
This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer compo ...
's
processors from the
4-bit
4-bit computing is the use of computer architectures in which integer (computer science), integers and other data (computer science), data units are 4 bits wide. 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures a ...
4004 (1971) to the present high-end offerings. Concise technical data is given for each product.
Latest
15th generation Core
Desktop - Core Ultra Series 2 (codenamed "
Arrow Lake")
Released on October 24, 2024. It follows on from Meteor Lake which saw Intel move from monolithic silicon to a disaggregated MCM design.
Meteor Lake was limited to a mobile release while
Arrow Lake includes desktop processors and mobile processors.
Desktop - Arrow Lake-S
Mobile - Arrow Lake-U
Arrow Lake-U uses refreshed
Meteor Lake silicon fabricated on the
Intel 3 node.
Mobile - Arrow Lake-H
Mobile - Arrow Lake-HX
13th and 14th generation Core
Desktop - Raptor Lake-S Refresh (codenamed "
Raptor Lake
Raptor Lake is Intel's List of Intel codenames, codename for the 13th and 14th generations of Intel Core processors based on a Heterogeneous computing, hybrid architecture, utilizing Raptor Cove performance cores and Gracemont (microarchitecture ...
") (14th Gen)
An iterative refresh of Raptor Lake-S desktop processors, called the 14th generation of Intel Core, was launched on October 17, 2023.
CPUs in bold below feature ECC memory support when paired with a motherboard based on the W680 chipset according to each respective Intel Ark product page.
Mobile - Raptor Lake-HX Refresh (codenamed "
Raptor Lake
Raptor Lake is Intel's List of Intel codenames, codename for the 13th and 14th generations of Intel Core processors based on a Heterogeneous computing, hybrid architecture, utilizing Raptor Cove performance cores and Gracemont (microarchitecture ...
") (14th Gen)
An iterative refresh of Raptor Lake-HX mobile processors, called the 14th generation of Intel Core, was launched on Jan 9, 2024
Mobile -
Meteor Lake-H
A meteor, known colloquially as a shooting star, is a glowing streak of a small body (usually meteoroid) going through Earth's atmosphere, after being heated to incandescence by collisions with air molecules in the upper atmosphere,
creating a ...
(14th gen)
155H, 165H, and 185H support P-core Turbo Boost 3.0 running at the same frequency as Turbo Boost 2.0.
Mobile -
Meteor Lake-U
A meteor, known colloquially as a shooting star, is a glowing streak of a small body (usually meteoroid) going through Earth's atmosphere, after being heated to incandescence by collisions with air molecules in the upper atmosphere,
creating a ...
(14th gen)
The integrated GPU is branded as "Intel Graphics" but still use the same GPU microarchitecture as "Intel Arc Graphics" on the H series models.
All models support DDR5 memory except 134U and 164U.
Desktop (codenamed "
Raptor Lake
Raptor Lake is Intel's List of Intel codenames, codename for the 13th and 14th generations of Intel Core processors based on a Heterogeneous computing, hybrid architecture, utilizing Raptor Cove performance cores and Gracemont (microarchitecture ...
") (13th Gen)
Mobile (codenamed "
Raptor Lake
Raptor Lake is Intel's List of Intel codenames, codename for the 13th and 14th generations of Intel Core processors based on a Heterogeneous computing, hybrid architecture, utilizing Raptor Cove performance cores and Gracemont (microarchitecture ...
") (13th Gen)
12th generation Core
Desktop (codenamed " Alder Lake")
Mobile (codenamed " Alder Lake")
11th generation Core
Desktop (codenamed "
Rocket Lake
Rocket Lake is Intel's codename for its 11th generation Core microprocessors. Released on March 30, 2021, it is based on the new Cypress Cove microarchitecture, a variant of Sunny Cove (used by Intel's Ice Lake mobile processors) backporte ...
")
Mobile (codenamed " Tiger Lake")
10th generation Core
Desktop (codenamed " Comet Lake")
Mobile (codenamed " Comet Lake", " Ice Lake", and " Amber Lake")
9th generation Core
Desktop (codenamed " Coffee Lake Refresh")
8th generation Core
Desktop (codenamed " Coffee Lake")
Mobile (codenamed " Coffee Lake", " Amber Lake" and " Whiskey Lake")
7th generation Core
Desktop (codenamed "
Kaby Lake
Kaby Lake is Intel's codename for its seventh generation Core microprocessor family announced on August 30, 2016. Like the preceding Skylake, Kaby Lake is produced using a 14 nanometer manufacturing process technology. Breaking with Intel's p ...
" and "
Skylake-X")
Mobile (codenamed "
Kaby Lake
Kaby Lake is Intel's codename for its seventh generation Core microprocessor family announced on August 30, 2016. Like the preceding Skylake, Kaby Lake is produced using a 14 nanometer manufacturing process technology. Breaking with Intel's p ...
" and "
Apollo Lake")
All processors
All processors are listed in chronological order.
The
4-bit
4-bit computing is the use of computer architectures in which integer (computer science), integers and other data (computer science), data units are 4 bits wide. 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures a ...
processors
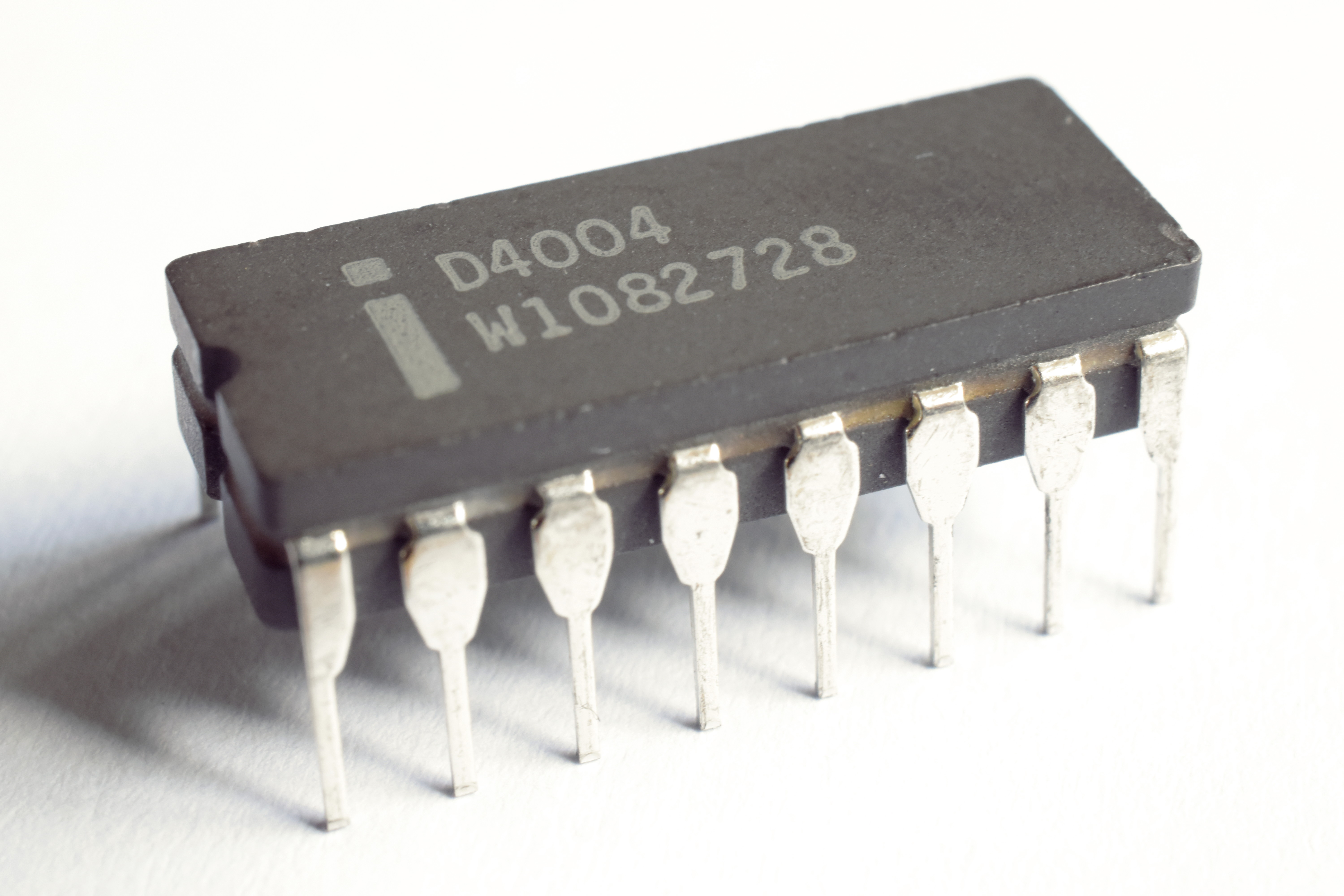

Intel 4004
The Intel 4004 was part of the 4 chip MCS-4 micro computer set, released by the Intel, Intel Corporation in November 1971; the 4004 being part of the first commercially marketed microprocessor chipset, and the first in a long line of List of I ...
First commercially available
microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
(single-chip IC processor)
* Introduced November 15, 1971
* Clock rate 740
kHz
* 0.07
MIPS
* Bus width: 4 bits (multiplexed address/data due to limited pins)
*
PMOS
* 2,300 transistors at 10
μm
*
Addressable memory 640
byte
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable un ...
s
*
Program memory 4
KB (4096 B)
* Originally designed to be used in
Busicom
was a Japanese company that manufactured and sold computer-related products headquartered in Taito, Tokyo. It owned the rights to Intel's first microprocessor, the Intel 4004, which they created in partnership with Intel in 1970.
Busicom aske ...
calculator
MCS-4 family:
* 4004 –
CPU
* 4001 –
ROM
Rom, or ROM may refer to:
Biomechanics and medicine
* Risk of mortality, a medical classification to estimate the likelihood of death for a patient
* Rupture of membranes, a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac
* ...
& 4-bit Port
* 4002 –
RAM
Ram, ram, or RAM most commonly refers to:
* A male sheep
* Random-access memory, computer memory
* Ram Trucks, US, since 2009
** List of vehicles named Dodge Ram, trucks and vans
** Ram Pickup, produced by Ram Trucks
Ram, ram, or RAM may also ref ...
& 4-bit Port
* 4003 – 10-bit Shift Register
* 4008 – Memory+I/O Interface
* 4009 – Memory+I/O Interface
* 4211 – General Purpose Byte I/O Port
* 4265 – Programmable General Purpose I/O Device
* 4269 – Programmable Keyboard Display Device
* 4289 – Standard Memory Interface for MCS-4/40
* 4308 – 8192-bit (1024 × 8) ROM w/ 4-bit I/O Ports
* 4316 – 16384-bit (2048 × 8) Static ROM
* 4702 – 2048-bit (256 × 8) EPROM
* 4801 – 5.185 MHz Clock Generator Crystal for 4004/4201A or 4040/4201A
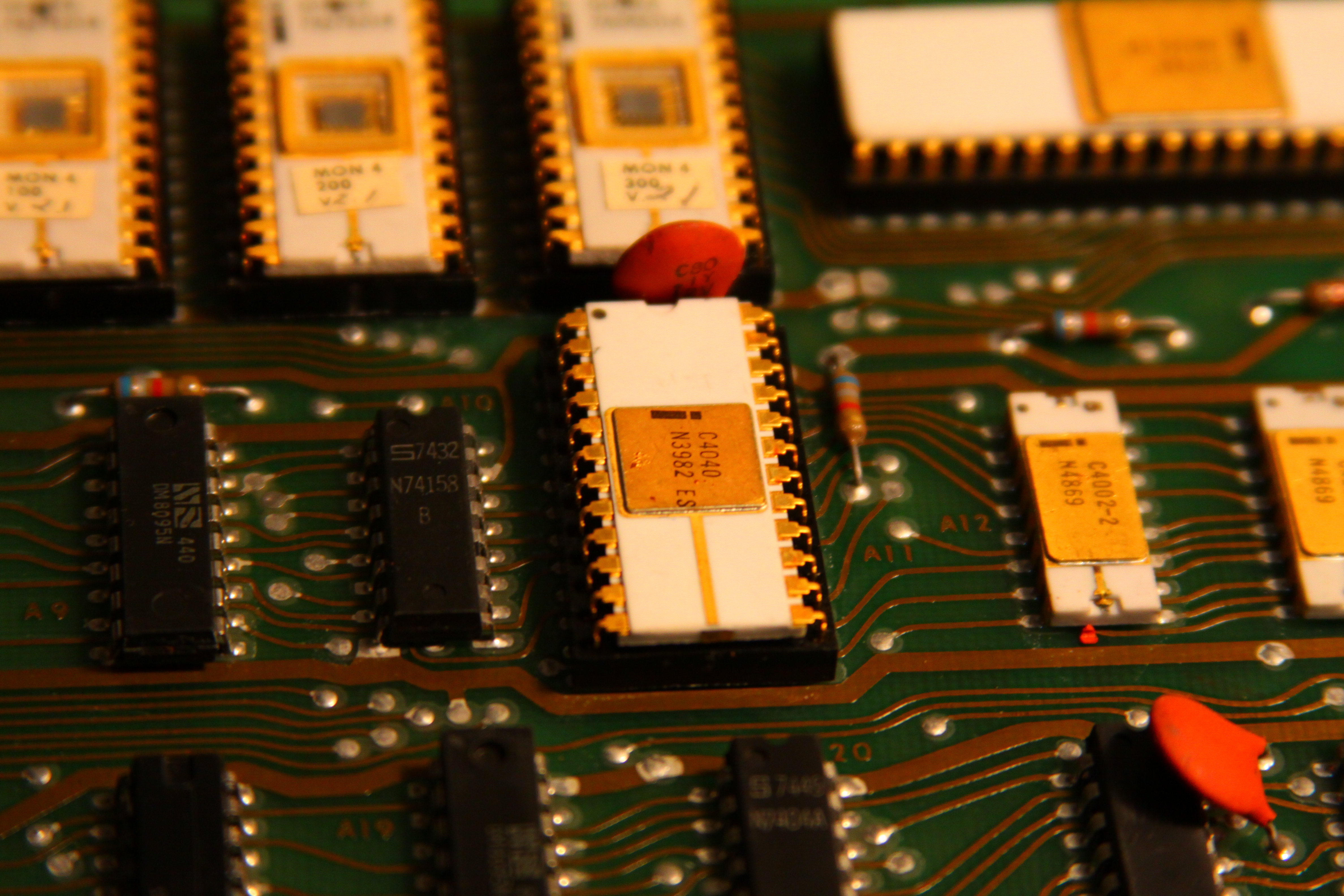
Intel 4040
* Introduced in 1974 by Intel
* Clock speed was 740 kHz (same as the 4004 microprocessor)
* 3,000 transistors
* Interrupt features were available
* Programmable memory size: 8 KB (8192 B)
* 640 bytes of data memory
* 24-pin DIP
The
8-bit
In computer architecture, 8-bit integers or other data units are those that are 8 bits wide (1 octet). Also, 8-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers or data bu ...
processors

8008
* Introduced April 1, 1972
* Clock rate 500 kHz (8008-1: 800 kHz)
* 0.05 MIPS
* Bus width: 8 bits (multiplexed address/data due to limited pins)
* Enhancement load
PMOS logic
PMOS or pMOS logic, from p-channel metal–oxide–semiconductor, is a family of digital circuits based on p-channel, enhancement mode metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). In the late 1960s and early 1970s, PMOS ...
* 3,500 transistors at 10 μm
* Addressable memory 16 KB
* Typical in early 8-bit microcomputers, dumb terminals, general calculators, bottling machines
* Developed in tandem with 4004
* Originally intended for use in the
Datapoint 2200
The Datapoint 2200 was a mass-produced programmable terminal usable as a computer, designed by Computer Terminal Corporation (CTC) founders Phil Ray and Gus Roche and announced by CTC in June 1970 (with units shipping in 1971). It was initially ...
microcomputer
* Key volume deployment in Texas Instruments 742 microcomputer in >3,000 Ford dealerships

8080
The Intel 8080 is Intel's second 8-bit microprocessor. Introduced in April 1974, the 8080 was an enhanced successor to the earlier Intel 8008 microprocessor, although without binary compatibility.'' Electronic News'' was a weekly trade newspa ...
* Introduced April 1, 1974
* Clock rate 2 MHz (very rare 8080B: 3 MHz)
* 0.29 MIPS
* Data bus width: 8 bits, address bus: 16 bits
* Enhancement load
NMOS logic
NMOS or nMOS logic (from N-type metal–oxide–semiconductor) uses n-type (-) MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) to implement logic gates and other digital circuits.
NMOS transistors operate by creating an inv ...
* 4,500 transistors at 6 μm
*
Assembly language
In computing, assembly language (alternatively assembler language or symbolic machine code), often referred to simply as assembly and commonly abbreviated as ASM or asm, is any low-level programming language with a very strong correspondence bet ...
downward compatible with 8008
* Addressable memory 64 KB (64 × 1024 B)
* Up to 10× the performance of the 8008
* Used in e.g. the
Altair 8800
The Altair 8800 is a microcomputer introduced in 1974 by Micro Instrumentation and Telemetry Systems (MITS) based on the Intel 8080 CPU. It was the first commercially successful personal computer. Interest in the Altair 8800 grew quickly after i ...
,
traffic light
Traffic lights, traffic signals, or stoplights – also known as robots in South Africa, Zambia, and Namibia – are signaling devices positioned at intersection (road), road intersections, pedestrian crossings, and other locations in order t ...
controller,
cruise missile
A cruise missile is an unmanned self-propelled guided missile that sustains flight through aerodynamic lift for most of its flight path. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large payload over long distances with high precision. Modern cru ...
* Required six support chips versus 20 for the 8008


