Hokkaido Prefecture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
is Japan's second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost prefecture, making up its own
 When establishing the Development Commission, the Meiji government decided to change the name of Ezochi. Matsuura Takeshirō submitted six proposals, including names such as and , to the government. The government eventually decided to use the name Hokkaidō, but decided to write it as , as a compromise between and because of the similarity with names such as . According to Matsuura, the name was thought up because the Ainu called the region ''Kai''. The ''kai'' element also strongly resembles the
When establishing the Development Commission, the Meiji government decided to change the name of Ezochi. Matsuura Takeshirō submitted six proposals, including names such as and , to the government. The government eventually decided to use the name Hokkaidō, but decided to write it as , as a compromise between and because of the similarity with names such as . According to Matsuura, the name was thought up because the Ainu called the region ''Kai''. The ''kai'' element also strongly resembles the
The phrase ' () has been a preferred choice among Japanese activists. Its primary meaning is the "land of humans", as opposed to the "land of gods" ('). When contrasted with ' (the land of the neighbors, often pointing to
Another phrase ' (ヤウンモシㇼ) has gained prominence. It literally means the "onshore land", as opposed to the "offshore land" (), which, depending on context, can refer to the Kuril Islands, Honshu, or any foreign country. If the speaker is a resident of Hokkaido, ' can refer to Hokkaido.
Yet another phrase ' (アコㇿモシㇼ) means " our (inclusive) land". If uttered among Hokkaido Ainus, it can refer to Hokkaido or Japan as a whole.
 During the
During the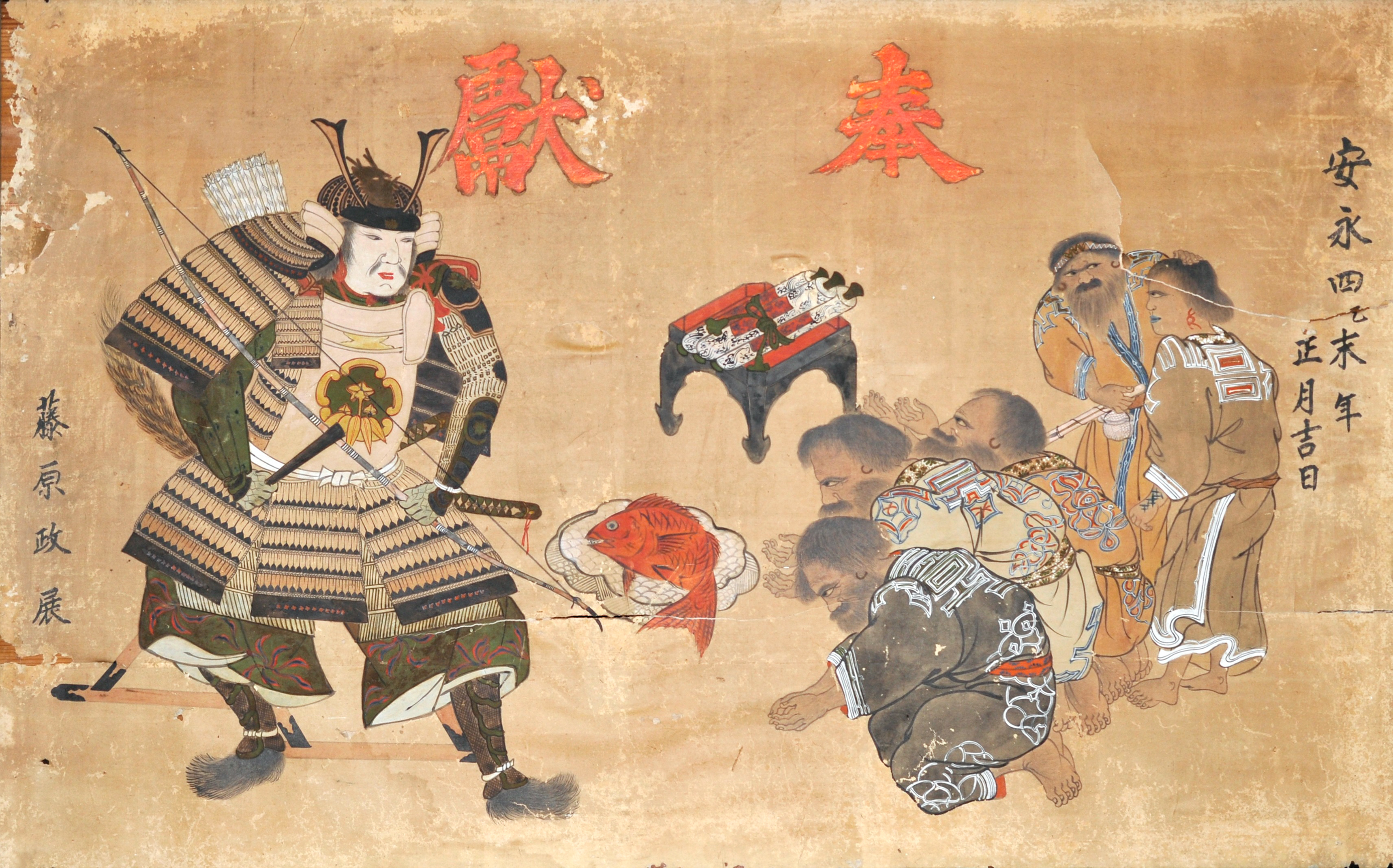  The Matsumae clan rule over the Ainu must be understood in the context of the expansion of the Japanese feudal state. Medieval military leaders in northern Honshu (ex. Northern Fujiwara, Akita clan) maintained only tenuous political and cultural ties to the imperial court and its proxies, the
The Matsumae clan rule over the Ainu must be understood in the context of the expansion of the Japanese feudal state. Medieval military leaders in northern Honshu (ex. Northern Fujiwara, Akita clan) maintained only tenuous political and cultural ties to the imperial court and its proxies, the  There were numerous revolts by the Ainu against the feudal rule. The last large-scale resistance was Shakushain's revolt in 1669–1672. In 1789, a smaller movement known as the Menashi–Kunashir rebellion was crushed. After that rebellion, the terms "Japanese" and "Ainu" referred to clearly distinguished groups, and the Matsumae were unequivocally Japanese.
According to John A. Harrison of the
There were numerous revolts by the Ainu against the feudal rule. The last large-scale resistance was Shakushain's revolt in 1669–1672. In 1789, a smaller movement known as the Menashi–Kunashir rebellion was crushed. After that rebellion, the terms "Japanese" and "Ainu" referred to clearly distinguished groups, and the Matsumae were unequivocally Japanese.
According to John A. Harrison of the

 The primary purpose of the Development Commission was to secure Hokkaidō before the
The primary purpose of the Development Commission was to secure Hokkaidō before the
File:130922 Lake Toya Toyako Hokkaido Japan03s3.jpg,
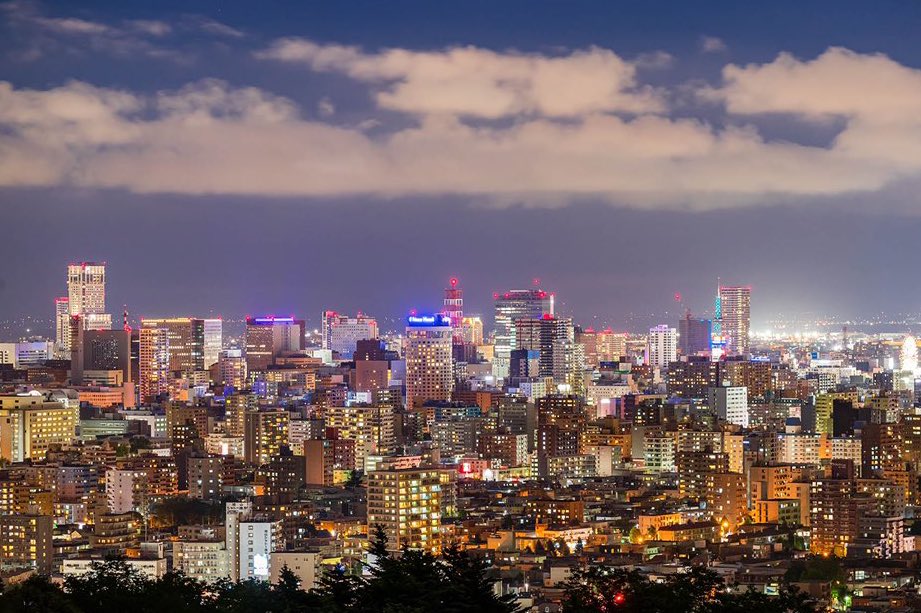 Hokkaidō has the third-largest population of Japan's five main islands, with 5,383,579 people . It has the lowest population-density in Japan with just 64.5/km2 (160/sq mi) (2016). By population, it ranks 21st globally. Major cities include
Hokkaidō has the third-largest population of Japan's five main islands, with 5,383,579 people . It has the lowest population-density in Japan with just 64.5/km2 (160/sq mi) (2016). By population, it ranks 21st globally. Major cities include
File:Kottaro situgen 2009.jpg, Overview of Kushiro Wetland
File:Lake Akan and Mount Oakan - 2005.jpg,
* Twelve prefectural natural parks (道立自然公園). The prefectural natural parks cover 146,802 ha, the largest area of any prefecture.
