Henry M. Jackson on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Henry Martin "Scoop" Jackson (May 31, 1912 – September 1, 1983) was an American lawyer and politician who served as a U.S. representative (1941–1953) and U.S. senator (1953–1983) from the state of Washington. A Cold War liberal and
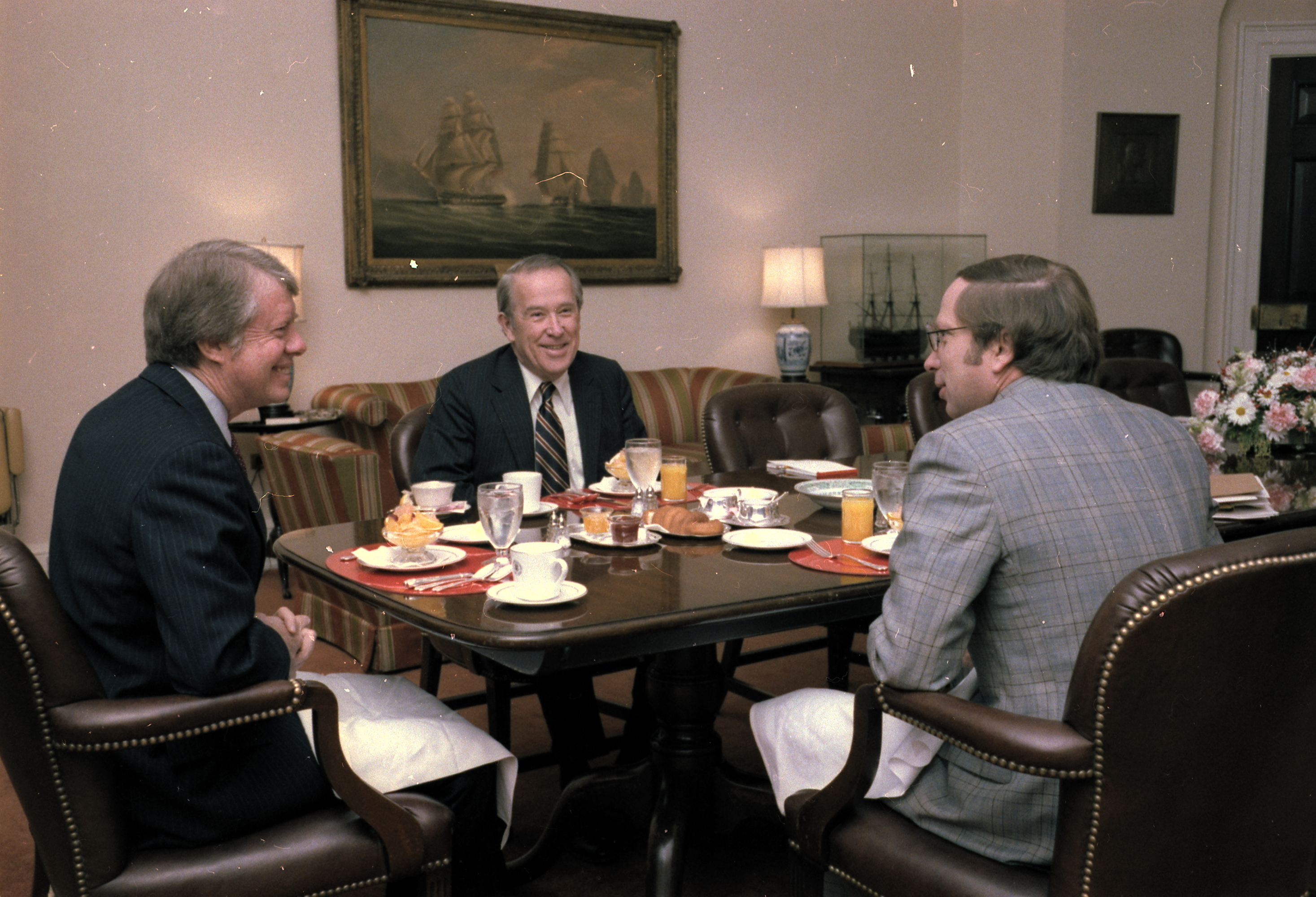 Jackson led the opposition within the Democratic Party against the
Jackson led the opposition within the Democratic Party against the
 Jackson raised his national profile by speaking out on Soviet-U.S. relations and Middle East policy regularly, and he was considered a front-runner for the nomination when he announced the start of his campaign in February 1975. Jackson received substantial financial support from Jewish-Americans who admired his pro-
Jackson raised his national profile by speaking out on Soviet-U.S. relations and Middle East policy regularly, and he was considered a front-runner for the nomination when he announced the start of his campaign in February 1975. Jackson received substantial financial support from Jewish-Americans who admired his pro-
Dems Need Another Scoop Jackson
",
", Henry Jackson Society, March 11, 2005. The organization is now based in London and hosts high-profile speaker events in the
Henry M. Jackson Collection
nbsp;– University of Washington Digital Collection * *
at 4president.org
Henry M Jackson Papers
, at the University of Washington
at the U.S. Senate
* ttp://www.hmjackson.org/ Henry M Jackson Foundation
The Henry Jackson Society
at the University of Cambridge
Henry M. Jackson—A Life in Politics
biography
Henry M. Jackson, late a senator
*
Guide to the Henry M. Jackson Papers
1912–1987. Approximately 1,240 Cubic Ft. At th
University of Washington Libraries Special Collections
Richard J. Brooks Papers.
