Hagfish on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hagfish, of the
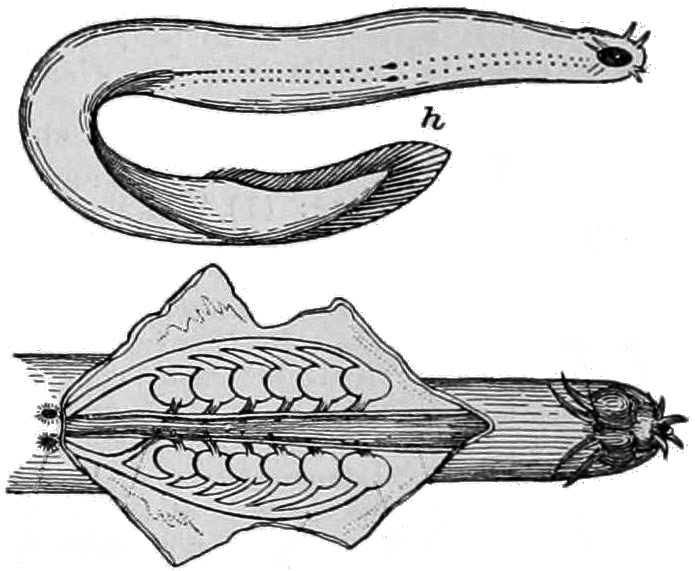
. Tree of Life Its skin is attached to the body only along the center ridge of the back and at the slime glands, and is filled with close to a third of the body's blood volume, giving the impression of a blood-filled sack. It is assumed this is an adaptation to survive predator attacks. The Atlantic hagfish, representative of the subfamily Myxininae, and the Pacific hagfish, representative of the subfamily Eptatretinae, differ in that the latter has muscle fibers embedded in the skin. The resting position of the Pacific hagfish also tends to be coiled, while that of the Atlantic hagfish is stretched.
 Hagfish can exude copious quantities of a milky and fibrous slime or
Hagfish can exude copious quantities of a milky and fibrous slime or
 The hagfish skeleton comprises the skull, the
The hagfish skeleton comprises the skull, the
 Originally, ''Myxine'' was included by
Originally, ''Myxine'' was included by

''Hagfishes: Champions of Slime''
Nature Australia, Spring 2001 ed., Australian Museum Trust, Sydney. pp. 61–69. * * * *
FishBase entry for MyxinidaeYouTube 5+ minute video of Scripps scientist/diver on hagfishMetacafe video of a University of Alberta grad student showing slime production of hagfish while in Bamfield, British Columbia
Beware the hagfish – repeller of sharks
''3 News'', 28 Oct 2011. Video.
Hagfish versus sharks : 1-0
''Te Papa Blog'', 28 October 2011.
Teen Spots Hagfish-Slurping Elephant Seal – YouTube
(2:11)
What happens when a shark attacks a hagfish – BBC
(0:39)
Vancouver Aquarium Hagfish Slime
{{Authority control Scavengers Taxa named by Constantine Samuel Rafinesque
class
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used d ...
Myxini (also known as Hyperotreti) and order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
...
Myxiniformes , are eel-shaped jawless fish
Agnatha (; ) or jawless fish is a paraphyletic infraphylum of animals in the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata, characterized by the lack of jaws. The group consists of both extant taxon, living (Cyclostomi, cyclostomes such as hagfish ...
(occasionally called slime eels). Hagfish are the only known living animals
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a ...
that have a skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
but no vertebral column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmente ...
, although they do have rudimentary vertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spina ...
e. Hagfish are marine predator
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common List of feeding behaviours, feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation ...
s and scavenger
Scavengers are animals that consume Corpse decomposition, dead organisms that have died from causes other than predation or have been killed by other predators. While scavenging generally refers to carnivores feeding on carrion, it is also a he ...