**

 , Hokkaidō has nine General Subprefectural Bureaus (総合振興局) and five Subprefectural Bureaus (振興局). Hokkaidō is one of eight prefectures in Japan that have subprefectures (支庁 ''shichō''). However, it is the only one of the eight to have such offices covering the whole of its territory outside the main cities (rather than having them just for outlying islands or remote areas). This is mostly because of its great size; many parts of the prefecture are simply too far away to be effectively administered by Sapporo. Subprefectural offices in Hokkaidō carry out many of the duties that prefectural offices fulfill elsewhere in Japan.
, Hokkaidō has nine General Subprefectural Bureaus (総合振興局) and five Subprefectural Bureaus (振興局). Hokkaidō is one of eight prefectures in Japan that have subprefectures (支庁 ''shichō''). However, it is the only one of the eight to have such offices covering the whole of its territory outside the main cities (rather than having them just for outlying islands or remote areas). This is mostly because of its great size; many parts of the prefecture are simply too far away to be effectively administered by Sapporo. Subprefectural offices in Hokkaidō carry out many of the duties that prefectural offices fulfill elsewhere in Japan.


 As Japan's coldest region, Hokkaidō has relatively cool summers and icy/snowy winters. Most of the island falls in the
As Japan's coldest region, Hokkaidō has relatively cool summers and icy/snowy winters. Most of the island falls in the
 Hokkaidō's largest city is the capital,
Hokkaidō's largest city is the capital,
File:4 Chome Sakaigawa, Chūō-ku, Sapporo-shi, Hokkaidō 064-0943, Japan - panoramio.jpg, Sapporo City
File:Asahibashi Bridge and Mt. Daisetsuzan Range.jpg,
 Although there is some
Although there is some  Tourism is an important industry, especially during the cool summertime when visitors are attracted to Hokkaidō's open spaces from hotter and more humid parts of Japan and other Asian countries. During the winter, skiing and other winter sports bring other tourists, and increasingly international ones, to the island.
Coal mining played an important role in the industrial development of Hokkaidō, with the Ishikari coalfield. Cities such as Muroran were primarily developed to supply the rest of the archipelago with coal.
Tourism is an important industry, especially during the cool summertime when visitors are attracted to Hokkaidō's open spaces from hotter and more humid parts of Japan and other Asian countries. During the winter, skiing and other winter sports bring other tourists, and increasingly international ones, to the island.
Coal mining played an important role in the industrial development of Hokkaidō, with the Ishikari coalfield. Cities such as Muroran were primarily developed to supply the rest of the archipelago with coal.
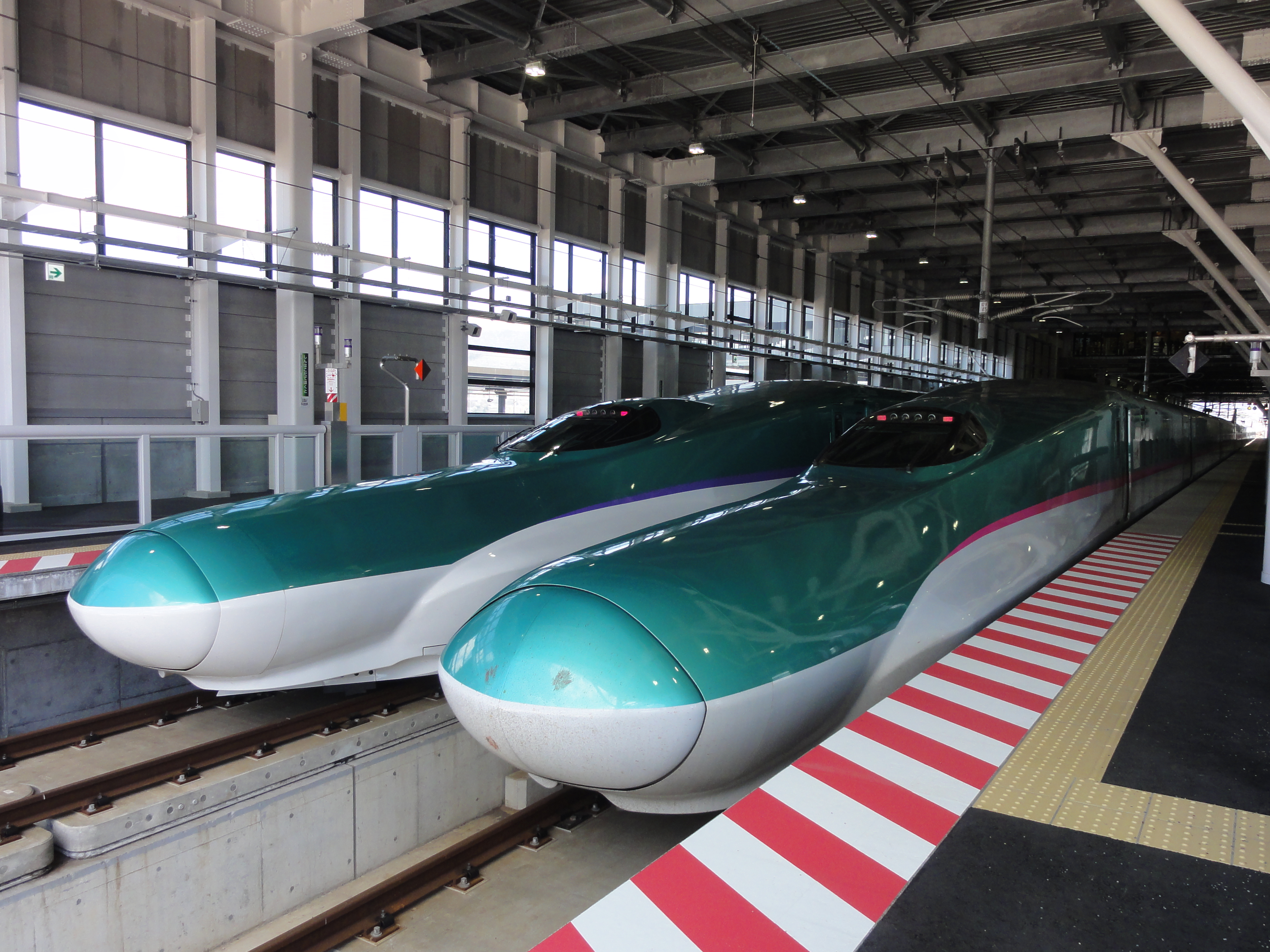 Hokkaidō's only land link to the rest of Japan is the
Hokkaidō's only land link to the rest of Japan is the
 * Sapporo ramen,
* Sapporo ramen,
 The
The
Members by electoral district and parliamentary group
General elections for the Hokkaido assembly are currently held together with gubernatorial elections in the unified local elections (last round: April 2015).
For the lower house of the National Diet, Hokkaidō is divided into twelve single-member electoral districts. In the 2017 election, candidates from the governing coalition of Liberal Democrats and
OCLC 8954556
* McDougall, Walter A. (1993). ''Let the Sea Make a Noise: A History of the North Pacific from Magellan to MacArthur''. New York: Basic Books.
OCLC 28017793
* Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric and Käthe Roth. (2005)
''Japan encyclopedia''
Cambridge:
OCLC 58053128
Hokkaido Official Website
(In English)
Hokkaido Ski Resort
{{Authority control Ainu geography Japanese archipelago Prefectures of Japan
region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics ( physical geography), human impact characteristics ( human geography), and the interaction of humanity an ...
. The Tsugaru Strait
The is a strait between Honshu and Hokkaido in northern Japan connecting the Sea of Japan with the Pacific Ocean. It was named after the western part of Aomori Prefecture. The Seikan Tunnel passes under it at its narrowest point 12.1 miles (1 ...
separates Hokkaidō from Honshu
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island se ...
; the two islands are connected by the undersea railway Seikan Tunnel
The Seikan Tunnel ( ja, 青函トンネル, or , ), is a dual-gauge railway tunnel in Japan, with a portion under the seabed of the Tsugaru Strait, which separates Aomori Prefecture on the main Japanese island of Honshu from the northern isl ...
.
The largest city on Hokkaidō is its capital, Sapporo
( ain, サッ・ポロ・ペッ, Satporopet, lit=Dry, Great River) is a city in Japan. It is the largest city north of Tokyo and the largest city on Hokkaido, the northernmost main island of the country. It ranks as the fifth most populous cit ...
, which is also its only ordinance-designated city. Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh ...
lies about 43 kilometers (26 mi) to the north of Hokkaidō, and to the east and northeast are the Kuril Islands
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands (; rus, Кури́льские острова́, r=Kuril'skiye ostrova, p=kʊˈrʲilʲskʲɪjə ɐstrɐˈva; Japanese: or ) are a volcanic archipelago currently administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast in the ...
, which are administered by Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
, though the four most southerly are claimed by Japan. Hokkaidō was formerly known as ''Ezo
(also spelled Yezo or Yeso) is the Japanese term historically used to refer to the lands to the north of the Japanese island of Honshu. It included the northern Japanese island of Hokkaido, which changed its name from "Ezo" to "Hokkaidō" in 18 ...