1956–2000. 7.62 cubic feet. 8 boxes, one vertical file, one oversize folder, one mapcase folder. At th
University of Washington Libraries Special Collections
Contains correspondence from Senator Henry M. Jackson. , - , - , - , - , - , - , - {{DEFAULTSORT:Jackson, Henry Martin 1912 births 1983 deaths American anti-communists American Christian Zionists American people of Norwegian descent American Presbyterians Candidates in the 1972 United States presidential election Candidates in the 1976 United States presidential election Deaths from aortic aneurysm Democratic National Committee chairs Democratic Party members of the United States House of Representatives from Washington (state) Democratic Party United States senators from Washington (state) Politicians from Everett, Washington Presidential Medal of Freedom recipients Sierra Club awardees Stanford University alumni University of Washington School of Law alumni Delta Chi members 20th-century United States senators 20th-century members of the United States House of Representatives
anti-Communist
Anti-communism is political and ideological opposition to communist beliefs, groups, and individuals. Organized anti-communism developed after the 1917 October Revolution in Russia, and it reached global dimensions during the Cold War, when th ...
member of the Democratic Party, Jackson supported higher military spending and a hard line against the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, while also supporting social welfare programs, civil rights
Civil and political rights are a class of rights that protect individuals' political freedom, freedom from infringement by governments, social organizations, and private individuals. They ensure one's entitlement to participate in the civil and ...
, and labor unions.
Born in Everett, Washington
Everett (; ) is the county seat and most populous city of Snohomish County, Washington, United States. It is north of Seattle and is one of the main cities in the Seattle metropolitan area, metropolitan area and the Puget Sound region. Everett ...
, to Norwegian immigrants, Jackson practiced law in Everett, after graduating from the University of Washington School of Law. He won election to Congress in 1940, and joined the Senate in 1953 after defeating incumbent Republican Party senator Harry P. Cain. Jackson supported the civil rights movement of the 1960s, and authored the National Environmental Policy Act
The National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) is a United States environmental law designed to promote the enhancement of the environment. It created new laws requiring U.S. federal government agencies to evaluate the environmental impacts of ...
, which helped establish the principle of publicly analyzing environmental impacts. He co-sponsored the Jackson–Vanik amendment
The Jackson–Vanik amendment to the Trade Act of 1974 is a 1974 provision in United States federal law intended to affect U.S. trade relations with countries with non-market economies (originally, countries of the Soviet Bloc) that restrict freed ...
, which denied normal trade relations to non-capitalist countries with restrictive emigration policies. Jackson served as chairman of the United States Senate Committee on Energy and Natural Resources
The United States Senate Committee on Energy and Natural Resources is a Standing committee (United States Congress), standing committee of the United States Senate. It has jurisdiction over matters related to energy and mineral resources, inclu ...
from 1963 to 1981. He was twice an unsuccessful candidate for the Democratic Party nomination in the 1972
Within the context of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) it was the longest year ever, as two leap seconds were added during this 366-day year, an event which has not since been repeated. (If its start and end are defined using Solar time, ...
and 1976
Events January
* January 2 – The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force.
* January 5 – The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea.
* January 18 – Full diplomatic ...
presidential elections. While still serving in the Senate, Jackson died in 1983.
His political beliefs were characterized by support of civil rights, human rights, and safeguarding the environment, but with an equally strong commitment to oppose totalitarianism
Totalitarianism is a political system and a form of government that prohibits opposition from political parties, disregards and outlaws the political claims of individual and group opposition to the state, and completely controls the public s ...
in general and — with the start of the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
— communist rule in particular. Jackson's political philosophies and positions have been cited as an influence on a number of key figures associated with neoconservatism
Neoconservatism (colloquially neocon) is a political movement which began in the United States during the 1960s among liberal hawks who became disenchanted with the increasingly pacifist Democratic Party along with the growing New Left and ...
, including Paul Wolfowitz
Paul Dundes Wolfowitz (born December 22, 1943) is an American political scientist and diplomat who served as the 10th President of the World Bank, U.S. Deputy Secretary of Defense, U.S. Ambassador to Indonesia, and dean of Paul H. Nitze Scho ...
and Richard Perle
Richard Norman Perle (born September 16, 1941) is an American political advisor who served as the Assistant Secretary of Defense for Global Strategic Affairs under President Ronald Reagan. He began his political career as a senior staff member to ...
, both of whom previously served as aides to Jackson.
Early life
Jackson was born in the home of his parents, Marine (née Andersen) and Peter Jackson, inEverett, Washington
Everett (; ) is the county seat and most populous city of Snohomish County, Washington, United States. It is north of Seattle and is one of the main cities in the Seattle metropolitan area, metropolitan area and the Puget Sound region. Everett ...
, on May 31, 1912. His mother and father were both immigrants from Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
. Peter Jackson was born Peter Gresseth in the Kristiansund
Kristiansund (, ; historically spelled Christianssund and earlier named Fosna) is a List of municipalities of Norway, municipality on the western coast of Norway in the Nordmøre district of Møre og Romsdal counties of Norway, county. The admin ...
area, and changed his name when he immigrated. He met Marine, who was born in Alvenes at the Lutheran church in Everett, where they were married in 1897. Henry was the fifth, and youngest, of the Jackson children; he was nicknamed "Scoop" by his sister in his childhood, after a comic strip character that he was said to have resembled. Jackson was a member of the National Honor Society
The National Honor Society (NHS) is one of the oldest, largest, and most widely recognized cocurricular student organizations in American high schools, with 1.4 million members.
The purpose of the NHS is to create enthusiasm for scholarship, to ...
. He went on to graduate with a B.A. degree from Stanford University
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth ...
, and a J.D. degree from the University of Washington School of Law, where he joined the Delta Chi
Delta Chi () is an international collegiate social fraternity. It was formed in 1890 at Cornell University as a professional fraternity for law students, becoming a social fraternity in 1922. In 1929. Delta Chi became one of the first internat ...
fraternity.
Early career
In 1935, the year of his law school graduation, he was admitted to the bar, and began to practice law in Everett. He found immediate success, and was elected to become the prosecuting attorney for Snohomish County from 1938 to 1940, where he made a name for himself prosecuting bootleggers and gamblers.Personal life
In 1961, Jackson, called by ''Time
Time is the continuous progression of existence that occurs in an apparently irreversible process, irreversible succession from the past, through the present, and into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequ ...
