Israeli-Palestinian conflict on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Israelis ( he, יִשְׂרָאֵלִים, translit=Yīśrāʾēlīm; ar, الإسرائيليين, translit=al-ʾIsrāʾīliyyin) are the citizens and nationals of the
 Among the Israeli-born Jewish population, most are descended from
Among the Israeli-born Jewish population, most are descended from
Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs 1 July 1999 As of 2013, the
 There is also a significant population of Israeli
There is also a significant population of Israeli
 In Israel, there are also a few thousand
In Israel, there are also a few thousand
 The Samaritans are an ethnoreligious group of the
The Samaritans are an ethnoreligious group of the
 The number and status of African refugees in Israel is disputed and controversial, but it is estimated that at least 16,000 refugees, mainly from Eritrea,
The number and status of African refugees in Israel is disputed and controversial, but it is estimated that at least 16,000 refugees, mainly from Eritrea,
by Rena Greenberg – Moscow, Russia, 19 March 2014 Many Israeli cultural events are hosted for the community, and many live part of the year in Israel. (To cater to the Israeli community, Israeli cultural centres are located in
, Statistics Canada
 The term "Israelite" refers to members of the Jewish tribes and polities of the Iron Age known from the
The term "Israelite" refers to members of the Jewish tribes and polities of the Iron Age known from the
 The largest cities in the country
The largest cities in the country
 According to the Israel Central Bureau of Statistics, at the end of 2014, 75% of Israelis were
According to the Israel Central Bureau of Statistics, at the end of 2014, 75% of Israelis were
 Due to its immigrant nature, Israel is one of the most multicultural and multilingual societies in the world.
Due to its immigrant nature, Israel is one of the most multicultural and multilingual societies in the world.
People of Israel
at the Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs
Official website
of the Israel Central Bureau of Statistics * {{Authority control Society of Israel Semitic-speaking peoples
State of Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
. The country's populace is composed primarily of Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
and Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, who respectively account for 75 percent and 20 percent of the national figure; followed by other ethnic and religious minorities, who account for 5 percent.
Early Israeli culture was largely defined by communities of the Jewish diaspora
The Jewish diaspora ( he, תְּפוּצָה, təfūṣā) or exile (Hebrew: ; Yiddish: ) is the dispersion of Israelites or Jews out of their ancient ancestral homeland (the Land of Israel) and their subsequent settlement in other parts of th ...
who had made ''aliyah
Aliyah (, ; he, עֲלִיָּה ''ʿălīyyā'', ) is the immigration of Jews from the diaspora to, historically, the geographical Land of Israel, which is in the modern era chiefly represented by the State of Israel. Traditionally descri ...
'' to British Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 i ...
from Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes A ...
, and North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
in the late-19th and early-20th centuries. Later Jewish immigration from Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, the states of the former Soviet Union, and the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
introduced new cultural elements to Israeli society and have had a profound impact on modern Israeli culture.
Since Israel's independence in 1948, Israelis and people of Israeli descent have a considerable diaspora, which largely overlaps with the Jewish diaspora but also with that of other ethnic and religious groups; it is estimated that almost 10 percent of the general Israeli population lives abroad, particularly in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
(with Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
housing the single largest Israeli community outside of Israel), India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
, the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, and throughout Europe.
Population
As of 2013, Israel's population is 8 million, of which the Israeli civil government records 75.3% asJews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, 20.7% as non-Jewish Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, and 4.0% other.http://www.cbs.gov.il/www/hodaot2013n/11_13_097e.pdf , Monthly Bulletin of Statistics, CBS Israel's official census includes Israeli settlers in the occupied territories
Military occupation, also known as belligerent occupation or simply occupation, is the effective military control by a ruling power over a territory that is outside of that power's sovereign territory.Eyāl Benveniśtî. The international law ...
(referred to as "disputed
Controversy is a state of prolonged public dispute or debate, usually concerning a matter of conflicting opinion or point of view. The word was coined from the Latin ''controversia'', as a composite of ''controversus'' – "turned in an opposite d ...
" by Israel). 280,000 Israeli settlers live in settlements in the Israeli-occupied West Bank, 190,000 in East Jerusalem
East Jerusalem (, ; , ) is the sector of Jerusalem that was held by Jordan during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, as opposed to the western sector of the city, West Jerusalem, which was held by Israel.
