Holy Thursday on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Maundy Thursday or Holy Thursday (also known as Great and Holy Thursday, Holy and Great Thursday, Covenant Thursday, Sheer Thursday, and Thursday of Mysteries, among other names) is the day during
 Use of the names "Maundy Thursday", "Holy Thursday", and others is not evenly distributed. The generally accepted name for the day varies according to geographical area and religious affiliation. Thus, although in England "Maundy Thursday" is the normal term, the term "Holy Thursday" is more commonly used in Ireland, Scotland, Canada and the United States, and is the official name used by the
Use of the names "Maundy Thursday", "Holy Thursday", and others is not evenly distributed. The generally accepted name for the day varies according to geographical area and religious affiliation. Thus, although in England "Maundy Thursday" is the normal term, the term "Holy Thursday" is more commonly used in Ireland, Scotland, Canada and the United States, and is the official name used by the
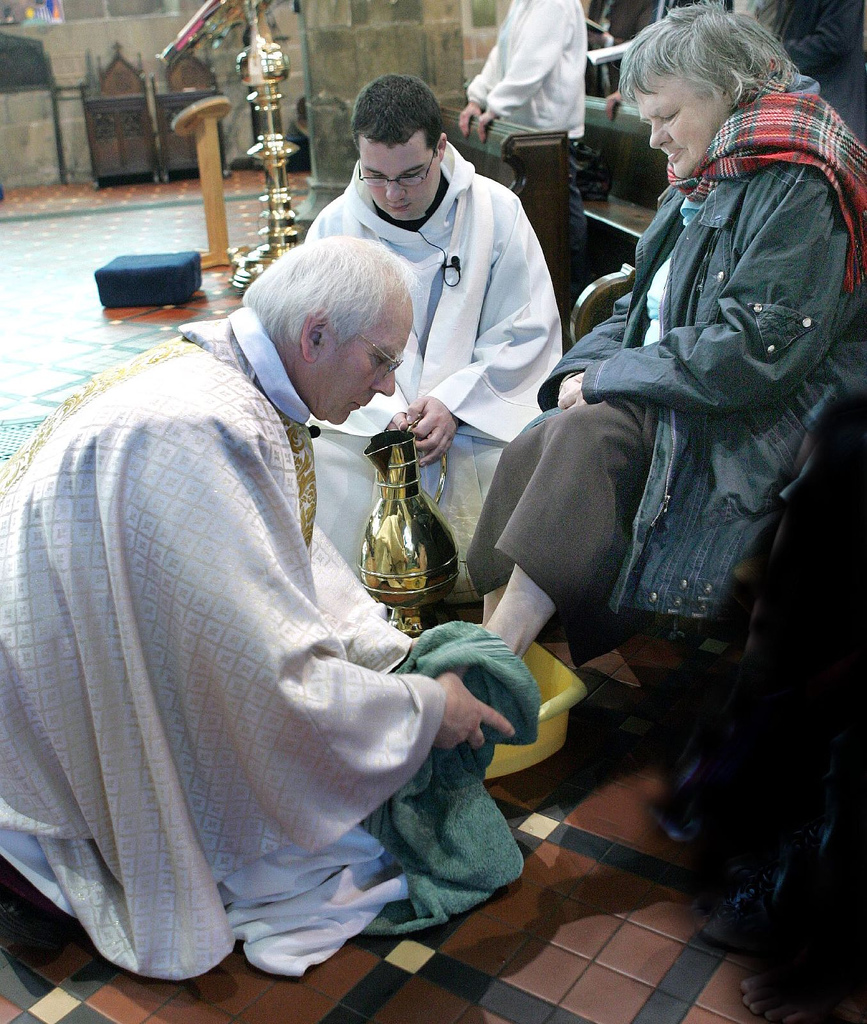

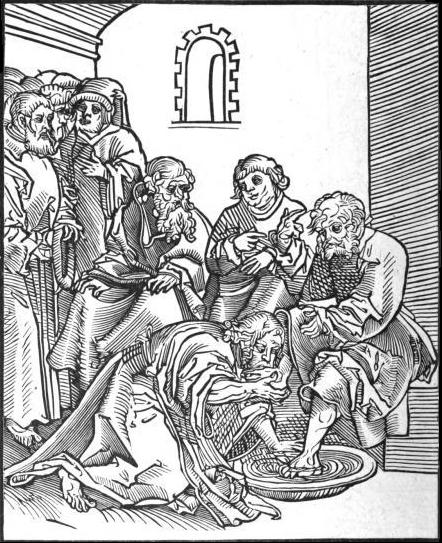
 '' Maundy'' is the name of the Christian rite of footwashing, which traditionally occurs during Maundy Thursday church services.
The English word '' maundy'' in the name for the day is derived through
'' Maundy'' is the name of the Christian rite of footwashing, which traditionally occurs during Maundy Thursday church services.
The English word '' maundy'' in the name for the day is derived through
 The Chrism Mass is a religious service held in Roman Catholicism, Lutheranism and Anglicanism.
Maundy Thursday is notable for being the day on which the Chrism Mass is celebrated in each
The Chrism Mass is a religious service held in Roman Catholicism, Lutheranism and Anglicanism.
Maundy Thursday is notable for being the day on which the Chrism Mass is celebrated in each
 In the
In the  In the evening, after the Liturgy, all of the hangings and
In the evening, after the Liturgy, all of the hangings and


 * If statues and crucifixes have been covered during
* If statues and crucifixes have been covered during
 Maundy Thursday is a public holiday in most countries that were part of the
Maundy Thursday is a public holiday in most countries that were part of the
File:Levoca Last Supper.jpg, "The Last Supper" – museum copy of
Pope Francis, "Homily for Chrism Mass"
''News.va'', March 28, 2013.
