Hirudinea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Leeches are segmented
 Some 680 species of leech have been described, of which around 100 are marine, 480 freshwater and the remainder terrestrial. Among
Some 680 species of leech have been described, of which around 100 are marine, 480 freshwater and the remainder terrestrial. Among
 The most ancient annelid group consists of the free-living polychaetes that evolved in the
The most ancient annelid group consists of the free-living polychaetes that evolved in the
 Like other annelids, the leech is a segmented animal, but unlike other annelids, the segmentation is masked by external ring markings (annulations). The number of annulations varies, both between different regions of the body and between species. In one species, the body surface is divided into 102 annuli, but the body consists of 33 segments, a number constant across all leech species. Of these segments, the first five are designated as the head and include the anterior brain, several
Like other annelids, the leech is a segmented animal, but unlike other annelids, the segmentation is masked by external ring markings (annulations). The number of annulations varies, both between different regions of the body and between species. In one species, the body surface is divided into 102 annuli, but the body consists of 33 segments, a number constant across all leech species. Of these segments, the first five are designated as the head and include the anterior brain, several
 The bodies of predatory leeches are similar, though instead of a jaw many have a protrusible
The bodies of predatory leeches are similar, though instead of a jaw many have a protrusible  Blood-sucking leeches use their anterior suckers to connect to hosts for feeding. Once attached, they use a combination of mucus and suction to stay in place while they inject hirudin into the hosts'
Blood-sucking leeches use their anterior suckers to connect to hosts for feeding. Once attached, they use a combination of mucus and suction to stay in place while they inject hirudin into the hosts'
File:Leech looping locomotion.jpg, alt=Sketches of the looping movement of a leech using its front and back suckers, Leeches move by looping using their front and back suckers.
File:20100214 Leech climbing door at Lake Leake, Tasmania.ogv, alt=Video of looping movement, Video of looping movement
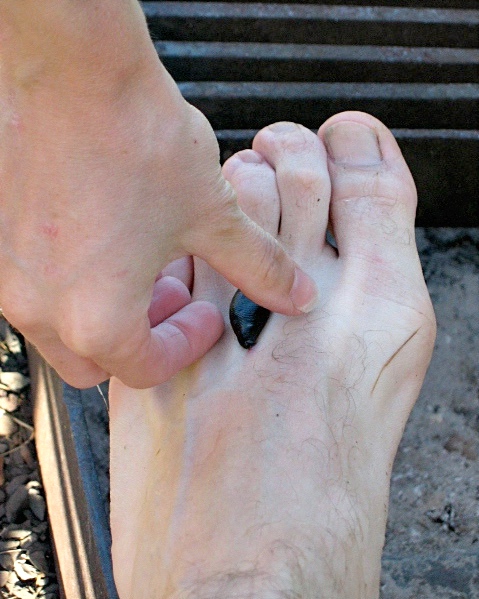
Victorian Poisons Information Centre. Retrieved 28 July 2007 An externally attached leech will detach and fall off on its own accord when it is satiated on blood, which may take from twenty minutes to a few hours; bleeding from the wound may continue for some time. Internal attachments, such as inside the nose, are more likely to require medical intervention. Bacteria, viruses, and protozoan parasites from previous blood sources can survive within a leech for months, so leeches could potentially act as vectors of pathogens. Nevertheless, only a few cases of leeches transmitting pathogens to humans have been reported. Leech saliva is commonly believed to contain
File:Leech Finders Costume of Yorkshire 1814.jpg , alt=Print from Costumes of Yorkshire 1814 showing three women searching for leeches in a pond, "Leech finders" from '' The Costume of Yorkshire'' by George Walker, 1814, engraved by Robert Havell
File:Pharmacy leech jar, England, 1830-1870 Wellcome L0058506.jpg, alt=Photograph of white and blue ceramic English pharmacy leech jar with airholes in the lid, Pharmacy leech jar with airholes in the lid. England, 1830–1870.
File:Three leeches in the role of physicians attend a grasshopper in the role of the patient and announce a course of bloodletting Wellcome V0011722.jpg, alt=Coloured lithograph cartoon showing three leech doctors treating a grasshopper patient, Three leech doctors decide on bloodletting for their
parasitic
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
or predatory
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the ...
worm
Worms are many different distantly related bilateral animals that typically have a long cylindrical tube-like body, no limbs, and no eyes (though not always).
