Human penis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 Three main parts of the human penis include:
*
Three main parts of the human penis include:
*  The
The  The penile raphe is the visible ridge between the
The penile raphe is the visible ridge between the
 *
*
 When the fetus is exposed to
When the fetus is exposed to
pp 267-69
/ref> The urethra within the penis (except within the glans) is developed from the
 An erection is the stiffening and rising of the penis, which occurs during sexual arousal, though it can also happen in non-sexual situations. Spontaneous erections frequently occur during adolescence due to friction with clothing, a full bladder or large intestine, hormone fluctuations, nervousness, and undressing in a nonsexual situation. It is also normal for erections to occur during sleep and upon waking. (See nocturnal penile tumescence.) The primary physiological mechanism that brings about erection is the autonomic dilation of
An erection is the stiffening and rising of the penis, which occurs during sexual arousal, though it can also happen in non-sexual situations. Spontaneous erections frequently occur during adolescence due to friction with clothing, a full bladder or large intestine, hormone fluctuations, nervousness, and undressing in a nonsexual situation. It is also normal for erections to occur during sleep and upon waking. (See nocturnal penile tumescence.) The primary physiological mechanism that brings about erection is the autonomic dilation of



 The most common form of body modification related to the penis is
The most common form of body modification related to the penis is
human anatomy
Human anatomy (gr. ἀνατομία, "dissection", from ἀνά, "up", and τέμνειν, "cut") is primarily the scientific study of the morphology of the human body. Anatomy is subdivided into gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. Gross ...
, the penis (; : penises or penes; from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''pēnis'', initially 'tail') is an external sex organ
A sex organ, also known as a reproductive organ, is a part of an organism that is involved in sexual reproduction. Sex organs constitute the primary sex characteristics of an organism. Sex organs are responsible for producing and transporting ...
( intromittent organ) through which males urinate
Urination is the release of urine from the bladder through the urethra in placental mammals, or through the cloaca in other vertebrates. It is the urinary system's form of excretion. It is also known medically as micturition, voiding, ure ...
and ejaculate
Ejaculation is the discharge of semen (the ''ejaculate''; normally containing sperm) from the penis through the urethra. It is the final stage and natural objective of male sexual stimulation, and an essential component of natural concepti ...
, as on other animals. Together with the testes
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone.
The ...
and surrounding structures, the penis functions as part of the male reproductive system
The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that play a role in the process of human reproduction. These organs are located on the outside of the body, and within the pelvic cavity, pelvis.
The main male sex organs are the hu ...
.
The main parts of the penis are the root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
, body, the epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
of the penis, including the shaft skin, and the foreskin
In male Human body, human anatomy, the foreskin, also known as the prepuce (), is the double-layered fold of Human skin, skin, Mucous membrane, mucosal and Muscle tissue, muscular tissue at the distal end of the human penis that covers the glans ...
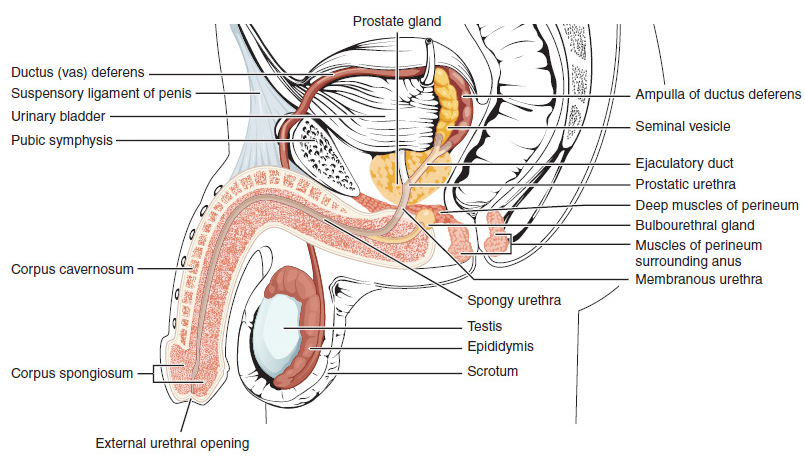
covering the glans. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue: two corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The urethra
The urethra (: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which Placentalia, placental mammals Urination, urinate and Ejaculation, ejaculate.
The external urethral sphincter is a striated ...
passes through the prostate gland
The prostate is an male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found in all male mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemica ...
, where it is joined by the ejaculatory duct
The ejaculatory ducts (''ductus ejaculatorii'') are paired structures in the male reproductive system. Each ejaculatory duct is formed by the union of the vas deferens with the Excretory duct of seminal gland, duct of the seminal vesicle. They pa ...
s, and then through the penis. The urethra goes across the corpus spongiosum and ends at the tip of the glans as the opening, the urinary meatus.
An erection
An erection (clinically: penile erection or penile tumescence) is a Physiology, physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, ...
is the stiffening expansion and orthogonal reorientation of the penis, which occurs during sexual arousal
Sexual arousal (also known as sexual excitement) describes the Physiology, physiological and psychological responses in preparation for sexual intercourse or when exposed to Sexual stimulation, sexual stimuli. A number of physiological response ...
. Erections can occur in non- sexual situations; spontaneous non-sexual erections frequently occur during adolescence and sleep. In its flaccid state, the penis is smaller, gives to pressure, and the glans is covered by the foreskin. In its fully erect state, the shaft becomes rigid and the glans becomes engorged but not rigid. An erect penis may be straight or curved and may point at an upward angle, a downward angle, or straight ahead. , the average erect human penis is long and has a circumference of . Neither age nor size of the flaccid penis accurately predicts erectile length. There are also several common body modification
Body modification (or body alteration) is the deliberate altering of the human anatomy or human physical appearance. In its broadest definition it includes skin tattooing, socially acceptable decoration (''e.g.'', common earring, ear piercing in ...
s to the penis, including circumcision
Circumcision is a procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, after which the foreskin is excised. T ...
and piercings.
