History of Kozhikode on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Kozhikode (
The Kozhikode (


 The ancient port of
The ancient port of  However, M.G.S. Narayanan in his book, Calicut: The City of Truth states that the Governor of Eranad, Mana Vikrama (who became the Zamorin of Calicut later) was, in fact, a favourite of the last Ceraman Perumal, Rama Kulasekara as the former was at the forefront of the wars with the
However, M.G.S. Narayanan in his book, Calicut: The City of Truth states that the Governor of Eranad, Mana Vikrama (who became the Zamorin of Calicut later) was, in fact, a favourite of the last Ceraman Perumal, Rama Kulasekara as the former was at the forefront of the wars with the
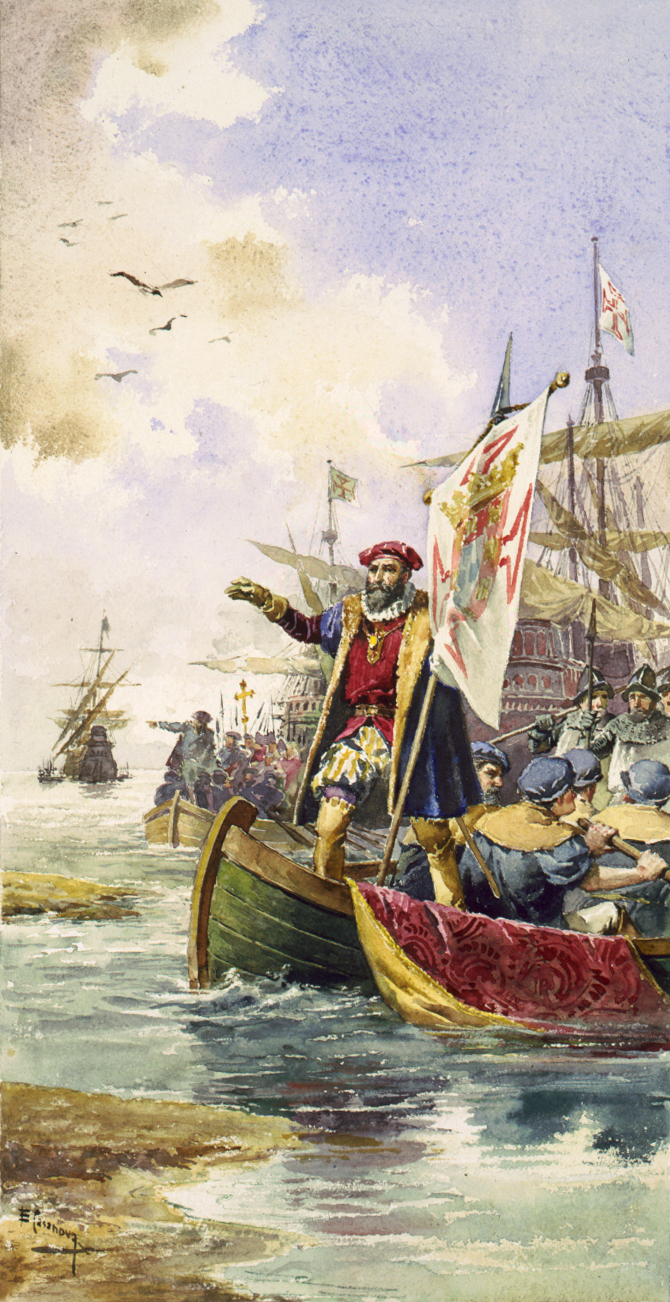
 This single event marked an epoch in the history of Kerala and India, not because Vasco da Gama 'discovered the sea route to India' as is in the common parlance (since the Chinese, the Middle East and the African kingdoms already traded directly with India) but unlike the others, the Portuguese yearned for political power and imperial domination. Vasco da Gama's fame is more often argued as due to historical reasons for which he was hardly responsiblePanickar.K.M, A History of Kerala(1959) Annamalai University in that he was accompanied by a Portuguese-speaking Arab merchant provided by the Sultan of Melinda in East Africa.
This single event marked an epoch in the history of Kerala and India, not because Vasco da Gama 'discovered the sea route to India' as is in the common parlance (since the Chinese, the Middle East and the African kingdoms already traded directly with India) but unlike the others, the Portuguese yearned for political power and imperial domination. Vasco da Gama's fame is more often argued as due to historical reasons for which he was hardly responsiblePanickar.K.M, A History of Kerala(1959) Annamalai University in that he was accompanied by a Portuguese-speaking Arab merchant provided by the Sultan of Melinda in East Africa.  With rising bonhomie between the Maharaja of Cochin and the Portuguese, there followed several wars in which the Portuguese propped up Cochin and Cannanore against the Zamorin. Scores of men perished in these wars on all sides starting in 1503 and continuing till the early 1570s. In February 1509, the defeat of the joint fleet of the
With rising bonhomie between the Maharaja of Cochin and the Portuguese, there followed several wars in which the Portuguese propped up Cochin and Cannanore against the Zamorin. Scores of men perished in these wars on all sides starting in 1503 and continuing till the early 1570s. In February 1509, the defeat of the joint fleet of the

Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 2 ...
