Internationalization and localization on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 According to ''Software without frontiers'', the design aspects to consider when internationalizing a product are "data encoding, data and documentation, software construction, hardware device support, user interaction"; while the key design areas to consider when making a fully internationalized product from scratch are "user interaction, algorithm design and data formats, software services, documentation".
Translation is typically the most time-consuming component of
According to ''Software without frontiers'', the design aspects to consider when internationalizing a product are "data encoding, data and documentation, software construction, hardware device support, user interaction"; while the key design areas to consider when making a fully internationalized product from scratch are "user interaction, algorithm design and data formats, software services, documentation".
Translation is typically the most time-consuming component of
Instantly Learn Localization Testing
* {{Translation navbox Business terms Globalization Information and communication technologies for development International trade Natural language and computing Technical communication Translation Transliteration Word coinage
 In
In computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, e ...
, internationalization and localization (American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
) or internationalisation and localisation (British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in ...
), often abbreviated i18n and L10n, are means of adapting computer software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
At the lowest programming level, executable code consists ...
to different languages, regional peculiarities and technical requirements of a target locale.
Internationalization is the process of designing a software application so that it can be adapted to various languages and regions without engineering changes. Localization is the process of adapting internationalized software for a specific region or language by translating text and adding locale-specific components.
Localization (which is potentially performed multiple times, for different locales) uses the infrastructure or flexibility provided by internationalization (which is ideally performed only once before localization, or as an integral part of ongoing development).
Naming
The terms are frequently abbreviated to thenumeronym
A numeronym is a number-based word. Most commonly, a numeronym is a word where a number is used to form an abbreviation (albeit not an acronym or an initialism). Pronouncing the letters and numbers may sound similar to the full word, as in " K9" ...
s ''i18n'' (where ''18'' stands for the number of letters between the first ''i'' and the last ''n'' in the word ''internationalization'', a usage coined at Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC ), using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president unt ...
in the 1970s or 1980s) and L10n for ''localization'', due to the length of the words. Some writers have the latter acronym capitalized to help distinguish the two.
Some companies, like IBM and Oracle
An oracle is a person or agency considered to provide wise and insightful counsel or prophetic predictions, most notably including precognition of the future, inspired by deities. As such, it is a form of divination.
Description
The word '' ...
, use the term ''globalization
Globalization, or globalisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is the process of interaction and integration among people, companies, and governments worldwide. The term ''globalization'' first appeared in the early 20t ...
'', ''g11n'', for the combination of internationalization and localization.
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washing ...
defines internationalization as a combination of world-readiness and localization. World-readiness is a developer task, which enables a product to be used with multiple scripts and cultures (globalization) and separating user interface resources in a localizable format (localizability, abbreviated to ''L12y'').
Hewlett-Packard
The Hewlett-Packard Company, commonly shortened to Hewlett-Packard ( ) or HP, was an American multinational information technology company headquartered in Palo Alto, California. HP developed and provided a wide variety of hardware components ...
and HP-UX
HP-UX (from "Hewlett Packard Unix") is Hewlett Packard Enterprise's proprietary implementation of the Unix operating system, based on Unix System V (initially System III) and first released in 1984. Current versions support HPE Integrity Ser ...
created a system called "National Language Support" or "Native Language Support" (NLS) to produce localizable software.
Scope
 According to ''Software without frontiers'', the design aspects to consider when internationalizing a product are "data encoding, data and documentation, software construction, hardware device support, user interaction"; while the key design areas to consider when making a fully internationalized product from scratch are "user interaction, algorithm design and data formats, software services, documentation".
Translation is typically the most time-consuming component of
According to ''Software without frontiers'', the design aspects to consider when internationalizing a product are "data encoding, data and documentation, software construction, hardware device support, user interaction"; while the key design areas to consider when making a fully internationalized product from scratch are "user interaction, algorithm design and data formats, software services, documentation".
Translation is typically the most time-consuming component of language localization
Language localisation (or language localization) is the process of adapting a product's translation to a specific country or region. It is the second phase of a larger process of product translation and cultural adaptation (for specific countries ...