Cosentino, Tony. "Chrism Mass: its Symbols and Their Meaning"
Diocese of St. Catherine's, Ontario. {{Authority control Thursday observances Eastern Orthodox liturgical days Holy Week March observances April observances Public holidays in Greece Greek traditions Public holidays in Argentina Public holidays in Colombia Public holidays in Costa Rica Public holidays in El Salvador Public holidays in Guatemala Public holidays in Honduras Public holidays in Mexico Public holidays in Nicaragua Public holidays in Paraguay Public holidays in Peru Public holidays in the Philippines Public holidays in Spain Public holidays in Venezuela Public holidays in Iceland Public holidays in Denmark Public holidays in Norway
Holy Week
Holy Week ( la, Hebdomada Sancta or , ; grc, Ἁγία καὶ Μεγάλη Ἑβδομάς, translit=Hagia kai Megale Hebdomas, lit=Holy and Great Week) is the most sacred week in the liturgical year in Christianity. In Eastern Churches, w ...
that commemorates the Washing of the Feet (Maundy) and Last Supper
Image:The Last Supper - Leonardo Da Vinci - High Resolution 32x16.jpg, 400px, alt=''The Last Supper'' by Leonardo da Vinci - Clickable Image, Depictions of the Last Supper in Christian art have been undertaken by artistic masters for centuries, ...
of Jesus Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
with the Apostles, as described in the canonical gospels
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words a ...
.
It is the fifth day of Holy Week, preceded by Holy Wednesday and followed by Good Friday
Good Friday is a Christian holiday commemorating the crucifixion of Jesus and his death at Calvary. It is observed during Holy Week as part of the Paschal Triduum. It is also known as Holy Friday, Great Friday, Great and Holy Friday (also Holy ...
. "Maundy" comes from the Latin word ''mandatum'', or commandment, reflecting Jesus' words "I give you a new commandment."
The day comes always between March 19 and April 22, inclusive, and will vary according to whether the Gregorian calendar
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It was introduced in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years d ...
or the Julian calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandri ...
is used. Eastern churches generally use the Julian system.
Maundy Thursday initiates the Paschal Triduum, the period which commemorates the passion, death
Death is the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain an organism. For organisms with a brain, death can also be defined as the irreversible cessation of functioning of the whole brain, including brainstem, and brain ...
, and resurrection of Jesus
The resurrection of Jesus ( grc-x-biblical, ἀνάστασις τοῦ Ἰησοῦ) is the Christian belief that God raised Jesus on the third day after his crucifixion, starting – or restoring – his exalted life as Christ and Lo ...
; this period includes Good Friday and Holy Saturday, and ends on the evening of Easter Sunday. The Mass of the Lord's Supper or service of worship is normally celebrated in the evening, when Friday begins according to Jewish tradition, as the Last Supper was held on the feast of Passover
Passover, also called Pesach (; ), is a major Jewish holiday that celebrates the Biblical story of the Israelites escape from slavery in Egypt, which occurs on the 15th day of the Hebrew month of Nisan, the first month of Aviv, or spring. ...
, according to the three Synoptic Gospels
The gospels of Matthew, Mark, and Luke are referred to as the synoptic Gospels because they include many of the same stories, often in a similar sequence and in similar or sometimes identical wording. They stand in contrast to John, whose ...
.
Names
 Use of the names "Maundy Thursday", "Holy Thursday", and others is not evenly distributed. The generally accepted name for the day varies according to geographical area and religious affiliation. Thus, although in England "Maundy Thursday" is the normal term, the term "Holy Thursday" is more commonly used in Ireland, Scotland, Canada and the United States, and is the official name used by the
Use of the names "Maundy Thursday", "Holy Thursday", and others is not evenly distributed. The generally accepted name for the day varies according to geographical area and religious affiliation. Thus, although in England "Maundy Thursday" is the normal term, the term "Holy Thursday" is more commonly used in Ireland, Scotland, Canada and the United States, and is the official name used by the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
in English.
The ''Book of Common Prayer
The ''Book of Common Prayer'' (BCP) is the name given to a number of related prayer books used in the Anglican Communion and by other Christian churches historically related to Anglicanism. The original book, published in 1549 in the reign ...
'' of the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Brit ...
, which is the mother Church of the Anglican Communion
The Anglican Communion is the third largest Christian communion after the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches. Founded in 1867 in London, the communion has more than 85 million members within the Church of England and other ...
, uses the name "Maundy Thursday" for this observance. The corresponding publication of the US Episcopal Church, which is another province of the Anglican Communion, also refers to the Thursday before Easter as "Maundy Thursday". Throughout the Anglican Communion, the term "Holy Thursday" is a synonym for Ascension Day
The Solemnity of the Ascension of Jesus Christ, also called Ascension Day, Ascension Thursday, or sometimes Holy Thursday, commemorates the Christian belief of the bodily Ascension of Jesus into heaven. It is one of the ecumenical (i.e., shared b ...
.
The Roman Rite
The Roman Rite ( la, Ritus Romanus) is the primary liturgical rite of the Latin Church, the largest of the ''sui iuris'' particular churches that comprise the Catholic Church. It developed in the Latin language in the city of Rome and, while di ...
of the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
uses the name "Holy Thursday" in its modern English-language liturgical books. The Latin books use the name ''Feria quinta in Cœna Domini'' ("Thursday of the Supper of the Lord"), along with Maundy Thursday as the English name, as given in ''The Saint Andrew Daily Missal''. The personal ordinariate
A personal ordinariate for former Anglicans, shortened as personal ordinariate or Anglican ordinariate,"...the liturgies approved for the Anglican ordinariates..." "Bishop Stephen Lopes of the Anglican Ordinariate of the Chair of St Peter..." i ...
s in the Catholic Church, which have an Anglican patrimony, retain the traditional English term "Maundy Thursday", however. An article in the 1911 ''Catholic Encyclopedia
The ''Catholic Encyclopedia: An International Work of Reference on the Constitution, Doctrine, Discipline, and History of the Catholic Church'' (also referred to as the ''Old Catholic Encyclopedia'' and the ''Original Catholic Encyclopedia'') i ...
