Interbreeding on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In biology, a hybrid is the offspring resulting from combining the qualities of two organisms of different breeds, varieties, species or genera through
In biology, a hybrid is the offspring resulting from combining the qualities of two organisms of different breeds, varieties, species or genera through
 The term hybrid is derived from Latin ', used for crosses such as of a tame sow and a wild boar. The term came into popular use in English in the 19th century, though examples of its use have been found from the early 17th century. Conspicuous hybrids are popularly named with portmanteau words, starting in the 1920s with the breeding of tiger–lion hybrids ( liger and tigon).
The term hybrid is derived from Latin ', used for crosses such as of a tame sow and a wild boar. The term came into popular use in English in the 19th century, though examples of its use have been found from the early 17th century. Conspicuous hybrids are popularly named with portmanteau words, starting in the 1920s with the breeding of tiger–lion hybrids ( liger and tigon).
 When two distinct types of organisms breed with each other, the resulting hybrids typically have intermediate traits (e.g., one plant parent has red flowers, the other has white, and the hybrid, pink flowers). Commonly, hybrids also combine traits seen only separately in one parent or the other (e.g., a bird hybrid might combine the yellow head of one parent with the orange belly of the other).
When two distinct types of organisms breed with each other, the resulting hybrids typically have intermediate traits (e.g., one plant parent has red flowers, the other has white, and the hybrid, pink flowers). Commonly, hybrids also combine traits seen only separately in one parent or the other (e.g., a bird hybrid might combine the yellow head of one parent with the orange belly of the other).
 A few animal species are the result of hybridization. The
A few animal species are the result of hybridization. The
 Hybridization between reproductively isolated species often results in hybrid offspring with lower fitness than either parental. However, hybrids are not, as might be expected, always intermediate between their parents (as if there were blending inheritance), but are sometimes stronger or perform better than either parental lineage or variety, a phenomenon called heterosis, hybrid vigour, or heterozygote advantage. This is most common with plant hybrids. A
Hybridization between reproductively isolated species often results in hybrid offspring with lower fitness than either parental. However, hybrids are not, as might be expected, always intermediate between their parents (as if there were blending inheritance), but are sometimes stronger or perform better than either parental lineage or variety, a phenomenon called heterosis, hybrid vigour, or heterozygote advantage. This is most common with plant hybrids. A
 There is a kind of continuum with three semi-distinct categories dealing with anthropogenic hybridization: hybridization without introgression, hybridization with widespread introgression (backcrossing with one of the parent species), and
There is a kind of continuum with three semi-distinct categories dealing with anthropogenic hybridization: hybridization without introgression, hybridization with widespread introgression (backcrossing with one of the parent species), and
 In agriculture and animal husbandry, the Green Revolution's use of conventional hybridization increased yields by breeding "
In agriculture and animal husbandry, the Green Revolution's use of conventional hybridization increased yields by breeding "
File:Zeedonk 800.jpg, A " zonkey", a zebra/donkey hybrid
File:Jaglion.jpg, A "
 Plant species hybridize more readily than animal species, and the resulting hybrids are fertile more often. Many plant species are the result of hybridization, combined with polyploidy, which duplicates the chromosomes. Chromosome duplication allows orderly meiosis and so viable seed can be produced.
Plant hybrids are generally given names that include an "×" (not in italics), such as ''Platanus'' × ''acerifolia'' for the London plane, a natural hybrid of '' P. orientalis'' (oriental plane) and '' P. occidentalis'' (American sycamore). The parent's names may be kept in their entirety, as seen in '' Prunus persica × Prunus americana'', with the female parent's name given first, or if not known, the parent's names given alphabetically.
Plant species that are genetically compatible may not hybridize in nature for various reasons, including geographical isolation, differences in flowering period, or differences in pollinators. Species that are brought together by humans in gardens may hybridize naturally, or hybridization can be facilitated by human efforts, such as altered flowering period or artificial pollination. Hybrids are sometimes created by humans to produce improved plants that have some of the characteristics of each of the parent species. Much work is now being done with hybrids between crops and their wild relatives to improve disease-resistance or
Plant species hybridize more readily than animal species, and the resulting hybrids are fertile more often. Many plant species are the result of hybridization, combined with polyploidy, which duplicates the chromosomes. Chromosome duplication allows orderly meiosis and so viable seed can be produced.
Plant hybrids are generally given names that include an "×" (not in italics), such as ''Platanus'' × ''acerifolia'' for the London plane, a natural hybrid of '' P. orientalis'' (oriental plane) and '' P. occidentalis'' (American sycamore). The parent's names may be kept in their entirety, as seen in '' Prunus persica × Prunus americana'', with the female parent's name given first, or if not known, the parent's names given alphabetically.
Plant species that are genetically compatible may not hybridize in nature for various reasons, including geographical isolation, differences in flowering period, or differences in pollinators. Species that are brought together by humans in gardens may hybridize naturally, or hybridization can be facilitated by human efforts, such as altered flowering period or artificial pollination. Hybrids are sometimes created by humans to produce improved plants that have some of the characteristics of each of the parent species. Much work is now being done with hybrids between crops and their wild relatives to improve disease-resistance or
File:Trilliumhybrid2.jpg, A sterile hybrid between '' Trillium cernuum'' and '' T. grandiflorum''
File:Lily Lilium 'Citronella' Flower.jpg, An ornamental lily hybrid known as ''Lilium'' 'Citronella'
Sterility in a non-polyploid hybrid is often a result of chromosome number; if parents are of differing chromosome pair number, the offspring will have an odd number of chromosomes, which leaves them unable to produce chromosomally-balanced gametes. While that is undesirable in a crop such as wheat, for which growing a crop that produces no seeds would be pointless, it is an attractive attribute in some fruits. Triploid bananas and watermelons are intentionally bred because they produce no seeds and are also parthenocarpic.
