History of Lesotho on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of people living in the area now known as

, Government of Lesotho Fearing defeat, Moshoeshoe made further appeals to High Commissioner
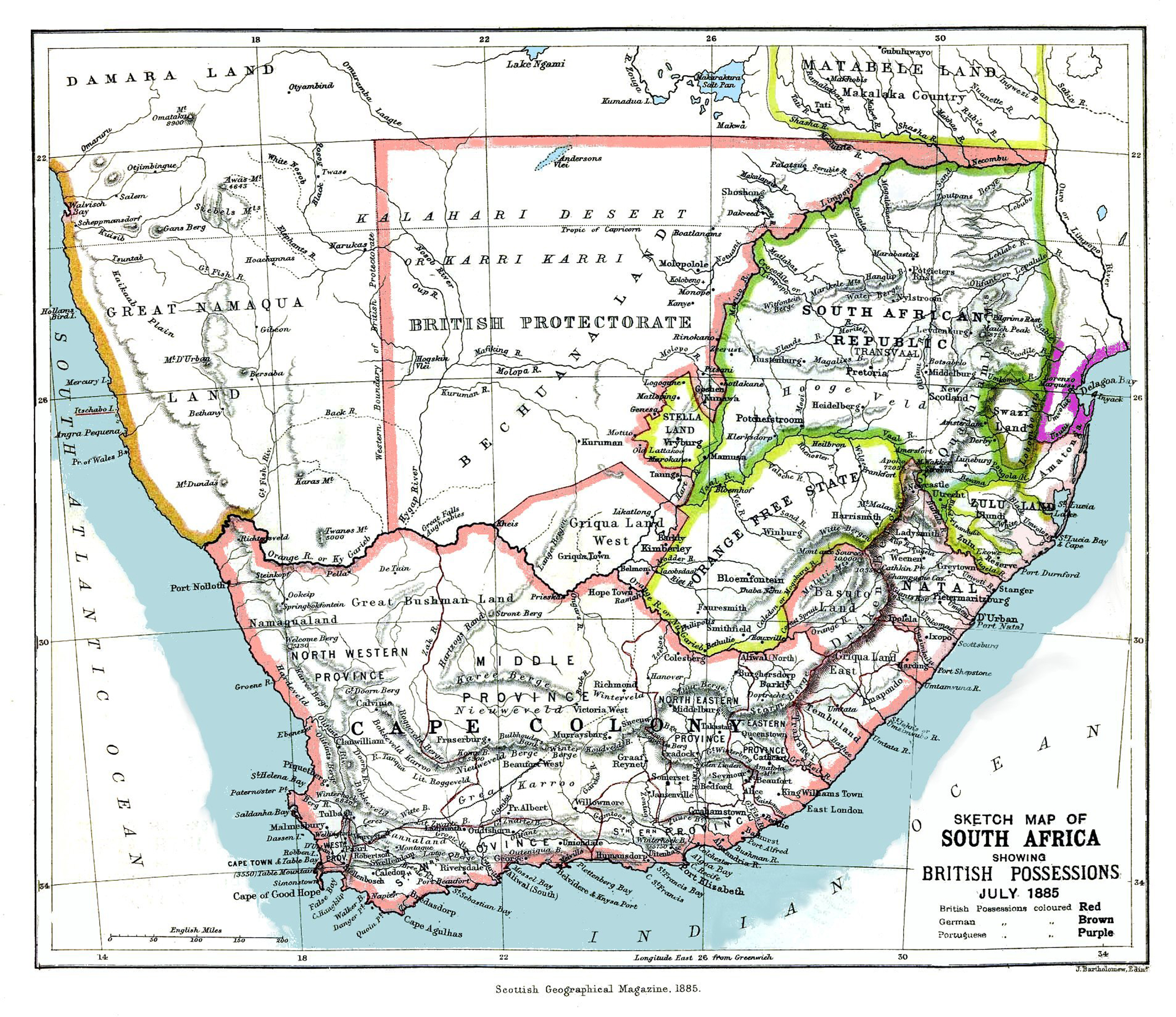 Cape Town's inability to control the territory led to its return to crown control in 1884 as the Territory of Basutoland. The colony was bound by the
Cape Town's inability to control the territory led to its return to crown control in 1884 as the Territory of Basutoland. The colony was bound by the
 On October 4, 1966, the Kingdom of Lesotho attained full independence, governed by a
On October 4, 1966, the Kingdom of Lesotho attained full independence, governed by a
Lesotho
Lesotho ( ), officially the Kingdom of Lesotho, is a country landlocked as an enclave in South Africa. It is situated in the Maloti Mountains and contains the highest mountains in Southern Africa. It has an area of over and has a populatio ...