Jerusalem was envisaged as a separ ...
, and 20,000 in the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
.
Among Jews, 70.3% were born in Israel (''sabras''), mostly from the second or third generation of their family in the country, and the rest are Jewish immigrants. Of the Jewish immigrants, 20.5% were from Europe and the Americas, and 9.2% were from Asia, Africa, and Middle Eastern countries. Nearly half of all Israeli Jews are descended from immigrants from the European Jewish diaspora. Approximately the same number are descended from immigrants from Arab countries, Iran, Turkey and Central Asia. Over 200,000 are of Ethiopian and Indian-Jewish descent.http://www.cbs.gov.il/reader/shnaton/templ_shnaton.html?num_tab=st02_23x&CYear=2005
The official Israel Central Bureau of Statistics estimate of the Israeli Jewish population does not include those Israeli citizens, mostly descended from immigrants from the Soviet Union, who are registered as "others", or their immediate family members. Defined as non-Jews and non-Arabs, they make up about 3.5% of Israelis (350,000), and were eligible for Israeli citizenship under the Law of Return.
Israel's two official languages are Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
and Arabic. Hebrew is the primary language of government and is spoken by the majority of the population. Arabic is spoken by the Arab minority and by some members of the Mizrahi Jewish community. English is studied in school and is spoken by the majority of the population as a second language. Other languages spoken in Israel include Russian, Yiddish, Spanish, Ladino, Amharic, Armenian, Romanian, and French.
In recent decades, between 650,000 and 1,300,000 Israelis have emigrated, a phenomenon known in Hebrew as '' yerida'' ("descent", in contrast to ''aliyah'', which means "ascent"). Emigrants have various reasons for leaving, but there is generally a combination of economic and political concerns. Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world ...
is home to the largest community of Israelis outside Israel.
Ethnic and religious groups
The main Israeliethnic
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established fo ...
and religious groups are as follows:
Jews
 Among the Israeli-born Jewish population, most are descended from
Among the Israeli-born Jewish population, most are descended from Ashkenazi Jews
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
, Mizrahi Jews
Mizrahi Jews ( he, יהודי המִזְרָח), also known as ''Mizrahim'' () or ''Mizrachi'' () and alternatively referred to as Oriental Jews or ''Edot HaMizrach'' (, ), are a grouping of Jewish communities comprising those who remained ...
