Hypothyroidism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as poor ability to tolerate cold, a feeling of tiredness,
 Delayed relaxation after testing the
Delayed relaxation after testing the
 Thyroid hormone is required for the normal functioning of numerous tissues in the body. In healthy individuals, the thyroid gland predominantly secretes thyroxine (T4), which is converted into
Thyroid hormone is required for the normal functioning of numerous tissues in the body. In healthy individuals, the thyroid gland predominantly secretes thyroxine (T4), which is converted into
 Hypothyroidism may be prevented in a population by adding iodine to commonly used foods. This public health measure has eliminated endemic childhood hypothyroidism in countries where it was once common. In addition to promoting the consumption of iodine-rich foods such as dairy and fish, many countries with moderate iodine deficiency have implemented universal salt iodization. Encouraged by the
Hypothyroidism may be prevented in a population by adding iodine to commonly used foods. This public health measure has eliminated endemic childhood hypothyroidism in countries where it was once common. In addition to promoting the consumption of iodine-rich foods such as dairy and fish, many countries with moderate iodine deficiency have implemented universal salt iodization. Encouraged by the
 In veterinary practice, dogs are the species most commonly affected by hypothyroidism. The majority of cases occur as a result of primary hypothyroidism, of which two types are recognized: lymphocytic thyroiditis, which is probably immune-driven and leads to destruction and fibrosis of the thyroid gland, and idiopathic atrophy, which leads to the gradual replacement of the gland by fatty tissue. There is often lethargy, cold intolerance, exercise intolerance, and weight gain. Furthermore, skin changes and fertility problems are seen in dogs with hypothyroidism, as well as a number of other symptoms. The signs of myxedema can be seen in dogs, with prominence of skin folds on the forehead, and cases of myxedema coma are encountered. The diagnosis can be confirmed by blood test, as the clinical impression alone may lead to overdiagnosis. Lymphocytic thyroiditis is associated with detectable antibodies against thyroglobulin, although they typically become undetectable in advanced disease. Treatment is with thyroid hormone replacement.
Other species that are less commonly affected include cats and horses, as well as other large domestic animals. In cats, hypothyroidism is usually the result of other medical treatment such as surgery or radiation. In young horses, congenital hypothyroidism has been reported predominantly in
In veterinary practice, dogs are the species most commonly affected by hypothyroidism. The majority of cases occur as a result of primary hypothyroidism, of which two types are recognized: lymphocytic thyroiditis, which is probably immune-driven and leads to destruction and fibrosis of the thyroid gland, and idiopathic atrophy, which leads to the gradual replacement of the gland by fatty tissue. There is often lethargy, cold intolerance, exercise intolerance, and weight gain. Furthermore, skin changes and fertility problems are seen in dogs with hypothyroidism, as well as a number of other symptoms. The signs of myxedema can be seen in dogs, with prominence of skin folds on the forehead, and cases of myxedema coma are encountered. The diagnosis can be confirmed by blood test, as the clinical impression alone may lead to overdiagnosis. Lymphocytic thyroiditis is associated with detectable antibodies against thyroglobulin, although they typically become undetectable in advanced disease. Treatment is with thyroid hormone replacement.
Other species that are less commonly affected include cats and horses, as well as other large domestic animals. In cats, hypothyroidism is usually the result of other medical treatment such as surgery or radiation. In young horses, congenital hypothyroidism has been reported predominantly in
constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the bowel moveme ...
, slow heart rate, depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
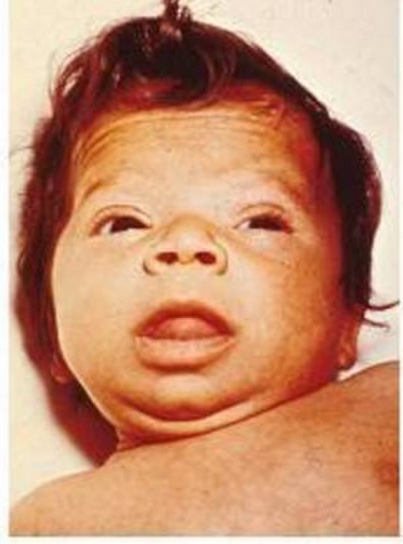
can lead to delays in growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome
Congenital iodine deficiency syndrome is a medical condition present at birth marked by impaired physical and mental development, due to insufficient thyroid hormone ( hypothyroidism) often caused by insufficient dietary iodine during pregnancy. ...
.
Worldwide, too little iodine in the diet is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in countries with sufficient dietary iodine. Less common causes include previous treatment with radioactive iodine, injury to the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus ...
or the anterior pituitary
A major organ of the endocrine system, the anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is the glandular, anterior lobe that together with the posterior lobe (posterior pituitary, or the neurohypophysis) makes up the pi ...
gland, certain medications, a lack of a functioning thyroid at birth, or previous thyroid surgery. The diagnosis of hypothyroidism, when suspected, can be confirmed with blood tests measuring thyroid-stimulating hormone
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (also known as thyrotropin, thyrotropic hormone, or abbreviated TSH) is a pituitary hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine (T4), and then triiodothyronine (T3) which stimulates the metabolism ...
(TSH) and thyroxine levels.
Salt iodization has prevented hypothyroidism in many populations. Thyroid hormone replacement with levothyroxine treats hypothyroidism. Medical professionals adjust the dose according to symptoms and normalization of the thyroxine and TSH levels. Thyroid medication is safe in pregnancy. Although an adequate amount of dietary iodine is important, too much may worsen specific forms of hypothyroidism.