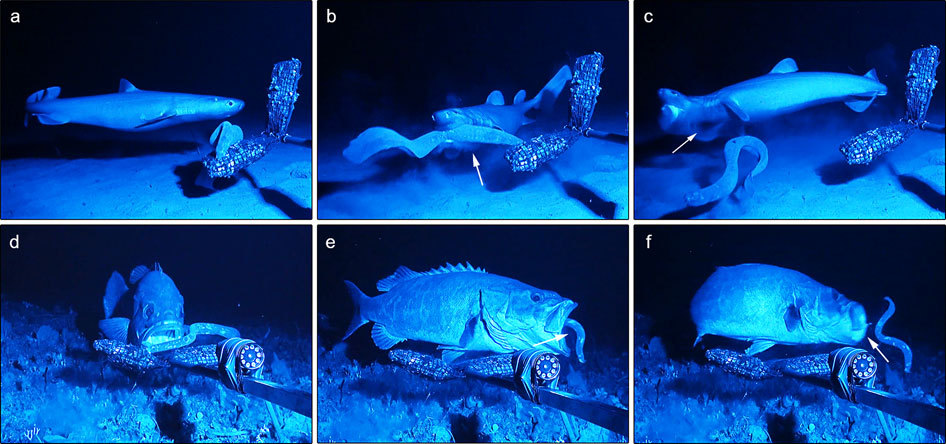
s that can defend themselves against other larger predators by releasing copious amounts of slime
Slime or slimy may refer to:
Science and technology Biology
* Slime coat, the coating of mucus covering the body of all fish
* Slime mold, an informal name for several eukaryotic organisms
* Biofilm, or slime, a syntrophic community of micr ...
from mucous glands in their skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
.
Although their exact relationship to the only other living
Living or The Living may refer to:
Common meanings
*Life, a condition that distinguishes organisms from inorganic objects and dead organisms
** Living species, one that is not extinct
*Personal life, the course of an individual human's life
* ...
group of jawless fish
Agnatha (; ) or jawless fish is a paraphyletic infraphylum of animals in the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata, characterized by the lack of jaws. The group consists of both extant taxon, living (Cyclostomi, cyclostomes such as hagfish ...
, the lamprey
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are a group of Agnatha, jawless fish comprising the order (biology), order Petromyzontiformes , sole order in the Class (biology), class Petromyzontida. The adult lamprey is characterize ...
s, was long the subject of controversy, genetic evidence suggests that hagfish and lampreys are more closely related to each other than to jawed vertebrates, thus forming the superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest-known stem group hagfish are known from the Late Carboniferous
Late or LATE may refer to:
Everyday usage
* Tardy, or late, not being on time
* Late (or the late) may refer to a person who is dead
Music
* Late (The 77s album), ''Late'' (The 77s album), 2000
* Late (Alvin Batiste album), 1993
* Late!, a pseudo ...
, around 310 million years ago, with modern representatives first being recorded in the mid-Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
around 100 million years ago.
Physical characteristics

Body features
Hagfish are typically about in length. The largest-known species is '' Eptatretus goliath'', with a specimen recorded at , while '' Myxine kuoi'' and '' Myxine pequenoi'' seem to reach no more than . Some have been seen as small as . Hagfish have elongated, eel-like bodies, and paddle-like tails. The skin is naked and covers the body like a loosely fitting sock. They are generally a dull pink color and look quite worm-like. They havecartilaginous
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints ...
skulls (although the part surrounding the brain is composed primarily of a fibrous sheath) and tooth-like structures composed of keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. It is the key structural material making up Scale (anatomy), scales, hair, Nail (anatomy), nails, feathers, horn (anatomy), horns, claws, Hoof, hoove ...
. Colors depend on the species, ranging from pink to blue-grey, and black or white spots may be present. Eyes are simple eyespots, not lensed eyes that can resolve images. Hagfish have no true fins and have six or eight barbels around the mouth and a single nostril. Instead of vertically articulating jaws like Gnathostomata
Gnathostomata (; from Ancient Greek: (') 'jaw' + (') 'mouth') are jawed vertebrates. Gnathostome diversity comprises roughly 60,000 species, which accounts for 99% of all extant vertebrates, including all living bony fishes (both ray-finned ...
(vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s with jaws), they have a pair of horizontally moving structures with tooth-like projections for pulling off food. The mouth of the hagfish has two pairs of horny, comb-shaped teeth on a cartilaginous plate that protracts and retracts. These teeth are used to grasp food and draw it toward the pharynx.Hyperotreti. Tree of Life Its skin is attached to the body only along the center ridge of the back and at the slime glands, and is filled with close to a third of the body's blood volume, giving the impression of a blood-filled sack. It is assumed this is an adaptation to survive predator attacks. The Atlantic hagfish, representative of the subfamily Myxininae, and the Pacific hagfish, representative of the subfamily Eptatretinae, differ in that the latter has muscle fibers embedded in the skin. The resting position of the Pacific hagfish also tends to be coiled, while that of the Atlantic hagfish is stretched.
