Intercalated Duct on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In anatomy and physiology, a duct is a circumscribed channel leading from an exocrine gland or
File:Gray1025.png, Section of submaxillary gland of
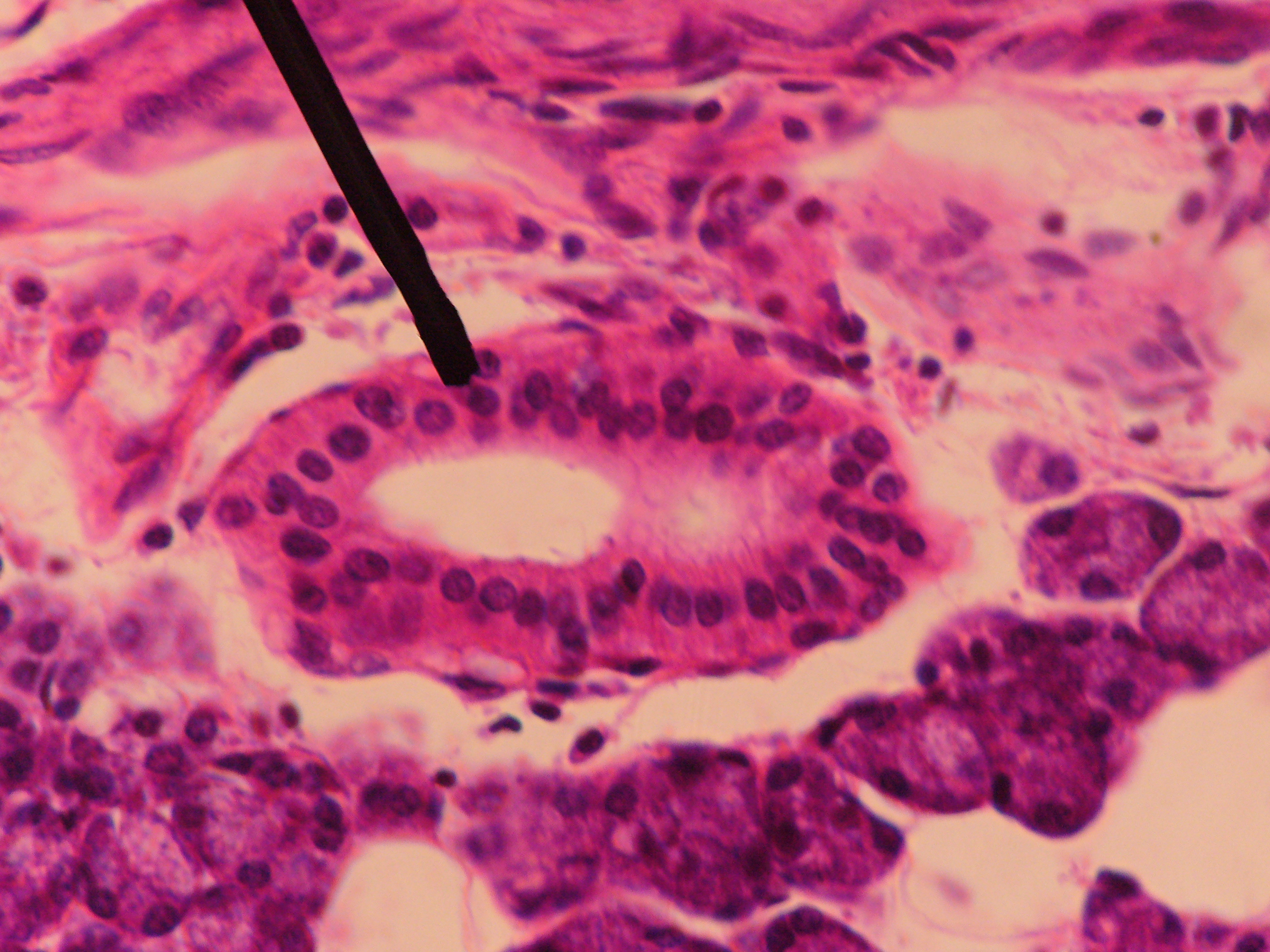 A striated duct (Pflüger's ducts ) is a
A striated duct (Pflüger's ducts ) is a
Overview at uwa.edu.au
{{Authority control Glands
organ
Organ may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a part of an organism
Musical instruments
* Organ (music), a family of keyboard musical instruments characterized by sustained tone
** Electronic organ, an electronic keyboard instrument
** Hammond ...
.
Types of ducts
Examples include:Duct system
As ducts travel from theacinus
An acinus (; plural, acini; adjective, acinar or acinous) refers to any cluster of cells that resembles a many-lobed "berry," such as a raspberry ('' acinus'' is Latin for "berry"). The berry-shaped termination of an exocrine gland, where the ...
which generates the fluid to the target, the ducts become larger and the epithelium becomes thicker. The parts of the system are classified as follows:
Some sources consider "lobar" ducts to be the same as "interlobar ducts", while others consider lobar ducts to be larger and more distal from the acinus. For sources that make the distinction, the interlobar ducts are more likely to classified with simple columnar epithelium
Simple columnar epithelium is a single layer of columnar epithelial cells which are tall and slender with oval-shaped nuclei located in the basal region, attached to the basement membrane. In humans, simple columnar epithelium lines most organ ...