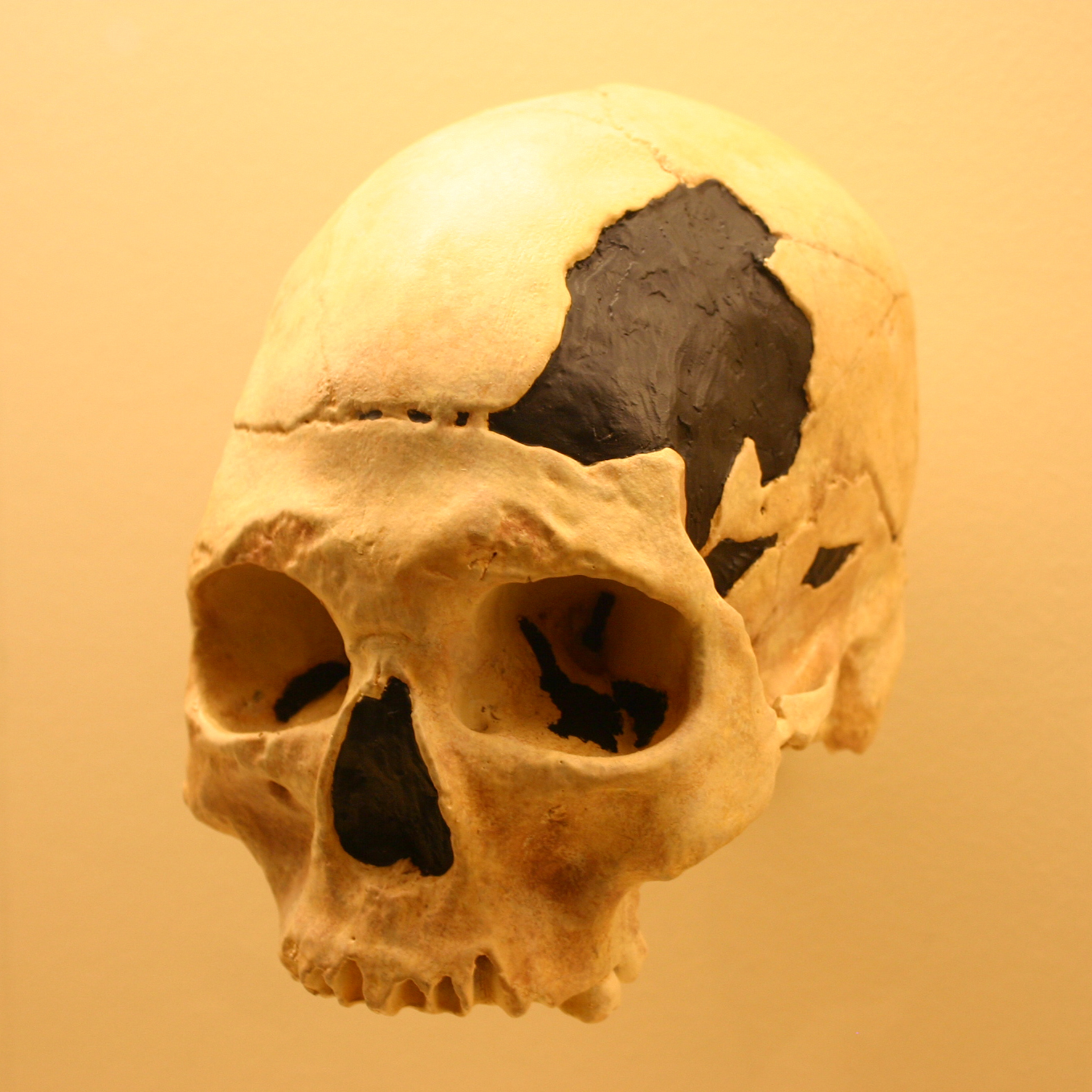 There is evidence of hybridisation between modern humans and other species of the genus ''
There is evidence of hybridisation between modern humans and other species of the genus ''
 Folk tales and myths sometimes contain mythological hybrids; the Minotaur was the offspring of a human, Pasiphaë, and a white bull. More often, they are composites of the physical attributes of two or more kinds of animals, mythical beasts, and humans, with no suggestion that they are the result of interbreeding, as in the centaur (man/horse), chimera (goat/lion/snake), hippocamp (fish/horse), and sphinx (woman/lion). The Old Testament mentions a first generation of half-human hybrid giants, the Nephilim, while the apocryphal Book of Enoch describes the Nephilim as the wicked sons of fallen angels and attractive women.
Folk tales and myths sometimes contain mythological hybrids; the Minotaur was the offspring of a human, Pasiphaë, and a white bull. More often, they are composites of the physical attributes of two or more kinds of animals, mythical beasts, and humans, with no suggestion that they are the result of interbreeding, as in the centaur (man/horse), chimera (goat/lion/snake), hippocamp (fish/horse), and sphinx (woman/lion). The Old Testament mentions a first generation of half-human hybrid giants, the Nephilim, while the apocryphal Book of Enoch describes the Nephilim as the wicked sons of fallen angels and attractive women.
Artificial Hybridisation
– Artificial Hybridisation in orchids
Evolution Revolution: Two Species Become One, Study Says (nationalgeographic.com)
nbsp;– Creation of new species through hybridization was thought to be common only in plants, and rare in animals.
What is a human admixed embryo?
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hybrid (Biology) Biology terminology Botanical nomenclature Evolutionary biology Population genetics Breeding
 In biology, a hybrid is the offspring resulting from combining the qualities of two organisms of different breeds, varieties, species or genera through
In biology, a hybrid is the offspring resulting from combining the qualities of two organisms of different breeds, varieties, species or genera through sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote th ...
