Hybridisation (biology) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 The term hybrid is derived from Latin ', used for crosses such as of a tame sow and a wild boar. The term came into popular use in English in the 19th century, though examples of its use have been found from the early 17th century. Conspicuous hybrids are popularly named with
The term hybrid is derived from Latin ', used for crosses such as of a tame sow and a wild boar. The term came into popular use in English in the 19th century, though examples of its use have been found from the early 17th century. Conspicuous hybrids are popularly named with
 A few animal species are the result of hybridization. The
A few animal species are the result of hybridization. The
 Hybridization between reproductively isolated species often results in hybrid offspring with lower fitness than either parental. However, hybrids are not, as might be expected, always intermediate between their parents (as if there were blending inheritance), but are sometimes stronger or perform better than either parental lineage or variety, a phenomenon called heterosis, hybrid vigour, or heterozygote advantage. This is most common with plant hybrids. A
Hybridization between reproductively isolated species often results in hybrid offspring with lower fitness than either parental. However, hybrids are not, as might be expected, always intermediate between their parents (as if there were blending inheritance), but are sometimes stronger or perform better than either parental lineage or variety, a phenomenon called heterosis, hybrid vigour, or heterozygote advantage. This is most common with plant hybrids. A
 There is a kind of continuum with three semi-distinct categories dealing with anthropogenic hybridization: hybridization without introgression, hybridization with widespread introgression (backcrossing with one of the parent species), and
There is a kind of continuum with three semi-distinct categories dealing with anthropogenic hybridization: hybridization without introgression, hybridization with widespread introgression (backcrossing with one of the parent species), and
 In agriculture and
In agriculture and
File:Zeedonk 800.jpg, A " zonkey", a zebra/donkey hybrid
File:Jaglion.jpg, A "
 Plant species hybridize more readily than animal species, and the resulting hybrids are fertile more often. Many plant species are the result of hybridization, combined with
Plant species hybridize more readily than animal species, and the resulting hybrids are fertile more often. Many plant species are the result of hybridization, combined with
File:Trilliumhybrid2.jpg, A sterile hybrid between ''
Sterility in a non-polyploid hybrid is often a result of chromosome number; if parents are of differing chromosome pair number, the offspring will have an odd number of chromosomes, which leaves them unable to produce chromosomally balanced
 There is evidence of hybridization between modern humans and other species of the genus ''
There is evidence of hybridization between modern humans and other species of the genus ''
Artificial Hybridisation
– Artificial Hybridisation in orchids
nbsp;– Creation of new species through hybridization was thought to be common only in plants, and rare in animals (archived 3 December 2008)
What is a human admixed embryo?
(archived 25 February 2012) {{DEFAULTSORT:Hybrid (Biology) Biology terminology Botanical nomenclature Evolutionary biology Population genetics Breeding
 In
In biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
, a hybrid is the offspring resulting from combining the qualities of two organisms of different varieties, subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morpholog ...
, species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
or genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ...
through sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote tha ...
. Generally, it means that each cell has genetic material from two different organisms, whereas an individual where some cells are derived from a different organism is called a chimera. Hybrids are not always intermediates between their parents such as in blending inheritance
Blending inheritance is an obsolete theory in biology from the 19th century. The theory is that the progeny inherits any characteristic as the average of the parents' values of that characteristic. As an example of this, a crossing of a red flo ...
(a now discredited theory in modern genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian ...
by particulate inheritance
Particulate inheritance is a pattern of inheritance discovered by Mendelian genetics theorists, such as William Bateson, Ronald Fisher or Gregor Mendel himself, showing that phenotypic traits can be passed from generation to generation through ...
), but can show hybrid vigor
Heterosis, hybrid vigor, or outbreeding enhancement is the improved or increased function of any biological quality in a Hybrid (biology), hybrid offspring. An offspring is heterotic if its trait (biology), traits are enhanced as a result of m ...
, sometimes growing larger or taller than either parent. The concept of a hybrid is interpreted differently in animal and plant breeding, where there is interest in the individual parentage. In genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian ...
, attention is focused on the numbers of chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
s. In taxonomy, a key question is how closely related the parent species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
are.
Species are reproductively isolated by strong barriers to hybridization, which include genetic and morphological differences, differing times of fertility, mating behaviors and cues, and physiological
Physiology (; ) is the science, scientific study of function (biology), functions and mechanism (biology), mechanisms in a life, living system. As a branches of science, subdiscipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ syst ...
rejection of sperm cells or the developing embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
. Some act before fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give ...
and others after it. Similar barriers exist in plants, with differences in flowering times, pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
vectors, inhibition of pollen tube growth, somatoplastic sterility, cytoplasmic-genic male sterility and the structure of the chromosomes. A few animal species and many plant species, however, are the result of hybrid speciation
Hybrid speciation is a form of speciation where hybridization between two different species leads to a new species, reproductively isolated from the parent species. Previously, reproductive isolation between two species and their parents was tho ...
, including important crop plants such as wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
, where the number of chromosomes has been doubled.
A form of often intentional human-mediated hybridization is the crossing of wild and domesticated species. This is common in both traditional horticulture
Horticulture (from ) is the art and science of growing fruits, vegetables, flowers, trees, shrubs and ornamental plants. Horticulture is commonly associated with the more professional and technical aspects of plant cultivation on a smaller and mo ...
and modern agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
; many commercially useful fruits, flowers, garden herbs, and trees have been produced by hybridization. One such flower, '' Oenothera lamarckiana'', was central to early genetics research into mutationism and polyploidy. It is also more occasionally done in the livestock and pet trades; some well-known wild × domestic hybrids are beefalo
Beefalo constitutes a hybrid offspring of domestic cattle (''Bos taurus''), usually a male in managed breeding programs, and the American bison (''Bison bison''), usually a female in managed breeding programs. The breed was created to combine ...
and wolfdog
A wolfdog is a canine produced by the mating of a domestic dog (''Canis familiaris'') with a gray wolf (''Canis lupus''), eastern wolf (''Canis lycaon''), red wolf (''Canis rufus''), or Ethiopian wolf (''Canis simensis'') to produce a ...
s. Human selective breeding
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant m ...
of domesticated animals
This page gives a list of domesticated animals, also including a list of domestication of animals, animals which are or may be currently undergoing the process of domestication and animals that have an extensive relationship with humans beyond simp ...
and plants
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria to produce sugars f ...
has also resulted in the development of distinct breed
A breed is a specific group of breedable domestic animals having homogeneous appearance (phenotype), homogeneous behavior, and/or other characteristics that distinguish it from other organisms of the same species. In literature, there exist seve ...
s (usually called cultivar
A cultivar is a kind of Horticulture, cultivated plant that people have selected for desired phenotypic trait, traits and which retains those traits when Plant propagation, propagated. Methods used to propagate cultivars include division, root a ...
s in reference to plants); crossbreed
A crossbreed is an organism with purebred parents of two different breeds, varieties, or populations. A domestic animal of unknown ancestry, where the breed status of only one parent or grandparent is known, may also be called a crossbreed though ...
s between them (without any wild stock
Stocks (also capital stock, or sometimes interchangeably, shares) consist of all the Share (finance), shares by which ownership of a corporation or company is divided. A single share of the stock means fractional ownership of the corporatio ...
) are sometimes also imprecisely referred to as "hybrids".
Hybrid humans existed in prehistory. For example, Neanderthal
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
s and anatomically modern humans are thought to have interbred as recently as 40,000 years ago.
Mythological hybrid
Hybrid beasts are creatures composed of parts from different animals, including humans, appearing in the folklore of a variety of cultures as legendary creatures.
In burial sites
Remains similar to those of mythological hybrids have been found ...
s appear in human culture in forms as diverse as the Minotaur
In Greek mythology, the Minotaur (, ''Mīnṓtauros''), also known as Asterion, is a mythical creature portrayed during classical antiquity with the head and tail of a bull and the body of a man or, as described by Roman poet Ovid, a being "par ...
