Italian Brazilians (, ) are
Brazilians
Brazilians (, ) are the citizens of Brazil. A Brazilian can also be a person born abroad to a Brazilian parent or legal guardian as well as a person who acquired Brazilian nationality law, Brazilian citizenship. Brazil is a multiethnic society, ...
of full or partial
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
descent, whose ancestors were
Italians
Italians (, ) are a European peoples, European ethnic group native to the Italian geographical region. Italians share a common Italian culture, culture, History of Italy, history, Cultural heritage, ancestry and Italian language, language. ...
who emigrated to
Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
during the
Italian diaspora
The Italian diaspora (, ) is the large-scale emigration of Italians from Italy.
There were two major Italian diasporas in Italian history. The first diaspora began around 1880, two decades after the Risorgimento, Unification of Italy, and ended ...
, or more recent Italian-born people who've settled in Brazil. Italian Brazilians are the largest number of people with full or partial Italian ancestry outside
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, with
São Paulo
São Paulo (; ; Portuguese for 'Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul') is the capital of the São Paulo (state), state of São Paulo, as well as the List of cities in Brazil by population, most populous city in Brazil, the List of largest cities in the ...
being the most populous city with Italian ancestry in the world. Nowadays, it is possible to find millions of descendants of Italians, from the
southeastern state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
of
Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is one of the 27 federative units of Brazil, being the fourth largest state by area and the second largest in number of inhabitants with a population of 20,539,989 according to the 2022 Brazilian census, 2022 census. Located in ...
to the
southernmost state of
Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul (, ; ; "Great River of the South") is a Federative units of Brazil, state in the South Region, Brazil, southern region of Brazil. It is the Federative units of Brazil#List, fifth-most populous state and the List of Brazilian s ...
, with the majority living in
São Paulo state
SAO or Sao may refer to:
Places
* Sao civilisation, in Middle Africa from 6th century BC to 16th century AD
* Sao, a town in Boussé Department, Burkina Faso
* Serb Autonomous Regions (''Srpska autonomna oblast'', SAO), during the breakup of ...
. Small southern Brazilian towns, such as
Nova Veneza, have as much as 95% of their population of Italian descent.
There are no official numbers of how many
Brazilians
Brazilians (, ) are the citizens of Brazil. A Brazilian can also be a person born abroad to a Brazilian parent or legal guardian as well as a person who acquired Brazilian nationality law, Brazilian citizenship. Brazil is a multiethnic society, ...
have Italian ancestry, as the national census conducted by
IBGE
The Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (; IBGE) is the agency responsible for official collection of statistical, geographic, cartographic, geodetic and environmental information in Brazil. IBGE performs a decennial national cen ...
does not ask the ancestry of the Brazilian people. In 1940, the last census to ask ancestry, 1,260,931 Brazilians were said to be the child of an Italian father, and 1,069,862 said to be the child of an Italian mother. Italians were 285,000 and naturalized Brazilians 40,000. Therefore, Italians and their children were, at most, just over 3.8% of Brazil's population in 1940.
[IBG]
Censo brasileiro de 1940
The
Embassy
A diplomatic mission or foreign mission is a group of people from a Sovereign state, state or organization present in another state to represent the sending state or organization officially in the receiving or host state. In practice, the phrase ...
of
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
in Brazil, in 2013, reported the number of 32 million descendants of Italian immigrants in Brazil (about 15% of the population),
half of them in the state of
São Paulo
São Paulo (; ; Portuguese for 'Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul') is the capital of the São Paulo (state), state of São Paulo, as well as the List of cities in Brazil by population, most populous city in Brazil, the List of largest cities in the ...
,
while there were around 450,000 Italian citizens in Brazil.
Brazilian culture has significant connections to Italian culture in terms of language, customs, and traditions. Brazil is also a strongly
Italophilic country as cuisine, fashion and lifestyle has been sharply influenced by
Italian immigration.
Italian immigration to Brazil
According to the Italian government, there are 31 million Brazilians of
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
descent. All figures relate to Brazilians of any Italian descent, not necessarily linked to Italian culture in any significant way. According to García,
[Immigrazione Italiana nell’America del Sud (Argentina, Uruguay e Brasile)](_blank)
p. 36. the number of Brazilians with actual links to Italian identity and culture would be around 3.5 to 4.5 million people. Scholar Luigi Favero, in a book on Italian emigration between 1876 and 1976, pinpointed that Italians were present in Brasil since the
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
:
Genoese sailors and merchants were between the first to settle in colonial Brazil since the first half of the 16th century, and so, because of the many descendants of Italians who emigrated there from
Columbus' times until 1860, the number of Brazilians with Italian roots should be increased to 35 million.
Although they were victims of some prejudice in the first decades and in spite of the persecution during World War II, Brazilians of Italian descent managed to integrate and assimilate seamlessly into the Brazilian society.
Many Brazilian politicians, artists, footballers, models, and personalities are or were of Italian descent. Italian-Brazilians have been state governors, representatives, mayors and ambassadors. Four
Presidents of Brazil were of Italian descent (but none of the first three directly elected to such a position):
Pascoal Ranieri Mazzilli
Pascoal Ranieri Mazzilli (; 27 April 1910 – 21 April 1975) was a Brazilian politician who served as Federal Deputy from 1951 to 1967 and President of the Chamber of Deputies (speaker of the house) from 1958 to 1965. During his term as speaker ...
(Senate president who served as interim president),
Itamar Franco
Itamar Augusto Cautiero Franco (; 28 June 19302 July 2011) was a Brazilian politician who served as the 33rd president of Brazil from 29 December 1992 to 1 January 1995. Previously, he was the 21st vice president of Brazil from 1990 until the ...
(elected vice-president under Fernando Collor, whom he eventually replaced as the latter was impeached),
Emílio Garrastazu Médici
Emílio Garrastazu Médici (; 4 December 1905 – 9 October 1985) was a Brazilian military leader and politician who was the 28th president of Brazil from 1969 to 1974. His authoritarian rule marked the apex of the Brazilian military regime.
...
(third of the series of generals who presided over Brazil during the military regime, also of Basque descent) and
Jair Messias Bolsonaro (elected in 2018).
Citizenship

According to the Brazilian Constitution,
anyone born in the country is a Brazilian citizen by birthright. In addition, many born in Italy have become
naturalized
Naturalization (or naturalisation) is the legal act or process by which a non-national of a country acquires the nationality of that country after birth. The definition of naturalization by the International Organization for Migration of the ...
citizens after they settled in Brazil. The Brazilian government used to prohibit
multiple citizenship
Multiple citizenship (or multiple nationality) is a person's legal status in which a person is at the same time recognized by more than one sovereign state, country under its nationality law, nationality and citizenship law as a national or cit ...
. However, that changed in 1994 by a new constitutional amendment. After the changes, over half a million Italian-Brazilians have requested recognition of their Italian citizenship.
According to Italian legislation,
an individual with an Italian parent is automatically recognized as an
Italian citizen. To exercise the rights and obligations of citizenship, individual must have all documents registered in Italy, which normally involves the local consulate or embassy. Some limitations are applied to the process of recognition such as the renouncement of the Italian citizenship by the individual or the parent (if before the child's birth), a second limitation is that women transferred citizenship to their children only after 1948. After a constitutional reform in Italy, Italian citizens abroad may elect representatives to the
Italian Chamber of Deputies
The Chamber of Deputies () is the lower house of the bicameral Italian Parliament, the upper house being the Senate of the Republic (Italy), Senate of the Republic. The two houses together form a perfect bicameral system, meaning they perform ...
and the
Italian Senate
The Senate of the Republic (), or simply the Senate ( ), is the upper house of the bicameral Italian Parliament, the lower house being the Chamber of Deputies. The two houses together form a perfect bicameral system, meaning they perform iden ...
. Italian citizens residing in Brazil elect representatives together with
Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
,
Uruguay
Uruguay, officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast, while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the A ...
and other countries in South America. According to Italian Senator Edoardo Pollastri, over half-a-million Brazilians are waiting to have their Italian citizenship recognized.
History
Italian crisis in late 19th century

Italy did not become a unified national state until 1861. Before then, Italy was politically divided into several kingdoms, duchies, and other small states. The legacy of political fragmentation influenced deeply the character of the Italian migrant: "Before 1914, the typical Italian migrant was a man without a clear national identity but with strong attachments to his town or village or region of birth, to which half of all migrants returned."
In the 19th century, many Italians fled the political persecutions in Italy led by the
Imperial Austrian government after the failure of Italian unification movements in 1848 and 1861. Although very small in numbers, the well-educated and revolutionary group of emigrants left a deep mark where they settled. In Brazil, the most famous Italian was then
Líbero Badaró (died 1830). However, the mass Italian immigration tide that would only be second to the Portuguese and German migrant movements in shaping modern Brazilian culture started only after the 1848-1871
Risorgimento
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the annexation of various states of the Italian peninsula and its outlying isles to the Kingdom of ...