Worldwide about one billion people are estimated to be iodine-deficient; however, it is unknown how often this results in hypothyroidism. In the United States, hypothyroidism occurs in 0.3–0.4% of people. Subclinical hypothyroidism, a milder form of hypothyroidism characterized by normal thyroxine levels and an elevated TSH level, is thought to occur in 4.3–8.5% of people in the United States. Hypothyroidism is more common in women than in men. People over the age of 60 are more commonly affected. Dogs are also known to develop hypothyroidism, as are cats and horses, albeit more rarely. The word ''hypothyroidism'' is from Greek ''hypo-'' 'reduced', ''thyreos'' 'shield', and ''eidos'' 'form'.
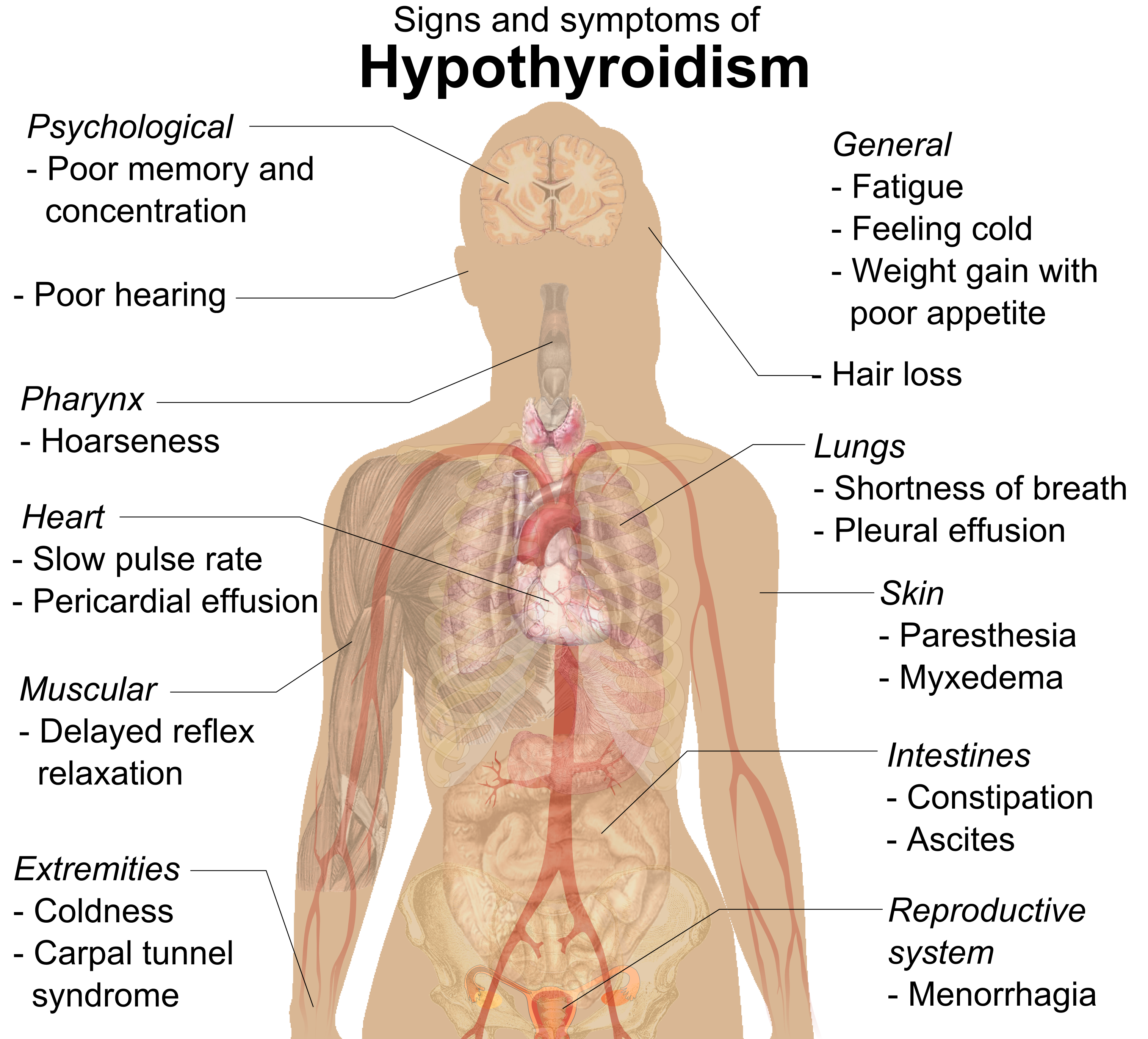
Signs and symptoms
People with hypothyroidism often have no or only mild symptoms. Numerous symptoms and signs are associated with hypothyroidism and can be related to the underlying cause, or a direct effect of having not enough thyroid hormones. Hashimoto's thyroiditis may present with the mass effect of a goiter (enlarged thyroid gland). In middle-aged women, the symptoms may be mistaken for those ofmenopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often d ...
.
 Delayed relaxation after testing the
Delayed relaxation after testing the ankle jerk reflex
The ankle jerk reflex, also known as the Achilles reflex, occurs when the Achilles tendon is tapped while the foot is dorsiflexed.
It is a type of stretch reflex that tests the function of the gastrocnemius muscle and the nerve that supplies it.
...
is a characteristic sign of hypothyroidism and is associated with the severity of the hormone deficit.