. Hybrids are not always intermediates between their parents (such as in blending inheritance), but can show hybrid vigor
Heterosis, hybrid vigor, or outbreeding enhancement is the improved or increased function of any biological quality in a hybrid offspring. An offspring is heterotic if its traits are enhanced as a result of mixing the genetic contributions of ...
, sometimes growing larger or taller than either parent. The concept of a hybrid is interpreted differently in animal and plant breeding, where there is interest in the individual parentage. In genetics, attention is focused on the numbers of chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
s. In taxonomy, a key question is how closely related the parent species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriat ...
are.
Species are reproductively isolated by strong barriers to hybridisation, which include genetic and morphological differences, differing times of fertility, mating behaviors and cues, and physiological rejection of sperm cells or the developing embryo. Some act before fertilization and others after it. Similar barriers exist in plants, with differences in flowering times, pollen vectors, inhibition of pollen tube growth, somatoplastic sterility, cytoplasmic-genic male sterility and the structure of the chromosomes. A few animal species and many plant species, however, are the result of hybrid speciation, including important crop plants such as wheat, where the number of chromosomes has been doubled.
Human impact on the environment has resulted in an increase in the interbreeding between regional species, and the proliferation of introduced species worldwide has also resulted in an increase in hybridisation. This genetic mixing may threaten many species with extinction, while genetic erosion
Genetic erosion (also known as genetic depletion) is a process where the limited gene pool of an endangered species diminishes even more when reproductive individuals die off before reproducing with others in their endangered low population. The ...
from monoculture in crop plants may be damaging the gene pools of many species for future breeding. A form of often intentional human-mediated hybridisation is the crossing of wild and domesticated species. This is common in both traditional horticulture
Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and no ...
and modern agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
; many commercially useful fruits, flowers, garden herbs, and trees have been produced by hybridisation. One such flower, '' Oenothera lamarckiana'', was central to early genetics research into mutationism and polyploidy. It is also more occasionally done in the livestock and pet trades; some well-known wild × domestic hybrids are beefalo and wolfdogs. Human selective breeding
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant ...
of domesticated animals and plants has resulted in the development of distinct breeds
A breed is a specific group of domestic animals having homogeneous appearance ( phenotype), homogeneous behavior, and/or other characteristics that distinguish it from other organisms of the same species. In literature, there exist several slig ...
(usually called cultivars in reference to plants); crossbreed
A crossbreed is an organism with purebred parents of two different breeds, varieties, or populations. ''Crossbreeding'', sometimes called "designer crossbreeding", is the process of breeding such an organism, While crossbreeding is used to main ...
s between them (without any wild stock) are sometimes also imprecisely referred to as "hybrids".
Hybrid humans existed in prehistory. For example, Neanderthals and anatomically modern humans are thought to have interbred as recently as 40,000 years ago.
Mythological hybrids appear in human culture in forms as diverse as the Minotaur, blends of animals, humans and mythical beasts such as centaurs and sphinxes, and the Nephilim of the Biblical apocrypha described as the wicked sons of fallen angels and attractive women.
Etymology
 The term hybrid is derived from Latin ', used for crosses such as of a tame sow and a wild boar. The term came into popular use in English in the 19th century, though examples of its use have been found from the early 17th century. Conspicuous hybrids are popularly named with portmanteau words, starting in the 1920s with the breeding of tiger–lion hybrids ( liger and tigon).
The term hybrid is derived from Latin ', used for crosses such as of a tame sow and a wild boar. The term came into popular use in English in the 19th century, though examples of its use have been found from the early 17th century. Conspicuous hybrids are popularly named with portmanteau words, starting in the 1920s with the breeding of tiger–lion hybrids ( liger and tigon).
As seen by different disciplines
Animal and plant breeding
From the point of view of animal and plant breeders, there are several kinds of hybrid formed from crosses within a species, such as between differentbreeds
A breed is a specific group of domestic animals having homogeneous appearance ( phenotype), homogeneous behavior, and/or other characteristics that distinguish it from other organisms of the same species. In literature, there exist several slig ...
.
Single cross hybrids result from the cross between two true-breeding organism
A true-breeding organism, sometimes also called a purebred ''(biology slang: pure line'' or ''true-breeding line)'', is an organism that always passes down certain phenotypic traits (i.e. physically expressed traits) to its offspring of many genera ...
s which produces an F1 hybrid (first filial generation). The cross between two different homozygous lines produces an F1 hybrid that is heterozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
...
; having two alleles, one contributed by each parent and typically one is dominant and the other recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant ( allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant an ...
. Typically, the F1 generation is also phenotypically
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological proper ...
homogeneous, producing offspring that are all similar to each other.
Double cross hybrids result from the cross between two different F1 hybrids (i.e., there are four unrelated grandparents).
Three-way cross hybrids result from the cross between an F1 hybrid and an inbred line. Triple cross hybrids result from the crossing of two different three-way cross hybrids. Top cross (or "topcross") hybrids result from the crossing of a top quality or pure-bred male and a lower quality female, intended to improve the quality of the offspring, on average.
Population hybrids result from the crossing of plants or animals in one population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction usi ...
with those of another population. These include interspecific hybrids or crosses between different breeds.
In horticulture
Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and no ...
, the term stable hybrid is used to describe an annual plant that, if grown and bred in a small monoculture free of external pollen (e.g., an air-filtered greenhouse) produces offspring that are "true to type" with respect to phenotype; i.e., a true-breeding organism.