.
During the last quarter of the 19th century, the newly united Italy suffered an economic crisis. The more industrial northern half of Italy was plagued with high unemployment caused in part by the introduction of modern agricultural techniques, while southern Italy remained underdeveloped and almost untouched by agrarian modernization programs. Even in the North, industrialization was still in its initial stages and illiteracy remained common.
[IBGE. Brasil 500 anos - Italianos - Regiões de Origem](_blank)
. Retrieved 10 September 2008. Thus, poverty and lack of jobs and income stimulated Northern (and Southern) Italians to emigrate. Most Italian immigrants were very poor rural workers ().
Brazilian need of immigrants


In 1850, under British pressure, Brazil finally passed a law that effectively banned transatlantic slave trade. The increased pressure of the abolitionist movement, on the other hand, made it clear that the days of slavery in Brazil were coming to an end. Slave trade was effectively suppressed, but the slave system still endured for almost four decades. Thus, Brazilian landowners claimed that such migrants were or would soon become indispensable for Brazilian agriculture. They would soon win the argument, and mass migration would begin in earnest.
An Agriculture Congress in 1878 in
Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro, or simply Rio, is the capital of the Rio de Janeiro (state), state of Rio de Janeiro. It is the List of cities in Brazil by population, second-most-populous city in Brazil (after São Paulo) and the Largest cities in the America ...
discussed the lack of labor and proposed to the government the stimulation of European immigration to Brazil. Immigrants from Italy, Portugal, and Spain were considered the best ones because they were Latin-based and mainly Catholic. In particular, Italian immigrants settled mainly in the São Paulo region, where there were vast coffee plantations.
At the end of the 19th century, the Brazilian government was influenced by
eugenics
Eugenics is a set of largely discredited beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of a human population. Historically, eugenicists have attempted to alter the frequency of various human phenotypes by inhibiting the fer ...
theories.
Beginning of Italian settlement in Brazil

The Brazilian government, with or following the Emperor's support, had created the first colonies of immigrants (''colônias de imigrantes'') in the early 19th century. The colonies were established in
rural
In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry are typically desc ...
areas of the country, being settled by European families.
The first groups of Italians arrived in 1875, but the boom of Italian immigration in Brazil happened between 1880 and 1900, when almost one million Italians arrived.
Many Italians were naturalized Brazilian at the end of the 19th century, when the 'Great Naturalization' automatically granted citizenship to all the immigrants residing in Brazil prior to 15 November 1889 "unless they declared a desire to keep their original nationality within six months."
During the end of the 19th century, denouncement of bad conditions in Brazil increased in the press. Reacting to the public clamor and many proved cases of mistreatment of Italian
immigrant
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as permanent residents. Commuters, tourists, and other short- ...
s, the government of
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
issued in 1902 the
Prinetti Decree
The Prinetti Decree was a ministerial normative act approved by the General Commissariat of Emigration in Italy on March 26, 1902, which prohibited sponsored emigration to Brazil. The ordinance was named after the then Italian foreign affairs min ...
forbidding subsidized immigration to Brazil. In consequence, the number of Italian immigrants in Brazil fell drastically in the beginning of the 20th century, but the wave of Italian immigration continued until 1920.
Over half of the Italian immigrants came from northern Italian regions of
Veneto
Veneto, officially the Region of Veneto, is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the Northeast Italy, north-east of the country. It is the fourth most populous region in Italy, with a population of 4,851,851 as of 2025. Venice is t ...
,
Lombardy
The Lombardy Region (; ) is an administrative regions of Italy, region of Italy that covers ; it is located in northern Italy and has a population of about 10 million people, constituting more than one-sixth of Italy's population. Lombardy is ...
and
Emilia-Romagna
Emilia-Romagna (, , both , ; or ; ) is an Regions of Italy, administrative region of northern Italy, comprising the historical regions of Emilia (region), Emilia and Romagna. Its capital is Bologna. It has an area of , and a population of 4.4 m ...
, and from the central Italian region of
Tuscany
Tuscany ( ; ) is a Regions of Italy, region in central Italy with an area of about and a population of 3,660,834 inhabitants as of 2025. The capital city is Florence.
Tuscany is known for its landscapes, history, artistic legacy, and its in ...
. About 30% emigrated from Veneto.
On the other hand, in the 20th century, southern Italians predominated in Brazil, coming from the regions of
Campania
Campania is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy located in Southern Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian Peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islan ...
,
Abruzzo
Abruzzo (, ; ; , ''Abbrìzze'' or ''Abbrèzze'' ; ), historically also known as Abruzzi, is a Regions of Italy, region of Southern Italy with an area of 10,763 square km (4,156 sq mi) and a population of 1.3 million. It is divided into four ...
,
Molise
Molise ( , ; ; , ) is a Regions of Italy, region in Southern Italy. Until 1963, it formed part of the region of Abruzzi e Molise together with Abruzzo. The split, which did not become effective until 1970, makes Molise the newest region in Ital ...
,
Basilicata
Basilicata (, ; ), also known by its ancient name Lucania (, , ), is an administrative region in Southern Italy, bordering on Campania to the west, Apulia to the north and east, and Calabria to the south. It has two coastlines: a 30-kilometr ...
and
Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
.
Prince Umberto's visit in 1924
In 1924, Umberto, Prince of Piedmont (the future King
Umberto II of Italy
Umberto II (; 15 September 190418 March 1983) was the last King of Italy. Umberto's reign lasted for 34 days, from 9 May 1946 until his formal deposition on 12 June 1946, although he had been the ''de facto'' head of state since 1944. Due to hi ...
) came to Brazil as part of a state visit to various South American countries. That was part of the political plan of the new fascist government to link Italian people living outside of Italy with their mother country and the interests of the regime. The visit was disrupted considerably by the ongoing
Tenente revolts
Tenentism () was a political philosophy of junior army officers (, , "lieutenants") who significantly contributed to the Brazilian Revolution of 1930 that ended the First Brazilian Republic.
Background
The first decades of the 20th century saw ...
, which made it impossible for Umberto to reach
Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro, or simply Rio, is the capital of the Rio de Janeiro (state), state of Rio de Janeiro. It is the List of cities in Brazil by population, second-most-populous city in Brazil (after São Paulo) and the Largest cities in the America ...
and
São Paulo
São Paulo (; ; Portuguese for 'Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul') is the capital of the São Paulo (state), state of São Paulo, as well as the List of cities in Brazil by population, most populous city in Brazil, the List of largest cities in the ...
. Nevertheless, he was hosted at
Bahia
Bahia () is one of the 26 Federative units of Brazil, states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region, Brazil, Northeast Region of the country. It is the fourth-largest Brazilian state by population (after São Paulo (state), São Paulo, Mina ...
, where members of the Italian colony in the city were very happy and proud about his visit, thus achieving some of the visit's purposes.
Statistics
1940 Brazilian census
The Brazilian census of 1940 asked Brazilians where their fathers came from. It revealed that at that time there were 3,275,732 Brazilians who were born to an immigrant father. Of those, 1,260,931 Brazilians were born to an Italian father. Italian was the main reported paternal immigrant origin, followed by Portuguese with 735,929 children, Spanish with 340,479 and German with 159,809 children.
[IBG]
Brazilian Census of 1940
The census also revealed that the 458,281 foreign mothers of 12 or more years who lived in Brazil had 2,852,427 children, of whom 2,657,974 were born alive. Italian women had more children than any other female immigrant community in Brazil: 1,069,862 Brazilians were born to an Italian mother, followed by 524,940 who were born to a Portuguese mother, 436,305 to a Spanish mother and 171,790 to a Japanese mother.
The 6,809,772 Brazilian-born mothers of 12 or more years had 38,716,508 children, of whom 35,777,402 were born alive.
Others
On the other hand, in 1998, the IBGE, within its preparation for the 2000 Census, experimentally introduced a question about "origem" (ancestry) in its "Pesquisa Mensal de Emprego" (Monthly Employment Survey) to test the viability of introducing that variable in the census
(the IBGE ended by deciding against the inclusion of questions about it in the Census). The research interviewed about 90,000 people in six metropolitan regions (São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Porto Alegre, Belo Horizonte, Salvador, and Recife).
.* Commissariato Generale dell'Emigrazione
.** Consulates
The 1920 census was the first one to show a more specific figure about the size of the Italian population in Brazil (558,405). However, since the 20th century, the arrival of new Italian immigrants to Brazil has been in steady decline. The previous censuses of 1890 and 1900 had limited information. In consequence, there are no official figures about the size of the Italian population in Brazil during the mass immigration period (1880–1900). There are estimates available, and the most reliable was done by Giorgio Mortara even though his figures may have underestimated the real size of the Italian population.