'' used the term "Maundy Thursday", and some Catholic writers use the same term either primarily, or alternatively.
The Methodist '' Book of Worship for Church and Home'' (1965) uses the term "Maundy Thursday"; the '' Book of Worship'' (1992) uses the term "Holy Thursday", and other official sources of the United Methodist Church
The United Methodist Church (UMC) is a worldwide mainline Protestant denomination based in the United States, and a major part of Methodism. In the 19th century, its main predecessor, the Methodist Episcopal Church, was a leader in evangelica ...
use both "Maundy Thursday" and "Holy Thursday".
Both names are used by other Christian denominations
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ� ...
as well, including the Lutheran Church
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
, and certain Reformed Church
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Cal ...
es. Certain Presbyterian Church
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their nam ...
es use the term "Maundy Thursday" to refer to the holy day in their official sources.
In the Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops via ...
, the name for the holy day is, in the Byzantine Rite
The Byzantine Rite, also known as the Greek Rite or the Rite of Constantinople, identifies the wide range of cultural, liturgical, and canonical practices that developed in the Eastern Christian Church of Constantinople.
The canonical hours a ...
, "Great and Holy Thursday" or "Holy Thursday", and in Western Rite Orthodoxy
Western Rite Orthodoxy, also called Western Orthodoxy or the Orthodox Western Rite, are congregations within the Eastern Orthodox tradition which perform their liturgy in Western forms.
Besides altered versions of the Tridentine Mass, congrega ...
"Maundy Thursday", "Holy Thursday" or both. The Coptic Orthodox Church
The Coptic Orthodox Church ( cop, Ϯⲉⲕ̀ⲕⲗⲏⲥⲓⲁ ⲛ̀ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ ⲛ̀ⲟⲣⲑⲟⲇⲟⲝⲟⲥ, translit=Ti.eklyseya en.remenkimi en.orthodoxos, lit=the Egyptian Orthodox Church; ar, الكنيسة القبطي� ...
uses the term "Covenant Thursday" or "Thursday of the Covenant".
In the Maronite Church
The Maronite Church is an Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern Catholic ''sui iuris'' particular church in full communion with the pope and the worldwide Catholic Church, with self-governance under the Code of Canons of the Eastern Churches. Th ...
and the Syriac Orthodox Church
, native_name_lang = syc
, image = St_George_Syriac_orthodox_church_in_Damascus.jpg
, imagewidth = 250
, alt = Cathedral of Saint George
, caption = Cathedral of Saint George, Damascus ...
, the name is "Thursday of Mysteries".
"Maundy Thursday" is the official name of the day in the civil legislation of England and the Philippines.
The day has also been known in English as ''Shere Thursday'' (also spelled ''Sheer Thursday''), from the word ''shere'' (meaning "clean" or "bright"). This name might refer to the act of cleaning, or to the fact that churches would switch liturgical colors
Liturgical colours are specific colours used for vestments and hangings within the context of Christian liturgy. The symbolism of violet, blue, white, green, red, gold, black, rose and other colours may serve to underline moods appropriate to ...
from the dark tones of Lent
Lent ( la, Quadragesima, 'Fortieth') is a solemn religious moveable feast#Lent, observance in the liturgical calendar commemorating the 40 days Jesus spent fasting in the desert and enduring Temptation of Jesus, temptation by Satan, according ...
, or because it was customary to shear the beard on that day, or for a combination of reasons. This name has cognates in the Nordic languages, such as Danish ''skærtorsdag'', Swedish ''skärtorsdag'', Norwegian ''skjærtorsdag'', Faroese ''skírhósdagur'' and ''skírisdagur'', Icelandic ''skírdagur'', and Finnish ''kiirastorstai''.
Derivation of the name "Maundy"

 '' Maundy'' is the name of the Christian rite of footwashing, which traditionally occurs during Maundy Thursday church services.
The English word '' maundy'' in the name for the day is derived through
'' Maundy'' is the name of the Christian rite of footwashing, which traditionally occurs during Maundy Thursday church services.
The English word '' maundy'' in the name for the day is derived through Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old Englis ...
and Old French
Old French (, , ; Modern French: ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France from approximately the 8th to the 14th centuries. Rather than a unified language, Old French was a linkage of Romance dialects, mutually intel ...
''mandé'', from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
''mandatum'' (also the origin of the English word "mandate"), the first word of the phrase "''Mandatum novum do vobis ut diligatis invicem sicut dilexi vos''" ("A new commandment I give unto you: That you love one another, as I have loved you, that you also love one another.") This statement by Jesus in chapter 13 of the Gospel of John by which Jesus explained to the Apostles the significance of his action of washing their feet. The phrase is used as the antiphon
An antiphon ( Greek ἀντίφωνον, ἀντί "opposite" and φωνή "voice") is a short chant in Christian ritual, sung as a refrain. The texts of antiphons are the Psalms. Their form was favored by St Ambrose and they feature prominentl ...
sung in the Roman Rite
The Roman Rite ( la, Ritus Romanus) is the primary liturgical rite of the Latin Church, the largest of the ''sui iuris'' particular churches that comprise the Catholic Church. It developed in the Latin language in the city of Rome and, while di ...
during the Maundy (Ecclesiastical Latin
Latin, also called Church Latin or Liturgical Latin, is a form of Latin developed to discuss Christian thought in Late Antiquity and used in Christian liturgy, theology, and church administration down to the present day, especially in the Cath ...
: "Mandatum") ceremony of the washing of the feet, which may be held during Mass or as a separate event, during which a priest or bishop (representing Christ) ceremonially washes the feet of others, typically 12 persons chosen as a cross-section of the community. In 2016, it was announced that the Roman Missal
The Roman Missal ( la, Missale Romanum) is the title of several missals used in the celebration of the Roman Rite. Along with other liturgical books of the Roman Rite, the Roman Missal contains the texts and rubrics for the celebration of th ...
had been revised to allow women to participate as part of the 12 in the Mandatum; previously, only males partook of the rite.