Myxedema coma
Myxedema coma
Myxedema coma is an extreme or decompensated form of hypothyroidism and while uncommon, is potentially lethal. A person may have laboratory values identical to a "normal" hypothyroid state, but a stressful event (such as an infection, myocardial ...
is a rare but life-threatening state of extreme hypothyroidism. It may occur in those with established hypothyroidism when they develop an acute illness. Myxedema coma can be the first presentation of hypothyroidism. People with myxedema coma typically have a low body temperature without shivering, confusion, a slow heart rate and reduced breathing effort. There may be physical signs suggestive of hypothyroidism, such as skin changes or enlargement of the tongue.
Pregnancy
Even mild or subclinical hypothyroidism leads to possible infertility and an increased risk of miscarriage. Hypothyroidism in early pregnancy, even with limited or no symptoms, may increase the risk of pre-eclampsia, offspring with lower intelligence, and the risk of infant death around the time of birth. Women are affected by hypothyroidism in 0.3–0.5% of pregnancies. Subclinical hypothyroidism during pregnancy is associated withgestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman without diabetes develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes generally results in few symptoms; however, it increases the risk of pre-eclampsia, depression, and ...
, low birth-weight, placental abruption, and the birth of the baby before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
Children
Newborn children with hypothyroidism may have normal birth weight and height (although the head may be larger than expected and the posterior fontanelle may be open). Some may have drowsiness, decreased muscle tone, a hoarse-sounding cry, feeding difficulties, constipation, an enlarged tongue,umbilical hernia
An umbilical hernia is a health condition where the abdominal wall behind the navel is damaged. It may cause the navel to bulge outwards—the bulge consisting of abdominal fat from the greater omentum or occasionally parts of the small intestine. ...
, dry skin, a decreased body temperature, and jaundice. A goiter is rare, although it may develop later in children who have a thyroid gland that does not produce functioning thyroid hormone. A goiter may also develop in children growing up in areas with iodine deficiency. Normal growth and development may be delayed, and not treating infants may lead to an intellectual impairment (IQ 6–15 points lower in severe cases). Other problems include the following: difficulty with large scale and fine motor skills and coordination, reduced muscle tone, squinting, decreased attention span, and delayed speaking. Tooth eruption may be delayed.
In older children and adolescents, the symptoms of hypothyroidism may include fatigue, cold intolerance, sleepiness, muscle weakness, constipation, a delay in growth, overweight for height, pallor, coarse and thick skin, increased body hair, irregular menstrual cycles in girls, and delayed puberty. Signs may include delayed relaxation of the ankle reflex and a slow heartbeat. A goiter may be present with a completely enlarged thyroid gland; sometimes only part of the thyroid is enlarged and it can be knobby.
Related disorders
Thyroid hormone abnormalities are common in major psychiatric disorders includingbipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevat ...
; clinical research has shown there is a high rate of thyroid dysfunction in mood disorders and schizophrenia-spectrum disorders, concluding that there is a case for screening for the latter among people with thyroid illness.
Causes
Hypothyroidism is caused by inadequate function of the gland itself (primary hypothyroidism), inadequate stimulation by thyroid-stimulating hormone from thepituitary gland
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The h ...
(secondary hypothyroidism), or inadequate release of thyrotropin-releasing hormone
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is a hypophysiotropic hormone produced by neurons in the hypothalamus that stimulates the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and prolactin from the anterior pituitary.
TRH has been used clinicall ...
from the brain's hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus ...
(tertiary hypothyroidism). Primary hypothyroidism is about a thousandfold more common than central hypothyroidism. Central hypothyroidism is the name used for secondary and tertiary, since hypothalamus and pituitary gland are at the center of thyroid hormone control.
Iodine deficiency is the most common cause of primary hypothyroidism and endemic goiter worldwide. In areas of the world with sufficient dietary iodine, hypothyroidism is most commonly caused by the autoimmune disease Hashimoto's thyroiditis (chronic autoimmune thyroiditis). Hashimoto's may be associated with a goiter. It is characterized by infiltration of the thyroid gland with T lymphocytes and autoantibodies against specific thyroid antigens such as thyroid peroxidase
Thyroid peroxidase, also called thyroperoxidase (TPO) or iodide peroxidase, is an enzyme expressed mainly in the thyroid where it is secreted into colloid. Thyroid peroxidase oxidizes iodide ions to form iodine atoms for addition onto tyrosine re ...
, thyroglobulin and the TSH receptor.
After women give birth, about 5% develop postpartum thyroiditis
Postpartum thyroiditis refers to thyroid dysfunction occurring in the first 12 months after pregnancy and may involve hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism or the two sequentially. According to the National Institute of Health, postpartum thyroiditis a ...
which can occur up to nine months afterwards. This is characterized by a short period of hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidis ...
followed by a period of hypothyroidism; 20–40% remain permanently hypothyroid.
Autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto's) is associated with other immune-mediated diseases such as diabetes mellitus type 1, pernicious anemia
Pernicious anemia is a type of vitamin B12 deficiency anemia, a disease in which not enough red blood cells are produced due to the malabsorption of vitamin B12. Malabsorption in pernicious anemia results from the lack or loss of intrinsic ...
, myasthenia gravis, celiac disease, rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are inv ...
and systemic lupus erythematosus. It may occur as part of autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndromes (APSs), also called polyglandular autoimmune syndromes (PGASs) or polyendocrine autoimmune syndromes (PASs), are a heterogeneous group of rare diseases characterized by autoimmune activity against more than one e ...
