Indo-European language family on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Indo-European languages are a
 Ottoman Turkish traveler Evliya Çelebi visited Vienna in 1665–1666 as part of a diplomatic mission and noted a few similarities between words in German and in Persian.
Gaston Coeurdoux and others made observations of the same type. Coeurdoux made a thorough comparison of Sanskrit, Latin and Greek conjugations in the late 1760s to suggest a relationship among them. Meanwhile, Mikhail Lomonosov compared different language groups, including Slavic, Baltic (" Kurlandic"), Iranian (" Medic"), Finnish, Chinese, "Hottentot" ( Khoekhoe), and others, noting that related languages (including Latin, Greek, German and Russian) must have separated in antiquity from common ancestors.M.V. Lomonosov (drafts for ''Russian Grammar'', published 1755). In: Complete Edition, Moscow, 1952, vol. 7, pp. 652–59
Ottoman Turkish traveler Evliya Çelebi visited Vienna in 1665–1666 as part of a diplomatic mission and noted a few similarities between words in German and in Persian.
Gaston Coeurdoux and others made observations of the same type. Coeurdoux made a thorough comparison of Sanskrit, Latin and Greek conjugations in the late 1760s to suggest a relationship among them. Meanwhile, Mikhail Lomonosov compared different language groups, including Slavic, Baltic (" Kurlandic"), Iranian (" Medic"), Finnish, Chinese, "Hottentot" ( Khoekhoe), and others, noting that related languages (including Latin, Greek, German and Russian) must have separated in antiquity from common ancestors.M.V. Lomonosov (drafts for ''Russian Grammar'', published 1755). In: Complete Edition, Moscow, 1952, vol. 7, pp. 652–59
: Представимъ долготу времени, которою сіи языки раздѣлились. ... Польской и россійской языкъ коль давно раздѣлились! Подумай же, когда курляндской! Подумай же, когда латинской, греч., нѣм., росс. О глубокая древность! magine the depth of time when these languages separated! ... Polish and Russian separated so long ago! Now think how long ago [this happened toKurlandic! Think when [this happened to] Latin, Greek, German, and Russian! Oh, great antiquity!] The hypothesis reappeared in 1786 when William Jones (philologist), Sir William Jones first lectured on the striking similarities among three of the oldest languages known in his time:

 Membership of languages in the Indo-European language family is determined by
Membership of languages in the Indo-European language family is determined by
 The division of the Indo-European languages into satem and centum groups was put forward by Peter von Bradke in 1890, although Karl Brugmann did propose a similar type of division in 1886. In the satem languages, which include the Balto-Slavic and Indo-Iranian branches, as well as (in most respects) Albanian and Armenian, the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European palatovelars remained distinct and were fricativized, while the labiovelars merged with the 'plain velars'. In the centum languages, the palatovelars merged with the plain velars, while the labiovelars remained distinct. The results of these alternative developments are exemplified by the words for "hundred" in Avestan (''satem'') and Latin (''centum'')—the initial palatovelar developed into a fricative in the former, but became an ordinary velar in the latter.
Rather than being a genealogical separation, the centum–satem division is commonly seen as resulting from innovative changes that spread across PIE dialect-branches over a particular geographical area; the centum–satem isogloss intersects a number of other isoglosses that mark distinctions between features in the early IE branches. It may be that the centum branches in fact reflect the original state of affairs in PIE, and only the satem branches shared a set of innovations, which affected all but the peripheral areas of the PIE dialect continuum. Kortlandt proposes that the ancestors of Balts and Slavs took part in satemization before being drawn later into the western Indo-European sphere.
The division of the Indo-European languages into satem and centum groups was put forward by Peter von Bradke in 1890, although Karl Brugmann did propose a similar type of division in 1886. In the satem languages, which include the Balto-Slavic and Indo-Iranian branches, as well as (in most respects) Albanian and Armenian, the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European palatovelars remained distinct and were fricativized, while the labiovelars merged with the 'plain velars'. In the centum languages, the palatovelars merged with the plain velars, while the labiovelars remained distinct. The results of these alternative developments are exemplified by the words for "hundred" in Avestan (''satem'') and Latin (''centum'')—the initial palatovelar developed into a fricative in the former, but became an ordinary velar in the latter.
Rather than being a genealogical separation, the centum–satem division is commonly seen as resulting from innovative changes that spread across PIE dialect-branches over a particular geographical area; the centum–satem isogloss intersects a number of other isoglosses that mark distinctions between features in the early IE branches. It may be that the centum branches in fact reflect the original state of affairs in PIE, and only the satem branches shared a set of innovations, which affected all but the peripheral areas of the PIE dialect continuum. Kortlandt proposes that the ancestors of Balts and Slavs took part in satemization before being drawn later into the western Indo-European sphere.
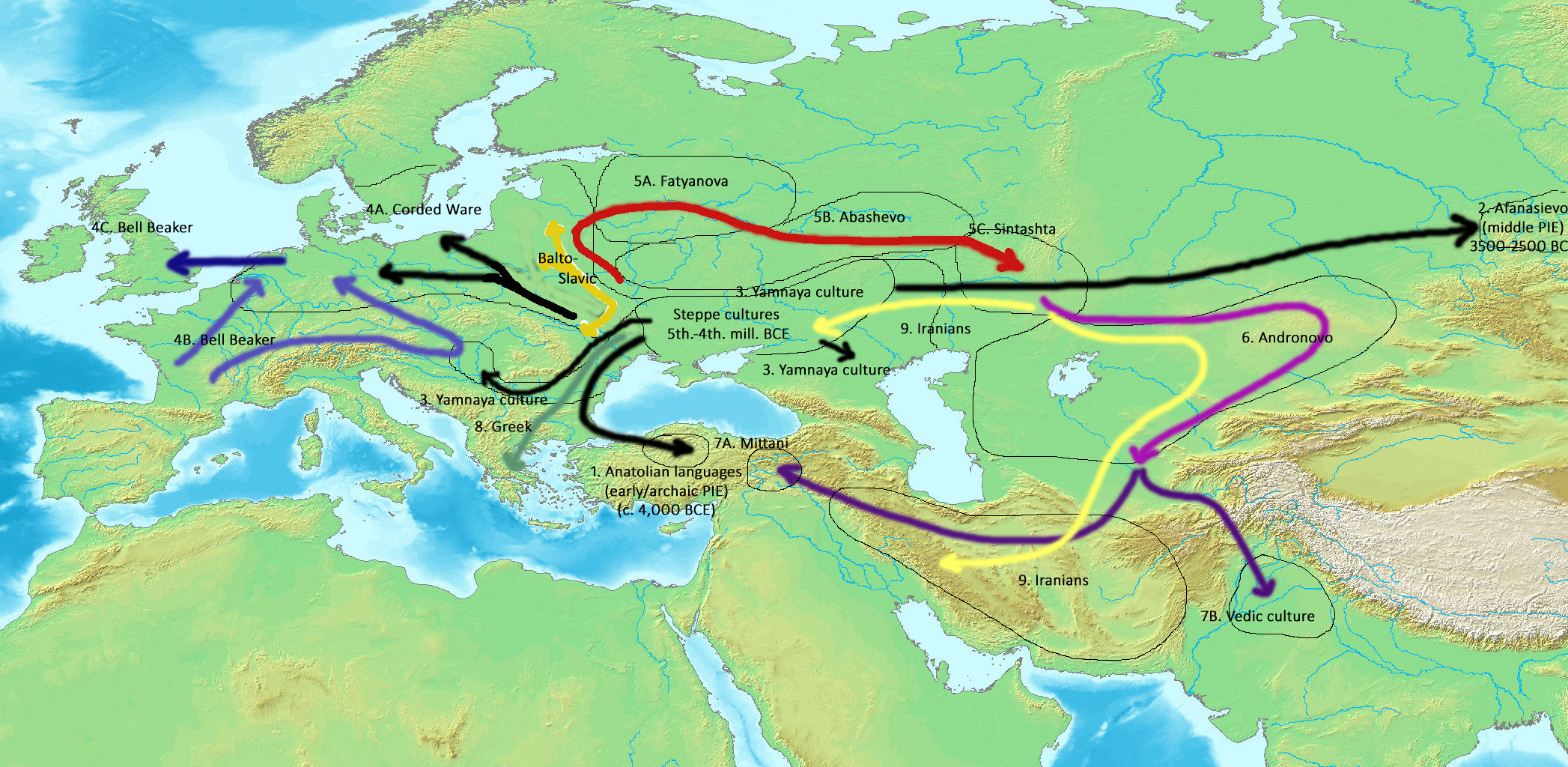 The proposed Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European languages, spoken by the Proto-Indo-Europeans. From the 1960s, knowledge of Anatolian became certain enough to establish its relationship to PIE. Using the method of internal reconstruction, an earlier stage, called Pre-Proto-Indo-European, has been proposed.
PIE was an inflected language, in which the grammatical relationships between words were signaled through inflectional morphemes (usually endings). The
The proposed Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European languages, spoken by the Proto-Indo-Europeans. From the 1960s, knowledge of Anatolian became certain enough to establish its relationship to PIE. Using the method of internal reconstruction, an earlier stage, called Pre-Proto-Indo-European, has been proposed.