'', ''Yezo'', ''Yeso'', or ''Yesso''. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Hokkaidō" in
Although there were Japanese settlers who ruled the southern tip of the island since the 16th century, Hokkaido was considered foreign territory that was inhabited by the indigenous people of the island, known as the Ainu people. While geographers such as Mogami Tokunai and Mamiya Rinzō
was a Japanese explorer of the late Edo period. He is best known for his exploration of Karafuto, now known as Sakhalin. He mapped areas of northeast Asia then unknown to Japanese.
Biography
Mamiya was born in 1775 in Tsukuba District, Hitac ...
explored the island in the Edo period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characte ...
, Japan's governance was limited to Oshima Peninsula
The Oshima Peninsula (渡島 半島 ''Oshima-hantō'') is the southernmost part of Hokkaidō, the northernmost of the Japanese islands. Where the peninsula starts is open to interpretation. A more generous interpretation is to draw a line southea ...
until the 17th century. The Japanese settlers began their migration to Hokkaido in the 17th century, which often resulted in clashes and revolts between Japanese and Ainu populations. In 1869, following the Meiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored practical imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Although there were ...
, Ezo was annexed by Japan under on-going colonial practices, and renamed Hokkaido. After this event, Japanese settlers started to colonize the island. While Japanese settlers colonized the island, the Ainu people were dispossessed of their land, forced to assimilate, and aggressively discriminated against by the Japanese settlers.
Etymology
On'yomi
are the logographic Chinese characters taken from the Chinese script and used in the writing of Japanese. They were made a major part of the Japanese writing system during the time of Old Japanese and are still used, along with the subsequ ...
, or Sino-Japanese, reading of the characters (''on'yomi'' as カイ ''kun'yomi
are the logographic Chinese characters taken from the Chinese script and used in the writing of Japanese. They were made a major part of the Japanese writing system during the time of Old Japanese and are still used, along with the subsequen ...
'' as えみし which have been used for over a thousand years in China and Japan as the standard orthographic form to be used when referring to Ainu and related peoples; it is possible that Matsuura's ''kai'' was actually an alteration, influenced by the Sino-Japanese reading of ''Ka-i'', of the Nivkh exonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
for the Ainu, namely ''Qoy'' or .
In 1947, Hokkaidō became a full-fledged prefecture. The historical suffix 道 (''-dō'') translates to "prefecture" in English, ambiguously the same as 府 (''-fu'') for Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of ...
and Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese language, Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin, Keihanshin metropolitan area along wi ...
, and 県 (''-ken'') for the rest of the "prefectures". ''Dō'', as shorthand, can be used to uniquely identify Hokkaido, for example as in 道道 (''dōdō'', "Hokkaido road") or 道議会 (''Dōgikai'', " Hokkaido Assembly"), the same way 都 (''-to'') is used for Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and List of cities in Japan, largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, ...
. "Hokkai-do-ken" (literally "North Sea Province Prefecture") is, therefore, technically speaking, a redundant term, although it is occasionally used to differentiate the government from the island. The prefecture's government calls itself the "Hokkaidō Government" rather than the "Hokkaidō Prefectural Government".
With the rise of indigenous rights movements, there emerges a normative notion that Hokkaido must have an Ainu language name. Whichever Ainu phrase is chosen, its original referent is critically different from the large geographical entity, however. The phrase ' () has been a preferred choice among Japanese activists. Its primary meaning is the "land of humans", as opposed to the "land of gods" ('). When contrasted with ' (the land of the neighbors, often pointing to
Honshu
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island se ...
or Japanese settlements on the southern tip of Hokkaido), it means the land of the Ainu people, which, depending on context, can refer to Hokkaido, although from a modern ethnolinguistic point of view, the Ainu people have extended their domain to a large part of Sakhalin and the entire Kuril Islands. Another phrase ' (ヤウンモシㇼ) has gained prominence. It literally means the "onshore land", as opposed to the "offshore land" (), which, depending on context, can refer to the Kuril Islands, Honshu, or any foreign country. If the speaker is a resident of Hokkaido, ' can refer to Hokkaido.
Yet another phrase ' (アコㇿモシㇼ) means " our (inclusive) land". If uttered among Hokkaido Ainus, it can refer to Hokkaido or Japan as a whole.
History
Early history
During the Jomon period the local culture and the associated hunter-gatherer lifestyle flourished in Hokkaidō, beginning over 15,000 years ago. In contrast to the island of Honshu, Hokkaidō saw an absence of conflict during this time period. Jomon beliefs in natural spirits are theorized to be the origins of Ainu spirituality. About 2,000 years ago, the island was colonized byYayoi
The started at the beginning of the Neolithic in Japan, continued through the Bronze Age, and towards its end crossed into the Iron Age.
Since the 1980s, scholars have argued that a period previously classified as a transition from the Jōmon p ...
people, and much of the island's population shifted away from hunting and gathering towards agriculture.
The '' Nihon Shoki'', finished in 720 AD, is often said to be the first mention of Hokkaidō in recorded history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world his ...
. According to the text, Abe no Hirafu
was a Japanese military strategist and commander of the Asuka period.
Some sources say he lived from c.575-664
Biography
Events in his life are accounted in the Nihon Shoki and Kojiki, both written several decades after his death. His father ...
''Japan Handbook'', p. 760 led a large navy and army to northern areas from 658 to 660 and came into contact with the Mishihase
The , also read as Ashihase and Shukushin, were a people of ancient Japan, believed to have lived along the northern portion of the coast of the Sea of Japan. The term Sushen, rendered 肅愼, is found in Chinese records, but is annotated as M ...
and Emishi. One of the places Hirafu went to was called , which is often believed to be present-day Hokkaidō. However, many theories exist concerning the details of this event, including the location of Watarishima and the common belief that the Emishi in Watarishima were the ancestors of the present-day Ainu people.
During the Nara
The National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) is an " independent federal agency of the United States government within the executive branch", charged with the preservation and documentation of government and historical records. It ...
and Heian period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kanmu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means "peace" in Japanese ...
s (710–1185), people in Hokkaidō conducted trade with Dewa Province
was a province of Japan comprising modern-day Yamagata Prefecture and Akita Prefecture, except for the city of Kazuno and the town of Kosaka. Dewa bordered on Mutsu and Echigō Provinces. Its abbreviated form name was .
History
Early per ...
, an outpost of the Japanese central government. From the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, the people in Hokkaidō began to be called Ezo
(also spelled Yezo or Yeso) is the Japanese term historically used to refer to the lands to the north of the Japanese island of Honshu. It included the northern Japanese island of Hokkaido, which changed its name from "Ezo" to "Hokkaidō" in 18 ...
. Hokkaidō subsequently became known as or . The Ezo mainly relied upon hunting and fishing and obtained rice and iron through trade with the Japanese.
Feudal Japan
 During the
During the Muromachi period
The is a division of Japanese history running from approximately 1336 to 1573. The period marks the governance of the Muromachi or Ashikaga shogunate (''Muromachi bakufu'' or ''Ashikaga bakufu''), which was officially established in 1338 by t ...
(1336–1573), the Japanese created a settlement at the south of the Oshima Peninsula
The Oshima Peninsula (渡島 半島 ''Oshima-hantō'') is the southernmost part of Hokkaidō, the northernmost of the Japanese islands. Where the peninsula starts is open to interpretation. A more generous interpretation is to draw a line southea ...
, with a series of fortified residences such as that of Shinoridate. As more people moved to the settlement to avoid battles, disputes arose between the Japanese and the Ainu. The disputes eventually developed into war. Takeda Nobuhiro
Takeda Nobuhiro (武田 信広), also known as Kakizaki Nobuhiro (蠣崎 信廣) (1431 – 1494) was the ancestor of the Matsumae clan, and is celebrated for his role in suppressing the 1457 Ainu revolt of Koshamain. The adopted son of Takeda ...
killed the Ainu leader, Koshamain, and defeated the opposition in 1457. Nobuhiro's descendants became the rulers of the Matsumae-han, which was granted exclusive trading rights with the Ainu in the Azuchi-Momoyama and Edo period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characte ...
s (1568–1868). The Matsumae family's economy relied upon trade with the Ainu. They held authority over the south of Ezochi until the end of the Edo period.
 The Matsumae clan rule over the Ainu must be understood in the context of the expansion of the Japanese feudal state. Medieval military leaders in northern Honshu (ex. Northern Fujiwara, Akita clan) maintained only tenuous political and cultural ties to the imperial court and its proxies, the
The Matsumae clan rule over the Ainu must be understood in the context of the expansion of the Japanese feudal state. Medieval military leaders in northern Honshu (ex. Northern Fujiwara, Akita clan) maintained only tenuous political and cultural ties to the imperial court and its proxies, the Kamakura shogunate
The was the feudal military government of Japan during the Kamakura period from 1185 to 1333. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Kamakura-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 459.
The Kamakura shogunate was established by Minamoto no ...
and Ashikaga shogunate
The , also known as the , was the feudal military government of Japan during the Muromachi period from 1336 to 1573.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Muromachi-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 669.
The Ashikaga shogunate was establi ...
