Indol2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Indole is an
 Indole chemistry began to develop with the study of the dye
Indole chemistry began to develop with the study of the dye
 In general, reactions are conducted between 200 and 500 °C. Yields can be as high as 60%. Other precursors to indole include formyltoluidine, 2-ethylaniline, and 2-(2-nitrophenyl)ethanol, all of which undergo cyclizations.
In general, reactions are conducted between 200 and 500 °C. Yields can be as high as 60%. Other precursors to indole include formyltoluidine, 2-ethylaniline, and 2-(2-nitrophenyl)ethanol, all of which undergo cyclizations.
 The Leimgruber–Batcho indole synthesis is an efficient method of synthesizing indole and substituted indoles. Originally disclosed in a patent in 1976, this method is high-yielding and can generate substituted indoles. This method is especially popular in the
The Leimgruber–Batcho indole synthesis is an efficient method of synthesizing indole and substituted indoles. Originally disclosed in a patent in 1976, this method is high-yielding and can generate substituted indoles. This method is especially popular in the

 One of the oldest and most reliable methods for synthesizing substituted indoles is the
One of the oldest and most reliable methods for synthesizing substituted indoles is the
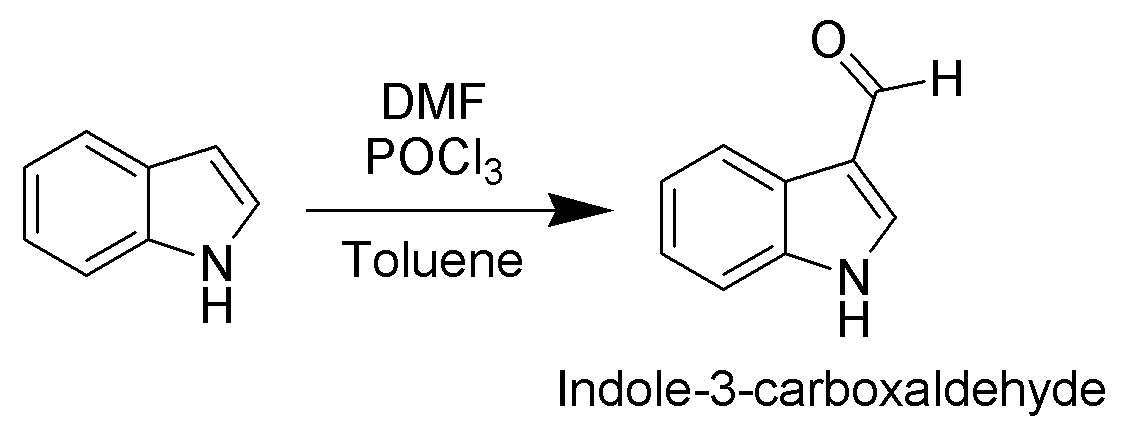 Since the pyrrolic ring is the most reactive portion of indole, electrophilic substitution of the carbocyclic (benzene) ring generally takes place only after N1, C2, and C3 are substituted. A noteworthy exception occurs when electrophilic substitution is carried out in conditions sufficiently acidic to exhaustively protonate C3. In this case, C5 is the most common site of electrophilic attack.
Since the pyrrolic ring is the most reactive portion of indole, electrophilic substitution of the carbocyclic (benzene) ring generally takes place only after N1, C2, and C3 are substituted. A noteworthy exception occurs when electrophilic substitution is carried out in conditions sufficiently acidic to exhaustively protonate C3. In this case, C5 is the most common site of electrophilic attack.


 Bergman and Venemalm developed a technique for lithiating the 2-position of unsubstituted indole, as did Katritzky.
Bergman and Venemalm developed a technique for lithiating the 2-position of unsubstituted indole, as did Katritzky.