PIE was an inflected language, in which the grammatical relationships between words were signaled through inflectional morphemes (usually endings). The

 Today, Indo-European languages are spoken by billions of native speakers across all inhabited continents, the largest number by far for any recognised language family. Of the 20 languages with the largest numbers of speakers according to ''Ethnologue'', 10 are Indo-European:
Today, Indo-European languages are spoken by billions of native speakers across all inhabited continents, the largest number by far for any recognised language family. Of the 20 languages with the largest numbers of speakers according to ''Ethnologue'', 10 are Indo-European:
Part II via Internet Archive
* ** Reprinted in * *
Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture (1997)
an online collection of introductory videos to Ancient Indo-European languages produced by the University of Göttingen
language family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in h ...
native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
. Some European languages of this family, English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their reli ...
in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic
The Balto-Slavic languages form a branch of the Indo-European family of languages, traditionally comprising the Baltic and Slavic languages. Baltic and Slavic languages share several linguistic traits not found in any other Indo-European br ...
, Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foo ...
, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct.
Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Hindi–Urdu, Spanish, Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
, French, Russian, Portuguese, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, and Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
, each with over 100 million native speakers; many others are small and in danger of extinction.
In total, 46% of the world's population (3.2 billion people) speaks an Indo-European language as a first language
A first language, native tongue, native language, mother tongue or L1 is the first language or dialect that a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother to ...
— by far the highest of any language family. There are about 445 living Indo-European languages, according to an estimate by '' Ethnologue'', with over two-thirds (313) of them belonging to the Indo-Iranian branch.
All Indo-European languages are descended from a single prehistoric language, linguistically reconstructed as Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo ...
, spoken sometime in the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
to Early Bronze Age. The geographical location where it was spoken, the Proto-Indo-European homeland
The Proto-Indo-European homeland (or Indo-European homeland) was the prehistoric linguistic homeland of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). From this region, its speakers migrated east and west, and went on to form the proto-communities o ...
, has been the object of many competing hypotheses; the academic consensus supports the Kurgan hypothesis
The Kurgan hypothesis (also known as the Kurgan theory, Kurgan model, or steppe theory) is the most widely accepted proposal to identify the Proto-Indo-European homeland from which the Indo-European languages spread out throughout Europe and pa ...
, which posits the homeland to be the Pontic–Caspian steppe in what is now Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
and southern Russia
Southern Russia or the South of Russia (russian: Юг России, ''Yug Rossii'') is a colloquial term for the southernmost geographic portion of European Russia generally covering the Southern Federal District and the North Caucasian Feder ...
, associated with the Yamnaya culture and other related archaeological cultures during the 4th millennium BC to early 3rd millennium BC. By the time the first written records appeared, Indo-European had already evolved into numerous languages spoken across much of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
, and part of Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes A ...
. Written evidence of Indo-European appeared during the Bronze Age in the form of Mycenaean Greek and the Anatolian languages
The Anatolian languages are an extinct branch of Indo-European languages that were spoken in Anatolia, part of present-day Turkey. The best known Anatolian language is Hittite, which is considered the earliest-attested Indo-European langua ...
of Hittite and Luwian. The oldest records are isolated Hittite words and names — interspersed in texts that are otherwise in the unrelated Akkadian language
Akkadian (, Akkadian: )John Huehnergard & Christopher Woods, "Akkadian and Eblaite", ''The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the World's Ancient Languages''. Ed. Roger D. Woodard (2004, Cambridge) Pages 218-280 is an extinct East Semitic language t ...
, a Semitic language
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, the Horn of Africa, and latterly North Africa, Malta, West Africa, Chad, and in large immigrant ...
— found in texts of the Assyrian
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyri ...
colony of Kültepe in eastern Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
dating to the 20th century BC. Although no older written records of the original Proto-Indo-European population remain, some aspects of their culture and their religion can be reconstructed from later evidence in the daughter cultures. The Indo-European family is significant to the field of historical linguistics
Historical linguistics, also termed diachronic linguistics, is the scientific study of language change over time. Principal concerns of historical linguistics include:
# to describe and account for observed changes in particular languages
# ...
as it possesses the second-longest recorded history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world his ...
of any known family, after the Afroasiatic family in the form of the pre-Arab Egyptian language and the Semitic languages. The analysis of the family relationships between the Indo-European languages, and the reconstruction of their common source, was central to the development of the methodology of historical linguistics as an academic discipline in the 19th century.
The Indo-European family is not known to be linked to any other language family through any more distant genetic relationship, although several disputed proposals to that effect have been made.
History of Indo-European linguistics
During the 16th century, European visitors to theIndian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
began to notice similarities among Indo-Aryan, Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
, and European languages. In 1583, English Jesuit missionary
A missionary is a member of a Religious denomination, religious group which is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Tho ...
and Konkani scholar Thomas Stephens wrote a letter from Goa to his brother (not published until the 20th century) in which he noted similarities between Indian languages and Greek and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
.
Another account was made by Filippo Sassetti
Filippo Sassetti (1540–1588) was a traveller and merchant from a long-established Florentine mercantile family, who was born in Florence in 1540. Though his father had sold family interests and he had to commence as a clerk in a merchant busine ...
, a merchant born in Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
in 1540, who travelled to the Indian subcontinent. Writing in 1585, he noted some word similarities between Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion ...
and Italian (these included ''devaḥ''/''dio'' "God", ''sarpaḥ''/''serpe'' "serpent", ''sapta''/''sette'' "seven", ''aṣṭa''/''otto'' "eight", and ''nava''/''nove'' "nine"). However, neither Stephens' nor Sassetti's observations led to further scholarly inquiry.
In 1647, Dutch linguist and scholar Marcus Zuerius van Boxhorn
Marcus Zuerius van Boxhorn (August 28, 1612 – October 3, 1653) was a Dutch scholar (his Latinized name was Marcus Zuerius Boxhornius). Born in Bergen op Zoom, he was professor at the University of Leiden. He discovered the similarity among Indo- ...
noted the similarity among certain Asian and European languages and theorized that they were derived from a primitive common language which he called Scythian. He included in his hypothesis Dutch, Albanian, Greek, Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
, Persian, and German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, later adding Slavic, Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foo ...
, and Baltic languages. However, Van Boxhorn's suggestions did not become widely known and did not stimulate further research.
 Ottoman Turkish traveler Evliya Çelebi visited Vienna in 1665–1666 as part of a diplomatic mission and noted a few similarities between words in German and in Persian.
Gaston Coeurdoux and others made observations of the same type. Coeurdoux made a thorough comparison of Sanskrit, Latin and Greek conjugations in the late 1760s to suggest a relationship among them. Meanwhile, Mikhail Lomonosov compared different language groups, including Slavic, Baltic (" Kurlandic"), Iranian (" Medic"), Finnish, Chinese, "Hottentot" ( Khoekhoe), and others, noting that related languages (including Latin, Greek, German and Russian) must have separated in antiquity from common ancestors.M.V. Lomonosov (drafts for ''Russian Grammar'', published 1755). In: Complete Edition, Moscow, 1952, vol. 7, pp. 652–59
Ottoman Turkish traveler Evliya Çelebi visited Vienna in 1665–1666 as part of a diplomatic mission and noted a few similarities between words in German and in Persian.
Gaston Coeurdoux and others made observations of the same type. Coeurdoux made a thorough comparison of Sanskrit, Latin and Greek conjugations in the late 1760s to suggest a relationship among them. Meanwhile, Mikhail Lomonosov compared different language groups, including Slavic, Baltic (" Kurlandic"), Iranian (" Medic"), Finnish, Chinese, "Hottentot" ( Khoekhoe), and others, noting that related languages (including Latin, Greek, German and Russian) must have separated in antiquity from common ancestors.M.V. Lomonosov (drafts for ''Russian Grammar'', published 1755). In: Complete Edition, Moscow, 1952, vol. 7, pp. 652–59: Представимъ долготу времени, которою сіи языки раздѣлились. ... Польской и россійской языкъ коль давно раздѣлились! Подумай же, когда курляндской! Подумай же, когда латинской, греч., нѣм., росс. О глубокая древность! magine the depth of time when these languages separated! ... Polish and Russian separated so long ago! Now think how long ago [this happened toKurlandic! Think when [this happened to] Latin, Greek, German, and Russian! Oh, great antiquity!] The hypothesis reappeared in 1786 when William Jones (philologist), Sir William Jones first lectured on the striking similarities among three of the oldest languages known in his time:
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
, Greek, and Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion ...
, to which he tentatively added Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
, Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foo ...
, and Persian, though his classification contained some inaccuracies and omissions. In one of the most famous quotations in linguistics, Jones made the following prescient statement in a lecture to the Asiatic Society of Bengal in 1786, conjecturing the existence of an earlier ancestor language, which he called "a common source" but did not name:
Thomas Young first used the term ''Indo-European'' in 1813, deriving it from the geographical extremes of the language family: from Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
to North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Cen ...
. A synonym is Indo-Germanic (''Idg.'' or ''IdG.''), specifying the family's southeasternmost and northwesternmost branches. This first appeared in French (''indo-germanique'') in 1810 in the work of Conrad Malte-Brun; in most languages this term is now dated or less common than ''Indo-European'', although in German ''indogermanisch'' remains the standard scientific term. A number of other synonymous terms have also been used.
Franz Bopp wrote in 1816 ''On the conjugational system of the Sanskrit language compared with that of Greek, Latin, Persian and Germanic'' and between 1833 and 1852 he wrote ''Comparative Grammar''. This marks the beginning of Indo-European studies
Indo-European studies is a field of linguistics and an interdisciplinary field of study dealing with Indo-European languages, both current and extinct. The goal of those engaged in these studies is to amass information about the hypothetical p ...
as an academic discipline. The classical phase of Indo-European comparative linguistics leads from this work to August Schleicher's 1861 ''Compendium'' and up to Karl Brugmann's '' Grundriss'', published in the 1880s. Brugmann's neogrammarian
The Neogrammarians (German: ''Junggrammatiker'', 'young grammarians') were a German school of linguists, originally at the University of Leipzig, in the late 19th century who proposed the Neogrammarian hypothesis of the regularity of sound chang ...
reevaluation of the field and Ferdinand de Saussure's development of the laryngeal theory may be considered the beginning of "modern" Indo-European studies. The generation of Indo-Europeanists active in the last third of the 20th century (such as Calvert Watkins, Jochem Schindler
Jochem "Joki" Schindler (8 November 1944 in Amstetten, Lower Austria – 24 December 1994 in Prague) was an Austrian Indo-Europeanist. In spite of his comparatively thin bibliography, he made important contributions, in particular to the theory of ...