'' the Senate's "most eligible bachelor", married Helen Hardin, a 28-year-old Senate receptionist who was 20 years his junior. Jackson did not move out of his childhood home, where he lived with his unmarried sisters for several years. The Jacksons had two children: Anna Marie Laurence and Peter Jackson. Peter went on to serve as a speechwriter for Governor Christine Gregoire
Christine Gregoire (; née O'Grady; born March 24, 1947) is an American attorney and politician who served as the List of governors of Washington, 22nd governor of Washington, from 2005 to 2013. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), D ...
and to lead the effort to found the Center for Human Rights at the University of Washington
The University of Washington (UW and informally U-Dub or U Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington, United States. Founded in 1861, the University of Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast of the Uni ...
, which now has a scholarship in his name.
In Congress
Jackson successfully ran for theU.S. Congress
The United States Congress is the legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is a bicameral legislature, including a lower body, the U.S. House of Representatives, and an upper body, the U.S. Senate. They both ...
as a Democrat in 1940 and took his seat in the House of Representatives with the 77th Congress on January 3, 1941. From then on, Jackson did not lose any congressional elections. Jackson joined the Army when the United States entered World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
but left when Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
ordered all representatives to return home or resign their seats. He visited the Buchenwald
Buchenwald (; 'beech forest') was a German Nazi concentration camp established on Ettersberg hill near Weimar, Germany, in July 1937. It was one of the first and the largest of the concentration camps within the Altreich (Old Reich) territori ...
concentration camp a few days after its liberation in 1945. He also visited his native Norway, where he observed the repatriation to Russia of Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
soldiers captured by the Nazis, in which he recalled"I remember how reluctant most Russians were to return to theHe attended the International Maritime Conference inSoviet Union The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet .... They knew they would have even less freedom there."
Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a population of 1.4 million in the Urban area of Copenhagen, urban area. The city is situated on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from Malmö, Sweden, by the ...
, Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
, in 1945 with the American delegation, and he was elected president of the same conference in 1946, when it was held in Seattle
Seattle ( ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Washington and in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. With a population of 780,995 in 2024, it is the 18th-most populous city in the United States. The city is the cou ...
. From 1945 to 1947, Jackson was also the chairman of the House Indian Affairs Committee. In the 1952 U.S. House election, Jackson relinquished his seat in the House for a run for one of Washington's Senate seats. Jackson soundly defeated Republican senator Harry P. Cain and remained a senator for over thirty years. He was Washington's first U.S. senator to be born in the state. Jackson died in office in 1983 after winning re-election for the fifth time in 1982.
Although Jackson opposed the excesses of Joe McCarthy, who had traveled to Washington state to campaign against him, he criticized Dwight Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was the 34th president of the United States, serving from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, he was Supreme Commander of the Allied Expeditionar ...
for not spending enough on national defense. Jackson called for more inter-continental ballistic missiles in the national arsenal, and his support for nuclear weapons resulted in a primary challenge from the left in 1958, when he handily defeated Seattle peace activist Alice Franklin Bryant before winning re-election with 67 percent of the vote, which he topped the next four times he ran for re-election.
During the 1960 Democratic Party presidential primaries, Jackson was the first choice of fellow senator John F. Kennedy for a running mate; Kennedy became convinced that a Southerner would better balance the ticket. Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), also known as LBJ, was the 36th president of the United States, serving from 1963 to 1969. He became president after the assassination of John F. Kennedy, under whom he had served a ...
was later selected. Jackson boasted one of the strongest records on civil rights during the civil rights movement. He supported the 1957 and the 1964 Civil Rights Acts. On July 22, 1965, Johnson signed the Water Resources Planning Act into law, citing Jackson as one of the Congress members to "have made a very invaluable and very farsighted contribution to America's future." In April 1968, responding to the assassination of Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. (born Michael King Jr.; January 15, 1929 – April 4, 1968) was an American Baptist minister, civil and political rights, civil rights activist and political philosopher who was a leader of the civil rights move ...
, Jackson gave a speech about the legacy and injustice of inequality.
In 1963, Jackson was made chairman of the Committee on Interior and Insular Affairs, which became the Committee on Energy and Natural Resources in 1977, a position he held until 1981. In the 1970s, Jackson joined with fellow senators Ernest Hollings and Edward Kennedy in a press conference to oppose Gerald Ford
Gerald Rudolph Ford Jr. (born Leslie Lynch King Jr.; July 14, 1913December 26, 2006) was the 38th president of the United States, serving from 1974 to 1977. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, Ford assumed the p ...
's request for Congress to end Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 until Resignation of Richard Nixon, his resignation in 1974. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican ...
's price controls on domestic oil, which had provoked oil companies into withholding gasoline during the 1973 oil crisis
In October 1973, the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC) announced that it was implementing a total oil embargo against countries that had supported Israel at any point during the 1973 Yom Kippur War, which began after Eg ...
. Kaufman writes that, after 1968, Jackson "emerged as an intellectual and political leader in the perennial struggle of U.S. foreign policy to reconcile ideals with self-interest."
Jackson authored the National Environmental Policy Act
The National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) is a United States environmental law designed to promote the enhancement of the environment. It created new laws requiring U.S. federal government agencies to evaluate the environmental impacts of ...
, which has been called one of the most influential environmental laws in history. It helped to stimulate similar laws and the principle of publicly analyzed environmental impact in other states and in much of the world. Jackson was also a leader of the fight for statehood for Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
and Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
. In 1974, Jackson sponsored the Jackson–Vanik amendment
The Jackson–Vanik amendment to the Trade Act of 1974 is a 1974 provision in United States federal law intended to affect U.S. trade relations with countries with non-market economies (originally, countries of the Soviet Bloc) that restrict freed ...
in the Senate (with Charles Vanik sponsoring it in the House), which denied normal trade relations to certain countries with non-market economies that restricted the freedom of emigration. The amendment was intended to help refugees, particularly minorities, specifically Jews, to emigrate from the Soviet Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
. Jackson and his assistant, Richard Perle
Richard Norman Perle (born September 16, 1941) is an American political advisor who served as the Assistant Secretary of Defense for Global Strategic Affairs under President Ronald Reagan. He began his political career as a senior staff member to ...
