Harlech Castle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Harlech Castle ( cy, Castell Harlech; ) in Harlech,
 Edward ordered the construction of a castle at Harlech, one of seven built across North Wales in the wake of the 1282 campaign. Money to pay for the initial phase arrived in mid-May and carpenters and 35 stonemasons were dispatched in June and July to commence work. By the winter of 1283, the first of the inner walls had been constructed, allowing the castle to be defended in the event of an attack, and a small, planned town had been founded alongside the castle.
Edward ordered the construction of a castle at Harlech, one of seven built across North Wales in the wake of the 1282 campaign. Money to pay for the initial phase arrived in mid-May and carpenters and 35 stonemasons were dispatched in June and July to commence work. By the winter of 1283, the first of the inner walls had been constructed, allowing the castle to be defended in the event of an attack, and a small, planned town had been founded alongside the castle.
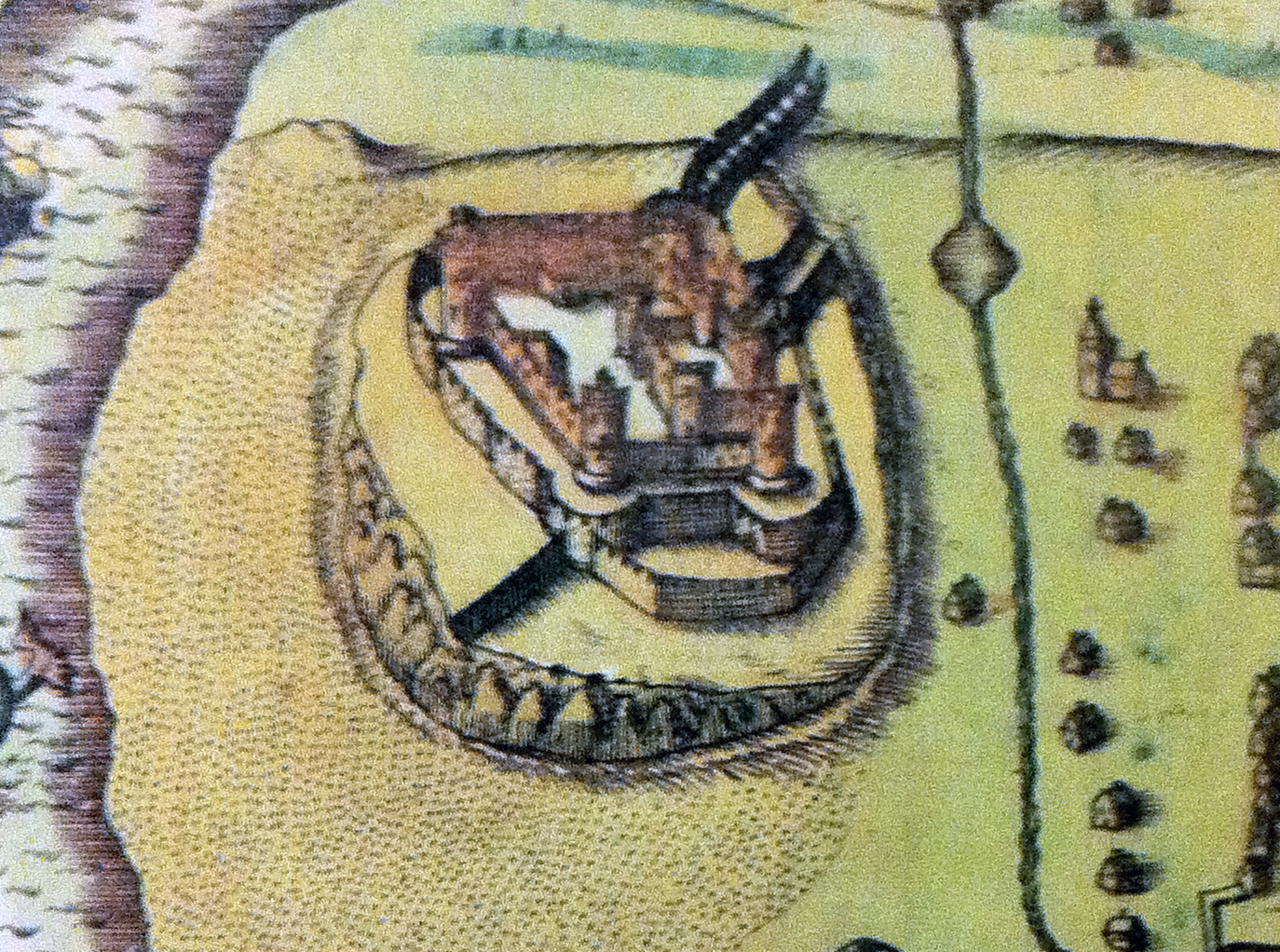 In 1400 a revolt broke out in North Wales against English rule, led by
In 1400 a revolt broke out in North Wales against English rule, led by
 In the late-18th and 19th centuries, the picturesque ruins of Harlech began to attract visits from prominent artists, including John Cotman, Henry Gastineau, Paul Sandby,
In the late-18th and 19th centuries, the picturesque ruins of Harlech began to attract visits from prominent artists, including John Cotman, Henry Gastineau, Paul Sandby,
 Harlech Castle rests upon part of the
Harlech Castle rests upon part of the  The gatehouse follows the design, sometimes termed the
The gatehouse follows the design, sometimes termed the
File:Harlech Castle - geograph.org.uk - 967968.jpg, View from the street upon arrival
File:Harlech - Castell 20180707-03.jpg, The equestrian sculpture of the Two Kings
File:Harlech Castle from Rehoboth Chapel - geograph.org.uk - 2884892.jpg, Aerial view of the castle and the village of Harlech
File:Harlech Castle - geograph.org.uk - 1067725.jpg, View from the A496 road
File:Harlech Castle - geograph.org.uk - 676139.jpg, View from Harlech beach and Morfa Harlech National Nature Reserve
File:Harlech Castle (22245229598).jpg, Ramparts and interior courtyard, featuring the Grand hall
Official Cadw page for Harlech Castle
{{Authority control Buildings and structures completed in 1289 Castles in Gwynedd Sieges World Heritage Sites in Wales Hill castles Harlech Grade I listed castles in Wales Grade I listed buildings in Gwynedd Castles and Town Walls of King Edward in Gwynedd
Gwynedd
Gwynedd (; ) is a county and preserved county (latter with differing boundaries; includes the Isle of Anglesey) in the north-west of Wales. It shares borders with Powys, Conwy County Borough, Denbighshire, Anglesey over the Menai Strait, an ...
, Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
, is a Grade I listed medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
fortification
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere ...
built onto a rocky knoll close to the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the C ...
. It was built by Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vas ...
during his invasion of Wales between 1282 and 1289 at the relatively modest cost of £8,190. Over the next few centuries, the castle played an important part in several wars, withstanding the siege of Madog ap Llywelyn between 1294 and 1295, but falling to Prince Owain Glyndŵr
Owain ap Gruffydd (), commonly known as Owain Glyndŵr or Glyn Dŵr (, anglicised as Owen Glendower), was a Welsh leader, soldier and military commander who led a 15 year long Welsh War of Independence with the aim of ending English rule in Wa ...
in 1404. It then became Glyndŵr's residence and military headquarters for the remainder of the uprising until being recaptured by English forces in 1409. During the 15th century Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses (1455–1487), known at the time and for more than a century after as the Civil Wars, were a series of civil wars fought over control of the throne of England, English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. These w ...
, Harlech was held by the Lancastrians for seven years, before Yorkist troops forced its surrender in 1468, a siege memorialised in the song "Men of Harlech
"Men of Harlech" or "The March of the Men of Harlech" ( Welsh: ) is a song and military march which is traditionally saidFuld, James J., ''The Book of World-famous Music: Classical, Popular, and Folk'', Dover, 5th ed. 2000, p. 394 to describe eve ...
". Following the outbreak of the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I (" Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of r ...
in 1642, the castle was held by forces loyal to Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
, holding out until 1647 when it became the last fortification to surrender to the Parliamentary
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of the ...
armies. In the 21st century the ruined castle is managed by Cadw
(, a Welsh verbal noun meaning "keeping/preserving") is the historic environment service of the Welsh Government and part of the Tourism and Culture group. works to protect the historic buildings and structures, the landscapes and heritage ...
, the Welsh Government's historic environment service, as a tourist attraction.
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
considers Harlech, with three others at Beaumaris, Conwy, Caernarfon
Caernarfon (; ) is a royal town, community and port in Gwynedd, Wales, with a population of 9,852 (with Caeathro). It lies along the A487 road, on the eastern shore of the Menai Strait, opposite the Isle of Anglesey. The city of Bangor ...