Worms vary in size from microscopic to over in length for marine polychaete wo ...
s that comprise the subclass Hirudinea within the phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclatur ...
Annelid
The annelids (Annelida , from Latin ', "little ring"), also known as the segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ec ...
a. They are closely related to the oligochaetes
Oligochaeta () is a subclass of animals in the phylum Annelida, which is made up of many types of aquatic and terrestrial worms, including all of the various earthworms. Specifically, oligochaetes comprise the terrestrial megadrile earthworm ...
, which include the earthworm
An earthworm is a terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. They exhibit a tube-within-a-tube body plan; they are externally segmented with corresponding internal segmentation; and they usually have setae on all segments. Th ...
, and like them have soft, muscular segmented bodies that can lengthen and contract. Both groups are hermaphrodite
In reproductive biology, a hermaphrodite () is an organism that has both kinds of reproductive organs and can produce both gametes associated with male and female sexes.
Many taxonomic groups of animals (mostly invertebrates) do not have se ...
s and have a clitellum
The clitellum is a thickened glandular and non-segmented section of the body wall near the head in earthworms and leeches, that secretes a viscid sac in which eggs are stored. It is located near the anterior end of the body, between the fourteent ...
, but leeches typically differ from the oligochaetes in having suckers at both ends and in having ring markings that do not correspond with their internal segmentation. The body is muscular and relatively solid, and the coelom
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in most animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, i ...
, the spacious body cavity found in other annelids, is reduced to small channels.
The majority of leeches live in freshwater habitats, while some species can be found in terrestrial or marine environments. The best-known species, such as the medicinal leech, ''Hirudo medicinalis
''Hirudo medicinalis'', the European medicinal leech, is one of several species of leeches used as "medicinal leeches".
Other species of ''Hirudo'' sometimes also used as medicinal leeches include '' H. orientalis'', ''H. troctina'', and '' H. ...
'', are hematophagous, attaching themselves to a host with a sucker and feeding on blood, having first secreted the peptide hirudin
Hirudin is a naturally occurring peptide in the salivary glands of blood-sucking leeches (such as ''Hirudo medicinalis'') that has a blood anticoagulant property. This is fundamental for the leeches’ habit of feeding on blood, since it keeps a h ...
to prevent the blood from clotting. The jaws used to pierce the skin are replaced in other species by a proboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elon ...
which is pushed into the skin. A minority of leech species are predatory, mostly preying on small invertebrates.
The eggs are enclosed in a cocoon, which in aquatic species is usually attached to an underwater surface; members of one family, Glossiphoniidae
Glossiphoniidae are a family of freshwater proboscis-bearing leeches. These leeches are generally flattened, and have a poorly defined anterior sucker. Most suck the blood of freshwater vertebrates like amphibians, crocodilians and aquatic tu ...
, exhibit parental care, the eggs being brooded by the parent. In terrestrial species, the cocoon is often concealed under a log, in a crevice or buried in damp soil. Almost seven hundred species of leech are currently recognised, of which some hundred are marine, ninety terrestrial and the remainder freshwater.
Leeches have been used in medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care p ...
from ancient times until the 19th century to draw blood from patients. In modern times, leeches find medical use in treatment of joint diseases such as epicondylitis Epicondylitis is a type of musculoskeletal disorder that refers to an inflammation of an epicondyle
An epicondyle () is a rounded eminence on a bone that lies upon a condyle ('' epi-'', "upon" + ''condyle'', from a root meaning "knuckle" or "round ...
and osteoarthritis, extremity vein diseases, and in microsurgery
Microsurgery is a general term for surgery requiring an operating microscope. The most obvious developments have been procedures developed to allow anastomosis of successively smaller blood vessels and nerves (typically 1 mm in diameter) whi ...
, while hirudin is used as an anticoagulant
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where they ...
drug to treat blood-clotting disorders.
Diversity and phylogeny
 Some 680 species of leech have been described, of which around 100 are marine, 480 freshwater and the remainder terrestrial. Among
Some 680 species of leech have been described, of which around 100 are marine, 480 freshwater and the remainder terrestrial. Among Euhirudinea
Euhirudinea, the true leeches, are an infraclass of the Hirudinea.
Taxonomy
These clitellate annelids are of somewhat unclear relationships; namely the relationships of Hirudinea with oligochaetes are in need of revision. It may be that the ...