, blends of animals, humans and mythical beasts such as centaur
A centaur ( ; ; ), occasionally hippocentaur, also called Ixionidae (), is a creature from Greek mythology with the upper body of a human and the lower body and legs of a horse that was said to live in the mountains of Thessaly. In one version o ...
s and sphinx
A sphinx ( ; , ; or sphinges ) is a mythical creature with the head of a human, the body of a lion, and the wings of an eagle.
In Culture of Greece, Greek tradition, the sphinx is a treacherous and merciless being with the head of a woman, th ...
es, and the Nephilim
The Nephilim (; ''Nəfīlīm'') are mysterious beings or humans in the Bible traditionally understood as being of great size and strength, or alternatively beings of great power and authority. The origins of the Nephilim are disputed. Some, ...
of the Biblical apocrypha
The Biblical apocrypha () denotes the collection of ancient books, some of which are believed by some to be of doubtful origin, thought to have been written some time between 200 BC and 100 AD.
The Catholic, Eastern Orthodox and Ori ...
described as the wicked sons of fallen angel
Fallen angels are angels who were expelled from Heaven. The literal term "fallen angel" does not appear in any Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic religious texts, but is used to describe angels cast out of heaven. Such angels are often described ...
s and attractive women.
Significance
In evolution
Hybridization between species plays an important role in evolution, though there is much debate about its significance. Roughly 25% of plants and 10% of animals are known to form hybrids with at least one other species. One example of an adaptive benefit to hybridization is that hybrid individuals can form a "bridge" transmitting potentially helpful genes from one species to another when the hybrid backcrosses with one of its parent species, a process calledintrogression
Introgression, also known as introgressive hybridization, in genetics is the transfer of genetic material from one species into the gene pool of another by the repeated backcrossing of an interspecific hybrid with one of its parent species. Introg ...
. Hybrids can also cause speciation
Speciation is the evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species. The biologist Orator F. Cook coined the term in 1906 for cladogenesis, the splitting of lineages, as opposed to anagenesis, phyletic evolution within ...
, either because the hybrids are genetically incompatible with their parents and not each other, or because the hybrids occupy a different niche than either parent.
Hybridization is a particularly common mechanism for speciation in plants, and is now known to be fundamental to the evolutionary history of plants. Plants frequently form polyploid
Polyploidy is a condition in which the biological cell, cells of an organism have more than two paired sets of (Homologous chromosome, homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have Cell nucleus, nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning ...
s, individuals with more than two copies of each chromosome. Whole genome doubling has occurred repeatedly in plant evolution. When two plant species hybridize, the hybrid may double its chromosome count by incorporating the entire nuclear genome of both parents, resulting in offspring that are reproductively incompatible with either parent because of different chromosome counts.
In conservation
Human impact on the environment
Human impact on the environment (or anthropogenic environmental impact) refers to changes to biophysical environments and to ecosystems, biodiversity, and natural resources caused directly or indirectly by humans. Modifying the environment to ...
has resulted in an increase in the interbreeding between regional species, and the proliferation of introduced species
An introduced species, alien species, exotic species, adventive species, immigrant species, foreign species, non-indigenous species, or non-native species is a species living outside its native distributional range, but which has arrived ther ...
worldwide has also resulted in an increase in hybridization. This has been referred to as genetic pollution
Genetic pollution is a term for uncontrolled gene flow into wild populations. It is defined as "the dispersal of contaminated altered genes from genetically engineered organisms to natural organisms, esp. by cross-pollination", but has come to be ...
out of concern that it may threaten many species with extinction. Similarly, genetic erosion from monoculture
In agriculture, monoculture is the practice of growing one crop species in a field at a time. Monocultures increase ease and efficiency in planting, managing, and harvesting crops short-term, often with the help of machinery. However, monocultur ...
in crop plants may be damaging the gene pools of many species for future breeding.
The conservation impacts of hybridization between species are highly debated. While hybridization could potentially threaten rare species or lineages by "swamping" the genetically "pure" individuals with hybrids, hybridization could also save a rare lineage from extinction by introducing genetic diversity. It has been proposed that hybridization could be a useful tool to conserve biodiversity by allowing organisms to adapt, and that efforts to preserve the separateness of a "pure" lineage could harm conservation by lowering the organisms' genetic diversity and adaptive potential, particularly in species with low populations. While endangered species are often protected by law, hybrids are often excluded from protection, resulting in challenges to conservation.
Etymology
 The term hybrid is derived from Latin ', used for crosses such as of a tame sow and a wild boar. The term came into popular use in English in the 19th century, though examples of its use have been found from the early 17th century. Conspicuous hybrids are popularly named with
The term hybrid is derived from Latin ', used for crosses such as of a tame sow and a wild boar. The term came into popular use in English in the 19th century, though examples of its use have been found from the early 17th century. Conspicuous hybrids are popularly named with portmanteau word
In linguistics, a blend—also known as a blend word, lexical blend, or portmanteau—is a word formed by combining the meanings, and parts of the sounds, of two or more words together.) Israeli שלט ''shalát'' 'remote control', an ellipsis ...
s, starting in the 1920s with the breeding of tiger–lion hybrids (liger
The liger is a hybrid (biology), hybrid offspring of a male lion (''Panthera leo'') and a tigress, or female tiger (''Panthera tigris''). The liger has parents in the same genus but of different species. The liger is distinct from the opposite ...
and tigon
The tigon is a hybrid offspring of a male tiger (''Panthera tigris'') and a female lion, or lioness (''Panthera leo'').breeds
A breed is a specific group of breedable domestic animals having homogeneous appearance (phenotype), homogeneous behavior, and/or other characteristics that distinguish it from other organisms of the same species. In literature, there exist seve ...
. Single cross hybrids result from the cross between two true-breeding organisms which produces an F1 hybrid
F1 hybrid (also known as filial 1 hybrid) is the first filial generation of offspring of distinctly different parental types. F1 hybrids are used in genetics, and in selective breeding, where the term F1 crossbreed may be used. The term is somet ...
(first filial generation). The cross between two different homozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mos ...
lines produces an F1 hybrid that is heterozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mos ...
; having two alleles
An allele is a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a particular location, or locus, on a DNA molecule.
Alleles can differ at a single position through single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), but they can also have insertions and deletions ...
, one contributed by each parent and typically one is dominant and the other recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and ...
. Typically, the F1 generation is also phenotypically homogeneous, producing offspring that are all similar to each other.
Double cross hybrids result from the cross between two different F1 hybrids (i.e., there are four unrelated grandparents).
Three-way cross hybrids result from the cross between an F1 hybrid and an inbred line. Triple cross hybrids result from the crossing of two different three-way cross hybrids. Top cross (or "topcross") hybrids result from the crossing of a top quality or pure-bred male and a lower quality female, intended to improve the quality of the offspring, on average.
Population hybrids result from the crossing of plants or animals in one population
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and pl ...
with those of another population. These include interspecific hybrids or crosses between different breeds. In biology, the result of crossing of two populations is called a synthetic population.
In horticulture
Horticulture (from ) is the art and science of growing fruits, vegetables, flowers, trees, shrubs and ornamental plants. Horticulture is commonly associated with the more professional and technical aspects of plant cultivation on a smaller and mo ...
, the term stable hybrid is used to describe an annual plant
An annual plant is a plant that completes its life cycle, from germination to the production of seeds, within one growing season, and then dies. Globally, 6% of all plant species and 15% of herbaceous plants (excluding trees and shrubs) are ...
that, if grown and bred in a small monoculture
In agriculture, monoculture is the practice of growing one crop species in a field at a time. Monocultures increase ease and efficiency in planting, managing, and harvesting crops short-term, often with the help of machinery. However, monocultur ...
free of external pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
(e.g., an air-filtered greenhouse) produces offspring that are "true to type" with respect to phenotype; i.e., a true-breeding organism.