. Feudal strongmen sometimes located themselves within medieval institutional order, taking shogunate titles, while in other times they assumed titles that seemed to give them a non-Japanese identity. In fact, many of the feudal strongmen were descended from Emishi military leaders who had been assimilated into Japanese society. The Matsumae clan were of Yamato descent like other ethnic Japanese people
The are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Japanese archipelago."人類学上は,旧石器時代あるいは縄文時代以来,現在の北海道〜沖縄諸島(南西諸島)に住んだ集団を祖先にもつ人々。" () Jap ...
, whereas the Emishi of northern Honshu were a distinctive group related to the Ainu. The Emishi were conquered and integrated into the Japanese state dating back as far as the 8th century and as result began to lose their distinctive culture and ethnicity as they became minorities. By the time the Matsumae clan ruled over the Ainu, most of the Emishi were ethnically mixed and physically closer to Japanese than they were to Ainu. From this, the "transformation" theory postulates that native Jōmon peoples changed gradually with the infusion of Yayoi immigrants into the Tōhoku, in contrast to the "replacement" theory that posits the Jōmon was ''replaced'' by the Yayoi.
 There were numerous revolts by the Ainu against the feudal rule. The last large-scale resistance was Shakushain's revolt in 1669–1672. In 1789, a smaller movement known as the Menashi–Kunashir rebellion was crushed. After that rebellion, the terms "Japanese" and "Ainu" referred to clearly distinguished groups, and the Matsumae were unequivocally Japanese.
According to John A. Harrison of the
There were numerous revolts by the Ainu against the feudal rule. The last large-scale resistance was Shakushain's revolt in 1669–1672. In 1789, a smaller movement known as the Menashi–Kunashir rebellion was crushed. After that rebellion, the terms "Japanese" and "Ainu" referred to clearly distinguished groups, and the Matsumae were unequivocally Japanese.
According to John A. Harrison of the University of Florida
The University of Florida (Florida or UF) is a public land-grant research university in Gainesville, Florida. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida, traces its origins to 1853, and has operated continuously on its ...
, prior to 1868 Japan used proximity as its claim Hokkaido, Saghalien
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh ...
and the Kuril Islands
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands (; rus, Кури́льские острова́, r=Kuril'skiye ostrova, p=kʊˈrʲilʲskʲɪjə ɐstrɐˈva; Japanese: or ) are a volcanic archipelago currently administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast in the ...
; however, Japan had never really explored, governed, or exploited the areas, and this claim was invalidated by the movement of Russia into the Northeast Pacific area and by Russian settlements on Kamchatka
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: полуостров Камчатка, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and west ...
, Saghalien and the Okhotsk Coast
The Okhotsk Coast is an informal name for the northwest coast of the Sea of Okhotsk. Although it was never an administrative unit there is some reason to treat it as a distinct region. Here in 1639 the Russians first reached the Pacific Ocean. ...
.
Leading up to the Meiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored practical imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Although there were ...
, the Tokugawa shogunate realized there was a need to prepare northern defenses against a possible Russian invasion and took over control of most of Ezochi. Many Japanese settlers regarded the Ainu as "inhumane and the inferior descendants of dogs." The shogunate also imposed various assimilation programs on the Ainu.
Meiji Restoration
Hokkaidō was known as Ezochi until the Meiji Restoration. Shortly after the Boshin War in 1868, a group of Tokugawa loyalists led by Enomoto Takeaki temporarily occupied the island (the polity is commonly but mistakenly known as theRepublic of Ezo
The was a short-lived separatist state established in 1869 on the island of Ezo, now Hokkaido, by a part of the former military of the Tokugawa shogunate at the end of the ''Bakumatsu'' period in Japan. It was the first government to attempt t ...
), but the rebellion was crushed in May 1869. Through colonial practices, Ezochi was annexed into Japanese territory, and renamed Hokkaido. Ezochi was subsequently put under control of , Hakodate Prefectural Government. When establishing the , the Meiji government introduced a new name. After 1869, the northern Japanese island was known as Hokkaidō; and regional subdivisions were established, including the provinces of Oshima, Shiribeshi, Iburi
is a subprefecture of Hokkaido Prefecture, Japan.
Geography
Located in south-central Hokkaido, Iburi stretches East-West and North-South. Iburi covers an area of . Iburi borders Oshima Subprefecture to the West, Shiribeshi, Ishikari, an ...
, Ishikari, Teshio, Kitami
is a city in Okhotsk Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the most populous city and the commercial center in the subprefecture, although the subprefecture capital is Abashiri.
Kitami is physically in the middle of Okhotsk Subprefecture. Th ...
, Hidaka, Tokachi, Kushiro
is a city in Kushiro Subprefecture on the island of Hokkaido, Japan. It serves as the subprefecture's capital and it is the most populated city in the eastern part of the island.
Geography
Mountains
* Mount Oakan
* Mount Meakan
* Mount Akan ...
, Nemuro Nemuro may refer to:
* Nemuro Subprefecture, Hokkaido Prefecture, Japan
** Nemuro, Hokkaido, a city
** Nemuro Peninsula
** Nemuro Strait
** Nemuro Bay
* Nemuro Province
was an old province in Japan in what is today Nemuro Subprefecture, Hokkai ...
and Chishima
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands (; rus, Кури́льские острова́, r=Kuril'skiye ostrova, p=kʊˈrʲilʲskʲɪjə ɐstrɐˈva; Japanese: or ) are a volcanic archipelago currently administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast in the ...
.
Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
extended their control of the Far East beyond Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, c ...
. The Japanese failed to settle in the interior lowlands of the island because of aboriginal resistance. The resistance was eventually destroyed, and the lowlands were under the control of the commission. The most important goal of the Japanese was to increase the farm population and to create a conducive environment for emigration and settlement. However, the Japanese did not have expertise in modern agricultural techniques, and only possessed primitive mining and lumbering methods. Kuroda Kiyotaka
Count , also known as , was a Japanese politician of the Meiji era. He was Prime Minister of Japan from 1888 to 1889. He was also vice chairman of the Hokkaido Development Commission ( Kaitaku-shi).
Biography
As a Satsuma ''samurai''
Ku ...
was put in charge of the project, and turned to the United States for help.
His first step was to journey to the United States and recruit Horace Capron, President Ulysses S. Grant's commissioner of agriculture. From 1871 to 1873 Capron bent his efforts to expounding Western agriculture and mining, with mixed results. Frustrated with obstacles to his efforts, Capron returned home in 1875. In 1876, William S. Clark arrived to found an agricultural college in Sapporo. Although he only remained a year, Clark left a lasting impression on Hokkaidō, inspiring the Japanese with his teachings on agriculture as well as Christianity. His parting words, ''"Boys, be ambitious!"'', can be found on public buildings in Hokkaidō to this day. The population of Hokkaidō boomed from 58,000 to 240,000 during that decade.
In 1882, the Development Commission was abolished. Transportation on the island was underdeveloped, so the prefecture was split into several "sub-prefectures" (支庁 ''shichō''), namely , , and , that could fulfill administrative duties of the prefectural government and keep tight control over the developing island. In 1886, the three prefectures were demoted, and Hokkaidō was put under the . These sub-prefectures still exist today, although they have much less power than they possessed before and during World War II; they now exist primarily to handle paperwork and other bureaucratic functions.
World War II
In mid-July 1945, various shipping ports, cities, and military facilities in Hokkaidō were attacked by theUnited States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
's Task Force 38
The Fast Carrier Task Force (TF 38 when assigned to Third Fleet, TF 58 when assigned to Fifth Fleet), was the main striking force of the United States Navy in the Pacific War from January 1944 through the end of the war in August 1945. The tas ...
. On 14–15 July, aircraft operating from the task force's aircraft carriers sank and damaged a large number of ships in ports along Hokkaidō's southern coastline as well as in northern Honshu. In addition, on 15 July a force of three battleships and two light cruisers bombarded the city of Muroran. Before the Japanese surrender
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, bringing the war's hostilities to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy ( ...
was formalized, the Soviet Union made preparations for an invasion of Hokkaidō, but U.S. President Harry Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. A leader of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 34th vice president from January to April 1945 under Franklin ...
made it clear that the surrender of all of the Japanese home islands
The Japanese archipelago (Japanese: 日本列島, ''Nihon rettō'') is a group of 6,852 islands that form the country of Japan, as well as the Russian island of Sakhalin. It extends over from the Sea of Okhotsk in the northeast to the East Chin ...
would be carried out by General Douglas MacArthur per the 1943 Cairo Declaration
The Cairo Declaration was the outcome of the Cairo Conference in Cairo, Egypt, on 27 November 1943. President Franklin Roosevelt of the United States, Prime Minister Winston Churchill of the United Kingdom, and Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek of ...
.
Present
Hokkaidō became equal with other prefectures in 1947, when the revised Local Autonomy Law became effective. The Japanese central government established the as an agency of thePrime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
's Office in 1949 to maintain its executive power in Hokkaidō. The agency was absorbed by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport in 2001. and the of the ministry still have a strong influence on public construction projects in Hokkaidō.
Geography
The island of Hokkaidō is located in the north of Japan, nearRussia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
(Sakhalin Oblast
Sakhalin Oblast ( rus, Сахали́нская о́бласть, r=Sakhalínskaya óblast', p=səxɐˈlʲinskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) comprising the island of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands in the Russian ...