, Sephardic Jews, Ethiopian Jews, and other Jewish ethnic divisions. Due to the historically large Mizrahi population and decades of ethnic intermixing, over 50% of Israel's current Jewish population is of at least partial Mizrahi descent.''My Promised Land'', by Ari Shavit, (London 2014)
The CBS traces the paternal country of origin of Israeli Jews as of 2010 is as follows.
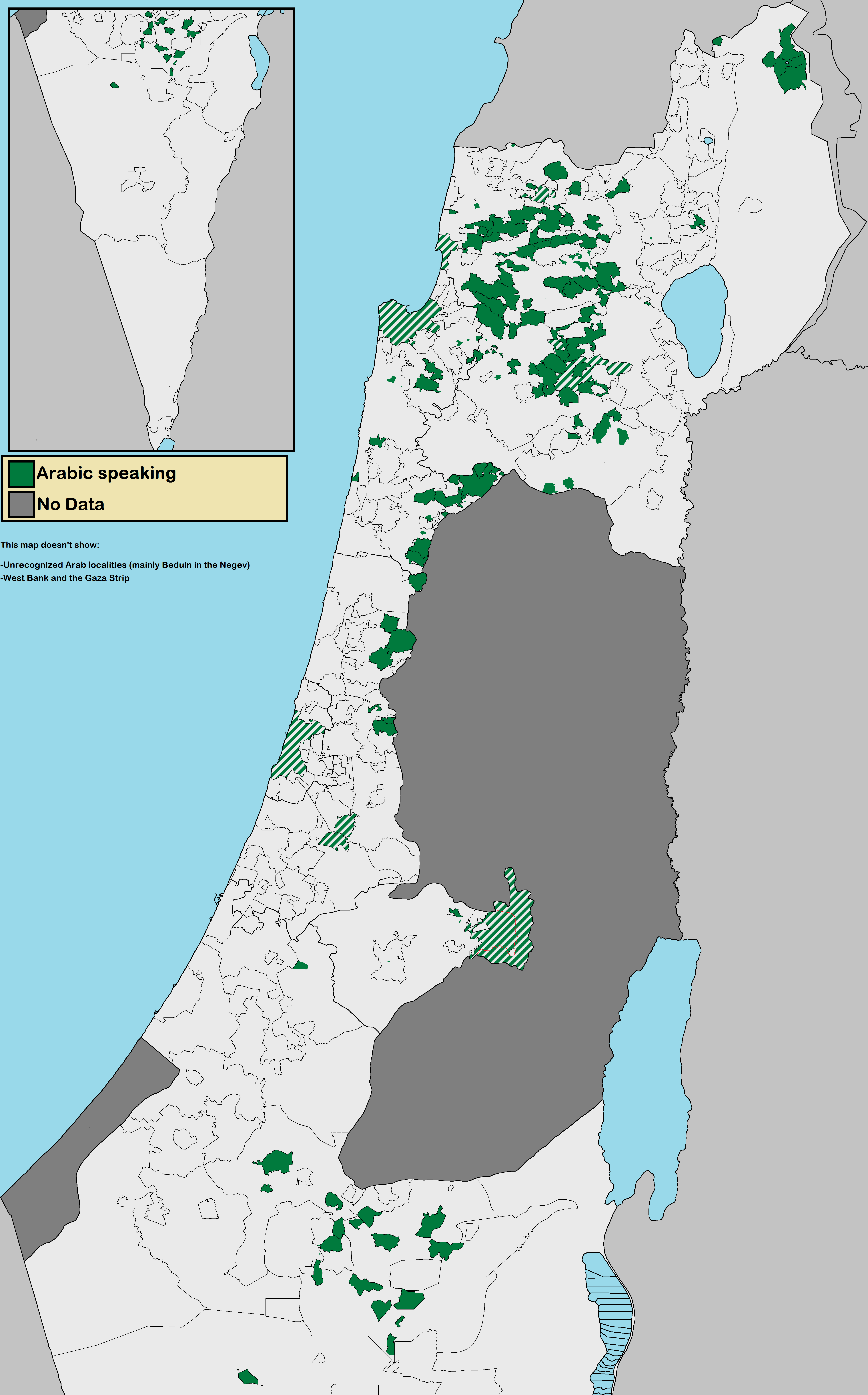
Arabic-speaking minorities

Arab Palestinians
A large part ofMandate
Mandate most often refers to:
* League of Nations mandates, quasi-colonial territories established under Article 22 of the Covenant of the League of Nations, 28 June 1919
* Mandate (politics), the power granted by an electorate
Mandate may also r ...
-period Arab Palestinians remained within Israel's borders following the 1948 exodus and are the largest group of Arabic-speaking and culturally Arab citizens of Israel. The vast majority of the Arab citizens of Israel are Sunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a dis ...
Muslim, while 9% of them are Christian, and 7.1% of them are Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
.
As of 2013, the Arab population of Israel amounts to 1,658,000, about 20.7% of the population. This figure include 209,000 Arabs (14% of the Israeli Arab population) in East Jerusalem, also counted in the Palestinian statistics, although 98 percent of East Jerusalem Palestinians have either Israeli residency or Israeli citizenship.
According to the Israeli Central Bureau of Statistics census in 2010, the Arab population in Israel lives in 134 Arabic towns and villages; around 44% of them live in towns, while 48% of them in villages with statues of Local council, and around 4% live in small villages that are part of Regional council
Regional Council may refer to:
* Regional Council (Hong Kong), disbanded in 1999
** Regional Council (constituency)
Regional council may refer to:
* Regional council (Cameroon)
* Regional council (France), the elected assembly of a region of Fran ...
. The Arab population in Israel is located in five main areas: Galilee (54.6% of total Israeli Arabs), Triangle (23.5% of total Israeli Arabs), Golan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
, East Jerusalem
East Jerusalem (, ; , ) is the sector of Jerusalem that was held by Jordan during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, as opposed to the western sector of the city, West Jerusalem, which was held by Israel.
Jerusalem was envisaged as a separ ...
, and Northern Negev
The Negev or Negeb (; he, הַנֶּגֶב, hanNegév; ar, ٱلنَّقَب, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its sout ...