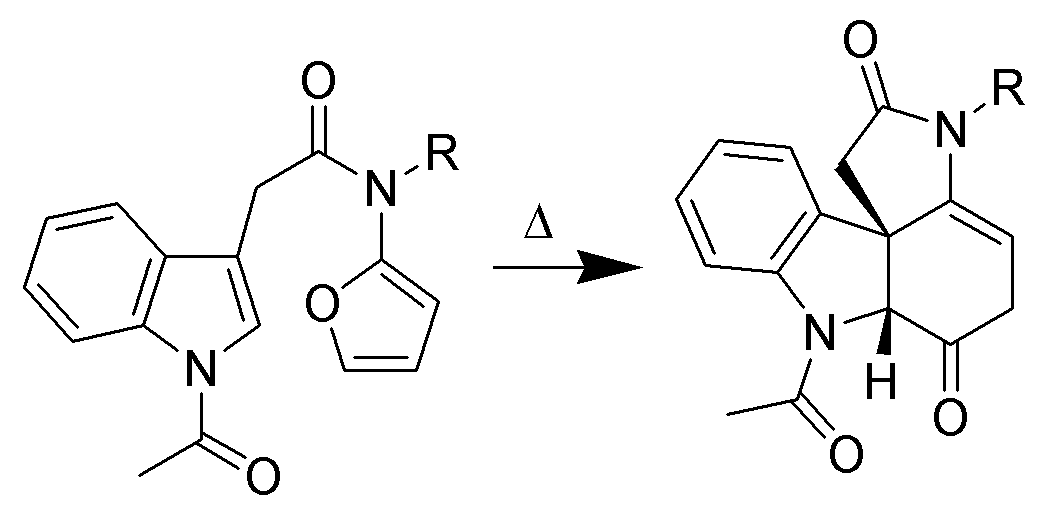 Despite mediocre yields, intermolecular cycloadditions of indole derivatives have been well documented. One example is the Pictet-Spengler reaction between
Despite mediocre yields, intermolecular cycloadditions of indole derivatives have been well documented. One example is the Pictet-Spengler reaction between

Synthesis of indoles (overview of recent methods)
at chemsynthesis.com {{Authority control Indoles, 5-HT3 receptor positive allosteric modulators Foul-smelling chemicals Simple aromatic rings Perfume ingredients Heterocyclic compounds with 2 rings Nitrogen heterocycles
organic compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-co ...
with the formula . Indole is classified as an aromatic
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated system, conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugati ...
heterocycle
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, proper ...
. It has a bicyclic
A bicyclic molecule () is a molecule that features two joined rings. Bicyclic structures occur widely, for example in many biologically important molecules like α-thujene and camphor. A bicyclic compound can be carbocyclic (all of the ring ...
structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hyd ...
ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic, aromatic, organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula . It is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., ''N''-methylpyrrol ...
ring. Indoles are derivatives of indole where one or more of the hydrogen atoms have been replaced by substituent
In organic chemistry, a substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces (one or more) atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule.
The suffix ''-yl'' is used when naming organic compounds that contain a single bond r ...
groups. Indoles are widely distributed in nature, most notably as amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromat ...
and neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, ...
.
General properties and occurrence
Indole is asolid
Solid is a state of matter where molecules are closely packed and can not slide past each other. Solids resist compression, expansion, or external forces that would alter its shape, with the degree to which they are resisted dependent upon the ...
at room temperature. It occurs naturally in human feces
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the ...
and has an intense fecal odor
An odor (American English) or odour ( Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is a smell or a scent caused by one or more volatilized chemical compounds generally found in low concentrations that humans and many animals can perceive ...
. At very low concentrations, however, it has a flowery smell, and is a constituent of many perfumes
Perfume (, ) is a mixture of fragrance, fragrant essential oils or aroma compounds (fragrances), Fixative (perfumery), fixatives and solvents, usually in liquid form, used to give the human body, animals, food, objects, and living-spaces an agre ...
. It also occurs in coal tar
Coal tar is a thick dark liquid which is a by-product of the production of coke and coal gas from coal. It is a type of creosote. It has both medical and industrial uses. Medicinally it is a topical medication applied to skin to treat psoria ...