( type 1 and type 2).
Iatrogenic hypothyroidism can be surgical (a result of thyroidectomy, usually for thyroid nodules or cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
) or following radioiodine ablation (usually for Graves' disease).
Pathophysiology
triiodothyronine
Triiodothyronine, also known as T3, is a thyroid hormone. It affects almost every physiological process in the body, including growth and development, metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate.
Production of T3 and its prohormone thyrox ...
(T3) in other organs by the selenium-dependent enzyme iodothyronine deiodinase. Triiodothyronine binds to the thyroid hormone receptor
The thyroid hormone receptor (TR) is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding thyroid hormone. TRs act as transcription factors, ultimately affecting the regulation of gene transcription and translation. These receptors also have ...
in the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
* Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
of cells, where it stimulates the turning on of particular gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s and the production of specific proteins. Additionally, the hormone binds to integrin αvβ3 on the cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
, thereby stimulating the sodium–hydrogen antiporter The sodium–hydrogen antiporter or sodium–proton exchanger (Na+/H+ exchanger) is a membrane protein that transports Na+ into the cell, and H+ out of the cell (antiport).
Function
They are found in the membranes of many cells, and especially ...
and processes such as formation of blood vessels and cell growth. In blood, almost all thyroid hormone (99.97%) are bound to plasma proteins such as thyroxine-binding globulin; only the free unbound thyroid hormone is biologically active.
The thyroid gland is the only source of thyroid hormone in the body; the process requires iodine and the amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the G ...
. Iodine in the bloodstream is taken up by the gland and incorporated into thyroglobulin molecules. The process is controlled by the thyroid-stimulating hormone
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (also known as thyrotropin, thyrotropic hormone, or abbreviated TSH) is a pituitary hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine (T4), and then triiodothyronine (T3) which stimulates the metabolism ...
(TSH, thyrotropin), which is secreted by the pituitary. Not enough iodine, or not enough TSH, can result in decreased production of thyroid hormones.
The hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis
The hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis (HPT axis for short, a.k.a. thyroid homeostasis or thyrotropic feedback control) is part of the neuroendocrine system responsible for the regulation of metabolism and also responds to stress.
As its n ...
plays a key role in maintaining thyroid hormone levels within normal limits. Production of TSH by the anterior pituitary gland is stimulated in turn by thyrotropin-releasing hormone
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is a hypophysiotropic hormone produced by neurons in the hypothalamus that stimulates the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and prolactin from the anterior pituitary.
TRH has been used clinicall ...
(TRH), released from the hypothalamus. Production of TSH and TRH is decreased by thyroxine by a negative feedback process. Not enough TRH, which is uncommon, can lead to not enough TSH and thereby to not enough thyroid hormone production.
Pregnancy leads to marked changes in thyroid hormone physiology. The gland is increased in size by 10%, thyroxine production is increased by 50%, and iodine requirements are increased. Many women have normal thyroid function but have immunological evidence of thyroid autoimmunity (as evidenced by autoantibodies) or are iodine deficient, and develop evidence of hypothyroidism before or after giving birth.
Diagnosis
Laboratory testing of thyroid stimulating hormone levels in the blood is considered the best initial test for hypothyroidism; a second TSH level is often obtained several weeks later for confirmation. Levels may be abnormal in the context of other illnesses, and TSH testing in hospitalized people is discouraged unless thyroid dysfunction is strongly suspected, as the cause of the acute illness. An elevated TSH level indicates that the thyroid gland is not producing enough thyroid hormone, and free T4 levels are then often obtained. Measuring T3 is discouraged by the AACE in the assessment for hypothyroidism. In England and Wales, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends routine T4 testing in children, and T3 testing in both adults and children if central hypothyroidism is suspected and the TSH is low. There are a number of symptom rating scales for hypothyroidism; they provide a degree of objectivity but have limited use for diagnosis. Many cases of hypothyroidism are associated with mild elevations in creatine kinase and liver enzymes in the blood. They typically return to normal when hypothyroidism has been fully treated. Levels ofcholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell memb ...
, low-density lipoprotein
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons (aka ULDL by the overall densi ...
and lipoprotein (a)
Lipoprotein(a) is a low-density lipoprotein variant containing a protein called apolipoprotein(a). Genetic and epidemiological studies have identified lipoprotein(a) as a risk factor for atherosclerosis and related diseases, such as coronary hea ...
can be elevated; the impact of subclinical hypothyroidism on lipid parameters is less well-defined.
Very severe hypothyroidism and myxedema coma are characteristically associated with low sodium levels in the blood together with elevations in antidiuretic hormone
Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travel ...
, as well as acute worsening of kidney function due to a number of causes. In most causes, however, it is unclear if the relationship is causal.
A diagnosis of hypothyroidism without any lumps or masses felt
Felt is a textile material that is produced by matting, condensing and pressing fibers together. Felt can be made of natural fibers such as wool or animal fur, or from synthetic fibers such as petroleum-based acrylic or acrylonitrile or wood ...
within the thyroid gland does not require thyroid imaging; however, if the thyroid feels abnormal, diagnostic imaging is then recommended. The presence of antibodies against thyroid peroxidase
Thyroid peroxidase, also called thyroperoxidase (TPO) or iodide peroxidase, is an enzyme expressed mainly in the thyroid where it is secreted into colloid. Thyroid peroxidase oxidizes iodide ions to form iodine atoms for addition onto tyrosine re ...
