IT risk management on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 IT risk management is the application of
IT risk management is the application of An IT risk management system (ITRMS) is a component of a broader
/ref>
The Certified Information Systems Auditor Review Manual 2006 by ISACA provides this definition of risk management: "''Risk management is the process of identifying
According to the NIST, "'' The American
The American
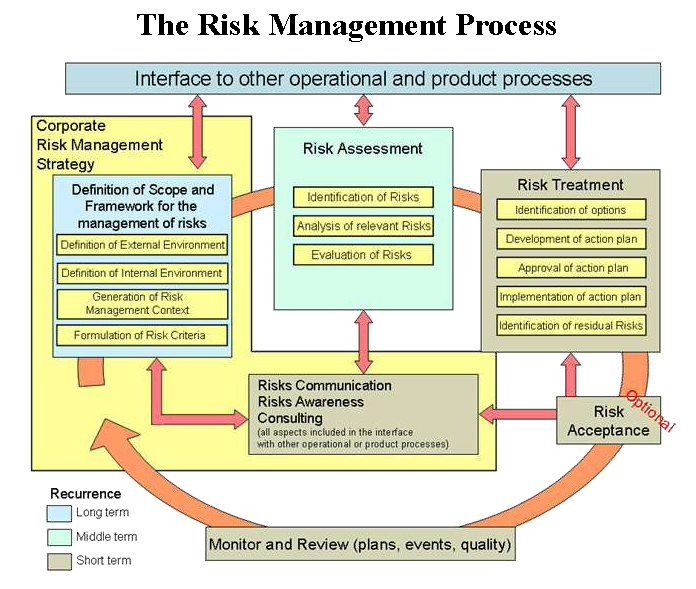
 Risk assessment, a critical component of IT risk management, is performed at specific points in time (e.g., annually or on-demand) and provides a snapshot of assessed risks. It forms the foundation for ongoing risk management, which includes analysis, planning, implementation, control, and monitoring of security measures.
Risk assessments may be iterative, beginning with high-level evaluations to identify major risks, followed by more detailed analysis in subsequent iterations. The following steps are typically involved:
# Risk identification – Recognizing potential loss sources such as
Risk assessment, a critical component of IT risk management, is performed at specific points in time (e.g., annually or on-demand) and provides a snapshot of assessed risks. It forms the foundation for ongoing risk management, which includes analysis, planning, implementation, control, and monitoring of security measures.
Risk assessments may be iterative, beginning with high-level evaluations to identify major risks, followed by more detailed analysis in subsequent iterations. The following steps are typically involved:
# Risk identification – Recognizing potential loss sources such as


 IT risk management is the application of
IT risk management is the application of risk management
Risk management is the identification, evaluation, and prioritization of risks, followed by the minimization, monitoring, and control of the impact or probability of those risks occurring. Risks can come from various sources (i.e, Threat (sec ...
methods to information technology
Information technology (IT) is a set of related fields within information and communications technology (ICT), that encompass computer systems, software, programming languages, data processing, data and information processing, and storage. Inf ...
in order to manage IT risk
It or IT may refer to:
* It (pronoun), in English
* Information technology
Arts and media Film and television
* ''It'' (1927 film), a film starring Clara Bow
* '' It! The Terror from Beyond Space'', a 1958 science fiction film
* ''It!'' (1967 ...
. Various methodologies exist to manage IT risks, each involving specific processes and steps.
enterprise risk management
Enterprise risk management (ERM) in business includes the methods and processes used by organizations to manage risks and seize opportunities related to the achievement of their objectives. ERM provides a framework for risk management, which typi ...