Slime
 Hagfish can exude copious quantities of a milky and fibrous slime or
Hagfish can exude copious quantities of a milky and fibrous slime or mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
, from specialized slime glands. When released in seawater, the slime expands to 10,000 times its original size in 0.4 seconds. This slime that hagfish excrete has very thin fibers that make it more durable and retentive than the slime excreted by other animals. The fibers are made of proteins and also make the slime flexible. If they are caught by a predator, they can quickly release a large amount of slime to escape. If they remain captured, they can tie themselves in an overhand knot
The overhand knot is one of the most fundamental knots, and it forms the basis of many others, including the simple noose, overhand loop, angler's loop, reef knot, fisherman's knot, half hitch, and water knot. The overhand knot is a stoppe ...
, and work their way from the head to the tail of the animal, scraping off the slime and freeing themselves from their captor. Rheological investigations showed that hagfish slime viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent drag (physics), resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for e ...
increases in elongational flow which favors gill clogging of suction feeding fish, while its viscosity decreases in shear which facilitates scraping off the slime by the travelling-knot.
Recently, the slime was reported to entrain water in its keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. It is the key structural material making up Scale (anatomy), scales, hair, Nail (anatomy), nails, feathers, horn (anatomy), horns, claws, Hoof, hoove ...
-like intermediate filament
Intermediate filaments (IFs) are cytoskeleton, cytoskeletal structural components found in the cells of vertebrates, and many invertebrates. Homologues of the IF protein have been noted in an invertebrate, the cephalochordate ''Branchiostoma' ...
s excreted by gland thread cells, creating a slow-to-dissipate, viscoelastic substance, rather than a simple gel. It has been shown to impair the function of a predator fish's gill
A gill () is a respiration organ, respiratory organ that many aquatic ecosystem, aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow r ...
s. In this case, the hagfish's mucus would clog the predator's gills, disabling their ability to respire. The predator would release the hagfish to avoid suffocation. Because of the mucus, few marine predators target the hagfish. Other predators of hagfish are varieties of birds or mammals.
Free-swimming hagfish also slime when agitated, and later clear the mucus using the same travelling-knot behavior. The reported gill-clogging effect suggests that the travelling-knot behavior is useful or even necessary to restore the hagfish's own gill function after sliming.
Hagfish thread keratin ( EsTKα and EsTKγ; and ), the protein that make up its slime filaments, is under investigation as an alternative to spider silk
Spider silk is a protein fibre or silk spun by spiders. Spiders use silk to make webs or other structures that function as adhesive traps to catch prey, to entangle and restrain prey before biting, to transmit tactile information, or as nest ...
for use in applications such as body armor. These alpha-keratin
Alpha-keratin, or α-keratin, is a type of keratin found in mammalian vertebrates. This protein is the primary component in hairs, horn (anatomy), horns, claws, Nail (anatomy), nails and the Epidermis, epidermis layer of the skin. α-keratin is a S ...
proteins in hagfish slime transform from an α-helical structure to a stiffer β sheet structure when stretched. With combined draw-processing (stretching) and chemical crosslinking, recombinant slime keratin turns into a very strong fiber with an elastic modulus
An elastic modulus (also known as modulus of elasticity (MOE)) is a quantity that describes an object's or substance's resistance to being deformed elastically (i.e., non-permanently) when a stress is applied to it.
Definition
The elastic modu ...
reaching 20 GPa.
When in 2017 a road accident on U.S. Highway 101 resulted in of hagfish being spilled, they emitted sufficient slime to cover the road and a nearby car.
Respiration
A hagfish generally respires by taking in water through itspharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates ...