Biogeography
Hybridization can occur in thehybrid zone
A hybrid zone exists where the ranges of two interbreeding species or diverged intraspecific lineages meet and cross-fertilize. Hybrid zones can form ''in situ'' due to the evolution of a new lineage but generally they result from secondary cont ...
s where the geographical ranges of species, subspecies, or distinct genetic lineages overlap. For example, the butterfly ''Limenitis arthemis
''Limenitis arthemis,'' the red-spotted purple or white admiral, is a North American butterfly species in the cosmopolitan genus ''Limenitis''. It has been studied for its evolution of mimicry, and for the several stable hybrid wing patterns wit ...
'' has two major subspecies in North America, ''L. a. arthemis'' (the white admiral) and ''L. a. astyanax'' (the red-spotted purple). The white admiral has a bright, white band on its wings, while the red-spotted purple has cooler blue-green shades. Hybridization occurs between a narrow area across New England, southern Ontario, and the Great Lakes, the "suture region". It is at these regions that the subspecies were formed. Other hybrid zones have formed between described species of plants and animals.
Genetics
From the point of view of genetics, several different kinds of hybrid can be distinguished. A genetic hybrid carries two differentallele
An allele is a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a particular location, or Locus (genetics), locus, on a DNA molecule.
Alleles can differ at a single position through Single-nucleotide polymorphism, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), ...
s of the same gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
, where for instance one allele may code for a lighter coat colour than the other. A structural hybrid results from the fusion of gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
s that have differing structure in at least one chromosome, as a result of structural abnormalities. A numerical hybrid results from the fusion of gametes having different haploid numbers of chromosomes. A permanent hybrid results when only the heterozygous genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
occurs, as in '' Oenothera lamarckiana'', because all homozygous combinations are lethal. In the early history of genetics, Hugo de Vries
Hugo Marie de Vries (; 16 February 1848 – 21 May 1935) was a Dutch botanist and one of the first geneticists. He is known chiefly for suggesting the concept of genes, rediscovering the laws of heredity in the 1890s while apparently unaware of ...
supposed these were caused by mutation.
Genetic complementation
Genetic complementation is a hybridization test widely used ingenetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian ...
to determine whether two separately isolated mutant
In biology, and especially in genetics, a mutant is an organism or a new genetic character arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is generally an alteration of the DNA sequence of the genome or chromosome of an organism. It i ...
s that have the same (or similar) phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological propert ...
are defective in the same gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
or in different gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s (see complementation). If a hybrid organism containing the genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
s of two different mutant parental organisms displays a wild type
The wild type (WT) is the phenotype of the typical form of a species as it occurs in nature. Originally, the wild type was conceptualized as a product of the standard "normal" allele at a locus, in contrast to that produced by a non-standard, " ...
phenotype, it is ordinarily considered that the two parental mutant organisms are defective in different genes. If the hybrid organism displays a distinctly mutant phenotype, the two mutant parental organisms are considered to be defective in the same gene. However, in some cases the hybrid organism may display a phenotype that is only weakly (or partially) wild-type, and this may reflect intragenic (interallelic) complementation.
Taxonomy
From the point of view oftaxonomy
image:Hierarchical clustering diagram.png, 280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy
Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme o ...
, hybrids differ according to their parentage.
Hybrids between different subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morpholog ...
(such as between the dog
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the gray wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it was selectively bred from a population of wolves during the Late Pleistocene by hunter-gatherers. ...
and Eurasian wolf
The Eurasian wolf (''Canis lupus lupus''), also known as the common wolf,Mech, L. David (1981), ''The Wolf: The Ecology and Behaviour of an Endangered Species'', University of Minnesota Press, p. 354, is a subspecies of grey wolf native to Euro ...
) are called intra-specific hybrids. Interspecific hybrids are the offspring from interspecies mating; these sometimes result in hybrid speciation. Intergeneric hybrids result from matings between different genera, such as between sheep
Sheep (: sheep) or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to d ...
and goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a species of Caprinae, goat-antelope that is mostly kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the ...
s. Interfamilial hybrids, such as between chickens and guineafowl
Guinea fowl () (or guineahen) are birds of the family Numididae in the order Galliformes. They are endemic to Africa and rank among the oldest of the gallinaceous birds. Phylogenetically, they branched off from the core Galliformes after the C ...
or pheasant
Pheasants ( ) are birds of several genera within the family Phasianidae in the order Galliformes. Although they can be found all over the world in introduced (and captive) populations, the pheasant genera's native range is restricted to Eura ...
s, are reliably described but extremely rare. Interordinal hybrids (between different orders) are few, but have been engineered between the sea urchin
Sea urchins or urchins () are echinoderms in the class (biology), class Echinoidea. About 950 species live on the seabed, inhabiting all oceans and depth zones from the intertidal zone to deep seas of . They typically have a globular body cove ...
''Strongylocentrotus purpuratus
''Strongylocentrotus purpuratus'' is a species of sea urchin in the family Strongylocentrotidae commonly known as the purple sea urchin. It lives along the eastern edge of the Pacific Ocean extending from Ensenada, Mexico, to British Columbi ...
'' (female) and the sand dollar '' Dendraster excentricus'' (male).
Biology
Expression of parental traits
When two distinct types of organisms breed with each other, the resulting hybrids typically have intermediate traits (e.g., one plant parent has red flowers, the other has white, and the hybrid, pink flowers). Commonly, hybrids also combine traits seen only separately in one parent or the other (e.g., a bird hybrid might combine the yellow head of one parent with the orange belly of the other).Mechanisms of reproductive isolation
Interspecific hybrids are bred by mating individuals from two species, normally from within the same genus. The offspring display traits and characteristics of both parents, but are oftensterile
Sterile or sterility may refer to:
*Asepsis, a state of being free from biological contaminants
* Sterile (archaeology), a sediment deposit which contains no evidence of human activity
*Sterilization (microbiology), any process that eliminates or ...
, preventing gene flow between the species. Sterility is often attributed to the different number of chromosomes between the two species. For example, donkey
The donkey or ass is a domesticated equine. It derives from the African wild ass, ''Equus africanus'', and may be classified either as a subspecies thereof, ''Equus africanus asinus'', or as a separate species, ''Equus asinus''. It was domes ...
s have 62 chromosomes
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most importa ...
, horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 mi ...
s have 64 chromosomes, and mule
The mule is a domestic equine hybrid between a donkey, and a horse. It is the offspring of a male donkey (a jack) and a female horse (a mare). The horse and the donkey are different species, with different numbers of chromosomes; of the two ...
s or hinnies
A hinny is a domestication, domestic equine Hybrid (biology), hybrid, the offspring of a male horse (a stallion) and a female donkey (a Female donkey, jenny). It is the reciprocal cross to the more common mule, which is the product of a male don ...
have 63 chromosomes. Mules, hinnies, and other normally sterile interspecific hybrids cannot produce viable gametes, because differences in chromosome structure prevent appropriate pairing and segregation during meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
, meiosis is disrupted, and viable sperm and eggs are not formed. However, fertility in female mules has been reported with a donkey as the father.
A variety of mechanisms limit the success of hybridization, including the large genetic difference between most species. Barriers include morphological differences, differing times of fertility, mating behaviors and cues, and physiological rejection of sperm cells or the developing embryo. Some act before fertilization; others after it.
In plants, some barriers to hybridization include blooming period differences, different pollinator vectors, inhibition of pollen tube growth, somatoplastic sterility, cytoplasmic-genic male sterility and structural differences of the chromosomes.
Speciation
 A few animal species are the result of hybridization. The
A few animal species are the result of hybridization. The Lonicera fly
The ''Lonicera'' fly, a Hybrid (biology), hybrid in the genus ''Rhagoletis'', is a North American fruit fly of the family Tephritidae. Its larvae feed on the berries of species of introduced species, introduced honeysuckle (''Lonicera'') that we ...
is a natural hybrid. The American red wolf
The red wolf (''Canis rufus'') is a Canis, canine native to the southeastern United States. Its size is intermediate between the coyote (''Canis latrans'') and Wolf, gray wolf (''Canis lupus'').
The red wolf's taxonomic classification as being ...
appears to be a hybrid of the gray wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the grey wolf or gray wolf, is a canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, including the dog and dingo, though gr ...
and the coyote
The coyote (''Canis latrans''), also known as the American jackal, prairie wolf, or brush wolf, is a species of canis, canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the Wolf, gray wolf, and slightly smaller than the c ...