8085
* Introduced March 1976
* Clock rate 3 MHz
* 0.37
MIPS
* Data bus width: 8 bits, address bus: 16 bits
* Depletion load
NMOS logic
NMOS or nMOS logic (from N-type metal–oxide–semiconductor) uses n-type (-) MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) to implement logic gates and other digital circuits.
NMOS transistors operate by creating an inv ...
* 6,500 transistors at
3 μm
*
Binary compatible
Binary-code compatibility (binary compatible or object-code compatible) is a property of a computer system, meaning that it can run the same executable code, typically machine code for a general-purpose computer central processing unit (CPU), ...
downward with the 8080
* Used in
Toledo scales. Also used as a computer peripheral controller – modems, hard disks, printers, etc.
*
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss
", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary an ...
80C85 in
Mars Sojourner,
Radio Shack Model 100 portable
Microcontrollers
They are ICs with CPU, RAM, ROM (or PROM or EPROM), I/O Ports, Timers & Interrupts

Intel 8048
* Single
accumulator Harvard architecture
The Harvard architecture is a computer architecture with separate computer storage, storage and signal pathways for Machine code, instructions and data. It is often contrasted with the von Neumann architecture, where program instructions and d ...
MCS-48 family:
* Intel 8020 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 1 KB ROM, 64 Byte RAM, 13 I/O ports
* Intel 8021 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 1 KB ROM, 64 Byte RAM, 21 I/O ports
* Intel 8022 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, With On-Chip A/D Converter
* Intel 8035 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 64 Byte RAM
* Intel 8039 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 128 Byte RAM
* Intel 8040 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 256 Byte RAM
* Intel 8048 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 1 KB ROM, 64 byte RAM, 27 I/O ports, 0.73 MIPS @ 11 MHz
* Intel 8049 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 2 KB ROM, 128 byte RAM, 27 I/O ports,
* Intel 8050 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 4 KB ROM, 256 byte RAM, 27 I/O ports,
* Intel 8748 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 1 KB EPROM, 64 byte RAM, 27 I/O ports,
* Intel 8749 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 2 KB EPROM, 128 byte RAM, 27 I/O ports,
* Intel 87P50 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, ext. ROM socket (2758/2716/2732), 256 byte RAM, 27 I/O ports
* Intel 8648 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 1 KB OTP EPROM, 64 byte RAM, 27 I/O ports
* Intel 8041 – Universal Peripheral Interface 8-bit Slave Microcontroller, 1 KB ROM, 64 byte RAM
* Intel 8041AH – Universal Peripheral Interface 8-bit Slave Microcontroller, 1 KB ROM, 128 byte RAM
* Intel 8641 – Universal Peripheral Interface 8-bit Slave Microcontroller ?
* Intel 8741 – Universal Peripheral Interface 8-bit Slave Microcontroller, 1 KB EPROM, 64 byte RAM
* Intel 8741AH – Universal Peripheral Interface 8-bit Slave Microcontroller, 1 KB EPROM, 128 byte RAM
* Intel 8042 – Universal Peripheral Interface 8-bit Slave Microcontroller, 2 KB ROM, 256 byte RAM
* Intel 8742 – Universal Peripheral Interface 8-bit Slave Microcontroller, 2 KB EPROM, 128 byte RAM
* Intel 8742AH – Universal Peripheral Interface 8-bit Slave Microcontroller, 2 KB OTP EPROM, 256 byte RAM
* Intel 8243 – Input/Output Expander. The available 28-pin
PLCC version in sampling for first quarter of 1986.
* Intel 8244 – General Purpose Graphics Display Device (ASIC NTSC/SECAM)
* Intel 8245 – General Purpose Graphics Display Device (ASIC PAL)

Intel 8051
* Single
accumulator Harvard architecture
The Harvard architecture is a computer architecture with separate computer storage, storage and signal pathways for Machine code, instructions and data. It is often contrasted with the von Neumann architecture, where program instructions and d ...
MCS-51
The Intel MCS-51 (commonly termed 8051) is a single-chip microcontroller (MCU) series developed by Intel in 1980 for use in embedded systems. The architect of the Intel MCS-51 instruction set was John H. Wharton.. Intel's original versions w ...
family:
* 8031 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8032 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8044 – High Performance 8-bit Microcontroller
* 8344 – High Performance 8-bit Microcontroller
* 8744 – High Performance 8-bit Microcontroller
* 8051 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8052 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8054 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8058 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8351 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8352 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8354 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8358 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8751 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8752 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8754 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8758 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
Intel 80151
* Single
accumulator Harvard architecture
The Harvard architecture is a computer architecture with separate computer storage, storage and signal pathways for Machine code, instructions and data. It is often contrasted with the von Neumann architecture, where program instructions and d ...
MCS-151 family:
* 80151 – High Performance 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 83151 – High Performance 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 87151 – High Performance 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 80152 – High Performance 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 83152 – High Performance 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
Intel 80251
* Single
accumulator Harvard architecture
The Harvard architecture is a computer architecture with separate computer storage, storage and signal pathways for Machine code, instructions and data. It is often contrasted with the von Neumann architecture, where program instructions and d ...
MCS-251 family:
* 80251 – 8/16/
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in a maximum of 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform la ...
Microcontroller
* 80252 – 8/16/32-bit Microcontroller
* 80452 – 8/16/32-bit Microcontroller
* 83251 – 8/16/32-bit Microcontroller
* 87251 – 8/16/32-bit Microcontroller
* 87253 – 8/16/32-bit Microcontroller
MCS-96 family
* 8061 – 16-bit Microcontroller (parent of MCS-96 family ROMless With A/D, most sold to Ford)
* 8094 –
16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two ...
Microcontroller (48-Pin ROMLess Without A/D)
* 8095 – 16-bit Microcontroller (48-Pin ROMLess With A/D)
* 8096 – 16-bit Microcontroller (68-Pin ROMLess Without A/D)
* 8097 – 16-bit Microcontroller (68-Pin ROMLess With A/D)
* 8394 – 16-bit Microcontroller (48-Pin With ROM Without A/D)
* 8395 – 16-bit Microcontroller (48-Pin With ROM With A/D)
* 8396 – 16-bit Microcontroller (68-Pin With ROM Without A/D)
* 8397 – 16-bit Microcontroller (68-Pin With ROM With A/D)
* 8794 – 16-bit Microcontroller (48-Pin With EROM Without A/D)
* 8795 – 16-bit Microcontroller (48-Pin With EROM With A/D)
* 8796 – 16-bit Microcontroller (68-Pin With EROM Without A/D)
* 8797 – 16-bit Microcontroller (68-Pin With EROM With A/D)
* 8098 – 16-bit Microcontroller
* 8398 – 16-bit Microcontroller
* 8798 – 16-bit Microcontroller
* 80196 – 16-bit Microcontroller
* 83196 – 16-bit Microcontroller
* 87196 – 16-bit Microcontroller
* 80296 – 16-bit Microcontroller
The bit-slice processor
3000 family


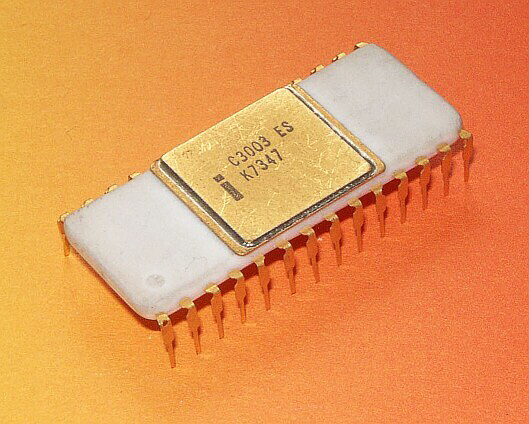
Introduced in the third quarter of 1974, these
bit-slicing components used
bipolar Schottky transistors. Each component implemented two bits of a
processor function; packages could be interconnected to build a processor with any desired word length.
Members of the 3000 family:
* 3001 – Microcontrol Unit
* 3002 – 2-bit Arithmetic Logic Unit slice
* 3003 – Look-ahead Carry Generator
* 3205 – High-performance 1 of 8 Binary Decoder
* 3207 – Quad Bipolar-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver
* 3208 – Hex Sense Amp and Latch for MOS Memories
* 3210 – TTL-to-MOS Level Shifter and High Voltage Clock Driver
* 3211 – ECL-to-MOS Level Shifter and High Voltage Clock Driver
* 3212 – Multimode Latch Buffer
* 3214 – Interrupt Control Unit
* 3216 – Parallel, Inverting Bi-Directional Bus Driver
* 3222 – Refresh Controller for 4K (4096 B) NMOS DRAMs
* 3226 – Parallel, Inverting Bi-Directional Bus Driver
* 3232 – Address Multiplexer and Refresh Counter for 4K DRAMs
* 3242 – Address Multiplexer and Refresh Counter for 16K (16 × 1024 B) DRAMs
* 3245 – Quad Bipolar TTL-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver for 4K
* 3246 – Quad Bipolar ECL-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver for 4K
* 3404 – High-performance 6-bit Latch
* 3408 – Hex Sense Amp and Latch for MOS Memories
* 3505 – Next generation processor
Bus width 2''n'' bits data/address (depending on number ''n'' of slices used)
The
16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two ...
processors: MCS-86 family
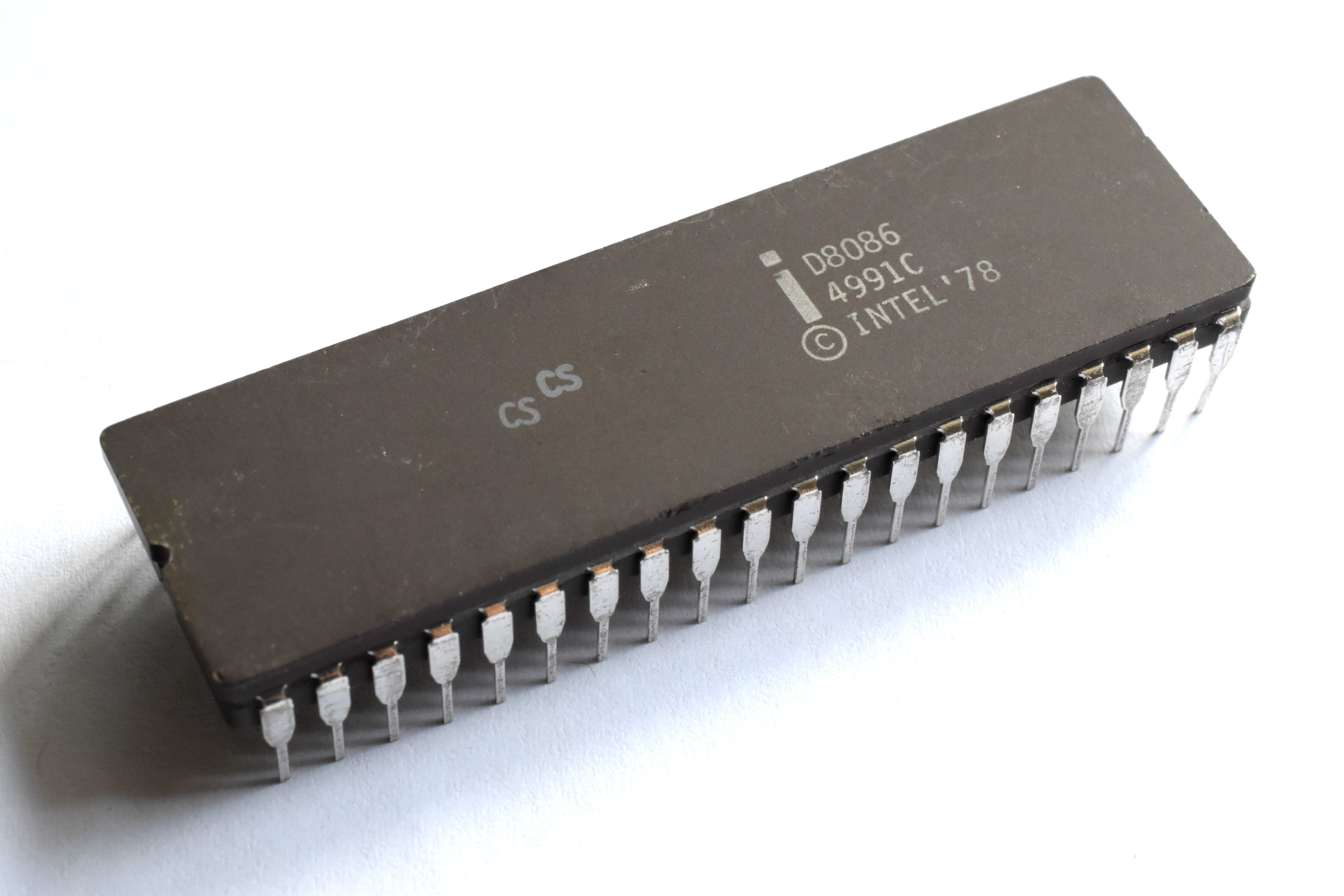
8086
The 8086 (also called iAPX 86) is a 16-bit microprocessor chip designed by Intel between early 1976 and June 8, 1978, when it was released. The Intel 8088, released July 1, 1979, is a slightly modified chip with an external 8-bit data bus (allo ...
* Introduced June 8, 1978
* Clock rates:
** 5 MHz, 0.33 MIPS
** 8 MHz, 0.66 MIPS
** 10 MHz, 0.75 MIPS
* The memory is divided into odd and even banks. It accesses both banks concurrently to read 16 bits of data in one clock cycle
* Data bus width: 16 bits, address bus: 20 bits
* 29,000 transistors at 3 μm
* Addressable memory 1 megabyte (1024B)
* Up to 10× the performance of 8080
* First used in the Compaq Deskpro IBM PC-compatible computers. Later used in portable computing, and in the
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
PS/2 Model 25 and
Model 30. Also used in the
AT&T PC6300 / Olivetti M24, a popular IBM PC-compatible (predating the IBM PS/2 line) and the WANG PC.
* Used
segment registers to access more than 64 KB of data at once, which many programmers complained made their work excessively difficult.
* The first x86 CPU
* Later renamed the iAPX 86
[Intel IAPX 86,88 User's Manual, August 1981, Intel order number 210201-001]

8088
* Introduced June 1, 1979
* Clock rates:
** 4.77 MHz, 0.33 MIPS
** 8 MHz, 0.66 MIPS
* 16-bit internal architecture
* External data bus width: 8 bits, address bus: 20 bits
* 29,000 transistors at 3 μm
* Addressable memory 1 megabyte
* Identical to 8086 except for its 8-bit external bus (hence an ''8'' instead of a ''6'' at the end); identical Execution Unit (EU), different Bus Interface Unit (BIU)
* Used in
IBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the List of IBM Personal Computer models, IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible ''de facto'' standard. Released on ...
and PC-XT and compatibles
* Later renamed the iAPX 88

80186
* Introduced 1982
* Clock rates
** 6 MHz, > 1 MIPS
* 55,000 transistors
* Included two timers, a
DMA controller, and an
interrupt controller
In computing, a programmable interrupt controller (PIC) is an integrated circuit that helps a microprocessor (or CPU) handle interrupt requests (IRQs) coming from multiple different sources (like external I/O devices) which may occur simultane ...
on the chip in addition to the processor (these were at fixed addresses which differed from the IBM PC, although it was used by several PC compatible vendors such as Australian company Cleveland)
* Added a few opcodes and exceptions to the 8086 design, otherwise identical instruction set to 8086 and 8088
** BOUND, ENTER, LEAVE
** INS, OUTS
** IMUL imm, PUSH imm, PUSHA, POPA
** RCL/RCR/ROL/ROR/SHL/SHR/SAL/SAR reg, imm
* Address calculation and shift operations are faster than 8086
* Used mostly in embedded applications – controllers, point-of-sale systems, terminals, and the like
* Used in several non-PC compatible
DOS computers including
RM Nimbus,
Tandy 2000
The Tandy 2000 is a personal computer introduced by Radio Shack in September 1983 based on the 8 MHz Intel 80186 microprocessor running MS-DOS. By comparison, the IBM PC XT (introduced in March 1983) used the older 4.77 MHz Intel 8088 ...
, and CP/M 86 Televideo PM16 server
* Later renamed to iAPX 186
80188
* A version of the 80186 with an 8-bit external data bus
* Later renamed the iAPX 188