The penis is homologous to the clitoris
In amniotes, the clitoris ( or ; : clitorises or clitorides) is a female sex organ. In humans, it is the vulva's most erogenous zone, erogenous area and generally the primary anatomical source of female Human sexuality, sexual pleasure. Th ...
in females.
Structure
 Three main parts of the human penis include:
*
Three main parts of the human penis include:
* Root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
: It is the attached part, consisting of the bulb
In botany, a bulb is a short underground stem with fleshy leaves or leaf basesBell, A.D. 1997. ''Plant form: an illustrated guide to flowering plant morphology''. Oxford University Press, Oxford, U.K. that function as food storage organs duri ...
in the middle and the crura, one crus on either side of the bulb. It lies within the superficial perineal pouch
The superficial perineal pouch (also superficial perineal compartment/space/sac) is a compartment of the perineum.
Structure
The superficial perineal pouch is an open compartment, due to the fact that anteriorly, the space communicates freely wi ...
. The crus is attached to the pubic arch.
* Shaft: The pendulous part of the penis. It has two surfaces: dorsal (posterosuperior in the erect penis) and ventral or urethral (facing downwards and backwards on the flaccid penis). The ventral surface is marked by the penile raphe. The base of the shaft is supported by the suspensory ligament, which is attached to the pubic symphysis.
* Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
of the penis consists of the shaft skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
, the foreskin
In male Human body, human anatomy, the foreskin, also known as the prepuce (), is the double-layered fold of Human skin, skin, Mucous membrane, mucosal and Muscle tissue, muscular tissue at the distal end of the human penis that covers the glans ...
(prepuce), and the preputial mucosa
The preputial mucosa of the Human penis, penis is the epithelium of the inside of the prepuce, or foreskin. To differentiate it from the cutaneous Human skin, skin of the outside of the Foreskin, prepuce, it is sometimes referred to as the inner mu ...
on the inside of it. The foreskin covers and protects the glans and shaft. The epithelium is not attached to the underlying shaft, so it is free to glide to and fro.
The human penis is made up of three columns of erectile tissue: two corpora cavernosa lie next to each other (separated by a fibrous septum
In biology, a septum (Latin language, Latin for ''something that encloses''; septa) is a wall, dividing a Body cavity, cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as septate.
Examples
Hum ...
) on the dorsal side and one corpus spongiosum lies between them on the ventral side. These columns are surrounded by a fibrous layer of connective tissue called the tunica albuginea. The corpora cavernosa are innervated by lesser and greater cavernous nerves and form most of the penis containing blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s that fill with blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
to help make an erection.
The crura are the proximal parts of the corpora cavernosa. The corpus spongiosum is an erectile tissue surrounding the urethra. The proximal parts of the corpus spongiosum form the bulb and the distal ends form the glans penis.
The enlarged and bulbous-shaped end of the corpus spongiosum forms the glans penis with two specific types of sinusoids, which supports the foreskin, a loose fold of skin that in adults can retract to expose the glans. The area on the underside of the glans, where the foreskin is attached, is called the frenulum. The rounded base of the glans is called the corona. The inner surface of the foreskin and corona is rich in sebaceous gland
A sebaceous gland or oil gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in ...
s that secrete smegma. The structure of the penis is supported by the pelvic floor muscles.
 The
The urethra
The urethra (: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which Placentalia, placental mammals Urination, urinate and Ejaculation, ejaculate.
The external urethral sphincter is a striated ...
, which is the last part of the urinary tract, traverses the corpus spongiosum ( spongy urethra) and opens through the urinary meatus on the tip of the glans.
 The penile raphe is the visible ridge between the
The penile raphe is the visible ridge between the lateral
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may also refer to:
Biology and healthcare
* Lateral (anatomy), a term of location meaning "towards the side"
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle, an intrinsic muscle of the larynx
* Lateral release ( ...
halves of the penis, found on the ventral or underside of the penis, running from the meatus and continuing as the perineal raphe across the scrotum
In most terrestrial mammals, the scrotum (: scrotums or scrota; possibly from Latin ''scortum'', meaning "hide" or "skin") or scrotal sac is a part of the external male genitalia located at the base of the penis. It consists of a sac of skin ...
and the perineum
The perineum (: perineums or perinea) in placentalia, placental mammals is the space between the anus and the genitals. The human perineum is between the anus and scrotum in the male or between the anus and vulva in the female. The perineum is ...
(area between scrotum and anus
In mammals, invertebrates and most fish, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is the external body orifice at the ''exit'' end of the digestive tract (bowel), i.e. the opposite end from the mouth. Its function is to facil ...
).
The human penis differs from those of most other mammals, as it has no baculum
The baculum (: bacula), also known as the penis bone, penile bone, ''os penis'', ''os genitale'', or ''os priapi'', is a bone in the penis of many placental mammals. It is not present in humans, but is present in the penises of some primates, ...
(or erectile bone) and instead relies entirely on engorgement with blood to reach its erect state. A distal ligament buttresses the glans penis and plays an integral role to the penile fibroskeleton, and the structure is called "os analog", a term coined by Geng Long Hsu in the ''Encyclopedia of Reproduction''. It is a remnant of the baculum that has likely evolved due to change in mating practice.
The human penis cannot be withdrawn into the groin, and it is larger than average in the animal kingdom in proportion to body mass. The human penis is reciprocating from a cotton soft to a bony rigidity resulting from penile arterial flow varied between 2–3 to 60–80 mL/Min implies the most ideal milieu to apply Pascal's law in the entire human body; the overall structure is unique.