, although its taxonomic status has been a subject of controversy. The European edible frog is a semi-permanent hybrid between pool frogs and marsh frog
The marsh frog (''Pelophylax ridibundus'') is a species of water frog native to Europe and parts of western Asia.
Description
The marsh frog is the largest type of frog in most of its range, with males growing to a size around 100 mm (3.9 ...
s; its population requires the continued presence of at least one of the parent species. Cave paintings indicate that the European bison
The European bison (: bison) (''Bison bonasus'') or the European wood bison, also known as the wisent ( or ), the zubr (), or sometimes colloquially as the European buffalo, is a European species of bison. It is one of two extant species of bi ...
is a natural hybrid of the aurochs
The aurochs (''Bos primigenius''; or ; pl.: aurochs or aurochsen) is an extinct species of Bovini, bovine, considered to be the wild ancestor of modern domestic cattle. With a shoulder height of up to in bulls and in cows, it was one of t ...
and the steppe bison
The steppe bison (''Bison'' ''priscus'', also less commonly known as the steppe wisent and the primeval bison) is an extinct species of bison which lived from the Middle Pleistocene to the Holocene. During the Late Pleistocene, it was widely dist ...
.
Plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
hybridization is more commonplace compared to animal hybridization. Many crop
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. In other words, a crop is a plant or plant product that is grown for a specific purpose such as food, Fiber, fibre, or fuel.
When plants of the same spe ...
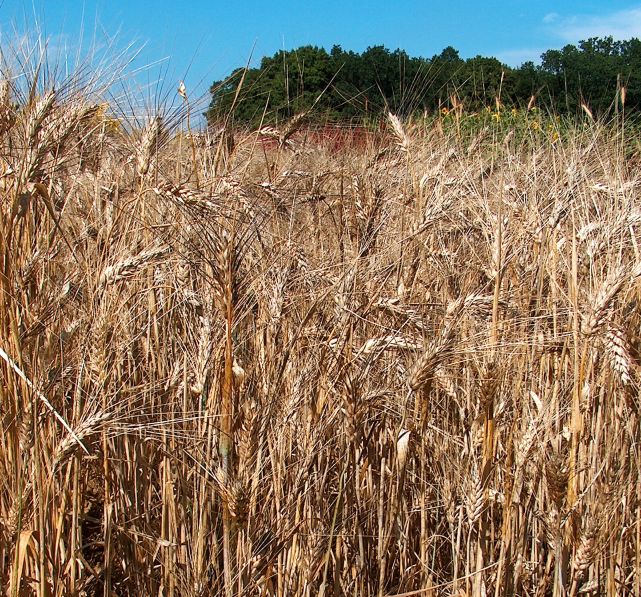
species are hybrids, including notably the polyploid wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
s: some have four sets of chromosomes (tetraploid) or six (hexaploid), while other wheat species have (like most eukaryotic
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
organisms) two sets (diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, ...
), so hybridization events likely involved the doubling of chromosome sets, causing immediate genetic isolation.
Hybridization may be important in speciation in some plant groups. However, homoploid hybrid speciation (not increasing the number of sets of chromosomes) may be rare: by 1997, only eight natural examples had been fully described. Experimental studies suggest that hybridization offers a rapid route to speciation, a prediction confirmed by the fact that early generation hybrids and ancient hybrid species have matching genomes, meaning that once hybridization has occurred, the new hybrid genome can remain stable.
Many hybrid zone
A hybrid zone exists where the ranges of two interbreeding species or diverged intraspecific lineages meet and cross-fertilize. Hybrid zones can form ''in situ'' due to the evolution of a new lineage but generally they result from secondary cont ...
s are known where the ranges of two species meet, and hybrids are continually produced in great numbers. These hybrid zones are useful as biological model systems for studying the mechanisms of speciation. Recently DNA analysis of a bear shot by a hunter in the Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of Provinces and territorie ...
confirmed the existence of naturally occurring and fertile grizzly–polar bear hybrids.
Hybrid vigour
 Hybridization between reproductively isolated species often results in hybrid offspring with lower fitness than either parental. However, hybrids are not, as might be expected, always intermediate between their parents (as if there were blending inheritance), but are sometimes stronger or perform better than either parental lineage or variety, a phenomenon called heterosis, hybrid vigour, or heterozygote advantage. This is most common with plant hybrids. A
Hybridization between reproductively isolated species often results in hybrid offspring with lower fitness than either parental. However, hybrids are not, as might be expected, always intermediate between their parents (as if there were blending inheritance), but are sometimes stronger or perform better than either parental lineage or variety, a phenomenon called heterosis, hybrid vigour, or heterozygote advantage. This is most common with plant hybrids. A transgressive phenotype
In genetics, transgressive segregation is the formation of extreme phenotypes, or transgressive phenotypes, observed in segregated hybrid populations compared to phenotypes observed in the parental lines. The appearance of these transgressive (ex ...
is a phenotype that displays more extreme characteristics than either of the parent lines. Plant breeders
Plant breeding is the science of changing the traits of plants in order to produce desired characteristics. It is used to improve the quality of plant products for use by humans and animals. The goals of plant breeding are to produce crop varie ...
use several techniques to produce hybrids, including line breeding and the formation of complex hybrids. An economically important example is hybrid maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
(corn), which provides a considerable seed yield advantage over open pollinated varieties. Hybrid seed In agriculture and gardening, hybrid seed is produced by deliberately cross-pollinating parent plants which are genetically distinct. The parents are usually two inbred strains.
Hybrid seed is common in industrial agriculture and home gardening. It ...
dominates the commercial maize seed market in the United States, Canada and many other major maize-producing countries.
In a hybrid, any trait that falls outside the range of parental variation (and is thus not simply intermediate between its parents) is considered heterotic. ''Positive heterosis'' produces more robust hybrids, they might be stronger or bigger; while the term ''negative heterosis'' refers to weaker or smaller hybrids. Heterosis is common in both animal and plant hybrids. For example, hybrids between a lion and a tigress (" ligers") are much larger than either of the two progenitors, while " tigons" (lioness × tiger) are smaller. Similarly, the hybrids between the common pheasant (''Phasianus colchicus
The common pheasant (''Phasianus colchicus''), ring-necked pheasant, or blue-headed pheasant, is a bird in the pheasant family (biology), family (Phasianidae). The genus name comes from Latin ''phasianus'' 'pheasant'. The species name ''colchic ...
'') and domestic fowl (''Gallus gallus
The red junglefowl (''Gallus gallus''), also known as the Indian red junglefowl (and formerly the bankiva or bankiva-fowl), is a species of Tropics, tropical, predominantly Terrestrial animal, terrestrial bird in the fowl and pheasant family, P ...
'') are larger than either of their parents, as are those produced between the common pheasant and hen golden pheasant ('' Chrysolophus pictus''). Spurs are absent in hybrids of the former type, although present in both parents.
Human influence
Anthropogenic hybridization
Hybridization is greatly influenced by human impact on the environment, through effects such ashabitat fragmentation
Habitat fragmentation describes the emergence of discontinuities (fragmentation) in an organism's preferred environment (habitat), causing population fragmentation and ecosystem decay. Causes of habitat fragmentation include geological proces ...
and species introductions. Such impacts make it difficult to conserve the genetics of populations undergoing introgressive hybridization. Humans have introduced species worldwide to environments for a long time, both intentionally for purposes such as biological control
Biological control or biocontrol is a method of controlling pests, whether pest animals such as insects and mites, weeds, or pathogens affecting animals or plants by using other organisms. It relies on predation, parasitism, herbivory, or o ...
, and unintentionally, as with accidental escapes of individuals. Introductions can drastically affect populations, including through hybridization.