Others theorize that the English name "Maundy Thursday" arose from "maundsor baskets" or "maundy purses" of alms which the king of England distributed to certain poor at Whitehall before attending Mass on that day. Thus, "maund" is connected to the Latin ''mendicare'', and French ''mendier'', to beg. A source from the Shepherd of the Springs, Lutheran Church likewise states that, if the name was derived from the Latin ''mandatum'', we would call the day Mandy Thursday, or Mandate Thursday, or even Mandatum Thursday; and that the term "Maundy" comes in fact from the Latin ''mendicare'', Old French ''mendier'', and English ''maund'', which as a verb means to beg and as a noun refers to a small basket held out by maunders as they maunded. Other sources reject this etymology.
Services
Western Christianity
Services
Maundy Thursday celebrations in theUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
(also called Royal Maundy
Royal Maundy is a religious service in the Church of England held on Maundy Thursday, the day before Good Friday. At the service, the British monarch or a royal official ceremonially distributes small silver coins known as "Maundy money" (legal ...
) today involve the Monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority ...
offering "alms" to deserving senior citizens – one man and one woman for each year of the sovereign's age. These coins, known as Maundy money
Royal Maundy is a religious service in the Church of England held on Maundy Thursday, the day before Good Friday. At the service, the British monarch or a royal official ceremonially distributes small silver coins known as "Maundy money" (lega ...
or Royal Maundy, are distributed in red and white purses, and is a custom dating back to King Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vassal o ...
. The red purse contains regular currency and is given in place of food and clothing; the white purse has money in the amount of one penny for each year of the Sovereign's age. Since 1822, rather than ordinary money, the Sovereign gives out Maundy coins, which are specially minted 1, 2, 3 and 4 penny pieces, and are legal tender. The service at which this takes place rotates around English and Welsh churches, though in 2008 it took place for the first time in Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label=Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is #Descriptions, variously described as ...
at Armagh Cathedral. Until the death of King James II, the Monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority ...
would also wash the feet of the selected poor people. There is an old sketch, done from life, of Queen Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
Eli ...
washing people's feet on Maundy Thursday.
With Maundy Thursday commemorating the Last Supper
Image:The Last Supper - Leonardo Da Vinci - High Resolution 32x16.jpg, 400px, alt=''The Last Supper'' by Leonardo da Vinci - Clickable Image, Depictions of the Last Supper in Christian art have been undertaken by artistic masters for centuries, ...
, Christian denominations who observe this day universally celebrate the sacrament
A sacrament is a Christian rite that is recognized as being particularly important and significant. There are various views on the existence and meaning of such rites. Many Christians consider the sacraments to be a visible symbol of the rea ...
of Holy Communion
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instituted ...
, which they teach was instituted by Jesus on this night.
The Maundy (washing of the feet) is practised among many Christian groups on Maundy Thursday, including the Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of t ...
/Protestant Episcopal
The Episcopal Church, based in the United States with additional dioceses elsewhere, is a member church of the worldwide Anglican Communion. It is a mainline Protestant denomination and is divided into nine provinces. The presiding bishop of ...
, Armenian, Ethiopian
Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of Ethiopia, as well as the global diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighboring Eritrea and other parts of ...
, Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched ...
, Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's ...
, Eastern Catholic
The Eastern Catholic Churches or Oriental Catholic Churches, also called the Eastern-Rite Catholic Churches, Eastern Rite Catholicism, or simply the Eastern Churches, are 23 Eastern Christian autonomous (''sui iuris'') particular churches of ...
, Schwarzenau (German Baptist) Brethren, Church of the Brethren
The Church of the Brethren is an Anabaptist Christian denomination in the Schwarzenau Brethren (german: link=no, Schwarzenauer Neutäufer "Schwarzenau New Baptists") tradition that was organized in 1708 by Alexander Mack in Schwarzenau, Germ ...
, Mennonite
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the R ...
, Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their n ...
and Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
traditions.
In the Catholic Church and in some Anglican churches, the Mass of the Lord's Supper begins as usual, but the Gloria
Gloria may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music Christian liturgy and music
* Gloria in excelsis Deo, the Greater Doxology, a hymn of praise
* Gloria Patri, the Lesser Doxology, a short hymn of praise
** Gloria (Handel)
** Gloria (Jenkins) ...
is accompanied by the ringing of church bell
A church bell in Christian architecture is a bell which is rung in a church for a variety of religious purposes, and can be heard outside the building. Traditionally they are used to call worshippers to the church for a communal service, and to ...
s, which are then silent until the Easter Vigil. After the homily the washing of feet may be performed. The Blessed Sacrament
The Blessed Sacrament, also Most Blessed Sacrament, is a devotional name to refer to the body and blood of Christ in the form of consecrated sacramental bread and wine at a celebration of the Eucharist. The term is used in the Latin Church of th ...
remains exposed, at least in the Catholic Mass, until the service concludes with a procession
A procession is an organized body of people walking in a formal or ceremonial manner.
History
Processions have in all peoples and at all times been a natural form of public celebration, as forming an orderly and impressive ceremony. Religious ...
taking it to the place of reposition. The altar is later stripped bare, as are all other altars in the church except the Altar of Repose. In pre-1970 editions, the Roman Missal
The Roman Missal ( la, Missale Romanum) is the title of several missals used in the celebration of the Roman Rite. Along with other liturgical books of the Roman Rite, the Roman Missal contains the texts and rubrics for the celebration of th ...
envisages this being done ceremonially, to the accompaniment of , a practice which continues in Anglican churches of Anglo-Catholic churchmanship
Churchmanship (or churchpersonship; or tradition in most official contexts) is a way of talking about and labelling different tendencies, parties, or schools of thought within the Church of England and the sister churches of the Anglican Commu ...