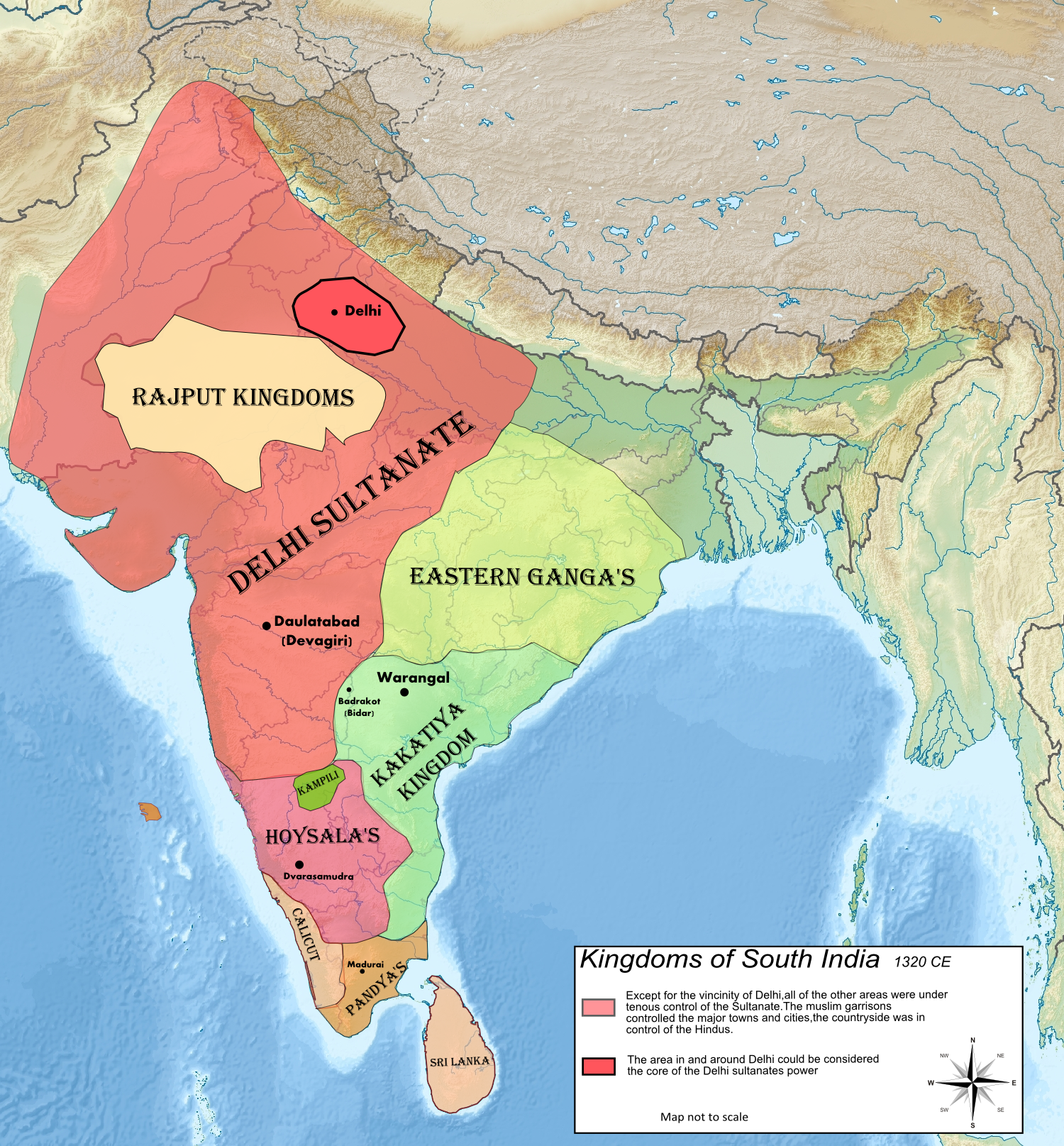
: ), also known as Calicut, was the kingdom of the Zamorin of Calicut
The Samoothiri (Anglicised as Zamorin; Malayalam: , Arabic: ''Sāmuri'', Portuguese: ''Samorim'', Dutch: ''Samorijn'', Chinese: ''Shamitihsi''Ma Huan's Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' 433 Translated and Edited ...
, in the present-day Indian state of Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South C ...
. Present-day Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second ...
is the second largest city in Kerala, as well as the headquarters of Kozhikode district
Kozhikode (), or Calicut district, is one of the 14 districts in the Indian state of Kerala, along its Southwestern Malabar Coast. The city of Kozhikode, also known as Calicut, is the district headquarters. The district is 67.15% urbanised.
T ...
.
Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second ...
was dubbed the "City of Spices" for its role as the major trading point of eastern spices during the Middle ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
and probably as early as Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations o ...
. The port at Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second ...
held the superior economic and political position in medieval Kerala coast, while Kannur, Kollam
Kollam (), also known by its former name Quilon , is an ancient seaport and city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is north of the state capital Thiruvananthapuram. The ci ...
, and Kochi
Kochi (), also known as Cochin ( ) ( the official name until 1996) is a major port city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is part of the district of Ernakulam in the state of ...
, were commercially important secondary ports, where the traders from various parts of the world would gather.''The Portuguese, Indian Ocean and European Bridgeheads 1500–1800''. Festschrift in Honour of Prof. K. S. Mathew (2001). Edited by: Pius Malekandathil and T. Jamal Mohammed. Fundacoa Oriente. Institute for Research in Social Sciences and Humanities of MESHAR (Kerala). It was once the capital of an independent kingdom by the same name and later of the erstwhile Malabar District
Malabar District, also known as Malayalam District, was an administrative district on the southwestern Malabar Coast of Bombay Presidency (1792-1800) and Madras Presidency (1800-1947) in British India, and independent India's Madras State (1 ...
. The port at Kozhikode acted as the gateway to medieval South India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union t ...
n coast for the Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
, the Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
s, the Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of v ...
, and finally the Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common genetic ancestry, common language, or both. Pan and Pfeil (2004 ...
.
Foundation

 The ancient port of
The ancient port of Tyndis
Tyndis ( grc, Τύνδις) was an ancient Indian seaport/harbor-town mentioned in the Graeco-Roman writings. According to the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea,'' Tyndis was located north of port Muziris in the country of the Cerobothra (presen ...
which was located on the northern side of Muziris
Muziris ( grc, Μουζιρίς, Old Malayalam: ''Muciri'' or ''Muciripattanam'' possibly identical with the medieval ''Muyirikode'') was an ancient harbour and an urban centre on the Malabar Coast. Muziris found mention in the ''Periplus ...
, as mentioned in the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' ( grc, Περίπλους τῆς Ἐρυθρᾶς Θαλάσσης, ', modern Greek '), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation an ...
'', was somewhere around Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second ...
. Its exact location is a matter of dispute. The suggested locations are Ponnani
Ponnani () is a municipality in Ponnani Taluk, Malappuram District, in the state of Kerala, India. It serves as the administrative center of the Taluk and Block Panchayat of the same name. It is situated at the estuary of Bharatappuzha (Riv ...
, Tanur, Beypore
Beypore or Beypur (formerly Beypoor) is an ancient port town and a locality town in Kozhikode district in the state of Kerala, India. It is located opposite to Chaliyam, the estuary where the river Chaliyar empties into Arabian Sea. Beypore is ...
-Chaliyam
Chaliyam is a village situated at the estuary of Chaliyar (River Beypore) in Kozhikode district of Kerala, India. Chaliyam forms an island, bounded by the Chaliyar in the north, and River Kadalundi in south, and the Conolly Canal in the east. ...
-Kadalundi
Kadalundi is a village in Kozhikode district, Kerala, India. It is a coastal village close to the Arabian Sea. Kadalundi is famous for its bird sanctuary, which is home to various migratory birds during certain seasons and has been recently decl ...