, also lobbied personally for some people who were affected by this law such as Natan Sharansky
Natan Sharansky (; born 20 January 1948) is an Israeli politician, human rights activist, and author. He served as Chairman of the Executive for the Jewish Agency for Israel, Jewish Agency from June 2009 to August 2018, and currently serves as ...
.
Throughout his time as senator, Jackson was a strong supporter of Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
. In 1970, he urged President Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 until his resignation in 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as the 36th vice president under P ...
to sell F-4 Phantom II
The McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II is an American tandem two-seat, twin-engine, all-weather, long-range supersonic jet interceptor and fighter-bomber that was developed by McDonnell Aircraft for the United States Navy.Swanborough and Bower ...
fighter jets to that country, on the terms that amounted to a grant. During the Yom Kippur War
The Yom Kippur War, also known as the Ramadan War, the October War, the 1973 Arab–Israeli War, or the Fourth Arab–Israeli War, was fought from 6 to 25 October 1973 between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states led by Egypt and S ...
, Jackson, alongside fellow Congressional leaders demanded an urgent resupply of weapons, to ensure that Israeli forces would have the material, diplomatic and political support necessary for a victory. When the Nixon administration balked at direct and visible material support, Jackson worked with Secretary of Defense James Schlesinger, Director of the Bureau of Political-Military Affairs Seymor Weiss, and senior American military commanders, notably Chief of Naval Operations
The chief of naval operations (CNO) is the highest-ranking officer of the United States Navy. The position is a statutory office () held by an Admiral (United States), admiral who is a military adviser and deputy to the United States Secretary ...
Elmo Zumwalt
Elmo Russell "Bud" Zumwalt Jr. (November 29, 1920 – January 2, 2000) was a United States Navy officer and the youngest person to serve as Chief of Naval Operations. As an Admiral (United States), admiral and later the 19th Chief of Naval Opera ...
, to secure the decision to airlift vital weapons and ammunition to a "gravely imperiled IDF". On December 1968 Jackson declined Nixon's offer to serve as Secretary of Defense.
In 1975, after President Ford announced he would not invite Soviet dissident Aleksander Solzhenitsyn to the White House, for fear of angering the Soviet Union, Jackson and a group of other senators asked Solzhenitsyn to speak at an office in the Capitol. Jackson was also one of the first senators to call for the normalization of relations with China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, and was instrumental in arranging many business, educational, and community contacts between Washington and China.
In March 1975, Jackson released a statement in which he expressed the view that it was paramount the Franklin Peroff case be found out to be either "an aberration or was symptomatic of much greater problem" within the Drug Enforcement Administration. In June 1975, Jackson stated that if accounts about the conduct of former director of the Drug Enforcement Agency John R. Bartels Jr. were correct then his actions amounted to obstruction of justice and that evidence disclosed "in the last two days would indicate that there was a conscious, premeditated plan involving misconduct at the highest levels of the D.E.A."
In July 1977, the Senate approved a funding for the experimental nuclear reactor compromise proposal by Jackson and Idaho senator Frank Church. While the initial version by Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (October 1, 1924December 29, 2024) was an American politician and humanitarian who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party ...
sought a decrease in funding from 150 million to 33 million, the Jackson and Church measure halved the funding to 75 million. In October 1979, the Senate voted in favor of Carter's energy mobilization board plan, Jackson labeling the plan the "centerpiece" of Carter's program that was essential to guaranteeing the effectiveness of the rest of the legislation and was noted for successfully persuading colleagues to reject amendments to the plan. Later that month, after the Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee voted in favor of the Alaska public lands legislation, Carter issued a statement thanking Jackson and other members for supporting the legislation.
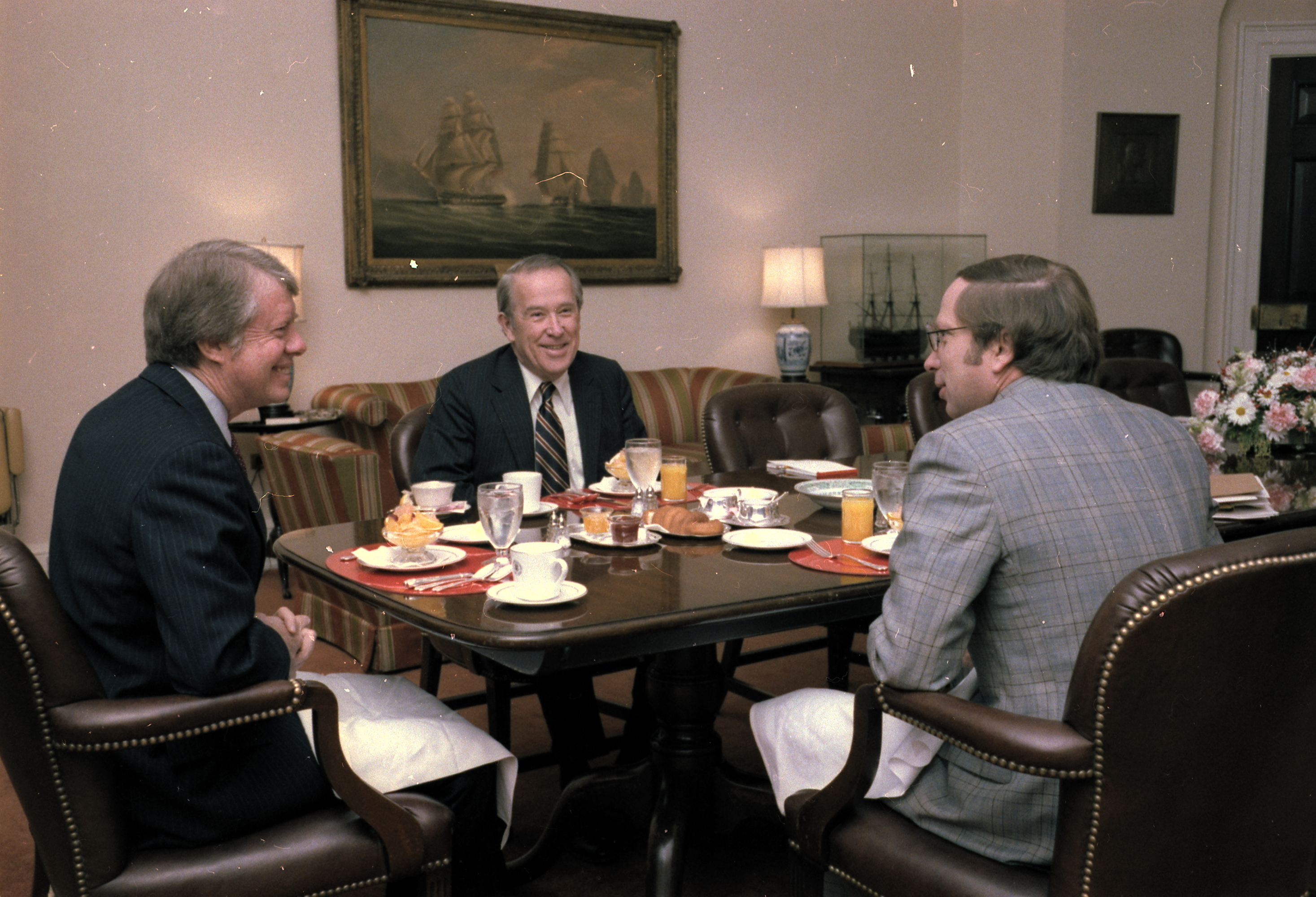 Jackson led the opposition within the Democratic Party against the