, the true leeches, the smallest is about long, and the largest is the giant Amazonian leech, ''Haementeria ghilianii
''Haementeria ghilianii'', the giant Amazon leech, is one of the world's largest species of leeches. It can grow to 450 mm (17.7 in) in length and 100 mm (3.9 in) in width. As adults, these leeches are a greyish-brown colour, ...
'', which can reach . Except for Antarctica, leeches are found throughout the world but are at their most abundant in temperate lakes and ponds in the northern hemisphere. The majority of freshwater leeches are found in the shallow, vegetated areas on the edges of ponds, lakes and slow-moving streams; very few species tolerate fast-flowing water. In their preferred habitats, they may occur in very high densities; in a favourable environment with water high in organic pollutants, over 10,000 individuals were recorded per square metre (over 930 per square foot) under rocks in Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockf ...
. Some species aestivate
Aestivation ( la, aestas (summer); also spelled estivation in American English) is a state of animal dormancy, similar to hibernation, although taking place in the summer rather than the winter. Aestivation is characterized by inactivity and a ...
during droughts, burying themselves in the sediment, and can lose up to 90% of their bodyweight and still survive. Among the freshwater leeches are the Glossiphoniidae
Glossiphoniidae are a family of freshwater proboscis-bearing leeches. These leeches are generally flattened, and have a poorly defined anterior sucker. Most suck the blood of freshwater vertebrates like amphibians, crocodilians and aquatic tu ...
, dorso-ventrally flattened animals mostly parasitic on vertebrates such as turtles, and unique among annelid
The annelids (Annelida , from Latin ', "little ring"), also known as the segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ec ...
s in both brooding their eggs and carrying their young on the underside of their bodies.
The terrestrial Haemadipsidae are mostly native to the tropics and subtropics, while the aquatic Hirudinidae have a wider global range; both of these feed largely on mammals, including humans. A distinctive family is the Piscicolidae, marine or freshwater ectoparasites chiefly of fish, with cylindrical bodies and usually well-marked, bell-shaped, anterior suckers. Not all leeches feed on blood; the Erpobdelliformes, freshwater or amphibious, are carnivorous and equipped with a relatively large, toothless mouth to ingest insect larvae, molluscs, and other annelid worms, which are swallowed whole. In turn, leeches are prey to fish, birds, and invertebrates.
The name for the subclass, Hirudinea, comes from the Latin ''hirudo'' (genitive
In grammar, the genitive case ( abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can ...
''hirudinis''), a leech; the element ''-bdella'' found in many leech group names is from the Greek βδέλλα ''bdella'', also meaning leech. The name ''Les hirudinées'' was given by Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, chevalier de Lamarck (1 August 1744 – 18 December 1829), often known simply as Lamarck (; ), was a French naturalist, biologist, academic, and soldier. He was an early proponent of the idea that biolog ...
in 1818. Leeches were traditionally divided into two infraclasses, the Acanthobdellidea (primitive leeches) and the Euhirudinea (true leeches). The Euhirudinea are divided into the proboscis-bearing Rhynchobdellida and the rest, including some jawed species, the " Arhynchobdellida", without a proboscis.
The phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological sp ...
of the leeches and their annelid relatives is based on molecular analysis (2019) of DNA sequences. Both the former classes "Polychaeta
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are m ...
" (bristly marine worms) and "Oligochaeta
Oligochaeta () is a subclass of animals in the phylum Annelida, which is made up of many types of aquatic and terrestrial worms, including all of the various earthworms. Specifically, oligochaetes comprise the terrestrial megadrile earthwor ...
" (including the earthworms) are paraphyletic
In taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In ...
: in each case the complete groups (clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
s) would include all the other groups shown below them in the tree. The Branchiobdellida
Branchiobdellida is an order of freshwater leech-like clitellates that are obligate ectosymbionts or ectoparasites, mostly of astacoidean crayfish. They are found in the Northern Hemisphere and have a holarctic distribution in East Asia, the Eu ...
are sister to the leech clade Hirudinida, which approximately corresponds to the traditional subclass Hirudinea. The main subdivision of leeches is into the Rhynchobdellida and the Arhynchobdellida, though the Acanthobdella are sister to the clade that contains these two groups.