. In other Christian denominations
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ� ...
, such as the Lutheran Church or Methodist Church, the stripping of the altar and other items on the chancel
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may terminate in an apse.
...
also occurs, as a preparation for the somber Good Friday
Good Friday is a Christian holiday commemorating the crucifixion of Jesus and his death at Calvary. It is observed during Holy Week as part of the Paschal Triduum. It is also known as Holy Friday, Great Friday, Great and Holy Friday (also Holy ...
service.
Chrism Mass
 The Chrism Mass is a religious service held in Roman Catholicism, Lutheranism and Anglicanism.
Maundy Thursday is notable for being the day on which the Chrism Mass is celebrated in each
The Chrism Mass is a religious service held in Roman Catholicism, Lutheranism and Anglicanism.
Maundy Thursday is notable for being the day on which the Chrism Mass is celebrated in each diocese
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associ ...
. Usually held in the diocesan cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the ''cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominations ...
, it is generally held on the morning of Maundy Thursday, but may in some dioceses take place on another day during Holy Week. It is often the largest annual gathering of clergy and faithful held in most dioceses. The Mass is a celebration of the institution of the priesthood. During the Mass, those present are called to renew their baptismal promises; priests/ministers and deacons also reaffirm their ministry by renewing the promises made at their ordination. The Mass takes its name from the blessing of the holy oils used in the sacraments throughout the year, which are then given to priests to take back to their parishes.
The service is a 1967 restoration of the rite recorded in the early 200s by the historian Hippolytus who writes of a ceremony taking place during the Easter Vigil at which two holy oils were blessed and one was consecrated. In the fifth century, the ceremony of the oils was transferred from the Holy Saturday Vigil to Holy Thursday during a special Mass for that purpose, distinct from the Mass of the Lord's Supper. In the decree renewing this rite Pope Paul VI
Pope Paul VI ( la, Paulus VI; it, Paolo VI; born Giovanni Battista Enrico Antonio Maria Montini, ; 26 September 18976 August 1978) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City, Vatican City State from 21 June 1963 to his ...
said, "The Chrism Mass is one of the principal expressions of the fullness of the bishop’s priesthood and signifies the closeness of the priests with him."
The Holy Oils are:
* Chrism
Chrism, also called myrrh, ''myron'', holy anointing oil, and consecrated oil, is a consecrated oil used in the Anglican, Assyrian, Catholic, Nordic Lutheran, Old Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and Latter Day Saint churches in th ...
– used in the sacraments of Baptism
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost ...
, Confirmation
In Christian denominations that practice infant baptism, confirmation is seen as the sealing of the covenant created in baptism. Those being confirmed are known as confirmands. For adults, it is an affirmation of belief. It involves laying on ...
and Holy Orders, as well as for the consecration of altars and the dedication of churches.
* the oil of catechumens – also used in the sacrament of Baptism, and
* the oil of the sick – used in the rite of the Anointing of the Sick
The oil of the catechumens and chrism are used on the upcoming Holy Saturday at the Easter Vigil, for the baptism
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost ...
and confirmation
In Christian denominations that practice infant baptism, confirmation is seen as the sealing of the covenant created in baptism. Those being confirmed are known as confirmands. For adults, it is an affirmation of belief. It involves laying on ...
of those entering the church. While the Oil of the Catechumens and the Oil of the Sick, are simply "blessed," the Sacred Chrism is "consecrated,". Holy chrism is a mixture of olive oil and balsam, an aromatic resin. Balsam is poured into the oil, which gives it a sweet smell intended to remind those who encounter it of the "odor of sanctity" to which those who are marked with it, are called to strive. The bishop breathes over the vessel containing the chrism, a gesture which symbolizes the Holy Spirit coming down to consecrate this oil, and recalls the actions of Jesus in John 20:22, when he breathed on the apostles and said, "Receive the Holy Spirit..."
With respect to Anglicanism, the 1979 Book of Common Prayer
The ''Book of Common Prayer'' (BCP) is the name given to a number of related prayer books used in the Anglican Communion and by other Christian churches historically related to Anglicanism. The original book, published in 1549 in the reign ...
(p. 307) calls for chrism to be consecrated by the bishop. In many dioceses, the consecration of chrism by the bishop may be done at a service of reaffirmation of ordination vows during Holy Week. During the Chrism Eucharist, the Bishop will bless the oils used throughout the next year for baptisms and healing. In addition, the Bishop and clergy in attendance will reaffirm their Ordination Vows.
Eastern Christianity
Eastern Orthodoxy
 In the
In the Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops via ...
, the liturgical colours are brighter, white being common. On this day alone during Holy Week, the fast is relaxed to permit consumption of wine and oil.
The primary service of this day is Vespers
Vespers is a service of evening prayer, one of the canonical hours in Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, Catholic (both Latin and Eastern), Lutheran, and Anglican liturgies. The word for this fixed prayer time comes from the Latin , mea ...
combined with the Liturgy of St. Basil the Great at which is read a Composite Gospel, primarily taken from Matthew
Matthew may refer to:
* Matthew (given name)
* Matthew (surname)
* ''Matthew'' (ship), the replica of the ship sailed by John Cabot in 1497
* ''Matthew'' (album), a 2000 album by rapper Kool Keith
* Matthew (elm cultivar), a cultivar of the Chi ...
, but with episodes inserted from John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
( the Washing of the Feet) and Luke ( Jesus sweating blood), and many of the normal hymns of the Divine Liturgy are substituted with the following troparion
A troparion (Greek , plural: , ; Georgian: , ; Church Slavonic: , ) in Byzantine music and in the religious music of Eastern Orthodox Christianity is a short hymn of one stanza, or organised in more complex forms as series of stanzas.
The wi ...
