instant centre of rotation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The instant center of rotation (also, instantaneous velocity center, instantaneous center, or instant center) is the point fixed to a body undergoing planar movement that has zero velocity at a particular instant of time. At this instant, the velocity vectors of the other points in the body generate a circular field around this point which is identical to what is generated by a pure rotation.
Planar movement of a body is often described using a plane figure moving in a two-dimensional plane. The instant center is the point in the moving plane around which all other points are rotating at a specific instant of time.
The continuous movement of a plane has an instant center for every value of the time parameter. This generates a curve called the moving centrode. The points in the fixed plane corresponding to these instant centers form the fixed centrode.
The generalization of this concept to 3-dimensional space is that of a twist around a screw. The screw has an axis which is a line in 3D space (not necessarily through the origin), and the screw also has a finite pitch (a fixed translation along its axis corresponding to a rotation about the screw axis).
 Consider the planar movement of a circular wheel rolling without slipping on a linear road; see sketch 3. The wheel rotates around its axis M, which translates in a direction parallel to the road. The point of contact P of the wheel with road does not slip, which means the point P has zero velocity with respect to the road. Thus, at the instant the point P on the wheel comes in contact with the road it becomes an instant center.
The set of points of the moving wheel that become instant centers is the circle itself, which defines the moving centrode. The points in the fixed plane that correspond to these instant centers is the line of the road, which defines the fixed centrode.
The velocity vector of a point A in the wheel is perpendicular to the segment AP and is proportional to the length of this segment. In particular, the velocities of points in the wheel are determined by the angular velocity of the wheel in rotation around P. The velocity vectors of a number of points are illustrated in sketch 3.
The further a point in the wheel is from the instant center P, the proportionally larger its speed. Therefore, the point at the top of the wheel moves in the same direction as the center M of the wheel, but twice as fast, since it is twice the distance away from P. All points that are a distance equal to the radius of the wheel 'r' from point P move at the same speed as the point M but in different directions. This is shown for a point on the wheel that has the same speed as M but moves in the direction tangent to the circle around P.
Consider the planar movement of a circular wheel rolling without slipping on a linear road; see sketch 3. The wheel rotates around its axis M, which translates in a direction parallel to the road. The point of contact P of the wheel with road does not slip, which means the point P has zero velocity with respect to the road. Thus, at the instant the point P on the wheel comes in contact with the road it becomes an instant center.
The set of points of the moving wheel that become instant centers is the circle itself, which defines the moving centrode. The points in the fixed plane that correspond to these instant centers is the line of the road, which defines the fixed centrode.
The velocity vector of a point A in the wheel is perpendicular to the segment AP and is proportional to the length of this segment. In particular, the velocities of points in the wheel are determined by the angular velocity of the wheel in rotation around P. The velocity vectors of a number of points are illustrated in sketch 3.
The further a point in the wheel is from the instant center P, the proportionally larger its speed. Therefore, the point at the top of the wheel moves in the same direction as the center M of the wheel, but twice as fast, since it is twice the distance away from P. All points that are a distance equal to the radius of the wheel 'r' from point P move at the same speed as the point M but in different directions. This is shown for a point on the wheel that has the same speed as M but moves in the direction tangent to the circle around P.