Size
Penile measurements vary, with studies that rely on self-measurement reporting a significantly higher average size than those which rely on measurements taken by health professional. A 2015 systematic review of 15,521 men in which the subjects were measured by health professionals showed that the average length of an erect human penis is 13.12 cm (5.17 inches) long, while the average circumference of an erect human penis is 11.66 cm (4.59 inches). Among all primates, the human penis is the largest in girth, but is comparable to thechimpanzee
The chimpanzee (; ''Pan troglodytes''), also simply known as the chimp, is a species of Hominidae, great ape native to the forests and savannahs of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed one. When its close rel ...
penis and the penises of certain other primates in length. Penis size is affected by genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian ...
, but also by environmental factors such as fertility medications and chemical/pollution exposure.
Normal variations
 *
*Pearly penile papules
Pearly penile papules (PPP; also known as hirsutoid papillomas or as , Latin for 'papillae of the corona of the glans') are benign, small bumps or spots on the human penis. They vary in size from 0.5-1 mm, are pearly or flesh-colored, smo ...
are raised bumps of somewhat paler color around the base (sulcus) of the glans, which typically develop in males aged 20 to 40. As of 1999, different studies had produced estimates of incidence ranging from 8 to 48 percent of all men. They may be mistaken for warts, but are not harmful or infectious and do not require treatment.
* Fordyce's spots are small, raised, yellowish-white spots 1–2 mm (roughly 0.05 inch) in diameter that may appear on the penis, which again are common and not infectious.
*''Sebaceous prominences'' are raised bumps similar to Fordyce's spots on the shaft of the penis, located at the sebaceous gland
A sebaceous gland or oil gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in ...
s and are normal.
*Phimosis
Phimosis (from Greek language, Greek φίμωσις ''phimōsis'' 'muzzling') is a condition in which the foreskin of the Human penis, penis cannot stretch to allow it to be pulled back past the Glans penis, glans. A balloon-like swelling under ...
is an inability to retract the foreskin fully. It is normal and harmless in infancy and pre-pubescence, occurring in about 8% of boys at age 10. According to the British Medical Association, treatment (topical steroid cream and/or manual stretching) does not need to be considered until age 19.
*Curvature: few penises are completely straight, with curves commonly seen in all directions (up, down, left, right). Sometimes the curve is very prominent but it rarely inhibits sexual intercourse
Sexual intercourse (also coitus or copulation) is a sexual activity typically involving the insertion of the Erection, erect male Human penis, penis inside the female vagina and followed by Pelvic thrust, thrusting motions for sexual pleasure ...
. Curvature as great as 30° is considered normal and medical treatment is rarely considered unless the angle exceeds 45°. Changes to the curvature of a penis may be caused by Peyronie's disease.
Development
 When the fetus is exposed to
When the fetus is exposed to testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
, the genital tubercle
A genital tubercle, phallic tubercle, or clitorophallic structure is a body of tissue present in the development of the reproductive system of amniotes. It forms in the ventral, caudal region of mammalian embryos of both sexes, and eventually ...
elongates ( primordial phallus) and develops into the glans and shaft of the penis and the urogenital folds fuse to become the penile raphe.Keith L. Moore, T. V. N. Persaud, Mark G. Torchia, The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology 10th Ed. Elsevier Health Sciences, 2015 pp 267-69
/ref> The urethra within the penis (except within the glans) is developed from the
urogenital sinus
The urogenital sinus is a body part of a human or other Placentalia, placental only present in the development of the urinary system, development of the urinary and development of the reproductive organs, reproductive organs. It is the ventral p ...
.
Growth in puberty
On enteringpuberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
, the penis, scrotum and testicles will enlarge toward maturity. During the process, pubic hair
Pubic hair (or pubes , ) is terminal hair, terminal body hair that is found in the sex organ, genital area and pubic region of adolescent and adult humans. The hair is located on and around the sex organs, and sometimes at the top of the inside ...
grows above and around the penis. A large-scale study assessing penis size in thousands of 17- to 19-year-old males found no difference in average penis size between 17-year-olds and 19-year-olds. From this, it can be concluded that penile growth is typically complete not later than age 17, and possibly earlier.
Physiological functions
Urination
Males expelurine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (mal ...
from the bladder through the urethra, which passes through the prostate
The prostate is an male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found in all male mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemica ...
where it is joined by the ejaculatory duct
The ejaculatory ducts (''ductus ejaculatorii'') are paired structures in the male reproductive system. Each ejaculatory duct is formed by the union of the vas deferens with the Excretory duct of seminal gland, duct of the seminal vesicle. They pa ...
s, and then onward through the penis. At the root of the penis (the proximal end of the corpus spongiosum) lies the external sphincter muscle. This is a small sphincter of striated muscle tissue
Striated muscle tissue is a muscle tissue that features repeating functional units called sarcomeres. Under the microscope, sarcomeres are visible along muscle fibers, giving a striated appearance to the tissue. The two types of striated muscle a ...
and is in healthy males, under voluntary control. Relaxing the urethral sphincter allows the urine in the upper urethra to enter the penis properly and thus empty the urinary bladder.
Physiologically, urination involves coordination between the central, autonomic, and somatic nervous system
The somatic nervous system (SNS), also known as voluntary nervous system, is a part of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) that links brain and spinal cord to skeletal muscles under conscious control, as well as to sensory receptors in the skin ...
s. In infants, some elderly individuals, and those with neurological injury, urination may occur as an involuntary reflex. Brain centers that regulate urination include the pontine micturition center, periaqueductal gray
The periaqueductal gray (PAG), also known as the central gray, is a brain region that plays a critical role in autonomic function, motivated behavior and behavioural responses to threatening stimuli. PAG is also the primary control center for ...
, and the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of Neuron, neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays ...
. During erection, these centers block the relaxation of the sphincter muscles, so as to act as a physiological separation of the excretory and reproductive function of the penis, and preventing urine from entering the upper portion of the urethra during ejaculation.
