Itter Castle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
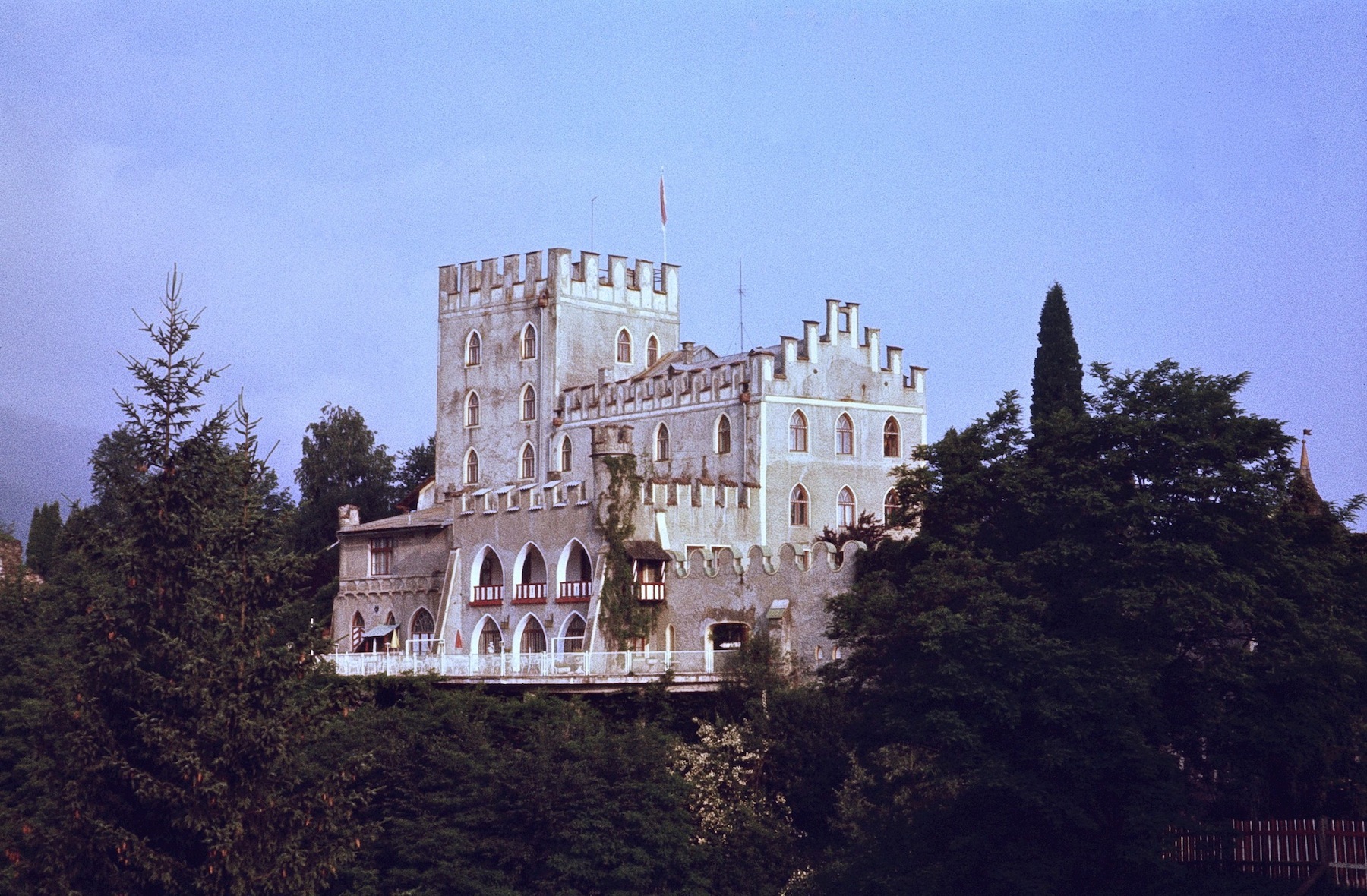
Itter Castle (german: Schloss Itter) is a 19th-century castle in Itter, a village in
 A fortress at the site was first mentioned in a 1241 deed; previous constructions may have existed since the 10th century. The Brixental originally was a possession of the Prince-Bishops of Regensburg; the castle was an administrative seat of the
A fortress at the site was first mentioned in a 1241 deed; previous constructions may have existed since the 10th century. The Brixental originally was a possession of the Prince-Bishops of Regensburg; the castle was an administrative seat of the
 After the 1938 ''
After the 1938 ''
Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
. In 1943, during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, it was turned into a Nazi prison for French VIPs. The castle was the site of an extraordinary instance of the U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cl ...
, German Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
, Austrian Resistance, and the prisoners themselves fighting side-by-side against the ''Waffen-SS
The (, "Armed SS") was the combat branch of the Nazi Party's ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with Waffen-SS foreign volunteers and conscripts, volunteers and conscripts from both occup ...
