Historic Centre Of Naples on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The historic center, or ''Centro Storico,'' of


 Only the ancient center, which incorporates the districts of San Giuseppe, Porto, Pendino, Mercato, San Lorenzo and Vicarìa which, more specifically, correspond almost to the area of the decumans of Naples, sees the existence of more than 200 historic churches to which the activity of famous exponents of Italian art are linked. Among the main artists there are: Giotto,
Only the ancient center, which incorporates the districts of San Giuseppe, Porto, Pendino, Mercato, San Lorenzo and Vicarìa which, more specifically, correspond almost to the area of the decumans of Naples, sees the existence of more than 200 historic churches to which the activity of famous exponents of Italian art are linked. Among the main artists there are: Giotto,
 These reforms determined in the city the "reconquest" of the sea which, since the advent of Partenope and until then, was no longer used.
These reforms determined in the city the "reconquest" of the sea which, since the advent of Partenope and until then, was no longer used.
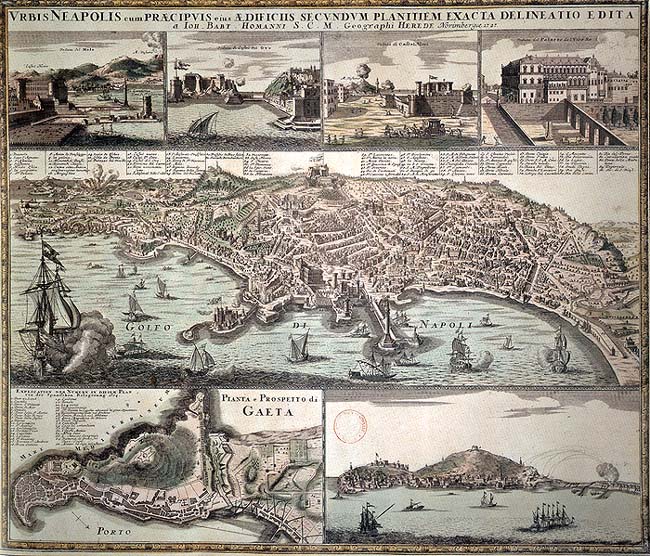 With the passage from the Spanish viceroyalty to the Bourbon kingdom, there is the definitive cultural leap in the city, which became the extreme destination of the ''European Grand Tour.''
Naples matures its own enlightenment conscience confirming itself as great European capital.Carlo Knight, ''Hamilton a Napoli. Cultura, svaghi, civiltà di una grande capitale europea'', Napoli Electa 2003 Within just twenty years (from 1730 to 1750) impressive buildings were born, symbol of the cultural level reached: the reggia di Capodimonte, the real Albergo dei Poveri and the
With the passage from the Spanish viceroyalty to the Bourbon kingdom, there is the definitive cultural leap in the city, which became the extreme destination of the ''European Grand Tour.''
Naples matures its own enlightenment conscience confirming itself as great European capital.Carlo Knight, ''Hamilton a Napoli. Cultura, svaghi, civiltà di una grande capitale europea'', Napoli Electa 2003 Within just twenty years (from 1730 to 1750) impressive buildings were born, symbol of the cultural level reached: the reggia di Capodimonte, the real Albergo dei Poveri and the
Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's admin ...
, Italy represents the historic nucleus of the city, spanning 27 centuries.
Almost the entirety of the historic center, approximately 1021 hectares, was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
in 1995, and included in the list of historic assets to be protected; its particular uniqueness lying in the ''almost total conservation and use'' of its ancient Greek road layout.
History
The historic center of Naples bears witness to the historical and artistic evolution of the city, from its first Greek settlement in the8th century BC
The 8th century BCE started the first day of 800 BC and ended the last day of 701 BC. The 8th century BC is a period of great change for several historically significant civilizations. In Egypt, the 23rd and 24th dynasties lead to rule from ...
along the area overlooking the sea,. the refounding of the same city in a more internal area, constituting the "ancient center (''Centro Storico'')", up to the Spanish Baroque city that saw the opening towards the west of the urban nucleus and to that center of the nineteenth-century cultural elite, with the flowering in the city of numerous noble and bourgeois villas that characterize the whole area of Posillipo
Posillipo (; nap, Pusilleco ) is an affluent residential quarter of Naples, southern Italy, located along the northern coast of the Gulf of Naples.
From the 1st century BC the Bay of Naples witnessed the rise of villas constructed by elite Roma ...
and Vomero.
