IRC 10216 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
CW Leonis or IRC +10216 is a
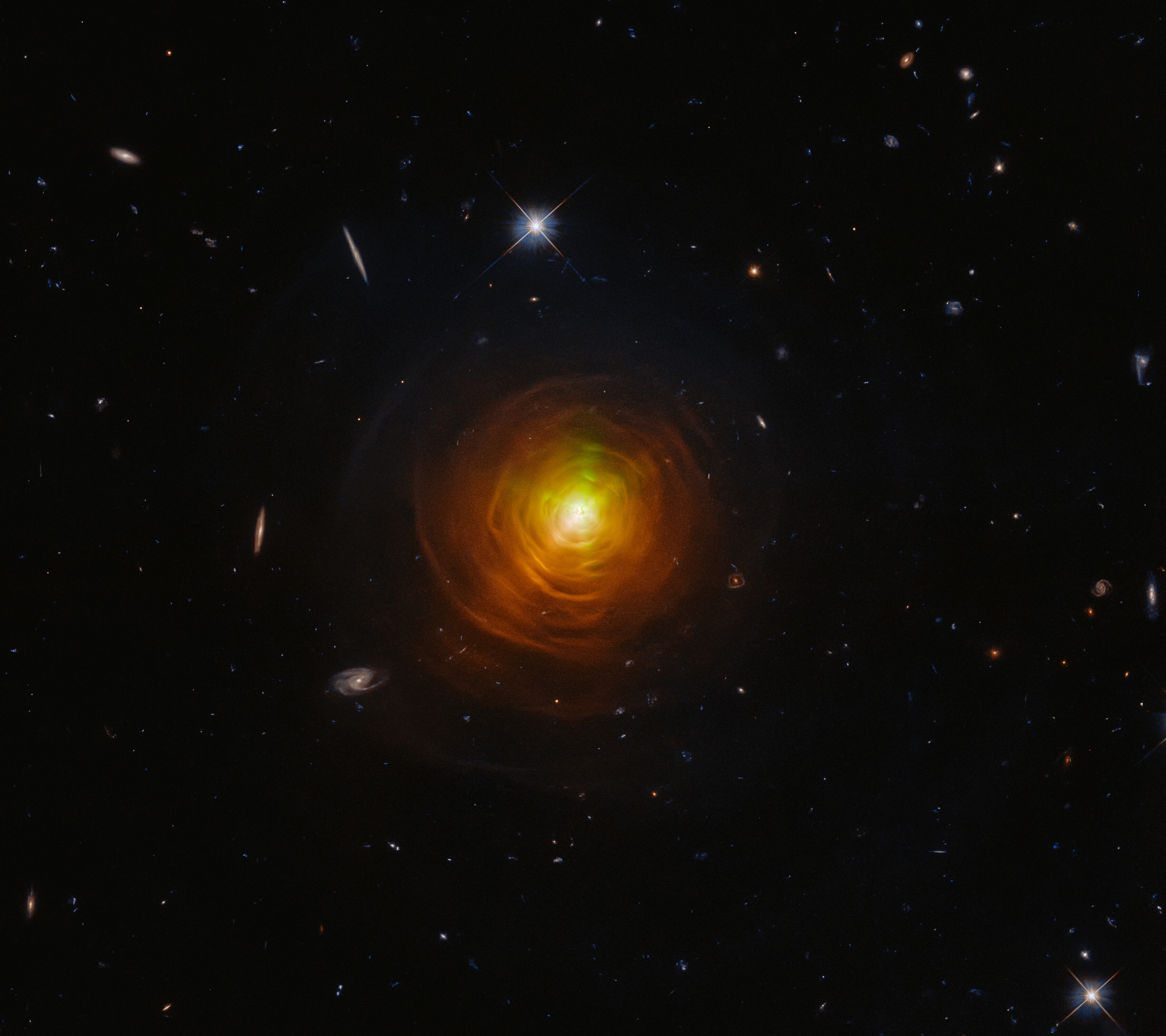
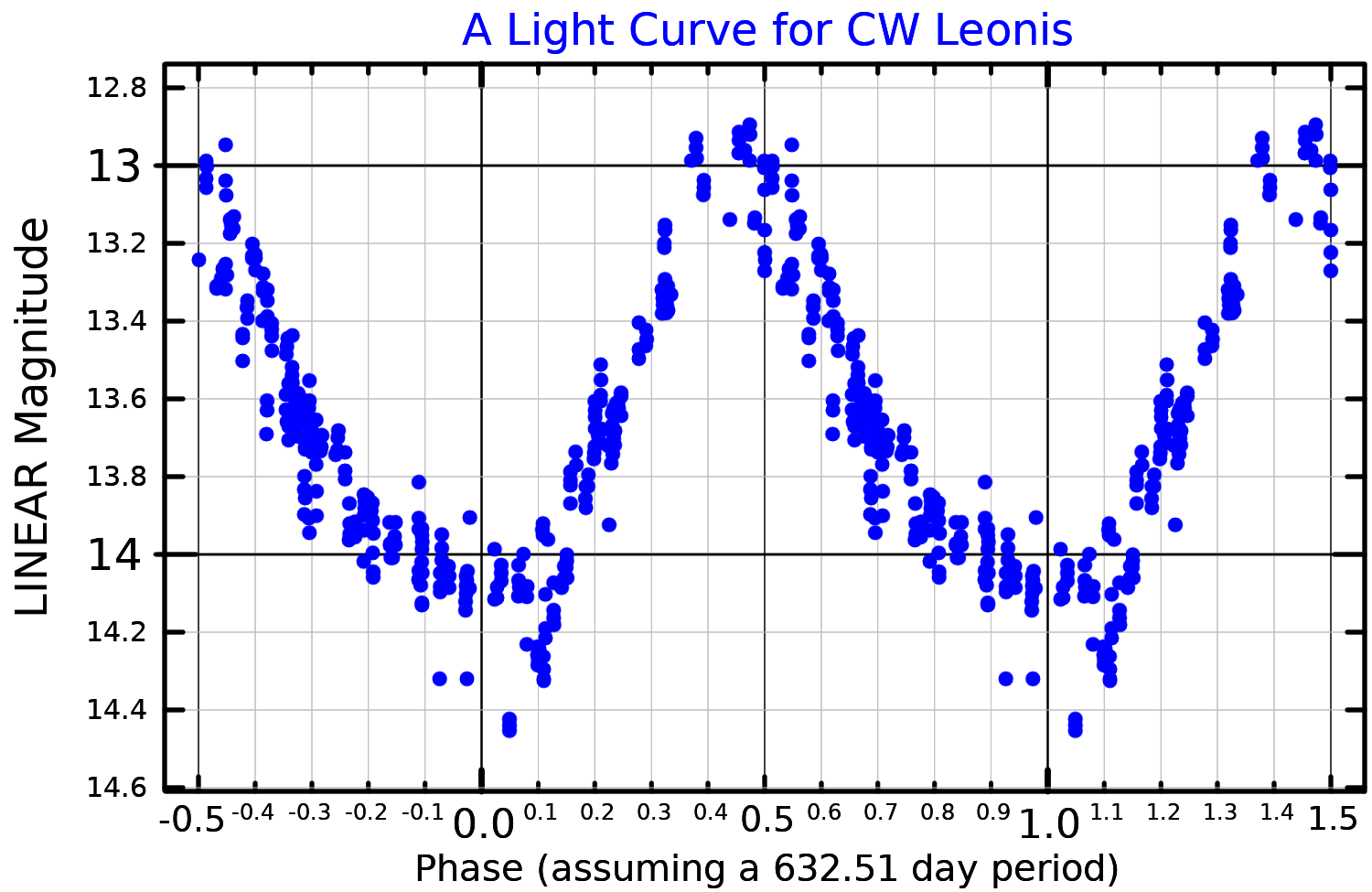 CW Leonis is believed to be in a late stage of its life, blowing off its own sooty atmosphere to form a
CW Leonis is believed to be in a late stage of its life, blowing off its own sooty atmosphere to form a
 If the distance to this star is assumed to be at the lower end of the estimate range, 120 pc, then the
If the distance to this star is assumed to be at the lower end of the estimate range, 120 pc, then the
Water Found Around Nearby Star CW Leonis
Astronomy Picture of the Day July 16th, 2001
revealed by aperture masking interferometry * http://jumk.de/astronomie/special-stars/cw-leonis.shtml * {{Stars of Leo Carbon stars Protoplanetary nebulae Leo (constellation) ? Mira variables Objects with variable star designations IRAS catalogue objects J09475740+1316435 Emission-line stars
carbon star
A carbon star (C-type star) is typically an asymptotic giant branch star, a luminous red giant, whose atmosphere contains more carbon than oxygen. The two elements combine in the upper layers of the star, forming carbon monoxide, which consumes mo ...
that is embedded in a thick dust envelope. It was first discovered in 1969 by a group of astronomers led by Eric Becklin, based upon infrared observations made with the Caltech Infrared Telescope at Mount Wilson Observatory
The Mount Wilson Observatory (MWO) is an astronomical observatory in Los Angeles County, California, United States. The MWO is located on Mount Wilson, a peak in the San Gabriel Mountains near Pasadena, northeast of Los Angeles.