. It has been identified in cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae that is widely accepted as being indigenous to and originating from the continent of Asia. However, the number of species is disputed, with as many as three species be ...
. It is the main volatile compound in stinky tofu
Stinky tofu ( zh, c=臭豆腐, p=chòu dòufu) is a Chinese form of fermented tofu that has a strong odor. It is usually sold at night markets or roadside stands as a snack, or in lunch bars as a side dish, rather than in restaurants. Traditio ...
.
When indole is a substituent
In organic chemistry, a substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces (one or more) atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule.
The suffix ''-yl'' is used when naming organic compounds that contain a single bond r ...
on a larger molecule, it is called an ''indolyl group'' by systematic nomenclature
Chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
IUPAC ...
.
Indole undergoes electrophilic substitution
Electrophilic substitution reactions are chemical reactions in which an electrophile displaces a functional group in a compound, which is typically, but not always, aromatic. Aromatic substitution reactions are characteristic of aromatic compounds ...
, mainly at position 3 (see diagram in right margin). Substituted
Substitution may refer to:
Arts and media
*Substitution (poetry), a variation in poetic scansion
*Substitution (theatre), an acting methodology
Music
*Chord substitution, swapping one chord for a related one within a chord progression
*Tritone ...
indoles are structural elements of (and for some compounds, the synthetic precursors for) the tryptophan-derived tryptamine
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole—a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the firs ...
alkaloids, which includes the neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, ...
and the hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
melatonin
Melatonin, an indoleamine, is a natural compound produced by various organisms, including bacteria and eukaryotes. Its discovery in 1958 by Aaron B. Lerner and colleagues stemmed from the isolation of a substance from the pineal gland of cow ...
, as well as the naturally occurring psychedelic drugs
Psychedelics are a subclass of Hallucinogen, hallucinogenic drugs whose primary effect is to trigger psychoactive drug, non-ordinary mental states (known as psychedelic experiences or "trips") and a perceived "expansion of consciousness". Also ...
dimethyltryptamine
Dimethyltryptamine (DMT), also known as ''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine (''N'',''N''-DMT), is a Psychedelic drug, serotonergic hallucinogen and Investigational New Drug, investigational drug of the substituted tryptamine, tryptamine family tha ...
and psilocybin
Psilocybin, also known as 4-phosphoryloxy-''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine (4-PO-DMT), is a natural product, naturally occurring tryptamine alkaloid and Investigational New Drug, investigational drug found in more than List of psilocybin mushroom ...
. Other indolic compounds include the plant hormone auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essent ...
(indolyl-3-acetic acid, IAA), tryptophol
Tryptophol is an aromatic alcohol that induces sleep in humans. It is found in wine as a secondary product of ethanol fermentation. It was first described by Felix Ehrlich in 1912. It is also produced by the trypanosomal parasite in sleeping ...
, the anti-inflammatory drug indomethacin
Indometacin, also known as indomethacin, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) commonly used as a prescription medication to reduce fever, pain, stiffness, and swelling from inflammation. It works by inhibiting the production of pr ...
, and the betablocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack (secondary prevention). ...
pindolol
Pindolol, sold under the brand name Visken among others, is a non-selective beta blocker which is used in the treatment of hypertension.Drugs.coInternational brand names for pindolol Page accessed Sept 4, 2015 It is also an antagonist of the se ...
.
The name ''indole'' is a portmanteau
In linguistics, a blend—also known as a blend word, lexical blend, or portmanteau—is a word formed by combining the meanings, and parts of the sounds, of two or more words together.
of the words '' indigo'' and '' oleum'', since indole was first isolated by treatment of the indigo dye with oleum.
History
 Indole chemistry began to develop with the study of the dye
Indole chemistry began to develop with the study of the dye indigo
InterGlobe Aviation Limited (d/b/a IndiGo), is an India, Indian airline headquartered in Gurgaon, Haryana, India. It is the largest List of airlines of India, airline in India by passengers carried and fleet size, with a 64.1% domestic market ...