The area considered a UNESCO heritage site covers approximately 1021 hectares
The hectare (; SI symbol: ha) is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100-metre sides (1 hm2), or 10,000 m2, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is ...
and contains the following quarters: Avvocata, Montecalvario, San Giuseppe, Porto
Porto or Oporto () is the second-largest city in Portugal, the capital of the Porto District, and one of the Iberian Peninsula's major urban areas. Porto city proper, which is the entire municipality of Porto, is small compared to its metropol ...
, Pendino, Mercato ( Municipalità I), Stella, San Carlo all'Arena, ( Municipalità III), Chiaia, San Ferdinando, San Lorenzo
San Lorenzo is the Italian and Spanish name for Saint Lawrence, the 3rd-century Christian martyr, and may refer to:
Places Argentina
* San Lorenzo, Santa Fe
* San Lorenzo Department, Chaco
* Monte San Lorenzo, a mountain on the border betwe ...
, Vicarìa and part of the Vomero and Posillipo hills.
The Irpinia earthquake of 1980 damaged part of the historical center and brought to light structural and social problems (even ancient ones) to which it is decided to remedy also urbanistic with the enactment of the law n. 219 1981, laying down provisions for the planning and control of building activity, sanctioning, recovery and rehabilitation of illegal construction.
Currently, a large part of the historic center of the city is in poor condition and suitable for conservation. Many structures, in addition to the already mentioned churches of art (fountains
A fountain, from the Latin "fons" (genitive "fontis"), meaning source or spring, is a decorative reservoir used for discharging water. It is also a structure that jets water into the air for a decorative or dramatic effect.
Fountains were or ...
, palaces
A palace is a grand residence, especially a royal residence, or the home of a head of state or some other high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word is derived from the Latin name palātium, for Palatine Hill in Rome which ...
, ancient architecture, sacred shrines, etc.) lie in conditions of extreme abandonment: to deal with this emergency, various citizens' organizations and committees are trying to get UNESCO to intervene.
A recent agreement signed between the Campania
(man), it, Campana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demog ...
region, the municipality and the Ministry of Cultural Heritage, meant that the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
allocated 100 million euros in June 2012 to carry out restoration work on the monuments of the historic center most at risk.

The Ancient Center
The city has two true and original ancient nucleuses: the first is the hill of Pizzofalcone on which the city of Partenope was born, while the second is the zone of the decumanus of Naples where the following ''Neapolis'' was born. In this last space, in particular, all the buildings over the centuries have concentrated until the16th century
The 16th century begins with the Julian year 1501 ( MDI) and ends with either the Julian or the Gregorian year 1600 ( MDC) (depending on the reckoning used; the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582).
The 16th cent ...
, with the opening towards the west of the city at the behest of the Spanish viceroy don Pedro de Toledo.
A particularly high number of cultural and artistic resources are on this site: obelisks, monasteries, cloisters, museums, the famous streets of the crib, catacombs, outdoor and underground archaeological excavations with Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
remains, including the Roman theater, statues and bas-reliefs, monumental friezes, as well as medieval columns supporting ancient historic buildings and much more.
 Only the ancient center, which incorporates the districts of San Giuseppe, Porto, Pendino, Mercato, San Lorenzo and Vicarìa which, more specifically, correspond almost to the area of the decumans of Naples, sees the existence of more than 200 historic churches to which the activity of famous exponents of Italian art are linked. Among the main artists there are: Giotto,
Only the ancient center, which incorporates the districts of San Giuseppe, Porto, Pendino, Mercato, San Lorenzo and Vicarìa which, more specifically, correspond almost to the area of the decumans of Naples, sees the existence of more than 200 historic churches to which the activity of famous exponents of Italian art are linked. Among the main artists there are: Giotto, Caravaggio
Michelangelo Merisi (Michele Angelo Merigi or Amerighi) da Caravaggio, known as simply Caravaggio (, , ; 29 September 1571 – 18 July 1610), was an Italian painter active in Rome for most of his artistic life. During the final four years of hi ...
, Donatello
Donato di Niccolò di Betto Bardi ( – 13 December 1466), better known as Donatello ( ), was a Florentine sculptor of the Renaissance period. Born in Florence, he studied classical sculpture and used this to develop a complete Renaissance s ...
, Giuseppe Sanmartino, Luca Giordano
Luca Giordano (18 October 1634 – 3 January 1705) was an Italian late-Baroque painter and printmaker in etching. Fluent and decorative, he worked successfully in Naples and Rome, Florence, and Venice, before spending a decade in Spain.
Earl ...
, Cosimo Fanzago
Cosimo Fanzago (Clusone, 12 October 1591 – Napoli, 13 February 1678) was an Italian architect and sculptor, generally considered the greatest such artist of the Baroque period in Naples, Italy.
Facade Santa Maria della Sapienza.
Biography
Fa ...