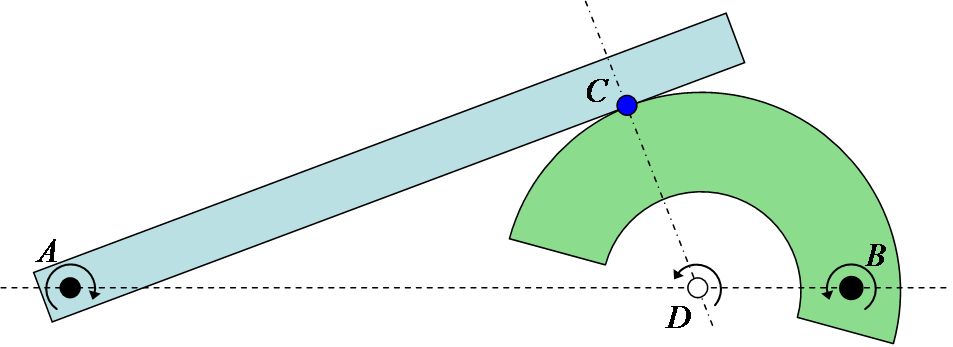 If two planar rigid bodies are in contact, and each body has its own distinct center of rotation, then the relative center of rotation between the bodies has to lie somewhere on the line connecting the two centers. As a result, since pure rolling can only exist when the center of rotation is at the point of contact (as seen above with the wheel on the road), it is only when the point of contact goes through the line connecting the two rotation centers that pure rolling can be achieved. This is known in involute gear design as the pitch point, where there is no relative sliding between the gears. In fact, the gearing ratio between the two rotating parts is found by the ratio of the two distances to the relative center. In the example in Sketch 4 the gearing ratio is
If two planar rigid bodies are in contact, and each body has its own distinct center of rotation, then the relative center of rotation between the bodies has to lie somewhere on the line connecting the two centers. As a result, since pure rolling can only exist when the center of rotation is at the point of contact (as seen above with the wheel on the road), it is only when the point of contact goes through the line connecting the two rotation centers that pure rolling can be achieved. This is known in involute gear design as the pitch point, where there is no relative sliding between the gears. In fact, the gearing ratio between the two rotating parts is found by the ratio of the two distances to the relative center. In the example in Sketch 4 the gearing ratio is
Pole of a planar displacement
The instant center can be considered the limiting case of the pole of a planar displacement. The planar displacement of a body from position 1 to position 2 is defined by the combination of a planarrotation
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional ...
and planar translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
. For any planar displacement there is a point in the moving body that is in the same place before and after the displacement. This point is the ''pole of the planar displacement'', and the displacement can be viewed as a rotation around this pole.
Construction for the pole of a planar displacement: First, select two points A and B in the moving body and locate the corresponding points in the two positions; see the illustration. Construct the perpendicular bisectors to the two segments A1A2 and B1B2. The intersection P of these two bisectors is the pole of the planar displacement. Notice that A1 and A2 lie on a circle around P. This is true for the corresponding positions of every point in the body.
If the two positions of a body are separated by an instant of time in a planar movement, then the pole of a displacement becomes the instant center. In this case, the segments constructed between the instantaneous positions of the points A and B become the velocity vectors VA and VB. The lines perpendicular to these velocity vectors intersect in the instant center.
The algebraic construction of the Cartesian coordinates can be arranged as follows: The midpoint between and
has the Cartesian coordinates
:
and the midpoint between and has the Cartesian coordinates
:
The two angles from to and from to measured counter-clockwise relative to the horizontal are determined by
:
taking the correct branches of the tangent
In geometry, the tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. Leibniz defined it as the line through a pair of infinitely close points on the curve. Mo ...
. Let the center of the rotation have distances and to the two midpoints. Assuming clockwise rotation (otherwise switch the sign of ):
:
Rewrite this as a 4 × 4 inhomogeneous system of linear equations
In mathematics, a system of linear equations (or linear system) is a collection of one or more linear equations involving the same variables.
For example,
:\begin
3x+2y-z=1\\
2x-2y+4z=-2\\
-x+\fracy-z=0
\end
is a system of three equations in t ...
with 4 unknowns (the two distances and the two coordinates of the center):
:
The coordinates of the center of the rotation are the first two components of the solution vector
:
Pure translation
If the displacement between two positions is a pure translation, then the perpendicular bisectors of the segments A1B1 and A2B2 form parallel lines. These lines are considered to intersect at a point on the line at infinity, thus the pole of this planar displacement is said to "lie at infinity" in the direction of the perpendicular bisectors. In the limit, pure translation becomes planar movement with point velocity vectors that are parallel. In this case, the instant center is said to lie at infinity in the direction perpendicular to the velocity vectors.Instant center of a wheel rolling without slipping
 Consider the planar movement of a circular wheel rolling without slipping on a linear road; see sketch 3. The wheel rotates around its axis M, which translates in a direction parallel to the road. The point of contact P of the wheel with road does not slip, which means the point P has zero velocity with respect to the road. Thus, at the instant the point P on the wheel comes in contact with the road it becomes an instant center.
The set of points of the moving wheel that become instant centers is the circle itself, which defines the moving centrode. The points in the fixed plane that correspond to these instant centers is the line of the road, which defines the fixed centrode.