. Indigo can be converted to isatin
Isatin, also known as tribulin, is an organic compound derived from indole with formula C8H5NO2. The compound was first obtained by Otto Linné Erdman and Auguste Laurent in 1840 as a product from the oxidation of indigo dye by nitric acid and ...
and then to oxindole
Oxindole (2-indolone) is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the formula . It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered nitrogen-containing ring. Oxindole is a modified indoline with a ...
. Then, in 1866, Adolf von Baeyer
Johann Friedrich Wilhelm Adolf von Baeyer (; 31 October 1835 – 20 August 1917) was a German chemist who synthesised indigo dye, indigo and developed a Von Baeyer nomenclature, nomenclature for cyclic compounds (that was subsequently extended a ...
reduced oxindole
Oxindole (2-indolone) is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the formula . It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered nitrogen-containing ring. Oxindole is a modified indoline with a ...
to indole using zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
dust. In 1869, he proposed a formula for indole.
Certain indole derivatives were important dyestuffs until the end of the 19th century. In the 1930s, interest in indole intensified when it became known that the indole substituent is present in many important alkaloid
Alkaloids are a broad class of natural product, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids.
Alkaloids are produced by a large varie ...
s, known as indole alkaloid
Indole alkaloids are a class of alkaloids containing a structural moiety of indole; many indole alkaloids also include isoprene groups and are thus called terpene indole or secologanin tryptamine alkaloids. Containing more than 4100 known differ ...
s (e.g., tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromat ...
and auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essent ...
s), and it remains an active area of research today.
Biosynthesis and function
Indole isbiosynthesized
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme- catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthesis) serve ...
in the shikimate pathway
The shikimate pathway (shikimic acid pathway) is a seven-step metabolic pathway used by bacteria, archaea, fungi, algae, some protozoans, and plants for the biosynthesis of folates and aromatic amino acids (tryptophan, phenylalanine, and tyrosine) ...
via anthranilate
Anthranilic acid is an aromatic acid with the formula C6H4(NH2)(CO2H) and has a sweetish taste. The molecule consists of a benzene ring, ''ortho''-substituted with a carboxylic acid and an amine. As a result of containing both acidic and basic f ...
. It is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromat ...
, where it stays inside the tryptophan synthase
Tryptophan synthase or tryptophan synthetase is an enzyme () that catalyzes the final two steps in the biosynthesis of tryptophan. It is commonly found in Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Protista, Fungi, and Plantae. However, it is absent from Animal ...
molecule between the removal of 3-phospho-glyceraldehyde and the condensation with serine
Serine
(symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − ...
. When indole is needed in the cell, it is usually produced from tryptophan by tryptophanase
The enzyme tryptophanase () catalyzes the chemical reaction
:L-tryptophan + H2O \rightleftharpoons indole + pyruvate + NH3
This enzyme belongs to the family of lyases, specifically in the "catch-all" class of carbon-carbon lyases. The system ...
.
:
As an intercellular signal molecule, indole regulates various aspects of bacterial physiology, including spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual reproduction, sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for biological dispersal, dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores fo ...
formation, plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria and ...
stability, resistance to drugs, biofilm
A biofilm is a Syntrophy, syntrophic Microbial consortium, community of microorganisms in which cell (biology), cells cell adhesion, stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy ext ...
formation, and virulence
Virulence is a pathogen's or microorganism's ability to cause damage to a host.
In most cases, especially in animal systems, virulence refers to the degree of damage caused by a microbe to its host. The pathogenicity of an organism—its abili ...
. A number of indole derivatives have important cellular functions, including neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
s such as serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, ...
.
Detection methods
Common classical methods applied for the detection of extracellular and environmental indoles, are Salkowski,Kovács
Kovács or Kovacs, meaning blacksmith, is one of the most common Hungarian family names.
History
The name is found in Hungary and Hungarian expatriate communities. There are similar names with the Kováts or Kovách spellings. The name means "bl ...