(TPO) makes it more likely that thyroid nodules are caused by autoimmune thyroiditis, but if there is any doubt, a needle biopsy
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is a diagnostic procedure used to investigate lumps or masses. In this technique, a thin (23–25 gauge (0.52 to 0.64 mm outer diameter)), hollow needle is inserted into the mass for sampling of cells that, aft ...
may be required.
Central
If the TSH level is normal or low and serum free T4 levels are low, this is suggestive of central hypothyroidism (not enough TSH or TRH secretion by the pituitary gland or hypothalamus). There may be other features of hypopituitarism, such as menstrual cycle abnormalities andadrenal insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal gland normally secretes glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol), mineralocorticoids (primarily aldosterone), and andro ...
. There might also be symptoms of a pituitary mass such as headaches and vision changes. Central hypothyroidism should be investigated further to determine the underlying cause.
Overt
In overt primary hypothyroidism, TSH levels are high and T4 and T3 levels are low. Overt hypothyroidism may also be diagnosed in those who have a TSH on multiple occasions of greater than 5mIU/L, appropriate symptoms, and only a borderline low T4. It may also be diagnosed in those with a TSH of greater than 10mIU/L.Subclinical
Subclinical hypothyroidism is a milder form of hypothyroidism characterized by an elevated serum TSH level, but with a normal serum free thyroxine level. This milder form of hypothyroidism is most commonly caused by Hashimoto's thyroiditis. In adults it is diagnosed when TSH levels are greater than 5 mIU/L and less than 10mIU/L. The presentation of subclinical hypothyroidism is variable and classic signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism may not be observed. Of people with subclinical hypothyroidism, a proportion will develop overt hypothyroidism each year. In those with detectable antibodies against thyroid peroxidase (TPO), this occurs in 4.3%, while in those with no detectable antibodies, this occurs in 2.6%. Those with subclinical hypothyroidism and detectable anti-TPO antibodies who do not require treatment should have repeat thyroid function tests more frequently (e.g. yearly) compared with those who do not have antibodies.Pregnancy
During pregnancy, the thyroid gland must produce 50% more thyroid hormone to provide enough thyroid hormone for the developing fetus and the expectant mother. In pregnancy, free thyroxine levels may be lower than anticipated due to increased binding to thyroid binding globulin and decreased binding toalbumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All the proteins of the albumin family are water- soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Album ...
. They should either be corrected for the stage of pregnancy, or total thyroxine levels should be used instead for diagnosis. TSH values may also be lower than normal (particularly in the first trimester) and the normal range should be adjusted for the stage of pregnancy.
In pregnancy, subclinical hypothyroidism is defined as a TSH between 2.5 and 10 mIU/L with a normal thyroxine level, while those with TSH above 10 mIU/L are considered to be overtly hypothyroid even if the thyroxine level is normal. Antibodies against TPO may be important in making decisions about treatment, and should, therefore, be determined in women with abnormal thyroid function tests.
Determination of TPO antibodies may be considered as part of the assessment of recurrent miscarriage
Recurrent miscarriage is three or more consecutive pregnancy losses. In contrast, infertility is the inability to conceive. In many cases the cause of RPL is unknown. After three or more losses, a thorough evaluation is recommended by American ...
, as subtle thyroid dysfunction can be associated with pregnancy loss, but this recommendation is not universal, and presence of thyroid antibodies may not predict future outcome.
Prevention
 Hypothyroidism may be prevented in a population by adding iodine to commonly used foods. This public health measure has eliminated endemic childhood hypothyroidism in countries where it was once common. In addition to promoting the consumption of iodine-rich foods such as dairy and fish, many countries with moderate iodine deficiency have implemented universal salt iodization. Encouraged by the
Hypothyroidism may be prevented in a population by adding iodine to commonly used foods. This public health measure has eliminated endemic childhood hypothyroidism in countries where it was once common. In addition to promoting the consumption of iodine-rich foods such as dairy and fish, many countries with moderate iodine deficiency have implemented universal salt iodization. Encouraged by the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
, 70% of the world's population across 130 countries are receiving iodized salt. In some countries, iodized salt is added to bread. Despite this, iodine deficiency has reappeared in some Western countries as a result of attempts to reduce salt intake.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women, who require 66% more daily iodine than non-pregnant women, may still not be getting enough iodine. The World Health Organization recommends a daily intake of 250 µg for pregnant and breastfeeding women. As many women will not achieve this from dietary sources alone, the American Thyroid Association
The American Thyroid Association (ATA) is a professional organization of over 1700 medical specialists devoted to thyroid biology and to the prevention and treatment of thyroid disease through excellence in research, clinical care, education, and ...
recommends a 150 µg daily supplement by mouth.
Screening
Screening
Screening may refer to:
* Screening cultures, a type a medical test that is done to find an infection
* Screening (economics), a strategy of combating adverse selection (includes sorting resumes to select employees)
* Screening (environmental), ...
for hypothyroidism is performed in the newborn period in many countries, generally using TSH. This has led to the early identification of many cases and thus the prevention of developmental delay. It is the most widely used newborn screening test worldwide. While TSH-based screening will identify the most common causes, the addition of T4 testing is required to pick up the rarer central causes of neonatal hypothyroidism. If T4 determination is included in the screening done at birth, this will identify cases of congenital hypothyroidism of central origin in 1:16,000 to 1:160,000 children. Considering that these children usually have other pituitary hormone deficiencies, early identification of these cases may prevent complications.