:
''Of Thy Mystical Supper, O Son of God, accept me today as a communicant; for I will not speak of Thy Mystery to Thine enemies, neither will I give Thee a kiss likeWhen necessary to replenish the sacrament for communing the sick at a time not following a divine liturgy, an additional Lamb (Host) is consecrated on this day, intincted, covered, and left to dry until Holy Saturday when it is divided, completely dried with a candle flame, and the pieces placed in the artophorion. InJudas Judas Iscariot (; grc-x-biblical, Ἰούδας Ἰσκαριώτης; syc, ܝܗܘܕܐ ܣܟܪܝܘܛܐ; died AD) was a disciple and one of the original Twelve Apostles of Jesus Christ. According to all four canonical gospels, Judas betr .... But like the Thief will I confess Thee: Remember me, O Lord, in Thy Kingdom.''
cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the ''cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominations ...
s and monasteries
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which ...
the ceremony of the Washing of Feet
Maundy (from Old French ''mandé'', from Latin ''mandatum'' meaning "command"), or Washing of the Saints' Feet, Washing of the Feet, or Pedelavium or Pedilavium, is a religious rite observed by various Christian denominations. The Latin wor ...
is normally performed. When there is need to consecrate
Consecration is the solemn dedication to a special purpose or service. The word ''consecration'' literally means "association with the sacred". Persons, places, or things can be consecrated, and the term is used in various ways by different grou ...
more chrism
Chrism, also called myrrh, ''myron'', holy anointing oil, and consecrated oil, is a consecrated oil used in the Anglican, Assyrian, Catholic, Nordic Lutheran, Old Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and Latter Day Saint churches in th ...
, that is performed by patriarchs and other heads of the various autocephalous
Autocephaly (; from el, αὐτοκεφαλία, meaning "property of being self-headed") is the status of a hierarchical Christian church whose head bishop does not report to any higher-ranking bishop. The term is primarily used in Eastern O ...
churches.
vestments
Vestments are liturgical garments and articles associated primarily with the Christian religion, especially by Eastern Churches, Catholics (of all rites), Anglicans, and Lutherans. Many other groups also make use of liturgical garments; th ...
are changed to black or some other dark colour, to signify the beginning of the Passion. Anticipating the Matins of Friday morning, the Holy Passion service of the reading of the Twelve Gospels is conducted. In these readings Christ's last instructions to his disciples are presented, as well as the prophecy of the drama of the Cross, Christ's prayer, and his new commandment. The twelve readings are:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Beginning on Holy and Great Thursday, the memorial service for the dead is forbidden until after Thomas Sunday.
=Local customs
= * In Greek practice, the Mystery ofUnction
Anointing is the ritual act of pouring aromatic oil over a person's head or entire body.
By extension, the term is also applied to related acts of sprinkling, dousing, or smearing a person or object with any perfumed oil, milk, butter, or ot ...
is performed on Great Wednesday as preparation for the reception of Holy Communion on Great Thursday and Pascha, a custom that originated when Greece was under Ottoman control and parish priests, being uneducated, were not permitted to hear confession, so this sacrament, by which sins are believed to be forgiven, came to be performed.
* In Greek tradition, a procession is made during the service of the Twelve Passion Gospels. It takes place after the reading of the fifth gospel during the singing of "Today He Who Hung". During this procession, a large cross with the body of Christ is carried throughout the church while lights are extinguished, bells are slowly tolled, and the faithful prostrate themselves. The cross, with Christ's body hung upon it, is placed in front of the Royal Doors. The icon of Christ on the cross (sometimes with nails affixing it) is struck upon the hands and feet with a stone multiple times, and is then stood up in front of the church, where it is censed.
* In some Slavic traditions, a lesser procession is made after the Twelve Passion Gospels immediately prior to the dismissal with an icon of Christ's crucifixion which is placed on the central icon stand, where it is censed by the clergy, and then venerated.
Oriental Orthodoxy
Oriental Orthodoxy including Coptic (Egyptian) and Ethiopian Orthodoxy which is under papacy of Pope Tawadros II The Copts celebrate Covenant Thursday on 16 April which is 1 week after the Catholics celebrate it. They have praises and vespers every day of week and on Thursday and Saturday they stay praising God and reading about the First Liturgy and Judas’ Betrayal. On Saturday they sing praises for the Entrance of the Messiah in Hades freeing all of the faithful ones including Moses and Abraham etc.Customs and names around the world


 * If statues and crucifixes have been covered during
* If statues and crucifixes have been covered during Passiontide
Passiontide (in the Christian liturgical year) is a name for the last two weeks of Lent, beginning on the Fifth Sunday of Lent, long celebrated as Passion Sunday, and continuing through Lazarus Saturday. The second week of Passiontide is Holy We ...
(the last 2 weeks of Lent, at least in the 1962 Catholic missal), the crucifix covers are allowed to be white instead of purple for Holy Thursday.
* The popular German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
name ''Gründonnerstag'' means either "mourning Thursday" or "green Thursday".
* In the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
and Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the ...
the day is called ''Zelený čtvrtek'' or ''Zelený štvrtok'' respectively, again meaning "Green Thursday", because the typical meals of this day were made of fresh, green vegetables etc. From that day there is no usage of the church bell
A church bell in Christian architecture is a bell which is rung in a church for a variety of religious purposes, and can be heard outside the building. Traditionally they are used to call worshippers to the church for a communal service, and to ...
s until Holy Saturday, here called "White Saturday", because "they have flown to Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
" (a euphemism), in some regions they are replaced by groups of children walking round their village (or around the church) and making noise with wooden rattles. This is to announce to the people approaching beginning of the liturgy and to call the people to church.
* The tradition of silent bells also occurs in Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
: the bells fall silent until Easter, because "they have flown to Rome for Confession", so children take to the streets, calling people to church with melancholy wooden rattling.
* In the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
and Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
, the day is called ''Witte Donderdag'' (White Thursday) referring to the liturgical colour of the day.