(ERM) system. ITRMS are also integrated into broader information security management systems (ISMS). The continuous update and maintenance of an ISMS is in turn part of an organisation's systematic approach for identifying, assessing, and managing information security risks.Enisa Risk management, Risk assessment inventory, page 46/ref>
Definitions
vulnerabilities
Vulnerability refers to "the quality or state of being exposed to the possibility of being attacked or harmed, either physically or emotionally." The understanding of social and environmental vulnerability, as a methodological approach, involves ...
and threats to the information resources used by an organization in achieving business objectives, and deciding what countermeasures, if any, to take in reducing risk to an acceptable level, based on the value of the information resource to the organization.''"Risk management
Risk management is the identification, evaluation, and prioritization of risks, followed by the minimization, monitoring, and control of the impact or probability of those risks occurring. Risks can come from various sources (i.e, Threat (sec ...
allows IT managers to balance the operational and economic costs of protective measures with mission goals by securing IT systems and data.''"
 The American
The American National Information Assurance Training and Education Center
The National Information Assurance Training and Education Center (NIATEC) is an American consortium of academic, industry, and government organizations to improve the literacy, awareness, training and education standards in Information Assurance ...
defines risk management in the IT field as:
# ''The total process to identify, control, and minimize the impact of uncertain events. The objective of the risk management program is to reduce risk and obtain and maintain DAA approval. The process facilitates the management of security risks by each level of management throughout the system life cycle. The approval process consists of three elements: risk analysis
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environ ...
, certification, and approval.''
# ''An element of managerial science concerned with the identification, measurement, control, and minimization of uncertain events. An effective risk management program encompasses the following four phases:''
## ''Risk assessment, as derived from an evaluation of threats and vulnerabilities.''
## ''Management decision.''
## ''Control implementation.''
## ''Effectiveness review.''
# ''The total process of identifying, measuring, and minimizing uncertain events affecting AIS resources. It includes risk analysis
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environ ...
, cost benefit analysis, safeguard selection, security test and evaluation, safeguard implementation, and systems review.''
# ''The total process of identifying, controlling, and eliminating or minimizing uncertain events that may affect system resources. lt includes risk analysis, cost benefit analysis, selection, implementation and test, security evaluation of safeguards, and overall security review.''
Methodology
While specific methods may vary, risk management processes generally include establishing context, conducting risk assessments, and managing risks. Risk management methodologies from standards such as ISO/IEC 27005, BS 7799, NIST SP 800-39, and Risk IT emphasize a structured approach to these processes. The following table compares key processes across leading frameworks:
Context establishment
The first step in the ISO/IEC 27005 framework is context establishment. This step involves gathering relevant information about the organization and defining the criteria, scope, and boundaries of the risk management activities. This includes complying with legal requirements, ensuring due diligence, and supporting the establishment of aninformation security management system
Information security management (ISM) defines and manages controls that an organization needs to implement to ensure that it is sensibly protecting the confidentiality, availability, and integrity of assets from threats and vulnerabilities. The co ...
(ISMS). The scope can encompass incident reporting plans, business continuity plans, or product certifications.
The key criteria include risk evaluation, risk acceptance, and impact assessment, influenced by:ISO/IEC, "Information technology -- Security techniques-Information security risk management" ISO/IEC FIDIS 27005:2008
* Legal and regulatory requirements
* The strategic value of information processes for the business
* Stakeholder expectations
* Negative consequences for the organization's reputation
Establishing the organization’s mission, values, structure, strategy, locations, and cultural environment is crucial, along with documenting constraints such as budgetary, cultural, political, and technical factors that will guide the risk management process.
Risk assessment
 Risk assessment, a critical component of IT risk management, is performed at specific points in time (e.g., annually or on-demand) and provides a snapshot of assessed risks. It forms the foundation for ongoing risk management, which includes analysis, planning, implementation, control, and monitoring of security measures.
Risk assessments may be iterative, beginning with high-level evaluations to identify major risks, followed by more detailed analysis in subsequent iterations. The following steps are typically involved:
# Risk identification – Recognizing potential loss sources such as
Risk assessment, a critical component of IT risk management, is performed at specific points in time (e.g., annually or on-demand) and provides a snapshot of assessed risks. It forms the foundation for ongoing risk management, which includes analysis, planning, implementation, control, and monitoring of security measures.