80286
* Introduced February 1, 1982
* Clock rates:
** 6 MHz, 0.9 MIPS
** 8 MHz, 10 MHz, 1.5 MIPS
** 12.5 MHz, 2.66 MIPS
** 16 MHz, 20 MHz and 25 MHz available.
* Data bus width: 16 bits, address bus: 24 bits
* Included memory protection hardware to support multitasking operating systems with per-process address space.
* 134,000 transistors at
1.5 μm
* Addressable memory 16
MB
* Added protected-mode features to 8086 with essentially the same instruction set
* 3–6× the performance of the 8086
* Widely used in
IBM PC AT
The IBM Personal Computer AT (model 5170, abbreviated as IBM AT or PC/AT) was released in 1984 as the fourth model in the IBM Personal Computer line, following the IBM PC/XT and its IBM Portable PC variant. It was designed around the Intel 802 ...
and AT clones contemporary to it
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in a maximum of 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform la ...
processors: the non-x86 microprocessors
iAPX 432
* Introduced January 1, 1981 as Intel's first
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in a maximum of 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform la ...
microprocessor
* Multi-chip CPU
* Object/capability architecture
* Microcoded operating system primitives
* One terabyte virtual address space
* Hardware support for fault tolerance
* Two-chip General Data Processor (GDP), consists of 43201 and 43202
* 43203 Interface Processor (IP) interfaces to I/O subsystem
* 43204 Bus Interface Unit (BIU) simplifies building multiprocessor systems
* 43205 Memory Control Unit (MCU)
* Architecture and execution unit internal data base paths: 32 bits
* Clock rates:
** 5 MHz
** 7 MHz
** 8 MHz
i960 a.k.a. 80960
* Introduced April 5, 1988
*
RISC
In electronics and computer science, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer architecture designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a comp ...
-like
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in a maximum of 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform la ...
architecture
* Predominantly used in embedded systems
* Evolved from the capability processor developed for the
BiiN
BiiN Corporation was a company created out of a joint research project by Intel and Siemens to develop fault tolerant high-performance multi-processor computers build on custom microprocessor designs. BiiN was an outgrowth of the Intel iAPX 43 ...
joint venture with
Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational technology conglomerate. It is focused on industrial automation, building automation, rail transport and health technology. Siemens is the largest engineering company in Europe, and holds the positi ...
* Many variants identified by two-letter suffixes
i860 a.k.a. 80860
* Initial version 80860XR Introduced February 26, 1989
*
RISC
In electronics and computer science, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer architecture designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a comp ...
32/
64-bit
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit central processing units (CPU) and arithmetic logic units (ALU) are those that are based on processor registers, a ...
architecture, with floating point pipeline characteristics very visible to programmer
* Used in the
Intel iPSC/860 Hypercube
In geometry, a hypercube is an ''n''-dimensional analogue of a square ( ) and a cube ( ); the special case for is known as a ''tesseract''. It is a closed, compact, convex figure whose 1- skeleton consists of groups of opposite parallel l ...
parallel supercomputer
* Mid-life kicker in the 80860XP processor (primarily a speed bump, some refinement/extension of instruction set)
* Used in the
Intel Delta massively parallel supercomputer prototype, emplaced at
California Institute of Technology
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech) is a private research university in Pasadena, California, United States. The university is responsible for many modern scientific advancements and is among a small group of institutes ...
* Used in the
Intel Paragon massively parallel supercomputer, emplaced at
Sandia National Laboratory
XScale
XScale is a microarchitecture for central processing units initially designed by Intel implementing the ARM architecture (version 5) instruction set. XScale comprises several distinct families: IXP, IXC, IOP, PXA and CE (see more below), with some ...
* Introduced August 23, 2000
*
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in a maximum of 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform la ...
RISC
In electronics and computer science, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer architecture designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a comp ...
microprocessor based on the
ARM architecture
ARM (stylised in lowercase as arm, formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a family of reduced instruction set computer, RISC instruction set architectures (ISAs) for central processing unit, com ...
* Many variants, such as the PXA2xx applications processors, IOP3xx I/O processors and IXP2xxx and IXP4xx network processors
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in a maximum of 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform la ...
processors: the 80386 range


80386DX
* Introduced October 17, 1985
* Clock rates:
** 16 MHz, 5 MIPS
** 20 MHz, 6 to 7 MIPS, introduced February 16, 1987
** 25 MHz, 7.5 MIPS, introduced April 4, 1988
** 33 MHz, 9.9 MIPS (9.4 SPECint92 on Compaq/i 16 KB L2), introduced April 10, 1989
* Data bus width: 32 bits, address bus: 32 bits
* 275,000 transistors at 1 μm
* Addressable memory 4
GB (4 × 1024 B)
*
Virtual memory
In computing, virtual memory, or virtual storage, is a memory management technique that provides an "idealized abstraction of the storage resources that are actually available on a given machine" which "creates the illusion to users of a ver ...
64
TB (64 × 1024 B)
* First x86 chip to handle
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in a maximum of 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform la ...
data sets
* Reworked and expanded memory protection support including
paged virtual memory and virtual-86 mode, features required at the time by
Xenix
Xenix is a discontinued Unix operating system for various microcomputer platforms, licensed by Microsoft from AT&T Corporation. The first version was released in 1980, and Xenix was the most common Unix variant during the mid- to late-1980s. T ...
and
Unix
Unix (, ; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, a ...
. This memory capability spurred the development and availability of
OS/2
OS/2 is a Proprietary software, proprietary computer operating system for x86 and PowerPC based personal computers. It was created and initially developed jointly by IBM and Microsoft, under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci, ...
and is a fundamental requirement for modern operating systems like
Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
,
Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
, and
macOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
* First used by Compaq in the
Deskpro 386. Used in desktop computing
* Unlike the DX naming convention of the 486 chips, it had no math co-processor
* Later renamed Intel386 DX
80386SX
The Intel 386, originally released as the 80386 and later renamed i386, is the third-generation x86 architecture microprocessor from Intel. It was the first 32-bit computing, 32-bit processor in the line, making it a significant evolution in ...
* Introduced June 16, 1988
* Clock rates:
** 16 MHz, 2.5 MIPS
** 20 MHz, 3.1 MIPS, introduced January 25, 1989
** 25 MHz, 3.9 MIPS, introduced January 25, 1989
** 33 MHz, 5.1 MIPS, introduced October 26, 1992
* 32-bit internal architecture
* External data bus width: 16 bits
* External address bus width: 24 bits
* 275,000 transistors at 1 μm
* Addressable memory 16 MB
* Virtual memory 64 TB
* Narrower buses enable low-cost 32-bit processing
* Used in entry-level desktop and portable computing
* No math co-processor
* No commercial software used protected mode or virtual storage for many years
* Later renamed Intel386 SX
80376

* Introduced January 16, 1989; discontinued June 15, 2001
* Variant of 386SX intended for embedded systems
* No "real mode", starts up directly in "protected mode"
* Replaced by much more successful
80386EX from 1994
80386SL
* Introduced October 15, 1990
* Clock rates:
** 20 MHz, 4.21 MIPS
** 25 MHz, 5.3 MIPS, introduced September 30, 1991
* 32-bit internal architecture
* External bus width: 16 bits
* 855,000 transistors at 1 μm
* Addressable memory 4 GB
* Virtual memory 64 TB
* First chip specifically made for portable computers because of low power consumption of chip
* Highly integrated, includes cache, bus, and memory controllers

80386EX
* Introduced August 1994
* Variant of 80386SX intended for
embedded system
An embedded system is a specialized computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is e ...
s
* Static core (i.e. may run as slowly (and thus, power efficiently) as desired) down to full halt
* On-chip peripherals:
** Clock and power management
** Timers/counters
**
Watchdog timer
A watchdog timer (WDT, or simply a ''watchdog''), sometimes called a ''computer operating properly timer'' (''COP timer''), is an electronic or software timer that is used to detect and recover from computer malfunctions. Watchdog timers are wide ...
** Serial I/O units (sync and async) and parallel I/O
**
DMA
** RAM refresh
**
JTAG test logic
* Significantly more successful than the 80376
* Used aboard several orbiting satellites and microsatellites
* Used in NASA's
FlightLinux project
32-bit processors: the 80486 range

80486DX
* Introduced April 10, 1989
* Clock rates:
** 25 MHz, 20 MIPS (16.8 SPECint92, 7.40 SPECfp92)
** 33 MHz, 27 MIPS (22.4 SPECint92 on Micronics M4P 128 KB L2), introduced May 7, 1990
** 50 MHz, 41 MIPS (33.4 SPECint92, 14.5 SPECfp92 on Compaq/50L 256 KB L2), introduced June 24, 1991
* Bus width: 32 bits
* 1.2 million transistors at 1 μm; the 50 MHz was at 0.8 μm
* Addressable memory 4 GB
* Virtual memory 64 TB
*
Level 1 cache of 8 KB on chip
* Math coprocessor on chip
* 50× performance of the 8088
* Officially named Intel486 DX
* Used in desktop computing and servers
* Family 4 model 1

80486SX
* Introduced April 22, 1991
* Clock rates:
** 16 MHz, 13 MIPS
** 20 MHz, 16.5 MIPS, introduced September 16, 1991
** 25 MHz, 20 MIPS (12 SPECint92), introduced September 16, 1991
** 33 MHz, 27 MIPS (15.86 SPECint92), introduced September 21, 1992
* Bus width: 32 bits
* 1.185 million transistors at 1 μm and 900,000 at 0.8 μm
* Addressable memory 4 GB
* Virtual memory 64 TB
* Identical in design to 486DX but without a math coprocessor. The first version was an 80486DX with disabled math coprocessor in the chip and different pin configuration. If the user needed math coprocessor capabilities, they must add 487SX which was actually a 486DX with different pin configuration to prevent the user from installing a 486DX instead of 487SX, so with this configuration 486SX+487SX you had 2 identical CPU's with only 1 effectively turned on
* Officially named Intel486 SX
* Used in low-cost entry to 486 CPU desktop computing, as well as extensively in low cost mobile computing
* Upgradable with the
Intel OverDrive processor
* Family 4 model 2

80486DX2
* Introduced March 3, 1992
* Runs at twice the speed of the external bus (FSB)
* Socket 3
* Clock rates:
** 40 MHz
** 50 MHz, 41 MIPS
** 66 MHz, 54 MIPS
* Officially named Intel486 DX2
* Family 4 model 3

80486SL
* Introduced November 9, 1992
* Clock rates:
** 20 MHz, 15.4 MIPS
** 25 MHz, 19 MIPS
** 33 MHz, 25 MIPS
* Bus width: 32 bits
* 1.4 million transistors at 0.8 μm
* Addressable memory 4 GB
* Virtual memory 64 TB
* Officially named Intel486 SL
* Used in notebook computers
* Family 4 model 4

80486DX4
* Introduced March 7, 1994
* Clock rates:
** 75 MHz, 53 MIPS (41.3 SPECint92, 20.1 SPECfp92 on Micronics M4P 256 KB L2)
** 100 MHz, 70.7 MIPS (54.59 SPECint92, 26.91 SPECfp92 on Micronics M4P 256 KB L2)
* 1.6 million transistors at 0.6 μm
* Bus width: 32 bits
* Addressable memory 4 GB
* Virtual memory 64 TB
*
Socket 3 168-pin
PGA Package, or 208
sq. ftP package
* Officially named Intel486 DX4
* Used in high performance entry-level desktops and value notebooks
* Family 4 model 8
32-bit processors: P5 microarchitecture


Original
Pentium
Pentium is a series of x86 architecture-compatible microprocessors produced by Intel from 1993 to 2023. The Pentium (original), original Pentium was Intel's fifth generation processor, succeeding the i486; Pentium was Intel's flagship proce ...
* Introduced March 22, 1993
* Bus width: 64 bits
* System bus clock rate 60 or 66 MHz
* Address bus: 32 bits
* Addressable memory 4 GB
* Virtual memory 64 TB
*
Superscalar
A superscalar processor (or multiple-issue processor) is a CPU that implements a form of parallelism called instruction-level parallelism within a single processor. In contrast to a scalar processor, which can execute at most one single in ...
architecture
* Runs on 3.3 volts (except the very first generation "P5")
* Used in desktops
* 8 KB of instruction
cache
* 8 KB of data cache
* P5 –
0.8 μm process technology
** Introduced March 22, 1993
** 3.1 million transistors
** The only Pentium to run on 5 Volts
**
Socket 4 273 pin PGA Package
** Package dimensions 2.16 in × 2.16 in
** Family 5 model 1
** Variants
*** 60 MHz, 100 MIPS (70.4 SPECint92, 55.1 SPECfp92 on Xpress 256 KB L2)
*** 66 MHz, 112 MIPS (77.9 SPECint92, 63.6 SPECfp92 on Xpress 256 KB L2)
* P54 –
0.6 μm process technology
**
Socket 5 296/320-pin PGA package
** 3.2 million transistors
** Variants
*** 75 MHz, 126.5 MIPS (2.31 SPECint95, 2.02 SPECfp95 on Gateway P5 256K L2)
**** Introduced October 10, 1994
*** 90, 100 MHz, 149.8 and 166.3 MIPS respectively (2.74 SPECint95, 2.39 SPECfp95 on Gateway P5 256K L2 and 3.30 SPECint95, 2.59 SPECfp95 on Xpress 1ML2 respectively)
**** Introduced March 7, 1994
* P54CQS –
0.35 μm process technology
**
Socket 5 296/320 pin PGA package
** 3.2 million transistors
** Variants
*** 120 MHz, 203 MIPS (3.72 SPECint95, 2.81 SPECfp95 on Xpress 1 MB L2)
**** Introduced March 27, 1995
*

P54CS –
0.35 μm process technology
** 3.3 million transistors
** 90 mm
2 die size
** Family 5 model 2
** Variants
**
Socket 5 296/320-pin PGA package
*** 133 MHz, 218.9 MIPS (4.14 SPECint95, 3.12 SPECfp95 on Xpress 1 MB L2)
**** Introduced June 12, 1995
*** 150, 166 MHz, 230 and 247 MIPS respectively
**** Introduced January 4, 1996
**
Socket 7 296/321-pin PGA package
*** 200 MHz, 270 MIPS (5.47 SPECint95, 3.68 SPECfp95)
**** Introduced June 10, 1996

Pentium with MMX Technology
* P55C –
0.35 μm process technology
** Introduced January 8, 1997
** Intel
MMX (instruction set)
MMX is a ''single instruction, multiple data'' (SIMD) instruction set architecture designed by Intel, introduced on January 8, 1997 with its Pentium P5 (microarchitecture) based line of microprocessors, named "Pentium with MMX Technology". It d ...
support
**
Socket 7 296/321 pin PGA (pin grid array) package
** 16 KB L1 instruction cache
** 16 KB data cache
** 4.5 million transistors
** System bus clock rate 66 MHz
** Basic P55C is family 5 model 4, mobile are family 5 model 7 and 8
** Variants
*** 166, 200 MHz introduced January 8, 1997
*** 233 MHz introduced June 2, 1997
*** 133 MHz (Mobile)
*** 166, 266 MHz (Mobile) introduced January 12, 1998
*** 200, 233 MHz (Mobile) introduced September 8, 1997
*** 300 MHz (Mobile) introduced January 7, 1999
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in a maximum of 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform la ...
processors:
P6/
Pentium M
The Pentium M is a family of mobile 32-bit single-core x86 microprocessors (with the modified Intel P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture) introduced in March 2003 and forming a part of the Intel Centrino#Carmel platform (2003), Carmel no ...
microarchitecture