Biogeography
Hybridisation can occur in the hybrid zones where the geographical ranges of species, subspecies, or distinct genetic lineages overlap. For example, the butterfly ''Limenitis arthemis
''Limenitis arthemis,'' the red-spotted purple or white admiral, is a North American butterfly species in the cosmopolitan genus '' Limenitis''. It has been studied for its evolution of mimicry, and for the several stable hybrid wing patterns w ...
'' has two major subspecies in North America, ''L. a. arthemis'' (the white admiral) and ''L. a. astyanax'' (the red-spotted purple). The white admiral has a bright, white band on its wings, while the red-spotted purple has cooler blue-green shades. Hybridisation occurs between a narrow area across New England, southern Ontario, and the Great Lakes, the "suture region". It is at these regions that the subspecies were formed. Other hybrid zones have formed between described species of plants and animals.
Genetics
From the point of view of genetics, several different kinds of hybrid can be distinguished. A genetic hybrid carries two differentallele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chrom ...
s of the same gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
, where for instance one allele may code for a lighter coat colour than the other. A structural hybrid results from the fusion of gamete
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce ...
s that have differing structure in at least one chromosome, as a result of structural abnormalities. A numerical hybrid results from the fusion of gametes having different haploid numbers of chromosomes. A permanent hybrid results when only the heterozygous genotype occurs, as in '' Oenothera lamarckiana'', because all homozygous combinations are lethal. In the early history of genetics, Hugo de Vries supposed these were caused by mutation.
Taxonomy
From the point of view of taxonomy, hybrids differ according to their parentage. Hybrids between different subspecies (such as between the Dog and Eurasian wolf) are called intra-specific hybrids. Interspecific hybrids are the offspring frominterspecies mating
Non-reproductive sexual behavior consists of sexual activities animals participate in that do not lead to the reproduction of the species. Although procreation continues to be the primary explanation for sexual behavior in animals, recent obser ...
; these sometimes result in hybrid speciation. Intergeneric hybrids result from matings between different genera, such as between sheep and goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the a ...
s. Interfamilial hybrids, such as between chickens and guineafowl
Guineafowl (; sometimes called "pet speckled hens" or "original fowl") are birds of the family Numididae in the order Galliformes. They are endemic to Africa and rank among the oldest of the gallinaceous birds. Phylogenetically, they branched ...
or pheasants, are reliably described but extremely rare. Interordinal hybrids (between different orders) are few, but have been engineered between the sea urchin '' Strongylocentrotus purpuratus'' (female) and the sand dollar '' Dendraster excentricus'' (male).
Biology
Expression of parental traits
 When two distinct types of organisms breed with each other, the resulting hybrids typically have intermediate traits (e.g., one plant parent has red flowers, the other has white, and the hybrid, pink flowers). Commonly, hybrids also combine traits seen only separately in one parent or the other (e.g., a bird hybrid might combine the yellow head of one parent with the orange belly of the other).
When two distinct types of organisms breed with each other, the resulting hybrids typically have intermediate traits (e.g., one plant parent has red flowers, the other has white, and the hybrid, pink flowers). Commonly, hybrids also combine traits seen only separately in one parent or the other (e.g., a bird hybrid might combine the yellow head of one parent with the orange belly of the other).
Mechanisms of reproductive isolation
Interspecific hybrids are bred by mating individuals from two species, normally from within the same genus. The offspring display traits and characteristics of both parents, but are oftensterile
Sterile or sterility may refer to:
*Asepsis
Asepsis is the state of being free from disease-causing micro-organisms (such as pathogenic bacteria, viruses, pathogenic fungi, and parasites). There are two categories of asepsis: medical and surgi ...
, preventing gene flow between the species. Sterility is often attributed to the different number of chromosomes between the two species. For example, donkeys have 62 chromosomes
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
, horses have 64 chromosomes, and mules or hinnies have 63 chromosomes. Mules, hinnies, and other normally sterile interspecific hybrids cannot produce viable gametes, because differences in chromosome structure prevent appropriate pairing and segregation during meiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately ...
, meiosis is disrupted, and viable sperm and eggs are not formed. However, fertility in female mules has been reported with a donkey as the father.
A variety of mechanisms limit the success of hybridisation, including the large genetic difference between most species. Barriers include morphological differences, differing times of fertility, mating behaviors and cues, and physiological rejection of sperm cells or the developing embryo. Some act before fertilization; others after it.Strickberger, M. 1978. ''Genética''. Omega, Barcelona, España, p.: 874–879. .Futuyma, D. 1998. ''Evolutionary biology'' (3ª edición). Sinauer, Sunderland.
In plants, some barriers to hybridisation include blooming period differences, different pollinator vectors, inhibition of pollen tube growth, somatoplastic sterility, cytoplasmic-genic male sterility and structural differences of the chromosomes.
Speciation
 A few animal species are the result of hybridization. The
A few animal species are the result of hybridization. The Lonicera fly
The ''Lonicera'' fly, a hybrid in the genus ''Rhagoletis'', is a North American fruit fly of the family Tephritidae. Its larvae feed on the berries of species of introduced honeysuckle (''Lonicera'') that were brought to America within the las ...
is a natural hybrid. The American red wolf appears to be a hybrid of the gray wolf and the coyote, although its taxonomic status has been a subject of controversy. The European edible frog is a semi-permanent hybrid between pool frogs and marsh frogs; its population requires the continued presence of at least one of the parent species. Cave paintings indicate that the European bison is a natural hybrid of the aurochs and the steppe bison
The steppe bisonSeveral literatures address the species as ''primeval bison''. or steppe wisent (''Bison'' ''priscus'')
– Y ...
.
– Y ...
Plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae excl ...
hybridization is more commonplace compared to animal hybridization. Many crop species are hybrids, including notably the polyploid wheats: some have four sets of chromosomes (tetraploid) or six (hexaploid), while other wheat species have (like most eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
organisms) two sets ( diploid), so hybridization events likely involved the doubling of chromosome sets, causing immediate genetic isolation.