Voiding position
The distal section of the urethra allows a human male to direct the stream of urine by holding the penis. This flexibility allows the male to choose the posture in which to urinate. In cultures where more than a minimum of clothing is worn, the penis allows the male to urinate while standing without removing much of the clothing. It is customary for some boys and men to urinate in seated or crouched positions. The preferred position may be influenced by cultural or religious beliefs. Research on the medical superiority of either position exists, but the data are heterogenic. Ameta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, th ...
summarizing the evidence found no superior position for young, healthy males. For elderly males with LUTS, however, the sitting position when compared to the standing position is differentiated by the following:
* the post void residual volume (PVR, ml) was significantly decreased
* the maximum urinary flow (Qmax, ml/s) was increased
* the voiding time (VT, s) was decreased
This urodynamic profile is related to a lower risk of urologic complications, such as cystitis and bladder stones.
Sexual stimulation and arousal
The penis incites sexual arousal when sexually stimulated, such as from mental stimuli (sexual fantasy
A sexual fantasy, or erotic fantasy, is an Autoeroticism, autoerotic mental image or pattern of thought that stirs a person's Human sexuality, sexuality and can create or enhance sexual arousal. A sexual Fantasy (psychology), fantasy can be crea ...
), partnered activity, or masturbation
Masturbation is a form of autoeroticism in which a person Sexual stimulation, sexually stimulates their own Sex organ, genitals for sexual arousal or other sexual pleasure, usually to the point of orgasm. Stimulation may involve the use of han ...
, which can lead to orgasm
Orgasm (from Greek , ; "excitement, swelling"), sexual climax, or simply climax, is the sudden release of accumulated sexual excitement during the sexual response cycle, characterized by intense sexual pleasure resulting in rhythmic, involu ...
.
The glans and the frenulum are erogenous zone
An erogenous zone (from Greek , ''érōs'' "love"; and English ''-genous'' "producing", from Greek , ''-genḗs'' "born") is an area of the human body that has heightened Sensory processing, sensitivity, the sexual stimulation, stimulation of wh ...
s of the penis. The glans has many nerve endings, which makes it the most sensitive. The most effective way to stimulate the penis is through oral
The word oral may refer to:
Relating to the mouth
* Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid
**Oral administration of medicines
** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or ora ...
stimulation (fellatio
Fellatio (also known as fellation, and in slang as blowjob, BJ, giving head, or sucking off) is an oral sex act consisting of the stimulation of a human penis, penis by using the mouth. Oral stimulation of the scrotum may also be termed ''fellat ...
), manual stimulation (a handjob
A handjob (also spelled hand job) is a manual sex act involving a person stimulating the penis or scrotum of another by using the hand. This is done to induce an erection for sexual pleasure, sexual arousal and may result in orgasm and ejaculat ...
or manual masturbation), or during sexual penetration
Sexual penetration is the insertion of a body part or other object into a body orifice, such as the mouth, vagina or anus, as part of human sexual activity or sexual behavior in non-human animals.
The term is most commonly used in statute la ...
. Frot is mutual penile stimulation between men.
Erection
 An erection is the stiffening and rising of the penis, which occurs during sexual arousal, though it can also happen in non-sexual situations. Spontaneous erections frequently occur during adolescence due to friction with clothing, a full bladder or large intestine, hormone fluctuations, nervousness, and undressing in a nonsexual situation. It is also normal for erections to occur during sleep and upon waking. (See nocturnal penile tumescence.) The primary physiological mechanism that brings about erection is the autonomic dilation of
An erection is the stiffening and rising of the penis, which occurs during sexual arousal, though it can also happen in non-sexual situations. Spontaneous erections frequently occur during adolescence due to friction with clothing, a full bladder or large intestine, hormone fluctuations, nervousness, and undressing in a nonsexual situation. It is also normal for erections to occur during sleep and upon waking. (See nocturnal penile tumescence.) The primary physiological mechanism that brings about erection is the autonomic dilation of arteries
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
supplying blood to the penis, which allows more blood to fill the three spongy erectile tissue chambers in the penis, the corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum, causing it to lengthen and stiffen. After vasocongestion, the now-engorged erectile tissue presses against and constricts the veins that carry blood away from the penis. More blood enters than leaves the penis until an equilibrium is reached where an equal volume of blood flows into the dilated arteries and out of the constricted veins; a constant erectile size is achieved at this equilibrium.
Erection facilitates sexual intercourse though it is not essential for various other sexual activities.
=Erection angle
= Although many erect penises point upwards, it is common and normal for erect penis to curve in any direction. Many penises are curved in right, left, upwards or downwards direction depending upon the tension of the suspensory ligament that holds it in position. The following table shows how common various erection angles are for a standing male, out of a sample of 81 males aged 21 through 67. In the table, zero degrees is pointing straight up against the abdomen, 90 degrees is horizontal and pointing straight forward, while 180 degrees would be pointing straight down to the feet. An upward pointing angle is most common.Ejaculation
Ejaculation is the ejection of semen from the penis. It is usually accompanied by orgasm. A series of muscular contractions delivers semen, containing malegametes
A gamete ( ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. The name gamete was introduced by the Ge ...
known as sperm cells or spermatozoa
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; : spermatozoa; ) is a motile sperm cell (biology), cell produced by male animals relying on internal fertilization. A spermatozoon is a moving form of the ploidy, haploid cell (biology), cell that is ...
, from the penis. Ejaculation usually happens as the result of sexual stimulation, but it can be due to prostatic disease in rare cases. Ejaculation may occur spontaneously during sleep (known as a nocturnal emission
A wet dream, sex dream, or sleep orgasm, is a spontaneous occurrence of sexual arousal during sleep that includes ejaculation (nocturnal emission) and orgasm for a male, and vaginal lubrication and/or orgasm for a female.