Pentium Pro
The Pentium Pro is a sixth-generation x86 microprocessor developed and manufactured by Intel and introduced on November 1, 1995. It implements the P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture (sometimes termed i686), and was the first x86 Intel C ...
* Introduced November 1, 1995
* Multichip Module (2 die)
* Precursor to Pentium II and III
* Primarily used in server systems
*
Socket 8 processor package (387 pins; Dual SPGA)
* 5.5 million transistors
* Family 6 model 1
*
0.6 μm process technology
** 16 KB L1 cache
** 256 KB integrated
L2 cache
** 60 MHz system bus clock rate
** Variants
*** 150 MHz
*
0.35 μm process technology, (two die, a 0.35 μm CPU with 0.6 μm L2 cache)
** 5.5 million transistors
** 512 KB or 256 KB integrated L2 cache
** 60 or 66 MHz system bus clock rate
** Variants
*** 150 MHz (60 MHz bus clock rate, 256 KB 0.6 μm cache) introduced November 1, 1995
*** 166 MHz (66 MHz bus clock rate, 512 KB 0.35 μm cache) introduced November 1, 1995
*** 180 MHz (60 MHz bus clock rate, 256 KB 0.6 μm cache) introduced November 1, 1995
*** 200 MHz (66 MHz bus clock rate, 256 KB 0.6 μm cache) introduced November 1, 1995
*** 200 MHz (66 MHz bus clock rate, 512 KB 0.35 μm cache) introduced November 1, 1995
*** 200 MHz (66 MHz bus clock rate, 1 MB 0.35 μm cache) introduced August 18, 1997
Pentium II
The Pentium II is a brand of sixth-generation Intel x86 microprocessors based on the P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture, introduced on May 7, 1997. It combined the ''P6'' microarchitecture seen on the Pentium Pro with the MMX (instruc ...
* Introduced May 7, 1997
* Pentium Pro with
MMX and improved
16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two ...
performance
* 242-pin
Slot 1
Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of Intel's microprocessors, including the Pentium Pro, Celeron, Pentium II and the Pentium III. Both single and dual processor configurations were impl ...
(SEC) processor package
* Voltage identification pins
* 7.5 million transistors
* 32 KB L1 cache
* 512 KB frequency external L2 cache
* The ''Performance Enhanced'' mobile Pentium II (codenamed Dixon) had a full-speed 256 KB L2 cache
* Klamath –
0.35 μm process technology (233, 266, 300 MHz)
** 66 MHz system bus clock rate
** Family 6 model 3
** Variants
*** 233, 266, 300 MHz introduced May 7, 1997
* Deschutes –
0.25 μm process technology (333, 350, 400, 450 MHz)
** Introduced January 26, 1998
** 66 MHz system bus clock rate (''333 MHz variant''), 100 MHz system bus clock rate for all subsequent models
** Family 6 model 5
** Variants
*** 333 MHz introduced January 26, 1998
*** 350, 400 MHz introduced April 15, 1998
*** 450 MHz introduced August 24, 1998
*** 233, 266 MHz (Mobile) introduced April 2, 1998
*** 333 MHz Pentium II Overdrive processor for Socket 8 Introduced August 10, 1998
*** 300 MHz (Mobile) introduced September 9, 1998
*** 333 MHz (Mobile) introduced January 25, 1999
Celeron
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor, microprocessors targeted at low-cost Personal computer, personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023.
The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, ...
(Pentium II-based)
* Covington –
0.25 μm process technology
** Introduced April 15, 1998
** 242-pin
Slot 1
Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of Intel's microprocessors, including the Pentium Pro, Celeron, Pentium II and the Pentium III. Both single and dual processor configurations were impl ...
SEPP (Single Edge Processor Package)
** 7.5 million transistors
** 66 MHz system bus clock rate
** Slot 1
** 32 KB L1 cache
** No L2 cache
** Variants
*** 266 MHz introduced April 15, 1998
*** 300 MHz introduced June 9, 1998
* Mendocino –
0.25 μm process technology
** Introduced August 24, 1998
** 242-pin
Slot 1
Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of Intel's microprocessors, including the Pentium Pro, Celeron, Pentium II and the Pentium III. Both single and dual processor configurations were impl ...
SEPP (Single Edge Processor Package),
Socket 370 PPGA package
** 19 million transistors
** 66 MHz system bus clock rate
** Slot 1, Socket 370
** 32 KB L1 cache
** 128 KB integrated cache
** Family 6 model 6
** Variants
*** 300, 333 MHz introduced August 24, 1998
*** 366, 400 MHz introduced January 4, 1999
*** 433 MHz introduced March 22, 1999
*** 466 MHz
*** 500 MHz introduced August 2, 1999
*** 533 MHz introduced January 4, 2000
*** 266 MHz (Mobile)
*** 300 MHz (Mobile)
*** 333 MHz (Mobile) introduced April 5, 1999
*** 366 MHz (Mobile)
*** 400 MHz (Mobile)
*** 433 MHz (Mobile)
*** 450 MHz (Mobile) introduced February 14, 2000
*** 466 MHz (Mobile)
*** 500 MHz (Mobile) introduced February 14, 2000
Pentium II Xeon ''(chronological entry)''
* Introduced June 29, 1998
Pentium III
The Pentium III (marketed as Intel Pentium III Processor, informally PIII or P3) brand refers to Intel's 32-bit x86 desktop and mobile CPUs based on the sixth-generation P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture introduced on February 28, 1999 ...
* Katmai –
0.25 μm process technology
** Introduced February 26, 1999
** Improved PII (i.e. P6-based core) now including
Streaming SIMD Extensions
In computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE) is a single instruction, multiple data ( SIMD) instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in its Pentium III series of central processing units (CPU ...
(SSE)
** 9.5 million transistors
** 512 KB (512 × 1024 B) bandwidth L2 External cache
** 242-pin
Slot 1
Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of Intel's microprocessors, including the Pentium Pro, Celeron, Pentium II and the Pentium III. Both single and dual processor configurations were impl ...
SECC2 (Single Edge Contact cartridge 2) processor package
** System bus clock rate 100 MHz, 133 MHz (B-models)
** Slot 1
** Family 6 model 7
** Variants
*** 450, 500 MHz introduced February 26, 1999
*** 550 MHz introduced May 17, 1999
*** 600 MHz introduced August 2, 1999
*** 533, 600 MHz introduced (133 MHz bus clock rate) September 27, 1999
* Coppermine –
0.18 μm process technology
** Introduced October 25, 1999
** 28.1 million transistors
** 256 KB (512 × 1024 B) Advanced Transfer L2 cache (integrated)
** 242-pin Slot-1 SECC2 (Single Edge Contact cartridge 2) processor package, 370-pin
FC-PGA (flip-chip pin grid array) package
** System Bus clock rate 100 MHz (E-models), 133 MHz (EB models)
** Slot 1, Socket 370
** Family 6 model 8
** Variants
*** 500 MHz (100 MHz bus clock rate)
*** 533 MHz
*** 550 MHz (100 MHz bus clock rate)
*** 600 MHz
*** 600 MHz (100 MHz bus clock rate)
*** 650 MHz (100 MHz bus clock rate) introduced October 25, 1999
*** 667 MHz introduced October 25, 1999
*** 700 MHz (100 MHz bus clock rate) introduced October 25, 1999
*** 733 MHz introduced October 25, 1999
*** 750, 800 MHz (100 MHz bus clock rate) introduced December 20, 1999
*** 850 MHz (100 MHz bus clock rate) introduced March 20, 2000
*** 866 MHz introduced March 20, 2000
*** 933 MHz introduced May 24, 2000
*** 1000 MHz introduced March 8, 2000 (not widely available at time of release)
*** 1100 MHz
*** 1133 MHz (first version recalled, later re-released)
*** 400, 450, 500 MHz (Mobile) introduced October 25, 1999
*** 600, 650 MHz (Mobile) introduced January 18, 2000
*** 700 MHz (Mobile) introduced April 24, 2000
*** 750 MHz (Mobile) introduced June 19, 2000
*** 800, 850 MHz (Mobile) introduced September 25, 2000
*** 900, 1000 MHz (Mobile) introduced March 19, 2001
* Tualatin –
0.13 μm process technology
** Introduced July 2001
** 28.1 million transistors
** 32 KB (32 × 1024 B) L1 cache
** 256 KB or 512 KB Advanced Transfer L2 cache (integrated)
** 370-pin
FC-PGA2 (flip-chip pin grid array) package
** 133 MHz system bus clock rate
** Socket 370
** Family 6 model 11
** Variants
*** 1133 MHz (256 KB L2)
*** 1133 MHz (512 KB L2)
*** 1200 MHz
*** 1266 MHz (512 KB L2)
*** 1333 MHz
*** 1400 MHz (512 KB L2)
Pentium II
Xeon
Xeon (; ) is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same archite ...
and Pentium III Xeon
* PII Xeon
** Variants
*** 400 MHz introduced June 29, 1998
*** 450 MHz (512 KB L2 cache) introduced October 6, 1998
*** 450 MHz (1 MB and 2 MB L2 cache) introduced January 5, 1999
* PIII Xeon
** Introduced October 25, 1999
** 9.5 million transistors at 0.25 μm or 28 million at 0.18 μm
** L2 cache is 256 KB, 1 MB, or 2 MB Advanced Transfer Cache (Integrated)
** Processor Package Style is Single Edge Contact Cartridge (S.E.C.C.2) or SC330
** System Bus clock rate 133 MHz (256 KB L2 cache) or 100 MHz (1–2 MB L2 cache)
** System Bus width: 64 bits
** Addressable memory: 64 GB
** Used in two-way servers and workstations (256 KB L2) or 4- and 8-way servers (1–2 MB L2)
** Family 6 model 10
** Variants
*** 500 MHz (
0.25 μm process) introduced March 17, 1999
*** 550 MHz (0.25 μm process) introduced August 23, 1999
*** 600 MHz (
0.18 μm process, 256 KB L2 cache) introduced October 25, 1999
*** 667 MHz (0.18 μm process, 256 KB L2 cache) introduced October 25, 1999
*** 733 MHz (0.18 μm process, 256 KB L2 cache) introduced October 25, 1999
*** 800 MHz (0.18 μm process, 256 KB L2 cache) introduced January 12, 2000
*** 866 MHz (0.18 μm process, 256 KB L2 cache) introduced April 10, 2000
*** 933 MHz (0.18 μm process, 256 KB L2 cache)
*** 1000 MHz (0.18 μm process, 256 KB L2 cache) introduced August 22, 2000
*** 700 MHz (0.18 μm process, 1–2 MB L2 cache) introduced May 22, 2000
Celeron
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor, microprocessors targeted at low-cost Personal computer, personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023.
The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, ...
(Pentium III Coppermine-based)
* Coppermine-128, 0.18 μm process technology
** Introduced March, 2000
**
Streaming SIMD Extensions
In computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE) is a single instruction, multiple data ( SIMD) instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in its Pentium III series of central processing units (CPU ...
(SSE)
**
Socket 370,
FC-PGA processor package
** 28.1 million transistors
** 66 MHz system bus clock rate, 100 MHz system bus clock rate from January 3, 2001
** 32 KB L1 cache
** 128 KB Advanced Transfer L2 cache
** Family 6 model 8
** Variants
*** 533 MHz
*** 566 MHz
*** 600 MHz
*** 633, 667, 700 MHz introduced June 26, 2000
*** 733, 766 MHz introduced November 13, 2000
*** 800 MHz introduced January 3, 2001
*** 850 MHz introduced April 9, 2001
*** 900 MHz introduced July 2, 2001
*** 950, 1000, 1100 MHz introduced August 31, 2001
*** 550 MHz (Mobile)
*** 600, 650 MHz (Mobile) introduced June 19, 2000
*** 700 MHz (Mobile) introduced September 25, 2000
*** 750 MHz (Mobile) introduced March 19, 2001
*** 800 MHz (Mobile)
*** 850 MHz (Mobile) introduced July 2, 2001
*** 600 MHz (LV Mobile)
*** 500 MHz (ULV Mobile) introduced January 30, 2001
*** 600 MHz (ULV Mobile)
XScale ''(chronological entry – non-x86 architecture)''
* Introduced August 23, 2000
Pentium 4 (not 4EE, 4E, 4F), Itanium, P4-based Xeon, Itanium 2 ''(chronological entries)''
* Introduced April 2000 – July 2002
Pentium III Tualatin-based
* Tualatin –
0.13 μm process technology
** 32 KB L1 cache
** 512 KB Advanced Transfer L2 cache
** 133 MHz system bus clock rate
** Socket 370
** Variants
*** 1.0 GHz
*** 1.13 GHz
*** 1.26 GHz
*** 1.4 GHz
Celeron
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor, microprocessors targeted at low-cost Personal computer, personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023.
The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, ...
(Pentium III Tualatin-based)
* Tualatin Celeron –
0.13 μm process technology
** 32 KB L1 cache
** 256 KB Advanced Transfer L2 cache
** 100 MHz system bus clock rate
** Socket 370
** Family 6 model 11
** Variants
*** 1.0 GHz
*** 1.1 GHz
*** 1.2 GHz
*** 1.3 GHz
*** 1.4 GHz
Pentium M
The Pentium M is a family of mobile 32-bit single-core x86 microprocessors (with the modified Intel P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture) introduced in March 2003 and forming a part of the Intel Centrino#Carmel platform (2003), Carmel no ...
* Banias
0.13 μm process technology
** Introduced March 2003
** 64 KB L1 cache
** 1 MB L2 cache (integrated)
** Based on Pentium III core, with
SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. SSE2 instructions allow the use of ...
SIMD instructions and deeper pipeline
** 77 million transistors
**
Micro-FCPGA,
Micro-FCBGA processor package
** Heart of the Intel mobile ''
Centrino'' system
** 400 MHz NetBurst-style system bus
** Family 6 model 9
** Variants
*** 900 MHz (ultra-low voltage)
*** 1.0 GHz (ultra-low voltage)
*** 1.1 GHz (low voltage)
*** 1.2 GHz (low voltage)
*** 1.3 GHz
*** 1.4 GHz
*** 1.5 GHz
*** 1.6 GHz
*** 1.7 GHz
* Dothan 0.09 μm (
90 nm) process technology
** Introduced May 2004
** 2 MB L2 cache
** 140 million transistors
** Revised data prefetch unit
** 400 MHz NetBurst-style system bus
** 21 W
TDP
** Family 6 model 13
** Variants
*** 1.00 GHz (Pentium M 723) (ultra-low voltage, 5 W TDP)
*** 1.10 GHz (Pentium M 733) (ultra-low voltage, 5 W TDP)
*** 1.20 GHz (Pentium M 753) (ultra-low voltage, 5 W TDP)
*** 1.30 GHz (Pentium M 718) (low voltage, 10 W TDP)
*** 1.40 GHz (Pentium M 738) (low voltage, 10 W TDP)
*** 1.50 GHz (Pentium M 758) (low voltage, 10 W TDP)
*** 1.60 GHz (Pentium M 778) (low voltage, 10 W TDP)
*** 1.40 GHz (Pentium M 710)
*** 1.50 GHz (Pentium M 715)
*** 1.60 GHz (Pentium M 725)
*** 1.70 GHz (Pentium M 735)
*** 1.80 GHz (Pentium M 745)
*** 2.00 GHz (Pentium M 755)
*** 2.10 GHz (Pentium M 765)
* Dothan 533 0.09 μm (
90 nm) process technology
** Introduced Q1 2005
** Same as Dothan except with a 533 MHz NetBurst-style system bus and 27 W
TDP
** Variants
*** 1.60 GHz (Pentium M 730)
*** 1.73 GHz (Pentium M 740)
*** 1.86 GHz (Pentium M 750)
*** 2.00 GHz (Pentium M 760)
*** 2.13 GHz (Pentium M 770)
*** 2.26 GHz (Pentium M 780)
* Stealey 0.09 μm (
90 nm) process technology
** Introduced Q2 2007
** 512 KB L2, 3 W TDP
** Variants
*** 600 MHz (A100)
*** 800 MHz (A110)
Celeron M
* Banias-512
0.13 μm process technology
** Introduced March 2003
** 64 KB L1 cache
** 512 KB L2 cache (integrated)
**
SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. SSE2 instructions allow the use of ...
SIMD instructions
** No
SpeedStep
Enhanced SpeedStep is a series of dynamic frequency scaling technologies (codenamed Geyserville and including SpeedStep, SpeedStep II, and SpeedStep III) built into some Intel's microprocessors that allow the clock speed of the processor to be ...
technology, is not part of the '
Centrino' package
** Family 6 model 9
** Variants
*** 310, 1.20 GHz
*** 320, 1.30 GHz
*** 330, 1.40 GHz
*** 340, 1.50 GHz
* Dothan-1024
90 nm process technology
** 64 KB L1 cache
** 1 MB L2 cache (integrated)
**
SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. SSE2 instructions allow the use of ...
SIMD instructions
** No
SpeedStep
Enhanced SpeedStep is a series of dynamic frequency scaling technologies (codenamed Geyserville and including SpeedStep, SpeedStep II, and SpeedStep III) built into some Intel's microprocessors that allow the clock speed of the processor to be ...
technology, is not part of the '
Centrino' package
** Variants
*** 350, 1.30 GHz
*** 350J, 1.30 GHz, with Execute Disable bit
*** 360, 1.40 GHz
*** 360J, 1.40 GHz, with Execute Disable bit
*** 370, 1.50 GHz, with Execute Disable bit
**** Family 6, Model 13, Stepping 8
*** 380, 1.60 GHz, with Execute Disable bit
*** 390, 1.70 GHz, with Execute Disable bit
*
Yonah-1024
65 nm process technology
** 64 KB L1 cache
** 1 MB L2 cache (integrated)
**
SSE3
SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions (PNI), is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 (x86) architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revis ...
SIMD instructions, 533 MHz front-side bus, execute-disable bit
** No
SpeedStep
Enhanced SpeedStep is a series of dynamic frequency scaling technologies (codenamed Geyserville and including SpeedStep, SpeedStep II, and SpeedStep III) built into some Intel's microprocessors that allow the clock speed of the processor to be ...
technology, is not part of the '
Centrino' package
** Variants
*** 410, 1.46 GHz
*** 420, 1.60 GHz,
*** 423, 1.06 GHz (ultra-low voltage)
*** 430, 1.73 GHz
*** 440, 1.86 GHz
*** 443, 1.20 GHz (ultra-low voltage)
*** 450, 2.00 GHz
Intel Core
Intel Core is a line of multi-core (with the exception of Core Solo and Core 2 Solo) central processing units (CPUs) for midrange, embedded, workstation, high-end and enthusiast computer markets marketed by Intel Corporation. These processors ...
*
Yonah 0.065 μm (
65 nm) process technology
** Introduced January 2006
** 533/667 MHz
front-side bus
The front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface ( bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between th ...
** 2 MB (Shared on Duo) L2 cache
**
SSE3
SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions (PNI), is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 (x86) architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revis ...
SIMD instructions
** 31W
TDP (T versions)
** Family 6, Model 14
** Variants:
*** Intel Core Duo T2700 2.33 GHz
*** Intel Core Duo T2600 2.16 GHz
*** Intel Core Duo T2500 2 GHz
*** Intel Core Duo T2450 2 GHz
*** Intel Core Duo T2400 1.83 GHz
*** Intel Core Duo T2300 1.66 GHz
*** Intel Core Duo T2050 1.6 GHz
*** Intel Core Duo T2300e 1.66 GHz
*** Intel Core Duo T2080 1.73 GHz
*** Intel Core Duo L2500 1.83 GHz (low voltage, 15 W
TDP)
*** Intel Core Duo L2400 1.66 GHz (low voltage, 15 W TDP)
*** Intel Core Duo L2300 1.5 GHz (low voltage, 15 W TDP)
*** Intel Core Duo U2500 1.2 GHz (ultra-low voltage, 9 W TDP)
*** Intel Core Solo T1350 1.86 GHz (533 FSB)
*** Intel Core Solo T1300 1.66 GHz
*** Intel Core Solo T1200 1.5 GHz
Dual-Core
Xeon
Xeon (; ) is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same archite ...
LV
*
Sossaman 0.065 μm (
65 nm) process technology
** Introduced March 2006
** Based on Yonah core, with
SSE3
SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions (PNI), is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 (x86) architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revis ...
SIMD instructions
** 667 MHz
frontside bus
** 2 MB shared L2 cache
** Variants
*** 2.0 GHz
32-bit processors:
NetBurst
The NetBurst microarchitecture, called P68 inside Intel, was the successor to the P6 microarchitecture in the x86 family of central processing units (CPUs) made by Intel. The first CPU to use this architecture was the Willamette-core Pentium ...
microarchitecture
Pentium 4
Pentium 4 is a series of single-core central processing unit, CPUs for Desktop computer, desktops, laptops and entry-level Server (computing), servers manufactured by Intel. The processors were shipped from November 20, 2000 until August 8, 20 ...
* 0.18 μm process technology (1.40 and 1.50 GHz)
** Introduced November 20, 2000
** L2 cache was 256 KB Advanced Transfer cache (integrated)
** Processor package Style was PGA423, PGA478
** System bus clock rate 400 MHz
**
SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. SSE2 instructions allow the use of ...
SIMD
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a type of parallel computer, parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy. SIMD describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data points simultaneousl ...
Extensions
** 42 million transistors
** Used in desktops and entry-level workstations
* 0.18 μm process technology (1.7 GHz)
** Introduced April 23, 2001
** See the 1.4 and 1.5 chips for details
* 0.18 μm process technology (1.6 and 1.8 GHz)
** Introduced July 2, 2001
** See 1.4 and 1.5 chips for details
** Core voltage is 1.15 volts in Maximum Performance Mode; 1.05 volts in battery optimized mode
** Power <1 watt in battery optimized mode
** Used in full-size and then light mobile PCs
* 0.18 μm process technology Willamette (1.9 and 2.0 GHz)
** Introduced August 27, 2001
** See 1.4 and 1.5 chips for details
* Family 15 model 1
* Pentium 4 (2 GHz, 2.20 GHz)
** Introduced January 7, 2002
* Pentium 4 (2.4 GHz)
** Introduced April 2, 2002
* 0.13 μm process technology Northwood A (1.7, 1.8, 1.9, 2, 2.2, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.8 (OEM), 3.0 (OEM) GHz)
** Improved branch prediction and other microcodes tweaks
** 512 KB integrated L2 cache
** 55 million transistors
** 400 MHz system bus
* Family 15 model 2
* 0.13 μm process technology Northwood B (2.26, 2.4, 2.53, 2.66, 2.8, 3.06 GHz)
** 533 MHz system bus. (3.06 includes Intel's
Hyper-Threading technology)
* 0.13 μm process technology Northwood C (2.4, 2.6, 2.8, 3.0, 3.2, 3.4 GHz)
** 800 MHz system bus (all versions include Hyper-Threading)
** 6500 to 10,000 MIPS
Itanium ''(chronological entry – new non-x86 architecture)''
* Introduced 2001
Xeon
Xeon (; ) is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same archite ...
(32-bit NetBurst)
* Official designation now Xeon; i.e. not "Pentium 4 Xeon"
* Xeon 1.4, 1.5, 1.7 GHz
** Introduced May 21, 2001
** L2 cache was 256 KB Advanced Transfer cache (integrated)
** Processor package
Organic Land Grid Array 603 (OLGA 603)
** System bus clock rate 400 MHz
** SSE2 SIMD Extensions
** Used in high-performance and mid-range dual processor enabled workstations
* Xeon 2.0 GHz and up to 3.6 GHz
** Introduced September 25, 2001
Itanium 2 ''(chronological entry – new non-x86 architecture)''
* Introduced July 2002
* ''See
main entry''
Mobile Pentium 4-M
* 0.13 μm process technology
* 55 million transistors
* 512 KB L2 cache
* BUS a 400 MHz
* Supports up to 1 GB of
DDR 266 MHz memory
* Supports
ACPI
Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) is an open standard that operating systems can use to discover and configure computer hardware components, to perform power management (e.g. putting unused hardware components to sleep), auto con ...
2.0 and
APM 1.2 System Power Management
* 1.3–1.2 V (
SpeedStep
Enhanced SpeedStep is a series of dynamic frequency scaling technologies (codenamed Geyserville and including SpeedStep, SpeedStep II, and SpeedStep III) built into some Intel's microprocessors that allow the clock speed of the processor to be ...
)
* Power: 1.2 GHz 20.8 W, 1.6 GHz 30 W, 2.6 GHz 35 W
* Sleep power 5 W (1.2 V)
* Deeper sleep power 2.9 W (1.0 V)
** 1.40 GHz – 23 April 2002
** 1.50 GHz – 23 April 2002
** 1.60 GHz – 4 March 2002
** 1.70 GHz – 4 March 2002
** 1.80 GHz – 23 April 2002
** 1.90 GHz – 24 June 2002
** 2.00 GHz – 24 June 2002
** 2.20 GHz – 16 September 2002
** 2.40 GHz – 14 January 2003
** 2.50 GHz – 16 April 2003
** 2.60 GHz – 11 June 2003
Pentium 4 EE
* Introduced September 2003
* "Extreme Edition"
* Built from the Xeon's "Gallatin" core, but with 2 MB cache
Pentium 4E
* Introduced February 2004
* Built on 0.09 μm (
90 nm) process technology Prescott (2.4 A, 2.8, 2.8 A, 3.0, 3.2, 3.4, 3.6, 3.8 ) 1 MB L2 cache
* 533 MHz system bus (2.4A and 2.8A only)
* 800 MHz system bus (all other models)
* 125 million transistors in 1 MB models
* 169 million transistors in 2 MB models
*
Hyper-Threading support is only available on CPUs using the 800 MHz system bus.
* The processor's integer
instruction pipeline
In computer engineering, instruction pipelining is a technique for implementing instruction-level parallelism within a single processor. Pipelining attempts to keep every part of the processor busy with some instruction by dividing incoming Mac ...
has been increased from 20 stages to 31 stages, which theoretically allows for even greater bandwidth
* 7500 to 11,000 MIPS
*
LGA 775 versions are in the 5xx series (32-bit) and 5''x''1 series (with Intel 64)
* The 6xx series has 2 MB L2 cache and
Intel 64
64-bit
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit central processing units (CPU) and arithmetic logic units (ALU) are those that are based on processor registers, a ...
processors:
IA-64
IA-64 (Intel Itanium architecture) is the instruction set architecture (ISA) of the discontinued Itanium family of 64-bit Intel microprocessors. The basic ISA specification originated at Hewlett-Packard (HP), and was subsequently implemented by ...
* New instruction set, not at all related to x86
* Before the feature was eliminated (
Montecito, July 2006) IA-64 processors supported 32-bit x86 in hardware, but
slowly (see its 2001
market reception and 2006
architectural changes)
Itanium
Itanium (; ) is a discontinued family of 64-bit computing, 64-bit Intel microprocessors that implement the Intel Itanium architecture (formerly called IA-64). The Itanium architecture originated at Hewlett-Packard (HP), and was later jointly dev ...
* Code name Merced
* Family 7
* Released May 29, 2001
* 733 MHz and 800 MHz
* 2 MB cache
* All recalled and replaced by Itanium 2
Itanium 2
Itanium (; ) is a discontinued family of 64-bit Intel microprocessors that implement the Intel Itanium architecture (formerly called IA-64). The Itanium architecture originated at Hewlett-Packard (HP), and was later jointly developed by HP and I ...
* Family 0x1F
* Released July 2002
* 900 MHz – 1.6 GHz
* McKinley 900 MHz 1.5 MB cache, Model 0x0
* McKinley 1 GHz, 3 MB cache, Model 0x0
* Deerfield 1 GHz, 1.5 MB cache, Model 0x1
* Madison 1.3 GHz, 3 MB cache, Model 0x1
* Madison 1.4 GHz, 4 MB cache, Model 0x1
* Madison 1.5 GHz, 6 MB cache, Model 0x1
* Madison 1.67 GHz, 9 MB cache, Model 0x1
* Hondo 1.4 GHz, 4 MB cache,
dual-core
A multi-core processor (MCP) is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit (IC) with two or more separate central processing units (CPUs), called ''cores'' to emphasize their multiplicity (for example, ''dual-core'' or ''quad-core''). Ea ...
MCM, Model 0x1
64-bit
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit central processing units (CPU) and arithmetic logic units (ALU) are those that are based on processor registers, a ...
processors: Intel 64 – NetBurst microarchitecture
* Intel Extended Memory 64 Technology
* Mostly compatible with
AMD
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California and maintains significant operations in Austin, Texas. AMD is a hardware and fabless company that de ...
's
AMD64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit extension of the x86 instruction set. It was announced in 1999 and first available in the AMD Opteron family in 2003. It introduces two new operating modes: 64-bit mode an ...
architecture
* Introduced Spring 2004, with the Pentium 4F (D0 and later P4 steppings)
Pentium 4F
* Prescott-2M built on 0.09 μm (
90 nm) process technology
* 2.8–3.8 GHz (model numbers 6''x''0)
* Introduced February 20, 2005
* Same features as Prescott with the addition of:
** 2 MB cache
** Intel
64-bit
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit central processing units (CPU) and arithmetic logic units (ALU) are those that are based on processor registers, a ...
** Enhanced Intel
SpeedStep
Enhanced SpeedStep is a series of dynamic frequency scaling technologies (codenamed Geyserville and including SpeedStep, SpeedStep II, and SpeedStep III) built into some Intel's microprocessors that allow the clock speed of the processor to be ...
Technology (EIST)
* Cedar Mill built on 0.065 μm (
65 nm) process technology
* 3.0–3.6 GHz (model numbers 6''x''1)
* Introduced January 16, 2006
* Die shrink of Prescott-2M
* Same features as Prescott-2M
* Family 15 Model 4
Pentium D
*
Dual-core
A multi-core processor (MCP) is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit (IC) with two or more separate central processing units (CPUs), called ''cores'' to emphasize their multiplicity (for example, ''dual-core'' or ''quad-core''). Ea ...
microprocessor
* No Hyper-Threading
* 800 (4×200) MHz
front-side bus
The front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface ( bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between th ...
*
LGA 775 (Socket T)
* Smithfield (Pentium D) –
90 nm process technology (2.66–3.2 GHz)