In adults, widespread screening of the general population is a matter of debate. Some organizations (such as the United States Preventive Services Task Force) state that evidence is insufficient to support routine screening, while others (such as the American Thyroid Association
The American Thyroid Association (ATA) is a professional organization of over 1700 medical specialists devoted to thyroid biology and to the prevention and treatment of thyroid disease through excellence in research, clinical care, education, and ...
) recommend either intermittent testing above a certain age in all sexes or only in women. Targeted screening may be appropriate in a number of situations where hypothyroidism is common: other autoimmune diseases, a strong family history
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kin ...
of thyroid disease, those who have received radioiodine or other radiation therapy to the neck, those who have previously undergone thyroid surgery, those with an abnormal thyroid examination, those with psychiatric disorders, people taking amiodarone or lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense soli ...
, and those with a number of health conditions (such as certain heart and skin conditions). Yearly thyroid function tests are recommended in people with Down syndrome
Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is usually associated with physical growth delays, mild to moderate intellectual d ...
, as they are at higher risk of thyroid disease. Guidelines for England and Wales from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommend testing for thyroid disease in people with type 1 diabetes and new-onset atrial fibrillation, and suggests testing in those with depression or unexplained anxiety (all ages), in children with abnormal growth, or unexplained change in behaviour or school performance. On diagnosis of autoimmune thyroid disease, NICE also recommends screening for celiac disease.
Management
Hormone replacement
Most people with hypothyroidism symptoms and confirmed thyroxine deficiency are treated with a synthetic long-acting form of thyroxine, known as levothyroxine (L-thyroxine). In young and otherwise healthy people with overt hypothyroidism, a full replacement dose (adjusted by weight) can be started immediately; in the elderly and people with heart disease a lower starting dose is recommended to prevent over supplementation and risk of complications. Lower doses may be sufficient in those with subclinical hypothyroidism, while people with central hypothyroidism may require a higher than average dose. Blood free thyroxine and TSH levels are monitored to help determine whether the dose is adequate. This is done 4–8 weeks after the start of treatment or a change in levothyroxine dose. Once the adequate replacement dose has been established, the tests can be repeated after 6 and then 12 months, unless there is a change in symptoms. Normalization of TSH does not mean that other abnormalities associated with hypothyroidism improve entirely, such as elevatedcholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell memb ...
levels.
In people with central/secondary hypothyroidism, TSH is not a reliable marker of hormone replacement and decisions are based mainly on the free T4 level. Levothyroxine is best taken 30–60 minutes before breakfast, or four hours after food, as certain substances such as food and calcium can inhibit the absorption of levothyroxine. There is no direct way of increasing thyroid hormone secretion by the thyroid gland.
Liothyronine
Treatment with liothyronine alone has not received enough study to make a recommendation as to its use; due to its shorter half-life it would need to be taken more often than levothyroxine. Adding liothyronine (synthetic T3) to levothyroxine has been suggested as a measure to provide better symptom control, but this has not been confirmed by studies. In 2007, the British Thyroid Association stated that combined T4 and T3 therapy carried a higher rate of side effects and no benefit over T4 alone. Similarly, American guidelines discourage combination therapy due to a lack of evidence, although they acknowledge that some people feel better when receiving combination treatment. Guidelines by NICE for England and Wales discourage liothyronine. People with hypothyroidism who do not feel well despite optimal levothyroxine dosing may request adjunctive treatment with liothyronine. A 2012 guideline from the European Thyroid Association recommends that support should be offered with regards to the chronic nature of the disease and that other causes of the symptoms should be excluded. Addition of liothyronine should be regarded as experimental, initially only for a trial period of 3 months, and in a set ratio to the current dose of levothyroxine. The guideline explicitly aims to enhance the safety of this approach and to counter its indiscriminate use.Desiccated animal thyroid
Desiccated thyroid extract
Desiccated thyroid, also known as thyroid extract, is thyroid gland that has been dried and powdered for medical use. It is used to treat hypothyroidism. It is less preferred than levothyroxine. It is taken by mouth. Maximal effects may take up t ...
is an animal-based thyroid gland extract, most commonly from pigs. It is a combination therapy, containing forms of T4 and T3. It also contains calcitonin
Calcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone secreted by parafollicular cells (also known as C cells) of the thyroid (or endostyle) in humans and other chordates. in the ultimopharyngeal body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing the ...
(a hormone produced in the thyroid gland involved in the regulation of calcium levels), T1 and T2; these are not present in synthetic hormone medication. This extract was once a mainstream hypothyroidism treatment, but its use today is unsupported by evidence; British Thyroid Association and American professional guidelines discourage its use, as does NICE.
Subclinical hypothyroidism
There is no evidence of a benefit from treating subclinical hypothyroidism in those who are not pregnant, and there are potential risks ofovertreatment
Unnecessary health care (overutilization, overuse, or overtreatment) is health care provided with a higher volume or cost than is appropriate.
In the United States, where health care costs are the highest as a percentage of GDP, overuse was the ...
. Untreated subclinical hypothyroidism may be associated with a modest increase in the risk of coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic pl ...
when the TSH is over 10 mIU/L. A 2007 review found no benefit of thyroid hormone replacement except for "some parameters of lipid profiles and left ventricular function". There is no association between subclinical hypothyroidism and an increased risk of bone fractures, nor is there a link with cognitive decline.