(13.5% of total Israeli Arabs). Around 8.4% of Israeli Arabs live in officially mixed Jewish-Arab cities (excluding Arab residents in East Jerusalem), in Haifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropol ...
, Lod, Ramle, Jaffa-Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( he, תֵּל־אָבִיב-יָפוֹ, translit=Tēl-ʾĀvīv-Yāfō ; ar, تَلّ أَبِيب – يَافَا, translit=Tall ʾAbīb-Yāfā, links=no), often referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the G ...
, Acre, Nof HaGalil, and Ma'alot Tarshiha.
Negev Bedouin
The Arab citizens of Israel also include the Bedouin. Israeli Bedouin include those who live in the north of the country, for the most part in villages and towns, and the Bedouin in theNegev
The Negev or Negeb (; he, הַנֶּגֶב, hanNegév; ar, ٱلنَّقَب, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its sout ...
, who are semi-nomadic or live in towns or unrecognized Bedouin villages. In 1999, 110,000 Bedouin lived in the Negev, 50,000 in the Galilee and 10,000 in the central region of Israel.The Bedouin in Israel: DemographyIsrael Ministry of Foreign Affairs 1 July 1999 As of 2013, the
Negev Bedouin
The Negev Bedouin ( ar, بدو النقب, ''Badū an-Naqab''; he, הבדואים בנגב, ''HaBedu'im BaNegev'') are traditionally pastoral nomadic Arab tribes ( Bedouin), who until the later part of the 19th century would wander between Sa ...
number 200,000–210,000.
Druze
 There is also a significant population of Israeli
There is also a significant population of Israeli Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
, estimated at 117,500 at the end of 2006. All Druze in British Mandate Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 i ...
became Israeli citizens upon the foundation of the State of Israel.
Maronites
There are about 7,000 Maronite Christian Israelis, living mostly in the Galilee but also inHaifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropol ...
, Nazareth, and Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
. They are mostly pro-Israeli Lebanese former militia members and their families who fled Lebanon after the 2000 withdrawal of IDF from South Lebanon. Some, however, are from local Galilean communities such as Jish.
Copts
There are about 1,000 Coptic Israeli citizens.Arameans
In September 2014, Israel recognized the "Aramean" ethnic identity of hundreds of the Christian citizens of Israel. This recognition comes after about seven years of activity by the Aramean Christian Foundation in Israel – Aram, led by IDF MajorShadi Khalloul Risho
Shadi may refer to:Arabic Name Meaning Servant or Seeker of knowledge
People
*Shadi (name)
Places
* Juy-ye Shadi, village in Bamyan Province, Afghanistan
* Shadi Township (沙堤乡), Yongding District, Zhangjiajie, Hunan, China
* Shadi, Ji ...
and the Israeli Christian Recruitment Forum, headed by Father Gabriel Naddaf
Gabriel Naddaf ( ar, جبرائيل نداف, he, גבריאל נדאף; born August 18, 1973) is an Israeli Greek Orthodox priest. He serves as a judge in Israel's religious court system and as a spokesman for the Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of ...
of the Greek-Orthodox Church and Major Ihab Shlayan. The Aramean ethnic identity will now encompass all the Christian Eastern Syriac churches in Israel, including the Maronite Church, Greek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church ( Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also cal ...
Church, Greek Catholic The term Greek Catholic Church can refer to a number of Eastern Catholic Churches following the Byzantine (Greek) liturgy, considered collectively or individually.
The terms Greek Catholic, Greek Catholic church or Byzantine Catholic, Byzantine C ...
Church, Syriac Catholic Church and Syriac Orthodox Church.
Assyrians
There are around 1,000 Assyrians living in Israel, mostly inJerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
and Nazareth. Assyrians are an Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated i ...
-speaking, Eastern Rite Christian minority who are descended from the ancient Mesopotamians. The old Syriac Orthodox monastery of Saint Mark lies in Jerusalem. Other than followers of the Syriac Orthodox Church, there are also followers of the Assyrian Church of the East and the Chaldean Catholic Church
, native_name_lang = syc
, image = Assyrian Church.png
, imagewidth = 200px
, alt =
, caption = Cathedral of Our Lady of Sorrows Baghdad, Iraq
, abbreviation =
, type ...
living in Israel.