, and Helmut Rix) developed a better understanding of morphology and of ablaut in the wake of Kuryłowicz's 1956 ''Apophony in Indo-European,'' who in 1927 pointed out the existence of the Hittite consonant ḫ. Kuryłowicz's discovery supported Ferdinand de Saussure's 1879 proposal of the existence of ''coefficients sonantiques'', elements de Saussure reconstructed to account for vowel length alternations in Indo-European languages. This led to the so-called laryngeal theory, a major step forward in Indo-European linguistics and a confirmation of de Saussure's theory.
Classification
The various subgroups of the Indo-European language family include ten major branches, listed below in alphabetical order: * Albanian, attested from the 13th century AD; Proto-Albanian evolved from an ancient Paleo-Balkan language, traditionally thought to be Illyrian, or otherwise a totally unattested Balkan Indo-European language that was closely related to Illyrian and Messapic. * Anatolian, extinct byLate Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English h ...
, spoken in Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, attested in isolated terms in Luwian/ Hittite mentioned in Semitic Old Assyrian texts from the 20th and 19th centuries BC, Hittite texts from about 1650 BC.
* Armenian, attested from the early 5th century AD.
* Balto-Slavic
The Balto-Slavic languages form a branch of the Indo-European family of languages, traditionally comprising the Baltic and Slavic languages. Baltic and Slavic languages share several linguistic traits not found in any other Indo-European br ...
, believed by most Indo-Europeanists to form a phylogenetic unit, while a minority ascribes similarities to prolonged language-contact.
** Slavic (from Proto-Slavic), attested from the 9th century AD ( possibly earlier), earliest texts in Old Church Slavonic. Slavic languages include Bulgarian, Russian, Polish, Czech, Slovak, Silesian, Kashubian, Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North Ma ...
, Serbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian () – also called Serbo-Croat (), Serbo-Croat-Bosnian (SCB), Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian (BCS), and Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS) – is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia an ...
( Bosnian, Croatian, Montenegrin, Serbian
Serbian may refer to:
* someone or something related to Serbia, a country in Southeastern Europe
* someone or something related to the Serbs, a South Slavic people
* Serbian language
* Serbian names
See also
*
*
* Old Serbian (disambiguation ...
), Sorbian, Slovenian
Slovene or Slovenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Slovenia, a country in Central Europe
* Slovene language, a South Slavic language mainly spoken in Slovenia
* Slovenes, an ethno-linguistic group mainly living in Slovenia
* Sl ...
, Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
, Belarusian, and Rusyn
Rusyn may refer to:
* Rusyn people, an East Slavic people
** Pannonian Rusyn people, a branch of Rusyn people
** Lemkos, a branch of Rusyn (or Ukrainian) people
** Boykos, a branch of Rusyn (or Ukrainian) people
* Rusyn language, an East Slavic l ...
.
** Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
, attested from the 14th century AD; although attested relatively recently, they retain many archaic features attributed to Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo ...
(PIE). Living examples are Lithuanian and Latvian.
* Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foo ...
(from Proto-Celtic
Proto-Celtic, or Common Celtic, is the ancestral proto-language of all known Celtic languages, and a descendant of Proto-Indo-European. It is not attested in writing but has been partly reconstructed through the comparative method. Proto-Celt ...
), attested since the 6th century BC; Lepontic
Lepontic is an ancient Alpine Celtic languageJohn T. Koch (ed.) ''Celtic culture: a historical encyclopedia'' ABC-CLIO (2005) that was spoken in parts of Rhaetia and Cisalpine Gaul (now Northern Italy) between 550 and 100 BC. Lepontic is att ...
inscriptions date as early as the 6th century BC; Celtiberian from the 2nd century BC; Primitive Irish
Primitive Irish or Archaic Irish ( ga, Gaeilge Ársa), also called Proto-Goidelic, is the oldest known form of the Goidelic languages. It is known only from fragments, mostly personal names, inscribed on stone in the ogham alphabet in Ireland ...
Ogham inscriptions from the 4th or 5th century AD, earliest inscriptions in Old Welsh from the 7th century AD. Modern Celtic languages include Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
, Cornish, Breton, Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well as ...
, Irish and Manx.
* Germanic (from Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic br ...
), earliest attestations in runic inscriptions from around the 2nd century AD, earliest coherent texts in Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
, 4th century AD. Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th ...
manuscript tradition from about the 8th century AD. Includes English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
, Frisian, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, Dutch, Scots, Danish, Swedish, Norwegian, Afrikaans
Afrikaans (, ) is a West Germanic language that evolved in the Dutch Cape Colony from the Dutch vernacular of Holland proper (i.e., the Hollandic dialect) used by Dutch, French, and German settlers and their enslaved people. Afrikaans gr ...
, Yiddish, Low German, Icelandic, Elfdalian
Elfdalian or Övdalian ( or , pronounced in Elfdalian, or in Swedish) is a North Germanic language spoken by up to 3,000 people who live or have grown up in the locality of Älvdalen ('), which is located in the southeastern part of Älvd ...
, and Faroese.
* Hellenic (from Proto-Greek, see also History of Greek); fragmentary records in Mycenaean Greek from between 1450 and 1350 BC have been found. Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
ic texts date to the 8th century BC.
* Indo-Iranian, attested circa 1400 BC, descended from Proto-Indo-Iranian (dated to the late 3rd millennium BC).
** Indo-Aryan, attested from around 1400 BC in Hittite texts from Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, showing traces of Indo-Aryan words. Epigraphically from the 3rd century BC in the form of Prakrit
The Prakrits (; sa, prākṛta; psu, 𑀧𑀸𑀉𑀤, ; pka, ) are a group of vernacular Middle Indo-Aryan languages that were used in the Indian subcontinent from around the 3rd century BCE to the 8th century CE. The term Prakrit is usu ...
(Edicts of Ashoka
The Edicts of Ashoka are a collection of more than thirty inscriptions on the Pillars of Ashoka, as well as boulders and cave walls, attributed to Emperor Ashoka of the Maurya Empire who reigned from 268 BCE to 232 BCE. Ashoka used the exp ...
). The Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only on ...
is assumed to preserve intact records via oral tradition dating from about the mid- second millennium BC in the form of Vedic Sanskrit. Includes a wide range of modern languages from Northern India, Eastern Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
and Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
, including Hindustani (Hindi
Hindi (Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been ...
, Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
'' Bengali Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to: *something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia * Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region * Bengali language, the language they speak ** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
, '' Bengali Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to: *something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia * Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region * Bengali language, the language they speak ** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
Odia
Odia, also spelled Oriya or Odiya, may refer to:
* Odia people in Odisha, India
* Odia language, an Indian language, belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family
* Odia alphabet, a writing system used for the Odia languag ...
, Assamese, Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
, Kashmiri Kashmiri may refer to:
* People or things related to the Kashmir Valley or the broader region of Kashmir
* Kashmiris, an ethnic group native to the Kashmir Valley
* Kashmiri language, their language
People with the name
* Kashmiri Saikia Baruah ...
, Gujarati
Gujarati may refer to:
* something of, from, or related to Gujarat, a state of India
* Gujarati people, the major ethnic group of Gujarat
* Gujarati language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by them
* Gujarati languages, the Western Indo-Aryan sub- ...
, Marathi, Sindhi
Sindhi may refer to:
*something from, or related to Sindh, a province of Pakistan
* Sindhi people, an ethnic group from the Sindh region
* Sindhi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by them
People with the name
* Sarkash Sindhi (1940–2012 ...
and Nepali
Nepali or Nepalese may refer to :
Concerning Nepal
* Anything of, from, or related to Nepal
* Nepali people, citizens of Nepal
* Nepali language, an Indo-Aryan language found in Nepal, the current official national language and a language spoken ...
, as well as Sinhala of Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
and Dhivehi
Dhivehi, also spelled Divehi, may refer to:
*Dhivehi people, an ethnic group native to the historic region of the Maldive Islands.
*Dhivehi language, an Indo-Aryan language predominantly spoken by about 350,000 people in the Republic of Maldives
...
of the Maldives
Maldives (, ; dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ, translit=Dhivehi Raajje, ), officially the Republic of Maldives ( dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ, translit=Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa, label=none, ), is an archipelag ...
and Minicoy
Minicoy, locally known as Maliku (), is an island in Lakshadweep, India. Along with Viringili, it is on ''Maliku atoll'', the southernmost atoll of Lakshadweep archipelago. Administratively, it is a census town in the Indian union territory o ...
.
** Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
or Iranic, attested from roughly 1000 BC in the form of Avestan. Epigraphically from 520 BC in the form of Old Persian ( Behistun inscription). Includes Persian, Pashto
Pashto (,; , ) is an Eastern Iranian language in the Indo-European language family. It is known in historical Persian literature as Afghani ().
Spoken as a native language mostly by ethnic Pashtuns, it is one of the two official langua ...
, Kurdish Balochi, Luri, and Ossetian.
** Nuristani (includes Kamkata-vari, Vasi-vari
Wasi-wari (Vasi-vari, Wasi-weri) is the language of the Wasi people, spoken in a few villages in the Pârun Valley (Prasun Valley) in Afghanistan. It also goes by the name Prasun or Paruni.
