Horatius Cocles on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Publius Horatius Cocles was an officer in the army of the early
Publius Horatius Cocles was an officer in the army of the early
 In 509 BC, King
In 509 BC, King
 Horatius was awarded a crown for his valor (akin to a modern military decoration) and conducted into the city by a singing crowd joined by a grateful city. Horatius was now disabled and so could no longer serve in the army or hold public office, but he was provided "as much of the public land as he himself could plow around in one day with a yoke of oxen," and each citizen of Rome was obligated to give him one day's ration of food. He would also be honoured with a bronze statue in the
Horatius was awarded a crown for his valor (akin to a modern military decoration) and conducted into the city by a singing crowd joined by a grateful city. Horatius was now disabled and so could no longer serve in the army or hold public office, but he was provided "as much of the public land as he himself could plow around in one day with a yoke of oxen," and each citizen of Rome was obligated to give him one day's ration of food. He would also be honoured with a bronze statue in the
 Livy viewed the story as legendary, dubious of Horatius' fully armed swim, noting "though many missiles fell over him he swam across in safety to his friends, an act of daring more famous than credible with posterity."
T.J. Cornell deems these various accounts invented by "unscrupulous annalists" as "face-saving victories in the immediate aftermath of these defeats", insisting "The annalists of the first century BC are thus seen principally as entertainers...."
Livy viewed the story as legendary, dubious of Horatius' fully armed swim, noting "though many missiles fell over him he swam across in safety to his friends, an act of daring more famous than credible with posterity."
T.J. Cornell deems these various accounts invented by "unscrupulous annalists" as "face-saving victories in the immediate aftermath of these defeats", insisting "The annalists of the first century BC are thus seen principally as entertainers...."
 The story of the redoubtable Horatius at the Bridge began to be depicted in art during the Renaissance, but was never an especially popular theme. It tended to be shown by artists who favored recondite classical stories, and appear in the minor arts, such as
The story of the redoubtable Horatius at the Bridge began to be depicted in art during the Renaissance, but was never an especially popular theme. It tended to be shown by artists who favored recondite classical stories, and appear in the minor arts, such as
 Publius Horatius Cocles was an officer in the army of the early
Publius Horatius Cocles was an officer in the army of the early Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
who famously defended the Pons Sublicius from the invading army of Etruscan King Lars Porsena
Lars Porsena (or Porsenna; Etruscan: ) was an Etruscan king (lar) known for his war against the city of Rome. He ruled over the city of Clusium ( Etruscan: ; modern Chiusi). There are no established dates for his rule, but Roman sources often ...
of Clusium
Clusium ( grc-gre, Κλύσιον, ''Klýsion'', or , ''Kloúsion''; Umbrian:''Camars'') was an ancient city in Italy, one of several found at the site. The current municipality of Chiusi ( Tuscany) partly overlaps this Roman walled city. The R ...
in the late 6th century BC, during the war between Rome and Clusium. By defending the narrow end of the bridge, he and his companions were able to hold off the attacking army long enough to allow other Romans to destroy the bridge behind him, blocking the Etruscans' advance and saving the city.
Background
Horatius was a member of the ancient patrician house of theHoratii
In the ancient Roman legend of the kingdom era, the Horatii were triplet warriors who lived during the reign of Tullus Hostilius. The accounts of their epic clash with the Curiatii and the murder of their sister by Publius, the sole survivor ...
, celebrated in legend since the combat between the Horatii and the Curiatii in the time of Tullus Hostilius
Tullus Hostilius (r. 672–640 BC) was the legendary third king of Rome. He succeeded Numa Pompilius and was succeeded by Ancus Marcius. Unlike his predecessor, Tullus was known as a warlike king who according to the Roman Historian Livy, bel ...
, the third Roman king
The king of Rome ( la, rex Romae) was the ruler of the Roman Kingdom. According to legend, the first king of Rome was Romulus, who founded the city in 753 BC upon the Palatine Hill. Seven legendary kings are said to have ruled Rome until 509 BC ...
.Dionysius of Halicarnassus
Dionysius of Halicarnassus ( grc, Διονύσιος Ἀλεξάνδρου Ἁλικαρνασσεύς,
; – after 7 BC) was a Greek historian and teacher of rhetoric, who flourished during the reign of Emperor Augustus. His literary styl ...