* In Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
, Holy Thursday is known as ''Ħamis ix-Xirka'' (Communion Thursday) and the tradition of visiting seven churches (see below) is called ''is-seba' visti'' or is-Sepulkri.
* Eastern Slavic cultures traditionally carried out a range of cleansing ceremonies on Maundy Thursday (sometimes known in Russian as "Clean Thursday" ( ru , Чистый четверг)).
* In Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
, Maundy Thursday is ''Dydd Iau Cablyd''.
* In Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
Maundy Thursday (skärtorsdagen) is connected to old folklore as the day of the witches. Young children often dress up as witches and knock on doors getting coins or candy for Easter eggs.
* In Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
Maundy Thursday is called ''Veliki Chetvurtuk'' (Great Thursday), and is traditionally the day when people color their Easter eggs and perform other household chores geared toward preparing for ''Razpeti Petuk'' (Crucifixion Friday), ''Velika Subota'' (Great Saturday) and ''Velikden'' (Easter Day).
* In Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South Ca ...
the day is called as '' Pesaha'' (പെസഹ), a Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry ( Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 22 scheduled languages of India. Malayalam wa ...
word derived from the Aramaic or Syriac word "''Peshai''" meaning Passover
Passover, also called Pesach (; ), is a major Jewish holiday that celebrates the Biblical story of the Israelites escape from slavery in Egypt, which occurs on the 15th day of the Hebrew month of Nisan, the first month of Aviv, or spring. ...
. Maundy Thursday and following Good Friday are observed as statewide public holiday declared by the Government of Kerala
Government of Kerala is the subnational government of the Indian state of Kerala. The government is led by a chief minister, who selects all the other ministers. The chief minister and their most senior ministers belong to the supreme decisio ...
, given the high number of Syrian Christians Syrian or Syriac Christians may refer to
* Adherents of Christianity in Syria
* Adherents of Syriac Christianity, various Christian bodies of Syriac traditions, especially:
** Syriac/Assyrian/Aramean people, Christian neo-Aramaic speakers through ...
in the state. The tradition of consuming '' Pesaha appam'' or ''Indariyappam'' is customary after special longer Holy Qurbana
The Holy Qurbana ( syr, ܩܘܼܪܒܵܢܵܐ ܩܲܕܝܫܵܐ, ''Qurbānā Qaddišā'' in Syriac language, Eastern Syriac or ''Qurbānā Qandišā'' in the Indian variant of Eastern Syriac, the "Holy Offering" or "Holy Sacrifice" in English), refers ...
, which are conducted on the or at midnight till morning in churches of Saint Thomas Christians
The Saint Thomas Christians, also called Syrian Christians of India, ''Marthoma Suriyani Nasrani'', ''Malankara Nasrani'', or ''Nasrani Mappila'', are an ethno-religious community of Indian Christians in the state of Kerala ( Malabar region) ...
. On the evening before Good Friday the Pesaha bread is made at home. It is made with unleavened flour and they use a sweet drink call ''Pesaha Paal'' made up of coconut milk and jaggery along with this bread. On the Pesaha night the bread is steamed in a new vessel, immediately after rice flour is mixed with water and they pierce it many times with handle of the spoon to let out the steam so that the bread will not rise. This bread is cut by the head of the family and shared among the family members after prayers. In some families, ''Pesaha Paal'' a creamy dip made up of jaggery and coconut milk is used along with the Pesaha bread. If the family is in mourning following a death, Pesaha bread is not made at their home, but some of the Saint Thomas Christian neighbours share their bread with them. The Saint Thomas Christians diaspora also celebrate this day by having Holy Communion services in the parishes according to their respective liturgies. The tradition of washing feet by priests is practiced in every parish commemorating Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
washing the feet of his disciples symbolizing humbleness.
* In the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, the day is officially known as ''Huwebes Santo'' (phonetic transliteration of Jueves Santo in Spanish, Holy Thursday) or "Maundy Thursday". Most businesses are closed during the Easter Triduum
The Paschal Triduum or Easter Triduum (Latin: ''Triduum Paschale''), Holy Triduum (Latin: ''Triduum Sacrum''), or the Three Days, is the period of three days that begins with the liturgy on the evening of Maundy Thursday, reaches its high poin ...
, with shopping malls opening on Black Saturday. Terrestrial television and radio stations either go completely off-air during the Triduum or operate on shorter hours with special programming; cable channels usually retain their normal programming. Newspapers do not publish on Good Friday and Black Saturday.
Public holiday
Spanish empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
(Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest ...
, Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the ...
, Costa Rica
Costa Rica (, ; ; literally "Rich Coast"), officially the Republic of Costa Rica ( es, República de Costa Rica), is a country in the Central American region of North America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the no ...
, El Salvador
El Salvador (; , meaning " The Saviour"), officially the Republic of El Salvador ( es, República de El Salvador), is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south ...
, Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by Hon ...
, Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. The republic of Honduras is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Oce ...
, Mexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
, Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the coun ...
, Paraguay
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to t ...
, Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
, the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
, Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
and Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
), countries that were part of the Danish colonial empire (Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
, Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
and United States Virgin Islands
The United States Virgin Islands,. Also called the ''American Virgin Islands'' and the ''U.S. Virgin Islands''. officially the Virgin Islands of the United States, are a group of Caribbean islands and an unincorporated and organized territory ...
), and in the Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South Ca ...
State of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
.
Certain German states declare a public holiday for public sector employees. In the UK, civil servants were traditionally granted a half-day holiday (known as "privilege leave") on this date, but that was abolished, by David Cameron, after 2012.
Seven Churches Visitation
The tradition of visiting seven churches on Holy Thursday is an ancient practice, probably originating inRome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
. and occurs among the faithful in countries around the world.
In India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, the custom is to visit fourteen churches, one per Station of the Cross
The Stations of the Cross or the Way of the Cross, also known as the Way of Sorrows or the Via Crucis, refers to a series of images depicting Jesus Christ on the day of his crucifixion and accompanying prayers. The stations grew out of imita ...