Vasi-vari belongs to the Indo-European language fami ...
, Askunu, Waigali
Waigali (') is a language spoken by about 10,000 Nuristani people of the Waigal Valley in Afghanistan's Nuristan Province. The native name is ''Kalaṣa-alâ'' 'Kalasha-language'. "Waigali" refers to the dialect of the Väy people of the up ...
, Tregami, and Zemiaki).
* Italic (from Proto-Italic), attested from the 7th century BC. Includes the ancient Osco-Umbrian languages, Faliscan, as well as Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
and its descendants, the Romance languages
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language ...
, such as Italian, Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
, Galician, Sardinian, Neapolitan
Neapolitan means of or pertaining to Naples, a city in Italy; or to:
Geography and history
* Province of Naples, a province in the Campania region of southern Italy that includes the city
* Duchy of Naples, in existence during the Early and Hig ...
, Sicilian, Spanish, Asturleonese, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, Romansh, Occitan, Portuguese, Romanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
** Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
***Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
**Romanian cuisine, traditiona ...
, and Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
.
* Tocharian, with proposed links to the Afanasevo culture of Southern Siberia. Extant in two dialects (Turfanian and Kuchean, or Tocharian A and B), attested from roughly the 6th to the 9th century AD. Marginalized by the Old Turkic Uyghur Khaganate and probably extinct by the 10th century.
In addition to the classical ten branches listed above, several extinct and little-known languages and language-groups have existed or are proposed to have existed:
* Ancient Belgian: hypothetical language associated with the proposed Nordwestblock cultural area. Speculated to be connected to Italic or Venetic, and to have certain phonological features in common with Lusitanian.
* Cimmerian: possibly Iranic, Thracian, or Celtic
* Dacian: possibly very close to Thracian
* Elymian: Poorly-attested language spoken by the Elymians, one of the three indigenous (i.e. pre-Greek and pre-Punic) tribes of Sicily. Indo-European affiliation widely accepted, possibly related to Italic or Anatolian.]
* Illyrian: possibly related to Albanian, Messapian, or both
* Liburnian language, Liburnian: evidence too scant and uncertain to determine anything with certainty
* Ligurian: possibly close to or part of Celtic.
* Lusitanian: possibly related to (or part of) Celtic, Ligurian, or Italic
* Ancient Macedonian: proposed relationship to Greek.
* Messapian: not conclusively deciphered
* Paionian: extinct language once spoken north of Macedon
* Phrygian: language of the ancient Phrygians. Very likely, but not certainly, a sister group to Hellenic.
* Sicel: an ancient language spoken by the Sicels (Greek Sikeloi, Latin Siculi), one of the three indigenous (i.e. pre-Greek and pre-Punic) tribes of Sicily. Proposed relationship to Latin or proto-Illyrian (Pre-Indo-European) at an earlier stage.
* Sorothaptic: proposed, pre-Celtic, Iberian language
* Thracian: possibly including Dacian
* Venetic
Venetic is an extinct Indo-European language, usually classified into the Italic subgroup, that was spoken by the Veneti people in ancient times in northeast Italy (Veneto and Friuli) and part of modern Slovenia, between the Po Delta and ...
: shares several similarities with Latin and the Italic languages, but also has some affinities with other IE languages, especially Germanic and Celtic.
 Membership of languages in the Indo-European language family is determined by
Membership of languages in the Indo-European language family is determined by genealogical
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kin ...
relationships, meaning that all members are presumed descendants of a common ancestor, Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo ...
. Membership in the various branches, groups and subgroups of Indo-European is also genealogical, but here the defining factors are ''shared innovations'' among various languages, suggesting a common ancestor that split off from other Indo-European groups. For example, what makes the Germanic languages a branch of Indo-European is that much of their structure and phonology can be stated in rules that apply to all of them. Many of their common features are presumed innovations that took place in Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic br ...
, the source of all the Germanic languages.
In the 21st century, several attempts have been made to model the phylogeny of Indo-European languages using Bayesian methodologies similar to those applied to problems in biological phylogeny. Although there are differences in absolute timing between the various analyses, there is much commonality between them, including the result that the first known language groups to diverge were the Anatolian and Tocharian language families, in that order.
Tree versus wave model
The " tree model" is considered an appropriate representation of the genealogical history of a language family if communities do not remain in contact after their languages have started to diverge. In this case, subgroups defined by shared innovations form a nested pattern. The tree model is not appropriate in cases where languages remain in contact as they diversify; in such cases subgroups may overlap, and the " wave model" is a more accurate representation. Most approaches to Indo-European subgrouping to date have assumed that the tree model is by-and-large valid for Indo-European; however, there is also a long tradition of wave-model approaches. In addition to genealogical changes, many of the early changes in Indo-European languages can be attributed to language contact. It has been asserted, for example, that many of the more striking features shared by Italic languages (Latin, Oscan, Umbrian, etc.) might well be areal features. More certainly, very similar-looking alterations in the systems of long vowels in the West Germanic languages greatly postdate any possible notion of a proto-language innovation (and cannot readily be regarded as "areal", either, because English and continental West Germanic were not a linguistic area). In a similar vein, there are many similar innovations in Germanic and Balto-Slavic that are far more likely areal features than traceable to a common proto-language, such as the uniform development of a high vowel (*''u'' in the case of Germanic, *''i/u'' in the case of Baltic and Slavic) before the PIE syllabic resonants *''ṛ, *ḷ, *ṃ, *ṇ'', unique to these two groups among IE languages, which is in agreement with the wave model. The Balkan sprachbund even features areal convergence among members of very different branches. An extension to the '' Ringe- Warnow model of language evolution'', suggests that early IE had featured limited contact between distinct lineages, with only the Germanic subfamily exhibiting a less treelike behaviour as it acquired some characteristics from neighbours early in its evolution. The internal diversification of especially West Germanic is cited to have been radically non-treelike.Proposed subgroupings
Specialists have postulated the existence of higher-order subgroups such as Italo-Celtic, Graeco-Armenian, Graeco-Aryan or Graeco-Armeno-Aryan, and Balto-Slavo-Germanic. However, unlike the ten traditional branches, these are all controversial to a greater or lesser degree. The Italo-Celtic subgroup was at one point uncontroversial, considered by Antoine Meillet to be even better established than Balto-Slavic. The main lines of evidence included the genitive suffix ''-ī''; the superlative suffix ''-m̥mo''; the change of /p/ to /kʷ/ before another /kʷ/ in the same word (as in ''penkʷe'' > ''*kʷenkʷe'' > Latin ''quīnque'', Old Irish ''cóic''); and the subjunctive morpheme ''-ā-''. This evidence was prominently challenged by Calvert Watkins, while Michael Weiss has argued for the subgroup. Evidence for a relationship between Greek and Armenian includes the regular change of the second laryngeal to ''a'' at the beginnings of words, as well as terms for "woman" and "sheep". Greek and Indo-Iranian share innovations mainly in verbal morphology and patterns of nominal derivation. Relations have also been proposed between Phrygian and Greek, and between Thracian and Armenian. Some fundamental shared features, like the aorist (a verb form denoting action without reference to duration or completion) having the perfect active particle -s fixed to the stem, link this group closer to Anatolian languages and Tocharian. Shared features with Balto-Slavic languages, on the other hand (especially present and preterit formations), might be due to later contacts. TheIndo-Hittite
In Indo-European linguistics, the term Indo-Hittite (also Indo-Anatolian) refers to Edgar Howard Sturtevant's 1926 hypothesis that the Anatolian languages may have split off a Pre- Proto-Indo-European language considerably earlier than the separat ...
hypothesis proposes that the Indo-European language family consists of two main branches: one represented by the Anatolian languages and another branch encompassing all other Indo-European languages. Features that separate Anatolian from all other branches of Indo-European (such as the gender or the verb system) have been interpreted alternately as archaic debris or as innovations due to prolonged isolation. Points proffered in favour of the Indo-Hittite hypothesis are the (non-universal) Indo-European agricultural terminology in Anatolia and the preservation of laryngeals. However, in general this hypothesis is considered to attribute too much weight to the Anatolian evidence. According to another view, the Anatolian subgroup left the Indo-European parent language comparatively late, approximately at the same time as Indo-Iranian and later than the Greek or Armenian divisions. A third view, especially prevalent in the so-called French school of Indo-European studies, holds that extant similarities in non- satem languages in general—including Anatolian—might be due to their peripheral location in the Indo-European language-area and to early separation, rather than indicating a special ancestral relationship. Hans J. Holm, based on lexical calculations, arrives at a picture roughly replicating the general scholarly opinion and refuting the Indo-Hittite hypothesis.
Satem and centum languages
 The division of the Indo-European languages into satem and centum groups was put forward by Peter von Bradke in 1890, although Karl Brugmann did propose a similar type of division in 1886. In the satem languages, which include the Balto-Slavic and Indo-Iranian branches, as well as (in most respects) Albanian and Armenian, the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European palatovelars remained distinct and were fricativized, while the labiovelars merged with the 'plain velars'. In the centum languages, the palatovelars merged with the plain velars, while the labiovelars remained distinct. The results of these alternative developments are exemplified by the words for "hundred" in Avestan (''satem'') and Latin (''centum'')—the initial palatovelar developed into a fricative in the former, but became an ordinary velar in the latter.
Rather than being a genealogical separation, the centum–satem division is commonly seen as resulting from innovative changes that spread across PIE dialect-branches over a particular geographical area; the centum–satem isogloss intersects a number of other isoglosses that mark distinctions between features in the early IE branches. It may be that the centum branches in fact reflect the original state of affairs in PIE, and only the satem branches shared a set of innovations, which affected all but the peripheral areas of the PIE dialect continuum. Kortlandt proposes that the ancestors of Balts and Slavs took part in satemization before being drawn later into the western Indo-European sphere.