, ''Romaike Archaiologia'', v. 24, 25. He was a nephew of the consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states throu ...
, Marcus Horatius Pulvillus, and is said to have obtained his agnomen
An ''agnomen'' (; plural: ''agnomina''), in the Roman naming convention, was a nickname, just as the '' cognomen'' was initially. However, the ''cognomina'' eventually became family names, so ''agnomina'' were needed to distinguish between sim ...
, ''Cocles'', meaning "one-eyed", because he lost an eye in the Battle of the Sublician Bridge. However, this may be a later elaboration, as the famous statue of Horatius, lame and one-eyed, which was still visible, though heavily weathered, in the time of Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
, was probably intended as a depiction of the god Vulcan, and only became identified with Horatius when its original subject was no longer recognizable.
Lars Porsena
Lars Porsena (or Porsenna; Etruscan: ) was an Etruscan king (lar) known for his war against the city of Rome. He ruled over the city of Clusium ( Etruscan: ; modern Chiusi). There are no established dates for his rule, but Roman sources often ...
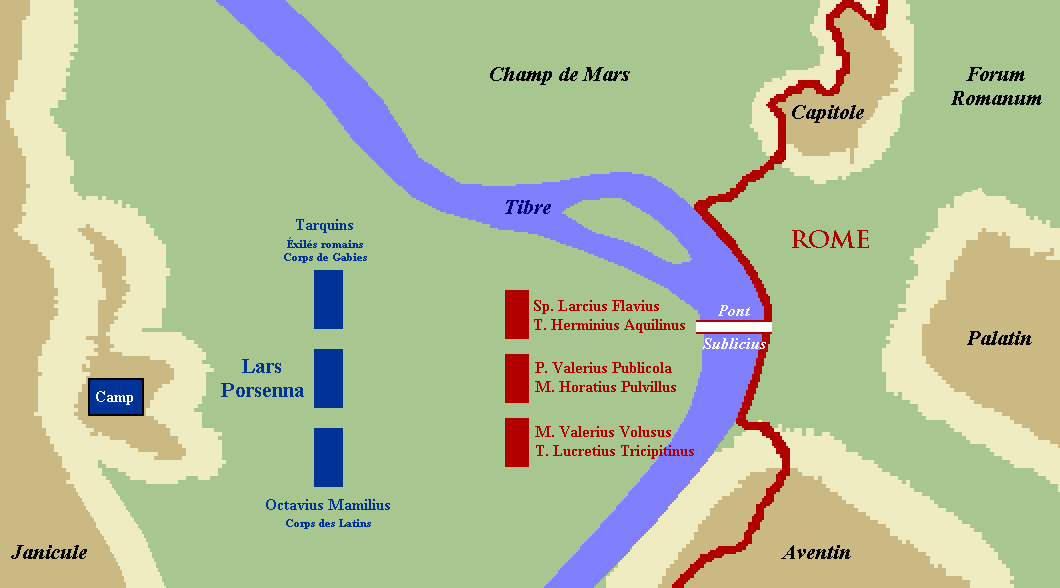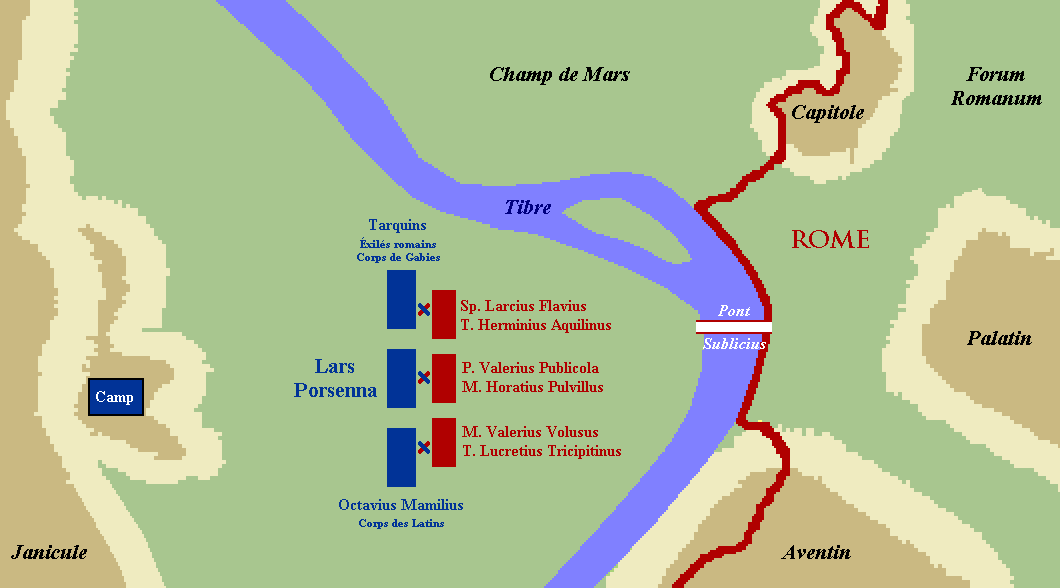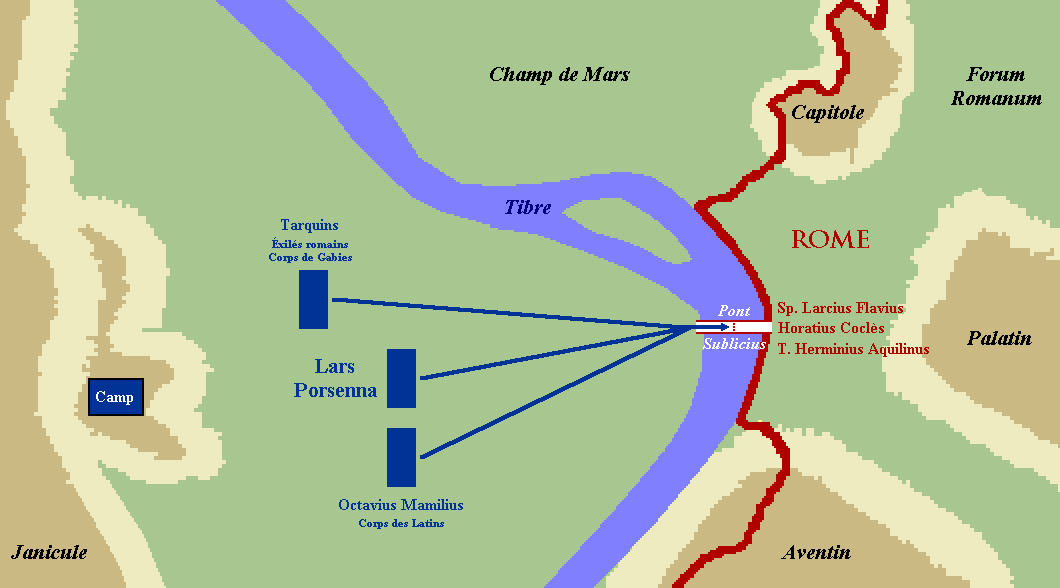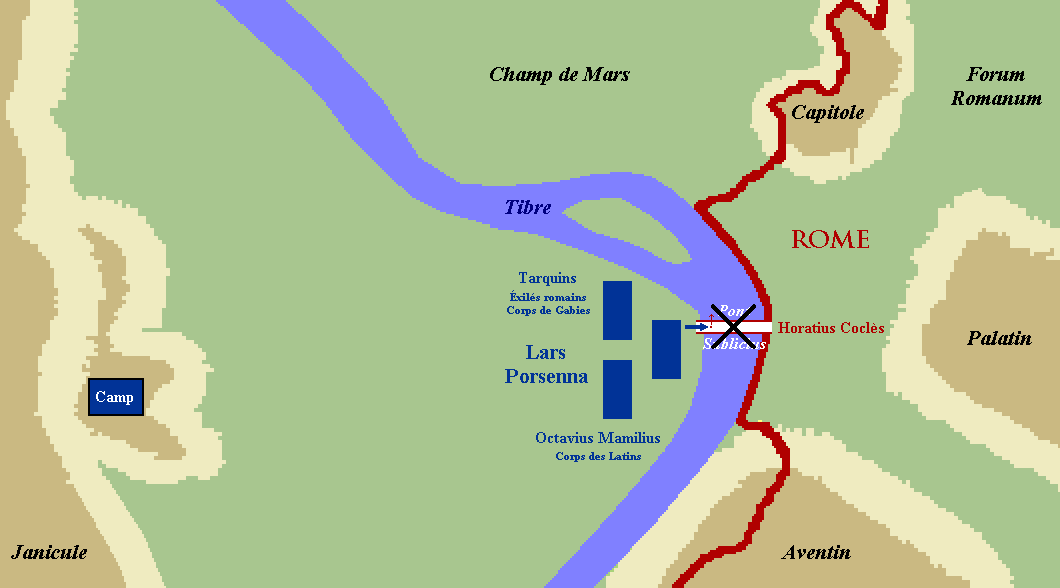
was at the head of an army that marched on Rome. Concentrating his forces on the Etruscan (west) side of the Tiber
The Tiber ( ; it, Tevere ; la, Tiberis) is the third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by th ...