). It has coastlines on the Sea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, i ...
(to the west of the island), the Sea of Okhotsk (to the north), and the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
(to the east). The center of the island is mountainous, with volcanic plateau
A volcanic plateau is a plateau produced by volcanic activity. There are two main types: lava plateaus and pyroclastic plateaus.
Lava plateau
Lava plateaus are formed by highly fluid basaltic lava during numerous successive eruptions throu ...
x. Hokkaidō has multiple plains such as the Ishikari Plain
Ishikari Plain () is a plain in western Hokkaido. The area of the plain is approximately 3800km. The central city is Sapporo. Rice cultivation
The history of rice cultivation is an interdisciplinary subject that studies archaeological and docume ...
, Tokachi Plain , the Kushiro Plain (the largest wetland in Japan) and Sarobetsu Plain . Hokkaidō is which make it the second-largest island of Japan.
The Tsugaru Strait
The is a strait between Honshu and Hokkaido in northern Japan connecting the Sea of Japan with the Pacific Ocean. It was named after the western part of Aomori Prefecture. The Seikan Tunnel passes under it at its narrowest point 12.1 miles (1 ...
separates Hokkaidō from Honshu (Aomori Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan in the Tōhoku region. The prefecture's capital, largest city, and namesake is the city of Aomori. Aomori is the northernmost prefecture on Japan's main island, Honshu, and is bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the eas ...
); La Pérouse Strait
La Pérouse Strait (russian: пролив Лаперуза), or Sōya Strait, is a strait dividing the southern part of the Russian island of Sakhalin from the northern part of the Japanese island of Hokkaidō, and connecting the Sea of Japan on t ...
separates Hokkaidō from the island of Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh ...
in Russia; Nemuro Strait Nemuro Strait, also called Notsuke Strait and Kunashirsky Strait (russian: Кунаширский пролив), is a strait, located at , separating Kunashir Island of the Kuril Islands, Russia ( claimed by Japan) from the Shiretoko Peninsula, Hok ...
separates Hokkaidō from Kunashir Island
, other_names = kz, Kün Ashyr; ja, 国後島
, location = Sea of Okhotsk
, locator_map = File:Kurily Kunashir.svg
, coordinates =
, archipelago = Kuril Islands
, total_islands =
, major_islands =
, area =
, length =
, width = f ...
in the Russian Kuril Islands
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands (; rus, Кури́льские острова́, r=Kuril'skiye ostrova, p=kʊˈrʲilʲskʲɪjə ɐstrɐˈva; Japanese: or ) are a volcanic archipelago currently administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast in the ...
.
The governmental jurisdiction of Hokkaidō incorporates several smaller islands, including Rishiri, Okushiri Island
is an island in Hokkaidō, Japan. It has an area of . The town of Okushiri and the Hiyama Prefectural Natural Park encompass the entire island. It has many pastures, beech tree forests, and a rocky coastline. There are two elementary schools, o ...
, and Rebun. (By Japanese reckoning, Hokkaidō also incorporates several of the Kuril Islands
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands (; rus, Кури́льские острова́, r=Kuril'skiye ostrova, p=kʊˈrʲilʲskʲɪjə ɐstrɐˈva; Japanese: or ) are a volcanic archipelago currently administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast in the ...
.) Hokkaidō Prefecture is the largest and northernmost Japanese prefecture. The island ranks 21st in the world by area.
Lake Tōya
is a volcanic caldera lake in Shikotsu-Toya National Park, Abuta District, Hokkaidō, Japan. It is part of "Toya Caldera and Usu Volcano Global Geopark" which joins in Global Geoparks Network. The stratovolcano of Mount Usu lies on the souther ...
, a volcanic caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ...
lake
File:Hokkaido-Japan-ISS-Space.png, Hokkaido seen from the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA ( ...
File:140829 Ichiko of Shiretoko Goko Lakes Hokkaido Japan04s3.jpg, Lake Shiretoko Goko in the town of Shari, Okhotsk Subprefecture
is a subprefecture of Hokkaido Prefecture, Japan. It was renamed from the earlier Abashiri Subprefecture on April 1, 2010. Abashiri Subprefecture was established in 1897.
Etymology
Abashiri Prefecture was named after the subprefectural offic ...
, Hokkaidō
File:Spring Bloom Colors the Pacific Near Hokkaido.jpg, The Oyashio Current
, also known as Oya Siwo, Okhotsk or the Kurile current, is a cold subarctic ocean current that flows south and circulates counterclockwise in the western North Pacific Ocean. The waters of the Oyashio Current originate in the Arctic Ocean an ...
colliding with the Kuroshio Current
The , also known as the Black or or the is a north-flowing, warm ocean current on the west side of the North Pacific Ocean basin. It was named for the deep blue appearance of its waters. Similar to the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic, the Ku ...
off the coast of Hokkaido
Population
 Hokkaidō has the third-largest population of Japan's five main islands, with 5,383,579 people . It has the lowest population-density in Japan with just 64.5/km2 (160/sq mi) (2016). By population, it ranks 21st globally. Major cities include
Hokkaidō has the third-largest population of Japan's five main islands, with 5,383,579 people . It has the lowest population-density in Japan with just 64.5/km2 (160/sq mi) (2016). By population, it ranks 21st globally. Major cities include Sapporo
( ain, サッ・ポロ・ペッ, Satporopet, lit=Dry, Great River) is a city in Japan. It is the largest city north of Tokyo and the largest city on Hokkaido, the northernmost main island of the country. It ranks as the fifth most populous cit ...
and Asahikawa
is a city in Kamikawa Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the capital of the subprefecture, and the second-largest city in Hokkaido, after Sapporo. It has been a core city since April 1, 2000. The city is currently well known for the Asahiy ...
in the central region and the port of Hakodate
is a city and port located in Oshima Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the capital city of Oshima Subprefecture. As of July 31, 2011, the city has an estimated population of 279,851 with 143,221 households, and a population density of 412.8 ...
facing Honshu
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island se ...
in the south. Sapporo is the largest city of Hokkaidō and 5th-largest in Japan. It had a population of 1,957,914 and a population density of .
Flora and fauna
There are three populations of theUssuri brown bear
The Ussuri brown bear (''Ursus arctos lasiotus''), also known as the Ezo brown bear, Russian bear, or the black grizzly bear, is a subspecies of the brown bear or a population of the Eurasian brown bear (''U. a. arctos''). One of the largest b ...
found on the island. There are more brown bears in Hokkaidō than anywhere else in Asia besides Russia. The Hokkaidō brown bear is separated into three distinct lineages. There are only eight lineages in the world. Those on Honshu died out long ago.
The native conifer species in northern Hokkaidō is the Sakhalin fir (''Abies sachalinensis
''Abies sachalinensis'', the Sakhalin fir, is a species of conifer in the family Pinaceae. It is found in Sakhalin island and southern Kurils (Russia), and also in northern Hokkaido ( Japan).
The first discovery by a European was by Carl Fri ...
''). The flowering plant '' Hydrangea hirta'' is also found on the island.
:
Geologic activity
Like many areas of Japan, Hokkaidō is seismically active. Aside from numerousearthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, fr ...
s, the following volcanoes are considered still active (at least one eruption since 1850):
* Hokkaido Koma-ga-take
, also , , or just is a andesitic stratovolcano on the border between Mori, Shikabe, and Nanae, all within the Oshima Subprefecture of Hokkaidō, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in ...
* Mount Usu and Shōwa-shinzan
is a volcanic lava dome in the Shikotsu-Toya National Park, Hokkaido, Japan, next to Mount Usu. The mountain was created between 28 December 1943 and September 1945.神沼克伊,小山悦郎 ''日本の火山を科学する 日本列島津� ...
* Mount Tarumae
is located in the Shikotsu-Toya National Park in Hokkaidō, Japan. It is located near both Tomakomai and Chitose towns and can be seen clearly from both. It is on the shores of Lake Shikotsu, a caldera lake. Tarumae is a 1,041 metre active and ...
* Mount Tokachi
* Mount Meakan
In 1993, an earthquake of magnitude 7.7 generated a tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater exp ...
which devastated Okushiri, killing 202 inhabitants. An earthquake of magnitude 8.3 struck near the island on September 26, 2003. On September 6, 2018, an earthquake of magnitude 6.6 struck with its epicenter near the city of Tomakomai
is a city and port in Iburi Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the largest city in the Iburi Subprefecture, and the fourth largest city in Hokkaido. As of 29 February 2012, it had an estimated population of 174,216, with 83,836 households ...
, causing a blackout across the whole island.
On May 16, 2021, an earthquake measuring 6.1 on the Richter scale struck off Japan's Hokkaidō prefecture.
Parks
Lake Akan
is a lake in Kushiro, Hokkaidō, Japan. It is located in Akan National Park and is a Ramsar Site.
History
Volcanic activity formed the lake some 6,000 years ago, when a lava dam was formed. The lake used to have a clarity of 8–9 meters i ...
and Mount Meakan
File:Image-2008 Lake Masshu.jpg, View of Lake Mashū
(Ainu language, Ainu: Kamuy-to) is an endorheic Volcanic crater lake, crater lake formed in the caldera of a potentially active volcano. It is located in Akan Mashu National Park on the island of Hokkaido, Japan. It has been called the clearest ...