'' in the battle for Castle Itter in early May 1945 before the end of the war in Europe.
Location
Thehill castle
A hill castle or mountain castle is a castle built on a natural feature that stands above the surrounding terrain. It is a term derived from the German ''Höhenburg'' used in categorising castle sites by their topographical location. Hill castles a ...
is atop a knoll at the entrance to the Brixental
The Brixental ("Brixen Valley") is a southeastern side valley of the Tyrolean Lower Inn Valley in Austria with a length of about 30 km (18.6 mi). Near Wörgl (513 m AMSL; 318 mi) the Brixental and Inn valleys meet. The Brixen ...
valley, about south of Wörgl
Wörgl () is a city in the Austrian state of Tyrol, in the Kufstein district. It is from the international border with Bavaria, Germany.
Population
Transport
Wörgl is an important railway junction between the line from Innsbruck to Munich, an ...
and west of Kitzbühel.
History
 A fortress at the site was first mentioned in a 1241 deed; previous constructions may have existed since the 10th century. The Brixental originally was a possession of the Prince-Bishops of Regensburg; the castle was an administrative seat of the
A fortress at the site was first mentioned in a 1241 deed; previous constructions may have existed since the 10th century. The Brixental originally was a possession of the Prince-Bishops of Regensburg; the castle was an administrative seat of the Counts of Ortenburg
The Counts of Ortenburg (german: Grafen von Ortenburg) were a comital family in the mediaeval Duchy of Carinthia. Though they had roots in Bavarian nobility, an affiliation with the Imperial Counts of Ortenburg, a branch line of the Rhenish Fra ...
in their capacity as '' Vogt'' bailiffs, and it also served to protect the Regensburg estates from incursions undertaken by the neighbouring Archbishops of Salzburg. Nevertheless, the Brixental was acquired by Salzburg in 1312, and in 1380 the Regensburg bishops finally sold Itter to Archbishop Pilgrim II of Salzburg.
Within the '' Burgfrieden'' jurisdiction of Itter, feuds and breach of the public peace were banned, nevertheless the castle was devastated during the German Peasants' War in 1526. In the 17th century, the seat of the local administration was moved to Hopfgarten, whereafter the premises decayed. The Brixental belonged to Salzburg until it fell to the newly established Kingdom of Bavaria
The Kingdom of Bavaria (german: Königreich Bayern; ; spelled ''Baiern'' until 1825) was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1805 and continued to exist until 1918. With the unification of Germany into the German ...
in 1805; the Bavarian government left the castle ruin to the Itter citizens who used it as a quarry. Upon the Final Act of the Vienna Congress, the valley became part of the Austrian, crown land of Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
in 1816.
The present-day building was erected on the foundations of the former one from 1878 onwards. Itter Castle was purchased as a residence in 1884 by Sophie Menter, pianist, composer, and student of Franz Liszt. Liszt himself as well as young Arthur Rubinstein stayed at the castle; Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky
Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky , group=n ( ; 7 May 1840 – 6 November 1893) was a Russian composer of the Romantic period. He was the first Russian composer whose music would make a lasting impression internationally. He wrote some of the most pop ...
orchestrated one of his compositions during a visit in 1892. Menter sold Itter Castle in 1902; it was again extensively remodeled in its present Tudor Revival
Tudor Revival architecture (also known as mock Tudor in the UK) first manifested itself in domestic architecture in the United Kingdom in the latter half of the 19th century. Based on revival of aspects that were perceived as Tudor architecture ...
style by later owners.
World War II
 After the 1938 ''
After the 1938 ''Anschluss
The (, or , ), also known as the (, en, Annexation of Austria), was the annexation of the Federal State of Austria into the German Reich on 13 March 1938.
The idea of an (a united Austria and Germany that would form a " Greater Germany ...
'' annexation of Austria by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
, the ''Reich
''Reich'' (; ) is a German noun whose meaning is analogous to the meaning of the English word "realm"; this is not to be confused with the German adjective "reich" which means "rich". The terms ' (literally the "realm of an emperor") and ' (lit ...
'' government officially leased the castle in late 1940 from its owner, Franz Grüner. Itter Castle was seized from Grüner by SS Lieutenant General Oswald Pohl under the orders of Heinrich Himmler
Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was of the (Protection Squadron; SS), and a leading member of the Nazi Party of Germany. Himmler was one of the most powerful men in Nazi Germany and a main architect of th ...
on February 7, 1943, and transformed into a prison by April 25, 1943. Established to incarcerate prominent French prisoners valuable to Nazi Germany, the facility was placed as a subcamp
Subcamps (german: KZ-Außenlager), also translated as satellite camps, were outlying detention centres (''Haftstätten'') that came under the command of a main concentration camp run by the SS in Nazi Germany and German-occupied Europe. The Nazi ...
under the administration of the Dachau concentration camp.