The division of the Indo-European languages into satem and centum groups was put forward by Peter von Bradke in 1890, although Karl Brugmann did propose a similar type of division in 1886. In the satem languages, which include the Balto-Slavic and Indo-Iranian branches, as well as (in most respects) Albanian and Armenian, the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European palatovelars remained distinct and were fricativized, while the labiovelars merged with the 'plain velars'. In the centum languages, the palatovelars merged with the plain velars, while the labiovelars remained distinct. The results of these alternative developments are exemplified by the words for "hundred" in Avestan (''satem'') and Latin (''centum'')—the initial palatovelar developed into a fricative in the former, but became an ordinary velar in the latter.
Rather than being a genealogical separation, the centum–satem division is commonly seen as resulting from innovative changes that spread across PIE dialect-branches over a particular geographical area; the centum–satem isogloss intersects a number of other isoglosses that mark distinctions between features in the early IE branches. It may be that the centum branches in fact reflect the original state of affairs in PIE, and only the satem branches shared a set of innovations, which affected all but the peripheral areas of the PIE dialect continuum. Kortlandt proposes that the ancestors of Balts and Slavs took part in satemization before being drawn later into the western Indo-European sphere.
Proposed external relations
From the very beginning of Indo-European studies, there have been attempts to link the Indo-European languages genealogically to other languages and language families. However, these theories remain highly controversial, and most specialists in Indo-European linguistics are sceptical or agnostic about such proposals. Proposals linking the Indo-European languages with a single language family include: *Indo-Uralic
Indo-Uralic is a controversial hypothetical language family consisting of Indo-European and Uralic.
The suggestion of a genetic relationship between Indo-European and Uralic is often credited to the Danish linguist Vilhelm Thomsen in 1869 (P ...
, joining Indo-European with Uralic
The Uralic languages (; sometimes called Uralian languages ) form a language family of 38 languages spoken by approximately 25million people, predominantly in Northern Eurasia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian lan ...
* Pontic, postulated by John Colarusso, which joins Indo-European with Northwest Caucasian
The Northwest Caucasian languages, also called West Caucasian, Abkhazo-Adyghean, Abkhazo-Circassian, Circassic, or sometimes ''Pontic languages'' (from the historical region of Pontus, in contrast to ''Caspian languages'' for the Northeast Cau ...
Other proposed families include:
* Nostratic, comprising all or some of the Eurasiatic languages and the Kartvelian, Dravidian (or wider, Elamo-Dravidian
The Elamo-Dravidian language family is a hypothesised language family that links the Dravidian languages of Pakistan, and Southern India to the extinct Elamite language of ancient Elam (present-day southwestern Iran). Linguist David McAlpin ...
) and Afroasiatic language families
* Eurasiatic, a theory championed by Joseph Greenberg
Joseph Harold Greenberg (May 28, 1915 – May 7, 2001) was an American linguist, known mainly for his work concerning linguistic typology and the genetic classification of languages.
Life Early life and education
Joseph Greenberg was born on ...
, comprising the Uralic
The Uralic languages (; sometimes called Uralian languages ) form a language family of 38 languages spoken by approximately 25million people, predominantly in Northern Eurasia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian lan ...
, Altaic and various 'Paleosiberian
Paleosiberian (or Paleo-Siberian) languages or Paleoasian (Paleo-Asiatic) (from , "ancient") are several linguistic isolates and small families of languages spoken in parts of northeastern Siberia and the Russian Far East. They are not kn ...
' families ( Ainu, Yukaghir, Nivkh, Chukotko-Kamchatkan, Eskimo–Aleut) and possibly others
Nostratic and Eurasiatic, in turn, have been included in even wider groupings, such as Borean, a language family separately proposed by Harold C. Fleming
Harold Crane Fleming (December 23, 1922 – April 29, 2015) was an anthropologist and historical linguist specializing in the cultures and languages of the Horn of Africa. As an adherent of the Four Field School of American anthropology, h ...
and Sergei Starostin that encompasses almost all of the world's natural languages with the exception of those native to sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
, New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torres ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
, and the Andaman Islands.
Objections to such groupings are not based on any theoretical claim about the likely historical existence or nonexistence of such macrofamilies
In historical linguistics, a macrofamily, also called a superfamily or phylum, is a proposed genetic relationship grouping together language families (also isolates) in a larger scale classification. Campbell, Lyle and Mixco, Mauricio J. (2007), ...
; it is entirely reasonable to suppose that they might have existed. The serious difficulty lies in identifying the details of actual relationships between language families, because it is very hard to find concrete evidence that transcends chance resemblance or is not equally likely explained as being due to borrowing, including ''Wanderwörter
A (, 'migrant word', plural ; capitalized like all German nouns) is a word that has spread as a loanword among numerous languages and cultures, especially those that are far away from one another, usually in connection with trade. As such, are ...
'', which can travel very long distances. Because the signal-to-noise ratio in historical linguistics declines over time, at great enough time-depths it becomes open to reasonable doubt that one can even distinguish between signal and noise.
Evolution
Proto-Indo-European
 The proposed Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European languages, spoken by the Proto-Indo-Europeans. From the 1960s, knowledge of Anatolian became certain enough to establish its relationship to PIE. Using the method of internal reconstruction, an earlier stage, called Pre-Proto-Indo-European, has been proposed.
PIE was an inflected language, in which the grammatical relationships between words were signaled through inflectional morphemes (usually endings). The
The proposed Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European languages, spoken by the Proto-Indo-Europeans. From the 1960s, knowledge of Anatolian became certain enough to establish its relationship to PIE. Using the method of internal reconstruction, an earlier stage, called Pre-Proto-Indo-European, has been proposed.
PIE was an inflected language, in which the grammatical relationships between words were signaled through inflectional morphemes (usually endings). The roots
A root is the part of a plant, generally underground, that anchors the plant body, and absorbs and stores water and nutrients.
Root or roots may also refer to:
Art, entertainment, and media
* ''The Root'' (magazine), an online magazine focusing ...
of PIE are basic morpheme
A morpheme is the smallest meaningful Constituent (linguistics), constituent of a linguistic expression. The field of linguistics, linguistic study dedicated to morphemes is called morphology (linguistics), morphology.
In English, morphemes are ...
s carrying a lexical meaning. By addition of suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns, adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can carr ...
es, they form stems, and by addition of endings
End, END, Ending, or variation, may refer to:
End
*In mathematics:
**End (category theory)
** End (topology)
**End (graph theory)
** End (group theory) (a subcase of the previous)
**End (endomorphism)
*In sports and games
** End (gridiron footbal ...
, these form grammatically inflected words ( nouns or verbs). The reconstructed Indo-European verb
Proto-Indo-European verbs reflect a complex system of morphology, more complicated than the substantive, with verbs categorized according to their aspect, using multiple grammatical moods and voices, and being conjugated according to person, nu ...
system is complex and, like the noun, exhibits a system of ablaut.
Diversification
BMAC in "IE languages c. 1500 BC" isBactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex
The Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex (short BMAC) or Oxus Civilization, recently dated to c. 2250–1700 BC,Lyonnet, Bertille, and Nadezhda A. Dubova, (2020b)"Questioning the Oxus Civilization or Bactria- Margiana Archaeological Cultu ...
The diversification of the parent language into the attested branches of daughter languages is historically unattested. The timeline of the evolution of the various daughter languages, on the other hand, is mostly undisputed, quite regardless of the question of Indo-European origins
The Proto-Indo-European homeland (or Indo-European homeland) was the prehistoric linguistic homeland of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). From this region, its speakers migrated east and west, and went on to form the proto-communities of ...
.
Using a mathematical analysis borrowed from evolutionary biology, Donald Ringe and Tandy Warnow propose the following evolutionary tree of Indo-European branches:
* Pre- Anatolian (before 3500 BC)
* Pre- Tocharian
* Pre-Italic and Pre-Celtic (before 2500 BC)
* Pre-Armenian and Pre-Greek (after 2500 BC)
* Proto- Indo-Iranian (2000 BC)
* Pre-Germanic and Pre-Balto-Slavic; proto-Germanic c. 500 BC
David Anthony proposes the following sequence:
* Pre- Anatolian (4200 BC)
* Pre- Tocharian (3700 BC)
* Pre-Germanic (3300 BC)
* Pre-Italic and Pre-Celtic (3000 BC)
* Pre-Armenian (2800 BC)
* Pre-Balto-Slavic (2800 BC)
* Pre-Greek (2500 BC)
* Proto- Indo-Iranian (2200 BC); split between Iranian and Old Indic 1800 BC
From 1500 BC the following sequence may be given:
* 1500–1000 BC: The Nordic Bronze Age develops pre-Proto-Germanic, and the (pre)-Proto-Celtic
Proto-Celtic, or Common Celtic, is the ancestral proto-language of all known Celtic languages, and a descendant of Proto-Indo-European. It is not attested in writing but has been partly reconstructed through the comparative method. Proto-Celt ...
Urnfield and Hallstatt
Hallstatt ( , , ) is a small town in the district of Gmunden, in the Austrian state of Upper Austria. Situated between the southwestern shore of Hallstätter See and the steep slopes of the Dachstein massif, the town lies in the Salzkammergut ...
cultures emerge in Central Europe, introducing the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ...
