IBM 5340 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The IBM System/34 was an

IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
midrange computer
Midrange computers, or midrange systems, were a class of computer systems that fell in between mainframe computers and microcomputers.
This class of machine emerged in the 1960s, with models from Digital Equipment Corporation ( PDP lines), Data ...
introduced in 1977. It was withdrawn from marketing in February 1985. It was a multi-user, multi-tasking successor to the single-user System/32. It included two processors, one based on the System/32 and the second based on the System/3
The IBM System/3 was an IBM midrange computer introduced in 1969, and marketed until 1985. It was produced by IBM Rochester in Minnesota as a low-end business computer aimed at smaller organizations that still used IBM 1400 series computers or un ...
. Like the System/32 and the System/3, the System/34 was primarily programmed in the RPG II language.
Hardware
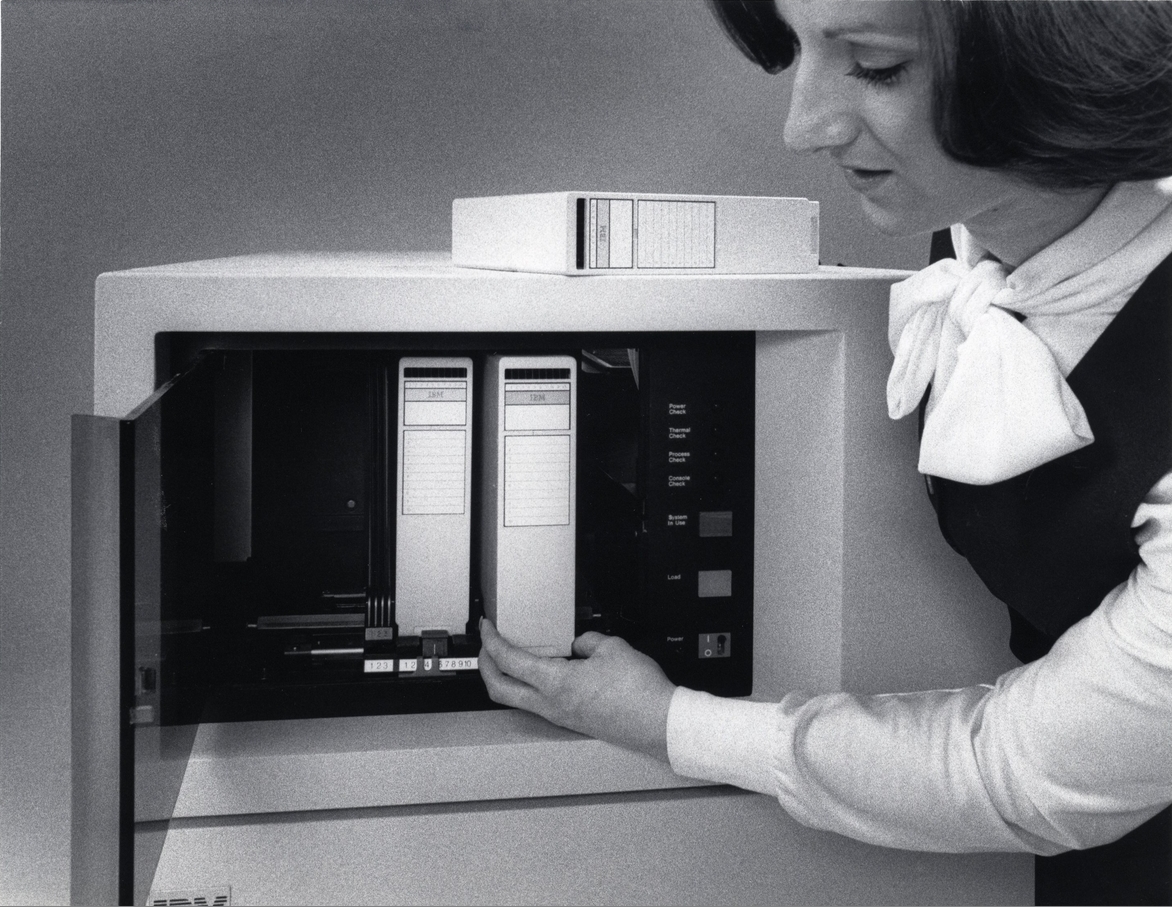
The 5340 System Unit contained the processing unit, the disk storage and the diskette drive. It had several access doors on both sides. Inside, were swing-out assemblies where the circuit boards and memory cards were mounted. It weighed and used 220V power. TheIBM 5250
IBM 5250 is a family of block-oriented terminals originally introduced with the IBM System/34 midrange computer systems in 1977. It also connects to the later System/36, System/38, and IBM AS/400 systems, and to IBM Power Systems systems running ...
series of terminals were the primary interface to the System/34.
Processors
S/34s had two processors, the Control Storage Processor (CSP), and the Main Storage Processor (MSP). The MSP was the workhorse, based onSystem/3
The IBM System/3 was an IBM midrange computer introduced in 1969, and marketed until 1985. It was produced by IBM Rochester in Minnesota as a low-end business computer aimed at smaller organizations that still used IBM 1400 series computers or un ...
architecture; it performed the instructions in the computer programs. The CSP was the governor, a different processor with different RISC
In electronics and computer science, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer architecture designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a comp ...
-like instruction set, based on System/32 architecture; it performed system functions in the background. The CSP also executed the optional ''Scientific Macroinstructions'', which were a set of emulated floating point operations used by the System/34 Fortran compiler and optionally in assembly code. The clock speed of the CPUs inside a System/34 was fixed at 1 MHz for the MSP and 4 MHz for the CSP. Special utility programs were able to make direct calls to the CSP to perform certain functions; these are usually system programs like $CNFIG which was used to configure the computer system.