. This may involve:
* For film, video, and audio, translation of spoken words or music lyrics, often using either dubbing
Dubbing (re-recording and mixing) is a post-production process used in filmmaking and video production, often in concert with sound design, in which additional or supplementary recordings are lip-synced and "mixed" with original production sou ...
or subtitles
* Text translation for printed materials, digital media (possibly including error messages and documentation)
* Potentially altering images and logos containing text to contain translations or generic icons
* Different translation length and differences in character sizes (e.g. between Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet or Roman alphabet is the collection of letters originally used by the ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered with the exception of extensions (such as diacritics), it used to write English and the o ...
letters and Chinese characters
Chinese characters () are logograms developed for the writing of Chinese. In addition, they have been adapted to write other East Asian languages, and remain a key component of the Japanese writing system where they are known as ''kanji' ...
) can cause layouts that work well in one language to work poorly in others
* Consideration of differences in dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of Linguistics, linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety (linguisti ...
, register
Register or registration may refer to:
Arts entertainment, and media Music
* Register (music), the relative "height" or range of a note, melody, part, instrument, etc.
* ''Register'', a 2017 album by Travis Miller
* Registration (organ), th ...
or variety
Variety may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Entertainment formats
* Variety (radio)
* Variety show, in theater and television
Films
* ''Variety'' (1925 film), a German silent film directed by Ewald Andre Dupont
* ''Variety'' (1935 film), ...
* Writing conventions like:
** Formatting of numbers (especially decimal separator
A decimal separator is a symbol used to separate the integer part from the fractional part of a number written in decimal form (e.g., "." in 12.45). Different countries officially designate different symbols for use as the separator. The cho ...
and digit grouping
A decimal separator is a symbol used to separate the integer part from the fractional part of a number written in decimal form (e.g., "." in 12.45). Different countries officially designate different symbols for use as the separator. The choi ...
)
** Date and time format, possibly including use of different calendars
Standard locale data
Computer software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
At the lowest programming level, executable code consists ...
can encounter differences above and beyond straightforward translation of words and phrases, because computer programs can generate content dynamically. These differences may need to be taken into account by the internationalization process in preparation for translation. Many of these differences are so regular that a conversion between languages can be easily automated. The Common Locale Data Repository
The Common Locale Data Repository Project, often abbreviated as CLDR, is a project of the Unicode Consortium to provide locale data in XML format for use in computer applications. CLDR contains locale-specific information that an operating syst ...
by Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology Technical standard, standard for the consistent character encoding, encoding, representation, and handling of Character (computing), text expre ...
provides a collection of such differences. Its data is used by major operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also in ...
s, including Microsoft Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for serv ...
, macOS
macOS (; previously OS X and originally Mac OS X) is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac computers. Within the market of desktop and lapt ...
and Debian
Debian (), also known as Debian GNU/Linux, is a Linux distribution composed of free and open-source software, developed by the community-supported Debian Project, which was established by Ian Murdock on August 16, 1993. The first version of D ...
, and by major Internet companies or projects such as Google
Google LLC () is an American multinational technology company focusing on search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and consumer electronics. ...
and the Wikimedia Foundation
The Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., or Wikimedia for short and abbreviated as WMF, is an American 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization headquartered in San Francisco, California and registered as a charitable foundation under local laws. Best kno ...
. Examples of such differences include:
* Different "scripts" in different writing systems
A writing system is a method of visually representing verbal communication, based on a script and a set of rules regulating its use. While both writing and speech are useful in conveying messages, writing differs in also being a reliable form ...
use different characters
Character or Characters may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''Character'' (novel), a 1936 Dutch novel by Ferdinand Bordewijk
* ''Characters'' (Theophrastus), a classical Greek set of character sketches attributed to The ...
– a different set of letters, syllograms, logograms, or symbols. Modern systems use the Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology Technical standard, standard for the consistent character encoding, encoding, representation, and handling of Character (computing), text expre ...
standard to represent many different languages with a single character encoding
Character encoding is the process of assigning numbers to Graphics, graphical character (computing), characters, especially the written characters of Language, human language, allowing them to be Data storage, stored, Data communication, transmi ...
.
* Writing direction
A writing system is a method of visually representing verbal communication, based on a script and a set of rules regulating its use. While both writing and speech are useful in conveying messages, writing differs in also being a reliable form ...
is left to right in most European languages, right-to-left in Hebrew and Arabic, or both in boustrophedon
Boustrophedon is a style of writing in which alternate lines of writing are reversed, with letters also written in reverse, mirror-style. This is in contrast to modern European languages, where lines always begin on the same side, usually the le ...
scripts, and optionally vertical in some Asian languages.