, Porsena
Lars Porsena (or Porsenna; Etruscan: ) was an Etruscan king (lar) known for his war against the city of Rome. He ruled over the city of Clusium ( Etruscan: ; modern Chiusi). There are no established dates for his rule, but Roman sources often ...
assaulted Janiculum
The Janiculum (; it, Gianicolo ), occasionally the Janiculan Hill, is a hill in western Rome, Italy. Although it is the second-tallest hill (the tallest being Monte Mario) in the contemporary city of Rome, the Janiculum does not figure among t ...
hill and seized it and all its materiel from the terrified Roman guard. Porsena left an Etruscan garrison to hold it, then proceeded towards the Pons Sublicius, the only regional bridge across the Tiber. The Romans awaited in the Naevian Meadow between Porsena and the bridge. The Tarquins commanded the Etruscan left wing facing the Roman troops of Spurius Larcius
Spurius Larcius (surnamed Flavus or Rufus; 509–482 BC) was one of the leading men of the early Roman Republic, of which he was twice consul. However, his greatest fame was won as one of the defenders of the Sublician bridge against the army ...
and Titus Herminius. Octavius Mamilius commanded the Etruscan right wing consisting of rebel Latins; they faced Romans under Marcus Valerius Volusus
Marcus Valerius Volusus (or Volesus, sometimes referred to as M. Valerius Volusus Maximus) was a Roman consul with Publius Postumius Tubertus in 505 BC.
He was the son of Volesus Valerius and brother to Publius Valerius Publicola (consul in 50 ...
and Titus Lucretius Tricipitinus
Titus Lucretius Tricipitinus was a politician and military leader in the early days of the Roman Republic. Twice, in the years 508 and 504 BC, he was elected Roman Consul, alongside Publius Valerius Poplicola. Also a military leader, he was victo ...
. Porsena commanded the center, facing the two Roman consuls. Porsena had the Romans outnumbered and intended to intimidate them into retreat.
Battle ensued. The Etruscan right wing was successful in wounding Valerius and Lucretius, the commanders of the Roman left wing. After both were carried off the field, the Romans began to panic and ran for the bridge. The enemy pursued.
Horatius at the bridge
Three Romans now defended the Pons Sublicius; the right wing's commandersSpurius Larcius
Spurius Larcius (surnamed Flavus or Rufus; 509–482 BC) was one of the leading men of the early Roman Republic, of which he was twice consul. However, his greatest fame was won as one of the defenders of the Sublician bridge against the army ...
and Titus Herminius Aquilinus, plus Publius Horatius Cocles, a junior officer "on guard at the bridge when he saw the Janiculum taken by a sudden assault and the enemy rushing down from it to the river ...."Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
, ''History of Rome
The history of Rome includes the history of the city of Rome as well as the civilisation of ancient Rome. Roman history has been influential on the modern world, especially in the history of the Catholic Church, and Roman law has influenced ...
'', ii. 10.
The three defenders withstood sword and missile attacks until the Roman troops had all crossed.
Livy's briefer and more skeptical account tells of no battle, only that Horatius' "own men, a panic-struck mob, were deserting their posts and throwing away their arms"; however, Horatius' courage manages to shame the two veteran commanders, Herminius and Lartius, to assist him momentarily with his defense of the bridge.
Dionysius' account explains, "Herminius and Lartius, their defensive arms being now rendered useless by the continual blows they received, began to retreat gradually." They order Horatius to retreat with them, but he stood his ground. Understanding the threat to Rome if the enemy were to cross the river, he ordered his men to destroy the bridge. The enemy was shocked not only by Horatius' suicidal last stand, but also by his decision to use a pile of bodies as a shield wall. Horatius was struck by enemy missiles many times including a spear in the buttocks. Hearing word from his men they'd torn up the bridge, he "leaped fully armed into the river and swimming across ... he emerged upon the shore without having lost any of his weapons."