[Angelo Trento. ] On the other hand, Angelo Trento believes that the Italian estimates are "certainly exaggerated"
and "lacking of any foundation"
since they found a figure of 1,837,887 Italians in Brazil for 1927. Another evaluation conducted by Bruno Zuculin found 997,887 Italians in Brazil in 1927. All of those figures include only people born in Italy, not their Brazilian-born descendants.
Main Italian settlements in Brazil
Areas of settlement
Among all Italians who immigrated to Brazil, 70% went to the
State of São Paulo
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
. In consequence, São Paulo has more people with Italian ancestry than any region of Italy itself.
The rest went mostly to the states of Rio Grande do Sul and
Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is one of the 27 federative units of Brazil, being the fourth largest state by area and the second largest in number of inhabitants with a population of 20,539,989 according to the 2022 Brazilian census, 2022 census. Located in ...
.

Internal migration made many second- and third-generation Italians move to other areas. In the early 20th century, many rural Italian workers from Rio Grande do Sul migrated to the west of
Santa Catarina and then farther north to Paraná.
More recently, third- and fourth-generation Italians have migrated to other areas and so people of Italian descent can be found in Brazilian regions in which the immigrants had never settled, such as in the
Cerrado
The Cerrado () is a vast ecoregion of Tropics, tropical savanna in central Brazil, being present in the states of Goiás, Mato Grosso do Sul, Mato Grosso, Tocantins, Maranhão, Piauí, Bahia, Minas Gerais, São Paulo (state), São Paulo, Paraná ...
region of
Central-West, in the
Northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A '' compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—eac ...
and in the
Amazon rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, also called the Amazon jungle or Amazonia, is a Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, moist broadleaf tropical rainforest in the Amazon biome that covers most of the Amazon basin of South America. This basin ...
area, in the extreme North of Brazil.
[COLLI, Antonello. Italiani in Brasile, 36 milioni di oriundi. L'Italia nel'Mondo Website](_blank)
. Retrieved 10 September 2008.
Southern Brazil

The main areas of Italian settlement in Brazil were the Southern and
Southeastern Regions, namely the states of
São Paulo
São Paulo (; ; Portuguese for 'Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul') is the capital of the São Paulo (state), state of São Paulo, as well as the List of cities in Brazil by population, most populous city in Brazil, the List of largest cities in the ...
,
Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul (, ; ; "Great River of the South") is a Federative units of Brazil, state in the South Region, Brazil, southern region of Brazil. It is the Federative units of Brazil#List, fifth-most populous state and the List of Brazilian s ...
,
Santa Catarina,
Paraná,
Espírito Santo
Espírito Santo (; ) is a state in southeastern Brazil. Its capital is Vitória, and its largest city is Serra. With an extensive coastline, the state hosts some of the country's main ports, and its beaches are significant tourist attracti ...
and
Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is one of the 27 federative units of Brazil, being the fourth largest state by area and the second largest in number of inhabitants with a population of 20,539,989 according to the 2022 Brazilian census, 2022 census. Located in ...
.
The first colonies to be populated by Italians were created in the highlands of Rio Grande do Sul (
Serra Gaúcha). They were
Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as (). In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as () or (). 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, revolutionary and republican. H ...
and
Bento Gonçalves. The immigrants were predominantly from Veneto, in northern Italy. After five years, in 1880, the great numbers of Italian immigrants arriving caused the Brazilian government to create another Italian colony,
Caxias do Sul
Caxias do Sul () is a city in Rio Grande do Sul, Southern Brazil, situated in the state's mountainous Serra Gaúcha region. It was established by Italian Brazilian, Italian immigrants on June 20, 1890. Today it is the second Largest cities in R ...
. After initially settling in the government-promoted colonies, many Italian immigrants spread into other areas of Rio Grande do Sul, seeking better opportunities, and created many other Italian colonies on their own, mainly in highlands, because the lowlands were already populated by German immigrants and native ''gaúchos''.
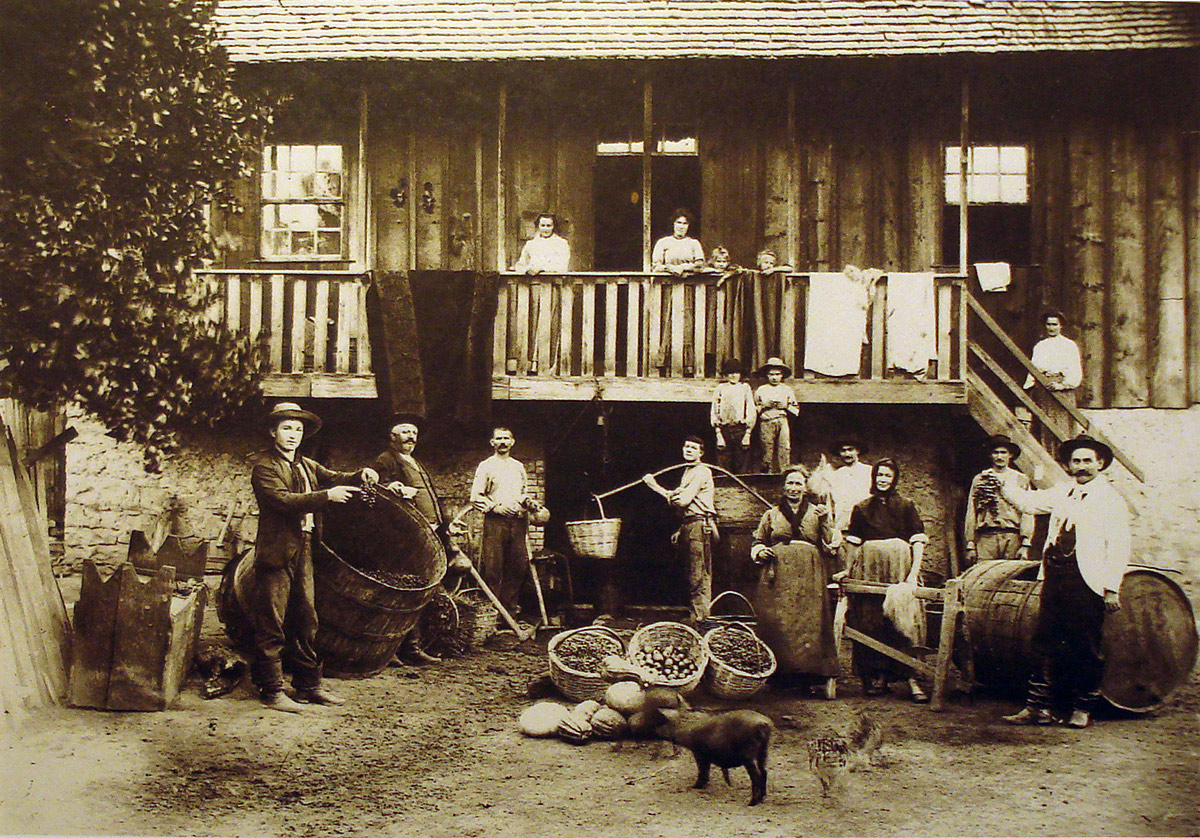
Italians established many vineyards in the region. The wine produced in those areas of Italian colonization in southern Brazil is much appreciated within the country, but little is available for export. In 1875, the first Italian colonies were established in
Santa Catarina, which lies immediately to the north of Rio Grande do Sul. The colonies gave rise to towns such as
Criciúma, and later also spread further north, to Paraná.
In the colonies of southern Brazil, Italian immigrants at first stuck to themselves, where they could speak their native
Italian dialects and keep their culture and traditions. With time, however, they would become thoroughly integrated economically and culturally into the larger society. In any case, Italian immigration to southern Brazil was very important to the economic development and the culture of the region.
Southeastern Brazil


Some of the immigrants settled in the colonies in Southern Brazil. However, most of them settled in Southeastern Brazil (mainly in the
State of São Paulo
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
). At first, the government was responsible for bringing the immigrants (in most cases, paying for their transportation by ship), but later, the farmers were responsible for making contracts with immigrants or specialized companies in recruiting Italian workers. Many posters were spread in Italy, with pictures of Brazil, selling the idea that everybody could become rich there by working with coffee, which was called by the Italian immigrants the ''green gold''. Most coffee plantations were in the States of
São Paulo
São Paulo (; ; Portuguese for 'Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul') is the capital of the São Paulo (state), state of São Paulo, as well as the List of cities in Brazil by population, most populous city in Brazil, the List of largest cities in the ...
and
Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is one of the 27 federative units of Brazil, being the fourth largest state by area and the second largest in number of inhabitants with a population of 20,539,989 according to the 2022 Brazilian census, 2022 census. Located in ...