() goes back as many as 400 years. The present Lesotho (then called Basotholand) emerged as a single polity
A polity is an identifiable political entity – a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources. A polity can be any other group of ...
under King Moshoeshoe I in 1822. Under Moshoeshoe I, Basotho joined other clans in their struggle against the Lifaqane associated with famine and the reign of Shaka Zulu
Shaka kaSenzangakhona ( – 22 September 1828), also known as Shaka Zulu () and Sigidi kaSenzangakhona, was the king of the Zulu Kingdom from 1816 to 1828. One of the most influential monarchs of the Zulu, he ordered wide-reaching reforms that ...
from 1818 to 1828.
Subsequent evolution of the state was shaped by contact with the British and Dutch colonists
A settler is a person who has migrated to an area and established a permanent residence there, often to colonize the area.
A settler who migrates to an area previously uninhabited or sparsely inhabited may be described as a pioneer.
Settle ...
from Cape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie), also known as the Cape of Good Hope, was a British colony in present-day South Africa named after the Cape of Good Hope, which existed from 1795 to 1802, and again from 1806 to 1910, when it united with th ...
. Missionaries invited by Moshoeshoe I developed orthography and printed works in the Sesotho language between 1837 and 1855. The country set up diplomatic channels and acquired guns for use against the encroaching Europeans and the Korana
The Korana is a river in central Croatia and west Bosnia and Herzegovina. The river has a total length of and watershed area of .
The river's name is derived from Proto-Indo-European ''*karr-'' 'rock'. It was recorded in the 13th century as '' ...
people. Territorial conflicts with both British and Boer
Boers ( ; af, Boere ()) are the descendants of the Dutch-speaking Free Burghers of the eastern Cape frontier in Southern Africa during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries. From 1652 to 1795, the Dutch East India Company controlled this are ...
settlers arose periodically, including Moshoeshoe's notable victory over the Boers in the Free State–Basotho War, but the final war in 1867 with an appeal to Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previ ...
, who agreed to make Basotholand a British suzerainty. In 1869, the British signed a treaty at Aliwal with the Boers that defined the boundaries of Basotholand and later Lesotho, which by ceding the western territories effectively reduced Moshoeshoe's kingdom to half its previous size.
The extent to which the British exerted direct control over Basotholand waxed and waned until Basotholand’s independence in 1966, when it became the Kingdom of Lesotho. However, when the ruling Basotho National Party
The Basotho National Party is a political party in Lesotho, founded in 1959 in colonial Basutoland as the Basutoland National Party by Leabua Jonathan. He was Prime Minister from the 1965 general election until the 1986 coup d'état.
In the ...
(BNP) lost the first post-independence general elections to the Basotho Congress Party (BCP), Leabua Jonathan
Joseph Leabua Jonathan (30 October 1914 – 5 April 1987) was the second prime minister of Lesotho. He succeeded Chief Sekhonyana Nehemia Maseribane following a by-election and held that post from 1965 to 1986.
Early life and career
Born in L ...
refused to cede and declared himself Tona Kholo (Sesotho translation of prime minister). The BCP began an insurrection that culminated in a January 1986 military coup, that then forced the BNP out of office. Power was transferred to King
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the t ...
Moshoeshoe II
Moshoeshoe II (2 May 1938 – 15 January 1996), previously known as Constantine Bereng Seeiso, was the Paramount Chief of Basutoland, succeeding paramount chief Seeiso from 1960 until the country gained full independence from Britain in 1966. ...