Hybridization may be important in speciation in some plant groups. However, homoploid hybrid speciation (not increasing the number of sets of chromosomes) may be rare: by 1997, only 8 natural examples had been fully described. Experimental studies suggest that hybridization offers a rapid route to speciation, a prediction confirmed by the fact that early generation hybrids and ancient hybrid species have matching genomes, meaning that once hybridization has occurred, the new hybrid genome can remain stable.
Many hybrid zones are known where the ranges of two species meet, and hybrids are continually produced in great numbers. These hybrid zones are useful as biological model systems for studying the mechanisms of speciation. Recently DNA analysis of a bear shot by a hunter in the North West Territories confirmed the existence of naturally-occurring and fertile grizzly–polar bear hybrid
A grizzly–polar bear hybrid (also named grolar bear, pizzly bear, zebra bear, grizzlar, or nanulak) is a rare ursid hybrid that has occurred both in captivity and in the wild. In 2006, the occurrence of this hybrid in nature was confirmed by t ...
s.
Hybrid vigour
 Hybridization between reproductively isolated species often results in hybrid offspring with lower fitness than either parental. However, hybrids are not, as might be expected, always intermediate between their parents (as if there were blending inheritance), but are sometimes stronger or perform better than either parental lineage or variety, a phenomenon called heterosis, hybrid vigour, or heterozygote advantage. This is most common with plant hybrids. A
Hybridization between reproductively isolated species often results in hybrid offspring with lower fitness than either parental. However, hybrids are not, as might be expected, always intermediate between their parents (as if there were blending inheritance), but are sometimes stronger or perform better than either parental lineage or variety, a phenomenon called heterosis, hybrid vigour, or heterozygote advantage. This is most common with plant hybrids. A transgressive phenotype
In genetics, transgressive segregation is the formation of extreme phenotypes, or transgressive phenotypes, observed in segregated hybrid populations compared to phenotypes observed in the parental lines. The appearance of these transgressive (extr ...
is a phenotype that displays more extreme characteristics than either of the parent lines. Plant breeders
Plant breeding is the science of changing the traits of plants in order to produce desired characteristics. It has been used to improve the quality of nutrition in products for humans and animals. The goals of plant breeding are to produce cro ...
use several techniques to produce hybrids, including line breeding and the formation of complex hybrids. An economically important example is hybrid maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American English, North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous ...
(corn), which provides a considerable seed yield advantage over open pollinated varieties. Hybrid seed dominates the commercial maize seed market in the United States, Canada and many other major maize-producing countries.
In a hybrid, any trait that falls outside the range of parental variation (and is thus not simply intermediate between its parents) is considered heterotic. ''Positive heterosis'' produces more robust hybrids, they might be stronger or bigger; while the term ''negative heterosis'' refers to weaker or smaller hybrids. Heterosis is common in both animal and plant hybrids. For example, hybrids between a lion and a tigress (" ligers") are much larger than either of the two progenitors, while "tigons
A tigon (), tiglon () (portmanteau of ''tiger'' and ''lion''), or tion () is the hybrid offspring of a male tiger (''Panthera tigris'') and a female lion (''Panthera leo'').
" (lioness × tiger) are smaller. Similarly, the hybrids between the common pheasant ('' Phasianus colchicus'') and domestic fowl ('' Gallus gallus'') are larger than either of their parents, as are those produced between the common pheasant and hen golden pheasant (''Chrysolophus pictus
The golden pheasant (''Chrysolophus pictus''), also known as the Chinese pheasant, and rainbow pheasant, is a gamebird of the order Galliformes (gallinaceous birds) and the family Phasianidae (pheasants). The genus name is from Ancient Greek ' ...
''). Spurs are absent in hybrids of the former type, although present in both parents.
Human influence
Anthropogenic hybridization
Hybridization is greatly influenced by human impact on the environment, through effects such as habitat fragmentation and species introductions. Such impacts make it difficult to conserve the genetics of populations undergoingintrogressive hybridization
Introgression, also known as introgressive hybridization, in genetics is the transfer of genetic material from one species into the gene pool of another by the repeated backcrossing of an interspecific hybrid with one of its parent species. Introg ...
. Humans have introduced species worldwide to environments for a long time, both intentionally for purposes such as biological control, and unintentionally, as with accidental escapes of individuals. Introductions can drastically affect populations, including through hybridization.
Management
 There is a kind of continuum with three semi-distinct categories dealing with anthropogenic hybridization: hybridization without introgression, hybridization with widespread introgression (backcrossing with one of the parent species), and
There is a kind of continuum with three semi-distinct categories dealing with anthropogenic hybridization: hybridization without introgression, hybridization with widespread introgression (backcrossing with one of the parent species), and hybrid swarm
A hybrid swarm is a population of hybrids that has survived beyond the initial hybrid generation, with interbreeding between hybrid individuals and backcrossing with its parent types. Such population are highly variable, with the genetic and phe ...
s (highly variable populations with much interbreeding as well as backcrossing with the parent species). Depending on where a population falls along this continuum, the management plans for that population will change. Hybridization is currently an area of great discussion within wildlife management and habitat management. Global climate change is creating other changes such as difference in population distributions which are indirect causes for an increase in anthropogenic hybridization.
Conservationists disagree on when is the proper time to give up on a population that is becoming a hybrid swarm, or to try and save the still existing pure individuals. Once a population becomes a complete mixture, the goal becomes to conserve those hybrids to avoid their loss. Conservationists treat each case on its merits, depending on detecting hybrids within the population. It is nearly impossible to formulate a uniform hybridization policy, because hybridization can occur beneficially when it occurs "naturally", and when hybrid swarms are the only remaining evidence of prior species, they need to be conserved as well.