, and in a smaller proportion also in the States of
Espírito Santo
Espírito Santo (; ) is a state in southeastern Brazil. Its capital is Vitória, and its largest city is Serra. With an extensive coastline, the state hosts some of the country's main ports, and its beaches are significant tourist attracti ...
and
Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro, or simply Rio, is the capital of the Rio de Janeiro (state), state of Rio de Janeiro. It is the List of cities in Brazil by population, second-most-populous city in Brazil (after São Paulo) and the Largest cities in the America ...
.
Rio de Janeiro was declining in the 19th century as a farming producer, and São Paulo had already taken the lead as a coffee producer/exporter in the early 20th century, as well as big producer of sugar and other important crops. Thus, migrants were naturally more attracted to the State of São Paulo and the southern states.
Italians migrated to Brazil as
families
Family (from ) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as ...
. The ''colono'', as a rural immigrant was called, had to sign a contract with the farmer to work in the
coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially a ...
plantation for a minimum period of time. However, the situation was not easy. Many Brazilian farmers were used to command slaves and treated the immigrants as
indentured servant
Indentured servitude is a form of Work (human activity), labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract called an "indenture", may be entered voluntarily for a prepaid lump sum, as paymen ...
s.
In Southern Brazil, the Italian immigrants were living in relatively well-developed colonies, but in Southeastern Brazil they were living in semislavery conditions in the coffee
plantation
Plantations are farms specializing in cash crops, usually mainly planting a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Plantations, centered on a plantation house, grow crops including cotton, cannabis, tob ...
s. Many rebellions against Brazilian farmers occurred, and public denouncements caused great commotion in Italy, forcing the
Italian government
The government of Italy is that of a democratic republic, established by the Italian constitution in 1948. It consists of Legislature, legislative, Executive (government), executive, and Judiciary, judicial subdivisions, as well as of a head of ...
to issue the Prinetti Decree, which established barriers to
immigration to Brazil
Immigration to Brazil is the movement to Brazil of foreign peoples to reside permanently. It should not be confused with the forcible bringing of people from Africa as slaves. Latin Europe accounted for four-fifths of the arrivals (1.8 mill ...
.

In 1901, 90% of industrial workers and 80% of construction workers in São Paulo were Italians.
São Carlos
São Carlos (Saint Charles, in English, ; named after Charles Borromeo, Saint Charles Borromeo) is a Brazilian city and municipality in the Interior of São Paulo, interior of the state of São Paulo, 254 kilometers from the city of São Paulo. ...
and
Ribeirão Preto
Ribeirão Preto (Portuguese pronunciation: Help:IPA/Portuguese, �ibejˈɾɐ̃w ˈpɾetu is a city and a metropolitan area located in the northeastern region of São Paulo (state), São Paulo state, Brazil.
Ribeirão Preto is the eighth-la ...
were two of the main coffee plantation centers. Both were respectively in the North-Central and Northeastern regions of São Paulo state, a zone known by its hot temperature and a fertile soil in which some of the richest coffee farms were and attracted most immigrants arriving in
São Paulo
São Paulo (; ; Portuguese for 'Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul') is the capital of the São Paulo (state), state of São Paulo, as well as the List of cities in Brazil by population, most populous city in Brazil, the List of largest cities in the ...
, including Italians, between 1901 and 1940.
Other parts of Brazil
In the State of
Mato Grosso do Sul
Mato Grosso do Sul ( ) is one of Federative units of Brazil, Brazil's 27 federal units, located in the southern part of the Central-West Region, Brazil, Central-West Region, bordering five Brazilian states: Mato Grosso (to the north), Goiás and ...
, Italian descendants are 5% of the population.
Decline of Italian immigration

In 1902, the Italian immigration to Brazil started to decline. From 1903 to 1920, only 306,652 Italians immigrated to Brazil, compared to 953,453 to
Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
and 3,581,322 to the United States. This was mainly due to the
Prinetti Decree
The Prinetti Decree was a ministerial normative act approved by the General Commissariat of Emigration in Italy on March 26, 1902, which prohibited sponsored emigration to Brazil. The ordinance was named after the then Italian foreign affairs min ...
in Italy, banning subsidized immigration to Brazil. The Prinetti Decree was issued because of the commotion in the Italian press about the poverty faced by most Italians in Brazil.
The end of slavery made most former slaves left the plantations and so there was a labour shortage on coffee plantations. Moreover, "natural inequality of human beings", "hierarchy of races",
Social Darwinism
Charles Darwin, after whom social Darwinism is named
Social Darwinism is a body of pseudoscientific theories and societal practices that purport to apply biological concepts of natural selection and survival of the fittest to sociology, economi ...
,
Positivism
Positivism is a philosophical school that holds that all genuine knowledge is either true by definition or positivemeaning '' a posteriori'' facts derived by reason and logic from sensory experience.John J. Macionis, Linda M. Gerber, ''Soci ...
and other theories were used to explain that the European workers were superior to the native workers. In consequence, passages were offered to Europeans (the so-called "subsidized immigration"), mostly to Italians, so that they could come to Brazil and work on the plantations.
Those immigrants were employed in enormous
latifundia
A ''latifundium'' (Latin: ''latus'', "spacious", and ''fundus'', "farm", "estate") was originally the term used by ancient Romans for great landed estates specialising in agriculture destined for sale: grain, olive oil, or wine. They were charac ...
(large-scale farms), formerly employing slaves. In Brazil, there were no
labour laws (the first concrete labour laws appeared only in the 1930s, under President
Getúlio Vargas
Getúlio Dornelles Vargas (; ; 19 April 1882 – 24 August 1954) was a Brazilian lawyer and politician who served as the 14th and 17th president of Brazil, from 1930 to 1945 and from 1951 until his suicide in 1954. Due to his long and contr ...
) and so workers had almost no legal protection. Contracts signed by the immigrants could easily be violated by the Brazilian landowners who were accustomed to dealing with African slaves.
The remnants of slavery influenced how Brazilian landowners dealt with Italian workers: immigrants were often monitored, with extensive hours of work. In some cases, they were obliged to buy products that they needed from the landowner. Moreover, the coffee farms were located in rather isolated regions. If the immigrants became sick, they would take hours to reach the nearest hospital.
The structure of labor used on farms included the labor of Italian women and children. Keeping their Italian culture was also made more difficult: the Catholic churches and Italian cultural centers were far from farms. The immigrants who did not accept the standards imposed by landowners were replaced by other immigrants. That forced them to accept the impositions of landowners, or they would have to leave their lands. Even though Italians were considered to be "superior" to blacks by Brazilian landowners, the situation faced by Italians in Brazil was so similar to that of the slaves that farmers called them ''escravos brancos'' (white slaves in
Portuguese).
The destitution faced by Italians and other immigrants in Brazil caused great commotion in the Italian press, which culminated in the Prinetti Decree in 1902. Many immigrants left Brazil after their experience on São Paulo's coffee farms. Between 1882 and 1914, 1.5 million immigrants of different nationalities came to São Paulo, and 695,000 left the state, or 45% of the total. The high numbers of Italians asking the Italian consulate a passage to leave Brazil was so significant that in 1907, most Italian funds for
repatriation
Repatriation is the return of a thing or person to its or their country of origin, respectively. The term may refer to non-human entities, such as converting a foreign currency into the currency of one's own country, as well as the return of mi ...
were used in Brazil. It is estimated that, between 1890 and 1904, 223,031 (14,869 annually) Italians left Brazil, mainly after failed experiences on coffee farms. Most of the Italians who left the country were unable to add the money they wanted. Most returned to Italy, but others remigrated to Argentina,
Uruguay
Uruguay, officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast, while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the A ...
or to the United States.
The output of immigrants concerned Brazilian landowners, who constantly complained about the lack of workers.
Spanish immigrants began arriving in greater numbers, but soon, Spain also started to create barriers for further immigration of Spaniards to coffee farms in Brazil. The continuing problem of lack of labor in the farms was, then, temporarily resolved with the arrival of
Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
immigrants, from 1908.
Despite the high numbers of immigrants leaving the country, most Italians remained in Brazil. Most of the immigrants remained only one year working on coffee farms and then left the plantations. A few earned enough money to buy their own lands and became farmers themselves. However, most migrated to Brazilian cities. Many Italians worked in factories (in 1901, 81% of the São Paulo's
factory workers were Italians). In Rio de Janeiro, many the factory workers were Italians. In São Paulo, those workers established themselves in the center of the city, living in
cortiços (degraded multifamily row houses). The agglomerations of Italians in cities gave birth to typically Italian neighborhoods, such as
Mooca, which is until today linked to its Italian past. Other Italians became traders, mostly itinerant traders, selling their products in different regions.