Since 2008, consensus American opinion has been that in general people with TSH under 10 to 20 mIU/L do not require treatment.
American guidelines recommend that treatment should be considered in people with symptoms of hypothyroidism, detectable antibodies against thyroid peroxidase, a history of heart disease or are at an increased risk for heart disease, if the TSH is elevated but below 10 mIU/L. NICE recommends that those with a TSH above 10 mIU/L should be treated in the same way as overt hypothyroidism. Those with an elevated TSH but below 10 mIU/L who have symptoms suggestive of hypothyroidism should have a trial of treatment but with the aim to stopping this if the symptoms persist despite normalisation of the TSH.
A recent meta-analysis, however, found an increased risk for cardiovascular death in subclinical hypothyroidism.
Myxedema coma
Myxedema coma
Myxedema coma is an extreme or decompensated form of hypothyroidism and while uncommon, is potentially lethal. A person may have laboratory values identical to a "normal" hypothyroid state, but a stressful event (such as an infection, myocardial ...
or severe decompensated hypothyroidism usually requires admission to the intensive care, close observation and treatment of abnormalities in breathing, temperature control, blood pressure, and sodium levels. Mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move a ...
may be required, as well as fluid replacement, vasopressor agents, careful rewarming, and corticosteroids (for possible adrenal insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal gland normally secretes glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol), mineralocorticoids (primarily aldosterone), and andro ...
which can occur together with hypothyroidism). Careful correction of low sodium levels may be achieved with hypertonic saline solutions or vasopressin receptor antagonist A vasopressin receptor antagonist (VRA) is an agent that interferes with action at the vasopressin receptors. Most commonly VRAs are used in the treatment of hyponatremia, especially in patients with congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis or SIAD ...
s. For rapid treatment of the hypothyroidism, levothyroxine or liothyronine may be administered intravenously, particularly if the level of consciousness is too low to be able to safely swallow medication. While administration through a nasogastric tube
Nasogastric intubation is a medical process involving the insertion of a plastic tube (nasogastric tube or NG tube) through the nose, down the oesophagus, and down into the stomach. Orogastric intubation is a similar process involving the inserti ...
is possible, this may be unsafe and is discouraged.
Pregnancy
In women with known hypothyroidism who become pregnant, it is recommended that serum TSH levels are closely monitored. Levothyroxine should be used to keep TSH levels within the normal range for that trimester. The first trimester normal range is below 2.5 mIU/L and the second and third trimesters normal range is below 3.0 mIU/L. Treatment should be guided by total (rather than free) thyroxine or by the free T4 index. Similarly to TSH, the thyroxine results should be interpreted according to the appropriate reference range for that stage of pregnancy. The levothyroxine dose often needs to be increased after pregnancy is confirmed, although this is based on limited evidence and some recommend that it is not always required; decisions may need to based on TSH levels. Women with anti-TPO antibodies who are trying to become pregnant (naturally or by assisted means) may require thyroid hormone supplementation even if the TSH level is normal. This is particularly true if they have had previous miscarriages or have been hypothyroid in the past. Supplementary levothyroxine may reduce the risk of preterm birth and possibly miscarriage. The recommendation is stronger in pregnant women with subclinical hypothyroidism (defined as TSH 2.5–10 mIU/L) who are anti-TPO positive, in view of the risk of overt hypothyroidism. If a decision is made not to treat, close monitoring of the thyroid function (every 4 weeks in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy) is recommended. If anti-TPO is not positive, treatment for subclinical hypothyroidism is not currently recommended. It has been suggested that many of the aforementioned recommendations could lead to unnecessary treatment, in the sense that the TSH cutoff levels may be too restrictive in some ethnic groups; there may be little benefit from treatment of subclinical hypothyroidism in certain cases.Alternative medicine
The effectiveness and safety of using Chinese herbal medicines to treat hypothyroidism is not known.Epidemiology
Worldwide about one billion people are estimated to be iodine deficient; however, it is unknown how often this results in hypothyroidism. In large population-based studies in Western countries with sufficient dietary iodine, 0.3–0.4% of the population have overt hypothyroidism. A larger proportion, 4.3–8.5%, have subclinical hypothyroidism. Undiagnosed hypothyroidism is estimated to affect about 4–7% of community-derived populations in the US and Europe. Of people with subclinical hypothyroidism, 80% have a TSH level below the 10 mIU/L mark regarded as the threshold for treatment. Children with subclinical hypothyroidism often return to normal thyroid function, and a small proportion develops overt hypothyroidism (as predicted by evolving antibody and TSH levels, the presence of celiac disease, and the presence of a goiter). Women are more likely to develop hypothyroidism than men. In population-based studies, women were seven times more likely than men to have TSH levels above 10 mU/L. 2–4% of people with subclinical hypothyroidism will progress to overt hypothyroidism each year. The risk is higher in those with antibodies against thyroid peroxidase. Subclinical hypothyroidism is estimated to affect approximately 2% of children; in adults, subclinical hypothyroidism is more common in the elderly, and inwhite people
White is a racialized classification of people and a skin color specifier, generally used for people of European origin, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, and point of view.
Description of populations as ...
. There is a much higher rate of thyroid disorders, the most common of which is hypothyroidism, in individuals with Down syndrome
Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is usually associated with physical growth delays, mild to moderate intellectual d ...
and Turner syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS), also known as 45,X, or 45,X0, is a genetic condition in which a female is partially or completely missing an X chromosome. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected. Often, a short and webbed neck, low-set ears, low h ...