, Luigi Vanvitelli, Jusepe de Ribera
Jusepe de Ribera (1591 – 1652) was a painter and printmaker, who along with Francisco de Zurbarán, Bartolomé Esteban Murillo, and the singular Diego Velázquez, are regarded as the major artists of Spanish Baroque painting. Referring ...
, Domenichino
Domenico Zampieri (, ; October 21, 1581 – April 6, 1641), known by the diminutive Domenichino (, ) after his shortness, was an Italian Baroque painter of the Bolognese School of painters.
Life
Domenichino was born in Bologna, son of a shoema ...
, Guido Reni
Guido Reni (; 4 November 1575 – 18 August 1642) was an Italian painter of the Baroque period, although his works showed a classical manner, similar to Simon Vouet, Nicolas Poussin, and Philippe de Champaigne. He painted primarily religiou ...
, Tino di Camaino, Marco dal Pino, Simone Martini
Simone Martini ( – 1344) was an Italian painter born in Siena.
He was a major figure in the development of early Italian painting and greatly influenced the development of the International Gothic style.
It is thought that Martini was a pupil ...
, Mattia Preti
Mattia Preti (24 February 1613 – 3 January 1699) was an Italian Baroque artist who worked in Italy and Malta. He was appointed a Member of the Order of Saint John.
Life
Born in the small town of Taverna in Calabria, Preti was called ''Il Cav ...
and many others.
During the medieval era, the city was divided into seats. These were: Capuana, Montagna, Nido, Porto, Portanova and Forcella. In this context the city was closed by its walls beyond which there was an absolute prohibition of construction. The characteristic that distinguished the ancient center of Naples, in fact, is the almost foreclosure of the development in extension of the city, thus favoring that "in height". The circumstance that the city rests on tufaceous soil has favored practices of raising existing buildings, drawing the material from the underground quarries already used since the first birth of the city.
However, the shift of political power to the Maschio Angioino was a first impulse for the local aristocracy to drag their noble residences towards the western part of the city.
The opening to the west with the Spanish viceroyalty
The expansion of the city to the west, which took place in the16th century
The 16th century begins with the Julian year 1501 ( MDI) and ends with either the Julian or the Gregorian year 1600 ( MDC) (depending on the reckoning used; the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582).
The 16th cent ...
with don Pedro de Toledo, entails the birth of the current "historic center". Thus the Spanish quarters were born, with Via Toledo, Largo di Palazzo, Via Medina up to the Pizzofalcone area and Chiaia.
The royal palace, specifically, was the reason for a real hoarding by the Neapolitan and foreign aristocrats of the empty spaces rising along the road that went directly to the residence of the viceroy, ie via Toledo. These reforms determined in the city the "reconquest" of the sea which, since the advent of Partenope and until then, was no longer used.
These reforms determined in the city the "reconquest" of the sea which, since the advent of Partenope and until then, was no longer used.
The great buildings of the Bourbon period
 With the passage from the Spanish viceroyalty to the Bourbon kingdom, there is the definitive cultural leap in the city, which became the extreme destination of the ''European Grand Tour.''
Naples matures its own enlightenment conscience confirming itself as great European capital.Carlo Knight, ''Hamilton a Napoli. Cultura, svaghi, civiltà di una grande capitale europea'', Napoli Electa 2003 Within just twenty years (from 1730 to 1750) impressive buildings were born, symbol of the cultural level reached: the reggia di Capodimonte, the real Albergo dei Poveri and the
With the passage from the Spanish viceroyalty to the Bourbon kingdom, there is the definitive cultural leap in the city, which became the extreme destination of the ''European Grand Tour.''
Naples matures its own enlightenment conscience confirming itself as great European capital.Carlo Knight, ''Hamilton a Napoli. Cultura, svaghi, civiltà di una grande capitale europea'', Napoli Electa 2003 Within just twenty years (from 1730 to 1750) impressive buildings were born, symbol of the cultural level reached: the reggia di Capodimonte, the real Albergo dei Poveri and the Teatro di San Carlo
The Real Teatro di San Carlo ("Royal Theatre of Saint Charles"), as originally named by the Bourbon monarchy but today known simply as the Teatro (di) San Carlo, is an opera house in Naples, Italy, connected to the Royal Palace and adjacent ...
.
With the advent of the neoclassicism of the early nineteenth century (and also of the eclecticism of the end of the century), the historical center is also extended to the area of Posillipo and Vomero, exploiting these "new" spaces characterized by landscapes of particular beauty and by a large surrounding natural space. Thus the Villa Floridiana, Villa Rosebery and many other important Neapolitan villas are born.
References
Notes
Bibliography
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Historic Centre Of Naples Historic districts NaplesNaples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's admin ...