A common presence on the streets of São Paulo were the Italian boys working as newspaper boys, as an Italian traveler observed: "In the crowd, we can see many Italian boys, shabby and barefoot, selling the newspapers from the city and from Rio de Janeiro, bothering the passersby with their offerings and their shouting of street roguish."
Despite the poverty and even semi-slavery conditions faced by many Italians in Brazil, most of the population achieved some personal success and changed their lower-class situation. Even though most of the first generation of immigrants still lived in poverty, their children, born in Brazil, often changed their social status as they diversified their field of work, leaving the poor conditions of their parents and often becoming part of the local elite.
Assimilation
Except for some isolated cases of violence between Brazilians and Italians, especially between 1892 and 1896, integration in Brazil was quick and peaceful. For Italians in São Paulo, scholars suggest that assimilation occurred within two generations. Research suggests that even first-generation immigrants born in Italy soon became assimilated in the new country. Even in Southern Brazil, where most of the Italians were living in isolated rural communities, with little contact with Brazilians, which kept the Italian
patriarchal
Patriarchy is a social system in which positions of authority are primarily held by men. The term ''patriarchy'' is used both in anthropology to describe a family or clan controlled by the father or eldest male or group of males, and in fem ...
family structure, and therefore the father chose the wife or husband for their children, giving preference to Italians, assimilation was also quick.
According to the 1940 census in Rio Grande do Sul, 393,934 people reported to speak German as their first language (11.86% of the state's population). In comparison, 295,995 reported to speak Italian, mostly dialects (8.91% of the state's population). Even though Italian immigration was larger and more recent than German immigration, the Italian group tended to be more easily assimilated due to the Latin cultural link. In the 1950 Census, the number of people in Rio Grande do Sul who reported to speak Italian dropped to 190,376.
In São Paulo, where more Italians settled, in the 1940 census 28,910 Italian-born people reported to speak Italian at home (only 13.6% of the state's Italian population). In comparison, 49.1% of the immigrants of other nationalities reported to keep speaking their native languages at home (with the exception of Portuguese). Thus, the prohibition of speaking Italian, German, and Japanese during World War II was not so serious to the Italian community as it was to the other two groups.
A major measure of the government occurred in 1889, when Brazilian citizenship was granted to all immigrants, but the act had little influence on their identity or assimilation process. Both the Italian newspapers in Brazil and the Italian government were uncomfortable with the assimilation of Italians in the country, which occurred mostly after the Great Naturalization period. Italian institutions encouraged the entry of Italians in Brazilian politics, but the presence of immigrants was initially small. Italian dialects came to dominate the streets of São Paulo and in some Southern localities. Over time, languages based on Italian dialects tended to disappear, and their presence is now small.
At first, especially in rural Southern Brazil, Italians tended to marry only other Italians. Over time and with the decrease of more immigrants arriving, in Southern Brazil they started to integrate themselves with Brazilians. About Italians in Santa Catarina, the Italian consul asserted:
There is little information about this trend, but it was noticed a large process of integration since World War I. However, some more closed members of the Italian community saw this integration process as negative.
Brazilian Indians were often treated as wild people, and conflicts between Italians and Indians for the occupation of lands in Southern Brazil were common.
Prosperity
Historically, Italians have been divided into two groups in Brazil. Those in Southern Brazil lived in rural colonies in contact with mostly other people of Italian descent. However, those in
Southeast Brazil
The Southeast Region of Brazil ( ) is composed of the states of Espírito Santo, Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo. It is the richest region of the country, responsible for approximately 53% of the Brazilian GDP (2022)
, as São Paulo, ...
, the most populated region of the country, integrated into Brazilian society quite quickly.
After some years working in coffee plantations, some immigrants earned enough money to buy their own land and become farmers themselves. Others left the rural areas and moved to cities, mainly São Paulo,
Campinas
Campinas (, ''Plains'' or ''Meadows'') is a Brazilian Municipalities of Brazil, municipality in São Paulo (state), São Paulo State, part of the country's Southeast Region, Brazil, Southeast Region. According to the 2020 estimate, the city's popul ...
,
São Carlos
São Carlos (Saint Charles, in English, ; named after Charles Borromeo, Saint Charles Borromeo) is a Brazilian city and municipality in the Interior of São Paulo, interior of the state of São Paulo, 254 kilometers from the city of São Paulo. ...
and
Ribeirão Preto
Ribeirão Preto (Portuguese pronunciation: Help:IPA/Portuguese, �ibejˈɾɐ̃w ˈpɾetu is a city and a metropolitan area located in the northeastern region of São Paulo (state), São Paulo state, Brazil.
Ribeirão Preto is the eighth-la ...
. A very few became very rich in the process and attracted more Italian immigrants. In the early 20th century, São Paulo became known as the ''City of the Italians'', because 31% of its inhabitants were of Italian nationality in 1900. The city of
São Paulo
São Paulo (; ; Portuguese for 'Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul') is the capital of the São Paulo (state), state of São Paulo, as well as the List of cities in Brazil by population, most populous city in Brazil, the List of largest cities in the ...
had the second-highest population of people with Italian ancestry in the world at this time, after only Rome.
In
Campinas
Campinas (, ''Plains'' or ''Meadows'') is a Brazilian Municipalities of Brazil, municipality in São Paulo (state), São Paulo State, part of the country's Southeast Region, Brazil, Southeast Region. According to the 2020 estimate, the city's popul ...
, street signs in Italian were common, a large commercial and services sector owned by Italian Brazilians developed, and more than 60% of the population had Italian surnames.
Italian immigrants were very important to the development of many big cities in Brazil, such as São Paulo,
Porto Alegre
Porto Alegre (, ; , ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Brazilian Federative units of Brazil, state of Rio Grande do Sul. Its population of roughly 1.4 million inhabitants (2022) makes it the List of largest cities in Brazil, 11th-most p ...
,
Curitiba
Curitiba () is the capital and largest city in the state of Paraná (state), Paraná in Southern Brazil. The city's population was 1,773,718 , making it the List of cities in Brazil by population, eighth most populous city in Brazil and the larg ...
and
Belo Horizonte
Belo Horizonte is the List of largest cities in Brazil, sixth-largest city in Brazil, with a population of around 2.3 million, and the third largest metropolitan area, containing a population of 6 million. It is the List of cities in Sout ...
. Bad conditions in rural areas made thousands of Italians move there. Most of them became laborers and participated actively in the industrialization of Brazil in the early 20th century. Others became investors, bankers and industrialists, such as
Count Matarazzo, whose family became the richest industrialists in São Paulo byholding of more than 200 industries and businesses. In
Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul (, ; ; "Great River of the South") is a Federative units of Brazil, state in the South Region, Brazil, southern region of Brazil. It is the Federative units of Brazil#List, fifth-most populous state and the List of Brazilian s ...
, 42% of the industrial companies have Italians roots.
Italians and their descendants were also quick to organize themselves and establish
mutual aid
Mutual aid is an organizational model where voluntary, collaborative exchanges of resources and services for common benefit take place amongst community members to overcome social, economic, and political barriers to meeting common needs. This ...
societies (such as the Circolo Italiano), hospitals, schools (such as the Istituto Colégio Dante Alighieri, in São Paulo),
labor union
A trade union (British English) or labor union (American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers whose purpose is to maintain or improve the conditions of their employment, such as attaining better wages ...
s, newspapers as Il Piccolo from
Mooca and Fanfulla (for the whole city of São Paulo), magazines, radio stations and
association football
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 Football player, players who almost exclusively use their feet to propel a Ball (association football), ball around a rectangular f ...
teams such as:
Clube Atlético Votorantim, the old Sport Club Savóia from
Sorocaba
Sorocaba () is a municipality in the interior of the state of São Paulo, Brazil. With over 723,000 inhabitants, it is the seventh-largest city in the state and the second-largest outside the Greater São Paulo region, ranking behind only Cam ...
,
Clube Atlético Juventus
Clube Atlético Juventus (Latin for ''Youth''), commonly referred to as Juventus da Mooca or simply Juventus, is a Brazilian professional football club in the district of Mooca, São Paulo, that competes in Campeonato Paulista Série A2, the s ...
of Italians Brazilians from
Mooca (old worker quarter from city of São Paulo),
Esporte Clube Juventude
Esporte Clube Juventude (), or simply Juventude, is a Brazilian football (soccer), football club in Caxias do Sul, Rio Grande do Sul. The club currently competes in the Campeonato Brasileiro Série A, the Brazilian football league system, fi ...
and the great clubs (which had the same name) Palestra Italia, later renamed to
Sociedade Esportiva Palmeiras
The Sociedade Esportiva Palmeiras (), commonly known as Palmeiras, is a Brazilian professional football club based in the city of São Paulo, in the district of Perdizes. Palmeiras is one of the most popular clubs in South America, with an ...
in São Paulo and
Cruzeiro Esporte Clube
Cruzeiro Esporte Clube () is a Brazilian professional football club, based in Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais. Cruzeiro is the greatest team of Minas Gerais. Although competing in a number of different sports, Cruzeiro is mostly known for its as ...
in Belo Horizonte.