. Traditionally, this is performed on Maundy Thursday evening but is more often done on the morning of Good Friday or on any day of Lent. Usually, whole families would participate, customarily fasting
Fasting is the abstention from eating and sometimes drinking. From a purely physiological context, "fasting" may refer to the metabolic status of a person who has not eaten overnight (see " Breakfast"), or to the metabolic state achieved after ...
for the duration of the rite. It is also undertaken by parish devotional groups.
In the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
the tradition is called '' Visita Iglesia'' ( Spanish, "church visit") – people visit churches to pray, usually reciting the Stations of the Cross
The Stations of the Cross or the Way of the Cross, also known as the Way of Sorrows or the Via Crucis, refers to a series of images depicting Jesus Christ on the day of Crucifixion of Jesus, his crucifixion and accompanying prayers. The station ...
. It is a chiefly urban custom, as churches are located closer to each other in cities
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
, and supposedly because it originates in visiting the seven churches of Intramuros
Intramuros (Latin for "inside the walls") is the historic walled area within the city of Manila, the capital of the Philippines. It is administered by the Intramuros Administration with the help of the city government of Manila.
Present-day ...
that stood until the 1945 Bombing of Manila
The Battle of Manila ( fil, Labanan sa Maynila; ja, マニラの戦い; es, Batalla de Manila; ) was a major battle of the Philippine campaign of 1944–45, during the Second World War. It was fought by forces from both the United States and ...
.Of the seven, only Manila Cathedral
The Minor Basilica and Metropolitan Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception ( fil, Basilika Menor at Kalakhang Katedral ng Kalinis-linisang Paglilihi; es, Basílica Menor y Catedral Metropolitana de la Inmaculada Concepción), also known as the ...
and San Agustín Church remain ''in situ
''In situ'' (; often not italicized in English) is a Latin phrase that translates literally to "on site" or "in position." It can mean "locally", "on site", "on the premises", or "in place" to describe where an event takes place and is used in ...
'' following the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
.
The original purpose of the ritual was to venerate the Blessed Sacrament
The Blessed Sacrament, also Most Blessed Sacrament, is a devotional name to refer to the body and blood of Christ in the form of consecrated sacramental bread and wine at a celebration of the Eucharist. The term is used in the Latin Church of th ...
in the Altar of Repose on Maundy Thursday night, but since no prayers were prescribed (apart from those for the Pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
), the Stations of the Cross were recited.
In Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
, the visiting of churches occurs shortly after the evening Mass of the Lord's Supper. Prayers at each church consist of seven repetitions of the Lord's Prayer
The Lord's Prayer, also called the Our Father or Pater Noster, is a central Christian prayer which Jesus taught as the way to pray. Two versions of this prayer are recorded in the gospels: a longer form within the Sermon on the Mount in the Gosp ...
, Ave Maria
The Hail Mary ( la, Ave Maria) is a traditional Christian prayer addressing Mary, the mother of Jesus. The prayer is based on two biblical passages featured in the Gospel of Luke: the Angel Gabriel's visit to Mary (the Annunciation) and Mary's ...
, and the ''Gloria Patri
The Gloria Patri, also known as the Glory Be to the Father or, colloquially, the Glory Be, is a doxology, a short hymn of praise to God in various Christian liturgies. It is also referred to as the Minor Doxology ''(Doxologia Minor)'' or Les ...
''. Due to the new trend of late Mass times (sometimes 7 or 8 pm) to allow for more churchgoers, eight churches are the maximum number visited (even in the city area, where these are closer to each other than in outer residential areas) before these close at midnight. A festive atmosphere exists, with the sale of drinks, hot cross buns and other local snacks like the traditional ''kueh ko chee''. Observant Catholics have a 'Last Supper' meal in anticipation of the next day's fast.
Gallery
Master Paul
Master or masters may refer to:
Ranks or titles
* Ascended master, a term used in the Theosophical religious tradition to refer to spiritually enlightened beings who in past incarnations were ordinary humans
*Grandmaster (chess), National Master ...
's sculpture
File:Passion Gospels - Great Thursday -- Annunciation, Toronto, 2015.JPG, Reading of the 12th Passion Gospel on Great and Holy Thursday
See also
* Corpus Christi *Easter Triduum
The Paschal Triduum or Easter Triduum (Latin: ''Triduum Paschale''), Holy Triduum (Latin: ''Triduum Sacrum''), or the Three Days, is the period of three days that begins with the liturgy on the evening of Maundy Thursday, reaches its high poin ...
* Friday of Sorrows (Friday before Palm Sunday)
* Life of Jesus in the New Testament
* Maundy
* Paschal cycle
* Tenebrae (service)
* Thursday of the Dead
* Tristis est anima mea (responsory)
Tristis est anima mea is the second responsory of the Tenebrae for Maundy Thursday. The Latin text refers to Christ's Agony in the Garden of Gethsemane, a part of his Passion.
Text
The theme of the text of the second responsory for Maundy Th ...
, second responsory for the Tenebrae at Maundy Thursday
References
Bibliography
*External links
Pope Francis, "Homily for Chrism Mass"
''News.va'', March 28, 2013.
Cosentino, Tony. "Chrism Mass: its Symbols and Their Meaning"
Diocese of St. Catherine's, Ontario. {{Authority control Thursday observances Eastern Orthodox liturgical days Holy Week March observances April observances Public holidays in Greece Greek traditions Public holidays in Argentina Public holidays in Colombia Public holidays in Costa Rica Public holidays in El Salvador Public holidays in Guatemala Public holidays in Honduras Public holidays in Mexico Public holidays in Nicaragua Public holidays in Paraguay Public holidays in Peru Public holidays in the Philippines Public holidays in Spain Public holidays in Venezuela Public holidays in Iceland Public holidays in Denmark Public holidays in Norway