** Introduced May 26, 2005
** 2.66–3.2 GHz (model numbers 805–840)
** 230 million transistors
** 1 MB × 2 (non-shared, 2 MB total) L2 cache
** Cache coherency between cores requires communication over the FSB
** Performance increase of 60% over similarly clocked Prescott
** 2.66 GHz (533 MHz FSB) Pentium D 805 introduced December 2005
** Contains 2× Prescott dies in one package
** Family 15 Model 4
*
Presler (Pentium D) –
65 nm process technology (2.8–3.6 GHz)
** Introduced January 16, 2006
** 2.8–3.6 GHz (model numbers 915–960)
** 376 million transistors
** 2× 2 MB (non-shared, 4 MB total) L2 cache
** Contains 2× Cedar Mill dies in one package
** Variants
*** Pentium D 945
Pentium Extreme Edition
* Dual-core microprocessor
* Enabled Hyper-Threading
* 800 (4×200) MHz
front-side bus
The front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface ( bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between th ...
* Smithfield (Pentium Extreme Edition) –
90 nm process technology (3.2 GHz)
** Variants
*** Pentium 840 EE – 3.20 GHz (2 × 1 MB L2)
* Presler (Pentium Extreme Edition) –
65 nm process technology (3.46, 3.73)
** 2 MB × 2 (non-shared, 4 MB total) L2 cache
** Variants
*** Pentium 955 EE – 3.46 GHz, 1066 MHz
front-side bus
The front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface ( bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between th ...
*** Pentium 965 EE – 3.73 GHz, 1066 MHz
front-side bus
The front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface ( bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between th ...
Xeon
Xeon (; ) is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same archite ...
(64-bit NetBurst)
* Nocona
** Introduced 2004
* Irwindale
** Introduced 2004
* Cranford
** Introduced April 2005
** MP version of Nocona
* Potomac
** Introduced April 2005
** Cranford with 8 MB of L3 cache
* Paxville DP (2.8 GHz)
** Introduced October 10, 2005
** Dual-core version of Irwindale, with 4 MB of L2 cache (2 MB per core)
** 2.8 GHz
** 800 MT/s front-side bus
* Paxville MP – 90 nm process (2.67 – 3.0 GHz)
** Introduced November 1, 2005
** Dual-core Xeon 7000 series
** MP-capable version of Paxville DP
** 2 MB of L2 cache (1 MB per core) or 4 MB of L2 (2 MB per core)
** 667 MT/s FSB or 800 MT/s FSB
* Dempsey – 65 nm process (2.67–3.73 GHz)
** Introduced May 23, 2006
** Dual-core Xeon 5000 series
** MP version of Presler
** 667 MT/s or 1066 MT/s FSB
** 4 MB of L2 cache (2 MB per core)
**
LGA 771 (Socket J).
* Tulsa – 65 nm process (2.5–3.4 GHz)
** Introduced August 29, 2006
** Dual-core Xeon 7100-series
** Improved version of Paxville MP
** 667 MT/s or 800 MT/s FSB
64-bit processors: Intel 64 – Core microarchitecture
Xeon (64-bit Core microarchitecture)
*
Woodcrest –
65 nm process technology
** Server and Workstation CPU (SMP support for dual CPU system)
** Introduced June 26, 2006
**
Intel VT-x, multiple
OS support
** EIST (Enhanced Intel
SpeedStep
Enhanced SpeedStep is a series of dynamic frequency scaling technologies (codenamed Geyserville and including SpeedStep, SpeedStep II, and SpeedStep III) built into some Intel's microprocessors that allow the clock speed of the processor to be ...
Technology) in 5140, 5148LV, 5150, 5160
**
Execute Disable Bit
**
TXT, enhanced security hardware extensions
**
SSSE3
Supplemental Streaming SIMD Extensions 3 (SSSE3 or SSE3S) is a SIMD instruction set created by Intel and is the fourth iteration of the SSE technology.
History
SSSE3 was first introduced with Intel processors based on the Core microarchitect ...
SIMD
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a type of parallel computer, parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy. SIMD describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data points simultaneousl ...
instructions
** iAMT2 (Intel Active Management Technology), remotely manage computers
** Variants
*** Xeon 5160, 3.00 GHz (4 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 80 W)
*** Xeon 5150, 2.66 GHz (4 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 65 W)
*** Xeon 5140, 2.33 GHz (4 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 65 W)
*** Xeon 5130, 2.00 GHz (4 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 65 W)
*** Xeon 5120, 1.86 GHz (4 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB, 65 W)
*** Xeon 5110, 1.60 GHz (4 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB, 65 W)
*** Xeon 5148LV, 2.33 GHz (4 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 40 W) (low voltage edition)
*
Clovertown –
65 nm process technology
** Server and Workstation CPU (SMP support for dual CPU system)
** Introduced December 13, 2006
**
Quad-core
**
Intel VT-x, multiple
OS support
** EIST (Enhanced Intel
SpeedStep
Enhanced SpeedStep is a series of dynamic frequency scaling technologies (codenamed Geyserville and including SpeedStep, SpeedStep II, and SpeedStep III) built into some Intel's microprocessors that allow the clock speed of the processor to be ...
Technology) in E5365, L5335
**
Execute Disable Bit
**
TXT, enhanced security hardware extensions
**
SSSE3
Supplemental Streaming SIMD Extensions 3 (SSSE3 or SSE3S) is a SIMD instruction set created by Intel and is the fourth iteration of the SSE technology.
History
SSSE3 was first introduced with Intel processors based on the Core microarchitect ...
SIMD
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a type of parallel computer, parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy. SIMD describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data points simultaneousl ...
instructions
** iAMT2 (Intel Active Management Technology), remotely manage computers
** Variants
*** Xeon X5355, 2.66 GHz (2×4 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 105 W)
*** Xeon E5345, 2.33 GHz (2×4 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 80 W)
*** Xeon E5335, 2.00 GHz (2×4 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 80 W)
*** Xeon E5320, 1.86 GHz (2×4 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB, 65 W)
*** Xeon E5310, 1.60 GHz (2×4 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB, 65 W)
*** Xeon L5320, 1.86 GHz (2×4 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB, 50 W) (low voltage edition)
Intel Core 2
*
Conroe –
65 nm process technology
** Desktop CPU (SMP support restricted to 2 CPUs)
** Two cores on one die
** Introduced July 27, 2006
**
SSSE3
Supplemental Streaming SIMD Extensions 3 (SSSE3 or SSE3S) is a SIMD instruction set created by Intel and is the fourth iteration of the SSE technology.
History
SSSE3 was first introduced with Intel processors based on the Core microarchitect ...
SIMD
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a type of parallel computer, parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy. SIMD describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data points simultaneousl ...
instructions
** 291 million transistors
** 64 KB of L1 cache per core (32+32 KB 8-way)
**
Intel VT-x, multiple
OS support
**
TXT, enhanced security hardware extensions
**
Execute Disable Bit
** EIST (Enhanced Intel
SpeedStep
Enhanced SpeedStep is a series of dynamic frequency scaling technologies (codenamed Geyserville and including SpeedStep, SpeedStep II, and SpeedStep III) built into some Intel's microprocessors that allow the clock speed of the processor to be ...
Technology)
** iAMT2 (Intel Active Management Technology), remotely manage computers
**
Intel Management Engine
The Intel Management Engine (ME), also known as the Intel Manageability Engine, is an autonomous subsystem that has been incorporated in virtually all of Intel's processor chipsets since 2008. It is located in the Platform Controller Hub of m ...
introduced
**
LGA 775
** Variants
*** Core 2 Duo E6850, 3.00 GHz (4 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E6800, 2.93 GHz (4 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E6750, 2.67 GHz (4 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 65 W)
*** Core 2 Duo E6700, 2.67 GHz (4 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E6600, 2.40 GHz (4 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB, 65 W)
*** Core 2 Duo E6550, 2.33 GHz (4 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E6420, 2.13 GHz (4 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E6400, 2.13 GHz (2 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E6320, 1.86 GHz (4 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB) Family 6, Model 15, Stepping 6
*** Core 2 Duo E6300, 1.86 GHz (2 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB)
*
Conroe XE –
65 nm process technology
** Desktop Extreme Edition CPU (SMP support restricted to 2 CPUs)
** Introduced July 27, 2006
** Same features as Conroe
**
LGA 775
** Variants
*** Core 2 Extreme X6800 – 2.93 GHz (4 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB)
*
Allendale (Intel Core 2) –
65 nm process technology
** Desktop CPU (SMP support restricted to 2 CPUs)
** Two CPUs on one die
** Introduced January 21, 2007
**
SSSE3
Supplemental Streaming SIMD Extensions 3 (SSSE3 or SSE3S) is a SIMD instruction set created by Intel and is the fourth iteration of the SSE technology.
History
SSSE3 was first introduced with Intel processors based on the Core microarchitect ...
SIMD
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a type of parallel computer, parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy. SIMD describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data points simultaneousl ...
instructions
** 167 million transistors
**
TXT, enhanced security hardware extensions
**
Execute Disable Bit
** EIST (Enhanced Intel
SpeedStep
Enhanced SpeedStep is a series of dynamic frequency scaling technologies (codenamed Geyserville and including SpeedStep, SpeedStep II, and SpeedStep III) built into some Intel's microprocessors that allow the clock speed of the processor to be ...
Technology)
** iAMT2 (Intel Active Management Technology), remotely manage computers
**
LGA 775
** Variants
*** Core 2 Duo E4700, 2.60 GHz (2 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E4600, 2.40 GHz (2 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E4500, 2.20 GHz (2 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E4400, 2.00 GHz (2 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E4300, 1.80 GHz (2 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB) Family 6, Model 15, Stepping 2
*
Merom –
65 nm process technology
** Mobile CPU (SMP support restricted to 2 CPUs)
** Introduced July 27, 2006
** Family 6, Model 15
** Same features as Conroe
**
Socket M /
Socket P / 479-ball Micro-FCBGA
** Variants
*** Core 2 Extreme X7900 2.80 GHz (4 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Extreme X7800 2.60 GHz (4 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo T7800, 2.60 GHz (4 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB) (
Santa Rosa platform)
*** Core 2 Duo T7700, 2.40 GHz (4 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo T7600, 2.33 GHz (4 MB L2, 667 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo T7500, 2.20 GHz (4 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo T7400, 2.16 GHz (4 MB L2, 667 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo T7300, 2.00 GHz (4 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo T7250, 2.00 GHz (2 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo T7200, 2.00 GHz (4 MB L2, 667 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo T7100, 1.80 GHz (2 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo T5600, 1.83 GHz (2 MB L2, 667 MHz FSB) Family 6, Model 15, Stepping 6
*** Core 2 Duo T5550, 1.83 GHz (2 MB L2, 667 MHz FSB, no VT)
*** Core 2 Duo T5500, 1.66 GHz (2 MB L2, 667 MHz FSB, no VT)
*** Core 2 Duo T5470, 1.60 GHz (2 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB, no VT) Family 6, Model 15, Stepping 13
*** Core 2 Duo T5450, 1.66 GHz (2 MB L2, 667 MHz FSB, no VT)
*** Core 2 Duo T5300, 1.73 GHz (2 MB L2, 533 MHz FSB, no VT)
*** Core 2 Duo T5270, 1.40 GHz (2 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB, no VT)
*** Core 2 Duo T5250, 1.50 GHz (2 MB L2, 667 MHz FSB, no VT)
*** Core 2 Duo T5200, 1.60 GHz (2 MB L2, 533 MHz FSB, no VT)
*** Core 2 Duo L7700, 1.80 GHz (4 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB) (low voltage) Family 6, Model 15, Stepping 11
*** Core 2 Duo L7500, 1.60 GHz (4 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB) (low voltage)
*** Core 2 Duo L7400, 1.50 GHz (4 MB L2, 667 MHz FSB) (low voltage)
*** Core 2 Duo L7300, 1.40 GHz (4 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB) (low voltage)
*** Core 2 Duo L7200, 1.33 GHz (4 MB L2, 667 MHz FSB) (low voltage)
*** Core 2 Duo U7700, 1.33 GHz (2 MB L2, 533 MHz FSB) (ultra low voltage)
*** Core 2 Duo U7600, 1.20 GHz (2 MB L2, 533 MHz FSB) (ultra low voltage)
*** Core 2 Duo U7500, 1.06 GHz (2 MB L2, 533 MHz FSB) (ultra low voltage)
*** Core 2 Duo U7100, 1.20 GHz (4 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB) (ultra low voltage) Family 6, Model 15, Stepping 11
*** Core 2 Solo U2100, 1.06 GHz (1 MB L2, 533 MHz FSB) (ultra low voltage)
*** Core 2 Solo U2200, 1.20 GHz (1 MB L2, 533 MHz FSB) (ultra low voltage)
*
Kentsfield –
65 nm process technology
** Two dual-core CPU dies in one package
** Desktop CPU quad-core (SMP support restricted to 4 CPUs)
** Introduced December 13, 2006
** Same features as Conroe but with 4 CPU cores
** 586 million transistors
**
LGA 775
** Family 6, Model 15, Stepping 11
** Variants
*** Core 2 Extreme QX6850, 3 GHz (2×4 MB L2 cache, 1333 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Extreme QX6800, 2.93 GHz (2×4 MB L2 cache, 1066 MHz FSB) (April 9, 2007)
*** Core 2 Extreme QX6700, 2.66 GHz (2×4 MB L2 cache, 1066 MHz FSB) (November 14, 2006)
*** Core 2 Quad Q6700, 2.66 GHz (2×4 MB L2 cache, 1066 MHz FSB) (July 22, 2007)
*** Core 2 Quad Q6600, 2.40 GHz (2×4 MB L2 cache, 1066 MHz FSB) (January 7, 2007)
*
Wolfdale –
45 nm process technology
** Die shrink of Conroe
** Same features as Conroe with the addition of:
*** 50% more cache, 6 MB as opposed to 4 MB
*** Intel Trusted Execution Technology
***
SSE4
SSE4 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 4) is a SIMD CPU instruction set used in the Intel Core microarchitecture and AMD K10 (K8L). It was announced on September 27, 2006, at the Fall 2006 Intel Developer Forum, with vague details in a white paper;< ...
SIMD
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a type of parallel computer, parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy. SIMD describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data points simultaneousl ...
instructions
** 410 million transistors
** Variants
*** Core 2 Duo E8600, 3.33 GHz (6 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E8500, 3.16 GHz (6 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E8435, 3.07 GHz (6 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E8400, 3.00 GHz (6 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E8335, 2.93 GHz (6 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E8300, 2.83 GHz (6 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E8235, 2.80 GHz (6 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E8200, 2.66 GHz (6 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E8135, 2.66 GHz (6 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E8190, 2.66 GHz (6 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, no TXT, no VT)
*
Wolfdale-3M (Intel Core 2) –
45 nm process technology
** Intel Trusted Execution Technology
** Variants
*** Core 2 Duo E7600, 3.06 GHz (3 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E7500, 2.93 GHz (3 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E7400, 2.80 GHz (3 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E7300, 2.66 GHz (3 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Duo E7200, 2.53 GHz (3 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB)
*
Yorkfield,
45 nm process technology
** Quad-core CPU
** Die shrink of Kentsfield
** Contains 2× Wolfdale dual-core dies in one package
** Same features as Wolfdale
** 820 million transistors
** Variants
*** Core 2 Extreme QX9770, 3.20 GHz (2×6 MB L2, 1600 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Extreme QX9650, 3.00 GHz (2×6 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Quad Q9705, 3.16 GHz (2×3 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Quad Q9700, 3.16 GHz (2×3 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Quad Q9650, 3 GHz (2×6 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB)
*** Core 2 Quad Q9550, 2.83 GHz (2×6 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 95 W TDP)
*** Core 2 Quad Q9550s, 2.83 GHz (2×6 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 65 W TDP)
*** Core 2 Quad Q9450, 2.66 GHz (2×6 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 95 W TDP)
*** Core 2 Quad Q9505, 2.83 GHz (2×3 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 95 W TDP)
*** Core 2 Quad Q9505s, 2.83 GHz (2×3 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 65 W TDP)
*** Core 2 Quad Q9500, 2.83 GHz (2×3 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 95 W TDP, no TXT)
*** Core 2 Quad Q9400, 2.66 GHz (2×3 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 95 W TDP)
*** Core 2 Quad Q9400s, 2.66 GHz (2×3 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 65 W TDP)
*** Core 2 Quad Q9300, 2.50 GHz (2×3 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 95 W TDP)
*** Core 2 Quad Q8400, 2.66 GHz (2×2 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 95 W TDP)
*** Core 2 Quad Q8400s, 2.66 GHz (2×2 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 65 W TDP)
*** Core 2 Quad Q8300, 2.50 GHz (2×2 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 95 W TDP)
*** Core 2 Quad Q8300s, 2.50 GHz (2×2 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 65 W TDP)
*** Core 2 Quad Q8200, 2.33 GHz (2×2 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 95 W TDP)
*** Core 2 Quad Q8200s, 2.33 GHz (2×2 MB L2, 1333 MHz FSB, 65 W TDP)
*** Core 2 Quad Q7600, 2.70 GHz (2×1 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB, no SSE4) (no Q7600 liste
here
* Intel Core2 Quad Mobile processor family –
45 nm process technology
** Quad-core CPU
** Variants
*** Core 2 Quad Q9100, 2.26 GHz (2×6 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB, 45 W TDP)
*** Core 2 Quad Q9000, 2.00 GHz (2×3 MB L2, 1066 MHz FSB, 45 W TDP)
Pentium Dual-Core
*
Allendale (Pentium Dual-Core) –
65 nm process technology
** Desktop CPU (SMP support restricted to 2 CPUs)
** Two cores on one die
** Introduced January 21, 2007
**
SSSE3
Supplemental Streaming SIMD Extensions 3 (SSSE3 or SSE3S) is a SIMD instruction set created by Intel and is the fourth iteration of the SSE technology.
History
SSSE3 was first introduced with Intel processors based on the Core microarchitect ...
SIMD
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a type of parallel computer, parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy. SIMD describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data points simultaneousl ...
instructions
** 167 million transistors
**
TXT, enhanced security hardware extensions
**
Execute Disable Bit
** EIST (Enhanced Intel
SpeedStep
Enhanced SpeedStep is a series of dynamic frequency scaling technologies (codenamed Geyserville and including SpeedStep, SpeedStep II, and SpeedStep III) built into some Intel's microprocessors that allow the clock speed of the processor to be ...
Technology)
** Variants
*** Intel Pentium E2220, 2.40 GHz (1 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Intel Pentium E2200, 2.20 GHz (1 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Intel Pentium E2180, 2.00 GHz (1 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Intel Pentium E2160, 1.80 GHz (1 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Intel Pentium E2140, 1.60 GHz (1 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*
Wolfdale-3M (Pentium Dual-Core) –
45 nm process technology
** Intel Pentium E6800, 3.33 GHz (2 MB L2,1066 MHz FSB)
** Intel Pentium E6700, 3.20 GHz (2 MB L2,1066 MHz FSB)
** Intel Pentium E6600, 3.06 GHz (2 MB L2,1066 MHz FSB)
** Intel Pentium E6500, 2.93 GHz (2 MB L2,1066 MHz FSB)
** Intel Pentium E6300, 2.80 GHz (2 MB L2,1066 MHz FSB)
** Intel Pentium E5800, 3.20 GHz (2 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
** Intel Pentium E5700, 3.00 GHz (2 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
** Intel Pentium E5500, 2.80 GHz (2 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
** Intel Pentium E5400, 2.70 GHz (2 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
** Intel Pentium E5300, 2.60 GHz (2 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
** Intel Pentium E5200, 2.50 GHz (2 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
** Intel Pentium E2210, 2.20 GHz (1 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
Celeron
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor, microprocessors targeted at low-cost Personal computer, personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023.
The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, ...
(64-bit Core microarchitecture)
*
Allendale (Celeron, 64-bit Core microarchitecture) –
65 nm process technology
** Variants
*** Intel Celeron E1600, 2.40 GHz (512 KB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Intel Celeron E1500, 2.20 GHz (512 KB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Intel Celeron E1400, 2.00 GHz (512 KB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Intel Celeron E1200, 1.60 GHz (512 KB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*
Wolfdale-3M (Celeron, 64-bit Core microarchitecture) –
45 nm process technology
** Variants
*** Intel Celeron E3500, 2.70 GHz (1 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Intel Celeron E3400, 2.60 GHz (1 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Intel Celeron E3300, 2.50 GHz (1 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Intel Celeron E3200, 2.40 GHz (1 MB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*
Conroe-L (Celeron, 64-bit Core microarchitecture) –
65 nm process technology
** Variants
*** Intel Celeron 450, 2.20 GHz (512 KB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Intel Celeron 440, 2.00 GHz (512 KB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Intel Celeron 430, 1.80 GHz (512 KB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Intel Celeron 420, 1.60 GHz (512 KB L2, 800 MHz FSB)
*** Intel Celeron 220, 1.20 GHz (512 KB L2, 533 MHz FSB)
*
Conroe-CL (Celeron, 64-bit Core microarchitecture) –
65 nm process technology
** LGA 771 package
** Variants
*** Intel Celeron 445, 1.87 GHz (512 KB L2, 1066 MHz FSB)
Celeron M (64-bit Core microarchitecture)
*
Merom-L 65 nm process technology
** 64 KB L1 cache
** 1 MB L2 cache (integrated)
**
SSE3
SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions (PNI), is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 (x86) architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revis ...
SIMD instructions, 533 MHz/667 MHz front-side bus, execute-disable bit, 64-bit
** No
SpeedStep
Enhanced SpeedStep is a series of dynamic frequency scaling technologies (codenamed Geyserville and including SpeedStep, SpeedStep II, and SpeedStep III) built into some Intel's microprocessors that allow the clock speed of the processor to be ...
technology, is not part of the '
Centrino' package
** Variants
*** 520, 1.60 GHz
*** 530, 1.73 GHz
*** 540, 1.86 GHz
*** 550, 2.00 GHz
*** 560, 2.13 GHz
*** 570, 2.26 GHz
*** 667 MHz FSB
**** 575, 2.00 GHz
**** 585, 2.16 GHz
64-bit processors: Intel 64 – Nehalem microarchitecture
Intel Pentium (Nehalem)
*
Clarkdale (Pentium, Nehalem microarchitecture) –
32 nm
The "32 nm" node is the step following the "45 nm" process in CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication. "32-nanometre" refers to the average half-pitch (i.e., half the distance between identical features) of a memory cell at this technolo ...
process technology (manufacturing 7 Jan 2010)
** 2 physical cores/2 threads
** 32+32 KB L1 cache
** 256 KB L2 cache
** 3 MB L3 cache
** Introduced January 2010
** Socket 1156 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3
** Integrated HD GPU
** Variants
*** G6950, 2.8 GHz (no
Hyper-Threading)
*** G6960, 2.933 GHz (no Hyper-Threading)
Core i3
Intel Core is a line of multi-core (with the exception of Core Solo and Core 2 Solo) central processing units (CPUs) for midrange, embedded, workstation, high-end and enthusiast computer markets marketed by Intel Corporation. These processors ...
(1st generation)
*
Clarkdale (Core i3 1st generation) –
32 nm
The "32 nm" node is the step following the "45 nm" process in CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication. "32-nanometre" refers to the average half-pitch (i.e., half the distance between identical features) of a memory cell at this technolo ...
process technology
** 2 physical cores/4 threads
** 32+32 KB L1 cache
** 256 KB L2 cache
** 4 MB L3 cache
** Introduced on January 7, 2010
** Socket 1156 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3
** Integrated HD GPU
** Variants
*** 530, 2.93 GHz Hyper-Threading
*** 540, 3.06 GHz Hyper-Threading
*** 550, 3.2 GHz Hyper-Threading
*** 560, 3.33 GHz Hyper-Threading
Core i5 (1st generation)
*
Lynnfield (Core i5 1st generation) –
45 nm process technology
** 4 physical cores/4 threads
** 32+32 KB L1 cache
** 256 KB L2 cache
** 8 MB L3 cache
** Introduced September 8, 2009
** Family 6 Model E (Ext. Model 1E)
**
Socket 1156 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3
** Variants
*** 750S, 2.40 GHz/3.20 GHz Turbo Boost
*** 750, 2.66 GHz/3.20 GHz Turbo Boost
*** 760, 2.80 GHz/3.33 GHz Turbo Boost
*
Clarkdale (Core i5 1st generation) –
32 nm
The "32 nm" node is the step following the "45 nm" process in CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication. "32-nanometre" refers to the average half-pitch (i.e., half the distance between identical features) of a memory cell at this technolo ...
process technology
** 2 physical cores/4 threads
** 32+32 KB L1 cache
** 256 KB L2 cache
** 4 MB L3 cache
** Introduced January, 2010
**
Socket 1156 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3
** Integrated HD GPU
** AES Support
** Variants
*** 650/655K, 3.2 GHz Hyper-Threading Turbo Boost
*** 660/661, 3.33 GHz Hyper-Threading Turbo Boost
*** 670, 3.46 GHz Hyper-Threading Turbo Boost
*** 680, 3.60 GHz Hyper-Threading Turbo Boost
Core i7 (1st generation)
*
Bloomfield (Core i7 1st generation) –
45 nm process technology
** 4 physical cores/8 threads
** 256 KB L2 cache
** 8 MB L3 cache
**
Front-side bus
The front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface ( bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between th ...
replaced with
QuickPath up to 6.4 GT/s
**
Hyper-Threading is again included. This had previously been removed at the introduction of
Core line
** 781 million
transistors
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
** Intel Turbo Boost Technology
** TDP 130 W
** Introduced November 17, 2008
** Socket 1366 LGA
** 3-channel DDR3
** Variants
*** 975 (extreme edition), 3.33 GHz/3.60 GHz Turbo Boost
*** 965 (extreme edition), 3.20 GHz/3.46 GHz Turbo Boost
*** 960, 3.20 GHz/3.46 GHz Turbo Boost
*** 950, 3.06 GHz/3.33 GHz Turbo Boost
*** 940, 2.93 GHz/3.20 GHz Turbo Boost
*** 930, 2.80 GHz/3.06 GHz Turbo Boost
*** 920, 2.66 GHz/2.93 GHz Turbo Boost
*
Lynnfield (Core i7 1st generation) –
45 nm process technology
** 4 physical cores/8 threads
** 32+32 KB L1 cache
** 256 KB L2 cache
** 8 MB L3 cache
** No
QuickPath, instead compatible with slower
DMI interface
**
Hyper-Threading is included
** Introduced September 8, 2009
** Socket 1156 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3
** Variants
*** 880, 3.06 GHz/3.73 GHz Turbo Boost (TDP 95 W)
*** 870/875K, 2.93 GHz/3.60 GHz Turbo Boost (TDP 95 W)
*** 870S, 2.67 GHz/3.60 GHz Turbo Boost (TDP 82 W)
*** 860, 2.80 GHz/3.46 GHz Turbo Boost (TDP 95 W)
*** 860S, 2.53 GHz/3.46 GHz Turbo Boost (TDP 82 W)
Westmere