* Complex text layout
Complex text layout (CTL) or complex text rendering is the typesetting of writing systems in which the shape or positioning of a grapheme depends on its relation to other graphemes. The term is used in the field of software internationalizatio ...
, for languages where characters change shape depending on context
* Capitalization exists in some scripts and not in others
* Different languages and writing systems have different text sorting rules
* Different languages have different numeral systems
A numeral system (or system of numeration) is a writing system for expressing numbers; that is, a mathematical notation for representing numbers of a given set, using digits or other symbols in a consistent manner.
The same sequence of symbo ...
, which might need to be supported if Western Arabic numerals
Arabic numerals are the ten numerical digits: , , , , , , , , and . They are the most commonly used symbols to write decimal numbers. They are also used for writing numbers in other systems such as octal, and for writing identifiers such as ...
are not used
* Different languages have different pluralization rules, which can complicate programs that dynamically display numerical content. Other grammar rules might also vary, e.g. genitive
In grammar, the genitive case (abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can al ...
.
* Different languages use different punctuation (e.g. quoting text using double-quotes (" ") as in English, or guillemet
Guillemets (, also , , ) are a pair of punctuation marks in the form of sideways double chevrons, and , used as quotation marks in a number of languages. In some of these languages "single" guillemets, and , are used for a quotation inside a ...
s (« ») as in French)
* Keyboard shortcut
computing, a keyboard shortcut also known as hotkey is a series of one or several keys to quickly invoke a software program or perform a preprogrammed action. This action may be part of the standard functionality of the operating system or ...
s can only make use of buttons actually on the keyboard layout
A keyboard layout is any specific physical, visual or functional arrangement of the keys, legends, or key-meaning associations (respectively) of a computer keyboard, mobile phone, or other computer-controlled typographic keyboard.
is the actua ...
which is being localized for. If a shortcut corresponds to a word in a particular language (e.g. Ctrl-s stands for "save" in English), it may need to be changed.
National conventions
Different countries have different economic conventions, including variations in: *Paper size
Paper size standards govern the size of sheets of paper used as writing paper, stationery, cards, and for some printed documents.
The ISO 216 standard, which includes the commonly used A4 size, is the international standard for paper size. ...
s
* Broadcast television systems
Broadcast television systems (or terrestrial television systems outside the US and Canada) are the encoding or formatting systems for the transmission and reception of terrestrial television signals.
Analog television systems were standardized by ...
and popular storage media
Data storage is the recording (storing) of information (data) in a storage medium. Handwriting, phonographic recording, magnetic tape, and optical discs are all examples of storage media. Biological molecules such as RNA and DNA are consi ...
* Telephone number formats
* Postal address formats, postal code
A postal code (also known locally in various English-speaking countries throughout the world as a postcode, post code, PIN or ZIP Code) is a series of letters or digits or both, sometimes including spaces or punctuation, included in a postal a ...
s, and choice of delivery services
* Currency
A currency, "in circulation", from la, currens, -entis, literally meaning "running" or "traversing" is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins.
A more general def ...
(symbols
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
, positions of currency markers, and reasonable amounts due to different inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reductio ...
histories) – ISO 4217
ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that defines alpha codes and numeric codes for the representation of currencies and provides information about the relationships between individual cu ...
codes are often used for internationalization
* System of measurement
A system of measurement is a collection of units of measurement and rules relating them to each other. Systems of measurement have historically been important, regulated and defined for the purposes of science and commerce. Systems of measurement i ...
* Battery sizes
This is a list of the sizes, shapes, and general characteristics of some common primary and secondary battery types in household, automotive and light industrial use.
The complete nomenclature for a battery specifies size, chemistry, terminal ...
* Voltage and current standards
In particular, the United States and Europe differ in most of these cases. Other areas often follow one of these.
Specific third-party services, such as online maps, weather reports, or payment service provider
A payment service provider (PSP) is a third-party company that assists businesses to accept electronic payments, such as credit cards and debit cards payments. PSPs act as intermediaries between those who make payments, i.e. consumers, and thos ...
s, might not be available worldwide from the same carriers, or at all.
Time zone
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, Commerce, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between Country, countries and their Administrative division, subdivisions instead of ...
s vary across the world, and this must be taken into account if a product originally only interacted with people in a single time zone. For internationalization, UTC is often used internally and then converted into a local time zone for display purposes.