The observat ...
. Its energy is emitted mostly at infrared wavelengths. At a wavelength of 5 μm
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer ( American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Uni ...
, it was found to have the highest flux of any object outside the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
.
Properties
 CW Leonis is believed to be in a late stage of its life, blowing off its own sooty atmosphere to form a
CW Leonis is believed to be in a late stage of its life, blowing off its own sooty atmosphere to form a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
. Based upon isotope ratios of magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
, the initial mass of this star has been constrained to lie between 3–5 solar mass
The solar mass () is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. It is approximately equal to the mass ...
es. The mass of the star's core, and the final mass of the star once it becomes a white dwarf, is about 0.7–0.9 solar masses. Its bolometric luminosity
Luminosity is an absolute measure of radiated electromagnetic power (light), the radiant power emitted by a light-emitting object over time. In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of electromagnetic energy emitted per unit of time by a ...
varies over the course of a 649-day pulsation cycle, ranging from a minimum of about 6,250 times the Sun's luminosity up to a peak of around 15,800 times. The overall output of the star is best represented by a luminosity of .
The carbon-rich gaseous envelope surrounding this star is at least 69,000 years old and the star is losing about solar mass
The solar mass () is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. It is approximately equal to the mass ...
es per year. The extended envelope contains at least 1.4 solar mass
The solar mass () is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. It is approximately equal to the mass ...
es of material. Speckle observations from 1999 show a complex structure to this dust envelope, including partial arcs and unfinished shells. This clumpiness may be caused by a magnetic cycle in the star that is comparable to the solar cycle
The solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a nearly periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun's surf ...
in the Sun and results in periodic increases in mass loss.
Various chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their atomic nucleus, nuclei, including the pure Chemical substance, substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements canno ...
s and about 50 molecules
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bio ...
have been detected in the outflows from CW Leonis, among others nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
and water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
, silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
and iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
. One theory was that the star was once surrounded by comets which melted once the star started expanding, but water is now thought to form naturally in the atmospheres of all carbon stars.
Distance
 If the distance to this star is assumed to be at the lower end of the estimate range, 120 pc, then the
If the distance to this star is assumed to be at the lower end of the estimate range, 120 pc, then the astrosphere
A stellar-wind bubble is a cavity light-years across filled with hot gas blown into the interstellar medium by the high-velocity (several thousand km/s) stellar wind from a single massive star of type O or B. Weaker stellar winds also blow bub ...
surrounding the star spans a radius of about 84,000 AU. The star and its surrounding envelope are advancing at a velocity of more than 91 km/s through the surrounding interstellar medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstella ...
. It is moving with a space velocity of , V, W= , km s−1.
Companion
Several papers have suggested that CW Leonis has a close binary companion. ALMA andastrometric
Astrometry is a branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies. It provides the kinematics and physical origin of the Solar System and this galaxy, the Milky Way.
Hist ...
measurements may show orbital motion. The astrometric measurements, combined with a model including the companion, provide a parallax measurement showing that CW Leonis is the closest carbon star
A carbon star (C-type star) is typically an asymptotic giant branch star, a luminous red giant, whose atmosphere contains more carbon than oxygen. The two elements combine in the upper layers of the star, forming carbon monoxide, which consumes mo ...
to the Earth.
See also
*List of largest stars
Below are lists of the largest stars currently known, ordered by radius and separated into categories by galaxy. The unit of measurement used is the radius of the Sun (approximately ).
The angular diameters of stars can be measured directly us ...
*List of most luminous stars
This is a list of stars arranged by their absolute magnitude – their intrinsic stellar luminosity. This cannot be observed directly, so instead must be calculated from the apparent magnitude (the brightness as seen from Earth), the distance t ...
References
External links
Water Found Around Nearby Star CW Leonis
Astronomy Picture of the Day July 16th, 2001
revealed by aperture masking interferometry * http://jumk.de/astronomie/special-stars/cw-leonis.shtml * {{Stars of Leo Carbon stars Protoplanetary nebulae Leo (constellation) ? Mira variables Objects with variable star designations IRAS catalogue objects J09475740+1316435 Emission-line stars