Management
 There is a kind of continuum with three semi-distinct categories dealing with anthropogenic hybridization: hybridization without introgression, hybridization with widespread introgression (backcrossing with one of the parent species), and
There is a kind of continuum with three semi-distinct categories dealing with anthropogenic hybridization: hybridization without introgression, hybridization with widespread introgression (backcrossing with one of the parent species), and hybrid swarm
A hybrid swarm is a population of hybrids that has survived beyond the initial hybrid generation, with interbreeding between hybrid individuals and backcrossing with its parent types. Such population are highly variable, with the genetic and ...
s (highly variable populations with much interbreeding as well as backcrossing with the parent species). Depending on where a population falls along this continuum, the management plans for that population will change. Hybridization is currently an area of great discussion within wildlife management
Wildlife management is the management process influencing interactions among and between wildlife, its Habitat, habitats and people to achieve predefined impacts. Wildlife management can include wildlife conservation, population control, gamekeepi ...
and habitat management. Global climate change is creating other changes such as difference in population distributions which are indirect causes for an increase in anthropogenic hybridization.
Conservationists disagree on when is the proper time to give up on a population that is becoming a hybrid swarm, or to try and save the still existing pure individuals. Once a population becomes a complete mixture, the goal becomes to conserve those hybrids to avoid their loss. Conservationists treat each case on its merits, depending on detecting hybrids within the population. It is nearly impossible to formulate a uniform hybridization policy, because hybridization can occur beneficially when it occurs "naturally", and when hybrid swarms are the only remaining evidence of prior species, they need to be conserved as well.
Genetic mixing and extinction
Regionally developedecotype
Ecotypes are organisms which belong to the same species but possess different phenotypical features as a result of environmental factors such as elevation, climate and predation. Ecotypes can be seen in wide geographical distributions and may event ...
s can be threatened with extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
when new alleles or genes are introduced that alter that ecotype. This is sometimes called genetic mixing. Hybridization and introgression, which can happen in natural and hybrid populations, of new genetic material can lead to the replacement of local genotypes
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
if the hybrids are more fit and have breeding advantages over the indigenous ecotype or species. These hybridization events can result from the introduction of non-native genotypes by humans or through habitat modification, bringing previously isolated species into contact. Genetic mixing can be especially detrimental for rare species in isolated habitats, ultimately affecting the population to such a degree that none of the originally genetically distinct population remains.
Effect on biodiversity and food security
 In agriculture and
In agriculture and animal husbandry
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, animal fiber, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, management, production, nutrition, selective breeding, and the raising ...
, the Green Revolution
The Green Revolution, or the Third Agricultural Revolution, was a period during which technology transfer initiatives resulted in a significant increase in crop yields. These changes in agriculture initially emerged in Developed country , devel ...
's use of conventional hybridization increased yields by breeding high-yielding varieties
High-yielding varieties (abbreviated as HYVs) of agricultural crops are Variety (botany), varieties of crops that are usually characterized by a combination of the following Phenotypic trait, traits in contrast to the conventional ones:
* Higher ...
. The replacement of locally indigenous breeds, compounded with unintentional cross-pollination and crossbreeding (genetic mixing), has reduced the gene pools of various wild and indigenous breeds resulting in the loss of genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It ranges widely, from the number of species to differences within species, and can be correlated to the span of survival for a species. It is d ...
. Since the indigenous breeds are often well-adapted to local extremes in climate and have immunity to local pathogens, this can be a significant genetic erosion of the gene pool for future breeding. Therefore, commercial plant geneticists strive to breed "widely adapted" cultivars to counteract this tendency.
Different taxa
In animals
Mammals
Familiar examples ofequid hybrid
Equid hybrids, also called hybrid equines, are created from the crossing of members from the horse family such as a horse, donkey and zebra.Equid Hybrids. (2014, June). Retrieved from http://www.best-top10-list.com/view/article/2811/equid-hybrids H ...
s are the mule, a cross between a female horse and a male donkey, and the hinny, a cross between a female donkey and a male horse. Pairs of complementary types like the mule and hinny are called reciprocal hybrids. Polar bear
The polar bear (''Ursus maritimus'') is a large bear native to the Arctic and nearby areas. It is closely related to the brown bear, and the two species can Hybrid (biology), interbreed. The polar bear is the largest extant species of bear ...
s and brown bear
The brown bear (''Ursus arctos'') is a large bear native to Eurasia and North America. Of the land carnivorans, it is rivaled in size only by its closest relative, the polar bear, which is much less variable in size and slightly bigger on av ...
s are another case of a hybridizing species pairs, and introgression
Introgression, also known as introgressive hybridization, in genetics is the transfer of genetic material from one species into the gene pool of another by the repeated backcrossing of an interspecific hybrid with one of its parent species. Introg ...
among non-sister species of bears appears to have shaped the Ursidae
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family (biology), family Ursidae (). They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats ...
family tree. Among many other mammal crosses are hybrid camels, crosses between a bactrian camel
The Bactrian camel (''Camelus bactrianus''), also known as the Mongolian camel, domestic Bactrian camel or two-humped camel, is a camel native to the steppes of Central Asia. It has two humps on its back, in contrast to the single-humped drome ...
and a dromedary
The dromedary (''Camelus dromedarius''), also known as the dromedary camel, Arabian camel and one-humped camel, is a large camel of the genus '' Camelus'' with one hump on its back. It is the tallest of the three camel species; adult males sta ...
. There are many examples of felid hybrids, including the liger
The liger is a hybrid (biology), hybrid offspring of a male lion (''Panthera leo'') and a tigress, or female tiger (''Panthera tigris''). The liger has parents in the same genus but of different species. The liger is distinct from the opposite ...
. The oldest-known animal hybrid bred by humans is the kunga equid hybrid produced as a draft animal and status symbol 4,500 years ago in Umm el-Marra
Umm el-Marra, (), east of modern Aleppo in the Jabbul Plain of northern Syria, was one of the ancient Near East's oldest cities, located on a crossroads of two trade routes northwest of Ebla, in a landscape that was much more fertile than it is t ...
, present-day Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
.
The first known instance of hybrid speciation in marine mammals was discovered in 2014. The clymene dolphin
The Clymene dolphin (''Stenella clymene''), in older texts known as the short-snouted spinner dolphin, is a dolphin endemic to the Atlantic Ocean. It is the only confirmed case of hybrid speciation in marine mammals, descending from the spinn ...
(''Stenella clymene'') is a hybrid of two Atlantic species, the spinner Spinner may refer to:
Technology
* Spinner (aeronautics), the aerodynamic cone at the hub of an aircraft propeller
* Spinner (cell culture), laboratory equipment for cultivating plant or mammalian cells
* Spinner (computing), a graphical widget in ...
and striped dolphins. In 2019, scientists confirmed that a skull found 30 years earlier was a hybrid between the beluga whale and narwhal
The narwhal (''Monodon monoceros'') is a species of toothed whale native to the Arctic. It is the only member of the genus ''Monodon'' and one of two living representatives of the family Monodontidae. The narwhal is a stocky cetacean with a ...
, dubbed the narluga.
Birds
Hybridization between species is common in birds. Hybrid birds are purposefully bred by humans, but hybridization is also common in the wild.Waterfowl
Anseriformes is an order of birds also known as waterfowl that comprises about 180 living species of birds in three families: Anhimidae (three species of screamers), Anseranatidae (the magpie goose), and Anatidae, the largest family, which i ...
have a particularly high incidence of hybridization, with at least 60% of species known to produce hybrids with another species. Among ducks
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family (biology), family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and goose, geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfam ...
, mallards widely hybridize with many other species, and the genetic relationships between ducks are further complicated by the widespread gene flow between wild and domestic mallards.
One of the most common interspecific hybrids in geese
A goose (: geese) is a bird of any of several waterfowl species in the family Anatidae. This group comprises the genera '' Anser'' (grey geese and white geese) and ''Branta'' (black geese). Some members of the Tadorninae subfamily (e.g., Egyp ...
occurs between Greylag and Canada geese ( Anser anser x Branta canadensis). One potential mechanism for the occurrence of hybrids in these geese is interspecific nest parasitism, where an egg is laid in the nest of another species to be raised by non-biological parents. The chick imprints upon and eventually seeks a mate among the species that raised it, instead of the species of its biological parents.