, to be one of "the finest examples of late 13th century and early 14th century military architecture in Europe", and it is classed as a World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
. The fortification is built of local stone and concentric
In geometry, two or more objects are said to be concentric, coaxal, or coaxial when they share the same center or axis. Circles, regular polygons and regular polyhedra, and spheres may be concentric to one another (sharing the same center p ...
in design, featuring a massive gatehouse that probably once provided high-status accommodation for the castle constable and visiting dignitaries. The sea originally came much closer to Harlech than in modern times, and a water-gate and a long flight of steps leads down from the castle to the former shore, which allowed the castle to be resupplied by sea during sieges. In keeping with Edward's other castles in the north of Wales, the architecture of Harlech has close links to that found in the County of Savoy during the same period, an influence probably derived from the Savoy origins of the main architect, James of Saint George
Master James of Saint George (–1309; French: , Old French: Mestre Jaks, Latin: Magister Jacobus de Sancto Georgio) was a master of works/architect from Savoy, described by historian Marc Morris as "one of the greatest architects of the Europ ...
.
History
13th–14th centuries
In local mythology, the site of Harlech Castle inNorth Wales
North Wales ( cy, Gogledd Cymru) is a regions of Wales, region of Wales, encompassing its northernmost areas. It borders Mid Wales to the south, England to the east, and the Irish Sea to the north and west. The area is highly mountainous and rural, ...
is associated with the legend of Branwen, a Welsh princess, but there is no evidence for a native Welsh fortification having been built there. The kings of England and the Welsh princes had vied for control of North Wales since the 1070s and the conflict was renewed during the 13th century, leading to Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vas ...
intervening in North Wales for the second time during his reign in 1282. Edward invaded with a huge army, pushing north from Carmarthen and westwards from Montgomery and Chester
Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the English–Welsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Loca ...
. English forces advanced down the Conwy valley and through Dolwyddelan and Castell y Bere, onto Harlech, which Sir Otton de Grandson
Otto de Grandson (c. 1238–1328), sometimes numbered Otto I to distinguish him from later members of his family with the same name, was the most prominent of the Savoyard knights in the service of King Edward I of England, to whom he was the cl ...
took with 560 infantry in May.
 Edward ordered the construction of a castle at Harlech, one of seven built across North Wales in the wake of the 1282 campaign. Money to pay for the initial phase arrived in mid-May and carpenters and 35 stonemasons were dispatched in June and July to commence work. By the winter of 1283, the first of the inner walls had been constructed, allowing the castle to be defended in the event of an attack, and a small, planned town had been founded alongside the castle.
Edward ordered the construction of a castle at Harlech, one of seven built across North Wales in the wake of the 1282 campaign. Money to pay for the initial phase arrived in mid-May and carpenters and 35 stonemasons were dispatched in June and July to commence work. By the winter of 1283, the first of the inner walls had been constructed, allowing the castle to be defended in the event of an attack, and a small, planned town had been founded alongside the castle. John de Bonvillars
Sir John de Bonvillars (c. ?–1287) was a medieval Savoyard knight in the service of Edward I. He was the brother in law of Otto de Grandson, and like William de Cicon, had been introduced to English service by Otto.
From Bonvillars in Savoy ...
was appointed the constable of the castle in 1285; after his death in 1287 his wife, Agnes, took up the role until 1290.
Construction continued under the overall direction of James of Saint George
Master James of Saint George (–1309; French: , Old French: Mestre Jaks, Latin: Magister Jacobus de Sancto Georgio) was a master of works/architect from Savoy, described by historian Marc Morris as "one of the greatest architects of the Europ ...
, a Savoy architect and military engineer. In 1286, at the height of the construction, the workforce comprised 546 general labourers, 115 quarriers, 30 blacksmiths, 22 carpenters and 227 stonemasons, and the project was costing nearly £240 a month.; The castle was essentially complete by the end of 1289, having cost an estimated £8,190, around 10 percent of the £80,000 that Edward spent on castle-building in Wales between 1277 and 1304.
Harlech was established with a garrison of 36 men: a constable, 30 men, including 10 crossbowmen, a chaplain, a smith, carpenter and stonemason, and Master James was rewarded by being made the constable of Harlech from 1290 to 1293. In 1294, Madog ap Llywelyn began an uprising against English rule that spread quickly through Wales. Several English-held towns were razed and Harlech, along with Criccieth Castle and Aberystwyth Castle, were besieged that winter. Fresh supplies were sent from Ireland by sea, arriving via Harlech's water gate, and the uprising was quashed. In the aftermath of the revolt, additional defences were built around the route down to the sea. Further work was undertaken between 1323 and 1324, following the Despenser War
The Despenser War (1321–22) was a baronial revolt against Edward II of England led by the Marcher Lords Roger Mortimer and Humphrey de Bohun. The rebellion was fuelled by opposition to Hugh Despenser the Younger, the royal favourite.Some his ...