Context
Nocturnal e ...
). Anejaculation
Anejaculation is the pathological inability to ejaculate despite an erection in males, with (''orgasmic'') or without ( ''anorgasmic'') orgasm.
Causes
It can depend on one or more of several causes, including:
* Sexual inhibition
* Pharmacolo ...
is the condition of being unable to ejaculate.
Sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
are produced in the testicle
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
s and stored in the attached epididymides
The epididymis (; : epididymides or ) is an elongated tubular genital organ attached to the posterior side of each one of the two male reproductive glands, the testicles. It is a single, narrow, tightly coiled tube in adult humans, in length; ...
. During ejaculation, sperm are propelled up the vasa deferentia, two ducts that pass over and behind the bladder. Fluids are added by the seminal vesicles and the vasa deferentia turn into the ejaculatory duct
The ejaculatory ducts (''ductus ejaculatorii'') are paired structures in the male reproductive system. Each ejaculatory duct is formed by the union of the vas deferens with the Excretory duct of seminal gland, duct of the seminal vesicle. They pa ...
s, which join the urethra inside the prostate
The prostate is an male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found in all male mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemica ...
. The prostate, as well as the bulbourethral glands, add further secretions (including pre-ejaculate), and the semen is expelled through the penis.
Ejaculation has two phases: emission and ejaculation proper. The emission phase of the ejaculatory reflex is under control of the sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS or SANS, sympathetic autonomic nervous system, to differentiate it from the somatic nervous system) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous sy ...
, while the ejaculatory phase is under control of a spinal reflex
The stretch reflex (myotatic reflex), or more accurately ''muscle stretch reflex'', is a muscle contraction in response to stretching a muscle. The function of the reflex is generally thought to be maintaining the muscle at a constant length but t ...
at the level of the spinal nerve
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries Motor neuron, motor, Sensory neuron, sensory, and Autonomic nervous system, autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each s ...
s S2–4 via the pudendal nerve
The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It is a Mixed nerve, mixed (motor and sensory) nerve and also conveys Sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic Autonomic nervous system, autonomic fibers. It carries sensation from the exter ...
. A refractory period succeeds the ejaculation, and sexual stimulation precedes it.
The ischiocavernosus muscle helps to stabilize the penis during erection by compressing the crus and slowing the return of blood through the veins. The bulbospongiosus muscle
The bulbospongiosus muscles (in older texts bulbocavernosus and, for female muscle, constrictor cunni) are a subgroup of the superficial muscles of the perineum. They have a slightly different origin, insertion and function in males and females. ...
also contributes to erection along with the expulsion of urine and semen.
Evolved adaptations
The human penis has been argued to have several evolutionary adaptations that maximise reproductive success and minimisesperm competition
Sperm competition is the competitive process between Spermatozoon, spermatozoa of two or more different males to fertility, fertilize the same Egg cell, egg during sexual reproduction. Competition can occur when females have multiple potential m ...
. Sperm competition is where the sperm of two males simultaneously occupy the reproductive tract of a female and they compete to fertilise the egg. If sperm competition results in the rival male's sperm fertilising the egg, cuckoldry could occur. This is the process whereby males unwittingly invest their resources into offspring of another male and, evolutionarily speaking, should be avoided.
The most researched human penis adaptations are penis size and semen displacement.
Penis size
Evolution has caused sexually selected adaptations to occur in penis size in order to maximise reproductive success and minimise sperm competition. Sperm competition has caused the human penis to evolve in length and size for sperm retention and displacement. To achieve this, the penis must be of sufficient length to reach any rival sperm and to maximally fill thevagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
. In order to ensure that the female retains the male's sperm, the adaptations in length of the human penis have occurred so that the ejaculate is placed close to the female cervix. This is achieved when complete penetration occurs and the penis pushes against the cervix. These adaptations have occurred in order to release and retain sperm to the highest point of the vaginal tract. As a result, this adaptation also leaves the sperm less vulnerable to sperm displacement and semen loss. Another reason for this adaptation is that, due to the nature of the human posture, gravity creates vulnerability for semen loss. Therefore, a long penis, which places the ejaculate deep in the vaginal tract, could reduce the loss of semen.
Another evolutionary theory of penis size is female mate choice
Mate choice is one of the primary mechanisms under which evolution can occur. It is characterized by a "selective response by animals to particular stimuli" which can be observed as behavior.Bateson, Paul Patrick Gordon. "Mate Choice." Mate Choi ...
and its associations with social judgements in modern-day society. A study which illustrates female mate choice as an influence on penis size presented females with life-size, rotatable, computer generated males. These varied in height, body shape and flaccid penis size, with these aspects being examples of masculinity. Female ratings of attractiveness for each male revealed that larger penises were associated with higher attractiveness ratings. These relations between penis size and attractiveness have therefore led to frequently emphasized associations between masculinity and penis size in popular media. This has led to a social bias existing around penis size with larger penises being preferred and having higher social status. This is reflected in the association between believed sexual prowess and penis size and the social judgement of penis size in relation to 'manhood'.