Different countries have different legal requirements, meaning for example:
* Regulatory compliance may require customization for a particular jurisdiction, or a change to the product as a whole, such as:
** Privacy law
Privacy law is the body of law that deals with the regulating, storing, and using of personally identifiable information, personal healthcare information, and financial information of individuals, which can be Personally identifiable information ...
compliance
** Additional disclaimer
A disclaimer is generally any statement intended to specify or delimit the scope of rights and obligations that may be exercised and enforced by parties in a legally recognized relationship. In contrast to other terms for legally operative langua ...
s on a web site or packaging
** Different consumer labelling requirements
** Compliance with export restrictions
Export restrictions, or a restriction on exportation, are limitations on the quantity of goods exported to a specific country or countries by a Government. Export restrictions could be aimed at achieving diverse policy objectives such as environ ...
and regulations on encryption
In cryptography, encryption is the process of encoding information. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative form known as ciphertext. Ideally, only authorized parties can decip ...
** Compliance with an Internet censorship
Internet censorship is the legal control or suppression of what can be accessed, published, or viewed on the Internet. Censorship is most often applied to specific internet domains (such as Wikipedia.org) but exceptionally may extend to all Int ...
regime or subpoena
A subpoena (; also subpœna, supenna or subpena) or witness summons is a writ issued by a government agency, most often a court, to compel testimony by a witness or production of evidence under a penalty for failure. There are two common types of ...
procedures
** Requirements for accessibility
Accessibility is the design of products, devices, services, vehicles, or environments so as to be usable by people with disabilities. The concept of accessible design and practice of accessible development ensures both "direct access" (i. ...
** Collecting different taxes, such as sales tax
A sales tax is a tax paid to a governing body for the sales of certain goods and services. Usually laws allow the seller to collect funds for the tax from the consumer at the point of purchase. When a tax on goods or services is paid to a govern ...
, value added tax
A value-added tax (VAT), known in some countries as a goods and services tax (GST), is a type of tax that is assessed incrementally. It is levied on the price of a product or service at each stage of production, distribution, or sale to the end ...
, or customs duties
A tariff is a tax imposed by the government of a country or by a supranational union on imports or exports of goods. Besides being a source of revenue for the government, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and poli ...
** Sensitivity to different political issues, like geographical naming disputes
Geographical renaming is the changing of the name of a geographical feature or area. This can range from the change of a street name to a change to the name of a country. Some names are changed locally but the new names are not recognised by oth ...
and disputed borders shown on maps (e.g., India has proposed a bill that would make failing to show Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
and other areas as intended by the government a crime)
* Government-assigned numbers have different formats (such as passports, Social Security Numbers and other national identification number
A national identification number, national identity number, or national insurance number or JMBG/EMBG is used by the governments of many countries as a means of tracking their citizens, permanent residents, and temporary residents for the purp ...
s)
Localization also may take into account differences in culture, such as:
* Local holidays
* Personal name
A personal name, or full name, in onomastic terminology also known as prosoponym (from Ancient Greek πρόσωπον / ''prósōpon'' - person, and ὄνομα / ''onoma'' - name), is the set of names by which an individual person is known ...
and title
A title is one or more words used before or after a person's name, in certain contexts. It may signify either generation, an official position, or a professional or academic qualification. In some languages, titles may be inserted between the f ...
conventions
* Aesthetics
Aesthetics, or esthetics, is a branch of philosophy that deals with the nature of beauty and taste, as well as the philosophy of art (its own area of philosophy that comes out of aesthetics). It examines aesthetic values, often expressed thr ...
* Comprehensibility and cultural appropriateness of images and color symbolism
Color symbolism in art and anthropology refers to the use of color as a symbol in various cultures. There is great diversity in the use of colors and their associations between cultures and even within the same culture in different time periods. ...
* Ethnicity
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
, clothing, and socioeconomic status of people and architecture of locations pictured
* Local customs and conventions, such as social taboos, popular local religions, or superstitions such as blood types in Japanese culture
The blood type personality theory is a pseudoscientific belief prevalent in Japan and South Korea, which states that a person's blood group system is predictive of a person's personality, temperament, and compatibility with others. The theory is ...
vs. astrological signs in other cultures
Business process for internationalizing software
In order to ''internationalize'' a product, it is important to look at a variety of markets that the product will foreseeably enter. Details such as field length for street addresses, unique format for the address, ability to make the postal code field optional to address countries that do not have postal codes or the state field for countries that do not have states, plus the introduction of new registration flows that adhere to local laws are just some of the examples that make internationalization a complex project. A broader approach takes into account cultural factors regarding for example the adaptation of the business process logic or the inclusion of individual cultural (behavioral) aspects. Already in the 1990s, companies such asBull
A bull is an intact (i.e., not castrated) adult male of the species ''Bos taurus'' (cattle). More muscular and aggressive than the females of the same species (i.e., cows), bulls have long been an important symbol in many religions,
includin ...
used machine translation
Machine translation, sometimes referred to by the abbreviation MT (not to be confused with computer-aided translation, machine-aided human translation or interactive translation), is a sub-field of computational linguistics that investigates t ...
