Institutional Analysis And Development Framework on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Institutional Analysis and Development framework (IAD) is a theoretical framework for investigating how people ("actors") interact with
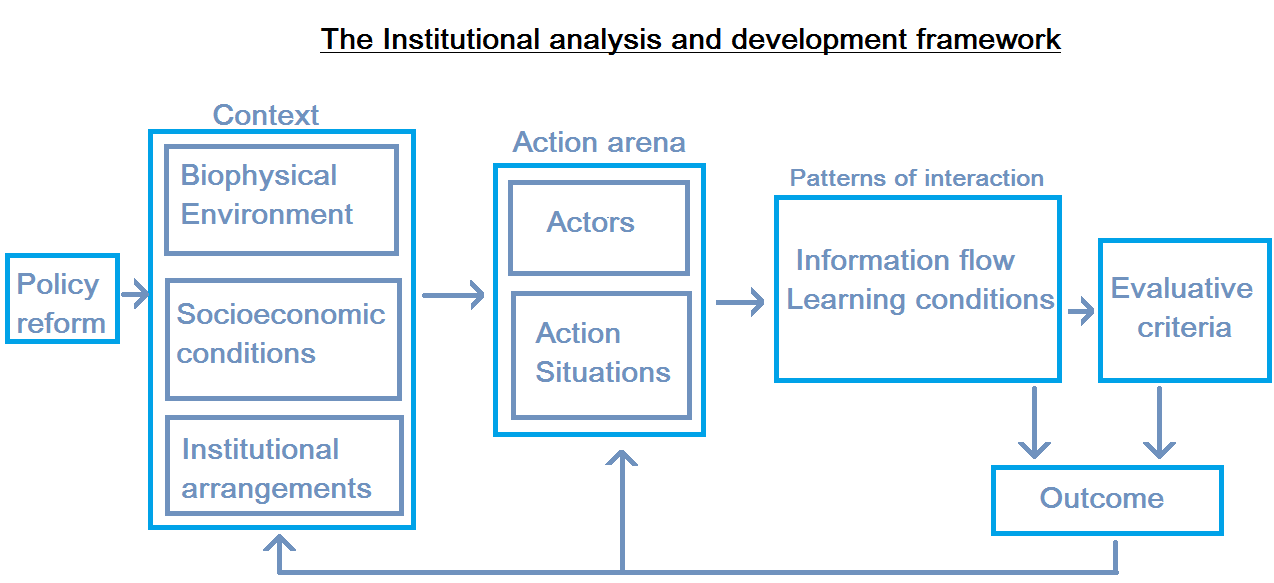 Ostrom thought of the IAD as a "multi-level conceptual map" with which one could zoom in and out of particular hierarchical parts of the governance structures in a social system.
The IAD framework helps to perceive complex collective action problems by dividing them into 'action arenas', that are smaller pieces of practically understandable function. The analyst assumes that the structure of the action situation is fixed in the short-term. For an action situation to exist, there must be "actors in positions" (the number of possible roles that are available in this recurring interaction situation). Actors have choices within the existing (rule) structure. In the study of outcomes from collective choice situations, actors are influenced by the institutional arrangements, the socio-economic conditions, and the physical environment. The institutional arrangements can be studied by seven rule types (as per below).
Ostrom thought of the IAD as a "multi-level conceptual map" with which one could zoom in and out of particular hierarchical parts of the governance structures in a social system.
The IAD framework helps to perceive complex collective action problems by dividing them into 'action arenas', that are smaller pieces of practically understandable function. The analyst assumes that the structure of the action situation is fixed in the short-term. For an action situation to exist, there must be "actors in positions" (the number of possible roles that are available in this recurring interaction situation). Actors have choices within the existing (rule) structure. In the study of outcomes from collective choice situations, actors are influenced by the institutional arrangements, the socio-economic conditions, and the physical environment. The institutional arrangements can be studied by seven rule types (as per below).
common-pool resources
In economics, a common-pool resource (CPR) is a type of good consisting of a natural or human-made resource system (e.g. an irrigation system or fishing grounds), whose size or characteristics makes it costly, but not impossible, to exclude potenti ...
(CPRs). CPRs are economic goods which are rivalrous (i.e. one person's use reduces the ability of others to use) and non-excludable (i.e. it's impractical to prevent people accessing it) - examples include forests as a source of timber, or fields as a source of pasture.
It was developed by Elinor Ostrom
Elinor Claire "Lin" Ostrom (née Awan; August 7, 1933 – June 12, 2012) was an American Political science, political scientist and Political economy, political economist whose work was associated with New institutional economics, New Institution ...
, an American political scientist
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and Power (social and political), power, and the analysis of political activities, political philosophy, political thought, polit ...
and the first woman to receive the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences
The Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, officially the Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel (), commonly referred to as the Nobel Prize in Economics(), is an award in the field of economic sciences adminis ...
in 2009. Ostrom researched which institutional structures supported CPR actors to sustainably use their resources, balancing individuals' use with the interest of a wider public. Under rational choice
Rational choice modeling refers to the use of decision theory (the theory of rational choice) as a set of guidelines to help understand economic and social behavior. The theory tries to approximate, predict, or mathematically model human behav ...
assumptions, the IAD was devised in an attempt to ''explain and predict'' outcomes by formally exploring and documenting governance structures, actors' positions, and informal and formal rules. Thus, the IAD is a systematic method to document policy analysis functions similar to analytic technique commonly used in physical and social science
Social science (often rendered in the plural as the social sciences) is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among members within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the ...
s to understand how institutions operate and change over a period of time.
Components of the framework
 Ostrom thought of the IAD as a "multi-level conceptual map" with which one could zoom in and out of particular hierarchical parts of the governance structures in a social system.
The IAD framework helps to perceive complex collective action problems by dividing them into 'action arenas', that are smaller pieces of practically understandable function. The analyst assumes that the structure of the action situation is fixed in the short-term. For an action situation to exist, there must be "actors in positions" (the number of possible roles that are available in this recurring interaction situation). Actors have choices within the existing (rule) structure. In the study of outcomes from collective choice situations, actors are influenced by the institutional arrangements, the socio-economic conditions, and the physical environment. The institutional arrangements can be studied by seven rule types (as per below).
Ostrom thought of the IAD as a "multi-level conceptual map" with which one could zoom in and out of particular hierarchical parts of the governance structures in a social system.
The IAD framework helps to perceive complex collective action problems by dividing them into 'action arenas', that are smaller pieces of practically understandable function. The analyst assumes that the structure of the action situation is fixed in the short-term. For an action situation to exist, there must be "actors in positions" (the number of possible roles that are available in this recurring interaction situation). Actors have choices within the existing (rule) structure. In the study of outcomes from collective choice situations, actors are influenced by the institutional arrangements, the socio-economic conditions, and the physical environment. The institutional arrangements can be studied by seven rule types (as per below).
References
Further reading
* * {{cite book, title=Historical Developments and Theoretical Approaches in Sociology., date=2010, publisher=Eolss Publishers, location=Ramsey, isbn=9781848263321 Social institutions Urban planning Political science Social systems