The velocity vector of a point A in the wheel is perpendicular to the segment AP and is proportional to the length of this segment. In particular, the velocities of points in the wheel are determined by the angular velocity of the wheel in rotation around P. The velocity vectors of a number of points are illustrated in sketch 3.
The further a point in the wheel is from the instant center P, the proportionally larger its speed. Therefore, the point at the top of the wheel moves in the same direction as the center M of the wheel, but twice as fast, since it is twice the distance away from P. All points that are a distance equal to the radius of the wheel 'r' from point P move at the same speed as the point M but in different directions. This is shown for a point on the wheel that has the same speed as M but moves in the direction tangent to the circle around P.
Consider the planar movement of a circular wheel rolling without slipping on a linear road; see sketch 3. The wheel rotates around its axis M, which translates in a direction parallel to the road. The point of contact P of the wheel with road does not slip, which means the point P has zero velocity with respect to the road. Thus, at the instant the point P on the wheel comes in contact with the road it becomes an instant center.
The set of points of the moving wheel that become instant centers is the circle itself, which defines the moving centrode. The points in the fixed plane that correspond to these instant centers is the line of the road, which defines the fixed centrode.
The velocity vector of a point A in the wheel is perpendicular to the segment AP and is proportional to the length of this segment. In particular, the velocities of points in the wheel are determined by the angular velocity of the wheel in rotation around P. The velocity vectors of a number of points are illustrated in sketch 3.
The further a point in the wheel is from the instant center P, the proportionally larger its speed. Therefore, the point at the top of the wheel moves in the same direction as the center M of the wheel, but twice as fast, since it is twice the distance away from P. All points that are a distance equal to the radius of the wheel 'r' from point P move at the same speed as the point M but in different directions. This is shown for a point on the wheel that has the same speed as M but moves in the direction tangent to the circle around P.
Relative center of rotation for two contacting planar bodies
 If two planar rigid bodies are in contact, and each body has its own distinct center of rotation, then the relative center of rotation between the bodies has to lie somewhere on the line connecting the two centers. As a result, since pure rolling can only exist when the center of rotation is at the point of contact (as seen above with the wheel on the road), it is only when the point of contact goes through the line connecting the two rotation centers that pure rolling can be achieved. This is known in involute gear design as the pitch point, where there is no relative sliding between the gears. In fact, the gearing ratio between the two rotating parts is found by the ratio of the two distances to the relative center. In the example in Sketch 4 the gearing ratio is
If two planar rigid bodies are in contact, and each body has its own distinct center of rotation, then the relative center of rotation between the bodies has to lie somewhere on the line connecting the two centers. As a result, since pure rolling can only exist when the center of rotation is at the point of contact (as seen above with the wheel on the road), it is only when the point of contact goes through the line connecting the two rotation centers that pure rolling can be achieved. This is known in involute gear design as the pitch point, where there is no relative sliding between the gears. In fact, the gearing ratio between the two rotating parts is found by the ratio of the two distances to the relative center. In the example in Sketch 4 the gearing ratio is
Instant center of rotation and mechanisms
Sketch 1 above shows afour-bar linkage
In the study of mechanisms, a four-bar linkage, also called a four-bar, is the simplest closed-chain movable linkage. It consists of four bodies, called ''bars'' or ''links'', connected in a loop by four joints. Generally, the joints are config ...
where a number of instant centers of rotation are illustrated. The rigid body noted by the letters BAC is connected with links P1-A and P2-B to a base or frame.
The three moving parts of this mechanism (the base is not moving) are: link P1-A, link P2-B, and body BAC. For each of these three parts an instant center of rotation may be determined.
Considering first link P1-A: all points on this link, including point A, rotate around point P1. Since P1 is the only point not moving in the given plane it may be called the instant center of rotation for this link. Point A, at distance P1-A from P1, moves in a circular motion in a direction perpendicular to the link P1-A, as indicated by vector VA.
The same applies to link P2-B: point P2 is the instant center of rotation for this link and point B moves in the direction as indicated by vector VB.
For determining the instant center of rotation of the third element of the linkage, the body BAC, the two points A and B are used because its moving characteristics are known, as derived from the information about the links P1-A and P2-B.