*
Gulftown,
32 nm
The "32 nm" node is the step following the "45 nm" process in CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication. "32-nanometre" refers to the average half-pitch (i.e., half the distance between identical features) of a memory cell at this technolo ...
process technology
** 6 physical cores
** 256 KB L2 cache
** 12 MB L3 cache
**
Front-side bus
The front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface ( bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between th ...
replaced with
QuickPath up to 6.4 GT/s
**
Hyper-Threading is included
** Intel Turbo Boost Technology
**
Socket 1366 LGA
** TDP 130 W
** Introduced 16 March 2010
** Variants
*** 990X Extreme Edition, 3.46 GHz/3.73 GHz Turbo Boost
*** 980X Extreme Edition, 3.33 GHz/3.60 GHz Turbo Boost
*** 970, 3.20 GHz/3.46 GHz Turbo Boost
* Clarksfield – Intel Core i7 Mobile processor family –
45 nm process technology
** 4 physical cores
**
Hyper-Threading is included
** Intel Turbo Boost Technology
** Variants
*** 940XM Extreme Edition, 2.13 GHz/3.33 GHz Turbo Boost (8 MB L3, TDP 55 W)
*** 920XM Extreme Edition, 2.00 GHz/3.20 GHz Turbo Boost (8 MB L3, TDP 55 W)
*** 840QM, 1.86 GHz/3.20 GHz Turbo Boost (8 MB L3, TDP 45 W)
*** 820QM, 1.73 GHz/3.06 GHz Turbo Boost (8 MB L3, TDP 45 W)
*** 740QM, 1.73 GHz/2.93 GHz Turbo Boost (6 MB L3, TDP 45 W)
*** 720QM, 1.60 GHz/2.80 GHz Turbo Boost (6 MB L3, TDP 45 W)
Xeon
Xeon (; ) is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same archite ...
(Nehalem microarchitecture)
*
Gainestown –
45 nm process technology
** Same processor dies as Bloomfield
** 256 KB L2 cache
** 8 MB L3 cache, 4 MB may be disabled
**
QuickPath up to 6.4 GT/s
**
Hyper-Threading is included in some models
** 781 million
transistors
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
** Introduced March 29, 2009
** Variants
*** W5590, X5570, X5560, X5550, E5540, E5530, L5530, E5520, L5520, L5518, 4 cores, 8 MB L3 cache, HT
*** E5506, L5506, E5504, 4 cores, 4 MB L3 cache, no HT
*** L5508, E5502, E5502, 2 cores, 4 MB L3 cache, no HT
64-bit processors: Intel 64 –
Sandy Bridge
Sandy Bridge is the List of Intel codenames, codename for Intel's 32 nm process, 32 nm microarchitecture used in the second generation of the Intel Core, Intel Core processors (Intel Core i7, Core i7, Intel Core i5, i5, Intel Core i3, i3). The Sa ...
/
Ivy Bridge microarchitecture
Celeron
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor, microprocessors targeted at low-cost Personal computer, personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023.
The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, ...
(Sandy Bridge/Ivy Bridge microarchitecture)
*
Sandy Bridge
Sandy Bridge is the List of Intel codenames, codename for Intel's 32 nm process, 32 nm microarchitecture used in the second generation of the Intel Core, Intel Core processors (Intel Core i7, Core i7, Intel Core i5, i5, Intel Core i3, i3). The Sa ...
(Celeron-branded) –
32 nm
The "32 nm" node is the step following the "45 nm" process in CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication. "32-nanometre" refers to the average half-pitch (i.e., half the distance between identical features) of a memory cell at this technolo ...
process technology
** 2 physical cores/2 threads (500 series), 1 physical core/1 thread (model G440) or 1 physical core/2 threads (models G460 & G465)
** 2 MB L3 cache (500 series), 1 MB (model G440) or 1.5 MB (models G460 & G465)
** Introduced 3rd quarter, 2011
**
Socket 1155 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3-1066
** 400 series has max TDP of 35 W
** 500-series variants ending in 'T' have a peak TDP of 35 W; others, 65 W
** Integrated GPU
*** All variants have peak GPU turbo frequencies of 1 GHz
*** Variants in the 400 series have GPUs running at a base frequency of 650 MHz
*** Variants in the 500 series ending in 'T' have GPUs running at a base frequency of 650 MHz; others at 850 MHz
*** All variants have 6 GPU execution units
** Variants
*** G440, 1.6 GHz
*** G460, 1.8 GHz
*** G465, 1.9 GHz
*** G470, 2.0 GHz
*** G530T, 2.0 GHz
*** G540T, 2.1 GHz
*** G550T, 2.2 GHz
*** G530, 2.4 GHz
*** G540, 2.5 GHz
*** G550, 2.6 GHz
*** G555, 2.7 GHz
Pentium
Pentium is a series of x86 architecture-compatible microprocessors produced by Intel from 1993 to 2023. The Pentium (original), original Pentium was Intel's fifth generation processor, succeeding the i486; Pentium was Intel's flagship proce ...
(Sandy Bridge/Ivy Bridge microarchitecture)
*
Sandy Bridge
Sandy Bridge is the List of Intel codenames, codename for Intel's 32 nm process, 32 nm microarchitecture used in the second generation of the Intel Core, Intel Core processors (Intel Core i7, Core i7, Intel Core i5, i5, Intel Core i3, i3). The Sa ...
(Pentium-branded) –
32 nm
The "32 nm" node is the step following the "45 nm" process in CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication. "32-nanometre" refers to the average half-pitch (i.e., half the distance between identical features) of a memory cell at this technolo ...
process technology
** 2 physical cores/2 threads
** 3 MB L3 cache
** 624 million transistors
** Introduced May, 2011
**
Socket 1155 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3-1333 (800 series) or DDR3-1066 (600 series)
** Variants ending in 'T' have a peak TDP of 35 W, others 65 W
** Integrated GPU (
HD 2000)
*** All variants have peak GPU turbo frequencies of 1.1 GHz
*** Variants ending in 'T' have GPUs running at a base frequency of 650 MHz; others at 850 MHz
*** All variants have 6 GPU execution units
** Variants
*** G620T, 2.2 GHz
*** G630T, 2.3 GHz
*** G640T, 2.4 GHz
*** G645T, 2.5 GHz
*** G860T, 2.6 GHz
*** G620, 2.6 GHz
*** G622, 2.6 GHz
*** G630, 2.7 GHz
*** G632, 2.7 GHz
*** G640, 2.8 GHz
*** G840, 2.8 GHz
*** G645, 2.9 GHz
*** G850, 2.9 GHz
*** G860, 3.0 GHz
*** G870, 3.1 GHz
*
Ivy Bridge (Pentium-branded) –
22 nm tri-gate transistor process technology
** 2 physical cores/2 threads
** 32+32 KB (per core) L1 cache
** 256 KB (per core) L2 cache
** 3 MB L3 cache
** Introduced September, 2012
**
Socket 1155 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3-1333 for G2000 series
** 2-channel DDR3-1600 for G2100 series
** All variants have GPU base frequencies of 650 MHz and peak GPU turbo frequencies of 1.05 GHz
** Variants ending in 'T' have a peak TDP of 35 W; others, TDP of 55 W
** Variants
*** G2020T, 2.5 GHz
*** G2030T, 2.6 GHz
*** G2100T, 2.6 GHz
*** G2120T, 2.7 GHz
*** G2010, 2.8 GHz
*** G2020, 2.9 GHz
*** G2030, 3.0 GHz
*** G2120, 3.1 GHz
*** G2130, 3.2 GHz
*** G2140, 3.3 GHz
Core i3
Intel Core is a line of multi-core (with the exception of Core Solo and Core 2 Solo) central processing units (CPUs) for midrange, embedded, workstation, high-end and enthusiast computer markets marketed by Intel Corporation. These processors ...
(2nd and 3rd generation)
*
Sandy Bridge
Sandy Bridge is the List of Intel codenames, codename for Intel's 32 nm process, 32 nm microarchitecture used in the second generation of the Intel Core, Intel Core processors (Intel Core i7, Core i7, Intel Core i5, i5, Intel Core i3, i3). The Sa ...
(Core i3 2nd generation) –
32 nm
The "32 nm" node is the step following the "45 nm" process in CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication. "32-nanometre" refers to the average half-pitch (i.e., half the distance between identical features) of a memory cell at this technolo ...
process technology
** 2 physical cores/4 threads
** 32+32 KB (per core) L1 cache
** 256 KB (per core) L2 cache
** 3 MB L3 cache
** 624 million transistors
** Introduced January, 2011
**
Socket 1155 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3-1333
** Variants ending in 'T' have a peak TDP of 35 W, others 65 W
** Integrated GPU
*** All variants have peak GPU turbo frequencies of 1.1 GHz
*** Variants ending in 'T' have GPUs running at a base frequency of 650 MHz; others at 850 MHz
*** Variants ending in '5' have Intel HD Graphics 3000 (12 execution units); others have Intel HD Graphics 2000 (6 execution units)
** Variants
*** i3-2100T, 2.5 GHz
*** i3-2120T, 2.6 GHz
*** i3-2100, 3.1 GHz
*** i3-2102, 3.1 GHz
*** i3-2105, 3.1 GHz
*** i3-2120, 3.3 GHz
*** i3-2125, 3.3 GHz
*** i3-2130, 3.4 GHz
*
Ivy Bridge (Core i3 3rd generation) –
22 nm tri-gate transistor process technology
** 2 physical cores/4 threads
** 32+32 KB (per core) L1 cache
** 256 KB (per core) L2 cache
** 3 MB L3 cache
** Introduced September, 2012
**
Socket 1155 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3-1600
** Variants ending in '5' have Intel HD Graphics 4000; others have Intel HD Graphics 2500
** All variants have GPU base frequencies of 650 MHz and peak GPU turbo frequencies of 1.05 GHz
** TDP 55 W
** Variants
*** i3-3220T, 2.8 GHz
*** i3-3240T, 2.9 GHz
*** i3-3210, 3.2 GHz
*** i3-3220, 3.3 GHz
*** i3-3225, 3.3 GHz
*** i3-3240, 3.4 GHz
*** i3-3250, 3.5 GHz
Core i5 (2nd and 3rd generation)
*
Sandy Bridge
Sandy Bridge is the List of Intel codenames, codename for Intel's 32 nm process, 32 nm microarchitecture used in the second generation of the Intel Core, Intel Core processors (Intel Core i7, Core i7, Intel Core i5, i5, Intel Core i3, i3). The Sa ...
(Core i5 2nd generation) –
32 nm
The "32 nm" node is the step following the "45 nm" process in CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication. "32-nanometre" refers to the average half-pitch (i.e., half the distance between identical features) of a memory cell at this technolo ...
process technology
** 4 physical cores/4 threads (except for i5-2390T which has 2 physical cores/4 threads)
** 32+32 KB (per core) L1 cache
** 256 KB (per core) L2 cache
** 6 MB L3 cache (except for i5-2390T which has 3 MB)
** 995 million transistors
** Introduced January, 2011
**
Socket 1155 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3-1333
** Variants ending in 'S' have a peak TDP of 65 W; others, 95 W except where noted
** Variants ending in 'K' have unlocked multipliers; others cannot be overclocked
** Integrated GPU
*** i5-2500T has a peak GPU turbo frequency of 1.25 GHz, others 1.1 GHz
*** Variants ending in 'T' have GPUs running at a base frequency of 650 MHz; others at 850 MHz
*** Variants ending in '5' or 'K' have Intel HD Graphics 3000 (12 execution units), except i5-2550K which has no GPU; others have Intel HD Graphics 2000 (6 execution units)
*** Variants ending in 'P' and the i5-2550K have no GPU
** Variants
*** i5-2390T, 2.7 GHz/3.5 GHz Turbo Boost (35 W max. TDP)
*** i5-2500T, 2.3 GHz/3.3 GHz Turbo Boost (45 W max. TDP)
*** i5-2400S, 2.5 GHz/3.3 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-2405S, 2.5 GHz/3.3 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-2500S, 2.7 GHz/3.7 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-2300, 2.8 GHz/3.1 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-2310, 2.9 GHz/3.2 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-2320, 3.0 GHz/3.3 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-2380P, 3.1 GHz/3.4 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-2400, 3.1 GHz/3.4 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-2450P, 3.2 GHz/3.5 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-2500, 3.3 GHz/3.7 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-2500K, 3.3 GHz/3.7 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-2550K, 3.4 GHz/3.8 GHz Turbo Boost
*
Ivy Bridge (Core i5 3rd generation) –
22 nm Tri-gate transistor process technology
** 4 physical cores/4 threads (except for i5-3470T which has 2 physical cores/4 threads)
** 32+32 KB (per core) L1 cache
** 256 KB (per core) L2 cache
** 6 MB L3 cache (except for i5-3470T which has 3 MB)
** Introduced April, 2012
**
Socket 1155 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3-1600
** Variants ending in 'S' have a peak TDP of 65 W, Variants ending in 'T' have a peak TDP of 35 or 45 W (see variants); others, 77 W except where noted
** Variants ending in 'K' have unlocked multipliers; others cannot be overclocked
** Variants ending in 'P' have no integrated GPU; others have Intel HD Graphics 2500 or Intel HD Graphics 4000 (i5-3475S and i5-3570K only)
** Variants
*** i5-3470T, 2.9 GHz/3.6 GHz max Turbo Boost (35 W TDP)
*** i5-3570T, 2.3 GHz/3.3 GHz max Turbo Boost (45 W TDP)
*** i5-3330S, 2.7 GHz/3.2 GHz max Turbo Boost
*** i5-3450S, 2.8 GHz/3.5 GHz max Turbo Boost
*** i5-3470S, 2.9 GHz/3.6 GHz max Turbo Boost
*** i5-3475S, 2.9 GHz/3.6 GHz max Turbo Boost
*** i5-3550S, 3.0 GHz/3.7 GHz max Turbo Boost
*** i5-3570S, 3.1 GHz/3.8 GHz max Turbo Boost
*** i5-3330, 3.0 GHz/3.2 GHz max Turbo Boost
*** i5-3350P, 3.1 GHz/3.3 GHz max Turbo Boost (69 W TDP)
*** i5-3450, 3.1 GHz/3.5 GHz max Turbo Boost
*** i5-3470, 3.2 GHz/3.6 GHz max Turbo Boost
*** i5-3550, 3.3 GHz/3.7 GHz max Turbo Boost
*** i5-3570, 3.4 GHz/3.8 GHz max Turbo Boost
*** i5-3570K, 3.4 GHz/3.8 GHz max Turbo Boost
Core i7 (2nd and 3rd generation)
*
Sandy Bridge
Sandy Bridge is the List of Intel codenames, codename for Intel's 32 nm process, 32 nm microarchitecture used in the second generation of the Intel Core, Intel Core processors (Intel Core i7, Core i7, Intel Core i5, i5, Intel Core i3, i3). The Sa ...
(Core i7 2nd generation) –
32 nm
The "32 nm" node is the step following the "45 nm" process in CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication. "32-nanometre" refers to the average half-pitch (i.e., half the distance between identical features) of a memory cell at this technolo ...
process technology
** 4 physical cores/8 threads
** 32+32 KB (per core) L1 cache
** 256 KB (per core) L2 cache
** 8 MB L3 cache
** 995 million transistors
** Introduced January, 2011
**
Socket 1155 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3-1333
** Variants ending in 'S' have a peak TDP of 65 W, others – 95 W
** Variants ending in 'K' have unlocked multipliers; others cannot be overclocked
** Integrated GPU
*** All variants have base GPU frequencies of 850 MHz and peak GPU turbo frequencies of 1.35 GHz
*** Variants ending in 'K' have Intel HD Graphics 3000 (12 execution units); others have Intel HD Graphics 2000 (6 execution units)
** Variants
*** i7-2600S, 2.8 GHz/3.8 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i7-2600, 3.4 GHz/3.8 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i7-2600K, 3.4 GHz/3.8 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i7-2700K, 3.5 GHz/3.9 GHz Turbo Boost
*
Sandy Bridge-E (Core i7 3rd generation X-Series) –
32 nm
The "32 nm" node is the step following the "45 nm" process in CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication. "32-nanometre" refers to the average half-pitch (i.e., half the distance between identical features) of a memory cell at this technolo ...
process technology
** Up to 6 physical cores/12 threads depending on model number
** 32+32 KB (per core) L1 cache
** 256 KB (per core) L2 cache
** Up to 20 MB L3 cache depending on model number
** 2.27 billion transistors
** Introduced November, 2011
**
Socket 2011 LGA
** 4-channel DDR3-1600
** All variants have a peak TDP of 130 W
** No integrated GPU
** Variants (all marketed under "Intel Core X-series processors")
*** i7-3820, 3.6 GHz/3.8 GHz Turbo Boost, 4 cores, 10 MB L3 cache
*** i7-3930K, 3.2 GHz/3.8 GHz Turbo Boost, 6 cores, 12 MB L3 cache
*** i7-3960X, 3.3 GHz/3.9 GHz Turbo Boost, 6 cores, 15 MB L3 cache
*** i7-3970X, 3.5 GHz/4.0 GHz Turbo Boost, 6 cores, 15 MB L3 cache
*
Ivy Bridge (Core i7 3rd generation) –
22 nm Tri-gate transistor process technology
** 4 physical cores/8 threads
** 32+32 KB (per core) L1 cache
** 256 KB (per core) L2 cache
** 8 MB L3 cache
** Introduced April, 2012
**
Socket 1155 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3-1600
** Variants ending in 'S' have a peak TDP of 65 W, variants ending in 'T' have a peak TDP of 45 W, others – 77 W
** Variants ending in 'K' have unlocked multipliers; others cannot be overclocked
** Integrated GPU Intel HD Graphics 4000
** Variants
*** i7-3770T – 2.5 GHz/3.7 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i7-3770S – 3.1 GHz/3.9 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i7-3770 – 3.4 GHz/3.9 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i7-3770K – 3.5 GHz/3.9 GHz Turbo Boost
64-bit processors: Intel 64 – Haswell microarchitecture
Core i3
Intel Core is a line of multi-core (with the exception of Core Solo and Core 2 Solo) central processing units (CPUs) for midrange, embedded, workstation, high-end and enthusiast computer markets marketed by Intel Corporation. These processors ...
(4th generation)
*
Haswell (Core i3 4th generation) –
22nm process technology
64-bit processors: Intel 64 – Broadwell microarchitecture
Core i3
Intel Core is a line of multi-core (with the exception of Core Solo and Core 2 Solo) central processing units (CPUs) for midrange, embedded, workstation, high-end and enthusiast computer markets marketed by Intel Corporation. These processors ...
(5th generation)
*
Broadwell (Core i3 5th generation) –
14nm process technology
Core i5 (5th generation)
*
Broadwell (Core i5 5th generation) –
14nm process technology
** 4 physical cores/4 threads
** 4 MB L3 cache
** Introduced Q2'15
**
Socket 1150 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3L-1333/1600
** Integrated GPU
** Variants
*** i5-5575R – 2.80 GHz/3.30 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-5675C – 3.10 GHz/3.60 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-5675R – 3.10 GHz/3.60 GHz Turbo Boost
Core i7 (5th generation, Including Core-X Series)
*
Broadwell (Core i7 5th generation) –
14nm process technology
** 4 physical cores/8 threads
** 6 MB L3 cache
** Introduced Q2'15
**
Socket 1150 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3L-1333/1600
** Integrated GPU
** Variants
*** i7-5775C – 3.30 GHz/3.70 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i7-5775R – 3.30 GHz/3.80 GHz Turbo Boost
*
Broadwell-E –
14nm process technology
** 6–10 physical cores/12–20 threads
** 15–25 MB L3 cache
** Introduced Q2'16
**
Socket 2011-v3 LGA
** 4-channel DDR4-2133/2400
** No Integrated GPU
** Variants (all marketed under "Intel Core X-series processors")
*** i7-6800K – 3.40 GHz/3.60 GHz Turbo Boost/3.80 GHz Turbo Boost Max Technology 3.0 Frequency 15 MB L3 cache
*** i7-6850K – 3.60 GHz/3.80 GHz Turbo Boost/4.00 GHz Turbo Boost Max Technology 3.0 Frequency 15 MB L3 cache
*** i7-6900K – 3.20 GHz/3.70 GHz Turbo Boost/4.00 GHz Turbo Boost Max Technology 3.0 Frequency 20 MB L3 cache
*** i7-6950X – 3.00 GHz/3.50 GHz Turbo Boost/4.00 GHz Turbo Boost Max Technology 3.0 Frequency 25 MB L3 cache
Other Broadwell CPUs
Not listed (yet) are several Broadwell-based CPU models:
* Server and workstation CPUs
** single-CPU: Pentium D15nn, Xeon D-15nn, Xeon E3-12nn v4, Xeon E5-16nn v4
** dual-CPU: Xeon E5-26nn v4
** quad-CPU: Xeon E5-46nn v4, Xeon E7-48nn v4
** octo-CPU: Xeon E7-88nn v4
* Embedded CPUs
** Core i7-57nnEQ, Core i7-58nnEQ
* Mobile CPUs
** Celeron 32nnU, Celeron 37nnU
** Pentium 38nnU
** Core M-5Ynn
** Core i3-50nnU
** Core i5-5nnnU
** Core i7-55nnU, Core i7-56nnU, Core i7-57nnHQ, Core i7-59nnHQ
Note: this list does not say that all processors that match these patterns are Broadwell-based or fit into this scheme. The model numbers may have suffixes that are not shown here.
64-bit
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit central processing units (CPU) and arithmetic logic units (ALU) are those that are based on processor registers, a ...
processors: Intel 64 –
Skylake microarchitecture
Core i3
Intel Core is a line of multi-core (with the exception of Core Solo and Core 2 Solo) central processing units (CPUs) for midrange, embedded, workstation, high-end and enthusiast computer markets marketed by Intel Corporation. These processors ...
(6th generation)
*
Skylake (Core i3 6th generation) –
14 nm process technology
** 2 physical cores/4 threads
** 3–4 MB L3 cache
** Introduced Q3'15
**
Socket 1151 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3L-1333/1600, DDR4-1866/2133
** Integrated GPU Intel HD Graphics 530 (only i3-6098P have HD Graphics 510)
** Variants
*** i3-6098P – 3.60 GHz
*** i3-6100T – 3.20 GHz
*** i3-6100 – 3.70 GHz
*** i3-6300T – 3.30 GHz
*** i3-6300 – 3.80 GHz
*** i3-6320 – 3.90 GHz
Core i5 (6th generation)
*
Skylake (Core i5 6th generation) –
14nm process technology
** 4 physical cores/4 threads
** 6 MB L3 cache
** Introduced Q3'15
**
Socket 1151 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3L-1333/1600, DDR4-1866/2133
** Integrated GPU Intel HD Graphics 530
** Variants
*** i5-6300HQ – 2.30/3.20 GHz Turbo Boost
***i5-6400T – 2.20 GHz/2.80 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-6400 – 2.70 GHz/3.30 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-6440hq
*** i5-6500T – 2.50 GHz/3.10 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-6500 – 3.20 GHz/3.60 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-6600T – 2.70 GHz/3.50 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-6600 – 3.30 GHz/3.90 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i5-6600K – 3.50 GHz/3.90 GHz Turbo Boost
Core i7 (6th generation)
*
Skylake (Core i7 6th generation) –
14nm process technology
** 4 physical cores/8 threads
** 8 MB L3 cache
** Introduced Q3'15
**
Socket 1151 LGA
** 2-channel DDR3L-1333/1600, DDR4-1866/2133
** Integrated GPU Intel HD Graphics 530
** Variants
*** i7-6700T – 2.80 GHz/3.60 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i7-6700 – 3.40 GHz/4.00 GHz Turbo Boost
*** i7-6700K – 4.00 GHz/4.20 GHz Turbo Boost
Other Skylake processors
Many Skylake-based processors are not yet listed in this section: mobile i3/i5/i7 processors (U, H, and M suffixes), embedded i3/i5/i7 processors (E suffix), certain i7-67nn/i7-68nn/i7-69nn.
Skylake-based "Core X-series" processors (certain i7-78nn and i9-79nn models) can be found under current models.
64-bit processors: Intel 64 (7th generation) –
Kaby Lake
Kaby Lake is Intel's codename for its seventh generation Core microprocessor family announced on August 30, 2016. Like the preceding Skylake, Kaby Lake is produced using a 14 nanometer manufacturing process technology. Breaking with Intel's p ...
microarchitecture
64-bit processors: Intel 64 (8th and 9th generation) – Coffee Lake microarchitecture
64-bit processors: Intel 64 – Cannon Lake microarchitecture
64-bit processors: Intel 64 (10th generation) – Ice Lake microarchitecture
64-bit processors: Intel 64 (10th generation) – Comet Lake microarchitecture
64-bit processors: Intel 64 (11th generation) – Tiger Lake microarchitecture
64-bit processors: Intel 64 (12th generation) – Alder Lake microarchitecture
64-bit processors: Intel 64 (13th generation) –
Raptor Lake
Raptor Lake is Intel's List of Intel codenames, codename for the 13th and 14th generations of Intel Core processors based on a Heterogeneous computing, hybrid architecture, utilizing Raptor Cove performance cores and Gracemont (microarchitecture ...
microarchitecture
Intel Tera-Scale
* 2007:
Teraflops Research Chip, an 80 core processor prototype.
* 2009:
Single-chip Cloud Computer, a research microprocessor containing the most Intel Architecture cores ever integrated on a silicon CPU chip: 48.
Intel 805xx product codes
Intel discontinued the use of part numbers such as 80486 in the marketing of mainstream x86-architecture processors with the introduction of the
Pentium
Pentium is a series of x86 architecture-compatible microprocessors produced by Intel from 1993 to 2023. The Pentium (original), original Pentium was Intel's fifth generation processor, succeeding the i486; Pentium was Intel's flagship proce ...
brand in 1993. However, numerical codes, in the 805xx range, continued to be assigned to these processors for internal and part numbering uses. The following is a list of such product codes in numerical order:
Intel 806xx product codes
Intel 807xx product codes
See also
*
List of AMD processors
This article gives a list of AMD microprocessors, sorted by generation and release year. If applicable and openly known, the designation(s) of each processor's core (versions) is (are) listed in parentheses. For an overview over concrete product, ...
*
List of PowerPC processors
*
List of NXP products
*
List of Intel Atom processors
Intel Atom is Intel's line of low-power, low-cost and low-performance x86 and x86-64 microprocessors. Atom, with codenames of ''Silverthorne (microprocessor), Silverthorne'' and ''Diamondville (microprocessor), Diamondville'', was first announc ...
*
List of Intel Xeon processors
The following is a list of Xeon, Intel Xeon microprocessors, by generation.
P6-based
Pentium II Xeon
* List of Intel Xeon processors (P6-based)#ark49943, Pentium II Xeon 400
* List of Intel Xeon processors (P6-based)#ark49942, Pentium II X ...
*
List of Intel Itanium processors
*
List of Intel Celeron processors
The Celeron was a family of microprocessors from Intel targeted at the low-end consumer market. CPUs in the Celeron brand have used designs from sixth- to eighth-generation CPU microarchitectures. It was replaced by the Intel Processor brand in ...
*
List of Intel Pentium processors
**
List of Intel Pentium Pro processors
**
List of Intel Pentium II processors
**
List of Intel Pentium III processors
The Pentium III from Intel is a sixth-generation Central processing unit, CPU targeted at the consumer market.
Desktop processors
Katmai (microprocessor), "Katmai" (250 nm)
* 9.5 million transistors
* All models support: MMX (instruction set) ...
**
List of Intel Pentium 4 processors
**
List of Intel Pentium D processors
**
List of Intel Pentium M processors
*
List of Intel Core processors
The following is a list of Intel Core processors. This includes Intel's original Core (Solo/Duo) mobile series based on the Enhanced Pentium M microarchitecture, as well as its Core 2- (Solo/Duo/Quad/Extreme), Core i3-, Core i5-, Core i7-, Co ...
*
List of Intel Core 2 processors
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but ...
*
List of Intel Core M processors
*
List of Intel Core i3 processors
The following is a list of Intel Core processors. This includes Intel's original Core (Solo/Duo) mobile series based on the Enhanced Pentium M microarchitecture, as well as its Core 2- (Solo/Duo/Quad/Extreme), Core i3-, Core i5-, Core i7-, Co ...
*
List of Intel Core i5 processors
The following is a list of Intel Core List of Intel processors, processors. This includes Intel's original Core (Solo/Duo) mobile series based on the Enhanced Pentium M List of Intel CPU microarchitectures, microarchitecture, as well as its Co ...
*
List of Intel Core i7 processors
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but ...
*
List of Intel Core i9 processors
The following is a list of Intel Core processors. This includes Intel's original Core (Solo/Duo) mobile series based on the Enhanced Pentium M microarchitecture, as well as its Core 2- (Solo/Duo/Quad/Extreme), Core i3-, Core i5-, Core i7-, Co ...
*
List of Intel CPU microarchitectures
*
List of Intel graphics processing units
This article contains information about Intel's GPUs (see Intel Graphics Technology) and motherboard graphics chipsets in table form. In 1982, Intel licensed the NEC μPD7220 and announced it as the Intel 82720 Graphics Display Controller.
...
*
List of quantum processors
This list contains quantum processors, also known as quantum processing units (QPUs). Some devices listed below have only been announced at press conferences so far, with no actual demonstrations or scientific publications characterizing the per ...
*
Apple silicon
Apple silicon is a series of system on a chip (SoC) and system in a package (SiP) processors designed by Apple Inc., mainly using the ARM architecture family, ARM architecture. They are used in nearly all of the company's devices including Mac ...
Notes
References
External links
Intel Museum: History of the Microprocessor
{{Intel
Intel microprocessors
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer compo ...
 This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of
This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of 