, past the velar chamber, and bringing the water through the internal gill
A gill () is a respiration organ, respiratory organ that many aquatic ecosystem, aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow r ...
pouches, which can vary in number from five to 16 pairs, depending on species. The gill pouches open individually, but in'' Myxine'', the openings have coalesced, with canals running backwards from each opening under the skin, uniting to form a common aperture on the ventral
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
side known as the branchial opening. The esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
is also connected to the left branchial opening, which is therefore larger than the right one, through a pharyngocutaneous duct (esophageocutaneous duct), which has no respiratory tissue. This pharyngocutaneous duct is used to clear large particles from the pharynx, a function also partly taking place through the nasopharyngeal canal. In other species, the coalescence of the gill openings is less complete, and in ''Bdellostoma'', each pouch opens separately to the outside, as in lampreys. The unidirectional water flow passing the gills is produced by rolling and unrolling velar folds located inside a chamber developed from the nasohypophyseal tract, and is operated by a complex set of muscles inserting into cartilages of the neurocranium, assisted by peristaltic contractions of the gill pouches and their ducts. Hagfish also have a well-developed dermal capillary network that supplies the skin with oxygen when the animal is buried in anoxic mud, as well as a high tolerance for both hypoxia and anoxia, with a well-developed anaerobic metabolism. Members of the group have spent 36 hours in water completely devoid of dissolved oxygen, and made a complete recovery. The skin has also been suggested to be capable of cutaneous respiration
Cutaneous respiration, or cutaneous gas exchange (sometimes called skin breathing), is a form of respiration in which gas exchange occurs across the skin or outer integument of an organism rather than gills or lungs. Cutaneous respiration may be ...
.
Nervous system
The origins of the vertebrate nervous system are of considerable interest to evolutionary biologists, and cyclostomes (hagfish and lampreys) are an important group for answering this question. The complexity of the hagfish brain has been an issue of debate since the late 19th century, with some morphologists suggesting that they do not possess acerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
, while others suggest that it is continuous with the midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, mo ...
. It is now considered that the hagfish neuroanatomy is similar to that of lampreys. A common feature of both cyclostomes is the absence of myelin
Myelin Sheath ( ) is a lipid-rich material that in most vertebrates surrounds the axons of neurons to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) pass along the axon. The myelinated axon can be lik ...
in neurons. The brain of a hagfish has specific parts similar to the brains of other vertebrates. The dorsal and ventral muscles located towards the side of the hagfish body are connected to spinal nerves
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into ...
. The spinal nerves that connect to the muscles of the pharyngeal wall grow individually to reach them.
Eye
The hagfish eye lacks a lens,extraocular muscles
The extraocular muscles, or extrinsic ocular muscles, are the seven extrinsic muscles of the eye in human eye, humans and other animals. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior oblique muscle, superior and inferior ...
, and the three motor cranial nerves (III, IV, and VI) found in more complex vertebrates, which is significant to the study of the evolution of more complex eyes. A parietal eye
A parietal eye (third eye, pineal eye) is a part of the epithalamus in some vertebrates. The eye is at the top of the head; is photoreceptive; and is associated with the pineal gland, which regulates circadian rhythmicity and hormone production ...
is also absent in extant hagfish. Hagfish eyespots, when present, can detect light, but as far as it is known, none can resolve detailed images. In ''Myxine'' and ''Neomyxine'', the eyes are partly covered by the trunk musculature. Paleontological evidence suggests, however, that the hagfish eye is not plesiomorphic
In phylogenetics, a plesiomorphy ("near form") and symplesiomorphy are synonyms for an ancestral character shared by all members of a clade, which does not distinguish the clade from other clades.
Plesiomorphy, symplesiomorphy, apomorphy, an ...
but rather degenerative, as fossils from the Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
have revealed hagfish-like vertebrates with complex eyes. This would suggest that ancestrally Myxini possessed complex eyes.