, until then a ceremonial monarch, but forced into exile when he lost favour with the military the following year. His son was installed as King Letsie III
Letsie III (born Seeiso Bereng; 17 July 1963) is King of Lesotho. He succeeded his father, Moshoeshoe II, who was forced into exile in 1990. His father was briefly restored in 1995 but died in a car crash in early 1996, and Letsie became king a ...
. Conditions remained tumultuous, including an August 1994 self-coup by Letsie III, until 1998 when the Lesotho Congress for Democracy (LCD) came to power in elections which were deemed fair by international observers. Despite protests from opposition parties, the country has remained relatively stable since.
Ancient history
At some stage during their migration south from a tertiary dispersal area Bantu speaking peoples came to settle the lands that now make up Lesotho as well as a more extensive territory of fertile lands that surround modern day Lesotho. These people spoke a unique "South Sotho" dialectseSotho
Sotho () or Sesotho () or Southern Sotho is a Southern Bantu language of the Sotho–Tswana ("S.30") group, spoken primarily by the Basotho in Lesotho, where it is the national and official language; South Africa (particularly the Free St ...
and called themselves the Basotho
The Sotho () people, also known as the Basuto or Basotho (), are a Bantu people, Bantu nation native to Lesotho, southern Africa. They split into different ethnic groups over time, due to regional conflicts and colonialism, which resulted in t ...
. There were several severe disruptions to the Basotho peoples in the early 19th century. One view states that the first of these were marauding Zulu clans, displaced from Zululand as part of the Lifaqane (or Mfecane
The Mfecane ( isiZulu, Zulu pronunciation: ̩fɛˈkǀaːne, also known by the Sesotho names Difaqane or Lifaqane (all meaning "crushing, scattering, forced dispersal, forced migration") is a historical period of heightened military conflict ...
), wrought havoc on the Basotho peoples they encountered as they moved first west and then north. The second that no sooner than the Zulu has passed to the north than the first Voortrekkers arrived, some of whom obtained hospitality during their difficult trek north. Early Voortrekker accounts describe how the lands surrounding the mountain retreat of the Basotho had been burnt and destroyed, in effect leaving a vacuum that subsequent Voortrekkers began to occupy.
However, this interpretation of history for the entire southern region of Africa is a matter of dispute. One attempt at refutation came by Norman Etherington in ''The Great Treks: The Transformation of Southern Africa, 1815-1854'' (Longman, 2001). Etherington argues that no such thing as the Mfecane occurred, the Zulu were no more marauding than any other group in the region, and the land the Voortrekkers saw as empty was not settled by either Zulu or Basotho because those people did not value open lowland plains as pasture.
Basutoland

Free State–Basotho Wars
In 1818, Moshoeshoe I consolidated various Basotho groupings and became their king. During Moshoeshoe's reign (1823–1870), a series of wars (1856–68) were fought with theBoers
Boers ( ; af, Boere ()) are the descendants of the Dutch-speaking Free Burghers of the eastern Cape frontier in Southern Africa during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries. From 1652 to 1795, the Dutch East India Company controlled this are ...
who had settled in traditional Basotho lands. These wars resulted in the extensive loss of land, now known as the "Lost Territory".
A treaty was signed with the Boers of Griqualand
The Griquas (; af, Griekwa, often confused with ''!Orana'', which is written as ''Korana'' or ''Koranna'') are a subgroup of heterogeneous former Khoe-speaking nations in Southern Africa with a unique origin in the early history of the Cap ...
in 1843 and an agreement was made with the British in 1853 following a minor war. The disputes with the Boers over land, however, were revived in 1858 with Senekal's War and again, more seriously, in 1865 with the Seqiti War. The Boers had a number of military successes, killing possibly 1,500 Basotho soldiers, and annexed an expanse of arable land
Arable land (from the la, arabilis, "able to be ploughed") is any land capable of being ploughed and used to grow crops.''Oxford English Dictionary'', "arable, ''adj''. and ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 2013. Alternatively, for th ...
which they were able to retain following a treaty at Thaba Bosiu
Thaba Bosiu is a sandstone plateau with an area of approximately and a height of 1,804 meters above sea level. It is located between the Orange and Caledon Rivers in the Maseru District of Lesotho, 24 km east of the country's capital Maseru. ...