.
Very severe hypothyroidism and myxedema coma are rare, with it estimated to occur in 0.22 per million people a year. The majority of cases occur in women over 60 years of age, although it may happen in all age groups.
Most hypothyroidism is primary in nature. Central/secondary hypothyroidism affects 1:20,000 to 1:80,000 of the population, or about one out of every thousand people with hypothyroidism.
History
In 1811, Bernard Courtois discovered iodine was present in seaweed, and iodine intake was linked with goiter size in 1820 by Jean-Francois Coindet.Gaspard Adolphe Chatin
Gaspard Adolphe Chatin (30 November 1813 – 13 January 1901) was a French physician, mycologist and botanist who was born in Isère, and died in Les Essarts-le-Roi. He was the first to prove that goiter was related of iodine deficiencies.
He stud ...
proposed in 1852 that endemic goiter was the result of not enough iodine intake, and Eugen Baumann demonstrated iodine in thyroid tissue in 1896.
The first cases of myxedema were recognized in the mid-19th century (the 1870s), but its connection to the thyroid was not discovered until the 1880s when myxedema was observed in people following the removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy). The link was further confirmed in the late 19th century when people and animals who had had their thyroid removed showed improvement in symptoms with transplantation of animal thyroid tissue. The severity of myxedema, and its associated risk of mortality and complications, created interest in discovering effective treatments for hypothyroidism. Transplantation of thyroid tissue demonstrated some efficacy, but recurrences of hypothyroidism was relatively common, and sometimes required multiple repeat transplantations of thyroid tissue.
In 1891, the English physician George Redmayne Murray introduced subcutaneously injected sheep thyroid extract, followed shortly after by an oral formulation. Purified thyroxine was introduced in 1914 and in the 1930s synthetic thyroxine became available, although desiccated animal thyroid extract remained widely used. Liothyronine was identified in 1952.
Early attempts at titrating therapy for hypothyroidism proved difficult. After hypothyroidism was found to cause a lower basal metabolic rate
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. It is reported in energy units per unit time ranging from watt (joule/second) to ml O2/min or joule per hour per kg body mass J/(h·kg). P ...
, this was used as a marker to guide adjustments in therapy in the early 20th century (around 1915). However, a low basal metabolic rate was known to be non-specific, also present in malnutrition. The first laboratory test to be helpful in assessing thyroid status was the serum protein-bound iodine, which came into use around the 1950s.
In 1971, the thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) radioimmunoassay was developed, which was the most specific marker for assessing thyroid status in patients. Many people who were being treated based on basal metabolic rate, minimizing hypothyroid symptoms, or based on serum protein-bound iodine, were found to have excessive thyroid hormone. The following year, in 1972, a T3 radioimmunoassay was developed, and in 1974, a T4 radioimmunoassay was developed.
Other animals
 In veterinary practice, dogs are the species most commonly affected by hypothyroidism. The majority of cases occur as a result of primary hypothyroidism, of which two types are recognized: lymphocytic thyroiditis, which is probably immune-driven and leads to destruction and fibrosis of the thyroid gland, and idiopathic atrophy, which leads to the gradual replacement of the gland by fatty tissue. There is often lethargy, cold intolerance, exercise intolerance, and weight gain. Furthermore, skin changes and fertility problems are seen in dogs with hypothyroidism, as well as a number of other symptoms. The signs of myxedema can be seen in dogs, with prominence of skin folds on the forehead, and cases of myxedema coma are encountered. The diagnosis can be confirmed by blood test, as the clinical impression alone may lead to overdiagnosis. Lymphocytic thyroiditis is associated with detectable antibodies against thyroglobulin, although they typically become undetectable in advanced disease. Treatment is with thyroid hormone replacement.
Other species that are less commonly affected include cats and horses, as well as other large domestic animals. In cats, hypothyroidism is usually the result of other medical treatment such as surgery or radiation. In young horses, congenital hypothyroidism has been reported predominantly in
In veterinary practice, dogs are the species most commonly affected by hypothyroidism. The majority of cases occur as a result of primary hypothyroidism, of which two types are recognized: lymphocytic thyroiditis, which is probably immune-driven and leads to destruction and fibrosis of the thyroid gland, and idiopathic atrophy, which leads to the gradual replacement of the gland by fatty tissue. There is often lethargy, cold intolerance, exercise intolerance, and weight gain. Furthermore, skin changes and fertility problems are seen in dogs with hypothyroidism, as well as a number of other symptoms. The signs of myxedema can be seen in dogs, with prominence of skin folds on the forehead, and cases of myxedema coma are encountered. The diagnosis can be confirmed by blood test, as the clinical impression alone may lead to overdiagnosis. Lymphocytic thyroiditis is associated with detectable antibodies against thyroglobulin, although they typically become undetectable in advanced disease. Treatment is with thyroid hormone replacement.
Other species that are less commonly affected include cats and horses, as well as other large domestic animals. In cats, hypothyroidism is usually the result of other medical treatment such as surgery or radiation. In young horses, congenital hypothyroidism has been reported predominantly in Western Canada
Western Canada, also referred to as the Western provinces, Canadian West or the Western provinces of Canada, and commonly known within Canada as the West, is a Canadian region that includes the four western provinces just north of the Canada� ...
and has been linked with the mother's diet.
References
External links
* * * * {{Thyroid disease Thyroid disease Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate (full) Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate Endocrine diseases Autoimmune diseases Iodine Metabolic disorders