File:Lake Shikotsu17n4272.jpg, Lake Shikotsu
is a caldera lake in Chitose, Hokkaidō, Japan. It is a part of the Shikotsu-Toya National Park.
Geography
Lake Shikotsu is located in the south-west part of Hokkaidō. It has an average depth of and a maximum depth of , making it the seco ...
File:Sounkyo1.jpg, Sōunkyō
is a range of gorges located in Kamikawa, Hokkaidō, Japan. Situated in the Daisetsuzan National Park, the area is known for its hotels and onsen (hot springs) resorts as well as waterfalls and magnificent cliffs scenery. The term "Sōunkyō" me ...
, a gorge in the Daisetsu-zan
, or Taisetsuzan is located in the mountainous center of the northern Japanese island of Hokkaidō. At , Daisetsuzan is the largest national park in Japan, and is approximately the size of Kanagawa Prefecture. Daisetsuzan, meaning "great snowy m ...
Volcanic Area
Akkeshi Prefectural Natural Park
is a Quasi-National Park in eastern Hokkaidō, Japan. Established in 2021, the park spans the municipalities of Akkeshi, Hamanaka, Kushiro, and Shibecha. It subsumes and replaces the former Akkeshi Prefectural Natural Park, established in 19 ...
** Esan Prefectural Natural Park
** Furano-Ashibetsu Prefectural Natural Park
** Hiyama Prefectural Natural Park
** Kariba-Motta Prefectural Natural Park
** Matsumae-Yagoshi Prefectural Natural Park
** North Okhotsk Prefectural Natural Park
**Nopporo Shinrin Kōen Prefectural Natural Park
is a Prefectural Natural Park in western Hokkaidō, Japan. Established in 1968, the park spans the municipalities of Ebetsu, Kitahiroshima, and Sapporo.
The park is home of a number of attractions such as, the Hokkaido Centennial Memorial Tow ...
** Notsuke-Fūren Prefectural Natural Park
** Sharidake Prefectural Natural Park
** Shumarinai Prefectural Natural Park
** Teshiodake Prefectural Natural Park
Subprefectures

Municipalities
Hokkaidō is divided into 179 municipalities.Cities
There are 35 cities in Hokkaidō:Towns and villages
These are the towns and villages in Hokkaido Prefecture:Climate

 As Japan's coldest region, Hokkaidō has relatively cool summers and icy/snowy winters. Most of the island falls in the
As Japan's coldest region, Hokkaidō has relatively cool summers and icy/snowy winters. Most of the island falls in the humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
zone with Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
''Dfb'' (hemiboreal
Hemiboreal means halfway between the temperate and subarctic (or boreal) zones. The term is most frequently used in the context of climates and ecosystems.
Botany
A hemiboreal forest has some characteristics of a boreal forest to the north, and ...
) in most areas but ''Dfa'' (hot summer humid continental) in some inland lowlands. The average August temperature ranges from , while the average January temperature ranges from , in both cases depending on elevation and distance from the ocean, though temperatures on the western side of the island tend to be a little warmer than on the eastern. The highest temperature ever recorded is on 26 May 2019.
The northern portion of Hokkaidō falls into the taiga
Taiga (; rus, тайга́, p=tɐjˈɡa; relates to Mongolic and Turkic languages), generally referred to in North America as a boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruc ...
biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
with significant snowfall. Snowfall varies widely from as much as on the mountains adjacent to the Sea of Japan down to around on the Pacific coast. The island tends to have isolated snowstorms that develop long-lasting snowbanks. Total precipitation varies from on the mountains of the Sea of Japan coast to around (the lowest in Japan) on the Sea of Okhotsk coast and interior lowlands and up to around on the Pacific side. The generally high quality of powder snow
Classifications of snow describe and categorize the attributes of snow-generating weather events, including the individual crystals both in the air and on the ground, and the deposited snow pack as it changes over time. Snow can be classified ...
and numerous mountains in Hokkaidō make it a popular region for snow sports. The snowfall usually commences in earnest in November and ski resorts (such as those at Niseko, Furano, Teine and Rusutsu) usually operate between December and April. Hokkaidō celebrates its winter weather at the Sapporo Snow Festival
The is a festival held annually in Sapporo, Japan, over seven days in February. Odori Park, Susukino, and Tsudome are the main sites of the festival.
In 2007 (57th festival), about two million people visited Sapporo to see the hundreds of ...
.
During the winter, passage through the Sea of Okhotsk is often complicated by large floes of drift ice
Drift ice, also called brash ice, is sea ice that is not attached to the shoreline or any other fixed object (shoals, grounded icebergs, etc.).Leppäranta, M. 2011. The Drift of Sea Ice. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. Unlike fast ice, which is "faste ...
. Combined with high winds that occur during winter, this frequently brings air travel and maritime activity to a halt beyond the northern coast of Hokkaidō. Ports on the open Pacific Ocean and Sea of Japan are generally ice-free year round, though most rivers freeze during the winter.
Unlike the other major islands of Japan, Hokkaidō is normally not affected by the June–July rainy season
The rainy season is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs.
Rainy Season may also refer to:
* ''Rainy Season'' (short story), a 1989 short horror story by Stephen King
* "Rainy Season", a 2018 song by Monni
* '' ...
and the relative lack of humidity and typically warm, rather than hot, summer weather makes its climate an attraction for tourists from other parts of Japan.
Temperature comparison
Major cities and towns
 Hokkaidō's largest city is the capital,
Hokkaidō's largest city is the capital, Sapporo
( ain, サッ・ポロ・ペッ, Satporopet, lit=Dry, Great River) is a city in Japan. It is the largest city north of Tokyo and the largest city on Hokkaido, the northernmost main island of the country. It ranks as the fifth most populous cit ...
, which is a designated city. The island has two core cities: Hakodate
is a city and port located in Oshima Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the capital city of Oshima Subprefecture. As of July 31, 2011, the city has an estimated population of 279,851 with 143,221 households, and a population density of 412.8 ...
in the south and Asahikawa
is a city in Kamikawa Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the capital of the subprefecture, and the second-largest city in Hokkaido, after Sapporo. It has been a core city since April 1, 2000. The city is currently well known for the Asahiy ...
in the central region. Other important population centers include Rumoi, Iwamizawa
is a city in Sorachi Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the capital of Sorachi Subprefecture.
As of September 30, 2016, the city has an estimated population of 84,127 and the density of 170 persons per km². The total area is .
On March 27, ...
, Kushiro
is a city in Kushiro Subprefecture on the island of Hokkaido, Japan. It serves as the subprefecture's capital and it is the most populated city in the eastern part of the island.
Geography
Mountains
* Mount Oakan
* Mount Meakan
* Mount Akan ...
, Obihiro
is a city in Tokachi Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. Obihiro is the only designated city in the Tokachi area. As of February 29, 2020, the city has an estimated population of 165,851. The next most populous municipality in Tokachi is the ...
, Kitami
is a city in Okhotsk Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the most populous city and the commercial center in the subprefecture, although the subprefecture capital is Abashiri.
Kitami is physically in the middle of Okhotsk Subprefecture. Th ...
, Abashiri
is a city located in Okhotsk Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan.
Abashiri is known as the site of the Abashiri Prison, a Meiji-era facility used for the incarceration of political prisoners. The old prison has been turned into a museum, but the cit ...
, Wakkanai
' meaning "cold water river" is a city located in Sōya Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the capital of Sōya Subprefecture. It contains Japan's northernmost point, Cape Sōya, from which the Russian island of Sakhalin can be seen.
As of 1 ...
, and Nemuro Nemuro may refer to:
* Nemuro Subprefecture, Hokkaido Prefecture, Japan
** Nemuro, Hokkaido, a city
** Nemuro Peninsula
** Nemuro Strait
** Nemuro Bay
* Nemuro Province
was an old province in Japan in what is today Nemuro Subprefecture, Hokkai ...
.
Gallery
Asahikawa
is a city in Kamikawa Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the capital of the subprefecture, and the second-largest city in Hokkaido, after Sapporo. It has been a core city since April 1, 2000. The city is currently well known for the Asahiy ...
File:Cityscapes of Hakodate Hokkaido pref Japan01n.jpg, Hakodate
is a city and port located in Oshima Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the capital city of Oshima Subprefecture. As of July 31, 2011, the city has an estimated population of 279,851 with 143,221 households, and a population density of 412.8 ...
File:Nusamai-Bridge.jpg, Kushiro
is a city in Kushiro Subprefecture on the island of Hokkaido, Japan. It serves as the subprefecture's capital and it is the most populated city in the eastern part of the island.
Geography
Mountains
* Mount Oakan
* Mount Meakan
* Mount Akan ...
File:ObihiroMainSummer.jpg, Obihiro
is a city in Tokachi Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. Obihiro is the only designated city in the Tokachi area. As of February 29, 2020, the city has an estimated population of 165,851. The next most populous municipality in Tokachi is the ...
File:春光町から北見市中心部方向 - panoramio.jpg, Kitami
is a city in Okhotsk Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the most populous city and the commercial center in the subprefecture, although the subprefecture capital is Abashiri.