. Migration of the Proto- Italic speakers into the Italian peninsula (Bagnolo stele
The Bagnolo steles are two stone boulders found in Ceresolo-Bagnolo, Malegno commune, Brescia province, Lombardia, Northern Italy, at the base of Monte Mignone, at an altitude of ca. 700 m. Bagnolo 1 was discovered in 1963, bearing depictions of ...
). Redaction of the Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only on ...
and rise of the Vedic civilization in the Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
. The Mycenaean civilization gives way to the Greek Dark Ages. Hittite goes extinct.
* 1000–500 BC: The Celtic languages
The Celtic languages (usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward ...
spread over Central and Western Europe. Baltic languages are spoken in a huge area from present-day Poland to the Ural Mountains. Proto Germanic. Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
and the beginning of Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
. The Vedic Civilization gives way to the Mahajanapadas. Siddhartha Gautama preaches Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
. Zoroaster composes the Gathas, rise of the Achaemenid Empire, replacing the Elamites and Babylonia. Separation of Proto-Italic into Osco-Umbrian and Latin-Faliscan. Genesis of the Greek and Old Italic alphabets. A variety of Paleo-Balkan languages are spoken in Southern Europe.
* 500 BC – 1 BC/AD: Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
: spread of Greek and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
throughout the Mediterranean and, during the Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
( Indo-Greeks), to Central Asia and the Hindukush. Kushan Empire, Mauryan Empire. Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic br ...
.
* 1 BC – AD 500: Late Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English h ...
, Gupta period
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gold ...
; attestation of Armenian. Proto-Slavic. The Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
and then the Migration period marginalize the Celtic languages to the British Isles. Sogdian, an Eastern Iranian language, becomes the '' lingua franca'' of the Silk Road in Central Asia leading to China, due to the proliferation of Sogdian merchants there. The last of the Anatolian languages are extinct.
* 500–1000: Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
. The Viking Age
The Viking Age () was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonizing, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. It followed the Migration Period and the Germ ...
forms an Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlement ...
koine spanning Scandinavia, the British Isles and Iceland. The Islamic conquest and the Turkic expansion results in the Arabization and Turkification of significant areas where Indo-European languages were spoken. Tocharian is extinct in the course of the Turkic expansion while Northeastern Iranian ( Scytho-Sarmatian) is reduced to small refugia. Slavic languages spread over wide areas in central, eastern and southeastern Europe, largely replacing Romance in the Balkans (with the exception of Romanian) and whatever was left of the paleo-Balkan languages with the exception of Albanian.
* 1000–1500: Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Ren ...
: Attestation of Albanian and Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
.
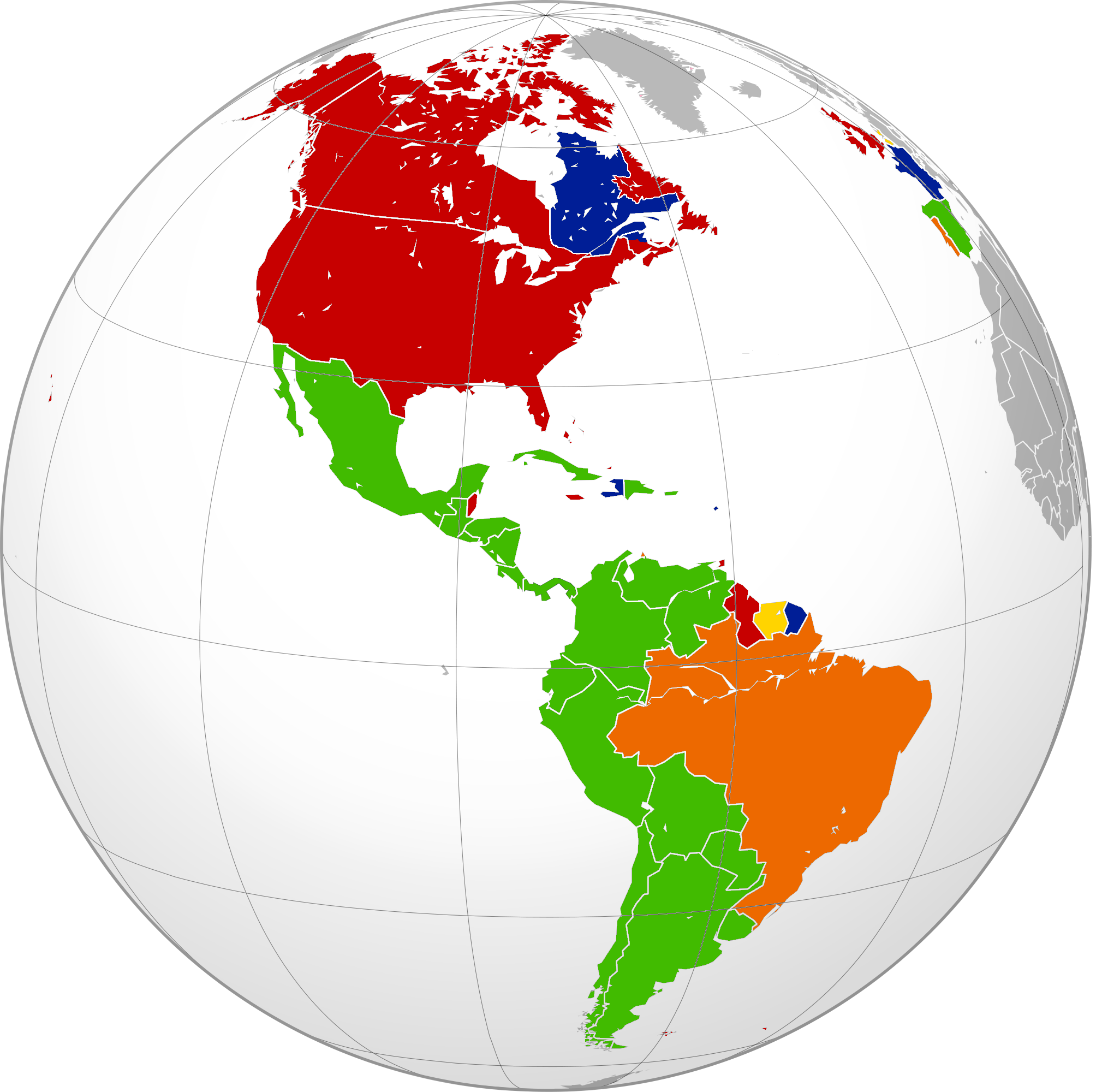
* 1500–2000: Early Modern period to present: Colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their reli ...
results in the spread of Indo-European languages to every continent, most notably Romance (North, Central and South America, North and Sub-Saharan Africa, West Asia), West Germanic (English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
in North America, Sub-Saharan Africa, East Asia and Australia; to a lesser extent Dutch and German), and Russian to Central Asia and North Asia.
Important languages for reconstruction
In reconstructing the history of the Indo-European languages and the form of theProto-Indo-European language
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-E ...
, some languages have been of particular importance. These generally include the ancient Indo-European languages that are both well-attested and documented at an early date, although some languages from later periods are important if they are particularly linguistically conservative (most notably, Lithuanian). Early poetry is of special significance because of the rigid poetic meter normally employed, which makes it possible to reconstruct a number of features (e.g. vowel length
In linguistics, vowel length is the perceived length of a vowel sound: the corresponding physical measurement is duration. In some languages vowel length is an important phonemic factor, meaning vowel length can change the meaning of the word ...
) that were either unwritten or corrupted in the process of transmission down to the earliest extant written manuscript
A manuscript (abbreviated MS for singular and MSS for plural) was, traditionally, any document written by hand – or, once practical typewriters became available, typewritten – as opposed to mechanically printed or reproduced i ...
s.
Most noticeable of all:
* Vedic Sanskrit (c. 1500–500 BC). This language is unique in that its source documents were all composed orally, and were passed down through oral tradition
Oral tradition, or oral lore, is a form of human communication wherein knowledge, art, ideas and Culture, cultural material is received, preserved, and transmitted orally from one generation to another.Jan Vansina, Vansina, Jan: ''Oral Traditio ...
( shakha schools) for c. 2,000 years before ever being written down. The oldest documents are all in poetic form; oldest and most important of all is the Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only on ...
(c. 1500 BC).
* Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic pe ...
(c. 750–400 BC). Mycenaean Greek (c. 1450 BC) is the oldest recorded form, but its value is lessened by the limited material, restricted subject matter, and highly ambiguous writing system. More important is Ancient Greek, documented extensively beginning with the two Homeric poems
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
(the ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Ody ...
'' and the ''Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; grc, Ὀδύσσεια, Odýsseia, ) is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the '' Iliad'', ...
'', c. 750 BC).
* Hittite (c. 1700–1200 BC). This is the earliest-recorded of all Indo-European languages, and highly divergent from the others due to the early separation of the Anatolian languages
The Anatolian languages are an extinct branch of Indo-European languages that were spoken in Anatolia, part of present-day Turkey. The best known Anatolian language is Hittite, which is considered the earliest-attested Indo-European langua ...
from the remainder. It possesses some highly archaic features found only fragmentarily, if at all, in other languages. At the same time, however, it appears to have undergone many early phonological and grammatical changes which, combined with the ambiguities of its writing system, hinder its usefulness somewhat.
Other primary sources:
* Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
, attested in a huge amount of poetic and prose material in the Classical period (c. 200 BC – 100 AD) and limited older material from as early as c. 600 BC.
* Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
(the most archaic well-documented Germanic language, c. 350 AD), along with the combined witness of the other old Germanic languages: most importantly, Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th ...
(c. 800–1000 AD), Old High German
Old High German (OHG; german: Althochdeutsch (Ahd.)) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally covering the period from around 750 to 1050.
There is no standardised or supra-regional form of German at this period, and Old Hig ...
(c. 750–1000 AD) and Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlement ...