 Introduced in the third quarter of 1974, these bit-slicing components used bipolar Schottky transistors. Each component implemented two bits of a processor function; packages could be interconnected to build a processor with any desired word length.
Members of the 3000 family:
* 3001 – Microcontrol Unit
* 3002 – 2-bit Arithmetic Logic Unit slice
* 3003 – Look-ahead Carry Generator
* 3205 – High-performance 1 of 8 Binary Decoder
* 3207 – Quad Bipolar-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver
* 3208 – Hex Sense Amp and Latch for MOS Memories
* 3210 – TTL-to-MOS Level Shifter and High Voltage Clock Driver
* 3211 – ECL-to-MOS Level Shifter and High Voltage Clock Driver
* 3212 – Multimode Latch Buffer
* 3214 – Interrupt Control Unit
* 3216 – Parallel, Inverting Bi-Directional Bus Driver
* 3222 – Refresh Controller for 4K (4096 B) NMOS DRAMs
* 3226 – Parallel, Inverting Bi-Directional Bus Driver
* 3232 – Address Multiplexer and Refresh Counter for 4K DRAMs
* 3242 – Address Multiplexer and Refresh Counter for 16K (16 × 1024 B) DRAMs
* 3245 – Quad Bipolar TTL-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver for 4K
* 3246 – Quad Bipolar ECL-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver for 4K
* 3404 – High-performance 6-bit Latch
* 3408 – Hex Sense Amp and Latch for MOS Memories
* 3505 – Next generation processor
Bus width 2''n'' bits data/address (depending on number ''n'' of slices used)
Introduced in the third quarter of 1974, these bit-slicing components used bipolar Schottky transistors. Each component implemented two bits of a processor function; packages could be interconnected to build a processor with any desired word length.
Members of the 3000 family:
* 3001 – Microcontrol Unit
* 3002 – 2-bit Arithmetic Logic Unit slice
* 3003 – Look-ahead Carry Generator
* 3205 – High-performance 1 of 8 Binary Decoder
* 3207 – Quad Bipolar-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver
* 3208 – Hex Sense Amp and Latch for MOS Memories
* 3210 – TTL-to-MOS Level Shifter and High Voltage Clock Driver
* 3211 – ECL-to-MOS Level Shifter and High Voltage Clock Driver
* 3212 – Multimode Latch Buffer
* 3214 – Interrupt Control Unit
* 3216 – Parallel, Inverting Bi-Directional Bus Driver
* 3222 – Refresh Controller for 4K (4096 B) NMOS DRAMs
* 3226 – Parallel, Inverting Bi-Directional Bus Driver
* 3232 – Address Multiplexer and Refresh Counter for 4K DRAMs
* 3242 – Address Multiplexer and Refresh Counter for 16K (16 × 1024 B) DRAMs
* 3245 – Quad Bipolar TTL-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver for 4K
* 3246 – Quad Bipolar ECL-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver for 4K
* 3404 – High-performance 6-bit Latch
* 3408 – Hex Sense Amp and Latch for MOS Memories
* 3505 – Next generation processor
Bus width 2''n'' bits data/address (depending on number ''n'' of slices used)