, Ehrlich’s reagent assays and HPLC
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), formerly referred to as high-pressure liquid chromatography, is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate, identify, and quantify specific components in mixtures. The mixtures can origina ...
. For intracellular indole detection and measurement genetically encoded indole-responsive biosensor
A biosensor is an analytical device, used for the detection of a chemical substance, that combines a biological component with a physicochemical detector.
The ''sensitive biological element'', e.g. tissue, microorganisms, organelles, cell rece ...
is applicable.
Medical applications
Indoles and their derivatives are promising againsttuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
, malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
, diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
, cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, migraines
Migraine (, ) is a complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea, and light and sound sensitivity. Other characterizing symptoms may includ ...
, convulsions
A convulsion is a medical condition where the body muscles contract and relax rapidly and repeatedly, resulting in uncontrolled shaking. Because epileptic seizures typically include convulsions, the term ''convulsion'' is often used as a synony ...
, hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
, bacterial infections of methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
'' (MRSA
Methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) is a group of gram-positive bacteria that are genetically distinct from other strains of ''Staphylococcus aureus''. MRSA is responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. ...
) and even viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almo ...
.
Synthetic routes
Indole and its derivatives can also be synthesized by a variety of methods. According to a 2011 review, all known syntheses fall into 9 categories. The main industrial routes start fromaniline
Aniline (From , meaning ' indigo shrub', and ''-ine'' indicating a derived substance) is an organic compound with the formula . Consisting of a phenyl group () attached to an amino group (), aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an in ...
via vapor-phase reaction with ethylene glycol
Ethylene glycol ( IUPAC name: ethane-1,2-diol) is an organic compound (a vicinal diol) with the formula . It is mainly used for two purposes: as a raw material in the manufacture of polyester fibers and for antifreeze formulations. It is an odo ...
in the presence of catalyst
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quick ...
s:
:Leimgruber–Batcho indole synthesis
: The Leimgruber–Batcho indole synthesis is an efficient method of synthesizing indole and substituted indoles. Originally disclosed in a patent in 1976, this method is high-yielding and can generate substituted indoles. This method is especially popular in the
The Leimgruber–Batcho indole synthesis is an efficient method of synthesizing indole and substituted indoles. Originally disclosed in a patent in 1976, this method is high-yielding and can generate substituted indoles. This method is especially popular in the pharmaceutical industry
The pharmaceutical industry is a medical industry that discovers, develops, produces, and markets pharmaceutical goods such as medications and medical devices. Medications are then administered to (or self-administered by) patients for curing ...
, where many pharmaceutical drugs
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via inhalation, injection, smoking, ingestio ...
are made up of specifically substituted indoles.
Fischer indole synthesis
:Fischer indole synthesis
The Fischer indole synthesis is a chemical reaction that produces the aromatic Heterocyclic compound, heterocycle indole from a (substituted) phenylhydrazine and an aldehyde or ketone under acidic conditions. The reaction was discovered in 1883 by ...
, developed in 1883 by Emil Fischer
Hermann Emil Louis Fischer (; 9 October 1852 – 15 July 1919) was a German chemist and List of Nobel laureates in Chemistry, 1902 recipient of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. He discovered the Fischer esterification. He also developed the Fisch ...
. Although the synthesis of indole itself is problematic using the Fischer indole synthesis, it is often used to generate indoles substituted in the 2- and/or 3-positions. Indole can still be synthesized, however, using the Fischer indole synthesis by reacting phenylhydrazine
Phenylhydrazine is the chemical compound with the formula . It is often abbreviated as . It is also found in edible mushrooms.
Properties
Phenylhydrazine forms monoclinic prisms that melt to an oil around room temperature which may turn yellow ...
with pyruvic acid
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the keto acids, alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate acid, conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an metabolic intermediate, intermediate in several m ...
followed by decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is ...
of the formed indole-2-carboxylic acid. This has also been accomplished in a one-pot synthesis using microwave irradiation.