-Vallikkunnu
Vallikkunnu is a village in Tirurangadi Taluk of Malappuram district in the state of Kerala, India with an area of 25 km2. It is located 5 km north of Parappanangadi town and comes under the jurisdiction of Parappanangadi Police St ...
, and Koyilandy
A Survey of Kerala History, A. Shreedhara Menon ar, Fundriya pt, Pandarani
, settlement_type = MunicipalityTaluk
, image_skyline = KadaloorPointLight 01.jpg
, image_alt =
, image_caption ...
. Tyndis was a major center of trade, next only to Muziris
Muziris ( grc, Μουζιρίς, Old Malayalam: ''Muciri'' or ''Muciripattanam'' possibly identical with the medieval ''Muyirikode'') was an ancient harbour and an urban centre on the Malabar Coast. Muziris found mention in the ''Periplus ...
, between the Cheras and the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medit ...
. Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ...
(1st century CE) states that the port of ''Tyndis
Tyndis ( grc, Τύνδις) was an ancient Indian seaport/harbor-town mentioned in the Graeco-Roman writings. According to the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea,'' Tyndis was located north of port Muziris in the country of the Cerobothra (presen ...
'' was located at the northwestern border of ''Keprobotos'' ( Chera dynasty).Gurukkal, R., & Whittaker, D. (2001). In search of Muziris. ''Journal of Roman Archaeology'', ''14'', 334–350. The North Malabar
North Malabar refers to the geographic area of southwest India covering the state of Kerala's present day Kasaragod, Kannur, and Wayanad districts, and the taluks of Vatakara, Koyilandy, and Thamarassery in the Kozhikode District of Kerala and t ...
region, which lies north of the port at ''Tyndis
Tyndis ( grc, Τύνδις) was an ancient Indian seaport/harbor-town mentioned in the Graeco-Roman writings. According to the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea,'' Tyndis was located north of port Muziris in the country of the Cerobothra (presen ...
'', was ruled by the kingdom of Ezhimala
Ezhimala, a hill reaching a height of , is located near Payyanur, in Kannur district of Kerala, south India. It is a part of a conspicuous and isolated cluster of hills, forming a promontory, north of Kannur (Cannanore). The Indian Naval Aca ...
during Sangam period
The Sangam period or age (, ), particularly referring to the third Sangam period, is the period of the history of ancient Tamil Nadu, Kerala and parts of Sri Lanka (then known as Tamilakam) spanning from c. 6th century BCE to c. 3rd century CE. ...
. According to the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' ( grc, Περίπλους τῆς Ἐρυθρᾶς Θαλάσσης, ', modern Greek '), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation an ...
'', a region known as ''Limyrike
Limyrikê is a historical region of present-day India, mentioned in the ancient Greco-Roman texts. It generally corresponds to the present-day Malabar Coast of Kerala.
Extent
According to the '' Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (53:17:15-2 ...
'' began at '' Naura'' and ''Tyndis
Tyndis ( grc, Τύνδις) was an ancient Indian seaport/harbor-town mentioned in the Graeco-Roman writings. According to the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea,'' Tyndis was located north of port Muziris in the country of the Cerobothra (presen ...
''. However the Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
mentions only ''Tyndis
Tyndis ( grc, Τύνδις) was an ancient Indian seaport/harbor-town mentioned in the Graeco-Roman writings. According to the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea,'' Tyndis was located north of port Muziris in the country of the Cerobothra (presen ...
'' as the ''Limyrike
Limyrikê is a historical region of present-day India, mentioned in the ancient Greco-Roman texts. It generally corresponds to the present-day Malabar Coast of Kerala.
Extent
According to the '' Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (53:17:15-2 ...
s starting point. The region probably ended at Kanyakumari
Kanniyakumari (; , referring to Devi Kanya Kumari), also known as Cape Comorin, is a city in Kanniyakumari district in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is the southern tip of the Indian subcontinent and the southernmost city in mainland I ...
; it thus roughly corresponds to the present-day Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
. The value of Rome's annual trade with the region was estimated at around 50,000,000 sesterces. Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ...
mentioned that ''Limyrike
Limyrikê is a historical region of present-day India, mentioned in the ancient Greco-Roman texts. It generally corresponds to the present-day Malabar Coast of Kerala.
Extent
According to the '' Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (53:17:15-2 ...
'' was prone by pirates. The Cosmas Indicopleustes
Cosmas Indicopleustes ( grc-x-koine, Κοσμᾶς Ἰνδικοπλεύστης, lit=Cosmas who sailed to India; also known as Cosmas the Monk) was a Greek merchant and later hermit from Alexandria of Egypt. He was a 6th-century traveller who m ...
mentioned that the ''Limyrike
Limyrikê is a historical region of present-day India, mentioned in the ancient Greco-Roman texts. It generally corresponds to the present-day Malabar Coast of Kerala.
Extent
According to the '' Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (53:17:15-2 ...
'' was a source of peppers.
During the Sangam period
The Sangam period or age (, ), particularly referring to the third Sangam period, is the period of the history of ancient Tamil Nadu, Kerala and parts of Sri Lanka (then known as Tamilakam) spanning from c. 6th century BCE to c. 3rd century CE. ...
(3rd4thcenturyBC), the land where Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second ...
now stands was an uninhabited region of the Chera Empire. This land, part of the larger Tamilakam
Tamiḻakam ( Tamil: தமிழகம்; Malayalam: തമിഴകം), refers to the geographical region inhabited by the ancient Tamil people, covering the southernmost region of the Indian subcontinent. Tamilakam covered today's Tamil Na ...
partly fell within the ''Kudanad'' (Western land; west of Kongunad) to the south and partly within ''Puzhinad'' (marshy tract) to the north. The dominion of the Cheras extended as far as present-day Vatakara
Vatakara, also spelled Vadakara (formerly Badagara), , french: Bargaret, is a Municipality in the state of Kerala, India. Vatakara is located between Kannur and Kozhikode. The municipality of Vatakara covers an area of and is bordered by M ...
, beyond which lay the kingdom of Eli ( Ezhi). The ports of the Chera empire played an important role in fostering trade relations between Kerala and the outside world. According to scholars, Tyndis or Tondi (present-day Kadalundi
Kadalundi is a village in Kozhikode district, Kerala, India. It is a coastal village close to the Arabian Sea. Kadalundi is famous for its bird sanctuary, which is home to various migratory birds during certain seasons and has been recently decl ...
or Ponnani
Ponnani () is a municipality in Ponnani Taluk, Malappuram District, in the state of Kerala, India. It serves as the administrative center of the Taluk and Block Panchayat of the same name. It is situated at the estuary of Bharatappuzha (Riv ...