Risk assessments may be iterative, beginning with high-level evaluations to identify major risks, followed by more detailed analysis in subsequent iterations. The following steps are typically involved:
# Risk identification – Recognizing potential loss sources such as assets
In financial accounting, an asset is any resource owned or controlled by a business or an economic entity. It is anything (tangible or intangible) that can be used to produce positive economic value. Assets represent value of ownership that can b ...
, threats, vulnerabilities
Vulnerability refers to "the quality or state of being exposed to the possibility of being attacked or harmed, either physically or emotionally." The understanding of social and environmental vulnerability, as a methodological approach, involves ...
, and business processes.
# Risk estimation – Evaluating the likelihood and impact of identified risks, often using either quantitative or qualitative methods.
# Risk evaluation – Comparing risk levels to predefined acceptance criteria and prioritizing risks for treatment.
The ISO 27005 framework divides the process into the following stages:
Risk identification
This process identifies the assets (both primary and supporting), threats, andvulnerabilities
Vulnerability refers to "the quality or state of being exposed to the possibility of being attacked or harmed, either physically or emotionally." The understanding of social and environmental vulnerability, as a methodological approach, involves ...
that may affect the organization. Additionally, it involves identifying business processes and existing or planned security measures. The result of this step is a list of risks, threats, and potential consequences related to the assets and business processes.

Risk estimation
Risk estimation assesses the likelihood and consequences of the identified risks. Two common approaches are: * Quantitative risk assessment – A mathematical calculation based on security metrics, such as Single loss expectancy (SLE) and Annualized Loss Expectancy (ALE). * Qualitative risk assessment – Descriptive methods, such as interviews and expert judgment, which are faster and less data-intensive but less precise. For both methods, risk values are calculated for each asset and the output is documented in a risk register.Risk evaluation
In this step, the results from the risk analysis are compared against the organization's risk acceptance criteria. The risk list is prioritized, and recommendations are made for risk treatment. Risks that are too costly to mitigate may be accepted or transferred (e.g., through insurance).
Risk mitigation
Risk mitigation involves prioritizing and implementing risk-reducing measures recommended during risk assessment. Since eliminating all risk is impractical, organizations must apply the most cost-effective controls to reduce risk to an acceptable level while minimizing the impact on other operations. The following strategies are typically considered: * Risk assumption – Accepting the potential risk and continuing operations. * Risk avoidance – Eliminating the risk by avoiding risk-prone activities. * Risk limitation – Implementing controls to minimize the impact of risks. * Risk transference – Using other options, such as purchasing insurance, to transfer the risk. Residual risks, those remaining after treatment, are estimated to ensure adequate protection, and further measures may be taken if necessary.Risk communication
Risk communication is a continuous, bidirectional process that ensures a common understanding of risk among all stakeholders. Effective communication influences decision-making and promotes a culture of risk awareness across the organization. One method to achieve this is the Risk Reduction Overview method, which presents risks, measures, and residual risks in a comprehensible manner.Risk monitoring and review
Risk management is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring and review to ensure that implemented security measures remain effective as business conditions, threats, and vulnerabilities change. Regular security audits and reviews are essential to validate security controls and assess residual risks. New vulnerabilities, such as zero-day attacks, must be addressed through continuous monitoring, patch management, and updating of controls. Benchmarking againstbest practices
A best practice is a method or technique that has been generally accepted as superior to alternatives because it tends to produce superior results. Best practices are used to achieve quality as an alternative to mandatory standards. Best practice ...
and engaging in professional development activities are important for maintaining state-of-the-art risk management practices.
IT evaluation and assessment
To ensure the effectiveness of security measures, controls should be continuously tested and validated, including both technical systems and procedural controls. Penetration tests and vulnerability assessments are common methods for verifying the effectiveness of security controls. Regular reviews and reauthorization of systems are necessary when significant changes are made. Risk management should also be integrated into theSystems Development Life Cycle
In systems engineering, information systems and software engineering, the systems development life cycle (SDLC), also referred to as the application development life cycle, is a process for planning, creating, testing, and deploying an informati ...
(SDLC) to ensure that risks are addressed throughout the life cycle of IT systems. Each phase of the SDLC benefits from specific risk management activities, from initial planning to system disposal.