Characteristics of Italian immigration in Brazil
Areas of origin
Most of the Italian immigrants to Brazil came from
Northern Italy
Northern Italy (, , ) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. The Italian National Institute of Statistics defines the region as encompassing the four Northwest Italy, northwestern Regions of Italy, regions of Piedmo ...
; however, they were not distributed homogeneously among the extensive Brazilian regions. In the State of São Paulo, the Italian community was more diverse including a large number of people from the South and the Center of Italy. Even today, 42% of the Italians in Brazil came from Northern Italy, 36% from
Central Italy
Central Italy ( or ) is one of the five official statistical regions of Italy used by the National Institute of Statistics (ISTAT), a first-level NUTS region with code ITI, and a European Parliament constituency. It has 11,704,312 inhabita ...
regions, and only 22% from
Southern Italy
Southern Italy (, , or , ; ; ), also known as () or (; ; ; ), is a macroregion of Italy consisting of its southern Regions of Italy, regions.
The term "" today mostly refers to the regions that are associated with the people, lands or cultu ...
. Brazil is the only American country with a large Italian community in which Southern Italian immigrants are a minority.
In the first decades, the vast majority of the immigrants came from the North. Since Southern Brazil received most of the early settlers, the vast majority of its immigrants came from the extreme North of Italy, mainly from Veneto and particularly from the provinces of
Vicenza
Vicenza ( , ; or , archaically ) is a city in northeastern Italy. It is in the Veneto region, at the northern base of the Monte Berico, where it straddles the Bacchiglione, River Bacchiglione. Vicenza is approximately west of Venice and e ...
(32%),
Belluno
Belluno (; ; ) is a town and province in the Veneto region of northern Italy. Located about north of Venice, Belluno is the Capital (political), capital of the province of Belluno and the most important city in the Eastern Dolomites region. W ...
(30%) and
Treviso
Treviso ( ; ; ) is a city and (municipality) in the Veneto region of northern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Treviso and the municipality has 87.322 inhabitants (as of December 2024). Some 3,000 live within the Venetian wall ...
(24%).
In Rio Grande do Sul, many came from
Cremona
Cremona ( , , ; ; ) is a city and (municipality) in northern Italy, situated in Lombardy, on the left bank of the Po (river), Po river in the middle of the Po Valley. It is the capital of the province of Cremona and the seat of the local city a ...
,
Mantua
Mantua ( ; ; Lombard language, Lombard and ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Italian region of Lombardy, and capital of the Province of Mantua, eponymous province.
In 2016, Mantua was designated as the "Italian Capital of Culture". In 2 ...
, from parts of
Brescia
Brescia (, ; ; or ; ) is a city and (municipality) in the region of Lombardy, in Italy. It is situated at the foot of the Alps, a few kilometers from the lakes Lake Garda, Garda and Lake Iseo, Iseo. With a population of 199,949, it is the se ...
, and also from
Bergamo
Bergamo ( , ; ) is a city in the Alps, alpine Lombardy region of northern Italy, approximately northeast of Milan, and about from the alpine lakes Lake Como, Como and Lake Iseo, Iseo and 70 km (43 mi) from Lake Garda, Garda and Lake ...
, in the region of
Lombardy
The Lombardy Region (; ) is an administrative regions of Italy, region of Italy that covers ; it is located in northern Italy and has a population of about 10 million people, constituting more than one-sixth of Italy's population. Lombardy is ...
, close to Veneto. The regions of
Trentino
Trentino (), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento (; ; ), is an Autonomous province#Italy, autonomous province of Italy in the Northern Italy, country's far north. Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the Regions of Italy, region of Tren ...
and of
Friuli-Venezia Giulia
Friuli-Venezia Giulia () is one of the 20 regions of Italy and one of five autonomous regions with special statute. The regional capital is Trieste on the Gulf of Trieste, a bay of the Adriatic Sea.
Friuli-Venezia Giulia has an area of and a ...
also sent many immigrants to the South of Brazil. Of the immigrants in Rio Grande do Sul, 54% came from the Veneto, 33% from Lombardy, 7% from Trentino, 4.5% from Friuli-Venezia Giulia and only 1.5% from other parts of Italy.
From the early 20th century, the agrarian crisis started to affect Southern Italy as well, and many people immigrated to Brazil, mostly to the state of São Paulo, since it needed workers to embrace the coffee plantations. The Italian immigrants in São Paulo came from mostly
Veneto
Veneto, officially the Region of Veneto, is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the Northeast Italy, north-east of the country. It is the fourth most populous region in Italy, with a population of 4,851,851 as of 2025. Venice is t ...
, Calabria,
Campania
Campania is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy located in Southern Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian Peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islan ...
.
After the end of World War II, a small number of
Istrian Italians
Istrian Italians (; ; ) are an ethnic group from the Adriatic region of Istria in modern northwestern Croatia and southwestern Slovenia. Istrian Italians descend from the original Latinized population of Roman Histria, from the Venetian-speaki ...
and
Dalmatian Italians
Dalmatian Italians (; ) are the historical Italian national minority living in the region of Dalmatia, now part of Croatia and Montenegro.
Historically, Italian language-speaking Dalmatians accounted for 12.5% of population in 1865, 5.8% in 18 ...
emigrated to Brazil during the
Istrian-Dalmatian exodus, leaving their homelands, which were lost to Italy and annexed to
Yugoslavia
, common_name = Yugoslavia
, life_span = 1918–19921941–1945: World War II in Yugoslavia#Axis invasion and dismemberment of Yugoslavia, Axis occupation
, p1 = Kingdom of SerbiaSerbia
, flag_p ...
after the
Treaty of Peace with Italy, 1947
The Treaty of Paris between Italy and the Allied Powers was signed on 10 February 1947, formally ending hostilities between both parties. It came into general effect on 15 September 1947.
Territorial changes
* Transfer of the Adriatic isl ...
.
Italian influences in Brazil
Language

Most Brazilians with Italian ancestry now speak
Brazilian Portuguese
Brazilian Portuguese (; ; also known as pt-BR) is the set of Variety (linguistics), varieties of Portuguese language native to Brazil. It is spoken by almost all of the 203 million inhabitants of Brazil and widely across the Brazilian diaspora ...
as their native language. During World War II, the public use of
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
, German, and Japanese was forbidden.
Italian dialects have influenced the Portuguese spoken in some areas of Brazil.
Italian was so widespread in São Paulo that the Portuguese traveler Sousa Pinto said that he could not speak with cart drivers in Portuguese because they all spoke Italian dialects and gesticulated as Neapolitans.
The Italian influence on Portuguese spoken in São Paulo is no longer as great as before, but the accent of the city's inhabitants still has some traces of the Italian accents common in the beginning of the 20th century like the intonation and such expressions as ''Belo'', ''Ma vá!'', ''Orra meu!'' and ''Tá entendendo?''. Other characteristic is the difficulty to speak Portuguese in plural, saying plural words as they were singulars. The lexical influence of Italian on Brazilian Portuguese, however, has remained quite small.
A similar phenomenon occurred in the countryside of Rio Grande do Sul
but encompassing almost exclusively those of Italian origin.
On the other hand, is a different phenomenon:
Talian Talian may refer to:
Places
* Talian, Iran, a village in Tehran province, Iran
* Dhok Talian, a village in Punjab, Pakistan
People
* Jozef Talian (born 1985), Slovak footballer
Other uses
*Talian dialect
Talian (, ), or Brazilian Venetian, or ...
, which emerged mostly in the northeastern part of the state (
Serra Gaúcha). Talian is a variant of the
Venetian language
Venetian, also known as wider Venetian or Venetan ( or ), is a Romance languages, Romance language spoken natively in the northeast of Italy,Ethnologue mostly in Veneto, where most of the five million inhabitants can understand it. It is som ...
with influences from other
Italian dialects and Portuguese.
[Enciclopédia de Línguas do Brasil - Línguas de Imigração Européia - Talian (Vêneto Brasileiro)](_blank)
Retrieved 11 September 2008. In Southern Brazilian rural areas marked by
bilingualism
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. When the languages are just two, it is usually called bilingualism. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolin ...
, even among the monolingual Portuguese-speaking population, the Italian-influenced accent is fairly typical.
Music
The Italian influence in Brazil affects also music with traditional Italian songs and the merging with other Brazilians music styles. One of the main results of the fusion is ''samba paulista'', a samba with strong Italians influence.
''Samba paulista'' was created by
Adoniran Barbosa (born João Rubinato), the son of Italians immigrants. His songs translated the life of the Italian neighborhoods in São Paulo and merged São Paulo dialect with samba, which latter made him known as the "people's poet."