Notable prisoners included: former Prime Ministers Édouard Daladier and Paul Reynaud
Paul Reynaud (; 15 October 1878 – 21 September 1966) was a French politician and lawyer prominent in the interwar period, noted for his stances on economic liberalism and militant opposition to Germany.
Reynaud opposed the Munich Agreement of ...
; Generals Maurice Gamelin and former commander-in-chief Maxime Weygand
Maxime Weygand (; 21 January 1867 – 28 January 1965) was a French military commander in World War I and World War II.
Born in Belgium, Weygand was raised in France and educated at the Saint-Cyr military academy in Paris. After graduating in 1 ...
, who had been prominent during the Phoney War
The Phoney War (french: Drôle de guerre; german: Sitzkrieg) was an eight-month period at the start of World War II, during which there was only one limited military land operation on the Western Front, when French troops invaded Germa ...
; former tennis champion Jean Borotra
Jean Laurent Robert Borotra (, ; 13 August 1898 – 17 July 1994) was a French tennis champion. He was one of the " Four Musketeers" from his country who dominated tennis in the late 1920s and early 1930s. Borotra was imprisoned in Itter Castle ...
, later General Commissioner of Sports in the Vichy regime; right-wing leader François de La Rocque
François de La Rocque (; 6 October 1885 – 28 April 1946) was the leader of the French right-wing league the Croix de Feu from 1930 to 1936 before he formed the more moderate nationalist French Social Party (1936–1940), which has been ...
, leader of the right-wing Croix de Feu movement; trade union leader Léon Jouhaux
Léon Jouhaux (1 July 1879 – 28 April 1954) was a French trade union leader who received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1951.
Biography
Jouhaux was born in Pantin, Seine-Saint-Denis, France. Jouhaux's father worked in a match factory in Aubervillie ...
; André François-Poncet
André François-Poncet (13 June 1887 – 8 January 1978) was a French politician and diplomat whose post as ambassador to Germany allowed him to witness first-hand the rise to power of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party, and the Nazi regime's pre ...
, a politician and diplomat; and Michel Clemenceau, politician and son of Georges Clemenceau
Georges Benjamin Clemenceau (, also , ; 28 September 1841 – 24 November 1929) was a French statesman who served as Prime Minister of France from 1906 to 1909 and again from 1917 until 1920. A key figure of the Independent Radicals, he was a ...
. The former republic president Albert Lebrun
Albert François Lebrun (; 29 August 1871 – 6 March 1950) was a French politician, President of France from 1932 to 1940. He was the last president of the Third Republic. He was a member of the centre-right Democratic Republican Alliance (A ...
was held at Itter for three months in 1943, before being sent back to France for health reasons; Marie-Agnès de Gaulle, Resistance member and sister of General Charles de Gaulle, was interned in the castle at the very end of the war, in April 1945.
Besides the French VIP prisoners, the Castle held a number of Eastern European prisoners detached from Dachau, who were used for maintenance and other menial work.
Battle for Castle Itter
On the afternoon of May 4, 1945, the prison's commander fled. Shortly after the '' SS-Totenkopfverbände'' guards followed, the prisoners armed themselves and awaited an anticipated attack from ''Waffen SS
The (, "Armed SS") was the combat branch of the Nazi Party's ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with volunteers and conscripts from both occupied and unoccupied lands.
The grew from th ...
'' troops still aggressively resisting surrender. Two Sherman tanks of the 23rd Tank Battalion of the U.S. 12th Armored Division under the command of Capt. John C. ‘Jack’ Lee Jr., and anti-Nazi elements of the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
under the command of Major Josef ‘Sepp’ Gangl, arrived. Together the three groups repelled probes by SS reconnaissance elements throughout the night. The battle continued through the morning of 5 May, with a strong force of 100–150 SS pressing the attack until reinforcements from the American 142nd Infantry Regiment arrived around 4 PM that day.
Castle Itter today
After the war, the castle fell into disrepair until 1950 when Willi Woldrich acquired it and turned it into a luxury hotel. However, the hotel encountered financial problems and it was acquired by a holding company before it was sold to a private owner in 1985. Since that time, it has remained in private ownership and is not open to the public. It is owned by attorney Dr. Ernst Bosin from the city ofKufstein
Kufstein (; Central Bavarian: ''Kufstoa'') is a town in the Austrian state of Tyrol, the administrative seat of Kufstein District. With a population of about 19,600 it is the second largest Tyrolean town after the state capital Innsbruck. The grea ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
.
References
Further reading
*External links
{{Authority control Castles in Tyrol (state) World War II prisoner of war camps in Germany