Evolution
 The most ancient annelid group consists of the free-living polychaetes that evolved in the
The most ancient annelid group consists of the free-living polychaetes that evolved in the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ag ...
period, being plentiful in the Burgess Shale
The Burgess Shale is a fossil-bearing deposit exposed in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils. At old (middle Cambrian), it is one of the earliest fos ...
about 500million years ago. Oligochaetes evolved from polychaetes and the leeches branched off from the oligochaetes. The oldest leech fossils are from the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
period around 150million years ago, but a fossil with external ring markings found in Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michi ...
in the 1980s, with what appears to be a large sucker, seems to extend the group's evolutionary history back to the Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozo ...
, some 437million years ago.
Anatomy and physiology
Leeches show a remarkable similarity to each other in morphology, very different from typical annelids which are cylindrical with a fluid-filled space, thecoelom
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in most animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, i ...
(body cavity). In leeches, most of the coelom is filled with botryoidal tissue, a loose connective tissue composed of clusters of cells of mesodermal origin. The remaining body cavity has been reduced to four slender longitudinal channels. Typically, the body is dorso-ventrally flattened and tapers at both ends. Longitudinal and circular muscles in the body wall are supplemented by diagonal muscles, giving the leech the ability to adopt a large range of body shapes and show great flexibility. Most leeches have a sucker at both the anterior (front) and posterior (back) ends, but some primitive leeches have a single sucker at the back.
ocelli
A simple eye (sometimes called a pigment pit) refers to a form of eye or an optical arrangement composed of a single lens and without an elaborate retina such as occurs in most vertebrates. In this sense "simple eye" is distinct from a multi-le ...
(eyespots) dorsally and the sucker ventrally. The following 21 mid-body segments each contain a nerve ganglion
A ganglion is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system there are both sympathe ...
, and between them contain two reproductive organs, a single female gonopore
A gonopore, sometimes called a gonadopore, is a genital pore in many invertebrates. Hexapods, including insects have a single common gonopore, except mayflies, which have a pair of gonopores. More specifically, in the unmodified female it is th ...
and nine pairs of testes
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testost ...
. The last seven segments contain the posterior brain and are fused to form the animal's tail sucker. The septa that separates the body segments in the majority of annelids have been lost in leeches, except for the primitive genus Acanthobdella which still have some septa.
The body wall consists of a cuticle
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non- homologous, differing in their origin, structu ...
, an epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water ...
and a thick layer of fibrous connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
in which are embedded the circular muscles, the diagonal muscles and the powerful longitudinal muscles. There are also dorso-ventral muscles. In leeches the original blood vascular system has been lost and replaced by the modified coelom known as the haemocoelomic system, and the coelomic fluid, called the haemocoelomic fluid, has taken over the role as blood. The haemocoelomic channels run the full length of the body, the two main ones being on either side. Part of the lining epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercel ...
consists of chloragogen cells which are used for the storage of nutrients and in excretion
Excretion is a process in which metabolic waste
is eliminated from an organism. In vertebrates this is primarily carried out by the lungs, kidneys, and skin. This is in contrast with secretion, where the substance may have specific tasks afte ...
. There are 10 to 17 pairs of metanephridia
The nephridium (plural ''nephridia'') is an invertebrate organ, found in pairs and performing a function similar to the vertebrate kidneys (which originated from the chordate nephridia). Nephridia remove metabolic wastes from an animal's body. ...
(excretory organs) in the mid-region of the leech. From these, ducts typically lead to a urinary bladder
The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine ent ...
, which empties to the outside at a nephridiopore A nephridiopore is part of the nephridium, an excretory organ found in many organisms, such as flatworms and annelids. Polychaetes typically release their gametes into the water column using nephridiopores.
Nephridia are homologous to nephrons ...
.
Reproduction and development
Leeches are hermaphrodites, with the malereproductive organs
A sex organ (or reproductive organ) is any part of an animal or plant that is involved in sexual reproduction. The reproductive organs together constitute the reproductive system. In animals, the testis in the male, and the ovary in the female ...
, the testes
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testost ...
, maturing first and the ovaries
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. T ...
later. In hirudinids, a pair will line up with the clitellar regions in contact, with the anterior end of one leech pointing towards the posterior end of the other; this results in the male gonopore of one leech being in contact with the female gonopore of the other. The penis passes a spermatophore
A spermatophore or sperm ampulla is a capsule or mass containing spermatozoa created by males of various animal species, especially salamanders and arthropods, and transferred in entirety to the female's ovipore during reproduction. Spermatophores ...
into the female gonopore and sperm is transferred to, and probably stored in, the vagina.