Semen displacement
The shape of the human penis is thought to have evolved as a result of sperm competition. Semen displacement is an adaptation of the shape of the penis to draw foreign semen away from the cervix. This means that in the event of a rival male's sperm occupying the reproductive tract of a female, the human penis is able to displace the rival sperm, replacing it with his own. Semen displacement has two main benefits for a male. Firstly, by displacing a rival male's sperm, the risk of the rival sperm fertilising the egg is reduced. Secondly, the male replaces the rival's sperm with his own, thereby increasing the probability of his fertilising the egg and successfully reproducing with the female. However, males have to ensure they do not displace their own sperm. It is thought that the relatively quick loss of erection after ejaculation, penile hypersensitivity following ejaculation, and the shallower, slower thrusting of the male after ejaculation prevent this from occurring. The coronal ridge is the part of the human penis thought to have evolved to allow for semen displacement. Research has studied how much semen is displaced by differently shaped artificial genitals. This research showed that, when combined with thrusting, the coronal ridge of the penis is able to remove the seminal fluid of a rival male from within the female reproductive tract. It does this by forcing the semen under the frenulum of the coronal ridge, causing it to collect behind the coronal ridge shaft. When model penises without a coronal ridge were used, less than half the artificial sperm was displaced, compared to penises with a coronal ridge. The presence of a coronal ridge alone, however, is not sufficient for effective semen displacement. It must be combined with adequate thrusting to be successful. It has been shown that the deeper the thrusting, the larger the semen displacement. No semen displacement occurs with shallow thrusting. Some have therefore termed thrusting as a semen displacement behaviour. The behaviours associated with semen displacement, namely thrusting (number of thrusts and depth of thrusts), and duration ofsexual intercourse
Sexual intercourse (also coitus or copulation) is a sexual activity typically involving the insertion of the Erection, erect male Human penis, penis inside the female vagina and followed by Pelvic thrust, thrusting motions for sexual pleasure ...
, have been shown to vary according to whether a male perceives the risk of partner infidelity
Infidelity (synonyms include non-consensual non-monogamy, cheating, straying, adultery, being unfaithful, two-timing, or having an affair) is a violation of a couple's emotional or sexual exclusivity that commonly results in feelings of anger, se ...
to be high or not. Males and females report greater semen displacement behaviours following allegations of infidelity. In particular, following allegations of infidelity, males and females report deeper and quicker thrusting during sexual intercourse.
Clinical significance
Disorders
*Paraphimosis
Paraphimosis is an uncommon medical condition in which the foreskin of a penis becomes trapped behind the glans penis, and cannot be ''reduced'' (pulled back to its normal flaccid position covering the glans). If this condition persists for severa ...
is an inability to move the foreskin forward over the glans. It can result from fluid trapped in a foreskin left retracted, perhaps following a medical procedure, or accumulation of fluid in the foreskin because of friction during vigorous sexual activity.
*In Peyronie's disease, anomalous scar tissue grows in the soft tissue of the penis, causing curvature. Severe cases can be improved by surgical correction.
*A thrombosis
Thrombosis () is the formation of a Thrombus, blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fib ...
can occur during periods of frequent and prolonged sexual activity, especially fellatio
Fellatio (also known as fellation, and in slang as blowjob, BJ, giving head, or sucking off) is an oral sex act consisting of the stimulation of a human penis, penis by using the mouth. Oral stimulation of the scrotum may also be termed ''fellat ...
. It is usually harmless and self-corrects within a few weeks.
*Sexually transmitted infection
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, e ...
s, for example, herpes virus, which can occur after sexual contact with an infected carrier; this may lead to the development of herpes sores.
*Balanitis
Balanitis is inflammation of the glans penis. Balanoposthitis is the proper term when the foreskin is also affected. Balanitis on boys in diapers must be distinguished from redness caused by ammoniacal dermatitis.
Etymology
The word ''balanit ...
is an inflammation, either infectious or not.
* Pudendal nerve entrapment is a condition characterized by pain on sitting and the loss of penile sensation and orgasm. Occasionally, there is a total loss of sensation and orgasm. The pudendal nerve
The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It is a Mixed nerve, mixed (motor and sensory) nerve and also conveys Sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic Autonomic nervous system, autonomic fibers. It carries sensation from the exter ...
can be damaged by narrow, hard bicycle seats and accidents.
* Penile fracture can occur if the erect penis is bent excessively. A popping or cracking sound and pain is normally associated with this event. Emergency medical assistance should be obtained as soon as possible. Prompt medical attention lowers the likelihood of permanent penile curvature.
*In diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
, peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropa ...
can cause tingling in the penile skin and possibly reduced or completely absent sensation. The reduced sensations can lead to injuries for either partner and their absence can make it impossible to have sexual pleasure through stimulation of the penis. Since the problems are caused by permanent nerve damage, preventive treatment through good control of the diabetes is the primary treatment. Some limited recovery may be possible through improved diabetes control.
*Erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also referred to as impotence, is a form of sexual dysfunction in males characterized by the persistent or recurring inability to achieve or maintain a Human penis, penile erection with sufficient rigidity and durat ...
is the inability to develop and maintain an erection sufficiently firm for satisfactory sexual performance. Diabetes is a leading cause, as is natural aging. A variety of treatments exist, most notably including the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor drugs (such as ''sildenafil
Sildenafil, sold under the brand name Viagra among others, is a medication used to treat erectile dysfunction and pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary arterial hypertension. It is also sometimes used off-label for the treatment of certain sym ...
citrate'', marketed as Viagra), which work by vasodilation
Vasodilation, also known as vasorelaxation, is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. Blood vessel wa ...
.
* Priapism, a form of persistent genital arousal disorder, is a painful and potentially harmful medical condition in which the erect penis does not return to its flaccid state. Priapism lasting over four hours is a medical emergency. The causative mechanisms are poorly understood but involve complex neurological and vascular factors. Potential complications include ischaemia, thrombosis
Thrombosis () is the formation of a Thrombus, blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fib ...
, and impotence
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also referred to as impotence, is a form of sexual dysfunction in males characterized by the persistent or recurring inability to achieve or maintain a Human penis, penile erection with sufficient rigidity and durat ...
. In serious cases the condition may result in gangrene, which may result in amputation
Amputation is the removal of a Limb (anatomy), limb or other body part by Physical trauma, trauma, medical illness, or surgery. As a surgical measure, it is used to control pain or a disease process in the affected limb, such as cancer, malign ...