(or pseudostratified epithelium
A pseudostratified epithelium is a type of epithelium that, though comprising only a single layer of cells, has its cell nuclei positioned in a manner suggestive of stratified epithelia. As it
rarely occurs as squamous or cuboidal epitheli ...
), reserving the stratified columnar for the lobar ducts.
kitten
A kitten is a juvenile cat. After being born, kittens display primary altriciality and are totally dependent on their mothers for survival. They normally do not open their eyes for seven to ten days. After about two weeks, kittens develop qu ...
. Duct semidiagrammatic. X 200.
File:Gray1173.png, Section of portion of mamma
Mama(s) or Mamma or Momma may refer to:
Roles
*Mother, a female parent
*Mama-san, in Japan and East Asia, a woman in a position of authority
*Mamas, a name for female associates of the Hells Angels
Places
*Mama, Russia, an urban-type settlement ...
.
Intercalated duct
The intercalated duct, also called intercalary duct (ducts of Boll), is the portion of an exocrine gland leading directly from theacinus
An acinus (; plural, acini; adjective, acinar or acinous) refers to any cluster of cells that resembles a many-lobed "berry," such as a raspberry ('' acinus'' is Latin for "berry"). The berry-shaped termination of an exocrine gland, where the ...
to a striated duct
In anatomy and physiology, a duct is a circumscribed channel leading from an exocrine gland or organ.
Types of ducts
Examples include:
Duct system
As ducts travel from the acinus which generates the fluid to the target, the ducts become larg ...
. The intercalated duct forms part of the intralobular duct. This duct has the thinnest epithelium of any part of the duct system, and the epithelium is usually classified as "low" simple cuboidal
Simple cuboidal epithelium is a type of epithelium that consists of a single layer of cuboidal (cube-like) cells which have large, spherical and central nuclei.
Simple cuboidal epithelium is found on the surface of ovaries, the lining of nephro ...
.
They are found in both the pancreas and in salivary glands.
Striated duct
gland
In animals, a gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances (such as hormones) for release into the bloodstream (endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface (exocrine gland).
Structure
De ...
duct which connects an intercalated duct to an interlobular duct. It is characterized by the basal infoldings of its plasma membrane, characteristic of ion-pumping activity by the numerous mitochondria. Along with the intercalated ducts, they function to modify salivary fluid by secreting HCO3− and K+ and reabsorbing Na+ and Cl− using the Na-K pump and the Cl-HCO3 pump, making the saliva hypotonic.
Their epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
can be simple cuboidal
Simple cuboidal epithelium is a type of epithelium that consists of a single layer of cuboidal (cube-like) cells which have large, spherical and central nuclei.
Simple cuboidal epithelium is found on the surface of ovaries, the lining of nephro ...
or simple columnar
Simple columnar epithelium is a single layer of columnar Epithelium#Cell types, epithelial cells which are tall and slender with oval-shaped Cell nucleus, nuclei located in the basal region, attached to the basement membrane. In humans, simple c ...
.
Striated ducts are part of the intralobular ducts.
They are found in the submandibular gland
The paired submandibular glands (historically known as submaxillary glands) are major salivary glands located beneath the floor of the mouth. They each weigh about 15 grams and contribute some 60–67% of unstimulated saliva secretion; on stimula ...
, sublingual duct, and the parotid gland, but are more developed in the parotid gland.
They are not present in pancreas.
Intralobular duct
An intralobular duct is the portion of an exocrine gland inside alobule
In anatomy, a lobe is a clear anatomical division or extension of an organ (as seen for example in the brain, lung, liver, or kidney) that can be determined without the use of a microscope at the gross anatomy level. This is in contrast to t ...
, leading directly from acinus
An acinus (; plural, acini; adjective, acinar or acinous) refers to any cluster of cells that resembles a many-lobed "berry," such as a raspberry ('' acinus'' is Latin for "berry"). The berry-shaped termination of an exocrine gland, where the ...
to an interlobular duct (between lobules). It is composed of two subdivisions, the intercalated duct and the striated duct
In anatomy and physiology, a duct is a circumscribed channel leading from an exocrine gland or organ.
Types of ducts
Examples include:
Duct system
As ducts travel from the acinus which generates the fluid to the target, the ducts become larg ...
.
In the human mammary gland, the intralobular duct is a part of the glandular system that resides within the lobules. Lobules contain clusters of ducts whose secretory alveolies are drained by the intralobular duct. The intralobular ducts are usually lined with simple cuboidal epithelial cells that are lined by myoepithelial cells as well.
The intralobular ducts of the lobules drain into the interlobular ducts between lobules.
They can be seen in:
* pancreas
* salivary glands
See also
* Ductal carcinoma * Endocrine glandReferences
External links
Overview at uwa.edu.au
{{Authority control Glands