Other citizens
African Hebrew Israelites
The African Hebrew Israelite Nation of Jerusalem is a small religious community whose members believe they are descended from the Ten Lost Tribes of Israel. Most of the over 5,000 members live in Dimona, Israel although there are additional, smaller, groups in Arad, Mitzpe Ramon, and theTiberias
Tiberias ( ; he, טְבֶרְיָה, ; ar, طبريا, Ṭabariyyā) is an Israeli city on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee. A major Jewish center during Late Antiquity, it has been considered since the 16th century one of Judaism's F ...
area. At least some of them consider themselves to be Jewish, but Israeli authorities do not accept them as such, nor are their religious practices consistent with "mainstream Jewish tradition." The group, which consists of African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
and their descendants, originated in Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Count ...
in the early 1960s, moved to Liberia for a few years, and then immigrated to Israel.
Armenians
There are about 4,000–10,000 Armenian citizens of Israel (not including Armenian Jews). They live mostly in Jerusalem, including the Armenian Quarter, but also in Tel Aviv, Haifa and Jaffa. Their religious activities center around the Armenian Patriarchate of Jerusalem as well as churches in Jerusalem, Haifa and Jaffa. Although Armenians of Old Jerusalem have Israeli identity cards, they are officially holders ofJordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
ian passports.
Caucasians
A number of immigrants also belong to various non-Slavic ethnic groups from the Former Soviet Union such asTatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turki ...
, in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turki ...
Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
, and Georgians.
Circassians
 In Israel, there are also a few thousand
In Israel, there are also a few thousand Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia ...
, living mostly in Kfar Kama (2,000) and Reyhaniye (1,000). These two villages were a part of a greater group of Circassian villages around the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
. The Circassians in Israel enjoy, like Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
s, a ''status aparte''. Male Circassians (at their leader's request) are mandated for military service, while females are not.
East Europeans
Non-Jewish immigrants from the former Soviet Union most of whom are Zera Yisrael (descendants of Jews) who areRussians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
, Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Ort ...
, Moldovans and Belarusians, who were eligible to immigrate due to having, or being married to somebody who has, at least one Jewish grandparent. In addition, a certain number of former Soviet citizens, primarily women of Russian and Ukrainian ethnicity, immigrated to Israel after marrying Arab citizens of Israel who went to study in the former Soviet Union in the 1970s and 1980s. The total number of those primarily of Slavic ancestry among Israeli citizens is around 300,000.
Finns
Although most Finns in Israel are either Finnish Jews or their descendants, a small number of Finnish Christians moved to Israel in the 1940s before the independence of the state and have since gained citizenship. For the most part the original Finnish settlers intermarried with other Israeli communities, and therefore remain very small in number. A ''moshav'' near Jerusalem named " Yad HaShmona", meaning the Memorial for the eight, was established in 1971 by a group of Finnish Christian Israelis, though today most members are Israeli, and predominantly Hebrew-speaking.Samaritans
 The Samaritans are an ethnoreligious group of the
The Samaritans are an ethnoreligious group of the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
. Ancestrally, they are descended from a group of Israelite
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stel ...
inhabitants who have connections to ancient Samaria
Samaria (; he, שֹׁמְרוֹן, translit=Šōmrōn, ar, السامرة, translit=as-Sāmirah) is the historic and biblical name used for the central region of Palestine, bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The first ...
from the beginning of the Babylonian captivity
The Babylonian captivity or Babylonian exile is the period in Jewish history during which a large number of Judeans from the ancient Kingdom of Judah were captives in Babylon, the capital city of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, following their defeat ...
up to the beginning of the Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the or ...
. Population estimates made in 2007 show that of the 712 Samaritans, half live in Holon in Israel and half at Mount Gerizim in the West Bank. The Holon community holds Israeli citizenship, while the Gerizim community resides at an Israeli-controlled enclave (Kiryat Luza
Kiryat Luza ( ar, قرية لوزة, he, קרית לוזה) is a Samaritan village situated on Mount Gerizim near the city of Nablus in the West Bank. It is under the joint control of Israel and the Palestinian National Authority, and ...
), holding dual Israeli-Palestinian citizenship.
Vietnamese
The number of Vietnamese people in Israel is estimated at 200–400. Most of them came to Israel between 1976 and 1979, after the Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin granted them political asylum. The Vietnamese people living in Israel are Israeli citizens who also serve in the Israel Defense Forces. Today, the majority of the community lives in the Gush Dan area in the center of Israel but also a few dozen Vietnamese-Israelis or Israelis of Vietnamese origin live inHaifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropol ...
, Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
and Ofakim.
Non-citizens
African refugees
 The number and status of African refugees in Israel is disputed and controversial, but it is estimated that at least 16,000 refugees, mainly from Eritrea,
The number and status of African refugees in Israel is disputed and controversial, but it is estimated that at least 16,000 refugees, mainly from Eritrea, Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
, South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of th ...
, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
and the Ivory Coast, reside and work in Israel. A check in late 2011, published in Ynet reported that the number just in Tel Aviv is 40,000, which represents 10 percent of the city's population. The vast majority lives in the southern parts of the city. There is also a significant African population in the southern Israeli cities of Eilat, Arad and Beer Sheva.
Other refugees
Approximately 100–200 refugees from Bosnia,Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a international recognition of Kosovo, partiall ...
, and North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and T ...
live in Israel as refugees, most of them with Israeli resident status.
Israeli diaspora
Through the years, the majority of Israelis who emigrated from Israel went to the United States, Canada and the United Kingdom. It is currently estimated that there are 330,000 native-born Israelis, including 230,000 Jews, living abroad, or even more. The number of immigrants to Israel who later returned to their home countries or moved elsewhere is more difficult to calculate. For many years definitive data on Israeli emigration was unavailable. In ''The Israeli Diaspora'' sociologist Stephen J. Gold maintains that calculation of Jewish emigration has been a contentious issue, explaining, "Since Zionism, the philosophy that underlies the existence of the Jewish state, calls for return home of the world's Jews, the opposite movement – Israelis leaving the Jewish state to reside elsewhere – clearly presents an ideological and demographic problem." Among the most common reasons for emigration of Israelis from Israel are most often due to Israel's ongoing security issues, economic constraints, economic characteristics, disappointment in the Israeli government, as well as the excessive role of religion in the lives of Israelis.United States
Many Israelis immigrated to the United States throughout the period of the declaration of the state of Israel and until today. Today, the descendants of these people are known as Israeli-Americans. According to the2000 United States Census
The United States census of 2000, conducted by the Census Bureau, determined the resident population of the United States on April 1, 2000, to be 281,421,906, an increase of 13.2 percent over the 248,709,873 people enumerated during the 1990 c ...
, 106,839 Americans also hold Israeli citizenship, but the number of Americans of Israeli descent is around half a million.
Russia
Moscow has the largest single Israeliexpatriate
An expatriate (often shortened to expat) is a person who resides outside their native country. In common usage, the term often refers to educated professionals, skilled workers, or artists taking positions outside their home country, either ...
community in the world, with 80,000 Israeli citizens living in the city as of 2014, almost all of them native Russian-speakers.Israelis Find A Lively Jewish Niche in Moscowby Rena Greenberg – Moscow, Russia, 19 March 2014 Many Israeli cultural events are hosted for the community, and many live part of the year in Israel. (To cater to the Israeli community, Israeli cultural centres are located in
Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
, Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
, Novosibirsk and Yekaterinburg.)
Canada
Many Israelis immigrated to Canada throughout the period of the declaration of the state of Israel and until today. Today, the descendants of these people are known as Israeli-Canadians. According to the Canada 2006 Census as many as 21,320 Israelis lived in Canada in 2006.Immigrant population by place of birth and period of immigration (2006 Census), Statistics Canada
United Kingdom
Many Israelis immigrated to the United Kingdom throughout and since the period of the declaration of the state of Israel. Today, the descendants of these people are known as Israeli-British. According to the United Kingdom 2001 Census, as many as 11,892 Israelis lived in the United Kingdom in 2001. The majority live inLondon
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
.