. Further conflict led to an unsuccessful attack on Thaba Bosiu and the death of a Boer commandant, Louw Wepener, but by 1867, much of Moshoeshoe's land and most of his fortresses had been taken.About Lesotho, Government of Lesotho Fearing defeat, Moshoeshoe made further appeals to High Commissioner
Philip Edmond Wodehouse
Sir Philip Edmond Wodehouse (27 February 1811 – 25 October 1887) was a British colonial administrator.
Biography
Wodehouse was the eldest child of Edmond Wodehouse and his wife and first cousin Lucy Wodehouse. His paternal grandfather T ...
for British assistance. On 12 March 1868, the British Cabinet agreed to place the territory under British protection and the Boers were ordered to leave. In February 1869, the British and the Boers agreed to the Convention of Aliwal North, which defined the boundaries of the protectorate. The arable land west of the Caledon River
The Caledon River ( st, Mohokare) is a major river located in central South Africa. Its total length is , rising in the Drakensberg Mountains on the Lesotho border, flowing southwestward and then westward before joining the Orange River near Bet ...
remained in Boer hands and is referred to as the Lost or Conquered Territory. Moshoeshoe died in 1870 and was buried atop Thaba Bosiu.
Annexation by Cape Colony
In 1871 the protectorate was annexed toCape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie), also known as the Cape of Good Hope, was a British colony in present-day South Africa named after the Cape of Good Hope, which existed from 1795 to 1802, and again from 1806 to 1910, when it united with th ...
. The Basotho resisted the British and in 1879 a southern chief, Moorosi, rose in revolt. His campaign was crushed, and he was killed in the fighting. The Basotho then began to fight amongst themselves over the division of Moorosi's lands. The British extended the Cape Peace Preservation Act of 1878 to cover Basutoland and attempted to disarm the natives. Much of the colony rose in revolt in the Gun War
The Basuto Gun War, also known as the Basutoland Rebellion, was a conflict between the Basuto and the British Cape Colony. It lasted from 13 September 1880 to 29 April 1881 and ended in a Basuto victory.
Following Basutoland's transformation in ...
(1880-1881), inflicting significant casualties upon the colonial British forces sent to subdue it. A peace treaty of 1881 failed to quell sporadic fighting.
Return to Crown colony
 Cape Town's inability to control the territory led to its return to crown control in 1884 as the Territory of Basutoland. The colony was bound by the
Cape Town's inability to control the territory led to its return to crown control in 1884 as the Territory of Basutoland. The colony was bound by the Orange River Colony
The Orange River Colony was the British colony created after Britain first occupied (1900) and then annexed (1902) the independent Orange Free State in the Second Boer War. The colony ceased to exist in 1910, when it was absorbed into the Union ...
, Natal Colony
The Colony of Natal was a British colony in south-eastern Africa. It was proclaimed a British colony on 4 May 1843 after the British government had annexed the Boer Republic of Natalia, and on 31 May 1910 combined with three other colonies to ...
, and Cape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie), also known as the Cape of Good Hope, was a British colony in present-day South Africa named after the Cape of Good Hope, which existed from 1795 to 1802, and again from 1806 to 1910, when it united with th ...
. It was divided into seven administrative districts: Berea, Leribe, Maseru
Maseru is the capital and largest city of Lesotho. It is also the capital of the Maseru District. Located on the Caledon River, Maseru lies directly on the Lesotho–South Africa border. Maseru had a population of 330,760 in the 2016 census. Th ...
, Mohale's Hoek
Mohale's Hoek is the capital city of Mohale's Hoek District in Lesotho. It had a population of approximately 40,040 in 2016.Lesotho Bureau of StatisticsCensus Pre Results2006.
History
Mohale's Hoek had first been inhabited by the San who were fo ...