. However, that is usually only the case if the organ is broke out and injured because of it. The condition has been associated with a variety of drugs including prostaglandin
Prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiology, physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids that have diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every Tissue (biology), tissue in humans and ot ...
. Contrary to common knowledge, sildenafil
Sildenafil, sold under the brand name Viagra among others, is a medication used to treat erectile dysfunction and pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary arterial hypertension. It is also sometimes used off-label for the treatment of certain sym ...
(Viagra) will not cause it.
* Lymphangiosclerosis is a hardened lymph vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessel ...
, although it can feel like a hardened, almost calcified or fibrous, vein. It tends not to share the common blue tint with a vein however. It can be felt as a hardened lump or "vein" even when the penis is flaccid, and is even more prominent during an erection. It is considered a benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
physical condition. It is fairly common and can follow a particularly vigorous sexual activity for men, and tends to go away if given rest and more gentle care, for example by use of lubricants.
* Carcinoma of the penis is rare with a reported rate of 1 person in 100,000 in developed countries. Some sources state that circumcision can protect against this disease, but this notion remains controversial among medical circles.
* Hard flaccid syndrome is a rare, chronic condition characterized by a flaccid penis that remains in a firm, semi-rigid state in the absence of sexual arousal.
* Cold glans syndrome is a condition marked by the persistent inability of the glans penis to maintain an erect state during sexual arousal, potentially leading to reduced sensitivity and erection difficulties.
Developmental disorders
*Hypospadias
Hypospadias is a common malformation in fetal development of the penis in which the urethra does not open from its usual location on the head of the penis. It is the second-most common birth defect of the male reproductive system, affecting about ...
is a developmental disorder
Developmental disorders comprise a group of psychiatric conditions originating in childhood that involve serious impairment in different areas. There are several ways of using this term. The most narrow concept is used in the category "Specific D ...
where the meatus is positioned wrongly at birth. Hypospadias can also occur iatrogenically by the downward pressure of an indwelling urethral catheter. It is usually corrected by surgery.
*A micropenis
A micropenis or microphallus is an unusually small Human penis, penis. A common criterion is a dorsal (measured on top) Human penis size, penile length of at least 2.5 standard deviations smaller than the mean human penis size for age. A micr ...
is a very small penis caused by developmental or congenital problems.
*Diphallia
Diphallia, penile duplication (PD), diphallic terata, or diphallasparatus is an extremely rare developmental abnormality in which a male is born with two Human penis, penises. The first reported case was by Johannes Jacob Wecker in 1609. Its occu ...
, or penile duplication (PD), is the rare condition of having two penises.
Alleged and observed psychological disorders
* Penis panic (''koro'' in Malaysian/ Indonesian) — delusion of shrinkage of the penis and retraction into the body. This appears to be culturally conditioned and largely limited to Ghana, Sudan, China, Japan, Southeast Asia, and West Africa. * In April 2008,Kinshasa
Kinshasa (; ; ), formerly named Léopoldville from 1881–1966 (), is the Capital city, capital and Cities of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, largest city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Kinshasa is one of the world's fastest-grow ...
, Democratic Republic of Congo, the West African police arrested 14 suspected victims (of penis snatching) and sorcerers accused of using black magic or witchcraft to steal (make disappear) or shrink men's penises to extort cash for cure, amid a wave of panic. Arrests were made in an effort to avoid bloodshed seen in Ghana a decade before, when 12 penis snatchers were beaten to death by mobs.
*Penis envy
Penis envy () is a stage in Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud ( ; ; born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating psychop ...
— the contested Freudian belief of all women inherently envying men for having penises.
Society and culture


Terminology
In many cultures, referring to the penis is considered taboo or vulgar, and a variety of slang words and euphemisms are used to talk about it. In English, these include ''member'', '' dick'', ''cock'', '' prick'', ''johnson'', ''dork'', ''peter'', ''pecker'', ''manhood'', ''stick'', ''rod'', ''third/middle leg'', ''dong'', ''willy'', ''schlong'', and ''todger''. Many of these are used asinsult
An insult is an expression, statement, or behavior that is often deliberately disrespectful, offensive, scornful, or derogatory towards an individual or a group.
Insults can be intentional or unintentional, and they often aim to belittle, of ...
s—though sometimes playfully—meaning an unpleasant or unworthy person. Among these, historically, the most commonly used euphemism for penis in English literature and society was ''member''.
Alteration
The penis is sometimes pierced or decorated by other body art. Other than circumcision, genital alterations are almost universally elective and usually for the purpose of aesthetics or increased sensitivity. Piercings of the penis include the Prince Albert, apadravya, ampallang, dydoe, deep shaft and frenum piercings. Foreskin restoration or stretching is a further form of body modification, as well as implants under the shaft of the penis. Another type of alteration to the penis is genital tattooing. Trans women who undergosex reassignment surgery
Gender-affirming surgery (GAS) is a surgical procedure, or series of procedures, that alters a person's physical appearance and sexual characteristics to resemble those associated with their gender identity. The phrase is most often associat ...
have their penis surgically modified into a vagina or clitoris via vaginoplasty or clitoroplasty respectively. Trans men
A trans man or transgender man is a man who was assigned female at birth. Trans men have a male gender identity, and many trans men undergo Gender transition, medical and social transition to alter their appearance in a way that aligns with th ...
who undergo such surgery have a phalloplasty or metoidioplasty.
Other practices that alter the penis are also performed, although they are rare in Western societies without a diagnosed medical condition. Apart from penectomy, perhaps the most radical of these is subincision, in which the urethra is split along the underside of the penis. Subincision originated among Australian Aborigines
Aboriginal Australians are the various indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, excluding the ethnically distinct people of the Torres Strait Islands.
Humans first migrated to Australia 50,000 to 65,000 years ...