Cagebird breeders sometimes breed bird hybrids known as mules between species of finch
The true finches are small to medium-sized passerine birds in the family Fringillidae. Finches generally have stout conical bills adapted for eating seeds and nuts and often have colourful plumage. They occupy a great range of habitats where the ...
, such as goldfinch × canary.
Amphibians
Among amphibians, Japanesegiant salamander
The Cryptobranchidae (commonly known as giant salamanders) are a family of large salamanders that are fully aquatic. The family includes some of the largest living amphibians. They are native to China, Japan, and the eastern United States. Giant ...
s and Chinese giant salamanders have created hybrids that threaten the survival of Japanese giant salamanders because of competition for similar resources in Japan.
Fish
Among fish, a group of about 50 natural hybrids betweenAustralian blacktip shark
The Australian blacktip shark (''Carcharhinus tilstoni'') is a species of requiem shark, in the family (biology), family Carcharhinidae, endemism, endemic to northern and eastern Australia. Favoring the upper and middle parts of the water column ...
and the larger common blacktip shark was found by Australia's eastern coast in 2012.
Russian sturgeon
The Russian sturgeon (''Huso gueldenstaedtii''), also known as the diamond sturgeon or Danube sturgeon, is a species of fish in the family Acipenseridae. It is found in Azerbaijan, Bulgaria, Georgia, Iran, Kazakhstan, Romania, Russia, Turkey, Tur ...
and American paddlefish
The American paddlefish (''Polyodon spathula''), also known as a Mississippi paddlefish, spoon-billed cat, or spoonbill, is a species of ray-finned fish. It is the last extant taxon, living species of paddlefish (Polyodontidae). This family is ...
were hybridized in captivity when sperm from the paddlefish and eggs from the sturgeon were combined, unexpectedly resulting in viable offspring. This hybrid is called a sturddlefish
The sturddlefish is a hybrid of the American paddlefish (''Polyodon spathula'') and the Russian sturgeon (''Acipenser gueldenstaedtii''), accidentally created by researchers in 2019 and announced in 2020. Obtaining living hybrids through breedi ...
.
Cephalochordates
The two genera ''Asymmetron
''Asymmetron'' is one of the few living genera of lancelets ( order Amphioxiformes). It is the type genus of family Branchiostomatidae.
''Asymmetron'' can grow to 60 mm. The species of this genus are found in world oceans
The ocean is th ...
'' and ''Branchiostoma
''Branchiostoma'' is one of the few living genera of lancelets ( order Amphioxiformes). It is the type genus of family Branchiostomatidae.
These small vaguely eel- or snake-like animals are close relatives of vertebrates. The scientific name m ...
'' are able to produce viable hybrid offspring, even if none have lived into adulthood so far, despite the parents' common ancestor living tens of millions of years ago.
Insects
Among insects, so-called killer bees were accidentally created during an attempt to breed a strain of bees that would both produce more honey and be better adapted to tropical conditions. It was done by crossing aEuropean honey bee
The western honey bee or European honey bee (''Apis mellifera'') is the most common of the 7–12 species of honey bees worldwide. The genus name ''Apis'' is Latin for 'bee', and ''mellifera'' is the Latin for 'honey-bearing' or 'honey-carrying', ...
and an African bee.
The '' Colias eurytheme'' and '' C. philodice'' butterflies have retained enough genetic compatibility to produce viable hybrid offspring. Hybrid speciation may have produced the diverse ''Heliconius
''Heliconius'' comprises a colorful and widespread genus of brush-footed butterflies commonly known as the longwings or heliconians. This genus is distributed throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of the New World, from South America ...
'' butterflies
Butterflies are winged insects from the lepidopteran superfamily Papilionoidea, characterized by large, often brightly coloured wings that often fold together when at rest, and a conspicuous, fluttering flight. The oldest butterfly fossi ...
, but that is disputed.
The two closely related harvester ant species ''Pogonomyrmex barbatus'' and ''Pogonomyrmex rugosus'' have evolved to depend on hybridization. When a queen fertilizes her eggs with sperm from males of her own species, the offspring is always new queens. And when she fertilizes the eggs with sperm from males of the other species, the offspring is always sterile worker ants (and because ants are haplodiploid
Haplodiploidy is a sex-determination system in which males develop from unfertilized eggs and are haploid, and females develop from fertilized eggs and are diploid. Haplodiploidy is sometimes called arrhenotoky.
Haplodiploidy determines the se ...
, unfertilized eggs become males). Without mating with males of the other species, the queens are unable to produce workers, and will fail to establish a colony of their own.
jaglion
A ''Panthera'' hybrid is a crossbreed between individuals of any of the five species of the genus ''Panthera'': the tiger, lion, jaguar, leopard, and snow leopard. Most hybrids would not be perpetuated in the wild as the territories of the par ...
", a jaguar/lion hybrid
File:Goldfinch Canary hybrid.JPG, A domestic canary/goldfinch hybrid
In plants
 Plant species hybridize more readily than animal species, and the resulting hybrids are fertile more often. Many plant species are the result of hybridization, combined with
Plant species hybridize more readily than animal species, and the resulting hybrids are fertile more often. Many plant species are the result of hybridization, combined with polyploidy
Polyploidy is a condition in which the cells of an organism have more than two paired sets of ( homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two complete sets of chromosomes, one fro ...
, which duplicates the chromosomes. Chromosome duplication allows orderly meiosis and so viable seed can be produced.
Plant hybrids are generally given names that include an "×" (not in italics), such as ''Platanus'' × ''hispanica'' for the London plane, a natural hybrid of '' P. orientalis'' (oriental plane) and '' P. occidentalis'' (American sycamore). The parent's names may be kept in their entirety, as seen in ''Prunus persica'' × ''Prunus americana'', with the female parent's name given first, or if not known, the parent's names given alphabetically.
Plant species that are genetically compatible may not hybridize in nature for various reasons, including geographical isolation, differences in flowering period, or differences in pollinator
A pollinator is an animal that moves pollen from the male anther of a flower to the female carpel, stigma of a flower. This helps to bring about fertilization of the ovules in the flower by the male gametes from the pollen grains.
Insects are ...
s. Species that are brought together by humans in gardens may hybridize naturally, or hybridization can be facilitated by human efforts, such as altered flowering period or artificial pollination. Hybrids are sometimes created by humans to produce improved plants that have some of the characteristics of each of the parent species. Much work is now being done with hybrids between crops and their wild relatives to improve disease resistance or climate resilience
Climate resilience is a concept to describe how well people or ecosystems are prepared to bounce back from certain climate hazard events. The formal definition of the term is the "capacity of social, economic and ecosystems to cope with a hazardou ...
for both agricultural and horticultural crops.
Some crop plants are hybrids from different genera (intergeneric hybrids), such as Triticale, × ''Triticosecale'', a wheat–rye
Rye (''Secale cereale'') is a grass grown extensively as a grain, a cover crop and a forage crop. It is grown principally in an area from Eastern and Northern Europe into Russia. It is much more tolerant of cold weather and poor soil than o ...
hybrid. Most modern and ancient wheat breeds are themselves hybrids; bread wheat
Common wheat (''Triticum aestivum''), also known as bread wheat, is a cultivated wheat species. About 95% of wheat produced worldwide is common wheat; it is the most widely grown of all crops and the cereal with the highest monetary yield.
Ta ...
, ''Triticum aestivum'', is a hexaploid hybrid of three wild grasses. Several commercial fruits including loganberry
The loganberry (''Rubus'' × ''loganobaccus'') is a hybrid of the North American blackberry ('' Rubus ursinus'') and the European raspberry (''Rubus idaeus''), accidentally bred in 1881 by James Harvey Logan, for whom they are named. They are ...
(''Rubus'' × ''loganobaccus'') and grapefruit
The grapefruit (''Citrus'' × ''paradisi'') is a subtropical citrus tree known for its relatively large, sour to semi-sweet, somewhat bitter fruit. The flesh of the fruit is segmented and varies in color from pale yellow to dark red.
Grapefru ...