 * Introduced January 16, 1989; discontinued June 15, 2001
* Variant of 386SX intended for embedded systems
* No "real mode", starts up directly in "protected mode"
* Replaced by much more successful 80386EX from 1994
* Introduced January 16, 1989; discontinued June 15, 2001
* Variant of 386SX intended for embedded systems
* No "real mode", starts up directly in "protected mode"
* Replaced by much more successful 80386EX from 1994








 P54CS – 0.35 μm process technology
** 3.3 million transistors
** 90 mm2 die size
** Family 5 model 2
** Variants
** Socket 5 296/320-pin PGA package
*** 133 MHz, 218.9 MIPS (4.14 SPECint95, 3.12 SPECfp95 on Xpress 1 MB L2)
**** Introduced June 12, 1995
*** 150, 166 MHz, 230 and 247 MIPS respectively
**** Introduced January 4, 1996
** Socket 7 296/321-pin PGA package
*** 200 MHz, 270 MIPS (5.47 SPECint95, 3.68 SPECfp95)
**** Introduced June 10, 1996
P54CS – 0.35 μm process technology
** 3.3 million transistors
** 90 mm2 die size
** Family 5 model 2
** Variants
** Socket 5 296/320-pin PGA package
*** 133 MHz, 218.9 MIPS (4.14 SPECint95, 3.12 SPECfp95 on Xpress 1 MB L2)
**** Introduced June 12, 1995
*** 150, 166 MHz, 230 and 247 MIPS respectively
**** Introduced January 4, 1996
** Socket 7 296/321-pin PGA package
*** 200 MHz, 270 MIPS (5.47 SPECint95, 3.68 SPECfp95)
**** Introduced June 10, 1996