Other indole-forming reactions
* Bartoli indole synthesis * Bischler–Möhlau indole synthesis * Cadogan-Sundberg indole synthesis * Fukuyama indole synthesis * Gassman indole synthesis * Hemetsberger indole synthesis * Larock indole synthesis * Madelung synthesis * Nenitzescu indole synthesis * Reissert indole synthesis *Baeyer–Emmerling indole synthesis
Baeyer–Emmerling indole synthesis is a method for synthesizing indole from a (substituted) ''ortho''-nitrocinnamic acid and iron powder in strongly basic solution. This reaction was discovered by Adolf von Baeyer and Adolph Emmerling in 1869.
...
* In the Diels–Reese reaction dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate
Ethane ( , ) is a naturally occurring organic chemical compound with chemical formula . At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas. Like many hydrocarbons, ethane is isolated on an industrial scale from natural ...
reacts with 1,2-diphenylhydrazine
Hydrazobenzene (1,2-diphenylhydrazine) is an aromatic organic compound consisting of two aniline groups joined via their nitrogen atoms. It is an important industrial chemical used in the manufacture of dyes, pharmaceuticals, and hydrogen peroxid ...
to an adduct, which in xylene
In organic chemistry, xylene or xylol (; IUPAC name: dimethylbenzene) are any of three organic compounds with the formula . They are derived from the substitution of two hydrogen atoms with methyl groups in a benzene ring; which hydrogens are su ...
gives dimethyl indole-2,3-dicarboxylate and aniline
Aniline (From , meaning ' indigo shrub', and ''-ine'' indicating a derived substance) is an organic compound with the formula . Consisting of a phenyl group () attached to an amino group (), aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an in ...
. With other solvents, other products are formed: with glacial acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main compone ...
a pyrazolone
Pyrazolone is 5-membered heterocycle containing two adjacent nitrogen atoms. It can be viewed as a derivative of pyrazole possessing an additional ketone, carbonyl (C=O) group. Compounds containing this functional group are useful commercially in ...
, and with pyridine
Pyridine is a basic (chemistry), basic heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom . It is a highly flammable, weak ...
a quinoline
Quinoline is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C9H7N. It is a colorless hygroscopic liquid with a strong odor. Aged samples, especially if exposed to light, become yellow and later brown. Quinoline is only sl ...
.
Chemical reactions of indole
Basicity
Unlike mostamine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
s, indole is not basic
Basic or BASIC may refer to:
Science and technology
* BASIC, a computer programming language
* Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base
* Basic access authentication, in HTTP
Entertainment
* Basic (film), ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film
...
: just like pyrrole
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic, aromatic, organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula . It is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., ''N''-methylpyrrol ...
, the aromatic character of the ring means that the lone pair
In chemistry, a lone pair refers to a pair of valence electrons that are not shared with another atom in a covalent bondIUPAC ''Gold Book'' definition''lone (electron) pair''/ref> and is sometimes called an unshared pair or non-bonding pair. Lone ...
of electrons on the nitrogen atom is not available for protonation. Strong acids such as hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is ...
can, however, protonate
In chemistry, protonation (or hydronation) is the adding of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), usually denoted by H+, to an atom, molecule, or ion, forming a conjugate acid. (The complementary process, when a proton is removed from a Brøn ...
indole. Indole is primarily protonated at the C3, rather than N1, owing to the enamine
An enamine is an unsaturated compound derived by the condensation of an aldehyde or ketone with a secondary amine. Enamines are versatile intermediates.
The word "enamine" is derived from the affix ''en''-, used as the suffix of alkene, and the r ...
-like reactivity of the portion of the molecule located outside of the benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hyd ...
ring. The protonated form has a p''K''a of −3.6. The sensitivity of many indolic compounds (e.g., tryptamine
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole—a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the firs ...
s) under acidic conditions is caused by this protonation.
Electrophilic substitution
The most reactive position on indole forelectrophilic aromatic substitution
Electrophilic aromatic substitution (SEAr) is an organic reaction in which an atom that is attached to an aromatic ring, aromatic system (usually hydrogen) is replaced by an electrophile. Some of the most important electrophilic aromatic substitut ...
is C3, which is 1013 times more reactive than benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hyd ...