; Edward II
Edward II (25 April 1284 – 21 September 1327), also called Edward of Caernarfon, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1307 until he was deposed in January 1327. The fourth son of Edward I, Edward became the heir apparent to ...
was threatened in the region by the Mortimer Marcher Lord
A Marcher lord () was a noble appointed by the king of England to guard the border (known as the Welsh Marches) between England and Wales.
A Marcher lord was the English equivalent of a margrave (in the Holy Roman Empire) or a marquis (in ...
family, and ordered his sheriff, Sir Gruffudd Llwyd, to extend the defences leading up to the gatehouse with additional towers.
15th–17th centuries
 In 1400 a revolt broke out in North Wales against English rule, led by
In 1400 a revolt broke out in North Wales against English rule, led by Owain Glyndŵr
Owain ap Gruffydd (), commonly known as Owain Glyndŵr or Glyn Dŵr (, anglicised as Owen Glendower), was a Welsh leader, soldier and military commander who led a 15 year long Welsh War of Independence with the aim of ending English rule in Wa ...
. By 1403 only a handful of castles, including Harlech, still stood against the rebels, but the castle was under-equipped and under-staffed to withstand a siege, the garrison having just three shields, eight helmets, six lances, ten pairs of gloves, and four guns. At the end of 1404, the castle fell to Glyndŵr. Harlech became his residence, family home and military headquarters for four years; he held his second parliament in Harlech in August 1405. In 1408 English forces under the command of the future Henry V Henry V may refer to:
People
* Henry V, Duke of Bavaria (died 1026)
* Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor (1081/86–1125)
* Henry V, Duke of Carinthia (died 1161)
* Henry V, Count Palatine of the Rhine (c. 1173–1227)
* Henry V, Count of Luxembourg (121 ...
placed Harlech and its commander, Edmund Mortimer, under siege, conducting a bombardment with cannon, probably destroying the south and east parts of the outer walls. When this failed to take the castle, Henry left John Talbot in charge of the siege and moved on to deal with Aberystwyth Castle. Supplies finally ran short, Mortimer and many of his men died of exhaustion, and Harlech fell in February 1409.
In the 15th century, Harlech was involved in the series of civil wars now known as the Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses (1455–1487), known at the time and for more than a century after as the Civil Wars, were a series of civil wars fought over control of the throne of England, English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. These w ...
that broke out between the rival factions of the House of Lancaster
The House of Lancaster was a cadet branch of the royal House of Plantagenet. The first house was created when King Henry III of England created the Earldom of Lancasterfrom which the house was namedfor his second son Edmund Crouchback in 126 ...
and House of York
The House of York was a cadet branch of the English royal House of Plantagenet. Three of its members became kings of England in the late 15th century. The House of York descended in the male line from Edmund of Langley, 1st Duke of Yor ...
. In 1460, following the Battle of Northampton, Queen Margaret of Anjou
Margaret of Anjou (french: link=no, Marguerite; 23 March 1430 – 25 August 1482) was Queen of England and nominally Queen of France by marriage to King Henry VI from 1445 to 1461 and again from 1470 to 1471. Born in the Duchy of Lorrain ...
fled to the castle and between 1461 and 1468 it was held by her Lancastrian supporters, under the command of Dafydd ap Ieuan, against the Yorkist Edward IV
Edward IV (28 April 1442 – 9 April 1483) was King of England from 4 March 1461 to 3 October 1470, then again from 11 April 1471 until his death in 1483. He was a central figure in the Wars of the Roses, a series of civil wars in Englan ...
. Thanks to its natural defences and the supply route by sea, Harlech held out and as other fortresses fell, eventually became the last major stronghold still under Lancastrian control. The castle became a base for their operations across the region: there were planned operations in 1464, Sir Richard Tunstall mounted attacks from Harlech in 1466 and Jasper Tudor landed there with French reinforcements in 1468, before then raiding the town of Denbigh
Denbigh (; cy, Dinbych; ) is a market town and a community in Denbighshire, Wales. Formerly, the county town, the Welsh name translates to "Little Fortress"; a reference to its historic castle. Denbigh lies near the Clwydian Hills.
History
...