The direction of speed of point A is indicated by vector VA. Its instant center of rotation must be perpendicular to this vector (as VA is tangentially located on the circumference of a circle). The only line that fills the requirement is a line colinear with link P1-A. Somewhere on this line there is a point P, the instant center of rotation for the body BAC.
What applies to point A also applies to point B, therefore this instant center of rotation P is located on a line perpendicular to vector VB, a line colinear with link P2-B. Therefore, the instant center of rotation P of body BAC is the point where the lines through P1-A and P2-B cross.
Since this instant center of rotation P is the center for all points on the body BAC for any random point, say point C, the speed and direction of movement may be determined: connect P to C. The direction of movement of point C is perpendicular to this connection. The speed is proportional to the distance to point P.
Continuing this approach with the two links P1-A and P2-B rotating around their own instant centers of rotation the centrode for instant center of rotation P may be determined. From this the path of movement for C or any other point on body BAC may be determined.
Examples of application
In biomechanical research the instant center of rotation is observed for the functioning of the joints in the upper and lower extremities. For example, in analysing theknee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the ...
,
ankle
The ankle, or the talocrural region, or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joi ...
, or shoulder
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone) as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder mak ...
joints.
Such knowledge assists in developing artificial joints and prosthesis
In medicine, a prosthesis (plural: prostheses; from grc, πρόσθεσις, prósthesis, addition, application, attachment), or a prosthetic implant, is an artificial device that replaces a missing body part, which may be lost through trau ...
, such as elbow or finger joints.
Study of the joints of horses: "...velocity vectors determined from the instant centers of rotation indicated that the joint surfaces slide on each other."
Studies on turning a vessel moving through water.
The braking characteristics of a car may be improved by varying the design of a brake pedal mechanism.
Designing the suspension of a bicycle, or of a car.
In the case of the coupler link in a four-bar linkage
In the study of mechanisms, a four-bar linkage, also called a four-bar, is the simplest closed-chain movable linkage. It consists of four bodies, called ''bars'' or ''links'', connected in a loop by four joints. Generally, the joints are config ...
, such as a double wishbone suspension
A double wishbone suspension is an independent suspension design for automobiles using two (occasionally parallel) wishbone-shaped arms to locate the wheel. Each wishbone or arm has two mounting points to the chassis and one joint at the knuckl ...
in front view, the perpendiculars to the velocity lie along the links joining the grounded link to the coupler link. This construction is used to establish the kinematic
Kinematics is a subfield of physics, developed in classical mechanics, that describes the motion of points, bodies (objects), and systems of bodies (groups of objects) without considering the forces that cause them to move. Kinematics, as a fie ...
roll center
The roll center of a vehicle is the notional point at which the cornering forces in the suspension are reacted to the vehicle body.
There are two definitions of roll center. The most commonly used is the geometric (or kinematic) roll center, wher ...
of the suspension.
See also
*Angular velocity
In physics, angular velocity or rotational velocity ( or ), also known as angular frequency vector,(UP1) is a pseudovector representation of how fast the angular position or orientation of an object changes with time (i.e. how quickly an object ...
* Burmester's theory
In kinematics, Burmester theory comprises geometric techniques for synthesis of linkages. It was introduced in the late 19th century by Ludwig Burmester (1840–1927). His approach was to compute the geometric constraints of the linkage direct ...
* Centrode
* Rigid body
In physics, a rigid body (also known as a rigid object) is a solid body in which deformation is zero or so small it can be neglected. The distance between any two given points on a rigid body remains constant in time regardless of external fo ...
* Roll center
The roll center of a vehicle is the notional point at which the cornering forces in the suspension are reacted to the vehicle body.
There are two definitions of roll center. The most commonly used is the geometric (or kinematic) roll center, wher ...
* Rotation around a fixed axis
Rotation around a fixed axis is a special case of rotational motion. The fixed- axis hypothesis excludes the possibility of an axis changing its orientation and cannot describe such phenomena as wobbling or precession. According to Euler's ...
* Screw axis
A screw axis (helical axis or twist axis) is a line that is simultaneously the axis of rotation and the line along which translation of a body occurs. Chasles' theorem shows that each Euclidean displacement in three-dimensional space has a scr ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Instant centre Of Rotation Classical mechanics Kinematics Rotation