( Systran) in large scale, for all their translation activity: human translators handled pre-editing (making the input machine-readable) and post-editing
Post-editing (or postediting) is the process whereby humans amend machine-generated translation to achieve an acceptable final product. A person who post-edits is called a post-editor. The concept of post-editing is linked to that of pre-editing. ...
.
Engineering
Both in re-engineering an existing software or designing a new internationalized software, the first step of internationalization is to split each potentially locale-dependent part (whether code, text or data) into a separate module. Each module can then either rely on a standard library/dependency or be independently replaced as needed for each locale. The current prevailing practice is for applications to place text in resource files which are loaded during program execution as needed. These strings, stored in resource files, are relatively easy to translate. Programs are often built to reference resource libraries depending on the selected locale data. The storage for translatable and translated strings is sometimes called a message catalog as the strings are called messages. The catalog generally comprises a set of files in a specific localization format and a standard library to handle said format. Onesoftware library
In computer science, a library is a collection of non-volatile resources used by computer programs, often for software development. These may include configuration data, documentation, help data, message templates, pre-written code and subr ...
and format that aids this is gettext
In computing, gettext is an internationalization and localization (i18n and l10n) system commonly used for writing multilingual programs on Unix-like computer operating systems. One of the main benefits of gettext is that it separates program ...
.
Thus to get an application to support multiple languages one would design the application to select the relevant language resource file at runtime. The code required to manage data entry verification and many other locale-sensitive data types also must support differing locale requirements. Modern development systems and operating systems include sophisticated libraries for international support of these types, see also Standard locale data above.
Many localization issues (e.g. writing direction, text sorting) require more profound changes in the software than text translation. For example, OpenOffice.org
OpenOffice.org (OOo), commonly known as OpenOffice, is a discontinued open-source office suite. Active successor projects include LibreOffice (the most actively developed), Apache OpenOffice, Collabora Online (enterprise ready LibreOffice) a ...
achieves this with compilation switches.
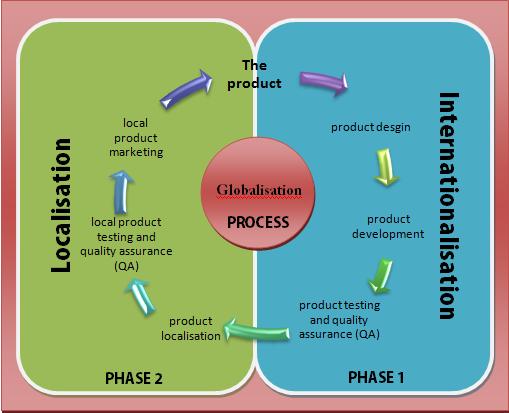
Process
A globalization method includes, after planning, three implementation steps: internationalization, localization and quality assurance. To some degree (e.g. forquality assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is the term used in both manufacturing and service industries to describe the systematic efforts taken to ensure that the product(s) delivered to customer(s) meet with the contractual and other agreed upon performance, design ...
), development teams include someone who handles the basic/central stages of the process which then enable all the others. Such persons typically understand foreign languages and cultures and have some technical background. Specialized technical writers are required to construct a culturally appropriate syntax for potentially complicated concepts, coupled with engineering resources to deploy and test the localization elements.
Once properly internationalized, software can rely on more decentralized models for localization: free and open source software
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is a term used to refer to groups of software consisting of both free software and open-source software where anyone is freely licensed to use, copy, study, and change the software in any way, and the source ...
usually rely on self-localization by end-users and volunteers, sometimes organized in teams. The KDE3
K Desktop Environment 3 is the third series of releases of the K Desktop Environment (after that called ''KDE Software Compilation''). There are six major releases in this series. After the release of KDE 4, version 3.5 was forked into the Trinit ...
project, for example, has been translated into over 100 languages; MediaWiki
MediaWiki is a free and open-source wiki software. It is used on Wikipedia and almost all other Wikimedia websites, including Wiktionary, Wikimedia Commons and Wikidata; these sites define a large part of the requirement set for MediaWiki ...
in 270 languages, of which 100 mostly complete .