. Tudor's arrival caused Edward IV to order William Herbert to mobilise an army, possibly up to 10,000 strong, to finally seize the castle. After a month's siege, the small garrison surrendered on 14 August. This siege is credited with inspiring the song ''Men of Harlech
"Men of Harlech" or "The March of the Men of Harlech" ( Welsh: ) is a song and military march which is traditionally saidFuld, James J., ''The Book of World-famous Music: Classical, Popular, and Folk'', Dover, 5th ed. 2000, p. 394 to describe eve ...
''.
The English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I (" Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of r ...
broke out in 1642 between the Royalist
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of gov ...
supporters of Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
and the supporters of Parliament. Harlech apparently had not been repaired following the 1468 siege, and had become completely dilapidated, with the exception of the gatehouse, which was used for the local assizes
The courts of assize, or assizes (), were periodic courts held around England and Wales until 1972, when together with the quarter sessions they were abolished by the Courts Act 1971 and replaced by a single permanent Crown Court. The assizes ...
. In 1644 Prince Rupert
Prince Rupert of the Rhine, Duke of Cumberland, (17 December 1619 (O.S.) / 27 December (N.S.) – 29 November 1682 (O.S.)) was an English army officer, admiral, scientist and colonial governor. He first came to prominence as a Royalist caval ...
appointed a local Royalist, Colonel William Owen, as the castle's constable, and Owen was entrusted with repairing the fortifications. A long siege ensued from June 1646 until 15 March 1647, when the garrison of 44 men surrendered to Major-General Thomas Mytton
Major General Thomas Mytton, also spelt Mitton, 1597 to November 1656, was a lawyer from Oswestry who served in the Parliamentarian army during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms and as MP for Shropshire in the First Protectorate Parliament.
Pa ...
. The castle was the last mainland royal fortress to surrender in the war, and the date marked the end of the first phase of the war. The castle was no longer required for the security of North Wales and, to prevent any further use by the Royalists, Parliament ordered its slighting, or destruction. The orders were only partially carried out, however, and the gatehouse staircases were destroyed and the castle rendered generally unusable, but it was not totally demolished. Stone from the castle was reused to build houses in the local town.
18th–21st centuries
 In the late-18th and 19th centuries, the picturesque ruins of Harlech began to attract visits from prominent artists, including John Cotman, Henry Gastineau, Paul Sandby,
In the late-18th and 19th centuries, the picturesque ruins of Harlech began to attract visits from prominent artists, including John Cotman, Henry Gastineau, Paul Sandby, J. M. W. Turner
Joseph Mallord William Turner (23 April 177519 December 1851), known in his time as William Turner, was an English Romantic painter, printmaker and watercolourist. He is known for his expressive colouring, imaginative landscapes and turbul ...
and John Varley John Varley may refer to:
* John Varley (canal engineer) (1740–1809), English canal engineer
* John Varley (painter) (1778–1842), English painter and astrologer
* John Varley (author) (born 1947), American science fiction author
* John Silvest ...
. In 1914 it was transferred from the Merioneth Crown Estate to the control of the Office of Works, who commenced a major restoration project after the end of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
. In 1969 the castle was transferred to the Welsh Office and then to Cadw
(, a Welsh verbal noun meaning "keeping/preserving") is the historic environment service of the Welsh Government and part of the Tourism and Culture group. works to protect the historic buildings and structures, the landscapes and heritage ...
, who manage the property in the 21st century as a tourist attraction. Harlech was declared part of the '' Castles and Town Walls of King Edward in Gwynedd'' World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
in 1986, UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
considering Harlech one of "the finest examples of late 13th century and early 14th century military architecture in Europe".
Architecture
 Harlech Castle rests upon part of the
Harlech Castle rests upon part of the Harlech Dome
The Harlech Dome is a geological dome in southern Snowdonia in north Wales. It extends approximately from Blaenau Ffestiniog in the north to Tywyn in the south, and includes Harlech, The Rhinogydd, Barmouth and Cadair Idris.
The geological la ...
, a spur of rock almost high; the land falls away sharply on the north and west, and a ditch cut into the rock protects the remaining approaches to the castle. The castle has a concentric design, with one line of defences enclosed by another, forming an inner and outer ward; the outer wall was originally somewhat taller than today. Harlech is built from local grey-green sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicat ...