) to the south of Kozhikode was a flourishing seaport. During the 9th century, this region became a part of the Second Chera Empire. The Cheras (also known as Perumals) ruled the territory until 1102.
The rise of Calicut as a major trading centre and a port city does not seem to have happened before the 13th century. The Zamorin of Calicut
The Samoothiri (Anglicised as Zamorin; Malayalam: , Arabic: ''Sāmuri'', Portuguese: ''Samorim'', Dutch: ''Samorijn'', Chinese: ''Shamitihsi''Ma Huan's Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' 433 Translated and Edited ...
was originally the ruler of Eranad, which was a minor principality located in the northern parts of present-day Malappuram district
Malappuram (), is one of the 14 districts in the Indian state of Kerala, with a coastline of . It is the most populous district of Kerala, which is home to around 13% of the total population of the state. The district was formed on 16 June 1 ...
. His headquarters was Nediyiruppu in Kondotty
Kondotty is a developing town, municipality, and aerotropolis in the Malappuram district state of Kerala, India which is located near Calicut International Airport, 24 km from Malappuram. It is the headquarters of Kondotty Taluk, which wa ...
. Later it was the ''Eradi'' (The ruler of Eranad), who came to be known as Zamorin, and developed the port at Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second ...
. Eranad was ruled by a Samanthan Nair clan known as Eradis, similar to the Vellodis of neighbouring Valluvanad and Nedungadi
Nedungadi is a Samanthan last name, originating in the Indian state of Kerala. Nedungadi belong to Samanthan section of the Malabar ruling class of Nairs.
Samanthans were the erstwhile rulers of small Nadus (Places) under the Chera Dynasty. The ...
s of Nedunganad. The rulers of Eranad were known by the title ''Eralppad''/''Eradi''. While the first reference to the Kingdom of Calicut and Saamoothiri
The Samoothiri (Anglicised as Zamorin; Malayalam: , Arabic: ''Sāmuri'', Portuguese: ''Samorim'', Dutch: ''Samorijn'', Chinese: ''Shamitihsi''Ma Huan's Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' 433 Translated and Edited ...
is made by Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berber Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, largely in the Muslim w ...
in his accounts (1342–1347), there is no reference to Calicut by Marco Polo
Marco Polo (, , ; 8 January 1324) was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in '' The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known as ''Book of the Ma ...
, who visited Kerala towards the end of the 13th Century. He does, however, mention the kingdom of Eli. This provides a clue to a plausible date for the rise of Calicut as a major kingdom on the Kerala coast. Nevertheless, Prof. Krishna Ayyar has assigned 1034CE as the year of the foundation of the city.Ayyar, K.V. Krishna, The Zamorins of Calicut- From the Earliest Times to A.D.1806(1938), Calicut.
According to the ''Keralolpathi
The Keralolpathi ( ml, കേരളോല്പത്തി; IAST:''kēraḷōlpatti''; ) is a Malayalam Brahmanical literary work that deals with the origin and legends of the land of Kerala. P. Shungunny Menon ascribes the authorship of this w ...
'' (''Genesis of Kerala''), the last of the Chera kings, Cheraman Perumal, partitioned the kingdom among his feudatories and secretly left for Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow val ...
with some Arab traders where he embraced Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
and lived the rest of his life in obscurity in Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
. The date of this partition is a significant turning point in the history of Kerala. It is now clear that the Cheraman Perumals ruled in the 8th, 9th and 10th centuries and that the last Cheraman Perumal was Rama Varma Kulasekhara (1089–1102). Although there is no basis for the last Perumal's conversion to Islam and pilgrimage to Mecca, it is now accepted that following his mysterious disappearance the land was partitioned and that the governors of different ''Nadus'' (fiefdoms) gained independence, proclaiming it as their 'gift' from the last sovereign. M.G.S. Narayanan,Calicut: The City of Truth(2006) Calicut University Publications
There is some ambiguity regarding the exact course of events that led to the establishment of the zamorin
The Samoothiri (Anglicised as Zamorin; Malayalam: , Arabic: ''Sāmuri'', Portuguese: ''Samorim'', Dutch: ''Samorijn'', Chinese: ''Shamitihsi''Ma Huan's Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' 433 Translated and Edited ...
's rule over Calicut. According to Prof. A. Sreedhara Menon (who entirely rejects the story of Cheraman Perumal's disappearance, his conversion to Islam and the subsequent gifts to his feudatories), immediately following the 'fall' of the Rama Kulasekhara, Calicut and its suburbs formed part of the Polanad Kingdom ruled by the ''Porlatiri'', which was a vassal state to the Kolathunadu
Kolattunādu (Kola Swarupam, as Kingdom of Cannanore in foreign accounts, Chirakkal (Chericul) in later times) was one of the four most powerful kingdoms on the Malabar Coast during the arrival of the Portuguese Armadas in India, along with ...
based at North Malabar
North Malabar refers to the geographic area of southwest India covering the state of Kerala's present day Kasaragod, Kannur, and Wayanad districts, and the taluks of Vatakara, Koyilandy, and Thamarassery in the Kozhikode District of Kerala and t ...
. The Eradis of Nediyirippu in Ernad (somewhere around present Kondotty) were land-locked and sought an outlet to the sea to initiate trade and commerce with distant lands. To accomplish this, the Eradis marched with their ''nair
The Nair , also known as Nayar, are a group of Indian Hindu castes, described by anthropologist Kathleen Gough as "not a unitary group but a named category of castes". The Nair include several castes and many subdivisions, not all of whom histo ...
s'' towards Panniyankara and besieged the ''Porlatiri'' in his headquarters, resulting in a 50-year war. The Eradis emerged victorious in their conquest of Polanad. After this, Menokkis were made as the ruler of ''Polanad'' and came to terms with the troops and people. After this, the town of Calicut was founded close to the palace at Tali. Then, the Eradis shifted their headquarters from Nediyirippu to Calicut. The Governor of Ernad built a fort at a place called Velapuram to safeguard his new interests. The fort most likely lent its name to ''Koyil Kotta'' the precursor to Calicut.
 However, M.G.S. Narayanan in his book, Calicut: The City of Truth states that the Governor of Eranad, Mana Vikrama (who became the Zamorin of Calicut later) was, in fact, a favourite of the last Ceraman Perumal, Rama Kulasekara as the former was at the forefront of the wars with the
However, M.G.S. Narayanan in his book, Calicut: The City of Truth states that the Governor of Eranad, Mana Vikrama (who became the Zamorin of Calicut later) was, in fact, a favourite of the last Ceraman Perumal, Rama Kulasekara as the former was at the forefront of the wars with the Chola
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil thalassocratic empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century BC ...