Genetic mixing and extinction
Regionally developedecotype
In evolutionary ecology, an ecotype,Greek: ''οίκος'' = home and ''τύπος'' = type, coined by Göte Turesson in 1922 sometimes called ecospecies, describes a genetically distinct geographic variety, population, or race within a species ...
s can be threatened with extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the Endling, last individual of the species, although the Functional ext ...
when new alleles or genes are introduced that alter that ecotype. This is sometimes called genetic mixing. Hybridization and introgression, which can happen in natural and hybrid populations, of new genetic material can lead to the replacement of local genotypes if the hybrids are more fit and have breeding advantages over the indigenous ecotype or species. These hybridization events can result from the introduction of non-native genotypes by humans or through habitat modification, bringing previously isolated species into contact. Genetic mixing can be especially detrimental for rare species in isolated habitats, ultimately affecting the population to such a degree that none of the originally genetically distinct population remains.
Effect on biodiversity and food security
 In agriculture and animal husbandry, the Green Revolution's use of conventional hybridization increased yields by breeding "
In agriculture and animal husbandry, the Green Revolution's use of conventional hybridization increased yields by breeding "high-yielding varieties High-yielding varieties (HYVs) of agricultural crops are usually characterized by a combination of the following traits in contrast to the conventional varieties:
* Higher crop yield per area (hectare)
* Dwarfness
* Improved response to fertilize ...
". The replacement of locally indigenous breeds, compounded with unintentional cross-pollination and crossbreeding (genetic mixing), has reduced the gene pools of various wild and indigenous breeds resulting in the loss of genetic diversity. Since the indigenous breeds are often well-adapted to local extremes in climate and have immunity to local pathogens, this can be a significant genetic erosion of the gene pool for future breeding. Therefore, commercial plant geneticists strive to breed "widely adapted" cultivars to counteract this tendency.
Different taxa
In animals
Mammals
Familiar examples ofequid hybrid Equid hybrids, also called hybrid equines, are created from the crossing of members from the horse family such as a horse, donkey and zebra.Equid Hybrids. (2014, June). Retrieved from http://www.best-top10-list.com/view/article/2811/equid-hybridsHYB ...
s are the mule, a cross between a female horse and a male donkey, and the hinny, a cross between a female donkey and a male horse. Pairs of complementary types like the mule and hinny are called reciprocal hybrids. Polar bears and brown bear
The brown bear (''Ursus arctos'') is a large bear species found across Eurasia and North America. In North America, the populations of brown bears are called grizzly bears, while the subspecies that inhabits the Kodiak Islands of Alaska is k ...
s are another case of a hybridizing species pairs, and introgression among non-sister species of bears appears to have shaped the Ursidae family tree. Among many other mammal crosses are hybrid camels, crosses between a bactrian camel and a dromedary
The dromedary (''Camelus dromedarius'' or ;), also known as the dromedary camel, Arabian camel, or one-humped camel, is a large even-toed ungulate, of the genus '' Camelus'', with one hump on its back.
It is the tallest of the three species o ...
. There are many examples of felid hybrid
A felid hybrid is any of a number of hybrids between various species of the cat family, Felidae. This article deals with hybrids between the species of the subfamily Felinae (feline hybrids).
For hybrids between two species of the genus ''Panth ...
s, including the liger. The oldest known animal hybrid bred by humans is the kunga equid hybrid produced as a draft animal and status symbol 4500 years ago to ancient Syria.
The first known instance of hybrid speciation in marine mammals was discovered in 2014. The clymene dolphin
The Clymene dolphin (''Stenella clymene''), in older texts known as the short-snouted spinner dolphin, is a dolphin endemic to the Atlantic Ocean. It is the only confirmed case of hybrid speciation in marine mammals, descending from the spinner ...
(''Stenella clymene'') is a hybrid of two Atlantic species, the spinner Technology
*Spinner (aeronautics), the aerodynamic cone at the hub of an aircraft propeller
* Spinner (cell culture), laboratory equipment for cultivating plant or mammalian cells
* Spinner (computing), a graphical widget in a GUI
* Spinner (MIT Med ...
and striped dolphins. In 2019, scientists confirmed that a skull found 30 years earlier was a hybrid between the beluga whale and narwhal; dubbed the narluga.
Birds
Cagebird breeders sometimes breed bird hybrids known as mules between species of finch, such as goldfinch ×canary
Canary originally referred to the island of Gran Canaria on the west coast of Africa, and the group of surrounding islands (the Canary Islands). It may also refer to:
Animals Birds
* Canaries, birds in the genera '' Serinus'' and ''Crithagra'' ...
.
Amphibians
Among amphibians, Japanese giant salamanders and Chinese giant salamanders have created hybrids that threaten the survival of Japanese giant salamanders because of competition for similar resources in Japan.Fish
Among fish, a group of about fifty natural hybrids betweenAustralian blacktip shark
The Australian blacktip shark (''Carcharhinus tilstoni'') is a species of requiem shark, in the family Carcharhinidae, endemic to northern and eastern Australia. Favoring the upper and middle parts of the water column, it can be found from the ...
and the larger common blacktip shark was found by Australia's eastern coast in 2012.
Russian sturgeon and American paddlefish were hybridized in captivity when sperm from the paddlefish and eggs from the sturgeon were combined, unexpectedly resulting in viable offspring. This hybrid is called a sturddlefish
The sturddlefish is a hybrid of the American paddlefish (''Polyodon spathula'') and the Russian sturgeon (''Acipenser gueldenstaedtii''), accidentally created by researchers in 2019 and announced in 2020. Obtaining living hybrids through breed ...