, Mafeteng
Mafeteng is a city in Lesotho, and the Camptown (Lesotho), Camptown (capital city) of the district of Mafeteng District, Mafeteng. It is located about 76 kilometres south of the country's capital, Maseru and has a population of approximately 61,00 ...
, Qacha's Nek
Qacha's Nek is, since 1888, the camptown (capital) of Qacha's Nek District in Lesotho, only two kilometers from the South African border at above sea level. It has a population of approximately 15,900 (2016). It is home to Machabeng Gover ...
and Quthing. The colony was ruled by the British Resident Commissioner, who worked through the ''pitso'' (national assembly) of hereditary native chiefs under one paramount chief. Each chief ruled a ward within the territory. The first paramount chief was Lerothodi, the son of Moshoeshoe. During the Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the South ...
the colony was neutral. The population grew from around 125,000 in 1875, to 310,000 in 1901, and to 349,000 by 1904.
When the Union of South Africa
The Union of South Africa ( nl, Unie van Zuid-Afrika; af, Unie van Suid-Afrika; ) was the historical predecessor to the present-day Republic of South Africa. It came into existence on 31 May 1910 with the unification of the Cape, Natal, Tra ...
was founded in 1910 the colony was still controlled by the British and moves were made to transfer it to the Union. However the people of Basutoland opposed this and it did not occur.
During the course of World War I, over 4,500 Basuto enlisted into the military, most of whom served in the South African Native Labour Corps
The South African Native Labour Corps (SANLC) was a force of workers formed in 1916 in response to a British request for workers at French ports. About 25,000 South Africans joined the Corps. The SANLC was utilized in various menial noncombat tas ...
which fought on the Western Front. In 1916, Basutoland raised over £40,000 for the war effort. A year later, the troopship SS Mendi
SS ''Mendi'' was a British passenger steamship that was built in 1905 and, as a troopship, sank after collision with great loss of life in 1917.
Alexander Stephen and Sons of Linthouse in Glasgow, Scotland launched her on 18 June 1905 for ...
was sunk off the coast of the Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight ( ) is a county in the English Channel, off the coast of Hampshire, from which it is separated by the Solent. It is the largest and second-most populous island of England. Referred to as 'The Island' by residents, the Isl ...
, over 100 Basuto were killed in the sinking.
The differing fates of the seSotho-speaking peoples in the Protectorate of Basotholand and in the lands that became the Orange Free State are worth noting. The Orange Free State became a Boer
Boers ( ; af, Boere ()) are the descendants of the Dutch-speaking Free Burghers of the eastern Cape frontier in Southern Africa during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries. From 1652 to 1795, the Dutch East India Company controlled this are ...
-ruled territory. At the end of the Boer War, it was colonised by the British, and this colony was subsequently incorporated by Britain into the Union of South Africa as one of four provinces. It is still part of the modern day Republic of South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring count ...
, now known as the Free State. In contrast, Basotholand, along with the two other British Protectorates in the sub-Saharan region ( Bechuanaland and Swaziland
Eswatini ( ; ss, eSwatini ), officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland ( ; officially renamed in 2018), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its no ...
), was precluded from incorporation into the Union of South Africa. These protectorates were individually brought to independence by Britain in the 1960s. By becoming a protectorate, Basotholand and its inhabitants were not subjected to Afrikaner rule, which saved them from experiencing Apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid wa ...
, and so generally prospered under more benevolent British rule. Basotho residents of Basotholand had access to better health services and to education, and came to experience greater political emancipation through independence. These lands protected by the British, however, had a much smaller capacity to generate income and wealth than had the "lost territory", which had been granted to the Boers.
Following the British entry into World War II, the decision was taken to draw recruits from the High Commission Territories (HTC) of Swaziland
Eswatini ( ; ss, eSwatini ), officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland ( ; officially renamed in 2018), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its no ...