- Pandya forces to the South and led the army to victory. The King, therefore, granted him, as a mark of favour, a small tract of land on the sea-coast in addition to his hereditary possessions. This patch of wasteland is called ''Cullikkad'' in the ''Keralolpathi''. To corroborate his assertion that Mana Vikrama was, in fact, a favourite of the last Perumal, Narayanan cites a stone inscription of the last ruler (1102) discovered at Kollam in South Kerala. It refers to ''Nalu taliyum ayiram arunurruvarum eranadu vazhkai Manavikiraman mutalayulla camantarum''-'The four Councillors, The Thousand, The Six Hundred, along with Mana Vikrama, the Governor of Eranad and other Feudatories'.
However, the Eradis being land-locked lacked direct access to the coastline as the territory of Polanad (''Porakilanad'') lay between Eranad and Calicut. Having been given the royal sword and the injunction ''Cattum konnum adakki kolka'' (conquer by courting and conferring death) by the last Ceraman (according to Keralolpathi), the Ernad ''Utayavar'' (Governor) waged war against the Porlatiri (''Porakilar Adhikari'') and attacked Panniyankara. M.G.S seems to indicate that the land sought by the Ernadis, lay in fact beyond and not within the kingdom of Polanad.
With the conquest of Polanad, the status of the ''Utayavar'' (Governor) increased and he came to be known as Swami Nambiyathiri Thirumulpad and the Kingdom of Calicut also came to known as ''Nediyiruppu Swarupam'' after the original house of the Eradis at Nediyiruppu. The king's title gradually evolved into ''Samoothirippadu'' or Saamoothiri
The Samoothiri (Anglicised as Zamorin; Malayalam: , Arabic: ''Sāmuri'', Portuguese: ''Samorim'', Dutch: ''Samorijn'', Chinese: ''Shamitihsi''Ma Huan's Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' 433 Translated and Edited ...
or ''Saamoori'' over the years. The Europeans called him Zamorin. The foundation of the city of Calicut was therefore laid during the initial years of the 12th century. The Sweetmeat Street (''Mittayi Theruvu'') was an important trading street under Zamorin's rule.
In the 14th century, Kozhikode conquered larger parts of central Kerala after the seize of Tirunavaya
Tirunavaya, also spelled as Thirunavaya, is a town in Malappuram, Kerala. Situated on the northern bank of Bharatappuzha (River Ponnani/Nila or Perar), it is one of major Hindu pilgrimage centres in Kerala. Tirunavaya, home to Tirunavaya Temple ...
region from Valluvanad, which were under the control of the king of ''Perumbadappu Swaroopam'' (Cochin). The ruler of Perumpadappu was forced to shift his capital (c. CE 1405) further south from Kodungallur
Kodungallur (; also Cranganore, Portuguese: Cranganor; formerly known as Mahodayapuram, Shingly, Vanchi, Muchiri, Muyirikkode, and Muziris) is a historically significant town situated on the banks of river Periyar on the Malabar Coast in T ...
to Kochi
Kochi (), also known as Cochin ( ) ( the official name until 1996) is a major port city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is part of the district of Ernakulam in the state of ...
. In the 15th century, the status of Cochin was reduced to a vassal state of Kozhikode, thus leading to the emergence of Kozhikode as the most powerful kingdom in medieval Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
.
The history of Kozhikode can roughly be divided into several periods marked by a few epoch-making events. These include the city's establishment, the arrival of the Portuguese, the arrival of the Dutch, the Mysorean Invasion, the rise of British Power, the beginning of the Indian Independence Movement
The Indian independence movement was a series of historic events with the ultimate aim of ending British rule in India. It lasted from 1857 to 1947.
The first nationalistic revolutionary movement for Indian independence emerged from Bengal. ...
and finally freedom from British rule in 1947.
Arrival of the Portuguese
 This single event marked an epoch in the history of Kerala and India, not because Vasco da Gama 'discovered the sea route to India' as is in the common parlance (since the Chinese, the Middle East and the African kingdoms already traded directly with India) but unlike the others, the Portuguese yearned for political power and imperial domination. Vasco da Gama's fame is more often argued as due to historical reasons for which he was hardly responsiblePanickar.K.M, A History of Kerala(1959) Annamalai University in that he was accompanied by a Portuguese-speaking Arab merchant provided by the Sultan of Melinda in East Africa.
This single event marked an epoch in the history of Kerala and India, not because Vasco da Gama 'discovered the sea route to India' as is in the common parlance (since the Chinese, the Middle East and the African kingdoms already traded directly with India) but unlike the others, the Portuguese yearned for political power and imperial domination. Vasco da Gama's fame is more often argued as due to historical reasons for which he was hardly responsiblePanickar.K.M, A History of Kerala(1959) Annamalai University in that he was accompanied by a Portuguese-speaking Arab merchant provided by the Sultan of Melinda in East Africa. Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira (; ; c. 1460s – 24 December 1524), was a Portuguese explorer and the first European to reach India by sea.
His initial voyage to India by way of Cape of Good Hope (1497–1499) was the first to link ...
was sent by the King of Portugal Dom Manuel I and landed in Calicut at Kappad in 17 May 1498. Following the discovery of sea route from Europe to Malabar
Malabar may refer to the following:
People
* Malabars, people originating from the Malabar region of India
* Malbars or Malabars, people of Tamil origin in Réunion
Places
* Malabar Coast, or Malabar, a region of the southwestern shoreline ...
in 1498, the Portuguese began to expand their territories and ruled the seas between Ormus
The Kingdom of Ormus (also known as Hormoz; fa, هرمز; pt, Ormuz) was located in the eastern side of the Persian Gulf and extended as far as Bahrain in the west at its zenith. The Kingdom was established in 11th century initially as a dep ...
and the Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
and south to Ceylon
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
. The navigator was received with traditional hospitality, but an interview with the Zamorin failed to produce any concrete results. Vasco da Gama's request for permission to leave a factor behind him in charge of the merchandise he could not sell was turned down by the King, who insisted that da Gama pay customs duty like any other trader, straining the relationship between the two. The next expedition was sent by the King of Portugal under the leadership of Pedro Álvares Cabral
Pedro Álvares Cabral ( or ; born Pedro Álvares de Gouveia; c. 1467 or 1468 – c. 1520) was a Portuguese nobleman, military commander, navigator and explorer regarded as the European discoverer of Brazil. He was the first human ...
in 1500. His agent secured a settlement to erect a factory at Calicut. This, however, precipitated matters between the Arabs and the Portuguese. The Portuguese capture of Arab vessels and ensuing massacre was retaliated by the locals who burned down the factory and butchered half of the Portuguese on land. Cabral sailed for Cochin
Kochi (), also known as Cochin ( ) ( the official name until 1996) is a major port city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is part of the district of Ernakulam in the state of ...