(''Citrus'' × ''paradisi'') are hybrids, as are garden herbs such as peppermint
Peppermint (''Mentha'' × ''piperita'') is a Hybrid (biology), hybrid species of Mentha, mint, a cross between Mentha aquatica, watermint and spearmint. Indigenous to Europe and the Middle East, the plant is now widely spread and cultivated in m ...
(''Mentha'' × ''piperita''), and trees such as the London plane
The London plane, or sometimes hybrid plane, ''Platanus'' × ''hispanica'', is a tree in the genus ''Platanus''. It is often known by the Synonym (taxonomy), synonym ''Platanus'' × ''acerifolia'', a later name. It is a Hybrid (biology ...
(''Platanus'' × ''hispanica''). Among many natural plant hybrids is '' Iris albicans'', a sterile hybrid that spreads by rhizome division, and '' Oenothera lamarckiana'', a flower that was the subject of important experiments by Hugo de Vries
Hugo Marie de Vries (; 16 February 1848 – 21 May 1935) was a Dutch botanist and one of the first geneticists. He is known chiefly for suggesting the concept of genes, rediscovering the laws of heredity in the 1890s while apparently unaware of ...
that produced an understanding of polyploidy.
Trillium cernuum
''Trillium cernuum'' is a species of flowering plant in the bunchflower family Melanthiaceae. The specific epithet ''cernuum'' means "drooping, curving forwards, facing downwards", a distinctive habit of its flower. It is commonly called noddi ...
'' and '' T. grandiflorum''
File:Lily Lilium 'Citronella' Flower.jpg, An ornamental lily hybrid known as ''Lilium'' 'Citronella'
gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
s. While that is undesirable in a crop such as wheat, for which growing a crop that produces no seeds would be pointless, it is an attractive attribute in some fruits. Triploid
Polyploidy is a condition in which the cells of an organism have more than two paired sets of ( homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two complete sets of chromosomes, one fro ...
banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large treelike herbaceous flowering plants in the genus '' Musa''. In some countries, cooking bananas are called plantains, distinguishing the ...
s and watermelon
The watermelon (''Citrullus lanatus'') is a species of flowering plant in the family Cucurbitaceae, that has a large, edible fruit. It is a Glossary of botanical terms#scandent, scrambling and trailing vine-like plant, and is plant breeding ...
s are intentionally bred because they produce no seeds and are also parthenocarpic.
In fungi
Hybridization betweenfungal
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the tradit ...
species is common and well established, particularly in yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom (biology), kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are est ...
. Yeast hybrids are widely found and used in human-related activities, such as brewing
Brewing is the production of beer by steeping a starch source (commonly cereal grains, the most popular of which is barley) in water and #Fermenting, fermenting the resulting sweet liquid with Yeast#Beer, yeast. It may be done in a brewery ...
and winemaking
Winemaking, wine-making, or vinification is the production of wine, starting with the selection of the fruit, its Ethanol fermentation, fermentation into alcohol, and the bottling of the finished liquid. The history of wine-making stretches over ...
. The production of lager beers for instance are known to be carried out by the yeast ''Saccharomyces pastorianus
''Saccharomyces pastorianus'' is a yeast used industrially for the production of lager beer, and was named in honour of Louis Pasteur by the German Max Reess in 1870. This yeast's complicated genome appears to be the result of Hybridisation (bio ...
'', a cryotolerant hybrid between ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungal microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have be ...
'' and '' Saccharomyces eubayanus'', which allows fermentation at low temperatures.
In humans
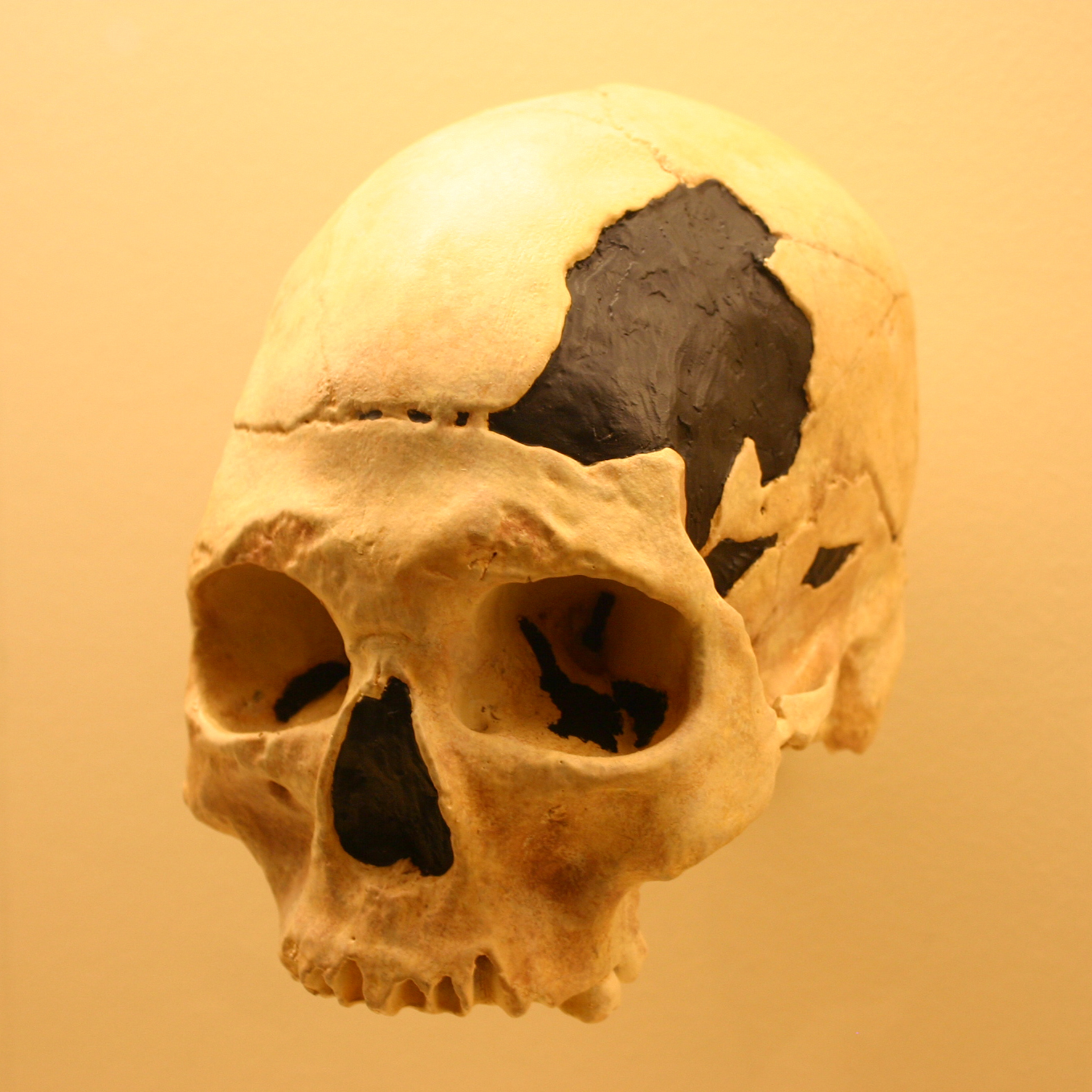
 There is evidence of hybridization between modern humans and other species of the genus ''
There is evidence of hybridization between modern humans and other species of the genus ''Homo
''Homo'' () is a genus of great ape (family Hominidae) that emerged from the genus ''Australopithecus'' and encompasses only a single extant species, ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), along with a number of extinct species (collectively called ...
''. In 2010, the Neanderthal genome project showed that 1–4% of DNA from all people living today, apart from most Sub-Saharan African
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and ...
s, is of Neanderthal heritage. Analyzing the genomes of 600 Europeans and East Asians found that combining them covered 20% of the Neanderthal genome that is in the modern human population. Ancient human populations lived and interbred with Neanderthals, Denisovans
The Denisovans or Denisova hominins ( ) are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human that ranged across Asia during the Lower Paleolithic, Lower and Middle Paleolithic, and lived, based on current evidence, from 285 thousand to 25 thou ...