, Basutoland and Bechuanaland. Black citizens from the HTC were to be recruited into the African Auxiliary Pioneer Corps (AAPC) labor unit due to Afrikaner
Afrikaners () are a South African ethnic group descended from predominantly Dutch settlers first arriving at the Cape of Good Hope in the 17th and 18th centuries.Entry: Cape Colony. ''Encyclopædia Britannica Volume 4 Part 2: Brain to Cast ...
opposition to armed black units. Mobilization for the AAPC was launched in late July 1941 and by October 18,000 personnel had arrived in the Middle East. The anti-colonial Basutoland Lekhorlu la Bufo (Commoner's League) was banned and its leaders were imprisoned for demanding that training for the recruits be improved and encouraging desertion. The AAPC performed a wide range of manual labor, providing logistical support to the Allied war effort during the North African
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in t ...
, Dodecanese
The Dodecanese (, ; el, Δωδεκάνησα, ''Dodekánisa'' , ) are a group of 15 larger plus 150 smaller Greek islands in the southeastern Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean, off the coast of Turkey's Anatolia, of which 26 are inhabited. ...
and Italian campaigns. During the Italian campaign some AAPC relieved British field artillery units of their duty.
On 1 May 1943, British troopship SS ''Erinpura'' was torpedoed and sunk, resulting in the loss of 694 men from AAPC's 1919th and 1927th Basuto Companies; the unit's worst loss of life during the war. A total of 21,000 Basuto enlisted during the war, 1,105 of whom perished during its course. Basuto women also contributed to the war effort by knitting warm clothing for the military.
From 1948, the South African National Party put its apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid wa ...
policies into place, indirectly terminating any support among Basutos and/or UK colonial authorities for the country's incorporation in South Africa.
After a 1955 request by the Basutoland Council to legislate its internal affairs, in 1959 a new constitution gave Basutoland its first elected legislature. This was followed in April 1965 with general legislative elections with universal adult suffrage in which the Basotho National Party
The Basotho National Party is a political party in Lesotho, founded in 1959 in colonial Basutoland as the Basutoland National Party by Leabua Jonathan. He was Prime Minister from the 1965 general election until the 1986 coup d'état.
In the ...
(BNP) won 31 and the Basutoland Congress Party
The Basutoland Congress Party is a pan-Africanist and left-wing political party in Lesotho.
The Basutoland African Congress (BAC) was founded in 1952 by Ntsu Mokhehle and Potlako Leballo. The party was renamed the Basutoland Congress Party (BCP) ...
(BCP) won 25 of the 65 seats contested.
Kingdom of Lesotho
 On October 4, 1966, the Kingdom of Lesotho attained full independence, governed by a
On October 4, 1966, the Kingdom of Lesotho attained full independence, governed by a constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies di ...
with a bicameral Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. ...
consisting of a Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the e ...
and an elected National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the repr ...
. Early results of the first post-independence elections in January 1970 indicated that the Basotho National Party
The Basotho National Party is a political party in Lesotho, founded in 1959 in colonial Basutoland as the Basutoland National Party by Leabua Jonathan. He was Prime Minister from the 1965 general election until the 1986 coup d'état.
In the ...
(BNP) might lose control. Under the leadership of Prime Minister Chief Leabua Jonathan
Joseph Leabua Jonathan (30 October 1914 – 5 April 1987) was the second prime minister of Lesotho. He succeeded Chief Sekhonyana Nehemia Maseribane following a by-election and held that post from 1965 to 1986.
Early life and career
Born in L ...
, the ruling BNP refused to cede power to the rival Basotholand Congress Party (BCP), although the BCP was widely believed to have won the elections. Citing election irregularities, Prime Minister Leabua Jonathan nullified the elections, declared a national state of emergency, suspended the constitution, and dissolved the Parliament. In 1973, an appointed Interim National Assembly was established. With an overwhelming pro-government majority, it was largely the instrument of the BNP, led by Prime Minister Jonathan. In addition to the Jonathan regime's alienation of Basotho powerbrokers and the local population, South Africa had virtually closed the country's land borders because of Lesotho support of cross-border operations of the African National Congress
The African National Congress (ANC) is a social-democratic political party in South Africa. A liberation movement known for its opposition to apartheid, it has governed the country since 1994, when the first post-apartheid election install ...