Kitami is physically in the middle of Okhotsk Subprefecture. Th ...
File:Hokkaido-prefectural-road R6 central-Iwamizawa.JPG, Iwamizawa
is a city in Sorachi Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the capital of Sorachi Subprefecture.
As of September 30, 2016, the city has an estimated population of 84,127 and the density of 170 persons per km². The total area is .
On March 27, ...
File:Abashiri River09n.jpg, Abashiri
is a city located in Okhotsk Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan.
Abashiri is known as the site of the Abashiri Prison, a Meiji-era facility used for the incarceration of political prisoners. The old prison has been turned into a museum, but the cit ...
File:Wakkanai station001.JPG, Wakkanai
' meaning "cold water river" is a city located in Sōya Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the capital of Sōya Subprefecture. It contains Japan's northernmost point, Cape Sōya, from which the Russian island of Sakhalin can be seen.
As of 1 ...
File:Hokkaido pref road No35 Nosappu Cape.jpg, Nemuro Nemuro may refer to:
* Nemuro Subprefecture, Hokkaido Prefecture, Japan
** Nemuro, Hokkaido, a city
** Nemuro Peninsula
** Nemuro Strait
** Nemuro Bay
* Nemuro Province
was an old province in Japan in what is today Nemuro Subprefecture, Hokkai ...
File:Rumoi city nightview.JPG, Rumoi
Economy
 Although there is some
Although there is some light industry
Light industry are industries that usually are less capital-intensive than heavy industry and are more consumer-oriented than business-oriented, as they typically produce smaller consumer goods. Most light industry products are produced for ...
(most notably paper milling and beer brewing) most of the population is employed by the service sector. In 2001, the service sector and other tertiary industries generated more than three-quarters of the gross domestic product.
Agriculture and other primary industries play a large role in Hokkaidō's economy. Hokkaidō has nearly one fourth of Japan's total arable land. It ranks first in the nation in the production of a host of agricultural products, including wheat, soybeans, potatoes, sugar beets, onions, pumpkins, corn, raw milk, and beef. Hokkaidō also accounts for 22% of Japan's forests with a sizable timber industry. The prefecture is first in the nation in production of marine products and aquaculture. The average farm size in Hokkaidō is 26 hectares per farmer in 2013, which is almost 11 times bigger than the national average of 2.4 hectares.
 Tourism is an important industry, especially during the cool summertime when visitors are attracted to Hokkaidō's open spaces from hotter and more humid parts of Japan and other Asian countries. During the winter, skiing and other winter sports bring other tourists, and increasingly international ones, to the island.
Coal mining played an important role in the industrial development of Hokkaidō, with the Ishikari coalfield. Cities such as Muroran were primarily developed to supply the rest of the archipelago with coal.
Tourism is an important industry, especially during the cool summertime when visitors are attracted to Hokkaidō's open spaces from hotter and more humid parts of Japan and other Asian countries. During the winter, skiing and other winter sports bring other tourists, and increasingly international ones, to the island.
Coal mining played an important role in the industrial development of Hokkaidō, with the Ishikari coalfield. Cities such as Muroran were primarily developed to supply the rest of the archipelago with coal.
Transportation
 Hokkaidō's only land link to the rest of Japan is the
Hokkaidō's only land link to the rest of Japan is the Seikan Tunnel
The Seikan Tunnel ( ja, 青函トンネル, or , ), is a dual-gauge railway tunnel in Japan, with a portion under the seabed of the Tsugaru Strait, which separates Aomori Prefecture on the main Japanese island of Honshu from the northern isl ...
. Most travellers travel to the island by air: the main airport is New Chitose Airport
is an international airport located south-southeast of Chitose and Tomakomai, Hokkaidō, Japan, serving the Sapporo metropolitan area. By both traffic and land area, it is the largest airport in Hokkaidō.
It is adjacent to Chitose Air Ba ...
at Chitose, just south of Sapporo. Tokyo–Chitose is in the top 10 of the world's busiest air routes, handling more than 40 widebody round trips on several airlines each day. One of the airlines, Air Do
, previously known as , is a Japanese regional airline headquartered in Sapporo, Japan. It operates scheduled service between the islands of Honshu and Hokkaido in cooperation with All Nippon Airways, from its hubs at New Chitose Airport in Sap ...
was named after Hokkaidō.
Hokkaidō can be reached by ferry from Sendai, Niigata and some other cities, with the ferries from Tokyo dealing only in cargo. The Hokkaido Shinkansen
The is a Japanese high-speed Shinkansen rail line that links up with the Tōhoku Shinkansen in northern Aomori Prefecture in Honshu and continues on into the interior of Hokkaido through the undersea Seikan Tunnel. Construction started in May ...
takes passengers from Tokyo to near Hakodate in slightly over four hours. There is a fairly well-developed railway network, but many cities can only be accessed by road. The coal railways were constructed around Sapporo and Horonai during the late 19th century, as advised by American engineer Joseph Crawford.
Hokkaidō is home to one of Japan's Melody Roads, which is made from grooves cut into the ground, which when driven over causes a tactile vibration and audible rumbling transmitted through the wheels into the car body.
Education
The Hokkaido Prefectural Board of Education oversees public schools (except colleges and universities) in Hokkaidō. Public elementary and junior high schools (except Hokkaido Noboribetsu Akebi Secondary School and schools attached to Hokkaidō University of Education) are operated by municipalities, and public high schools are operated by either the prefectural board or municipalities.Senior High Schools
see List of high schools in Japan :ja:北海道高等学校一覧 As of 2016, there are 291 high schools in Hokkaido: 4 national schools, 55 private schools, 233 public schools, and 2 integrated junior-senior schools.Colleges and Universities
seeList of universities in Japan
The following is a comprehensive list of universities in Japan, categorized by prefecture.
The list contains only universities or colleges, either four-year or two-year, that still exist today and are classified as "schools" according to Article ...
Hokkaidō has 34 universities (7 national, 6 local public, and 21 private universities), 15 junior colleges, and 6 colleges of technology (3 national, 1 local public, and 2 private colleges).
Culture
 * Sapporo ramen,
* Sapporo ramen, Jingisukan
is a Japanese grilled mutton dish prepared on a convex metal skillet or other grill. It is often cooked alongside beansprouts, onions, mushrooms, and bell peppers, and served with a sauce based in either soy sauce or sake. The dish is particula ...
* Hokkaidō Heritage
* Hokkaido Museum
opened in Sapporo, Hokkaidō, Japan in 2015. Located within Nopporo Shinrin Kōen Prefectural Natural Park, the permanent exhibition is dedicated to the nature, history, and culture of Hokkaido. Also known as , the museum integrates and replaces ...
* Hokkaido Museum of Northern Peoples
The opened in Abashiri, Hokkaidō, Japan in 1991. Dedicated to the various peoples of the North, across Eurasia and the Americas, the collection includes items relating to the Sámi, Nanai, and Northwest Coast Indians, as well as the more loc ...
* Hokkaido Museum of Modern Art
* Historical Village of Hokkaido
* Hokkaido Archaeological Operations Center
opened in Ebetsu, Hokkaidō, Japan in 1999. Its aim is to protect, preserve, and utilize buried cultural properties.
History
In December 2017, researchers from the Hokkaido Archaeological Operations Center announced the discovery of the olde ...
* Pacific Music Festival The Pacific Music Festival (パシフィック・ミュージック・フェスティバル) is an international classical music festival held annually in Sapporo, Japan. It was founded in 1990 by Leonard Bernstein, along with the London Symphony Or ...
Sports
 The
The 1972 Winter Olympics
The 1972 Winter Olympics, officially the and commonly known as Sapporo 1972 ( ja, 札幌1972), was a winter multi-sport event held from February 3 to 13, 1972, in Sapporo, Japan. It was the first Winter Olympic Games to take place outside Euro ...
were held in Sapporo.
The sports teams listed below are based in Hokkaidō.
*Hokkaido American Football Association
The Hokkaido American Football Association (北海道アメリカンフットボール協会) or HAFA is an American college football league made up of colleges and universities on the island of Hokkaido, Japan
is Japan, Japan's Japanese arch ...
*Consadole Sapporo
is a Japanese professional football club, which plays in the J1 League. The team is based in Sapporo, on the island of Hokkaido.
The club name of "Consadole" is made from ''consado'', a reverse of the Japanese word and the Spanish express ...
(Association football)
*Hokkaido Nippon-Ham Fighters
The are a Japanese professional Baseball in Japan, baseball team based in Kitahiroshima, Hokkaidō. They compete in the Pacific League of Nippon Professional Baseball, playing the majority of their home games at ES CON Field Hokkaido. The Figh ...
* Levanga Hokkaido (basketball)
* Japan Basketball League
* Nippon Paper Cranes (Ice hockey)
*Oji Eagles
Red Eagles Hokkaido (レッドイーグルス北海道) are a professional ice hockey team based in Tomakomai city on Hokkaidō, Japan. They are members of the Asia League Ice Hockey.
History
The club was founded as the Oji Eagles in 1925. They h ...