Memory and storage
The smallest S/34 had 48K of RAM and an 8.6 MB hard drive. The largest configured S/34 could support 256K of RAM and 256MB of disk space. S/34 hard drives contained a feature called "the extra cylinder," so that bad spots on the drive were detected and dynamically mapped out to good spots on the extra cylinder. Disk space on the System/34 was organized by blocks of 2560 bytes. The System/34 supportedmemory paging
In computer operating systems, memory paging is a memory management scheme that allows the physical memory used by a program to be non-contiguous. This also helps avoid the problem of memory fragmentation and requiring compaction to reduce fr ...
, referring to as ''swapping''. The System/34 could either swap out entire programs, or individual segments of a program in order to free up memory for other programs to run.
One of the machine's most distinctive features was an off-line storage mechanism that utilized ""—boxes of 8-inch floppies that the machine could load and eject in a nonsequential fashion.
Software

Operating System
TheSystem Support Program
''System Support Program (SSP)'' is the operating system of the IBM System/34 and System/36 minicomputers. SSP was released in 1977.
History
SSP originally contained 60 or so commands that were implemented on the System/34 from 1977 to 198 ...
(SSP) was the only operating system of the S/34. It contained support for multiprogramming, multiple processors, 36 devices, job queues, printer queues, security, indexed file
An indexed file is a computer file with an index that allows easy random access to any record given its file key.
The key must be such that it uniquely identifies a record. If more than one index is present the other ones are called ''alternate ...
support. Fully installed, it was about 5 MB. The Operational Control Language (OCL) was the control language of SSP.
Programming
The System/34's initial programming languages were limited to RPG II and Basic Assembler when introduced in 1977. FORTRAN was fully available six months after the 34's introduction, andCOBOL
COBOL (; an acronym for "common business-oriented language") is a compiled English-like computer programming language designed for business use. It is an imperative, procedural, and, since 2002, object-oriented language. COBOL is primarily ...
was available as a PRPQ. BASIC
Basic or BASIC may refer to:
Science and technology
* BASIC, a computer programming language
* Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base
* Basic access authentication, in HTTP
Entertainment
* Basic (film), ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film
...
was introduced later.
Successor systems
TheIBM System/38
The System/38 is a discontinued minicomputer and midrange computer manufactured and sold by
IBM. The system was announced in 1978. The System/38 has 48-bit addressing, which was unique for the time, and a novel integrated database system. It was ...
was intended to be the successor of the System/34 and the earlier System/3x systems. However, due to the delays in the development of the System/38 and the high cost of the hardware once complete, IBM developed the simpler and cheaper System/36
The IBM System/36 (often abbreviated as S/36) was a midrange computer marketed by IBM from 1983 to 2000 - a multi-user, Computer multitasking, multi-tasking successor to the IBM System/34, System/34.
Like the System/34 and the older IBM Syst ...
platform which was more widely adopted than the System/38. The System/36 was an evolution of the System/34 design, but the two machines were not object-code compatible. Instead, the System/36 offered source code compatibility, allowing System/34 applications to be recompiled on a System/36 with little to no changes. Some System/34 hardware was incompatible with the System/36.
A third-party product from ''California Software Products, Inc.'' named BABY/34 allowed System/34 applications to be ported to IBM PC compatible
An IBM PC compatible is any personal computer that is hardware- and software-compatible with the IBM Personal Computer (IBM PC) and its subsequent models. Like the original IBM PC, an IBM PC–compatible computer uses an x86-based central p ...
hardware running MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few op ...
.
References
Further reading
* * *External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Ibm System 34System 34
The IBM System/34 was an IBM midrange computer introduced in 1977. It was withdrawn from marketing in February 1985. It was a multi-user, multi-tasking successor to the single-user System/32. It included two processors, one based on the System/ ...
Computer-related introductions in 1977
16-bit computers