Some jawless leeches (Rhynchobdellida) and proboscisless leeches (Arhynchobdellida) lack a penis, and in these, sperm is passed from one individual to another by hypodermic injection. The leeches intertwine and grasp each other with their suckers. A spermatophore is pushed by one through the integument of the other, usually into the clitellar region. The sperm is liberated and passes to the ovisacs, either through the coelomic channels or interstitially through specialist "target tissue" pathways.
Some time after copulation, the small, relatively yolkless eggs are laid. In most species, an albumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All the proteins of the albumin family are water- soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Albumin ...
-filled cocoon is secreted by the clitellum and receives one or more eggs as it passes over the female gonopore. In the case of the North American '' Erpobdella punctata'', the clutch size is about five eggs, and some ten cocoons are produced. Each cocoon is fixed to a submerged object, or in the case of terrestrial leeches, deposited under a stone or buried in damp soil. The cocoon of ''Hemibdella soleae
''Hemibdella soleae'' is a marine species of leech in the family Piscicolidae and the type taxon of its genus. Found in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, it is a parasite of flatfish such as the common sole.
Description
This small leech grows ...
'' is attached to a suitable fish host
A host is a person responsible for guests at an event or for providing hospitality during it.
Host may also refer to:
Places
* Host, Pennsylvania, a village in Berks County
People
* Jim Host (born 1937), American businessman
* Michel Hos ...
. The glossiphoniids brood their eggs, either by attaching the cocoon to the substrate and covering it with their ventral surface, or by securing the cocoon to their ventral surface, and even carrying the newly hatched young to their first meal.
When breeding, most marine leeches leave their hosts and become free-living in estuaries. Here they produce their cocoons, after which the adults of most species die. When the eggs hatch, the juveniles seek out potential hosts when these approach the shore. Leeches mostly have an annual or biannual life cycle.
Feeding and digestion
About three quarters of leech species areparasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
s that feed on the blood of a host, while the remainder are predators
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill th ...
. Leeches either have a pharynx that they can protrude, commonly called a proboscis, or a pharynx that they cannot protrude, which in some groups is armed with jaws.
In the proboscisless leeches, the jaws (if any) of Arhynchobdellids are at the front of the mouth, and have three blades set at an angle to each other. In feeding, these slice their way through the skin of the host, leaving a Y-shaped incision. Behind the blades is the mouth, located ventrally at the anterior end of the body. It leads successively into the pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its str ...
, a short oesophagus, a crop
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. When the plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. Most crops are cultivated in agriculture or hydropo ...
(in some species), a stomach and a hindgut, which ends at an anus located just above the posterior sucker. The stomach may be a simple tube, but the crop, when present, is an enlarged part of the midgut with a number of pairs of ceca that store ingested blood. The leech secretes an anticoagulant, hirudin
Hirudin is a naturally occurring peptide in the salivary glands of blood-sucking leeches (such as ''Hirudo medicinalis'') that has a blood anticoagulant property. This is fundamental for the leeches’ habit of feeding on blood, since it keeps a h ...
, in its saliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can ...
which prevents the blood from clotting before ingestion. A mature medicinal leech
''Hirudo medicinalis'', the European medicinal leech, is one of several species of leeches used as "medicinal leeches".
Other species of ''Hirudo'' sometimes also used as medicinal leeches include '' H. orientalis'', ''H. troctina'', and '' H. ...
may feed only twice a year, taking months to digest a blood meal.
 The bodies of predatory leeches are similar, though instead of a jaw many have a protrusible
The bodies of predatory leeches are similar, though instead of a jaw many have a protrusible proboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elon ...
, which for most of the time they keep retracted into the mouth. Such leeches are often ambush predator
Ambush predators or sit-and-wait predators are carnivorous animals that capture or trap prey via stealth, luring or by (typically instinctive) strategies utilizing an element of surprise. Unlike pursuit predators, who chase to capture pr ...
s that lie in wait until they can strike prey with the proboscises in a spear-like fashion. Predatory leeches feed on small invertebrates such as snails, earthworms and insect larvae. The prey is usually sucked in and swallowed whole. Some Rhynchobdellida however suck the soft tissues from their prey, making them intermediate between predators and blood-suckers.
blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in th ...
. In general, blood-feeding leeches are non host-specific, and do little harm to their host, dropping off after consuming a blood meal. Some marine species however remain attached until it is time to reproduce. If present in great numbers on a host, these can be debilitating, and in extreme cases, cause death.