Cardiac function, circulation, and fluid balance
Hagfish are known to have one of the lowest blood pressures among the vertebrates. One of the most primitive types of fluid balance found in animals is among these creatures; whenever a rise in extracellular fluid occurs, the blood pressure rises and this, in turn, is sensed by the kidney, which excretes excess fluid. They also have the highest blood volume to body mass of any chordate, with 17 ml of blood per 100 g of mass. The hagfish circulatory system has been of considerable interest to evolutionary biologists and present day readers of physiology. Some observers first believed that the hagfish heart was not innervated (as the hearts of jawed vertebrates are), but further investigation revealed that the hagfish does have a true innervated heart. The hagfish circulatory system also includes multiple accessory pumps throughout the body, which are considered auxiliary "hearts". Hagfish are the only known vertebrates with osmoregulation isosmotic to their external environment. Their renal function remains poorly described. There is a hypothesis that they excrete ions in bile salts.Musculoskeletal system
Hagfish musculature differs from jawed vertebrates in that they have neither a horizontal septum nor a vertical septum, which in jawed vertebrates are junctions of connective tissue that separate the hypaxial musculature and epaxial musculature. They do, however, have true myomeres and myosepta like all vertebrates. The mechanics of their craniofacial muscles in feeding have been investigated, revealing advantages and disadvantages of their dental plate. In particular, hagfish muscles have increased force and gape size compared to similar-sized jawed vertebrates, but lack the speed amplification given by jawed vertebrates' muscles, suggesting that jaws are faster acting than hagfish dental plates. The hagfish skeleton comprises the skull, the
The hagfish skeleton comprises the skull, the notochord
The notochord is an elastic, rod-like structure found in chordates. In vertebrates the notochord is an embryonic structure that disintegrates, as the vertebrae develop, to become the nucleus pulposus in the intervertebral discs of the verteb ...
, and the caudal fin rays. The first diagram of the hagfish endoskeleton was made by Frederick Cole in 1905. In Cole's monograph, he described sections of the skeleton that he termed "pseudo-cartilage", referring to its distinct properties compared to jawed chordates. The lingual apparatus of hagfish is composed of a cartilage base bearing two teeth-covered plates (dental plates) articulated with a series of large cartilage shafts. The nasal capsule is considerably expanded in hagfish, comprising a fibrous sheath lined with cartilage rings. In contrast to lampreys, the braincase is noncartilaginous. The role of their branchial arches is still highly speculative, as hagfish embryos undergo a caudal shift of the posterior pharyngeal pouches; thus, the branchial arches do not support gills. While parts of the hagfish skull are thought to be homologous with lampreys, they are thought to have very few elements homologous with jawed vertebrates.
Reproduction
Very little is known about hagfish reproduction. Obtaining embryos and observing reproductive behavior are difficult due to the deep-sea habitat of many hagfish species. In the wild, females outnumber males, with the exact sex-ratio differing depending on the species. ''E. burgeri'', for example, has nearly a 1:1 ratio, while ''M. glutinosa'' females are significantly more common than males. Some species of hagfish are sexually undifferentiated before maturation, and possess gonadal tissue for both ovaries and testis. It has been suggested that females develop earlier than males, and that this may be the reason for unequal sex ratios. Hagfish testis are relatively small. Depending on species, females lay from one to 30 tough, yolky eggs. These tend to aggregate due to havingVelcro
Velcro IP Holdings LLC, trading as Velcro Companies and commonly referred to as Velcro (pronounced ), is a British privately held company, founded by Swiss electrical engineer George de Mestral in the 1950s. It is the original manufacturer of ho ...
-like tufts at either end. It is unclear how hagfish go about laying eggs, although researchers have proposed three hypotheses based on observations of the low percentage of males and small testis. The hypotheses are that female hagfish lay eggs in small crevices in rock formations, the eggs are laid in burrow beneath the sand, and the slime produced by the hagfish is used to hold the eggs in a small area. It is worth noting that no direct evidence has been found to support any of these hypotheses. Hagfish do not have a larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase ...
l stage, in contrast to lamprey
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are a group of Agnatha, jawless fish comprising the order (biology), order Petromyzontiformes , sole order in the Class (biology), class Petromyzontida. The adult lamprey is characterize ...
s.
Hagfish have a mesonephric kidney and are often neotenic of their pronephric kidney. The kidney(s) are drained via mesonephric/ archinephric duct. Unlike many other vertebrates, this duct is separate from the reproductive tract, and the proximal tubule of the nephron
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structu ...
is also connected with the coelom
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in many animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, i ...
, providing lubrication. The single testicle or ovary has no transportation duct. Instead, the gametes are released into the coelom until they find their way to the posterior end of the caudal region, whereby they find an opening in the digestive system.