(c. 1100–1300 AD, with limited earlier sources dating to c. 200 AD).
* Old Avestan (c. 1700–1200 BC) and Younger Avestan
Avestan (), or historically Zend, is an umbrella term for two Old Iranian languages: Old Avestan (spoken in the 2nd millennium BCE) and Younger Avestan (spoken in the 1st millennium BCE). They are known only from their conjoined use as the scrip ...
(c. 900 BC). Documentation is sparse, but nonetheless quite important due to its highly archaic nature.
* Modern Lithuanian, with limited records in Old Lithuanian
Lithuanian ( ) is an Eastern Baltic language belonging to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the official language of Lithuania and one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.8 millio ...
(c. 1500–1700 AD).
* Old Church Slavonic (c. 900–1000 AD).
Other secondary sources, of lesser value due to poor attestation:
* Luwian, Lycian, Lydian and other Anatolian languages
The Anatolian languages are an extinct branch of Indo-European languages that were spoken in Anatolia, part of present-day Turkey. The best known Anatolian language is Hittite, which is considered the earliest-attested Indo-European langua ...
(c. 1400–400 BC).
* Oscan
Oscan is an extinct Indo-European language of southern Italy. The language is in the Osco-Umbrian or Sabellic branch of the Italic languages. Oscan is therefore a close relative of Umbrian.
Oscan was spoken by a number of tribes, including t ...
, Umbrian
Umbrian is an extinct Italic language formerly spoken by the Umbri in the ancient Italian region of Umbria. Within the Italic languages it is closely related to the Oscan group and is therefore associated with it in the group of Osco-Umbrian ...
and other Old Italic languages (c. 600–200 BC).
* Old Persian (c. 500 BC).
* Old Prussian (c. 1350–1600 AD); even more archaic than Lithuanian.
Other secondary sources, of lesser value due to extensive phonological changes and relatively limited attestation:
* Old Irish
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic ( sga, Goídelc, Ogham script: ᚌᚑᚔᚇᚓᚂᚉ; ga, Sean-Ghaeilge; gd, Seann-Ghàidhlig; gv, Shenn Yernish or ), is the oldest form of the Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive writte ...
(c. 700–850 AD).
* Tocharian (c. 500–800 AD), underwent large phonetic shifts and mergers in the proto-language, and has an almost entirely reworked declension system.
* Classical Armenian (c. 400–1000 AD).
* Albanian (c. 1450–current time).
Sound changes
As the Proto-Indo-European (PIE) language broke up, its sound system diverged as well, changing according to varioussound law
A sound change, in historical linguistics, is a change in the pronunciation of a language. A sound change can involve the replacement of one speech sound (or, more generally, one phonetic feature value) by a different one (called phonetic cha ...
s evidenced in the daughter language
In historical linguistics, a daughter language, also known as descendant language, is a language descended from another language, its mother language, through a process of genetic descent. If more than one language has developed from the same pr ...
s.
PIE is normally reconstructed with a complex system of 15 stop consonant
In phonetics, a plosive, also known as an occlusive or simply a stop, is a pulmonic consonant in which the vocal tract is blocked so that all airflow ceases.
The occlusion may be made with the tongue tip or blade (, ), tongue body (, ), li ...
s, including an unusual three-way phonation ( voicing) distinction between voiceless, voiced and "voiced aspirated
Breathy voice (also called murmured voice, whispery voice, soughing and susurration) is a phonation in which the vocal folds vibrate, as they do in normal (modal) voicing, but are adjusted to let more air escape which produces a sighing-like ...
" (i.e. breathy voiced
Breathy voice (also called murmured voice, whispery voice, soughing and susurration) is a phonation in which the vocal folds vibrate, as they do in normal (modal) voicing, but are adjusted to let more air escape which produces a sighing-like ...
) stops, and a three-way distinction among velar consonant
Velars are consonants place of articulation, articulated with the back part of the tongue (the dorsum) against the soft palate, the back part of the roof of the mouth (known also as the Soft palate, velum).
Since the velar region of the roof of ...
s (''k''-type sounds) between "palatal" ''ḱ ǵ ǵh'', "plain velar" ''k g gh'' and labiovelar ''kʷ gʷ gʷh''. (The correctness of the terms ''palatal'' and ''plain velar'' is disputed; see Proto-Indo-European phonology.) All daughter languages have reduced the number of distinctions among these sounds, often in divergent ways.
As an example, in English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
, one of the Germanic languages, the following are some of the major changes that happened:
None of the daughter-language families (except possibly Anatolian, particularly Luvian) reflect the plain velar stops differently from the other two series, and there is even a certain amount of dispute whether this series existed at all in PIE. The major distinction between ''centum'' and ''satem'' languages corresponds to the outcome of the PIE plain velars:
* The "central" ''satem'' languages ( Indo-Iranian, Balto-Slavic
The Balto-Slavic languages form a branch of the Indo-European family of languages, traditionally comprising the Baltic and Slavic languages. Baltic and Slavic languages share several linguistic traits not found in any other Indo-European br ...
, Albanian, and Armenian) reflect both "plain velar" and labiovelar stops as plain velars, often with secondary palatalization before a front vowel (''e i ē ī''). The "palatal" stops are palatalized and often appear as sibilants (usually but not always distinct from the secondarily palatalized stops).
* The "peripheral" ''centum'' languages ( Germanic, Italic, Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foo ...
, Greek, Anatolian and Tocharian) reflect both "palatal" and "plain velar" stops as plain velars, while the labiovelars continue unchanged, often with later reduction into plain labial
The term ''labial'' originates from '' Labium'' (Latin for "lip"), and is the adjective that describes anything of or related to lips, such as lip-like structures. Thus, it may refer to:
* the lips
** In linguistics, a labial consonant
** In zoolog ...
or velar consonant
Velars are consonants place of articulation, articulated with the back part of the tongue (the dorsum) against the soft palate, the back part of the roof of the mouth (known also as the Soft palate, velum).
Since the velar region of the roof of ...
s.
The three-way PIE distinction between voiceless, voiced and voiced aspirated stops is considered extremely unusual from the perspective of linguistic typology—particularly in the existence of voiced aspirated stops without a corresponding series of voiceless aspirated stops. None of the various daughter-language families continue it unchanged, with numerous "solutions" to the apparently unstable PIE situation:
* The Indo-Aryan languages preserve the three series unchanged but have evolved a fourth series of voiceless aspirated consonants.
* The Iranian language
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian languages are groupe ...
s probably passed through the same stage, subsequently changing the aspirated stops into fricatives.
* Greek converted the voiced aspirates into voiceless aspirates.
* Italic probably passed through the same stage, but reflects the voiced aspirates as voiceless fricatives, especially ''f'' (or sometimes plain voiced stops in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
).
* Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foo ...
, Balto-Slavic
The Balto-Slavic languages form a branch of the Indo-European family of languages, traditionally comprising the Baltic and Slavic languages. Baltic and Slavic languages share several linguistic traits not found in any other Indo-European br ...
, Anatolian, and Albanian merge the voiced aspirated into plain voiced stops.
* Germanic and Armenian change all three series in a chain shift (e.g. with ''bh b p'' becoming ''b p f'' (known as '' Grimm's law'' in Germanic)).
Among the other notable changes affecting consonants are:
* The Ruki sound law (''s'' becomes before ''r, u, k, i'') in the '' satem'' languages.
* Loss of prevocalic ''p'' in Proto-Celtic
Proto-Celtic, or Common Celtic, is the ancestral proto-language of all known Celtic languages, and a descendant of Proto-Indo-European. It is not attested in writing but has been partly reconstructed through the comparative method. Proto-Celt ...
.
* Development of prevocalic ''s'' to ''h'' in Proto-Greek, with later loss of ''h'' between vowels.
* Verner's law in Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic br ...
.
* Grassmann's law (dissimilation of aspirates) independently in Proto-Greek and Proto-Indo-Iranian.
The following table shows the basic outcomes of PIE consonants in some of the most important daughter languages for the purposes of reconstruction. For a fuller table, see Indo-European sound laws.
:Notes:
* C- At the beginning of a word.
* -C- Between vowels.
* -C At the end of a word.
* `-C- Following an unstressed vowel ( Verner's law).
* -C-(rl) Between vowels, or between a vowel and (on either side).
* CT Before a (PIE) stop ().
* CT− After a (PIE) obstruent (, etc.; ).
* C(T) Before or after an obstruent (, etc.; ).
* CH Before an original laryngeal.
* CE Before a (PIE) front vowel ().
* CE' Before secondary (post-PIE) front-vowels.
* Ce Before .
* C(u) Before or after a (PIE) (boukólos rule
The boukólos rule is a phonological rule of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). It states that a labiovelar stop () dissimilates to an ordinary velar stop () next to the vowel or its corresponding glide .
The rule is named after an exampl ...
).
* C(O) Before or after a (PIE) (boukólos rule
The boukólos rule is a phonological rule of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). It states that a labiovelar stop () dissimilates to an ordinary velar stop () next to the vowel or its corresponding glide .
The rule is named after an exampl ...
).
* Cn− After .
* CR Before a sonorant ().
* C(R) Before or after a sonorant ().
* C(r),l,u− Before or after .
* Cruki− After ( Ruki sound law).
* C..Ch Before an aspirated consonant in the next syllable ( Grassmann's law, also known as dissimilation of aspirates).
* CE..Ch Before a (PIE) front vowel () as well as before an aspirated consonant in the next syllable ( Grassmann's law, also known as dissimilation of aspirates).
* C(u)..Ch Before or after a (PIE) as well as before an aspirated consonant in the next syllable ( Grassmann's law, also known as dissimilation of aspirates).