Jackson led the opposition within the Democratic Party against the SALT II
The Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT) were two rounds of bilateral conferences and corresponding international treaties involving the United States and the Soviet Union. The Cold War superpowers dealt with arms control in two rounds of ...
treaty. For decades, Democrats who support a strong international presence for the United States have been called "Scoop Jackson Democrats," and the term was still used to describe Democrats such as Joe Lieberman
Joseph Isadore Lieberman (; February 24, 1942 – March 27, 2024) was an American politician and lawyer who served as a United States senator from Connecticut from 1989 to 2013. Originally a member of the Democratic Party (United States), Dem ...
and R. James Woolsey Jr by the aughts.
Jackson served for all but the last three years of his Senate tenure with Democratic colleague and friend Warren G. Magnuson. As a result, he spent 28 years as the state's junior senator, even though he had more seniority than all but a few of his colleagues. "Scoop" and "Maggie", as they affectionately called each other, gave Washington clout in national politics well beyond its population. They were one of the most effective delegations in the history of the Senate in terms of "bringing home the bacon" for their home state. Washington received nearly a sixth of public works appropriations but ranked only 23rd in population.
Criticism
Jackson was known as a hawkish Democrat. He was often criticized for his support for theVietnam War
The Vietnam War (1 November 1955 – 30 April 1975) was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) and South Vietnam (Republic of Vietnam) and their allies. North Vietnam w ...
and his close ties to the defense industries of his state. His proposal of Fort Lawton
Fort Lawton was a United States Army Military base, post located in the Magnolia, Seattle, Washington, Magnolia neighborhood of Seattle, Washington (state), Washington overlooking Puget Sound. In 1973 a large majority of the property, 534 acre ...
as a site for an anti-ballistic missile
An anti-ballistic missile (ABM) is a surface-to-air missile designed to Missile defense, destroy in-flight ballistic missiles. They achieve this explosively (chemical or nuclear), or via hit-to-kill Kinetic projectile, kinetic vehicles, which ma ...
system was strongly opposed by local residents, and Jackson was forced to modify his position on the location of the site several times, but continued to support ABM development. American Indian rights activists who protested Jackson's plan to give Fort Lawton to Seattle, instead of returning it to local tribes, staged a sit-in
A sit-in or sit-down is a form of direct action that involves one or more people occupying an area for a protest, often to promote political, social, or economic change. The protestors gather conspicuously in a space or building, refusing to mo ...
. In the eventual compromise, most of Fort Lawton became Discovery Park, with leased to United Indians of All Tribes, who opened the Daybreak Star Cultural Center
The Daybreak Star Indian Cultural Center is a Native Americans in the United States, Native American cultural center in Seattle, Washington, described by its parent organization United Indians of All Tribes as "an urban base for Native Amer ...
there in 1977.
Opponents derided him as "the senator from Boeing
The Boeing Company, or simply Boeing (), is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product support s ...
", as well as a "whore for Boeing", because of his consistent support for additional military spending on weapons systems and accusations of wrongful contributions from the company; in 1965, 80% of Boeing's contracts were military. Jackson and Magnuson's campaigning for an expensive government supersonic transport plane project eventually failed. In addition, contrary to claims that he was an environmentalist, Jackson was almost as much a "whore for logging companies" as for Boeing, according Carsten Lien's book ''Olympic Battleground''.
After his death, critics pointed to Jackson's support for Japanese American internment
During World War II, the United States forcibly relocated and incarcerated about 120,000 people of Japanese descent in ten concentration camps operated by the War Relocation Authority (WRA), mostly in the western interior of the country. Abou ...
camps during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
as a reason to protest the placement of his bust at the University of Washington. Jackson was both an enthusiastic defender of the evacuation and a staunch proponent of the campaign to keep the Japanese-Americans from returning to the Pacific Coast after the war.