. For example, it is alkylated by phosphorylated serine in the biosynthesis of the amino acid tryptophan. Vilsmeier–Haack formylation
Formylation refers to any chemical processes in which a compound is functionalized with a formyl group (-CH=O). In organic chemistry, the term is most commonly used with regards to aromatic compounds (for example the conversion of benzene to benz ...
of indole will take place at room temperature exclusively at C3.
: Since the pyrrolic ring is the most reactive portion of indole, electrophilic substitution of the carbocyclic (benzene) ring generally takes place only after N1, C2, and C3 are substituted. A noteworthy exception occurs when electrophilic substitution is carried out in conditions sufficiently acidic to exhaustively protonate C3. In this case, C5 is the most common site of electrophilic attack.
Since the pyrrolic ring is the most reactive portion of indole, electrophilic substitution of the carbocyclic (benzene) ring generally takes place only after N1, C2, and C3 are substituted. A noteworthy exception occurs when electrophilic substitution is carried out in conditions sufficiently acidic to exhaustively protonate C3. In this case, C5 is the most common site of electrophilic attack.
Gramine
Gramine (also called donaxine) is a naturally occurring indole alkaloid present in several plant species. Gramine may play a defensive role in these plants, since it is toxic to many organisms.
Occurrence
Gramine has been found in the giant reed, ...
, a useful synthetic intermediate, is produced via a Mannich reaction
In organic chemistry, the Mannich reaction is a three-component organic reaction that involves the amino alkylation of an acidic proton next to a carbonyl () functional group by formaldehyde () and a primary or secondary amine () or ammonia () ...
of indole with dimethylamine
Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable gas with an ammonia-like odor. Dimethylamine is commonly encountered commercially as a solution in water at concentrations up to around ...
and formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is an organic compound with the chemical formula and structure , more precisely . The compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde. It is stored as ...
. It is the precursor to indole-3-acetic acid and synthetic tryptophan.
:
N–H acidity and organometallic indole anion complexes
The N–H center has a p''K''a of 21 inDMSO
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is an organosulfur compound with the formula . This colorless liquid is the sulfoxide most widely used commercially. It is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds and is ...
, so that very strong base
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word "base": '' Arrhenius bases'', '' Brønsted bases'', and '' Lewis bases''. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acids, as originally proposed by G. ...
s such as sodium hydride
Sodium hydride is the chemical compound with the empirical formula Na H. This alkali metal hydride is primarily used as a strong yet combustible base in organic synthesis. NaH is a saline (salt-like) hydride, composed of Na+ and H− ions, in co ...
or ''n''-butyl lithium and water-free conditions are required for complete deprotonation
Deprotonation (or dehydronation) is the removal (transfer) of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), (H+) from a Brønsted–Lowry acid in an acid–base reaction.Henry Jakubowski, Biochemistry Online Chapter 2A3, https://employees.csbsju.ed ...
. The resulting organometalic derivatives can react in two ways. The more ionic salts such as the sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
or potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
compounds tend to react with electrophile
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively Electric charge, charged, have an ...
s at nitrogen-1, whereas the more covalent
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
magnesium compounds (''indole Grignard reagents
Grignard reagents or Grignard compounds are chemical compounds with the general formula , where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride and phenylmagnesium bromide ...
'') and (especially) zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
complexes tend to react at carbon 3 (see figure below). In analogous fashion, polar
Polar may refer to:
Geography
* Geographical pole, either of the two points on Earth where its axis of rotation intersects its surface
** Polar climate, the climate common in polar regions
** Polar regions of Earth, locations within the polar circ ...
aprotic solvent
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas ...
s such as DMF and DMSO
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is an organosulfur compound with the formula . This colorless liquid is the sulfoxide most widely used commercially. It is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds and is ...
tend to favour attack at the nitrogen, whereas nonpolar solvents such as toluene
Toluene (), also known as toluol (), is a substituted aromatic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula , often abbreviated as , where Ph stands for the phenyl group. It is a colorless, water
Water is an inorganic compound with the c ...
favour C3 attack.