, although it is now done by some in the U.S. and Europe.
Circumcision
 The most common form of body modification related to the penis is
The most common form of body modification related to the penis is circumcision
Circumcision is a procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, after which the foreskin is excised. T ...
: removal of part or all of the foreskin. It is most commonly performed as an elective procedure for prophylactic, cultural
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
, or religious
Religion is a range of social- cultural systems, including designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relate humanity to supernatural ...
reasons. For infant circumcision, modern devices such as the Gomco clamp, Plastibell, and Mogen clamp are available. The ethics of circumcision
Male circumcision is the surgical removal of the foreskin (prepuce) from the human penis.
There is substantial disagreement amongst bioethicists and theologians over the practice of circumcision, with many believing that the routine circumcisi ...
in children is a source of controversy
Controversy (, ) is a state of prolonged public dispute or debate, usually concerning a matter of conflicting opinion or point of view. The word was coined from the Latin '' controversia'', as a composite of ''controversus'' – "turned in an op ...
. Among the world's major medical organizations, there is a consensus that circumcision reduces heterosexual HIV infection rates in high-risk populations during penile-vaginal sex. There are differing perspectives on the prophylactic efficacy and cost effectiveness of circumcision in developed nations
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for evalu ...
. Circumcision plays a significant role in many of the world's cultures. When performed for religious reasons, it is most common among both Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
and Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
, among whom it is near-universal.
Potential regeneration
There are efforts by scientists to partially or fully regenerate the structures of the human penis. Patients who can benefit most from this field are those who have congenital defects, cancer, and injuries that have excised parts of theirgenitalia
A sex organ, also known as a reproductive organ, is a part of an organism that is involved in sexual reproduction. Sex organs constitute the primary sex characteristics of an organism. Sex organs are responsible for producing and transporting ...
. Some organizations which perform research into, or conduct regeneration procedures, include the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine and the United States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and superv ...
. The first successful penis allotransplant surgery was done in September 2005 in a military hospital in Guangzhou
Guangzhou, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Canton or Kwangchow, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Guangdong Provinces of China, province in South China, southern China. Located on the Pearl River about nor ...
, China. A man at 44 sustained an injury after an accident and his penis was severed; urination
Urination is the release of urine from the bladder through the urethra in Placentalia, placental mammals, or through the cloaca in other vertebrates. It is the urinary system's form of excretion. It is also known medically as micturition, v ...
became difficult as his urethra was partly blocked. A recently brain-dead man, aged 23, was selected for the transplant. Despite atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), malnutrition, poor nourishment, poor circulatory system, circulation, loss of hormone, ...
of blood vessels and nerves, the arteries
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
, veins
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal c ...
, nerves and the corpora spongiosa were successfully matched. But, on 19 September (after two weeks), the surgery was reversed because of a severe psychological
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ...
problem (rejection) by the recipient and his wife.
In 2009, researchers Chen, Eberli, Yoo and Atala have produced bioengineered penises and implanted them on rabbits. They were able to obtain erection
An erection (clinically: penile erection or penile tumescence) is a Physiology, physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, ...
and copulate, with 10 of 12 rabbits achieving ejaculation
Ejaculation is the discharge of semen (the ''ejaculate''; normally containing sperm) from the penis through the urethra. It is the final stage and natural objective of male sexual stimulation, and an essential component of natural conception. ...
. This study shows that in the future it could be possible to produce artificial penises for replacement surgeries or phalloplasties. In 2015, the world's first successful penis transplant took place in Cape Town
Cape Town is the legislature, legislative capital city, capital of South Africa. It is the country's oldest city and the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. Cape Town is the country's List of municipalities in South Africa, second-largest ...
, South Africa in a nine-hour operation performed by surgeons from Stellenbosch University
Stellenbosch University (SU) (, ) is a public research university situated in Stellenbosch, a town in the Western Cape province of South Africa. Stellenbosch is the oldest university in South Africa and the oldest extant university in Sub-Sahara ...
and Tygerberg Hospital. The 21-year-old recipient, who had been sexually active, had lost his penis in a botched circumcision at 18.
See also
* Buried penis * Castration anxiety * Dick joke *Dildo
A dildo is a sex toy, often explicitly phallic in appearance, intended for sexual penetration or other sexual activity during masturbation or with sex partners. Dildos are made from a number of materials. The shape and size are typically t ...
* Genital ulcer
* Crotch
In humans, the crotch is the bottom of the pelvis (the region of the body where the legs join the torso) and is the part of the body that includes the groin and genitals.
Etymology
''Crotch'' is derived from ''crutch''; it was first used in 1 ...
(in clothing) – a pouch-shaped area built to accommodate a penis and scrotum
* Penile enlargement
* Penis removal
* Phallic architecture
Phallic architecture consciously or unconsciously creates a symbolic representation of the human penis. Buildings intentionally or unintentionally resembling the human penis are a source of amusement to locals and tourists in various places around ...
* Phallus – an object or image that resembles a penis
* Preputioplasty
Preputioplasty or prepuce plasty, also known as limited dorsal slit with transverse closure, is a plastic surgical operation on the prepuce or foreskin of the penis, to widen a narrow non-retractile foreskin which cannot comfortably be drawn back ...
– an operation performed to facilitate retraction of the foreskin
* Stunt cock
A stunt cock is a substitute (sometimes prosthetic) penis that is used during filmmaking, typically in pornographic films. The stunt cock is typically filmed up close so as not to identify its bearer, the goal being to deceive the viewer into thin ...
– a substitute penis used for filmmaking
* Vulva
In mammals, the vulva (: vulvas or vulvae) comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female sex organ, genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, lab ...
– the external, visible structures of the human female genitalia
References
{{Authority control Human anatomy Human male reproductive system Mammal male reproductive system Men's health Penis Urinary system Sex organs