Presidential campaigns
Jackson was not only successful as a politician in Washington state, but he also found recognition on the national level. He rose to the position of chairman of theDemocratic National Committee
The Democratic National Committee (DNC) is the principal executive leadership board of the United States's Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party. According to the party charter, it has "general responsibility for the affairs of the ...
in 1960, after being considered for the vice presidential ticket spot that eventually went to fellow senator Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), also known as LBJ, was the 36th president of the United States, serving from 1963 to 1969. He became president after the assassination of John F. Kennedy, under whom he had served a ...
. Jackson ran for president twice, and both campaigns were noted for the hostile reception they received from the left wing of the Democratic Party. Jackson's one-on-one campaigning skills, which were extremely successful in Washington state, did not translate as well to the national stage. Even his supporters admitted that he suffered from a certain lack of charisma.
1972 presidential campaign
Jackson was little known nationally when he first ran in1972
Within the context of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) it was the longest year ever, as two leap seconds were added during this 366-day year, an event which has not since been repeated. (If its start and end are defined using Solar time, ...
. George McGovern
George Stanley McGovern (July 19, 1922 – October 21, 2012) was an American politician, diplomat, and historian who was a U.S. representative and three-term U.S. senator from South Dakota, and the Democratic Party (United States), Democ ...
, who eventually won the nomination, even accused Jackson of racism for his opposition to busing
Desegregation busing (also known as integrated busing, forced busing, or simply busing) was an attempt to diversify the racial make-up of schools in the United States by transporting students to more distant schools with less diverse student pop ...
despite Jackson's longstanding record on civil rights issues. Jackson's high point in the campaign was a distant third in the early Florida primary, but he failed to stand out of the pack of better-known rivals, and he made real news only later in the campaign, as part of the "Stop McGovern" coalition, which raised what would be known as the "Acid, Amnesty and Abortion" questions about McGovern. Jackson suspended active campaigning in May after a weak showing in the Ohio primary and finishing well behind McGovern, Ed Muskie, George Wallace, and Hubert Humphrey
Hubert Horatio Humphrey Jr. (May 27, 1911 – January 13, 1978) was an American politician who served from 1965 to 1969 as the 38th vice president of the United States. He twice served in the United States Senate, representing Minnesota from 19 ...
in early primaries.
Jackson re-emerged at the July Democratic convention after the runner-up, Humphrey, dropped out of the race. Jackson's name was placed in nomination by Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
governor Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (October 1, 1924December 29, 2024) was an American politician and humanitarian who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party ...
, and he finished second in the delegate roll call, well behind nominee McGovern. While campaigning in New York City, Jackson invited Meir Kahane, the leader of the violent organization the Jewish Defense League, to stand with him on stage in order to gain favor with Jewish Americans.
1976 presidential campaign
 Jackson raised his national profile by speaking out on Soviet-U.S. relations and Middle East policy regularly, and he was considered a front-runner for the nomination when he announced the start of his campaign in February 1975. Jackson received substantial financial support from Jewish-Americans who admired his pro-
Jackson raised his national profile by speaking out on Soviet-U.S. relations and Middle East policy regularly, and he was considered a front-runner for the nomination when he announced the start of his campaign in February 1975. Jackson received substantial financial support from Jewish-Americans who admired his pro-Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
views, but his support of the Vietnam War resulted in hostility from the left wing of the Democratic Party. Jackson chose to run on social issues, emphasizing law and order and his opposition to busing. He was hoping for support from labor, but the possibility that Hubert Humphrey
Hubert Horatio Humphrey Jr. (May 27, 1911 – January 13, 1978) was an American politician who served from 1965 to 1969 as the 38th vice president of the United States. He twice served in the United States Senate, representing Minnesota from 19 ...
might enter the race caused unions to offer only lukewarm support. Jackson made the fateful decision not to compete in the early Iowa caucus and New Hampshire primary, which Carter won after liberals split their votes among four other candidates. Even though Jackson won the Massachusetts and New York primaries, he dropped out on May 1 after losing the critical Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
primary to Carter by 12% and running out of money.
Death
On the evening of September 1, 1983, Jackson suffered a heart attack at his home in Everett, and was pronounced dead at nearby Providence Hospital at the age of 71. His death came suddenly, occurring hours after he had given a news conference condemning the Soviet attack onKorean Air Lines Flight 007
Korean Air Lines Flight 007 (KE007/KAL007)In aviation, two types of Airline codes, airline designators are used. The flight number KAL 007, with the ICAO code for Korean Air Lines, was used by air traffic control. In ticketing, however, IAT ...
.
Jackson's death was greatly mourned. New York Senator Daniel Patrick Moynihan
Daniel Patrick Moynihan (; March 16, 1927 – March 26, 2003) was an American politician, diplomat and social scientist. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he represented New York (state), New York in the ...
stated that "Henry Jackson is proof of the old belief in the Judaic tradition that at any moment in history goodness in the world is preserved by the deeds of 36 just men who do not know that this is the role the Lord has given them. Henry Jackson was one of those men." Jackson is buried in Evergreen Cemetery in Everett.
