
.
Henry Purcell set to music ( Z. 481) a satirical poem by an unidentified author, ridiculing Monmouth and his parentage:
A grasshopper and a fly,In summer hot and dry,
In eager argument were met
About priority.
Says the fly to the grasshopper:
"From mighty race I spring,
Bright Phoebus was my dad 'tis known,
And I eat and drink with a king."
Says the grasshopper to the fly:
"Such rogues are still preferr'd;
Your father might be of high degree,
But your mother was but a turd."
So, rebel Jemmy Scott,
That did to the empire soar,
His father might be the Lord knows what,
But his mother we knew a whore".
Children

 His marriage to Anne Scott, 1st Duchess of Buccleuch resulted in the birth of six children:
* Charles Scott, Earl of Doncaster (24 August 1672 – 9 February 1673/1674)
*
His marriage to Anne Scott, 1st Duchess of Buccleuch resulted in the birth of six children:
* Charles Scott, Earl of Doncaster (24 August 1672 – 9 February 1673/1674)
* James Scott, Earl of Dalkeith
Sir James Scott, Earl of Dalkeith KT (23 May 1674 – 14 March 1705) was a Scottish nobleman and politician. He was the son of James Scott, 1st Duke of Monmouth, and Anne Scott, 1st Duchess of Buccleuch. He was also the grandson of Charles II of ...
(23 May 1674 – 14 March 1705). He was married on 2 January 1693/1694 to Henrietta Hyde, daughter of Laurence Hyde, 1st Earl of Rochester. They were parents to Francis Scott, 2nd Duke of Buccleuch.
* Lady Anne Scott (17 February 1675 – 13 August 1685)
* Henry Scott, 1st Earl of Deloraine (1676 – 25 December 1730)
* Francis Scott (died an infant; buried 8 December 1679)
* Lady Charlotte Scott (died an infant; buried 5 September 1683)
His affair with his mistress
Mistress is the feminine form of the English word "master" (''master'' + ''-ess'') and may refer to:
Romance and relationships
* Mistress (lover), a term for a woman who is in a sexual and romantic relationship with a man who is married to a d ...
Eleanor Needham, daughter of Sir Robert Needham of Lambeth
Lambeth () is a district in South London, England, in the London Borough of Lambeth, historically in the County of Surrey. It is situated south of Charing Cross. The population of the London Borough of Lambeth was 303,086 in 2011. The area e ...
resulted in the birth of three children:
* James Crofts (died March 1732), major-general in the Army.
* Henrietta Crofts ( – 27 February 1730). She was married around 1697 to Charles Paulet, 2nd Duke of Bolton.
* Isabel Crofts (died young)
Toward the end of his life he conducted an affair with Henrietta, Baroness Wentworth.
Family tree
References
Sources
* * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * , - , - , - , - , - {{DEFAULTSORT:Monmouth, James Scott, 1st Duke Of 1649 births 1685 deaths 17th-century English nobility 17th-century Scottish peers British Life Guards officers Chancellors of the University of Cambridge 101 English generals English Protestants Executed English people Executed royalty J James Illegitimate children of Charles II of England Knights of the Garter Lord-Lieutenants of Staffordshire Lord-Lieutenants of the East Riding of Yorkshire Lords of the Admiralty Members of the Privy Council of England Military personnel from Rotterdam People executed under the Stuarts for treason against England Dukes in the Peerage of England English politicians convicted of crimes People executed by Stuart England by decapitation Executed Dutch people People convicted under a bill of attainder Executions at the Tower of London Pretenders to the English throne Pretenders to the Scottish throne Prisoners in the Tower of London Man in the Iron Mask Monmouth Rebellion Peers of England created by Charles II Peers of Scotland created by Charles II Sons of kings