Comparison of conjugations
The following table presents a comparison of conjugations of the thematicpresent indicative
The present tense (abbreviated or ) is a grammatical tense whose principal function is to locate a situation or event in the present time. The present tense is used for actions which are happening now. In order to explain and understand present t ...
of the verbal root * of the English verb '' to bear'' and its reflexes in various early attested IE languages and their modern descendants or relatives, showing that all languages had in the early stage an inflectional verb system.
While similarities are still visible between the modern descendants and relatives of these ancient languages, the differences have increased over time. Some IE languages have moved from synthetic Synthetic things are composed of multiple parts, often with the implication that they are artificial. In particular, 'synthetic' may refer to:
Science
* Synthetic chemical or compound, produced by the process of chemical synthesis
* Synthetic ...
verb systems to largely periphrastic systems. In addition, the pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun ( abbreviated ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase.
Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not ...
s of periphrastic forms are in parentheses when they appear. Some of these verbs have undergone a change in meaning as well.
* In Modern Irish ''beir'' usually only carries the meaning ''to bear'' in the sense of bearing a child; its common meanings are ''to catch, grab''. Apart from the first person, the forms given in the table above are dialectical or obsolete. The second and third person forms are typically instead conjugated periphrastically by adding a pronoun after the verb: ''beireann tú, beireann sé/sí, beireann sibh, beireann siad''.
* The Hindustani (Hindi
Hindi (Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been ...
and Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
'' present indicative The present tense (abbreviated or ) is a grammatical tense whose principal function is to locate a situation or event in the present time. The present tense is used for actions which are happening now. In order to explain and understand present t ...
, now have the meaning of future subjunctive. The loss of the '' present indicative The present tense (abbreviated or ) is a grammatical tense whose principal function is to locate a situation or event in the present time. The present tense is used for actions which are happening now. In order to explain and understand present t ...
present indicative
The present tense (abbreviated or ) is a grammatical tense whose principal function is to locate a situation or event in the present time. The present tense is used for actions which are happening now. In order to explain and understand present t ...
in Hindustani is roughly compensated by the periphrastic habitual indicative construction, using the habitual participle (etymologically from the Sanskrit present participle ''bʰarant-'') and an auxiliary: ''ma͠i bʰartā hū̃, tū bʰartā hai, vah bʰartā hai, ham bʰarte ha͠i, tum bʰarte ho, ve bʰarte ha͠i'' (masculine forms).
* German is not directly descended from Gothic, but the Gothic forms are a close approximation of what the early West Germanic forms of c. 400 AD would have looked like. The descendant of Proto-Germanic ''*beraną'' (English ''bear'') survives in German only in the compound ''gebären'', meaning "bear (a child)".
* The Latin verb ''ferre'' is irregular, and not a good representative of a normal thematic verb. In most Romance languages such as Portuguese, other verbs now mean "to carry" (e.g. Pt. ''portar'' < Lat. ''portare'') and ''ferre'' was borrowed and nativized only in compounds such as "to suffer" (from Latin ''sub-'' and ''ferre'') and "to confer" (from Latin "con-" and "ferre").
* In Modern Greek, ''phero'' φέρω (modern transliteration ''fero'') "to bear" is still used but only in specific contexts and is most common in such compounds as αναφέρω, διαφέρω, εισφέρω, εκφέρω, καταφέρω, προφέρω, προαναφέρω, προσφέρω etc. The form that is (very) common today is ''pherno'' φέρνω (modern transliteration ''ferno'') meaning "to bring". Additionally, the perfective form of ''pherno'' (used for the subjunctive voice and also for the future tense) is also ''phero''.
* The dual forms are archaic in standard Lithuanian, and are only presently used in some dialects (e.g. Samogitian).
* Among modern Slavic languages, only Slovene continues to have a dual number in the standard variety.
Comparison of cognates
Present distribution

 Today, Indo-European languages are spoken by billions of native speakers across all inhabited continents, the largest number by far for any recognised language family. Of the 20 languages with the largest numbers of speakers according to ''Ethnologue'', 10 are Indo-European:
Today, Indo-European languages are spoken by billions of native speakers across all inhabited continents, the largest number by far for any recognised language family. Of the 20 languages with the largest numbers of speakers according to ''Ethnologue'', 10 are Indo-European: English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
, Hindustani, Spanish, Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, Russian, Portuguese, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, Persian and Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a British Th ...
, each with 100 million speakers or more. Additionally, hundreds of millions of persons worldwide study Indo-European languages as secondary or tertiary languages, including in cultures which have completely different language families and historical backgrounds—there are around 600 million learners of English alone.
The success of the language family, including the large number of speakers and the vast portions of the Earth that they inhabit, is due to several factors. The ancient Indo-European migrations and widespread dissemination of Indo-European culture throughout Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
, including that of the Proto-Indo-Europeans themselves, and that of their daughter cultures including the Indo-Aryans, Iranian peoples
The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of Indo-European peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities.
The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate ...
, Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient ...
, Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, ot ...
, Romans, Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
, and Slavs, led to these peoples' branches of the language family already taking a dominant foothold in virtually all of Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
except for swathes of the Near East, North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
and East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea ...
, replacing many (but not all) of the previously-spoken pre-Indo-European languages of this extensive area. However Semitic languages
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, the Horn of Africa, and latterly North Africa, Malta, West Africa, Chad, and in large immigrant ...
remain dominant in much of the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
and North Africa, and Caucasian languages in much of the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
region. Similarly in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
and the Urals the Uralic languages
The Uralic languages (; sometimes called Uralian languages ) form a language family of 38 languages spoken by approximately 25million people, predominantly in Northern Eurasia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian ...
(such as Hungarian, Finnish, Estonian etc.) remain, as does Basque, a pre-Indo-European isolate.
Despite being unaware of their common linguistic origin, diverse groups of Indo-European speakers continued to culturally dominate and often replace the indigenous languages of the western two-thirds of Eurasia. By the beginning of the Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the or ...
, Indo-European peoples controlled almost the entirety of this area: the Celts western and central Europe, the Romans southern Europe, the Germanic peoples northern Europe, the Slavs eastern Europe, the Iranian peoples most of western and central Asia and parts of eastern Europe, and the Indo-Aryan peoples in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
, with the Tocharians inhabiting the Indo-European frontier in western China. By the medieval period, only the Semitic, Dravidian, Caucasian, and Uralic languages
The Uralic languages (; sometimes called Uralian languages ) form a language family of 38 languages spoken by approximately 25million people, predominantly in Northern Eurasia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian ...
, and the language isolate Basque remained of the (relatively) indigenous languages of Europe and the western half of Asia.
Despite medieval invasions by Eurasian nomads, a group to which the Proto-Indo-Europeans had once belonged, Indo-European expansion reached another peak in the early modern period with the dramatic increase in the population of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
and European expansionism throughout the globe during the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafa ...
, as well as the continued replacement and assimilation of surrounding non-Indo-European languages and peoples due to increased state centralization and nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of peo ...
. These trends compounded throughout the modern period due to the general global population growth and the results of European colonization
The historical phenomenon of colonization is one that stretches around the globe and across time. Ancient and medieval colonialism was practiced by the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Turks, and the Arabs.
Colonialism in the modern sense be ...
of the Western Hemisphere and Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
, leading to an explosion in the number of Indo-European speakers as well as the territories inhabited by them.
Due to colonization and the modern dominance of Indo-European languages in the fields of politics, global science, technology, education, finance, and sports, even many modern countries whose populations largely speak non-Indo-European languages have Indo-European languages as official languages, and the majority of the global population speaks at least one Indo-European language. The overwhelming majority of languages used on the Internet are Indo-European, with English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
continuing to lead the group; English in general has in many respects become the ''lingua franca'' of global communication.
See also
* Grammatical conjugation * '' The Horse, the Wheel, and Language'' (book) *Indo-European copula
A feature common to all Indo-European languages is the presence of a verb corresponding to the English verb ''to be''.
General features
This verb has two basic meanings:
*In a less marked context it is a simple copula (''I’m tired''; ''That ...
* Indo-European sound laws
* Indo-European studies
Indo-European studies is a field of linguistics and an interdisciplinary field of study dealing with Indo-European languages, both current and extinct. The goal of those engaged in these studies is to amass information about the hypothetical p ...
* Indo-Semitic languages
The Indo-Semitic hypothesis maintains that a genetic relationship exists between Indo-European and Semitic and that the Indo-European and the Semitic language families descend from a prehistoric language ancestral to them both. The theory has ne ...
* Indo-Uralic languages
Indo-Uralic is a controversial hypothetical language family consisting of Indo-European and Uralic.
The suggestion of a genetic relationship between Indo-European and Uralic is often credited to the Danish linguist Vilhelm Thomsen in 1869 (P ...
* Eurasiatic languages
* Language family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in h ...
* Languages of Asia
A wide variety of languages are spoken throughout Asia, comprising different language families and some unrelated isolates. The major language families include Austroasiatic, Austronesian, Caucasian, Dravidian, Indo-European, Afroasiatic, Tur ...
* Languages of Europe
* Languages of India
Languages spoken in India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-European languages spoken by 78.05% of Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 19.64% of Indians, both families together are sometimes know ...
* List of Indo-European languages
* Proto-Indo-European root
* Proto-Indo-European religion
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * Paperback: ISBN 978-9027211866. * * * * * * * * * * * * *Part II via Internet Archive
* ** Reprinted in * *
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture (1997)
Databases
* * * * . * *an online collection of introductory videos to Ancient Indo-European languages produced by the University of Göttingen
Lexica
* * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Indo-European Languages Languages Language families