2013 Supreme Court ruling on nationality
In 2013 a three-judge panel of the Supreme Court of Israel's headed by Court President Asher Grunis rejected an appeal requesting that state-issued identification cards state the nationality of citizens as "Israeli" rather than their religion of origin. In his opinion, Grunis stated that it was not within the court's purview to determine new categories of ethnicity or nationhood. The court's decision responded to a petition by Uzzi Ornan, who refused to be identified as Jewish in 1948 at the foundation of the state of Israel, claiming instead that he was "Hebrew." This was permitted by Israeli authorities at the time. However, by 2000, Ornan wanted to register his nationality as "Israeli". The Interior Ministry refused to allow this, prompting Ornan to file a suit. In 2007, Ornan's suit was joined by former minister Shulamit Aloni and other activists. In the ruling, Justice Hanan Melcer noted Israel currently considers "citizenship and nationality o beseparate."History
 The term "Israelite" refers to members of the Jewish tribes and polities of the Iron Age known from the
The term "Israelite" refers to members of the Jewish tribes and polities of the Iron Age known from the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Kingdom of Israel The Kingdom of Israel may refer to any of the historical kingdoms of ancient Israel, including: Fully independent (c. 564 years) *Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy) (1047–931 BCE), the legendary kingdom established by the Israelites and uniting ...
uniting all twelve biblical Israelite tribes, with the common capital known as the '' Kingdom of Israel The Kingdom of Israel may refer to any of the historical kingdoms of ancient Israel, including: Fully independent (c. 564 years) *Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy) (1047–931 BCE), the legendary kingdom established by the Israelites and uniting ...
City of David "City of David" is a biblical and religious epithet for the ancient city of Jerusalem.
It may also refer to:
* City of David (archaeological site) - an archaeological excavation associated with ancient Jerusalem
* Jerusalem Walls National Park
...
(Jerusalem); and a period in which the northern tribes split away to form an independent Kingdom of Israel
The Kingdom of Israel may refer to any of the historical kingdoms of ancient Israel, including:
Fully independent (c. 564 years)
*Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy) (1047–931 BCE), the legendary kingdom established by the Israelites and uniting ...
, while the southern tribes became part of the Kingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah ( he, , ''Yəhūdā''; akk, 𒅀𒌑𒁕𒀀𒀀 ''Ya'údâ'' 'ia-ú-da-a-a'' arc, 𐤁𐤉𐤕𐤃𐤅𐤃 ''Bēyt Dāwīḏ'', " House of David") was an Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. C ...
. Archaeological research only partially agrees with the biblical narrative.
According to the biblical account, the United Monarchy was formed when there was a large popular expression in favour of introducing a monarchy to rule over the previously decentralised Israelite tribal confederacy. Increasing pressure from the Philistines
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek ( LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, whe ...
and other neighboring tribes is said by the Bible to have forced the Israelites
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
to unite as a more singular state.
The northern Kingdom of Israel was destroyed in ca. 720 BCE by the Neo-Assyrian Empire and its population was forcibly restructured through imperial policy. The southern Kingdom of Judah was conquered by the Neo-Babylonian Empire (586 BCE), inherited by the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
, conquered by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
(332 BCE), ruled by the resulting Hellenistic empires, from which it regained authonomy and eventually independence under the Hasmoneans, conquered by the Roman Republic in 63 BCE, ruled by the client kings of the Herodian dynasty, and finally transformed into a Roman province during the first century CE. Two Jewish revolts, the second one ending in 135 CE, led to the large-scale decimation of the Jewish population in Judea and the end of any type of Jewish territorial self-rule in the Land of Israel or Palestine, as it then came to be known, for many centuries to come.
Palestine was part of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
from 1516 until it was taken by British forces in 1918. The British establishment of colonial political boundaries allowed the Jews to develop autonomous institutions such as the Histadrut and the Knesset. Since the late nineteenth century, the Zionist movement encouraged Jews to immigrate to Palestine and refurbish its land area, considerable but partially uninhabitable due to an abundance of swamps and desert. The resulting influx of Jewish immigrants, as well as the creation of many new settlements, was crucial for the functioning of these new institutions in what would, on 14 May 1948, become the State of Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
.
Culture
 The largest cities in the country
The largest cities in the country Haifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropol ...
, Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( he, תֵּל־אָבִיב-יָפוֹ, translit=Tēl-ʾĀvīv-Yāfō ; ar, تَلّ أَبِيب – يَافَا, translit=Tall ʾAbīb-Yāfā, links=no), often referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the G ...
, and Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
are also the major cultural centers, known for art museums, and many towns and kibbutzim have smaller high-quality museums. Israeli music is very versatile and combines elements of both western and eastern, religious and secular music. It tends to be very eclectic and contains a wide variety of influences from the Diaspora
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of Greeks in the Hellenic world, and later Jews after ...
and more modern cultural importation: Hassidic songs, Asian and Arab pop, especially by Yemenite singers, and Israeli hip hop or heavy metal. Folk dancing, which draws upon the cultural heritage of many immigrant groups, is popular. There is also flourishing modern dance.