Legacy
Jackson was posthumously awarded thePresidential Medal of Freedom
The Presidential Medal of Freedom is the highest civilian award of the United States, alongside the Congressional Gold Medal. It is an award bestowed by decision of the president of the United States to "any person recommended to the President ...
in 1984. Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan (February 6, 1911 – June 5, 2004) was an American politician and actor who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He was a member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party a ...
called him "one of the greatest lawmakers of our century", and stated:
Soviet dissident and later Israeli politician Natan Sharansky
Natan Sharansky (; born 20 January 1948) is an Israeli politician, human rights activist, and author. He served as Chairman of the Executive for the Jewish Agency for Israel, Jewish Agency from June 2009 to August 2018, and currently serves as ...
recalled when he was imprisoned by the KGB
The Committee for State Security (, ), abbreviated as KGB (, ; ) was the main security agency of the Soviet Union from 1954 to 1991. It was the direct successor of preceding Soviet secret police agencies including the Cheka, Joint State Polit ...
that:
In 1983, Jackson was awarded Delta Chi of the Year. One of Jackson's last acts as Senator was to sponsor legislation creating what became the Henry M. Jackson Foundation for the Advancement of Military Medicine, which was named after him after his death. Jackson's extended community of staff, colleagues and family members created the Henry M. Jackson Foundation from public monies and private donations to give grants to nonprofits and educational institutions. Its board members have included Richard Perle, Tom Foley, and Jeane Kirkpatrick
Jeane Duane Kirkpatrick (née Jordan; November 19, 1926December 7, 2006) was an American diplomat and political scientist who played a major role in the foreign policy of the Ronald Reagan administration. An ardent anticommunist, she was a lon ...
.
The U.S. Navy ballistic missile submarine
A ballistic missile submarine is a submarine capable of deploying submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) with nuclear warheads. These submarines became a major weapon system in the Cold War because of their nuclear deterrence capabi ...
was named after him, in recognition of his longtime support of the nation's military. It is the only Ohio-class submarine not named after a U.S. state. On March 28, 1981, Jackson gave the principal address at the christening of the USS ''Bremerton'' (SSN 698). The ''Bremerton'' was the second ship to have the name, preceded by the USS ''Bremerton'' (CA 130). It was christened by Mrs. Henry M. Jackson on July 22, 1978. The USS ''Bremerton'' (SSN 698) was mentioned in the classic Tom Clancy
Thomas Leo Clancy Jr. (April 12, 1947 – October 1, 2013) was an American novelist. He is best known for his technically detailed espionage and military science, military-science storylines set during and after the Cold War. Seventeen of ...
novel, '' The Hunt for Red October''. The University of Washington
The University of Washington (UW and informally U-Dub or U Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington, United States. Founded in 1861, the University of Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast of the Uni ...
has named the Jackson School of International Studies in his honor. However, students objecting to Jackson's hawkish views on the Cold War in the mid-1980s caused the university to move a bust of the senator to the end of an abandoned corridor until it was restored to a more prominent place outside the Jackson School in 2006.
In 1983, the Snohomish County Public Utility District began operation of the Henry M. Jackson Hydroelectric Project outside Sultan, Washington. In 1994, the Everett School District completed construction of Henry M. Jackson High School in Mill Creek, Washington. The Henry M. Jackson Wilderness Area was created in his honor by the 1984 Washington Wilderness Act. The Jewish Institute for National Security Affairs, with the cooperation of the Jackson family, awards a Henry M. "Scoop" Jackson Distinguished Service Award to individuals for their career dedication to U.S. national security. Jackson won the first award in 1982, and it was named after him after his death. Winners include Max Cleland
Joseph Maxwell Cleland (August 24, 1942 – November 9, 2021) was an American politician from Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he was a disabled United States Army, U.S. Army vete ...
, Joe Lieberman
Joseph Isadore Lieberman (; February 24, 1942 – March 27, 2024) was an American politician and lawyer who served as a United States senator from Connecticut from 1989 to 2013. Originally a member of the Democratic Party (United States), Dem ...
, Dick Cheney
Richard Bruce Cheney ( ; born January 30, 1941) is an American former politician and businessman who served as the 46th vice president of the United States from 2001 to 2009 under President George W. Bush. He has been called vice presidency o ...
, Jane Harman
Jane Margaret Harman (née Lakes, June 28, 1945) is an American former politician who served as the U.S. representative for from 1993 to 1999 and again from 2001 to 2011. A member of the Democratic Party, she was the ranking member on the ...
, and Paul Wolfowitz
Paul Dundes Wolfowitz (born December 22, 1943) is an American political scientist and diplomat who served as the 10th President of the World Bank, U.S. Deputy Secretary of Defense, U.S. Ambassador to Indonesia, and dean of Paul H. Nitze Scho ...
.
The Seattle-based Henry M. Jackson Foundation was created in 1983 by his former colleagues and staff, as well as his widow and other family members, to further his work. In 1987, the Department of Defense gave to the Jackson Foundation a one-time, $10 million appropriation for its endowment, in honor of the Senator. To date, the Foundation has awarded over $26 million in grants to educational and non-profit institutions. Jackson also sponsored legislation to form the Foundation to Advance Military Medicine, which was later renamed in his honor at the time of his death, to the Henry M. Jackson Foundation for the Advancement of Military Medicine.
Influence on neoconservatism
Jackson believed that evil should be confronted with power. His support forcivil rights
Civil and political rights are a class of rights that protect individuals' political freedom, freedom from infringement by governments, social organizations, and private individuals. They ensure one's entitlement to participate in the civil and ...
and equality at home, married to his opposition to ''détente
''Détente'' ( , ; for, fr, , relaxation, paren=left, ) is the relaxation of strained relations, especially political ones, through verbal communication. The diplomacy term originates from around 1912, when France and Germany tried unsucces ...
'', his support for human rights, along with that of democratic allies, and his firm belief that the United States could be a force for good in the world, and inspired a legion of loyal aides who went on to propound Jackson's philosophy as part of neoconservatism. In addition to Richard Perle, neoconservatives Paul Wolfowitz
Paul Dundes Wolfowitz (born December 22, 1943) is an American political scientist and diplomat who served as the 10th President of the World Bank, U.S. Deputy Secretary of Defense, U.S. Ambassador to Indonesia, and dean of Paul H. Nitze Scho ...
, Bill Kristol
William Kristol (; born December 23, 1952) is an American neoconservative writer. A frequent commentator on several networks including CNN, he was the founder and editor-at-large of the political magazine ''The Weekly Standard''. Kristol is edi ...