(Ice hockey)
*Loco Solare
The is a curling club in Tokoro Town, Kitami City, Hokkaido Island, Japan. The club has about 40 teams, including a team .
Background
Hokkaido Island, Japan and Alberta, Canada became sister province in 1980.
Then, curling was introduced to ...
(Curling)
Winter festivals
*Sapporo Snow Festival
The is a festival held annually in Sapporo, Japan, over seven days in February. Odori Park, Susukino, and Tsudome are the main sites of the festival.
In 2007 (57th festival), about two million people visited Sapporo to see the hundreds of ...
* Asahikawa Ice Festival
* Sōunkyō Ice Festival
* Big Air – snowboarding freestyle competition
* Shōwa-Shinzan International Yukigassen - competitive snowballing
International relations
Hokkaidō has relationships with several provinces, states, and other entities worldwide. *Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
, Canada, since 1980
* Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang () formerly romanized as Heilungkiang, is a province in northeast China. The standard one-character abbreviation for the province is (). It was formerly romanized as "Heilungkiang". It is the northernmost and easternmost province ...
, China, since 1980
* Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut Massachusett_writing_systems.html" ;"title="nowiki/> məhswatʃəwiːsət.html" ;"title="Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət">Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət'' En ...
, United States, since 1988
* Sakhalin Oblast
Sakhalin Oblast ( rus, Сахали́нская о́бласть, r=Sakhalínskaya óblast', p=səxɐˈlʲinskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) comprising the island of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands in the Russian ...
, Russia, since 1998
* Busan
Busan (), officially known as is South Korea's most populous city after Seoul, with a population of over 3.4 million inhabitants. Formerly romanized as Pusan, it is the economic, cultural and educational center of southeastern South Korea, ...
, South Korea, since 2005
* Gyeongsangnam-do, South Korea, since 2006
* Seoul
Seoul (; ; ), officially known as the Seoul Special City, is the capital and largest metropolis of South Korea.Before 1972, Seoul was the ''de jure'' capital of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea) as stated iArticle 103 of ...
, South Korea, since 2010
* Chiang Mai, Thailand, since 2013
* Thimphu
Thimphu (; dz, ཐིམ་ཕུག ) is the capital and largest city of Bhutan. It is situated in the western central part of Bhutan, and the surrounding valley is one of Bhutan's ''dzongkhags'', the Thimphu District. The ancient capital city ...
, Bhutan
* Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
, United States of America
, 74 individual municipalities in Hokkaidō have sister city agreements with 114 cities in 21 countries worldwide.
Politics
Governor
The currentgovernor of Hokkaido
The is the head of the local government of Hokkaido, Japan's largest prefecture. The seat of the local government is located in Sapporo, the capital city of the prefecture. The current governor is Naomichi Suzuki.
List of governors
This is t ...
is Naomichi Suzuki
is a Japanese politician who currently serves as Governor of Hokkaidō. He previously served as mayor of Yūbari city for two consecutive terms from 2011 to 2019. He had also served in Regional Sovereignty Strategy Office of Cabinet Office a ...
. He won the governorship in the gubernatorial election in 2019 as an independent. In 1999, Hori was supported by all major non-Communist parties and Itō ran without party support. Before 1983, the governorship had been held by Liberal Democrats Naohiro Dōgakinai and Kingo Machimura for 24 years. In the 1971 election when Machimura retired, the Socialist candidate Shōhei Tsukada lost to Dōgakinai by only 13,000 votes; Tsukada was also supported by the Communist Party – the leftist cooperation in opposition to the US-Japanese security treaty had brought joint Socialist-Communist candidates to victory in many other prefectural and local elections in the 1960s and 1970s. In 1959, Machimura had defeated Yokomichi's father Setsuo in the race to succeed Hokkaidō's first elected governor, Socialist Toshibumi Tanaka who retired after three terms. Tanaka had only won the governorship in 1947 in a run-off election against Democrat
Democrat, Democrats, or Democratic may refer to:
Politics
*A proponent of democracy, or democratic government; a form of government involving rule by the people.
*A member of a Democratic Party:
**Democratic Party (United States) (D)
**Democratic ...
Eiji Arima because no candidate had received the necessary vote share to win in the first round as required by law at the time.
Assembly
The Hokkaido Legislative Assembly has 100 members from 47 electoral districts. , the LDP caucus holds a majority with 51 seats, the DPJ-led group has 26 members. Other groups are the ''Hokkaidō Yūshikai'' ofNew Party Daichi
The New Party Daichi (新党大地 ''Shintō Daichi'') is a Japanese political party. The party works based on jurisdiction and administrative divisions. The party's leader is Muneo Suzuki, a former Representative for the Liberal Democratic P ...
and independents with twelve seats, Kōmeitō
, formerly New Komeito and abbreviated NKP, is a conservative political party in Japan founded by lay members of the Buddhist Japanese new religious movement Soka Gakkai in 1964. Since 2012, it has served in government as the junior coalit ...
with eight, and the Japanese Communist Party
The is a Left-wing politics, left-wing to Far-left politics, far-left List of political parties in Japan, political party in Japan. With approximately 270,000 members belonging to 18,000 branches, it is one of the largest non-governing Communis ...
with four members.Hokkaido Prefectural AssemblyMembers by electoral district and parliamentary group
General elections for the Hokkaido assembly are currently held together with gubernatorial elections in the unified local elections (last round: April 2015).
Kōmeitō
, formerly New Komeito and abbreviated NKP, is a conservative political party in Japan founded by lay members of the Buddhist Japanese new religious movement Soka Gakkai in 1964. Since 2012, it has served in government as the junior coalit ...
won seven districts and the main opposition Constitutional Democrats
)
, newspaper = ''Rech''
, ideology = ConstitutionalismConstitutional monarchismLiberal democracyParliamentarism Political pluralismSocial liberalism
, position = Centre to centre-left
, international =
, colours ...
five. For the proportional election segment, Hokkaidō and Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and List of cities in Japan, largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, ...
are the only two prefectures that form a regional "block" district of their own. The Hokkaido proportional representation block
The or in official usage the "Hokkaidō electoral district" (北海道選挙区, ''Hokkaidō senkyo-ku'') is one of eleven proportional representation (PR) blocks for the House of Representatives in the Diet of Japan. It consists of Hokkaidō and ...
elects eight Representatives. In 2017, the Liberal Democratic Party received 28.8% of the proportional vote and won three seats, the Constitutional Democratic Party won three (26.4% of the vote), one seat each went to Kibō no Tō
was a conservative political party in Japan founded by Tokyo Governor Yuriko Koike. The party was founded just before the call of the 2017 general election. The party's ideology was mainly Japanese conservatism and nationalism.
Kibō no Tō ...
(12.3%) and Kōmeitō (11.0%). The Japanese Communist Party
The is a Left-wing politics, left-wing to Far-left politics, far-left List of political parties in Japan, political party in Japan. With approximately 270,000 members belonging to 18,000 branches, it is one of the largest non-governing Communis ...
, who won a seat in 2014
File:2014 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Stocking up supplies and personal protective equipment (PPE) for the Western African Ebola virus epidemic; Citizens examining the ruins after the Chibok schoolgirls kidnapping; Bundles of wat ...
, lost their seat in 2017 while receiving 8.5% of the votes.
In the upper house of the National Diet, a major reapportionment in the 1990s halved the number of Councillors from Hokkaidō per election from four to two. After the elections of 2010 and 2013, the Hokkaido electoral district – like most two-member districts for the upper house – is represented by two Liberal Democrats and two Democrats. In the 2016 upper house election, the district magnitude will be raised to three, Hokkaidō will then temporarily be represented by five members and six after the 2019 election.
See also
*Former Hokkaidō Government Office
The facilities of the former Hokkaidō Government Office in Sapporo, Japan, include a conference room, a museum shop, a tourist information office, and a few historical exhibition rooms and libraries. Visitors can enter the building for free. Flow ...
* Hokkaido dialects
The , commonly called , originate in relatively recent settlement from mainland Japan. The greater part of Hokkaidō was settled from a mix of areas, especially the Tōhoku and Hokuriku regions, from the Meiji period onwards, so that various Ja ...
* People from Hokkaido
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, ...
* Sankebetsu brown bear incident
* Sinnoh, a fictional region in the '' Pokémon'' franchise which is based on Hokkaido.
* List of cities in Hokkaido by population
The following list sorts all cities (including towns and villages) in the Japanese prefecture of Hokkaido with a population of more than 10,000 according to the 2020 Census. As of October 1, 2020, 55 places fulfill this criterion and are listed ...
Notes
Citations
Explanatory notes
Source: English edition of Sightseeing in Hokkaido, Winter Festival and EventsGeneral references
* * Bisignani, J. D. (1993). ''Japan Handbook''. Chico, California: Moon Publications. ;OCLC 8954556
* McDougall, Walter A. (1993). ''Let the Sea Make a Noise: A History of the North Pacific from Magellan to MacArthur''. New York: Basic Books.
OCLC 28017793
* Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric and Käthe Roth. (2005)
''Japan encyclopedia''
Cambridge:
Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retir ...
. OCLC 58053128
External links
Hokkaido Official Website
(In English)
Hokkaido Ski Resort
{{Authority control Ainu geography Japanese archipelago Prefectures of Japan