One of the main example is ''
Samba Italiano'', which that has a Brazilian rhythm and theme but (mostly) Italian lyrics. Below, the lyrics of this song have the parts in (mangled) Portuguese in bold and the parts in Italian in a normal font:

Cuisine

Italians brought new recipes and types of food to Brazil and also helped in the development of the cuisine of Brazil. Italian staple dishes like pizza and pasta are very common and popular in Brazil. Pasta is extremely common, either simple unadorned pasta with butter or oil or accompanied by a
tomato
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible Berry (botany), berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originate ...
- or
bechamel-based sauce.
Aside from the typical Italian cuisine like pizza, pasta, risotto, panettone, milanesa, polenta, calzone, and ossobuco, Italians helped to create new dishes that today are typically considered Brazilian. ''Galeto'' (from the Italian ''galletto'', little rooster), ''frango com polenta'' (chicken with fried polenta), ''Bife à parmegiana'' (a steak prepared with
Parmigiano-Reggiano), ''
Mortadella sandwich'' (a sandwich made of mortadella sausage, Provolone cheese, sourdough bread, mayonnaise and Dijon mustard),
Catupiry cheese, new types of sausage like ''linguiça Calabresa'' and ''linguiça Toscana'' (literally Calabrian and Tuscan sausage), ''chocotone'' (panettone with chocolate chips) and many other recipes were created or influenced by the Italian community.
The ''nhoque de 29'' ("gnocchi of 29") defines the widespread custom in some South American countries of eating a plate of
gnocchi
Gnocchi are a varied family of pasta-like dumplings in Italian cuisine. They are made of small rolls of dough, such as those composed of a simple combination of wheat flour,Buonassisi, recipe #831-833 potato,Buonassisi, recipe #854-857 egg,Buonas ...
, a type of Italian
pasta
Pasta (, ; ) is a type of food typically made from an Leavening agent, unleavened dough of wheat flour mixed with water or Eggs as food, eggs, and formed into sheets or other shapes, then cooked by boiling or baking. Pasta was originally on ...
, on the 29th of each month. The custom is widespread especially in the states of the
Southern Cone
The Southern Cone (, ) is a geographical and cultural subregion composed of the southernmost areas of South America, mostly south of the Tropic of Capricorn. Traditionally, it covers Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay, bounded on the west by the Pac ...
such as Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay, Uruguay;
these countries being recipients of a considerable Italian immigration between the end of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century. There is a ritual that accompanies lunch with gnocchi, namely putting money under the plate which symbolizes the desire for new gifts. It is also customary to leave a banknote or coin under the plate to attract luck and prosperity to the dinner.
The tradition of serving gnocchi on the 29th of each month stems from a legend based on the story of
Saint Pantaleon, a young doctor from
Nicomedia
Nicomedia (; , ''Nikomedeia''; modern İzmit) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek city located in what is now Turkey. In 286, Nicomedia became the eastern and most senior capital city of the Roman Empire (chosen by the emperor Diocletian who rul ...
who, after converting to Christianity, made a pilgrimage through northern Italy. There Pantaleon practiced miraculous cures for which he was canonized. According to legend, on one occasion when he asked Venetian peasants for bread, they invited him to share their poor table. In gratitude, Pantaleon announced a year of excellent fishing and excellent harvests. That episode occurred on 29 July, and for this reason that day is remembered with a simple meal represented by gnocchi.
Other influences
* Use of ''
ciao
( , ) is an informal salutation in the Italian language that is used for both " hello" and "goodbye".
Originally from the Venetian language, it has entered the vocabulary of English and of many other languages around the world. Its dual mea ...
'' ("tchau" in
Brazilian-Portuguese) as a '
goodbye' salutation (all of Brazil)
* Wine production (in the South)
* 218
loanwords
A loanword (also a loan word, loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language (the recipient or target language), through the process of borrowing. Borrowing is a metaphorical term t ...
(
italianisms), such as ''agnolotti'', ''rigatoni'', ''sugo'' as regards gastronomy, ''ambasciata'', ''cittadella'', ''finta'' as regards sport, ''lotteria'', ''tombola'' as regards games, ''raviolatrice'', ''vasca'' as regards technology and ''stiva'' as regards the navy.
* Early introduction of more advanced low-scale farming techniques (
Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is one of the 27 federative units of Brazil, being the fourth largest state by area and the second largest in number of inhabitants with a population of 20,539,989 according to the 2022 Brazilian census, 2022 census. Located in ...
, São Paulo and all Southern Brazil)
Education
Italian international schools in Brazil:
*
Scuola Italiana Eugenio Montale - São Paulo
*
Istituto Italo-Brasiliano Biculturale Fondazione Torino - Belo Horizonte
Current Italian emigration in Brazil
In 2019, 11,663 people with Italian nationality emigrated from Italy to Brazil according to the Italian World Report 2019, totaling 447,067 Italian citizens living in Brazil until 2019.
Notable people
Arts and Entertainment
*
André Abujamra, Brazilian score composer, musician, singer, actor and comedian
*
Bruna Abdullah, Brazilian actress
*
Fernanda Andrade, Brazilian actress, model and singer
*Laura Petracco, Brazilian-Italian theatre actor
*
Lélia Abramo, Italian-Brazilian actress
*
Morena Baccarin
Morena Silva de Vaz Setta Baccarin (; born June 2, 1979) is an American actress. She is known for portraying Adria in season 10 of the TV series ''Stargate SG-1'', Inara Serra in the sci-fi television series ''Firefly (TV series), Firefly'' (20 ...
, Brazilian-born American actress
*
Rodrigo Santoro
Rodrigo Junqueira Reis Santoro (; born 22 August 1975) is a Brazilian actor. He is known in Brazil for his appearance on local telenovelas and internationally for his portrayal of Persian King Xerxes I of Persia, Xerxes in the film ''300 (film), ...
, Brazilian actor
Politics and Economists
*
Carlos Bolsonaro (born 1982), Brazilian politician, Jair Bolsonaro's son
*
Eduardo Bolsonaro (born 1984), Brazilian lawyer, federal police officer and politician; Jair Bolsonaro's son
*
Flávio Bolsonaro (born 1981), Brazilian lawyer, entrepreneur and politician; Jair Bolsonaro's son
*
Itamar Franco
Itamar Augusto Cautiero Franco (; 28 June 19302 July 2011) was a Brazilian politician who served as the 33rd president of Brazil from 29 December 1992 to 1 January 1995. Previously, he was the 21st vice president of Brazil from 1990 until the ...
, Brazilian former politician, 33rd president of Brazil.
*
Guido Mantega
Guido Mantega (; born 7 April 1949) is an Italian-born Brazilian economist and politician.
Mantega served as Minister of Finance from 2006 to 2015 under the presidencies of Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva and Dilma Rousseff. His tenure as Ministe ...
, Italian-born Brazilian economist and politician
*
Jair Bolsonaro
Jair Messias Bolsonaro (; born 21 March 1955) is a Brazilian politician and former military officer who served as the 38th president of Brazil from 2019 to 2023. He previously served as a member of Brazil's Chamber of Deputies (Brazil), Chamb ...
(born 1955), 38th President of Brazil
*
Roger Agnelli, Brazilian investment banker and entrepreneur
*
Romeu Zema, Brazilian businessman, administrator and politician
*
Sergio Moro, Brazilian jurist, former federal judge, college professor and politician
Religious people
*
Geraldo Agnelo, Brazilian prelate
Royal family
*
Dom Afonso, Prince Imperial and heir apparent to the throne of the Empire of Brazil
Sports (football)
*
Adam Adami, professional footballer
*
Alex Meshini, football coach and former footballer
*
Andre Anderson, professional footballer
*
Amphilóquio Guarisi, former national footballer
*
Angelo Sormani
Angelo Benedicto Miguel Sormani (; ; born 3 July 1939) is a Brazilian-born Italian former football manager and player, who played as a forward; he was capable of playing anywhere along the front-line, as a centre-forward, as well as in an att ...
, former national footballer
*
Dino da Costa, former national footballer
*
Éder, former national footballer
*
Emerson Palmieri, Italian national team footballer
*
Gabriel Martinelli, Brazilian national team footballer
*
Jorginho, Italian national team footballer
*
José Altafini
José João Altafini (; born 24 July 1938), also known as "Mazzola" in Brazil, is an Italian-Brazilian former association football, footballer, who played as a Forward (association football), forward. Although, he began his career with Sociedade ...
, former national footballer
*
Luiz Felipe, Italian national team footballer
*
Otávio Fantoni, former national footballer
*
Raphinha, Brazilian national team footballer
*
Rafael Tolói, Italian national team footballer
*
Thiago Motta
Thiago Motta (; ; born 28 August 1982) is a professional Association football, football manager and former player who was most recently the head coach of club Juventus FC, Juventus.