, Elliot Abrams, Charles Horner, and Douglas Feith were former Democratic aides to Jackson who, disillusioned with the Carter administration, supported Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan (February 6, 1911 – June 5, 2004) was an American politician and actor who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He was a member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party a ...
and joined his administration in 1981, later becoming prominent foreign policy makers in the 21st-century Bush administration. Neoconservative Ben Wattenberg was a prominent political aide to Jackson's 1972 and 1976 presidential campaigns. Wolfowitz has called himself a "Scoop Jackson Republican" on multiple occasions. Many journalists and scholars across the political spectrum have noted links between Senator Jackson and modern neoconservatism.Harrop, Froma.Dems Need Another Scoop Jackson
",
RealClearPolitics
RealClearPolitics (RCP) is an American political news website and polling data aggregator. It was founded in 2000 by former options trader John McIntyre and former advertising agency account executive Tom Bevan. It features selected polit ...
, November 23, 2005.
Jackson's influence on foreign policy has been cited as foundational to the George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician and businessman who was the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Bush family and the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he i ...
administration's foreign policy, and the Iraq War
The Iraq War (), also referred to as the Second Gulf War, was a prolonged conflict in Iraq lasting from 2003 to 2011. It began with 2003 invasion of Iraq, the invasion by a Multi-National Force – Iraq, United States-led coalition, which ...
. Jackson biographer Robert Kaufman says "There is no question in my mind that the people who supported Iraq are supporting Henry Jackson's instincts." Peter Beinart, author of '' The Good Fight: Why Liberals—and Only Liberals—Can Win the War on Terror and Make America Great Again'', argues that the Democratic Party should return to Jackson's values in its foreign policy, criticizing current-day neoconservatives for failing to adopt Jackson's domestic policy views along with his foreign policy views.
Henry Jackson Society
In 2005, the Henry Jackson Society was formed at theUniversity of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a Public university, public collegiate university, collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209, the University of Cambridge is the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, wo ...
, England. The non-partisan British group is dedicated to "pursuit of a robust foreign policy ... based on clear universal principles such as the global promotion of the rule of law, liberal democracy, civil rights, environmental responsibility and the market economy" as part of "Henry Jackson's legacy."Statement of Principles", Henry Jackson Society, March 11, 2005. The organization is now based in London and hosts high-profile speaker events in the
House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of ...
.
Jackson Papers controversy
Jackson's documents were donated to theUniversity of Washington
The University of Washington (UW and informally U-Dub or U Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington, United States. Founded in 1861, the University of Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast of the Uni ...
shortly after his death in 1983, and have been archived there ever since. When the materials were donated in 1983, university staff removed all information considered classified
Classified may refer to:
General
*Classified information, material that a government body deems to be sensitive
*Classified advertising or "classifieds"
Music
*Classified (rapper) (born 1977), Canadian rapper
* The Classified, a 1980s American ro ...
at the time. Additional materials were added to the collection until 1995. At some point, library staff discovered a classified document in the collection and sent it to the government for declassification. In response, in the summer of 2004, a man who identified himself as an employee of the Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA; ) is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States tasked with advancing national security through collecting and analyzing intelligence from around the world and ...
(CIA) called the University of Washington
The University of Washington (UW and informally U-Dub or U Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington, United States. Founded in 1861, the University of Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast of the Uni ...
asking to inspect Senator Jackson's archived documents housed there. He found a document labeled as classified and showed this to a librarian.
In February 2005, 22 years after Jackson's death, a five-person team including staff of the CIA, Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the Army, Navy, Marines, Air Force, Space Force, ...
, the Department of Energy, and the Information Security Oversight Office came to the library to review all of Jackson's papers to remove anything still considered classified, or reclassified since then. The Department of Energy found nothing of concern, but the CIA blanked lines in about 20 papers and pulled 8 documents out of collection. , some files in the collection are available only to those regarded by the library as "serious researchers", who must first sign a release not to divulge some of the information contained in the files.
Electoral history
See also
* Henry M. Jackson High School * List of United States Democratic Party presidential tickets *List of United States Congress members who died in office (1950–1999)
The following is a list of United States senators and representatives who died of natural or accidental causes, or who killed themselves, while serving their terms between 1950 and 1999. For a list of members of Congress who were killed while i ...
* United States congressional delegations from Washington
These are tables of United States Congress, congressional delegations from the state of Washington (state), Washington to the United States Senate and United States House of Representatives.
The current dean of the Washington delegation is United ...
References
External links
Henry M. Jackson Collection
nbsp;– University of Washington Digital Collection * *
at 4president.org
Henry M Jackson Papers
, at the University of Washington
at the U.S. Senate
* ttp://www.hmjackson.org/ Henry M Jackson Foundation
The Henry Jackson Society
at the University of Cambridge
Henry M. Jackson—A Life in Politics
biography
Henry M. Jackson, late a senator
*
Archives
Guide to the Henry M. Jackson Papers
1912–1987. Approximately 1,240 Cubic Ft. At th
University of Washington Libraries Special Collections
Richard J. Brooks Papers.
1956–2000. 7.62 cubic feet. 8 boxes, one vertical file, one oversize folder, one mapcase folder. At th
University of Washington Libraries Special Collections
Contains correspondence from Senator Henry M. Jackson. , - , - , - , - , - , - , - {{DEFAULTSORT:Jackson, Henry Martin 1912 births 1983 deaths American anti-communists American Christian Zionists American people of Norwegian descent American Presbyterians Candidates in the 1972 United States presidential election Candidates in the 1976 United States presidential election Deaths from aortic aneurysm Democratic National Committee chairs Democratic Party members of the United States House of Representatives from Washington (state) Democratic Party United States senators from Washington (state) Politicians from Everett, Washington Presidential Medal of Freedom recipients Sierra Club awardees Stanford University alumni University of Washington School of Law alumni Delta Chi members 20th-century United States senators 20th-century members of the United States House of Representatives