Leeches are unusual in that they do not produce certain digestive enzyme
Digestive enzymes are a group of enzymes that break down polymeric macromolecules into their smaller building blocks, in order to facilitate their absorption into the cells of the body. Digestive enzymes are found in the digestive tracts of ani ...
s such as amylase
An amylase () is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of starch (Latin ') into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large amount ...
s, lipase
Lipase ( ) is a family of enzymes that catalyzes the hydrolysis of fats. Some lipases display broad substrate scope including esters of cholesterol, phospholipids, and of lipid-soluble vitamins and sphingomyelinases; however, these are usually t ...
s or endopeptidase
Endopeptidase or endoproteinase are proteolytic peptidases that break peptide bonds of nonterminal amino acids (i.e. within the molecule), in contrast to exopeptidases, which break peptide bonds from end-pieces of terminal amino acids. For this ...
s. A deficiency of these enzymes and of B complex vitamins is compensated for by enzymes and vitamins produced by endosymbiotic
An ''endosymbiont'' or ''endobiont'' is any organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism most often, though not always, in a mutualistic relationship.
(The term endosymbiosis is from the Greek: ἔνδον ''endon'' "within" ...
microflora. In ''Hirudo medicinalis'', these supplementary factors are produced by an obligatory mutualistic relationship with the bacterial species, ''Aeromonas veronii''. Non-bloodsucking leeches, such as ''Erpobdella octoculata'', are host to morew bacterial symbionts. In addition, leeches produce intestinal exopeptidases which remove amino acids from the long protein molecules one by one, possibly aided by protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the fo ...
s from endosymbiotic bacteria in the hindgut. This evolutionary choice of exopeptic digestion in Hirudinea distinguishes these carnivorous clitellates from oligochaetes, and may explain why digestion in leeches is so slow.
Nervous system
A leech's nervous system is formed of a few largenerve cells
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. No ...
; their large size makes leeches convenient as model organisms
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the working ...
for the study of invertebrate nervous systems. The main nerve centre consists of the cerebral ganglion above the gut and another ganglion beneath it, with connecting nerves forming a ring around the pharynx a little way behind the mouth. A nerve cord runs backwards from this in the ventral coelomic channel, with 21 pairs of ganglia in segments six to 26. In segments 27 to 33, other paired ganglia fuse to form the caudal ganglion. Several sensory nerves connect directly to the cerebral ganglion; there are sensory and motor nerve cells connected to the ventral nerve cord ganglia in each segment.
Leeches have between two and ten pigment spot ocelli, arranged in pairs towards the front of the body. There are also sensory papillae arranged in a lateral row in one annulation of each segment. Each papilla contains many sensory cells. Some rhynchobdellids have the ability to change colour dramatically by moving pigment in chromatophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contras ...
cells; this process is under the control of the nervous system but its function is unclear as the change in hue seems unrelated to the colour of the surroundings.
Leeches can detect touch, vibration, movement of nearby objects, and chemicals secreted by their hosts; freshwater leeches crawl or swim towards a potential host standing in their pond within a few seconds. Species that feed on warm-blooded hosts move towards warmer objects. Many leeches avoid light, though some blood feeders move towards light when they are ready to feed, presumably increasing the chances of finding a host.
Gas exchange
Leeches live in damp surroundings and in general respire through their body wall. The exception to this is in the Piscicolidae, where branching or leaf-like lateral outgrowths from the body wall formgill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they ar ...
s. Some rhynchobdellid leeches have an extracellular haemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythro ...
pigment, but this only provides for about half of the leech's oxygen transportation needs, the rest occurring by diffusion.
Movement
Leeches move using their longitudinal and circular muscles in a modification of the locomotion byperistalsis
Peristalsis ( , ) is a radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagate in a wave down a tube, in an anterograde direction. Peristalsis is progression of coordinated contraction of involuntary circular muscles, whic ...
, self-propulsion by alternately contracting and lengthening parts of the body, seen in other annelids such as earthworms. They use their posterior and anterior suckers (one on each end of the body) to enable them to progress by looping or inching along, in the manner of geometer moth
The geometer moths are moths belonging to the family Geometridae of the insect order Lepidoptera, the moths and butterflies. Their scientific name derives from the Ancient Greek ''geo'' γεω (derivative form of or "the earth"), and ''me ...
caterpillars. The posterior end is attached to the substrate, and the anterior end is projected forward peristaltically by the circular muscles until it touches down, as far as it can reach, and the anterior end is attached. Then the posterior end is released, pulled forward by the longitudinal muscles, and reattached; then the anterior end is released, and the cycle repeats. Leeches explore their environment with head movements and body waving. The Hirudinidae and Erpobdellidae can swim rapidly with up-and-down or sideways undulations of the body; the Glossiphoniidae in contrast are poor swimmers and curl up and fall to the sediment below when disturbed.