:Carbon acidity and C2 lithiation
After the N–H proton, the hydrogen at C2 is the next most acidic proton on indole. Reaction of ''N''-protected indoles withbutyl lithium Butyllithium may refer to one of 5 isomeric organolithium reagents of which 3 are commonly used in chemical synthesis:
* ''n''-Butyllithium, abbreviated BuLi or nBuLi
* ''sec''-Butyllithium, abbreviated ''sec''-BuLi or sBuLi, has 2 stereoisomers, ...
or lithium diisopropylamide
Lithium diisopropylamide (commonly abbreviated LDA) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula . It is used as a strong base and has been widely utilized due to its good solubility in non-polar organic solvents and non-nucleophilic nature ...
results in lithiation exclusively at the C2 position. This strong nucleophile can then be used as such with other electrophiles.
: Bergman and Venemalm developed a technique for lithiating the 2-position of unsubstituted indole, as did Katritzky.
Bergman and Venemalm developed a technique for lithiating the 2-position of unsubstituted indole, as did Katritzky.
Oxidation of indole
Due to the electron-rich nature of indole, it is easilyoxidized
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
. Simple oxidants such as ''N''-bromosuccinimide will selectively oxidize indole 1 to oxindole
Oxindole (2-indolone) is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the formula . It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered nitrogen-containing ring. Oxindole is a modified indoline with a ...
(4 and 5).
:
Cycloadditions of indole
Only the C2–C3pi bond
In chemistry, pi bonds (π bonds) are covalent chemical bonds, in each of which two lobes of an orbital on one atom overlap with two lobes of an orbital on another atom, and in which this overlap occurs laterally. Each of these atomic orbital ...
of indole is capable of cycloaddition reaction
In organic chemistry, a cycloaddition is a chemical reaction in which "two or more unsaturated molecules (or parts of the same molecule) combine with the formation of a cyclic adduct in which there is a net reduction of the bond multiplicity". T ...
s. Intramolecular variants are often higher-yielding than intermolecular cycloadditions. For example, Padwa ''et al.'' have developed this Diels-Alder reaction to form advanced strychnine
Strychnine (, , American English, US chiefly ) is a highly toxicity, toxic, colorless, bitter, crystalline alkaloid used as a pesticide, particularly for killing small vertebrates such as birds and rodents. Strychnine, when inhaled, swallowed, ...
intermediates. In this case, the 2-aminofuran is the diene
In organic chemistry, a diene ( ); also diolefin, ) or alkadiene) is a covalent compound that contains two double bonds, usually among carbon atoms. They thus contain two alk''ene'' units, with the standard prefix ''di'' of systematic nome ...
, whereas the indole is the dienophile. Indoles also undergo intramolecular [2+3] and [2+2] cycloadditions.
: Despite mediocre yields, intermolecular cycloadditions of indole derivatives have been well documented. One example is the Pictet-Spengler reaction between
Despite mediocre yields, intermolecular cycloadditions of indole derivatives have been well documented. One example is the Pictet-Spengler reaction between tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromat ...
derivatives and aldehydes, which produces a mixture of diastereomers, leading to reduced chemical yield, yield of the desired product.
Hydrogenation
Indoles are susceptible to hydrogenation of the imine subunitZhu, G.; Zhang, X. ''Tetrahedron: Asymmetry'' 1998, ''9'', 2415. to give indolines.
See also
* Indole-3-butyric acid * Indole test * Isoindole * Isoindoline * Skatole (3-methylindole)References
General references
* * * * *External links
Synthesis of indoles (overview of recent methods)
at chemsynthesis.com {{Authority control Indoles, 5-HT3 receptor positive allosteric modulators Foul-smelling chemicals Simple aromatic rings Perfume ingredients Heterocyclic compounds with 2 rings Nitrogen heterocycles