Illuminant D65 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
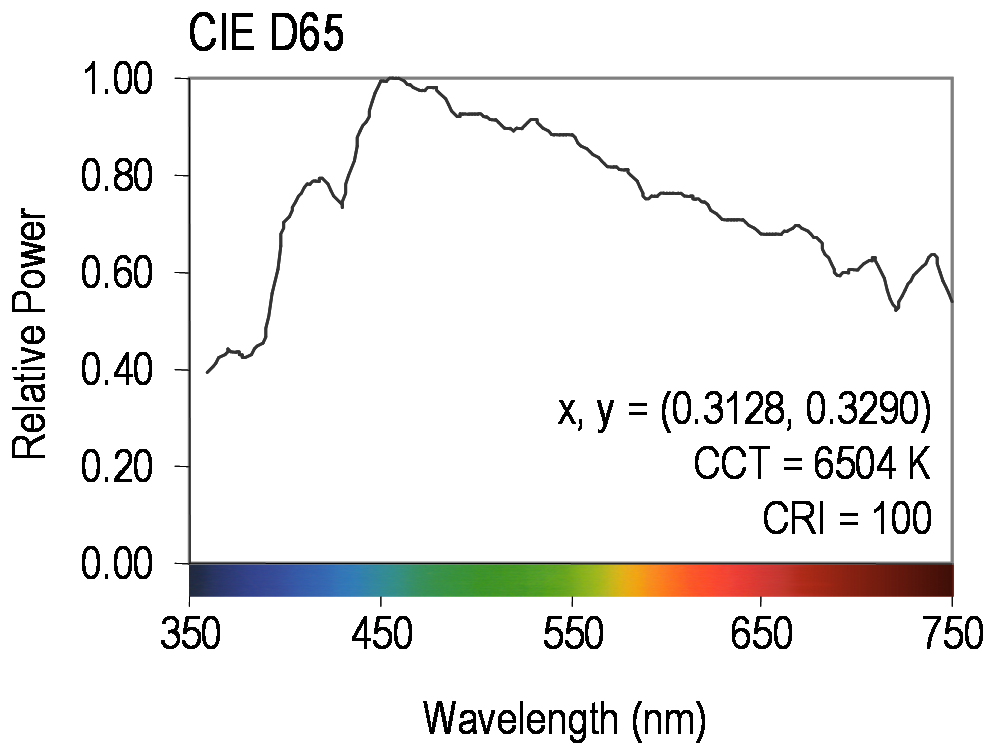 CIE standard illuminant D65 (sometimes written D65) is a commonly used standard illuminant defined by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE). It is part of the D series of illuminants that try to portray standard illumination conditions at open-air in different parts of the world.
D65 corresponds roughly to the average midday light in
CIE standard illuminant D65 (sometimes written D65) is a commonly used standard illuminant defined by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE). It is part of the D series of illuminants that try to portray standard illumination conditions at open-air in different parts of the world.
D65 corresponds roughly to the average midday light in 
Selected colorimetric tables in Excel
CIE. Light Standard illuminants
 CIE standard illuminant D65 (sometimes written D65) is a commonly used standard illuminant defined by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE). It is part of the D series of illuminants that try to portray standard illumination conditions at open-air in different parts of the world.
D65 corresponds roughly to the average midday light in
CIE standard illuminant D65 (sometimes written D65) is a commonly used standard illuminant defined by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE). It is part of the D series of illuminants that try to portray standard illumination conditions at open-air in different parts of the world.
D65 corresponds roughly to the average midday light in Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
/ Northern Europe (comprising both direct sunlight and the light diffused by a clear sky), hence it is also called a daylight illuminant. As any standard illuminant is represented as a table of averaged
In mathematics and statistics, the arithmetic mean ( ) or arithmetic average, or just the ''mean'' or the ''average'' (when the context is clear), is the sum of a collection of numbers divided by the count of numbers in the collection. The coll ...
spectrophotometric data, any light source which statistically has the same relative spectral power distribution (SPD) can be considered a D65 light source. There are no actual D65 light sources, only simulators. The quality of a simulator can be assessed with the CIE metamerism index.
The CIE positions D65 as the standard daylight illuminant:

History
The CIE introduced three standard illuminants in 1931: * A:Incandescent bulb
An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas to protect the filament from oxid ...
simulator
* B: Daylight simulator (direct)
* C: Daylight simulator (shade)
B and C were derived from A by using liquid filters. The approximation to real light this provided was found lacking, so in 1967 the CIE accepted a proposal by Judd, MacAdam, and Wyszecki for a new series of daylight simulators, bearing the initial D.
Definition
D65 is a tabulated SPD in increments of 5 nm from 300 nm to 830 nm, using linear interpolation on the original data binned at 10 nm. The CIE recommends using linear interpolation of the component SPDs, S0, S1, and S2 if the application requires greater precision, but there is a proposal to use spline interpolation instead. Using the standard 2° observer, the CIE 1931 color spacechromaticity coordinate
The CIE 1931 color spaces are the first defined quantitative links between distributions of wavelengths in the electromagnetic visible spectrum, and physiologically perceived colors in human color vision. The mathematical relationships that defin ...
s of D65 are
Normalizing for relative luminance (i.e. set ), the XYZ tristimulus values are
For the supplementary 10° observer,
and the corresponding XYZ tristimulus values are
Since D65 represents white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White ...
light, its coordinates are also a white point, corresponding to a correlated color temperature of 6504 K. Rec. 709, used in HDTV
High-definition television (HD or HDTV) describes a television system which provides a substantially higher image resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since 1936; in more recent times, it refers to the g ...
systems, truncates the CIE 1931 coordinates to x=0.3127, y=0.329.
Color Temperature
The name D65 suggests that the correlated color temperature (CCT) should be 6500 K, while in truth it is closer to 6504 K. This discrepancy is due to the scientific community's 1968 revision of the constants in Planck's law after the definition of the illuminant. This shifted the Planckian locus, affecting all CCTs, which are calculated by finding the nearest point on the locus to the white point. The same discrepancy applies to all illuminants in the D series—D50, D55, D65, D75—and can be "rectified" by multiplying the nominal color temperature by ; for example for D65.References
{{reflist, 30emExternal links
Selected colorimetric tables in Excel
CIE. Light Standard illuminants