, where he was cordially received and allowed to load his ships. Vasco da Gama reached Calicut the second time with 15 ships and 800 men in February 1502. In January 1502, the First Battle of Cannanore
The First Battle of Cannanore was a naval engagement between the Third Portuguese Armada under João da Nova and the naval forces of Calicut, which had been assembled by the Zamorin against the Portuguese in order to prevent their return to Po ...
between the Third Portuguese Armada and Kingdom of Cochin
The Kingdom of Cochin, named after its capital in the city of Kochi (Cochin), was a kingdom in the central part of present-day Kerala state. It commenced at the early part of the 12th century and continued to rule until 1949, when monarchy ...
under João da Nova
João da Nova ( gl, Xoán de Novoa, Joam de Nôvoa; es, Juan de Nova; ; born c. 1460 in Maceda, Ourense, Galicia; died July 16, 1509 in Kochi, India) was a Portuguese-Galician explorer of the Atlantic and Indian Oceans at the service of Portug ...
and Zamorin of Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second ...
's navy marked the beginning of Portuguese conflicts in the Indian Ocean. When da Gama's call to expel all Muslims from Calicut was vehemently turned down, he bombarded the city and captured several rice vessels, cutting off the crew's hands, ears and noses.
 With rising bonhomie between the Maharaja of Cochin and the Portuguese, there followed several wars in which the Portuguese propped up Cochin and Cannanore against the Zamorin. Scores of men perished in these wars on all sides starting in 1503 and continuing till the early 1570s. In February 1509, the defeat of the joint fleet of the
With rising bonhomie between the Maharaja of Cochin and the Portuguese, there followed several wars in which the Portuguese propped up Cochin and Cannanore against the Zamorin. Scores of men perished in these wars on all sides starting in 1503 and continuing till the early 1570s. In February 1509, the defeat of the joint fleet of the Sultan of Gujarat
The Gujarat Sultanate (or the Sultanate of Guzerat), was a Medieval Indian kingdom established in the early 15th century in Western India, primarily in the present-day state of Gujarat, India. The dynasty was founded by Sultan Zafar Khan Muza ...
, the Mamlûk Burji Sultanate of Egypt, and the Zamorin
The Samoothiri (Anglicised as Zamorin; Malayalam: , Arabic: ''Sāmuri'', Portuguese: ''Samorim'', Dutch: ''Samorijn'', Chinese: ''Shamitihsi''Ma Huan's Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' 433 Translated and Edited ...
of Calicut
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second ...
with support of the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia ...
and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
in Battle of Diu marked the beginning of Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Por ...
dominance of the Spice trade and the Indian Ocean. In the same year, Afonso de Albuquerque
Afonso de Albuquerque, 1st Duke of Goa (; – 16 December 1515) was a Portuguese general, admiral, and statesman. He served as viceroy of Portuguese India from 1509 to 1515, during which he expanded Portuguese influence across the Indian Ocea ...
was appointed the second Viceroy of the Portuguese possessions in the East. A new fleet under Marshall Coutinho arrived with specific instructions to destroy the power of Calicut. The Zamorin's palace was captured and destroyed and the city was set on fire. But the King's forces rallied fast to kill Marshall Coutinho and wounded Albuquerque. Albuquerque nevertheless was clever enough to patch up his quarrel and entered into a treaty with the Zamorin in 1513 to protect Portuguese interests in Kerala. Hostilities were renewed when the Portuguese attempted to assassinate the Zamorin sometime between 1515 and 1518. From the 1520s the Zamorin's naval fleet was administered by the Kunjali Marakkars who inflicted heavy damages to Portuguese property till 1589. King Zamorin was assisted mainly by four ministers namely Mangatachan the Chief Minister, Dharmoth Panicker, Army Chief and Teacher of Martial Arts, Kuthiravatathu Nair, Finance Minister and Kunjali Marakars, Chief of Naval Force.
In 1503, the Portuguese had built a fort in Chaliyam
Chaliyam is a village situated at the estuary of Chaliyar (River Beypore) in Kozhikode district of Kerala, India. Chaliyam forms an island, bounded by the Chaliyar in the north, and River Kadalundi in south, and the Conolly Canal in the east. ...
with the consent of the Raja of the Kingdom of Tanur
Kingdom of Tanur (Vettathunadu, Vettom, Tanur Swaroopam, Prakashabhu, Kingdom of Light) was one of the numerous feudal principalities on Malabar Coast during the Middle Ages. It was ruled by a Hindu dynasty, claiming Kshatriya status, known as ...
(Vettattnad) from where they re-established supremacy over Indian waters. It provided the Portuguese ample opportunities to harass the Zamorin and enter the heart of his kingdom in the event of war. The Chaliyam fort was 'like a pistol held at the Zamorin's throat'. The Zamorin attacked Chaliyam and recaptured the fort in 1571 coinciding with the defeat of the ruler of Vijayanagara
Vijayanagara () was the capital city of the historic Vijayanagara Empire. Located on the banks of the Tungabhadra River, it spread over a large area and included the modern era Group of Monuments at Hampi site in Vijayanagara district, Be ...
, an ally of the Portuguese. The Portuguese were forced to abandon the fort, which was then completely demolished. The fall of Chaliyam fort marked the beginning of the end for the Portuguese in the great game of the East. The Portuguese approached the Zamorin again in 1578 for reconciliation. By 1588 they were settled in Calicut and in 1591 built a church on land donated by the Zamorin (who even laid the foundation stone). The Zamorin's growing friendship was nevertheless a result of his gradual estrangement with the Kunjali Marakkars.
By 1663, the Portuguese flag ceased to fly in Kerala as the Dutch arrived at the scene and captured all their strongholds of Quilon, Cranganore, Purakkadm, Cochin and Cannanore.