Livy's version has him uttering this prayer to Father Tiber: "Tiberinus, holy father, I pray thee to receive into thy propitious stream these arms and this thy warrior."
comitium
The Comitium ( it, Comizio) was the original open-air public meeting space of Ancient Rome, and had major religious and prophetic significance. The name comes from the Latin word for "assembly". The Comitium location at the northwest corner of th ...
.
Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail.
Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed ...
' account uses Horatius as an example of the men who have "devoted themselves to inevitable death...to save the lives of other citizens.... threw himself into the river with his armor, and there lost his life as he had designed."
Aftermath
Horatius' defense stymied Lars Porsena's direct assault on the city walls, forcing him into a siege. The siege would conclude with a peace treaty, leaving Rome intact.Skeptical points of view
The story of Horatius at the Bridge appears in many ancient sources, includingPlutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for hi ...
, Dionysius of Halicarnassus
Dionysius of Halicarnassus ( grc, Διονύσιος Ἀλεξάνδρου Ἁλικαρνασσεύς,
; – after 7 BC) was a Greek historian and teacher of rhetoric, who flourished during the reign of Emperor Augustus. His literary styl ...
, and Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
. Florus tacitly acknowledges the extraordinary nature of the story: "It was on this occasion that those three prodigies and marvels of Rome made their appearance, Horatius, Mucius and Cloelia, who, were they not recorded in our annals, would seem fabulous characters at the present day." Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
notes in passing that "when omewas surrendered, ars Porsenadid not violate the seat of Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
" (Rome's most important temple). This could be understood to mean that Rome surrendered during or after this battle.Later uses of the theme
 The story of the redoubtable Horatius at the Bridge began to be depicted in art during the Renaissance, but was never an especially popular theme. It tended to be shown by artists who favored recondite classical stories, and appear in the minor arts, such as
The story of the redoubtable Horatius at the Bridge began to be depicted in art during the Renaissance, but was never an especially popular theme. It tended to be shown by artists who favored recondite classical stories, and appear in the minor arts, such as plaquette
A plaquette (, ''small plaque'') is a small low relief sculpture in bronze or other materials. These were popular in the Italian Renaissance and later. They may be commemorative, but especially in the Renaissance and Mannerist periods were of ...
s and maiolica
Maiolica is tin-glazed pottery decorated in colours on a white background. Italian maiolica dating from the Renaissance period is the most renowned. When depicting historical and mythical scenes, these works were known as ''istoriato'' wares ...
.
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
, after the battle of Klausen, nicknamed General Thomas-Alexandre Dumas "The Horatius Cocles of Tyrol" for his solo defense of a bridge over the River Eisack.
The story of "Horatius at the Bridge" is retold in verse in the poem " Horatius" in ''Lays of Ancient Rome
''Lays of Ancient Rome'' is an 1842 collection of narrative poems, or lays, by Thomas Babington Macaulay. Four of these recount heroic episodes from early Roman history with strong dramatic and tragic themes, giving the collection its name. M ...
'' by Thomas Babington Macaulay
Thomas Babington Macaulay, 1st Baron Macaulay, (; 25 October 1800 – 28 December 1859) was a British historian and Whig politician, who served as the Secretary at War between 1839 and 1841, and as the Paymaster-General between 1846 and 1 ...
, which enjoyed great popularity in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century. The details of the poem often vary from the traditional tale by poetic license. Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
wrote that while he "stagnated in the lowest form" at Harrow, he gained a prize open to the whole school by reciting the whole "twelve hundred lines" of "Horatius".Winston Churchill, ''My Early Life'', chapter 2. A biographical film about Churchill, '' Into the Storm'' (2009), begins with the much older Churchill reciting from "Horatius": "And how can man die better, than facing fearful odds, for the ashes of his fathers, and the temples of his gods." Later in the film, the same verses feature prominently in a nostalgic and morose address Churchill delivers to his war cabinet. Churchill also recites from "Horatius" in a scene from the biographical film ''Darkest Hour'', and these lines occur in numerous works of fiction.