.
Cephalochordates
The two generaAsymmetron
''Asymmetron'' is a genus of lancelets belonging to the family Branchiostomatidae
Branchiostomatidae is a family of lancelets belonging to the class Leptocardii, order unknown.
Genera:
* '' Asymmetron'' Andrews, 1893
* ''Branchiostoma
''B ...
and Branchiostoma are able to produce viable hybrid offspring, even if none have lived into adulthood so far, despite the parents' common ancestor living tens of millions of years ago.
Insects
Among insects, so-called killer bees were accidentally created during an attempt to breed a strain of bees that would both produce more honey and be better adapted to tropical conditions. It was done by crossing a European honey bee and an African bee. The ''Colias eurytheme
''Colias eurytheme'', the orange sulphur, also known as the alfalfa butterfly and in its larval stage as the alfalfa caterpillar, is a butterfly of the family Pieridae, where it belongs to the lowland group of " clouded yellows and sulphurs" sub ...
'' and '' C. philodice'' butterflies have retained enough genetic compatibility to produce viable hybrid offspring. Hybrid speciation may have produced the diverse '' Heliconius'' butterflies, but that is disputed.
The two closely related harvester ant species Pogonomyrmex barbatus and Pogonomyrmex rugosus have evolved to depend on hybridization. When a queen fertilize her eggs with sperm from males of her own species, the offspring is always new queens. And when she fertilize the eggs with sperm from males of the other species, the offspring is always sterile worker ants (and because ants are haplodiploid, unfertilized eggs become males). Without mating with males of the other species, the queens are unable to produce workers, and will fail to establish a colony of their own.
jaglion
A ''Panthera'' hybrid is a crossbreed between individuals of any of the five species of the genus ''Panthera'': the tiger, lion, jaguar, leopard, and snow leopard. Most hybrids would not be perpetuated in the wild as the territories of the pa ...
", a jaguar/lion hybrid
File:Goldfinch Canary hybrid.JPG, A domestic canary/goldfinch hybrid
In plants
 Plant species hybridize more readily than animal species, and the resulting hybrids are fertile more often. Many plant species are the result of hybridization, combined with polyploidy, which duplicates the chromosomes. Chromosome duplication allows orderly meiosis and so viable seed can be produced.
Plant hybrids are generally given names that include an "×" (not in italics), such as ''Platanus'' × ''acerifolia'' for the London plane, a natural hybrid of '' P. orientalis'' (oriental plane) and '' P. occidentalis'' (American sycamore). The parent's names may be kept in their entirety, as seen in '' Prunus persica × Prunus americana'', with the female parent's name given first, or if not known, the parent's names given alphabetically.
Plant species that are genetically compatible may not hybridize in nature for various reasons, including geographical isolation, differences in flowering period, or differences in pollinators. Species that are brought together by humans in gardens may hybridize naturally, or hybridization can be facilitated by human efforts, such as altered flowering period or artificial pollination. Hybrids are sometimes created by humans to produce improved plants that have some of the characteristics of each of the parent species. Much work is now being done with hybrids between crops and their wild relatives to improve disease-resistance or
Plant species hybridize more readily than animal species, and the resulting hybrids are fertile more often. Many plant species are the result of hybridization, combined with polyploidy, which duplicates the chromosomes. Chromosome duplication allows orderly meiosis and so viable seed can be produced.
Plant hybrids are generally given names that include an "×" (not in italics), such as ''Platanus'' × ''acerifolia'' for the London plane, a natural hybrid of '' P. orientalis'' (oriental plane) and '' P. occidentalis'' (American sycamore). The parent's names may be kept in their entirety, as seen in '' Prunus persica × Prunus americana'', with the female parent's name given first, or if not known, the parent's names given alphabetically.
Plant species that are genetically compatible may not hybridize in nature for various reasons, including geographical isolation, differences in flowering period, or differences in pollinators. Species that are brought together by humans in gardens may hybridize naturally, or hybridization can be facilitated by human efforts, such as altered flowering period or artificial pollination. Hybrids are sometimes created by humans to produce improved plants that have some of the characteristics of each of the parent species. Much work is now being done with hybrids between crops and their wild relatives to improve disease-resistance or climate resilience
Climate resilience is defined as the "capacity of social, economic and ecosystems to cope with a hazardous event or trend or disturbance".IPCC, 2022Summary for Policymakers .-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, M. Tignor, ...
for both agricultural and horticultural crops.
Some crop plants are hybrids from different genera (intergeneric hybrids), such as Triticale, × ''Triticosecale'', a wheat– rye hybrid. Most modern and ancient wheat breeds are themselves hybrids; bread wheat, ''Triticum aestivum'', is a hexaploid hybrid of three wild grasses. Several commercial fruits including loganberry (''Rubus'' × ''loganobaccus'') and grapefruit (''Citrus'' × ''paradisi'') are hybrids, as are garden herbs such as peppermint
Peppermint (''Mentha'' × ''piperita'') is a hybrid species of mint, a cross between watermint and spearmint. Indigenous to Europe and the Middle East, the plant is now widely spread and cultivated in many regions of the world.Euro+Med Plantb ...
(''Mentha'' × ''piperita''), and trees such as the London plane (''Platanus'' × ''acerifolia''). Among many natural plant hybrids is ''Iris albicans
''Iris albicans'', also known as the cemetery iris, white cemetery iris, or the white flag iris, is a species of iris which was planted on graves in Muslim regions and grows in many countries throughout the Middle East and northern Africa. It was ...
'', a sterile hybrid that spreads by rhizome division, and '' Oenothera lamarckiana'', a flower that was the subject of important experiments by Hugo de Vries that produced an understanding of polyploidy.