Religion
 According to the Israel Central Bureau of Statistics, at the end of 2014, 75% of Israelis were
According to the Israel Central Bureau of Statistics, at the end of 2014, 75% of Israelis were Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
by religion (adherents of Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in th ...
), 17.5% were Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s, 2% Christian, 1.6% Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
and the remaining 3.9% (including immigrants) were not classified by religion.
Roughly 12% of Israeli Jews defined as ''haredim
Haredi Judaism ( he, ', ; also spelled ''Charedi'' in English; plural ''Haredim'' or ''Charedim'') consists of groups within Orthodox Judaism that are characterized by their strict adherence to ''halakha'' (Jewish law) and traditions, in oppos ...
'' (ultra-orthodox religious); an additional 9% are "religious"; 35% consider themselves "traditionalists" (not strictly adhering to Jewish religious law); and 43% are "secular" (termed " hiloni"). Among the seculars, 53% believe in God. However, 78% of all Israelis (and virtually all Israeli Jews) participate in a Passover seder.
Unlike North American Jews, Israelis tend not to align themselves with a movement of Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in th ...
(such as Reform Judaism
Reform Judaism, also known as Liberal Judaism or Progressive Judaism, is a major Jewish denomination that emphasizes the evolving nature of Judaism, the superiority of its ethical aspects to its ceremonial ones, and belief in a continuous sear ...
or Conservative Judaism) but instead tend to define their religious affiliation by degree of their religious practice. Israeli religious life, unlike much of North American Jewish life, does not solely revolve around synagogues or religious community centers.
Among Arab Israelis
The Arab citizens of Israel are the largest ethnic minority in the country. They comprise a hybrid community of Israeli citizens with a heritage of Palestinian citizenship, mixed religions (Muslim, Christian or Druze), bilingual in Arabic an ...
, 82.6% were Muslim (including Ahmadis
Ahmadiyya (, ), officially the Ahmadiyya Muslim Community or the Ahmadiyya Muslim Jama'at (AMJ, ar, الجماعة الإسلامية الأحمدية, al-Jamāʿah al-Islāmīyah al-Aḥmadīyah; ur, , translit=Jamā'at Aḥmadiyyah Musl ...
), 8.8% were Christian and 8.4% were Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
.
The Baháʼí World Centre
The Baháʼí World Centre is the name given to the spiritual and administrative centre of the Baháʼí Faith, representing sites in or near the cities of Acre and Haifa, Israel.
Much of the international governance and coordination of th ...
, which includes the Universal House of Justice
The Universal House of Justice ( fa, بیتالعدل اعظم) is the nine-member supreme ruling body of the Baháʼí Faith. It was envisioned by Baháʼu'lláh, the founder of the Baháʼí Faith, as an institution that could legislate ...
, in Haifa attracts Baháʼí pilgrims from all over the world.
Languages
 Due to its immigrant nature, Israel is one of the most multicultural and multilingual societies in the world.
Due to its immigrant nature, Israel is one of the most multicultural and multilingual societies in the world. Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
and Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
are the official languages in the country, while English and Russian are the two most widely spoken non-official languages. Yiddish (2%) and French (2%) are also spoken. A certain degree of English is spoken widely, and is the language of choice for many Israeli businesses. Courses of Hebrew and English are mandatory in the Israeli matriculation exams (''bagrut''), and most schools also offer one or more out of Arabic, Spanish, German or French. The Israeli government also offers free intensive Hebrew-language courses, known as '' ulpanim'' (singular ''ulpan''), for new Jewish immigrants, to try to help them integrate into Israeli society.
See also
* Demographics of Israel * Culture of Israel *Modern Hebrew
Modern Hebrew ( he, עברית חדשה, ''ʿivrít ḥadašá ', , '' lit.'' "Modern Hebrew" or "New Hebrew"), also known as Israeli Hebrew or Israeli, and generally referred to by speakers simply as Hebrew ( ), is the standard form of the He ...
(Israeli Hebrew)
References
External links
People of Israel
at the Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs
Official website
of the Israel Central Bureau of Statistics * {{Authority control Society of Israel Semitic-speaking peoples