When translating existing text to other languages, it is difficult to maintain the parallel versions of texts throughout the life of the product. For instance, if a message displayed to the user is modified, all of the translated versions must be changed.
Commercial considerations
In a commercial setting, the benefit from localization is access to more markets. In the early 1980s,Lotus 1-2-3
Lotus 1-2-3 is a discontinued spreadsheet program from Lotus Software (later part of IBM). It was the first killer application of the IBM PC, was hugely popular in the 1980s, and significantly contributed to the success of IBM PC-compatibles i ...
took two years to separate program code and text and lost the market lead in Europe over Microsoft Multiplan. MicroPro found that using an Austrian translator for the West German market caused its WordStar
WordStar is a word processor application for microcomputers. It was published by MicroPro International and originally written for the CP/M-80 operating system, and later written also for MS-DOS and other 16-bit PC OSes. Rob Barnaby was the so ...
documentation to, an executive said, not "have the tone it should have had".
However, there are considerable costs involved, which go far beyond engineering. Further, business operations must adapt to manage the production, storage and distribution of multiple discrete localized products, which are often being sold in completely different currencies, regulatory environments and tax regimes.
Finally, sales, marketing and technical support must also facilitate their own operations in the new languages, in order to support customers for the localized products. Particularly for relatively small language populations, it may never be economically viable to offer a localized product. Even where large language populations could justify localization for a given product, and a product's internal structure already permits localization, a given software developer or publisher may lack the size and sophistication to manage the ancillary functions associated with operating in multiple locales.
See also
* Subcomponents and standards **Bidirectional script support
A bidirectional text contains two text directionalities, right-to-left (RTL) and left-to-right (LTR). It generally involves text containing different types of alphabets, but may also refer to boustrophedon, which is changing text direction in eac ...
** International Components for Unicode
International Components for Unicode (ICU) is an open-source project of mature C/ C++ and Java libraries for Unicode support, software internationalization, and software globalization. ICU is widely portable to many operating systems and environ ...
** Language code
A language code is a code that assigns letters or numbers as identifiers or classifiers for languages. These codes may be used to organize library collections or presentations of data, to choose the correct localizations and translations in comput ...
** Language localization
Language localisation (or language localization) is the process of adapting a product's translation to a specific country or region. It is the second phase of a larger process of product translation and cultural adaptation (for specific countries ...
** Website localization
Website localization is the process of adapting an existing website to local language and culture in the target market. It is the process of adapting a website into a different linguistic and cultural context— involving much more than the simple ...
* Related concepts
** Computer accessibility
Computer accessibility (also known as accessible computing) refers to the accessibility of a computer system to all people, regardless of disability type or severity of impairment. The term ''accessibility'' is most often used in reference to spe ...
** Computer Russification, localization into Russian language
** Separation of concerns
In computer science, separation of concerns is a design principle for separating a computer program into distinct sections. Each section addresses a separate '' concern'', a set of information that affects the code of a computer program. A concern ...
* Methods and examples
** Game localization
Video game localization (American English), or video game localisation (British English; see spelling differences), is the process of preparing a video game for a market outside of where it was originally published. The game's name, art assets, ...
** Globalization Management System
A translation management system (TMS), formerly globalization management system (GMS), is a type of software for automating many parts of the human language translation process and maximizing translator efficiency. The idea of a translation mana ...
** Pseudolocalization, a software testing
Software testing is the act of examining the artifacts and the behavior of the software under test by validation and verification. Software testing can also provide an objective, independent view of the software to allow the business to apprecia ...
method for testing a software product's readiness for localization.
* Other
** Input method editor
An input method (or input method editor, commonly abbreviated IME) is an operating system component or program that enables users to generate characters not natively available on their input devices by using sequences of characters (or mouse o ...
** Language industry
The language industry is the sector of activity dedicated to facilitating multilingual communication, both oral and written. According to the European Commission's Directorate-General of Translation, the language industry comprises the activitie ...
References
Further reading
* * * *External links
*Instantly Learn Localization Testing
* {{Translation navbox Business terms Globalization Information and communication technologies for development International trade Natural language and computing Technical communication Translation Transliteration Word coinage