A Midfielder#Defensive midfielder, defensive midfielder, Mott ...
, Italian football manager and former national footballer
Sports (bull riding)
*
Guilherme Marchi, Brazilian bull rider
Sports (mixed martial arts)
*
Tabatha Ricci,
UFC
The Ultimate Fighting Championship (UFC) is an American mixed martial arts (MMA) promotion company based in Las Vegas, Nevada. It is owned and operated by TKO Group Holdings, a majority owned subsidiary of Endeavor Group Holdings. The larg ...
fighter
See also
*
Brazil–Italy relations
Brazil–Italy relations are the diplomatic relations between Brazil and Italy. Both nations enjoy friendly and semi-privileged relations, the importance of which centres on the history of Italian migration to Brazil. Approximately 31 million Br ...
*
Brazilians in Italy
*
Italian Americans
Italian Americans () are Americans who have full or partial Italians, Italian ancestry. The largest concentrations of Italian Americans are in the urban Northeastern United States, Northeast and industrial Midwestern United States, Midwestern ...
*
Italian Argentines
Italian Argentines (; , or ''tanos'' in Rioplatense Spanish) are Argentine-born citizens who are fully or partially of Italian descent, whose ancestors were Italians who emigrated to Argentina during the Italian diaspora, or Italian-born people ...
*
Italian Australians
Italian Australians () are Australian-born citizens who are fully or partially of Italian descent, whose ancestors were Italians who emigrated to Australia during the Italian diaspora, or Italian-born people in Australia.
Italian Australian ...
*
Italian Canadians
Italian Canadians or Italo-Canadians (; ) are Canadian-born citizens who are fully or partially of Italian descent, whose ancestors were Italians who migrated to Canada as part of the Italian diaspora, or Italian-born people in Canada. Accordin ...
*
Italian Chileans
Italian Chileans (; ) are Chilean-born citizens who are fully or partially of Italian descent, whose ancestors were Italians who emigrated to Chile during the Italian diaspora, or Italian-born people in Chile. It is estimated that about 800,000 C ...
*
Italian Colombians
*
Italian Peruvians
*
Italian Uruguayans
Italian Uruguayans (; or ''tanos'' in Rioplatense Spanish) are Uruguayan-born citizens who are fully or partially of Italian descent, whose ancestors were Italians who emigrated to Uruguay during the Italian diaspora, or Italian-born people in U ...
*
Italo-Venezuelans
Italian Venezuelans (; ) are Venezuelan-born citizens who are fully or partially of Italian descent, whose ancestors were Italians who emigrated to Venezuela during the Italian diaspora, or Italian-born people in Venezuela. Italians were among th ...
*
Italian diaspora
The Italian diaspora (, ) is the large-scale emigration of Italians from Italy.
There were two major Italian diasporas in Italian history. The first diaspora began around 1880, two decades after the Risorgimento, Unification of Italy, and ended ...
*
Italian immigration in Minas Gerais
*
Demography of Brazil
Brazil had an official resident population of 203 million in 2022, according to IBGE.. Brazil is the seventh most populous country in the world and the second most populous in the Americas and Western Hemisphere.
Brazilians are mainly concentr ...
*
White Brazilians
White Brazilians ( ) refers to Brazilian citizens who are considered or self-identify as "white", typically because of Ethnic groups in Europe, European or Levant, Levantine Asian ancestry.
The main ancestry of current white Brazilians is Portu ...
*
White Latin Americans
White Latin Americans () are Latin Americans of total or predominantly European diaspora, European or West Asia, West Asian ancestry.
Population with majority (or unique) ancestry of European settlers who arrived in Americas, the Americas duri ...
*
List of Portuguese words of Italian origin
*
Italian language in Brazil
*
Memória do Bixiga Museum
References
Further reading
* Bertonha, João Fábio. ''Os italianos''. Editora Contexto. São Paulo, 2005
* Cenni, Franco. ''Os italianos no Brasil''. EDUSP. São Paulo, 2003
* Clemente, Elvo (et al.). ''Italianos no Brasil: contribuições na literatura e nas ciências, séculos XIX e XX'' EDIPUCRS. Porto Alegre, 1999
* Franzina, Emilio. ''Storia dell'emigrazione italiana''. Donzelli Editore. Roma, 2002
* Favero, Luigi y Tassello, Graziano. ''Cent'anni di emigrazione italiana (1876–1976)''. Cser. Roma, 1978.
* Trento, Ângelo. ''Do outro lado do Atlântico''. Studio Nobel. São Paulo, 1988
External links
oriundi.net a site for descendants from Italians in Brazil
Italianisms in Brazilian Portuguese(In Italian)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Brazilian, Italian
*
Italian Brazilian
Italian Brazilians (, ) are Brazilians of full or partial Italy, Italian descent, whose ancestors were Italians who emigrated to Brazil during the Italian diaspora, or more recent Italian-born people who've settled in Brazil. Italian Brazilians ...
 According to the Italian government, there are 31 million Brazilians of
According to the Italian government, there are 31 million Brazilians of  According to the Brazilian Constitution, anyone born in the country is a Brazilian citizen by birthright. In addition, many born in Italy have become
According to the Brazilian Constitution, anyone born in the country is a Brazilian citizen by birthright. In addition, many born in Italy have become 
 In 1850, under British pressure, Brazil finally passed a law that effectively banned transatlantic slave trade. The increased pressure of the abolitionist movement, on the other hand, made it clear that the days of slavery in Brazil were coming to an end. Slave trade was effectively suppressed, but the slave system still endured for almost four decades. Thus, Brazilian landowners claimed that such migrants were or would soon become indispensable for Brazilian agriculture. They would soon win the argument, and mass migration would begin in earnest.
An Agriculture Congress in 1878 in
In 1850, under British pressure, Brazil finally passed a law that effectively banned transatlantic slave trade. The increased pressure of the abolitionist movement, on the other hand, made it clear that the days of slavery in Brazil were coming to an end. Slave trade was effectively suppressed, but the slave system still endured for almost four decades. Thus, Brazilian landowners claimed that such migrants were or would soon become indispensable for Brazilian agriculture. They would soon win the argument, and mass migration would begin in earnest.
An Agriculture Congress in 1878 in  The Brazilian government, with or following the Emperor's support, had created the first colonies of immigrants (''colônias de imigrantes'') in the early 19th century. The colonies were established in
The Brazilian government, with or following the Emperor's support, had created the first colonies of immigrants (''colônias de imigrantes'') in the early 19th century. The colonies were established in  Internal migration made many second- and third-generation Italians move to other areas. In the early 20th century, many rural Italian workers from Rio Grande do Sul migrated to the west of Santa Catarina and then farther north to Paraná.
More recently, third- and fourth-generation Italians have migrated to other areas and so people of Italian descent can be found in Brazilian regions in which the immigrants had never settled, such as in the
Internal migration made many second- and third-generation Italians move to other areas. In the early 20th century, many rural Italian workers from Rio Grande do Sul migrated to the west of Santa Catarina and then farther north to Paraná.
More recently, third- and fourth-generation Italians have migrated to other areas and so people of Italian descent can be found in Brazilian regions in which the immigrants had never settled, such as in the  The main areas of Italian settlement in Brazil were the Southern and Southeastern Regions, namely the states of
The main areas of Italian settlement in Brazil were the Southern and Southeastern Regions, namely the states of 
 Some of the immigrants settled in the colonies in Southern Brazil. However, most of them settled in Southeastern Brazil (mainly in the
Some of the immigrants settled in the colonies in Southern Brazil. However, most of them settled in Southeastern Brazil (mainly in the  In 1901, 90% of industrial workers and 80% of construction workers in São Paulo were Italians.
In 1901, 90% of industrial workers and 80% of construction workers in São Paulo were Italians.
 In 1902, the Italian immigration to Brazil started to decline. From 1903 to 1920, only 306,652 Italians immigrated to Brazil, compared to 953,453 to
In 1902, the Italian immigration to Brazil started to decline. From 1903 to 1920, only 306,652 Italians immigrated to Brazil, compared to 953,453 to  Most Brazilians with Italian ancestry now speak
Most Brazilians with Italian ancestry now speak  Italians brought new recipes and types of food to Brazil and also helped in the development of the cuisine of Brazil. Italian staple dishes like pizza and pasta are very common and popular in Brazil. Pasta is extremely common, either simple unadorned pasta with butter or oil or accompanied by a
Italians brought new recipes and types of food to Brazil and also helped in the development of the cuisine of Brazil. Italian staple dishes like pizza and pasta are very common and popular in Brazil. Pasta is extremely common, either simple unadorned pasta with butter or oil or accompanied by a