Integration into the system development life cycle
Effective risk management is fully integrated into theSystems Development Life Cycle
In systems engineering, information systems and software engineering, the systems development life cycle (SDLC), also referred to as the application development life cycle, is a process for planning, creating, testing, and deploying an informati ...
(SDLC). The SDLC typically involves five phases: initiation, development or acquisition, implementation, operation or maintenance, and disposal. Risk management activities remain consistent throughout these phases, ensuring that potential risks are identified, assessed, and mitigated during each stage.
Security in the SDLC
Incorporating security into the SDLC is essential to prevent costly vulnerabilities from emerging later in the system’s life. Early integration of security measures during the initiation and development phases can significantly reduce the cost of mitigating security vulnerabilities. It also enables the reuse of established security strategies and tools, resulting in improved security and cost efficiency. The following security considerations are integrated into the SDLC: * Security requirements for information systems: Security needs are incorporated into the system's design from the start. * Correct processing in applications: Protecting against errors and ensuring the integrity of data. * Cryptographic controls: Ensuring that data is encrypted both at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access. * Security of system files: Implementing version control, access restrictions, and thorough testing of system files. * Technical vulnerability management: Monitoring for vulnerabilities and applying timely patches to protect against emerging threats. By incorporating these practices, organizations can ensure that their IT systems are secure from the outset, reducing the likelihood of vulnerabilities and costly security incidents later in the system's life cycle.Critique of risk management as a methodology
Risk management as a methodology has been criticized for its subjectivity, particularly in assessing the value of assets and the likelihood and impact of threats. The probabilistic models often used may oversimplify complex risks. Despite these criticisms, risk management remains an essential tool for managing IT risks.Risk management methods
Various methods support the IT risk management process. Some of the most widely used include: *CRAMM {{More citations needed, date=September 2022
CRAMM (CCTA Risk Analysis and Management Method) is a risk management methodology, currently on its fifth version, CRAMM Version 5.0.
History
CRAMM was created in 1987 by the Central Computer and Telec ...
– Developed by the British government, compliant with ISO/IEC 17799 and other standards.
* EBIOS – Developed by the French government, compliant with major security standards.
* Factor Analysis of Information Risk
Factor analysis of information risk (FAIR) is a taxonomy of the factors that contribute to risk and how they affect each other. It is primarily concerned with establishing accurate probabilities for the frequency and magnitude of data loss events ...
(FAIR) – A rigorous approach to defining and analyzing IT risk factors.
* OCTAVE – Developed by Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. The institution was established in 1900 by Andrew Carnegie as the Carnegie Technical Schools. In 1912, it became the Carnegie Institu ...
, it is widely used for risk-based security assessments.
Standards
Various standards provide guidance for IT risk management, including ISO/IEC 27000-series andNIST
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical s ...
SP 800-30.
See also
* *Information security management
Information security management (ISM) defines and manages controls that an organization needs to implement to ensure that it is sensibly protecting the confidentiality, availability, and integrity of assets from threats and vulnerabilities. The ...
* ISO/IEC 27001
ISO/IEC 27001 is an information security standard. It specifies the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining and continually improving an information security management system (ISMS). Organizations with an ISMS that meet the st ...
* Vulnerability assessment (computing)
* Penetration test
A penetration test, colloquially known as a pentest, is an authorized simulated cyberattack on a computer system, performed to evaluate the security of the system; this is not to be confused with a vulnerability assessment. The test is perform ...
* Threat
A threat is a communication of intent to inflict harm or loss on another person. Intimidation is a tactic used between conflicting parties to make the other timid or psychologically insecure for coercion or control. The act of intimidation f ...
* Vulnerability (computing)
Vulnerabilities are flaws or weaknesses in a system's design, implementation, or management that can be exploited by a malicious actor to compromise its security.
Despite a system administrator's best efforts to achieve complete correctness, vi ...
References
* {{DEFAULTSORT:IT Risk Management IT risk management Data security Security compliance