, and at least one other extinct ''Homo'' species. Thus, Neanderthal and Denisovan DNA has been incorporated into human DNA by introgression.
In 1998, a complete prehistorical skeleton found in Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
, the Lapedo child, had features of both anatomically modern humans and Neanderthal
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
s. Some ancient human skulls with especially large nasal cavities and unusually shaped braincases represent human-Neanderthal hybrids. A 37,000- to 42,000-year-old human jawbone found in Romania's Oase cave contains traces of Neanderthal ancestry from only four to six generations earlier. All genes from Neanderthals in the current human population are descended from Neanderthal fathers and human mothers.
Mythology
Folk tales and myths sometimes contain mythological hybrids; theMinotaur
In Greek mythology, the Minotaur (, ''Mīnṓtauros''), also known as Asterion, is a mythical creature portrayed during classical antiquity with the head and tail of a bull and the body of a man or, as described by Roman poet Ovid, a being "par ...
was the offspring of a human, Pasiphaë
In Greek mythology, Pasiphaë (; , derived from πᾶσι (dative plural) "for all" and φάος/φῶς ''phaos/phos'' "light") was a queen of Crete. The daughter of Helios and the Oceanid nymph Perse (mythology), Perse, Pasiphaë is notable a ...
, and a white bull. More often, they are composites of the physical attributes of two or more kinds of animals, mythical beasts, and humans, with no suggestion that they are the result of interbreeding, as in the centaur
A centaur ( ; ; ), occasionally hippocentaur, also called Ixionidae (), is a creature from Greek mythology with the upper body of a human and the lower body and legs of a horse that was said to live in the mountains of Thessaly. In one version o ...
(man/horse), chimera (goat/lion/snake), hippocamp (fish/horse), and sphinx
A sphinx ( ; , ; or sphinges ) is a mythical creature with the head of a human, the body of a lion, and the wings of an eagle.
In Culture of Greece, Greek tradition, the sphinx is a treacherous and merciless being with the head of a woman, th ...
(woman/lion). The Old Testament
The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Isr ...
mentions a first generation of half-human hybrid giants
A giant is a being of human appearance, sometimes of prodigious size and strength, common in folklore.
Giant(s) or The Giant(s) may also refer to:
Mythology and religion
*Giants (Greek mythology)
* Jötunn, a Germanic term often translated as 'g ...
, the Nephilim
The Nephilim (; ''Nəfīlīm'') are mysterious beings or humans in the Bible traditionally understood as being of great size and strength, or alternatively beings of great power and authority. The origins of the Nephilim are disputed. Some, ...
, while the apocryphal
Apocrypha () are biblical or related writings not forming part of the accepted canon of scripture, some of which might be of doubtful authorship or authenticity. In Christianity, the word ''apocryphal'' (ἀπόκρυφος) was first applied to ...
Book of Enoch
The Book of Enoch (also 1 Enoch;
Hebrew language, Hebrew: סֵפֶר חֲנוֹךְ, ''Sēfer Ḥănōḵ''; , ) is an Second Temple Judaism, ancient Jewish Apocalyptic literature, apocalyptic religious text, ascribed by tradition to the Patriar ...
describes the Nephilim as the wicked sons of fallen angel
Fallen angels are angels who were expelled from Heaven. The literal term "fallen angel" does not appear in any Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic religious texts, but is used to describe angels cast out of heaven. Such angels are often described ...
s and attractive women.
See also
*AquAdvantage salmon
AquAdvantage salmon is a genetically engineered (GE) fish, a GE Atlantic salmon developed by AquaBounty Technologies in 1989. The typical growth hormone-regulating gene in the Atlantic salmon was replaced with the growth hormone-regulating gen ...
* Bird hybrid
* Canid hybrid
Canid hybrids are the result of interbreeding between the species of the subfamily ''Caninae''.
Genetic considerations
The wolf-like canids are a group of large carnivores that are genetically closely related because they all possess 78 chromos ...
* Chimera (genetics)
A genetic chimerism or chimera ( or ) is a single organism composed of cells of different genotype, genotypes. Animal chimeras can be produced by the fusion of two (or more) embryos. In plants and some animal chimeras, Mosaic (genetics), mos ...
* Chloroplast capture (botany)
* Eukaryote hybrid genome
* Endogenous retrovirus
Endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) are endogenous viral elements in the genome that closely resemble and can be derived from retroviruses. They are abundant in the genomes of jawed vertebrates, and they comprise up to 5–8% of the human genome ( ...
* Retrovirus
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. After invading a host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase e ...
* Reticulate evolution
* Felid hybrids
* Genetic admixture
Genetic admixture occurs when previously isolated populations interbreed resulting in a population that is descended from multiple sources. It can occur between species, such as with hybrids, or within species, such as when geographically dista ...
* Genetic erosion
* Grex (horticulture)
The term ''grex'' (plural ''greges'' or ''grexes''; abbreviation gx), derived from the Latin language, Latin noun , , meaning 'flock', has been expanded in botanical nomenclature to describe hybrids of orchids, based solely on their parentage. G ...
* Hybridity
Hybridity, in its most basic sense, refers to mixture. The term originates from biology and was subsequently employed in linguistics and in racial theory in the nineteenth century. Young, Robert. ''Colonial Desire: Hybridity in Theory, Culture and ...
* Intergradation
* Hybridogenesis
* Hybrot
* Inbreeding
Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the mating or breeding of individuals or organisms that are closely genetic distance, related genetically. By analogy, the term is used in human reproduction, but more commonly refers to the genet ...
* Breeding back
Breeding back is a form of artificial selection by the deliberate selective breeding of domestication, domestic (but not exclusively) animals, in an attempt to achieve an animal breed with a phenotype that resembles a wild type ancestor, usually ...
* Interspecific pregnancy
Interspecific pregnancy (literally ''pregnancy between species'', also called interspecies pregnancy or xenopregnancy)Page 126 in: is the pregnancy involving an embryo or fetus belonging to another species than the carrier. Strictly, it excludes ...
*
*
* Horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the e ...
* Inferring horizontal gene transfer
* GloFish
The GloFish is a patented and trademarked brand of fluorescently colored genetically modified fish, genetically modified aquarium fish. They have been created from several different species of fish: zebrafish were the first GloFish available in ...
* Agrobacterium
''Agrobacterium'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria established by Harold J. Conn, H. J. Conn that uses horizontal gene transfer to cause tumors in plants. ''Agrobacterium tumefaciens'' is the most commonly studied species in this genus. ''Agr ...
, a bacterium well known for its ability to transfer DNA between itself and plants.
* Gene delivery
Gene delivery is the process of introducing foreign genetic material, such as DNA or RNA, into host cells. Gene delivery must reach the genome of the host cell to induce gene expression. Successful gene delivery requires the foreign gene deliver ...
* List of plant hybrids
* List of genetic hybrids
This is a list of genetic hybrids which is limited to well documented cases of animals of differing species able to create hybrid offspring which may or may not be infertile.
Hybrids should not be confused with Chimera (genetics), genetic chimera ...
* Macropod hybrids
* Purebred
Purebreds are cultivars of an animal species achieved through the process of selective breeding. When the lineage of a purebred animal is recorded, that animal is said to be pedigreed. Purebreds breed true-to-type, which means the progeny of l ...
* Selective breeding
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant m ...
* Genetic use restriction technology
Genetic use restriction technology (GURT), also known as terminator technology or suicide seeds, is designed to restrict access to "genetic materials and their associated Phenotypic trait, phenotypic traits." The technology works by activating (o ...
* Gynogenesis
* Multiregional origin of modern humans
Notes
References
External links
Artificial Hybridisation
– Artificial Hybridisation in orchids
nbsp;– Creation of new species through hybridization was thought to be common only in plants, and rare in animals (archived 3 December 2008)
What is a human admixed embryo?
(archived 25 February 2012) {{DEFAULTSORT:Hybrid (Biology) Biology terminology Botanical nomenclature Evolutionary biology Population genetics Breeding