The hagfish embryo can develop for as long as 11 months before hatching, which is shorter in comparison to other jawless vertebrates. Not much was known about hagfish embryology until recently, when husbandry advances enabled considerable insight into the group's evolutionary development. New insights into the evolution of neural crest cells
The neural crest is a ridge-like structure that is formed transiently between the epidermal ectoderm and neural plate during vertebrate development. Neural crest cells originate from this structure through the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, an ...
, support the consensus that all vertebrates share these cells, which might be regulated by a common subset of genes. Their genome has a large number of microchromosomes which are lost during the animal's development, leaving only the reproductive organs with a complete genome. Hagfish possess gonadotropins which secrete from pituitary glands to the gonads to stimulate development. This suggests that hagfish have an early version of the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis
The hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis (HPG axis, also known as the hypothalamic–pituitary–ovarian/testicular axis) refers to the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and gonadal glands as if these individual endocrine glands were a single en ...
, a system which once thought to be exclusive to the Gnathostomes.Some species of hagfish reproduce seasonally, stimulated by hormones from their pituitary gland. ''E. burgeri'' is known to reproduce and migrate annually.
Feeding
Whilepolychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called c ...
marine worm
Any worm that lives in a ocean, marine environment (biophysical), environment is considered a sea or marine worm. Marine worms are found in several different phylum (biology), phyla, including the Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, Annelida (segmented ...
s on or near the sea floor are a major food source, hagfish can feed upon and often even enter and eviscerate the bodies of dead and dying/injured sea creatures much larger than themselves. They are known to devour their prey from the inside. Hagfish have the ability to absorb dissolved organic matter across the skin and gill, which may be an adaptation to a scavenging lifestyle, allowing them to maximize sporadic opportunities for feeding. From an evolutionary perspective, hagfish represent a transitory state between the generalized nutrient absorption pathways of aquatic invertebrates and the more specialized digestive systems of aquatic vertebrates.
Like leech
Leeches are segmented parasitism, parasitic or Predation, predatory worms that comprise the Class (biology), subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the Oligochaeta, oligochaetes, which include the earthwor ...
es, they have a sluggish metabolism and can survive months between feedings; their feeding behavior, however, appears quite vigorous. Analysis of the stomach content of several species has revealed a large variety of prey, including polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called c ...
s, shrimp, hermit crab
Hermit crabs are anomuran Decapoda, decapod crustaceans of the superfamily (taxonomy), superfamily Paguroidea that have adapted to occupy empty scavenged mollusc shells to protect their fragile exoskeletons. There are over 800 species of hermit c ...
s, cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symm ...
s, brittle star
Brittle stars, serpent stars, or ophiuroids (; ; referring to the serpent-like arms of the brittle star) are echinoderms in the class Ophiuroidea, closely related to starfish. They crawl across the sea floor using their flexible arms for locomot ...
s, bony fish
Osteichthyes ( ; ), also known as osteichthyans or commonly referred to as the bony fish, is a Biodiversity, diverse clade of vertebrate animals that have endoskeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondricht ...
es, sharks, birds, and whale flesh.
In captivity, hagfish are observed to use the overhand-knot behavior in reverse (tail-to-head) to assist them in gaining mechanical advantage to pull out chunks of flesh from fish or cetacean carrion
Carrion (), also known as a carcass, is the decaying flesh of dead animals.
Overview
Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures ...
, eventually making an opening to permit entry to the interior of the body cavity of larger carcasses. A healthy larger sea creature likely would be able to outfight or outswim this sort of assault.
This energetic opportunism on the part of the hagfish can be a great nuisance to fishermen, as they can devour or spoil entire deep drag-netted catches before they can be pulled to the surface. Since hagfish are typically found in large clusters on and near the bottom, a single trawler's catch could contain several dozen or even hundreds of hagfish as bycatch, and all the other struggling, captive sea life make easy prey for them.
The digestive tract of the hagfish is unique among chordates because the food in the gut is enclosed in a permeable membrane, analogous to the peritrophic matrix of insects. They are also able to absorb nutrients directly through their skin.
Hagfish have also been observed actively hunting
Hunting is the Human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, and killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to obtain the animal's body for meat and useful animal products (fur/hide (sk ...
the red bandfish, '' Cepola haastii'', in its burrow, possibly using their slime to suffocate the fish before grasping it with their dental plates and dragging it from the burrow.