(ANC). Moreover, South Africa publicly threatened to pursue more direct action against Lesotho if the Jonathan government did not root out the ANC presence in the country. This internal and external opposition to the government combined to produce violence and internal disorder in Lesotho that eventually led to a military takeover in 1986.
Under a January 1986 Military Council decree, state executive and legislative powers were transferred to the King who was to act on the advice of the Military Council, a self-appointed group of leaders of the Royal Lesotho Defense Force (RLDF). A military government chaired by Justin Lekhanya
General Justin Metsing Lekhanya (7 April 1938 – 20 January 2021) was the Minister of Defence and Chairman of the Military Council of Lesotho from 24 January 1986 to 2 May 1991.
Background
Born in Thaba-Tseka in 1938, Lekhanya completed his pri ...
ruled Lesotho in coordination with King Moshoeshoe II
Moshoeshoe II (2 May 1938 – 15 January 1996), previously known as Constantine Bereng Seeiso, was the Paramount Chief of Basutoland, succeeding paramount chief Seeiso from 1960 until the country gained full independence from Britain in 1966. ...
and a civilian cabinet appointed by the King.
In February 1990, King Moshoeshoe II was stripped of his executive and legislative powers and exiled by Lekhanya, and the Council of Ministers was purged. Lekhanya accused those involved of undermining discipline within the armed forces, subverting existing authority, and causing an impasse on foreign policy that had been damaging to Lesotho's image abroad. Lekhanya announced the establishment of the National Constituent Assembly
A constituent assembly (also known as a constitutional convention, constitutional congress, or constitutional assembly) is a body assembled for the purpose of drafting or revising a constitution. Members of a constituent assembly may be elected b ...
to formulate a new constitution for Lesotho with the aim of returning the country to democratic, civilian rule by June 1992. Before this transition, however, Lekhanya was ousted in 1991 by a mutiny
Mutiny is a revolt among a group of people (typically of a military, of a crew or of a crew of pirates) to oppose, change, or overthrow an organization to which they were previously loyal. The term is commonly used for a rebellion among member ...
of junior army officers that left Phisoane Ramaema as Chairman of the Military Council.
Because Moshoeshoe II initially refused to return to Lesotho under the new rules of the government in which the King was endowed only with ceremonial powers, Moshoeshoe's son was installed as King Letsie III
Letsie III (born Seeiso Bereng; 17 July 1963) is King of Lesotho. He succeeded his father, Moshoeshoe II, who was forced into exile in 1990. His father was briefly restored in 1995 but died in a car crash in early 1996, and Letsie became king a ...
. In 1992, Moshoeshoe II returned to Lesotho as a regular citizen until 1995 when King Letsie abdicated the throne in favor of his father. After Moshoeshoe II died in a car accident in 1996, King Letsie III ascended to the throne again.
In 1993, a new constitution was implemented leaving the King without any executive authority and proscribing him from engaging in political affairs. Multiparty elections were then held in which the BCP ascended to power with a landslide victory. Prime Minister Ntsu Mokhehle headed the new BCP government that had gained every seat in the 65-member National Assembly. In early 1994, political instability increased as first the army, followed by the police and prisons services, engaged in mutinies. In August 1994, King Letsie III, in collaboration with some members of the military, staged a coup, suspended Parliament, and appointed a ruling council. As a result of domestic and international pressures, however, the constitutionally elected government was restored within a month.
In 1995, there were isolated incidents of unrest, including a police strike in May to demand higher wages. For the most part, however, there were no serious challenges to Lesotho's constitutional order in the 1995-96 period. In January 1997, armed soldiers put down a violent police mutiny and arrested the mutineers.
In 1997, tension within the BCP leadership caused a split in which Dr. Mokhehle abandoned the BCP and established the Lesotho Congress for Democracy (LCD) followed by two-thirds of the parliament. This move allowed Mokhehle to remain as Prime Minister and leader of a new ruling party, while relegating the BCP to opposition status. The remaining members of the BCP refused to accept their new status as the opposition party and ceased attending sessions. Multiparty elections were again held in May 1998.