Arrival of the Dutch
In 1602, theZamorin
The Samoothiri (Anglicised as Zamorin; Malayalam: , Arabic: ''Sāmuri'', Portuguese: ''Samorim'', Dutch: ''Samorijn'', Chinese: ''Shamitihsi''Ma Huan's Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' 433 Translated and Edited ...
sent messages to Aceh
Aceh ( ), officially the Aceh Province ( ace, Nanggroë Acèh; id, Provinsi Aceh) is the westernmost province of Indonesia. It is located on the northernmost of Sumatra island, with Banda Aceh being its capital and largest city. Granted a s ...
promising the Dutch a fort at Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second ...
if they would come and trade there. Two factors, Hans de Wolff and Lafer, were sent on an Asian ship from Aceh, but the two were captured by the chief of Tanur, and handed over to the Portuguese.Sanjay Subrahmanyam. "The Political Economy of Commerce: Southern India 1500–1650". Cambridge University Press, 2002 A Dutch fleet under Admiral Steven van der Hagen arrived at Kozhikode in November 1604. It marked the beginning of the Dutch presence in Kerala and they concluded a treaty with Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second ...
on 11 November 1604, which was also the first treaty that the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
made with an Indian ruler. By this time the kingdom and the port of Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second ...
was much reduced in importance. The treaty provided for a mutual alliance between the two to expel the Portuguese from Malabar. In return the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
was given facilities for trade at Kozhikode and Ponnani
Ponnani () is a municipality in Ponnani Taluk, Malappuram District, in the state of Kerala, India. It serves as the administrative center of the Taluk and Block Panchayat of the same name. It is situated at the estuary of Bharatappuzha (Riv ...
, including spacious storehouses. It provided for a mutual alliance between the Zamorin and the Dutch to expel the Portuguese from Indian soil. In return, they were given facilities for trade at Calicut, including spacious storehouses. The Dutch could not, however, stay for long. Their force weakened after constant wars with Marthanda Varma of Travancore (until 1753) and was forced to surrender to a British force that marched from Calicut to Cochin on 20 October 1795 (as part of the larger Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
between Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former province on the western coast of the Netherlands. From the 10th to the 16th ...
and England in Europe). Travancore
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
became the most dominant state in Kerala by defeating the powerful Zamorin
The Samoothiri (Anglicised as Zamorin; Malayalam: , Arabic: ''Sāmuri'', Portuguese: ''Samorim'', Dutch: ''Samorijn'', Chinese: ''Shamitihsi''Ma Huan's Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' 433 Translated and Edited ...
of Kozhikode in the battle of Purakkad in 1755.
The Mysore invasions
Hyder Ali ascended the throne of Mysore in 1761. By 1764, he obtained a pledge of neutrality from the British at Tellicherry in the event of a conflict with the Kerala powers. In February 1766, Hyder Ali marched into northern Kerala. Except for a few decisive battles, he faced meagre opposition and entered Calicut. The Zamorin sent the members of his family to Ponnani, blew up his palace and to avoid the humiliation of surrender committed self-immolation. A revenue officer named Madanna was appointed Civil Governor of Malabar with headquarters at Calicut. The rebellion soon broke out and the Mysorean garrison was besieged by the Nairs. Hyder Ali rushed to crush the rebellion devastating the countryside and employed draconian measures to suppress the Nairs including defrocking of their social status Successfully achieving his objectives, he had to return to Mysore soon to deal with theMaratha
The Marathi people ( Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as ...
threat. Rebellion broke out again. Hyder Ali engaged in diplomacy this time through Madanna and agreed to withdraw his forces for which a war indemnity was to be paid to him. But he made a second attempt in December 1773 and re-established his authority in Malabar. However, with the help of the British, the Nairs led by the famous Ravi Varma of Padinjare Kovilakam, wiped out the Mysorean garrison in Calicut by 1778. By 1783 Tipu Sultan established his authority over Northern Kerala. He planned to shift the capital from Calicut to the south of the city on the banks of the river Chaliyar
Chaliyar River is the fourth longest river in Kerala at 169 km in length. The Chaliyar is also known as Chulika River, Nilambur River or Beypore River as it nears the sea. Pothukal, Chungathara, Nilambur, Mampad, Edavanna, Kavanoor, P ...
and even named it 'Farookhabad' now called Feroke
Feroke (), is a Municipality and a part of Kozhikode metropolitan area under Kozhikode Development Authority (K.D.A) in the Kozhikode district of the Indian state of Kerala.
Feroke municipality shares the border with Kozhikode corporation, ...
. This ambitious plan soon failed. In November 1788, Calicut was attacked by the Nairs under Ravi Varma of the Padinjare Kovilakam. Tipu returned in 1789 to re-establish his authority. This, however, brought him in direct conflict with the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
based in Madras
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast o ...
, which resulted in four Anglo-Mysore Wars
The Anglo-Mysore Wars were a series of four wars fought during the last three decades of the 18th century between the Sultanate of Mysore on the one hand, and the British East India Company (represented chiefly by the neighbouring Madras Pre ...
. Calicut and the surrounding districts were among the territories ceded to the British after the Third Anglo-Mysore War
The Third Anglo-Mysore War (1790–1792) was a conflict in South India between the Kingdom of Mysore and the British East India Company, the Kingdom of Travancore, the Maratha Empire, and the Nizam of Hyderabad. It was the third of four A ...
by the Treaties of Seringapatam with the British on 22 February and 18 March 1792. The newly acquired possessions on the Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
were organised into the Malabar District
Malabar District, also known as Malayalam District, was an administrative district on the southwestern Malabar Coast of Bombay Presidency (1792-1800) and Madras Presidency (1800-1947) in British India, and independent India's Madras State (1 ...
of Madras Presidency
The Madras Presidency, or the Presidency of Fort St. George, also known as Madras Province, was an administrative subdivision (presidency) of British India. At its greatest extent, the presidency included most of southern India, including th ...
, and Calicut became the district capital.

British domination
The arrival ofBritish
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
in Kerala can be traced back to the year 1615, when a group under the leadership of Captain William Keeling
Captain William Keeling (1577 – 19 September 1619), of the East India Company, was a British sea captain. He commanded the ''Susanna'' on the second East India Company voyage in 1604. During this voyage his crew was reduced to fourteen men and ...
arrived at Kozhikode, using three ships. It was in these ships that Sir Thomas Roe went to visit Jahangir
Nur-ud-Din Muhammad Salim (30 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was the fourth Mughal Emperor, who ruled from 1605 until he died in 1627. He was named after the Indian Sufi saint, Salim Chishti.
Ear ...
, the fourth Mughal emperor
The Mughal emperors ( fa, , Pādishāhān) were the supreme heads of state of the Mughal Empire on the Indian subcontinent, mainly corresponding to the modern countries of India, Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh. The Mughal rulers styl ...