Classification
 Originally, ''Myxine'' was included by
Originally, ''Myxine'' was included by Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming o ...
(1758
Events
January–March
* January 1 – Swedish biologist Carl Linnaeus (Carl von Linné) publishes in Stockholm the first volume (''Animalia'') of the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'', the starting point of modern zoologic ...
) in Vermes. The fossil hagfish '' Myxinikela siroka'', from the Late Carboniferous of the United States, is the oldest-known member of the group. It is in some respects more similar to lampreys, but shows key autapomorphies of hagfish. In recent years, hagfish have become of special interest for genetic analysis investigating the relationships among chordate
A chordate ( ) is a bilaterian animal belonging to the phylum Chordata ( ). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five distinctive physical characteristics ( synapomorphies) that distinguish them from ot ...
s. Their classification as agnatha
Agnatha (; ) or jawless fish is a paraphyletic infraphylum of animals in the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata, characterized by the lack of jaws. The group consists of both extant taxon, living (Cyclostomi, cyclostomes such as hagfish ...
ns places hagfish as elementary vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s in between invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s and gnathostomes. However, discussion has long occurred in scientific literature about whether the hagfish were even invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
. Using fossil data, paleontologists posited that lampreys are more closely related to gnathostomes than hagfish. The term "Craniata" was used to refer to animals that had a developed skull, but were not considered true vertebrates. Molecular evidence in the early 1990s first began suggesting that lampreys and hagfish were more closely related to each other than to gnathostomes. The validity of the taxon "Craniata" was further examined by Delarbre et al. (2002) using mtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the DNA contained in ...
sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is cal ...
data, concluding the Myxini are more closely related to the Hyperoartia than to the Gnathostomata—i.e., that modern jawless fishes form a clade called the Cyclostomata
Cyclostomi, often referred to as Cyclostomata , from Ancient Greek κύκλος (kúklos), meaning "circle", and στόμα (stóma), meaning "mouth",
is a superclass of vertebrates that comprises the living jawless fish classes: the lamp ...
. The argument is that if the Cyclostomata are indeed monophyletic, Vertebrata would return to its old content (Gnathostomata
Gnathostomata (; from Ancient Greek: (') 'jaw' + (') 'mouth') are jawed vertebrates. Gnathostome diversity comprises roughly 60,000 species, which accounts for 99% of all extant vertebrates, including all living bony fishes (both ray-finned ...
+ Cyclostomata) and the name Craniata, being superfluous, would become a junior synonym. Nowadays, molecular data are almost unanimously in consensus of cyclostome monophyly, with more recent work being directed at shared microRNAs between cyclostomes and gnathostomes. The current classification supported by molecular analyses (which show that lampreys and hagfishes are sister taxa), as well as the fact that hagfishes do, in fact, have rudimentary vertebrae, which places hagfishes in Cyclostomata.
Phylogeny
Hagfish are in the groupCyclostomata
Cyclostomi, often referred to as Cyclostomata , from Ancient Greek κύκλος (kúklos), meaning "circle", and στόμα (stóma), meaning "mouth",
is a superclass of vertebrates that comprises the living jawless fish classes: the lamp ...
which includes jawless fish. The group Cyclostomata
Cyclostomi, often referred to as Cyclostomata , from Ancient Greek κύκλος (kúklos), meaning "circle", and στόμα (stóma), meaning "mouth",
is a superclass of vertebrates that comprises the living jawless fish classes: the lamp ...
is characterized by two significant characteristics; keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. It is the key structural material making up Scale (anatomy), scales, hair, Nail (anatomy), nails, feathers, horn (anatomy), horns, claws, Hoof, hoove ...
ous tooth plates and movement of postotic myomeres to the orbitals. According to fossil record, hagfish and lamprey
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are a group of Agnatha, jawless fish comprising the order (biology), order Petromyzontiformes , sole order in the Class (biology), class Petromyzontida. The adult lamprey is characterize ...
s have been estimated to have diverged from one another during the Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma a ...
period. An experiment used an estimation of synonymous and nonsynonymous substitutions for nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
s and supplemented that data with pre-existing data into a clock that would calculate divergence times for the taxon
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
s '' Myxine'' and '' Eptatretus''. This data found that the lineage diverged around 93–28 Mya; however, later studies have found even earlier divergence times within the group, with ''Myxine'' and ''Eptatretus'' diverging during the Triassic and the ancestor of '' Rubicundus'' diverging during other extant hagfishes during the Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years, from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the s ...