Although Mokhehle completed his term as Prime Minister, due to his failing health, he did not vie for a second term in office. The elections saw a landslide victory for the LCD, gaining 79 of the 80 seats contested in the newly expanded Parliament. As a result of the elections, Mokhehle's Deputy Prime Minister, Pakalitha Mosisili
Bethuel Pakalitha Mosisili (born 14 March 1945) is a former Mosotho politician who was the fourth prime minister of Lesotho from May 1998 to June 2012 and again from March 2015 to June 2017.Langa Commission, a commission appointed by
BBC News In August, after Thabane attempted to remove Lieutenant General Kennedy Tlai Kamoli from the head of the army, the Prime Minister fled the country alleging a coup was taking place. Kamoli denied that any coup had occurred.
Southern African Development Community
The Southern African Development Community (SADC) is an inter-governmental organization headquartered in Gaborone, Botswana.
Its goal is to further regional socio-economic cooperation and integration as well as political and security coopera ...
(SADC) to investigate the electoral process, however, was consistent with the view of international observers and local courts that the outcome of the elections was not affected by these incidents. Despite the fact that the election results were found to reflect the will of the people, opposition protests in the country intensified. The protests culminated in a violent demonstration outside the royal palace in early August 1998 and in an unprecedented level of violence, looting, casualties, and destruction of property. In early September, junior members of the armed services mutinied. The Government of Lesotho requested that a SADC task force intervene to prevent a military coup and restore stability to the country. To this end, Operation Boleas, consisting of South African and (later) Botswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label= Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kalah ...
troops, entered Lesotho on September 22, 1998 to put down the mutiny and restore the democratically elected government. The army mutineers were brought before a court-martial
A court-martial or court martial (plural ''courts-martial'' or ''courts martial'', as "martial" is a postpositive adjective) is a military court or a trial conducted in such a court. A court-martial is empowered to determine the guilt of mem ...
.
After stability returned to Lesotho, the SADC task force withdrew from the country in May 1999, leaving only a small task force (joined by Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and Moz ...
an troops) to provide training to the LDF. In the meantime, an Interim Political Authority (IPA), charged with reviewing the electoral structure in the country, was created in December 1998 and devised a proportional electoral system to ensure that there be opposition in the National Assembly. The new system retained the existing 80 elected Assembly seats, but added 40 seats to be filled on a proportional basis. Elections were held under this new system in May 2002, and the LCD won again, gaining 54% of the vote. For the first time, however, opposition political parties won significant numbers of seats, and despite some irregularities and threats of violence from Major General Lekhanya, Lesotho experienced its first peaceful election. Nine opposition parties now hold all 40 of the proportional seats, with the BNP having the largest share (21). The LCD has 79 of the 80 constituency-based seats.
In June 2014, Prime Minister Thomas Thabane suspended parliament because of conflict within his coalition, leading to criticisms that he was undermining the government.Lesotho 'coup' forces PM Thabane to South AfricaBBC News In August, after Thabane attempted to remove Lieutenant General Kennedy Tlai Kamoli from the head of the army, the Prime Minister fled the country alleging a coup was taking place. Kamoli denied that any coup had occurred.
See also
*History of Africa
The history of Africa begins with the emergence of hominids, archaic humans and — around 300–250,000 years ago—anatomically modern humans (''Homo sapiens''), in East Africa, and continues unbroken into the present as a patchwork of dive ...
* History of South Africa
* History of Southern Africa
*History of Swaziland
Artifacts indicating human activity dating back to the early Stone Age have been found in the Kingdom of Eswatini. The earliest known inhabitants of the region were Khoisan hunter-gatherers. Later, the population became predominantly Nguni dur ...
* List of heads of government of Lesotho
*List of Kings of Lesotho
This article list the monarchs (''Marena'') of Lesotho (also known as Basutoland until 1966).
Succession
The Succession to the throne of Lesotho is laid down in Chapter V of the African kingdom's constitution. The current King is Letsie III.
...
* Politics of Lesotho
References
Sources
* * * * * {{Lesotho topics