, as British envoy. The British concluded a treaty of trade under which, among others, the English were to assist Calicut in expelling the Portuguese from Cochin and Cranganore, a term that the British never fulfilled. In 1664, Zamorin gave the English permission to build a factory in Calicut but did not extend any other favours as he was by now growing suspicious of all European traders. The English maintained neutrality in the conflict between Mysore and the Kerala powers in 1766 and was an important factor which facilitated early success to Hyder Ali. However, tensions between the English and Mysore arose soon. The English army under Major Abington helped Ravi Varma of Padinjare Kovilakam in the recapture of Calicut in 1782 from Mysore. The East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sout ...
however did not stand by Lord Cornwallis' promise to the exiled rulers that they will be restored after the expulsion of Tipu. By 1792, the whole of Malabar including Calicut came under the British dominion. Ravi Varma now turned against the company but was soon captured in 1793. The rebellion continued even after the capture of Ravi Varma till 1797. Under British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was him ...
, it acted as the headquarters of Malabar District
Malabar District, also known as Malayalam District, was an administrative district on the southwestern Malabar Coast of Bombay Presidency (1792-1800) and Madras Presidency (1800-1947) in British India, and independent India's Madras State (1 ...
, one of the two districts in the western coast of erstwhile Madras Presidency
The Madras Presidency, or the Presidency of Fort St. George, also known as Madras Province, was an administrative subdivision (presidency) of British India. At its greatest extent, the presidency included most of southern India, including th ...
. During the British rule, Malabar's chief importance lay in producing pepper
Pepper or peppers may refer to:
Food and spice
* Piperaceae or the pepper family, a large family of flowering plant
** Black pepper
* ''Capsicum'' or pepper, a genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family Solanaceae
** Bell pepper
** Chili ...
. Kozhikode municipality was formed on 1 November 1866 according to the Madras Act 10 of 1865 (Amendment of the Improvements in Towns act 1850) of the British Indian Empire
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was him ...
, making it the first modern municipality in the state.
National movement
The city also witnessed several movements as part of the struggle for Indian independence from the British. A conference of the Congress was held at Calicut in 1904 with C. Vijayaraghavachariar in the chair. A branch of the All India Home Rule League founded by Ms. Annie Besant started functioning in the city. In 1916, Sri K.P.Kesava Menon staged a walk out of the Town Hall when he was denied permission by the Collector Mr Innes to address the meeting inMalayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 2 ...
. The period saw a rise in political journalism as well. The ''Mathrubhumi
''Mathrubhumi'' is a Malayalam newspaper that is published from Kerala, India. It was founded by K. P. Kesava Menon, an active volunteer in the Indian independence movement, Indian freedom struggle against the British Raj, British. The word "M ...
'' in March 1923 and ''Al Amin'' in October 1924 were started by Sri K.P.Kesava Menon and Muhammad Abdur Rahiman respectively to foster the spirit of Nationalism. On 12 May 1930, Satyagrahi's assembled at Calicut beach under the leadership of Muhammad Abdur Rahiman to break the 'Salt laws' were attacked by the police injuring more than 30 people. K.P.Krishna Pillai and R.V.Sharma defended the National flag from forcible seizure by the police on this occasion. During the Second Civil Disobedience Movement (1932), all four hundred delegates who attended the All Kerala Political Conference in September 1932 were arrested. The incident wherein Mrs L.S.Prabhu (of Thalassery
Thalassery (), formerly Tellicherry, is a municipality, Commercial City on the Malabar Coast in Kannur district, in the state of Kerala, India, bordered by the districts of Mahé (Pondicherry), Kozhikode, Wayanad, Kasaragod and Kodagu (Ka ...
), who courted arrest during the conference, was ordered to surrender all her gold ornaments including the ''tali'' or mangalsutra
A mangala sutra (), or thaali (ISO: ''tāḷi''), is a necklace that the groom ties around the bride's neck in the Indian subcontinent, in a ceremony called ''Mangalya Dharanam'' (). The necklace serves as a visual marker of status as a m ...
received nationwide condemnation. Calicut was also a major centre for the rising Communist Party of Malabar (1939) and the Quit India Movement
The Quit India Movement, also known as the August Kranti Movement, was a movement launched at the Bombay session of the All India Congress Committee by Mahatma Gandhi on 8th August 1942, during World War II, demanding an end to British rule i ...
(1942). Kerala chapter of the Communist Party was formed in a secret meeting held at Kallai Road in the year 1937.
After Indian Independence in 1947, Madras Presidency was renamed the Madras State
Madras State was a state of India during the mid-20th century. At the time of its formation in 1950, it included the whole of present-day Tamil Nadu (except Kanyakumari district), Coastal Andhra, Rayalaseema, the Malabar region of North and ...
. In 1956 when the Indian states were reorganised along linguistic lines, Malabar District was combined with the state of Travancore-Cochin to form the new state of Kerala on 1 November 1956. Malabar District was later split into the districts of Kannur
Kannur (), formerly known in English as Cannanore, is a city and a municipal corporation in the state of Kerala, India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Kannur district and situated north of the major port city and commercial hu ...
, Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second ...
, and Palakkad
Palakkad (), formerly known as Palghat, historically known as Palakkattussery is a city and municipality in the Indian state of Kerala. It is the administrative headquarters of the Palakkad District. Palakkad is most densely populated municipa ...
on 1 January 1957. Kozhikode was upgraded as a Municipal Corporation in 1962, making it the second-oldest Municipal Corporation in the state.
See also
*Saamoothiri
The Samoothiri (Anglicised as Zamorin; Malayalam: , Arabic: ''Sāmuri'', Portuguese: ''Samorim'', Dutch: ''Samorijn'', Chinese: ''Shamitihsi''Ma Huan's Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' 433 Translated and Edited ...
References
Further reading
* * M. G. S. Narayanan, ''Calicut: The City of Truth Revisited'' Kerala. University of Calicut, 2006 * A. Sreedhara Menon, ''A Survey of Kerala History'', (1967), Madras, 1991 * (The English translation of the historic bookTuhfat Ul Mujahideen
'Tuhfat al-Mujahidin fi ba‘d Akhbar al-Burtughaliyin' (Arabic:تحفة المجاهدين في بعض اخبار البرتغاليين, often shortened as 'Tuhfat al-Mujahidin') is a historical work by Zainuddin Makhdoom II on the struggle betwe ...
written about the society of Kozhikode by Zainuddin Makhdoom II
Sheikh Ahmad Zainuddin Makhdoom bin Sheikh Muhammad Al Gazzali (Arabic: شيخ احمد زين الدين بن شيخ محمد غزالي المليباري; Ahmad Zayn al-Din ibn Muhammad al-Ghazāli al-Malibári), grandson of Sheikh Zainud ...
during sixteenth century CE)
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Kozhikode
Colonial Kerala