In humans
 There is evidence of hybridisation between modern humans and other species of the genus ''
There is evidence of hybridisation between modern humans and other species of the genus ''Homo
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus '' Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' ( modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely rela ...
''. In 2010, the Neanderthal genome project
The Neanderthal genome project is an effort of a group of scientists to sequence the Neanderthal genome, founded in July 2006.
It was initiated by 454 Life Sciences, a biotechnology company based in Branford, Connecticut in the United States and ...
showed that 1–4% of DNA from all people living today, apart from most Sub-Saharan African
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the African co ...
s, is of Neanderthal heritage. Analyzing the genomes of 600 Europeans and East Asians found that combining them covered 20% of the Neanderthal genome that is in the modern human population. Ancient human populations lived and interbred with Neanderthals, Denisovans, and at least one other extinct ''Homo'' species. Thus, Neanderthal and Denisovan DNA has been incorporated into human DNA by introgression.
In 1998, a complete prehistorical skeleton found in Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of th ...
, the Lapedo child, had features of both anatomically modern humans and Neanderthals. Some ancient human skulls with especially large nasal cavities and unusually shaped braincases represent human-Neanderthal hybrids. A 37,000- to 42,000-year-old human jawbone found in Romania's Oase cave contains traces of Neanderthal ancestry from only four to six generations earlier. All genes from Neanderthals in the current human population are descended from Neanderthal fathers and human mothers.
Mythology
 Folk tales and myths sometimes contain mythological hybrids; the Minotaur was the offspring of a human, Pasiphaë, and a white bull. More often, they are composites of the physical attributes of two or more kinds of animals, mythical beasts, and humans, with no suggestion that they are the result of interbreeding, as in the centaur (man/horse), chimera (goat/lion/snake), hippocamp (fish/horse), and sphinx (woman/lion). The Old Testament mentions a first generation of half-human hybrid giants, the Nephilim, while the apocryphal Book of Enoch describes the Nephilim as the wicked sons of fallen angels and attractive women.
Folk tales and myths sometimes contain mythological hybrids; the Minotaur was the offspring of a human, Pasiphaë, and a white bull. More often, they are composites of the physical attributes of two or more kinds of animals, mythical beasts, and humans, with no suggestion that they are the result of interbreeding, as in the centaur (man/horse), chimera (goat/lion/snake), hippocamp (fish/horse), and sphinx (woman/lion). The Old Testament mentions a first generation of half-human hybrid giants, the Nephilim, while the apocryphal Book of Enoch describes the Nephilim as the wicked sons of fallen angels and attractive women.
See also
* Canid hybrid * Chimera (genetics) * Chloroplast capture (botany) * Eukaryote hybrid genome *Felid hybrid
A felid hybrid is any of a number of hybrids between various species of the cat family, Felidae. This article deals with hybrids between the species of the subfamily Felinae (feline hybrids).
For hybrids between two species of the genus ''Panth ...
s
* Genetic admixture
* Genetic erosion
Genetic erosion (also known as genetic depletion) is a process where the limited gene pool of an endangered species diminishes even more when reproductive individuals die off before reproducing with others in their endangered low population. The ...
* Grex (horticulture)
* Hybridogenesis
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek grc, παρθένος, translit=parthénos, lit=virgin, label=none + grc, γένεσις, translit=génesis, lit=creation, label=none) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and development ...
* Hybrot
* Inbreeding
Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the mating or breeding of individuals or organisms that are closely related genetically. By analogy, the term is used in human reproduction, but more commonly refers to the genetic disorders a ...
* Breeding back
Breeding back is a form of artificial selection by the deliberate selective breeding of domestic (but not exclusively) animals, in an attempt to achieve an animal breed with a phenotype that resembles a wild type ancestor, usually one that ha ...
* Interspecific pregnancy
*
*
* Horizontal gene transfer
* Inferring horizontal gene transfer Horizontal or lateral gene transfer (HGT or LGT) is the transmission of portions of genomic DNA between organisms through a process decoupled from vertical inheritance. In the presence of HGT events, different fragments of the genome are the resu ...
* Agrobacterium
''Agrobacterium'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria established by H. J. Conn that uses horizontal gene transfer to cause tumors in plants. ''Agrobacterium tumefaciens'' is the most commonly studied species in this genus. ''Agrobacterium ...
, a bacterium well known for its ability to transfer DNA between itself and plants.
* List of plant hybrids
This is a list of plant hybrids created intentionally or by chance and exploited commercially in agriculture or horticulture. The hybridization
Hybridization (or hybridisation) may refer to:
*Hybridization (biology), the process of combining dif ...
* List of genetic hybrids
* Macropod hybrids
Macropod hybrids are hybrids of animals within the family Macropodidae, which includes kangaroos and wallabies. Several macropod hybrids have been experimentally bred, including:
Some hybrids between similar species have been achieved by housin ...
* Purebred
Purebreds are " cultivated varieties" of an animal species achieved through the process of selective breeding. When the lineage of a purebred animal is recorded, that animal is said to be "pedigreed". Purebreds breed true-to-type which means the ...
* Selective breeding
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant ...
* Genetic use restriction technology
Genetic use restriction technology (GURT), also known as terminator technology or suicide seeds, is the name given to proposed methods for restricting the use of genetically modified crops by activating (or deactivating) some genes only in respon ...
Notes
References
External links
Artificial Hybridisation
– Artificial Hybridisation in orchids
Evolution Revolution: Two Species Become One, Study Says (nationalgeographic.com)
nbsp;– Creation of new species through hybridization was thought to be common only in plants, and rare in animals.
What is a human admixed embryo?
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hybrid (Biology) Biology terminology Botanical nomenclature Evolutionary biology Population genetics Breeding