, with large, regular blocks used for the towers and irregular material, possibly taken from the ditch, used for the walls. A softer yellow sandstone is used for the decorative work in the castle, possibly quarried from around Egryn Abbey near Barmouth
Barmouth ( cy, Abermaw (formal); ''Y Bermo'' (colloquial)) is a seaside town and community in the county of Gwynedd, northwestern Wales, lying on the estuary of the Afon Mawddach and Cardigan Bay. Located in the historic county of Merioneth ...
.
The main entrance to the castle would have involved crossing a stone bridge between the two easterly ditch bridge towers and the main gatehouse; little remains of the bridge towers today and a timber entrance way to the gatehouse replaces the bridge. A water gate overlooks a protected stairway of 127 steps that runs down to the foot of the cliffs. In the 13th century, the sea came up close to the stairway, allowing resupply by sea, but today the sea has retreated significantly, making it more difficult to envisage the concept in its original setting.
 The gatehouse follows the design, sometimes termed the
The gatehouse follows the design, sometimes termed the Tonbridge
Tonbridge ( ) is a market town in Kent, England, on the River Medway, north of Royal Tunbridge Wells, south west of Maidstone and south east of London. In the administrative borough of Tonbridge and Malling, it had an estimated population ...
-style, that became popular during the 13th century, with two massive "D-shaped" defensive towers flanking the entrance. The passage into the castle was guarded by three portcullis
A portcullis (from Old French ''porte coleice'', "sliding gate") is a heavy vertically-closing gate typically found in medieval fortifications, consisting of a latticed grille made of wood, metal, or a combination of the two, which slides down ...
es and at least two heavy doors. The gatehouse has two upper floors, broken up into various rooms. Each floor has three large windows overlooking the inner ward; the second floor has two additional grand windows on the sides of the gatehouse; the gatehouse was fitted with fireplaces and would originally have had prominent chimneys. The use of these rooms has been the subject of academic debate: historian Arnold Taylor argued that the first floor of the gatehouse was used by the constable as living accommodation, with the second floor used by senior visitors; Jeremy Ashbee has since challenged this interpretation, suggesting the high status accommodation may instead have been in the inner ward, and the gatehouse used for other purposes.
The inner ward is guarded by four large circular towers. Over time these acquired various names: in 1343, clockwise from the north-east, they were called Le Prisontour, Turris Ultra Gardinium, Le Wedercoktour and Le Chapeltour, but by 1564 they had been renamed the Debtors', Mortimer, Bronwen and Armourer's Towers respectively. Le Prisontour incorporated a dungeon and the Le Chapeltour may have contained an artillery workshop in the 16th century. Several ranges of buildings were built around the inner ward, including a chapel, kitchen, service buildings, a granary and a great hall. The battlements may originally have been built with triple finial
A finial (from '' la, finis'', end) or hip-knob is an element marking the top or end of some object, often formed to be a decorative feature.
In architecture, it is a small decorative device, employed to emphasize the apex of a dome, spire, towe ...
s in a similar fashion to Conwy, although little remains of these in the modern era.
The architecture of Harlech has close links to that found in the kingdom of Savoy
The Kingdom of Sardinia,The name of the state was originally Latin: , or when the kingdom was still considered to include Corsica. In Italian it is , in French , in Sardinian , and in Piedmontese . also referred to as the Kingdom of Savoy-S ...
in the same period. These include semi-circular door arches, window styles, corbel
In architecture, a corbel is a structural piece of stone, wood or metal jutting from a wall to carry a superincumbent weight, a type of bracket. A corbel is a solid piece of material in the wall, whereas a console is a piece applied to the s ...
led towers and positioning of putlog
Scaffolding, also called scaffold or staging, is a temporary structure used to support a work crew and materials to aid in the construction, maintenance and repair of buildings, bridges and all other man-made structures. Scaffolds are widely use ...
holes, and are usually ascribed to the influence of the Savoy architect Master James. The links between the Harlech and Savoy are not straightforward, however, as in some cases the relevant Savoy structures were built after James had left the region. The similarity in architectural details may, therefore, be the result of the wider role played by Savoy craftsmen and engineers on the Harlech project.
Gallery
See also
*Castles in Great Britain and Ireland
Castles have played an important military, economic and social role in Great Britain and Ireland since their introduction following the Norman invasion of England in 1066. Although a small number of castles had been built in England in the 1050 ...
* List of castles in Wales
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Official Cadw page for Harlech Castle
{{Authority control Buildings and structures completed in 1289 Castles in Gwynedd Sieges World Heritage Sites in Wales Hill castles Harlech Grade I listed castles in Wales Grade I listed buildings in Gwynedd Castles and Town Walls of King Edward in Gwynedd