Interactions with humans
Bites
Leech bites are generally alarming rather than dangerous, though a small percentage of people have severe allergic or anaphylactic reactions and require urgent medical care. Symptoms of these reactions include red blotches or an itchy rash over the body, swelling around the lips or eyes, a feeling of faintness or dizziness, and difficulty in breathing.Victorian Poisons Information Centre: LeechesVictorian Poisons Information Centre. Retrieved 28 July 2007 An externally attached leech will detach and fall off on its own accord when it is satiated on blood, which may take from twenty minutes to a few hours; bleeding from the wound may continue for some time. Internal attachments, such as inside the nose, are more likely to require medical intervention. Bacteria, viruses, and protozoan parasites from previous blood sources can survive within a leech for months, so leeches could potentially act as vectors of pathogens. Nevertheless, only a few cases of leeches transmitting pathogens to humans have been reported. Leech saliva is commonly believed to contain
anaesthetic
An anesthetic (American English) or anaesthetic (British English; see spelling differences) is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into two ...
compounds to numb the bite area, but this has never been proven. Although morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. The ...
-like substances have been found in leeches, they have been found in the neural tissues, not the salivary tissues. They are used by the leeches in modulating their own immunocytes and not for anaesthetising bite areas on their hosts. Depending on the species and size, leech bites can be barely noticeable or they can be fairly painful.
In human culture
The leech appears inProverbs
A proverb (from la, proverbium) is a simple and insightful, traditional saying that expresses a perceived truth based on common sense or experience. Proverbs are often metaphorical and use formulaic language. A proverbial phrase or a proverbia ...
30:15 as an archetype of insatiable greed
Greed (or avarice) is an uncontrolled longing for increase in the acquisition or use of material gain (be it food, money, land, or animate/inanimate possessions); or social value, such as status, or power. Greed has been identified as unde ...
. More generally, a leech is a persistent social parasite or sycophant
In modern English, sycophant denotes an "insincere flatterer" and is used to refer to someone practising sycophancy (i.e., insincere flattery to gain advantage). The word has its origin in the legal system of Classical Athens. Most legal cases ...
.
The medicinal leech ''Hirudo medicinalis'', and some other species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate ...
, have been used for clinical bloodletting
Bloodletting (or blood-letting) is the withdrawal of blood from a patient to prevent or cure illness and disease. Bloodletting, whether by a physician or by leeches, was based on an ancient system of medicine in which blood and other bodily flu ...
for at least 2,500 years: Ayurvedic
Ayurveda () is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. The theory and practice of Ayurveda is pseudoscientific. Ayurveda is heavily practiced in India and Nepal, where around 80% of the population repor ...
texts describe their use for bloodletting in ancient India. In ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
, bloodletting was practised according to the theory of humours found in the Hippocratic Corpus
The Hippocratic Corpus ( Latin: ''Corpus Hippocraticum''), or Hippocratic Collection, is a collection of around 60 early Ancient Greek medical works strongly associated with the physician Hippocrates and his teachings. The Hippocratic Corpus co ...
of the fifth centuryBC, which maintained that health depended on a balance of the four humours: blood, phlegm
Phlegm (; , ''phlégma'', "inflammation", "humour caused by heat") is mucus produced by the respiratory system, excluding that produced by the nasal passages. It often refers to respiratory mucus expelled by coughing, otherwise known as sputum. ...
, black bile and yellow bile. Bloodletting using leeches enabled physicians to restore balance if they considered blood was present in excess.
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ...
reported in his '' Natural History'' that the horse leech could drive elephants mad by climbing up inside their trunks to drink blood. Pliny also noted the medicinal use of leeches in ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 ...
, stating that they were often used for gout
Gout ( ) is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of a red, tender, hot and swollen joint, caused by deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals. Pain typically comes on rapidly, reaching maximal intensi ...