" A Nation Once Again" was a popular Irish rebel song, written in the early to mid-1840s by Thomas Osborne Davis (1814–1845) in furtherance of Irish nationalism. First published in ''The Nation'' on 13 July 1844 (two years after Macaulay's ''Horatius''), the first verse refers to the heroism of "ancient freemen, For Greece and Rome who bravely stood, three hundred men and three men", references the three hundred Spartans at Thermopylae
Thermopylae (; Ancient Greek and Katharevousa: (''Thermopylai'') , Demotic Greek (Greek): , (''Thermopyles'') ; "hot gates") is a place in Greece where a narrow coastal passage existed in antiquity. It derives its name from its hot sulphur ...
, and the three defenders at the Pons Sublicius.
Horatius figures prominently in Jessie Pope's 1915 poem "The Longest Odds" about the exploits of a highlander
Highlander may refer to:
Regional cultures
* Gorals (lit. ''Highlanders''), a culture in southern Poland and northern Slovakia
* Hill people, who live in hills and mountains
* Merina people, an ethnic group from the central plateau of Madagasca ...
who single-handedly clears an entire German trench before being killed. His actions are likewise compared to both the Spartans and the Roman defenders.
The story of Horatius is echoed in a poem about Sven Dufva, "The Tales of Ensign Stål
''The Tales of Ensign Stål'' (Swedish language, Swedish original title: , fi, Vänrikki Stoolin tarinat, or year 2007 translation ) is an epic poem written in Swedish by the Finland-Swedish author Johan Ludvig Runeberg, the national poet of Fin ...
," recounting the story of a simple-minded but honest and dutiful soldier in the Finnish War
The Finnish War ( sv, Finska kriget, russian: Финляндская война, fi, Suomen sota) was fought between the Kingdom of Sweden and the Russian Empire from 21 February 1808 to 17 September 1809 as part of the Napoleonic Wars. As a re ...
who heroically holds back an attack by Russian forces at a bridge by himself, but dies in the effort.
In the 2013 film '' Oblivion'', the protagonist paraphrases Macaulay's "Horatius", and quotes many parts of the poem before confronting an overwhelming enemy.
See also
*Horatia gens
The gens Horatia was a patrician family at ancient Rome. In legend, the gens dates back to the time of Tullus Hostilius, the third King of Rome. One of its members, Marcus Horatius Pulvillus, was consul ''suffectus'' in 509 BC, the first year o ...
* Vulcanal
The Shrine of Vulcan ( it, Volcanale), or Vulcanal, or Volcanal, was an 8th-century BC sacred precinct on the future site of the Roman Forum in Rome, modern Italy. Dedicated to Vulcan (mythology), Vulcan, the Roman god of fire, it was tradition ...
, a statue in honour of Horatius Cocles was said to have been set up here.
Footnotes
References
Bibliography
*Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail.
Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed ...
, '' Historiae'' (The Histories).
* Dionysius of Halicarnassus
Dionysius of Halicarnassus ( grc, Διονύσιος Ἀλεξάνδρου Ἁλικαρνασσεύς,
; – after 7 BC) was a Greek historian and teacher of rhetoric, who flourished during the reign of Emperor Augustus. His literary styl ...
, ''Romaike Archaiologia'' (Roman Antiquities).
* Titus Livius (Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
), ''History of Rome
The history of Rome includes the history of the city of Rome as well as the civilisation of ancient Rome. Roman history has been influential on the modern world, especially in the history of the Catholic Church, and Roman law has influenced ...
''.
* Gaius Plinius Secundus (Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
), '' Historia Naturalis'' (Natural History).
* Publius Cornelius Tacitus, '' Historiae''.
* Lucius Annaeus Florus, ''Epitome de T. Livio Bellorum Omnium Annorum DCC'' (Epitome of Livy: All the Wars of Seven Hundred Years).
* Michael Grant, ''Roman Myths'', Dorset Press (1971).
* T.J. Cornell, "The Formation of the Historical Tradition of Early Rome", in ''Past Perspectives: Studies in Greek and Roman Historical Writing'', T.J. Cornell, I.S. Moxon, John Woodman, eds., Cambridge University Press (1986).
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cocles, Horatius Ancient Roman soldiers Characters in Roman mythology 6th-century BC Romans Cocles Last stands