, and that patients became addicted to the treatment. In Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
, ''lǣce'' was the name for a physician as well as for the animal, though the words had different origins, and ''lǣcecraft'', leechcraft, was the art of healing.
grasshopper
Grasshoppers are a group of insects belonging to the suborder Caelifera. They are among what is possibly the most ancient living group of chewing herbivorous insects, dating back to the early Triassic around 250 million years ago.
Grasshoppe ...
patient. Lithograph by F.-J.-V. Broussais from a cartoon by J. J. Grandville,
William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth (7 April 177023 April 1850) was an English Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romantic Age in English literature with their joint publication '' Lyrical Ballads'' (1798).
Wordsworth's ...
's 1802 poem " Resolution and Independence" describes one of the last of the leech-gatherers, people who travelled Britain catching leeches from the wild, and causing a sharp decline in their abundance, though they remain numerous in Romney Marsh
Romney Marsh is a sparsely populated wetland area in the counties of Kent and East Sussex in the south-east of England. It covers about . The Marsh has been in use for centuries, though its inhabitants commonly suffered from malaria until the ...
. By 1863, British hospitals had switched to imported leeches, some seven million being imported to hospitals in London that year.
In the nineteenth century, demand for leeches was sufficient for hirudiculture, the farming of leeches, to become commercially viable. Leech usage declined with the demise of humoral theory, but made a small-scale comeback in the 1980s after years of decline, with the advent of microsurgery
Microsurgery is a general term for surgery requiring an operating microscope. The most obvious developments have been procedures developed to allow anastomosis of successively smaller blood vessels and nerves (typically 1 mm in diameter) whi ...
, where venous congestion can arise due to inefficient venous drainage. Leeches can reduce swelling in the tissues and promote healing, helping in particular to restore circulation after microsurgery to reattach body parts. Other clinical applications include varicose veins
Varicose veins, also known as varicoses, are a medical condition in which superficial veins become enlarged and twisted. These veins typically develop in the legs, just under the skin. Varicose veins usually cause few symptoms. However, some indi ...
, muscle cramps, thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis is a phlebitis (inflammation of a vein) related to a thrombus (blood clot). When it occurs repeatedly in different locations, it is known as thrombophlebitis migrans ( migratory thrombophlebitis).
Signs and symptoms
The following ...
, and joint diseases such as epicondylitis and osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone which affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the ...
.
Leech secretions contain several bioactive substances with anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory is the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation or swelling. Anti-inflammatory drugs, also called anti-inflammatories, make up about half of analgesics. These drugs remedy pain by reducing inflammation as o ...
, anticoagulant
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where they ...
and antimicrobial effects. One active component of leech saliva is a small protein, hirudin. It is widely used as an anticoagulant drug to treat blood-clotting disorders, and manufactured by recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be fo ...
technology.
In 2012 and 2018, Ida Schnell and colleagues trialled the use of '' Haemadipsa'' leeches to gather data on the biodiversity of their mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fu ...
ian hosts in the tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equat ...
of Vietnam, where it is hard to obtain reliable data on rare and cryptic mammals. They showed that mammal mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DN ...
, amplified by the polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) ...
, can be identified from a leech's blood meal for at least four months after feeding. They detected Annamite striped rabbit, small-toothed ferret-badger, Truong Son muntjac
The Truong Son muntjac or Annamite muntjac (''Muntiacus truongsonensis'') is a species of muntjac deer. It is one of the smallest muntjac species, at about , half the size of the Indian muntjac
The Indian muntjac or the common muntjac (''Mun ...
, and serow
The serows ( or ) are four species of medium-sized goat-like or antelope-like mammals of the genus ''Capricornis''. All four species of serow were until recently also classified under '' Naemorhedus'', which now only contains the gorals.
Extan ...
in this way.
Water pollution
Exposure to synthetic estrogen as used in contraceptive medicines, which may enter freshwater ecosystems from municipalwastewater
Wastewater is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of domestic, industri ...
, can affect leeches' reproductive systems. Although not as sensitive to these compounds as fish, leeches showed physiological changes after exposure, including longer sperm sacs and vaginal bulbs, and decreased epididymis
The epididymis (; plural: epididymides or ) is a tube that connects a testicle to a vas deferens in the male reproductive system. It is a single, narrow, tightly-coiled tube in adult humans, in length. It serves as an interconnection between t ...
weight.
Notes
References
General bibliography
*External links
* * * {{featured article Articles containing video clips Clitellata Extant Silurian first appearances