. Hagfish are excluded from the subphylum Gnathostomata
Gnathostomata (; from Ancient Greek: (') 'jaw' + (') 'mouth') are jawed vertebrates. Gnathostome diversity comprises roughly 60,000 species, which accounts for 99% of all extant vertebrates, including all living bony fishes (both ray-finned ...
because of morphological characteristics including the hagfish arched tongue. Hagfish embryos have characteristics of gnathostomes and may be plesiomorphic; however, these characteristics drastically change morphologically as the hagfish matures. The following hagfish and lamprey phylogeny is an adaptation based on the 2019 work of Miyashita et al.
Commercial use

As food
In most of the world, hagfish are not often eaten. But inKorea
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically Division of Korea, divided at or near the 38th parallel north, 3 ...
, the hagfish is a valued food, where it is generally skinned, coated in spicy sauce, and grilled over charcoal or stir-fried. It is especially popular in the southern port cities of the peninsula, such as Busan
Busan (), officially Busan Metropolitan City, is South Korea's second list of cities in South Korea by population, most populous city after Seoul, with a population of over 3.3 million as of 2024. Formerly romanized as Pusan, it is the economi ...
and coastal cities in South Gyeongsang Province
South Gyeongsang Province (, ) is a province in the southeast of South Korea. The provincial capital is at Changwon. It is adjacent to the major metropolitan center and port of Busan. The UNESCO World Heritage Site Haeinsa, a Buddhist temple tha ...
.
Due to their value in Korean cuisine
Korean cuisine is the set of foods and culinary styles which are associated with Korean culture. This cuisine has evolved through centuries of social and political change. Originating from ancient Prehistoric Korea, agricultural and nomad ...
, most hagfish caught for food elsewhere in the world is fished with intent of being exported to South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
. The inshore hagfish, found in the northwest Pacific, is eaten in Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
and South Korea. As hagfish slime binds vast amounts of liquid even at low temperatures, it was proposed as an energy-saving alternative for the production of tofu
or bean curd is a food prepared by Coagulation (milk), coagulating soy milk and then pressing the resulting curds into solid white blocks of varying softness: ''silken'', ''soft'', ''firm'', and ''extra (or super) firm''. It originated in Chin ...
that does not require heating.
In textiles
The hagfish slime threads can be used as ultra-strong fiber for clothing. Douglas Fudge, ofChapman University
Chapman University is a private research university in Orange, California, United States. Encompassing eleven colleges, the university is classified among "R2: Doctoral Universities – High research activity". The school maintains its foundi ...
, has conducted research in this area.
Skins
Hagfish skin, used in a variety of clothing accessories, is usually referred to as "eel skin". It produces a particularly durable leather, especially suitable for wallets and belts.References
Further reading
* * * *Brodal, A. and Fänge, R. (ed.) (1963). The Biology of Myxine, Universitetsforlaget, Oslo. * *Hardisty, M. W. (1982). Lampreys and hagfishes: Analysis of cyclostome relationships. In The Biology of Lampreys, (ed. M. W. Hardisty and I. C. Potter), Vol.4B, pp. 165–259. Academic Press, London. *Janvier, P. (1996). Early vertebrates. Oxford Monographs in Geology and Geophysics, 33, Oxford University Press, Oxford. * * * * * * * *Ewoldt, R. H., Winegard, T. M. and Fudge D. S. (2010). Non-linear viscoelasticity of hagfish slime. Int. J. Lin. Mech. 46: 627–636. *Fudge, D. (2001)''Hagfishes: Champions of Slime''
Nature Australia, Spring 2001 ed., Australian Museum Trust, Sydney. pp. 61–69. * * * *
External links
FishBase entry for Myxinidae
Beware the hagfish – repeller of sharks
''3 News'', 28 Oct 2011. Video.
Hagfish versus sharks : 1-0
''Te Papa Blog'', 28 October 2011.
Teen Spots Hagfish-Slurping Elephant Seal – YouTube
(2:11)
What happens when a shark attacks a hagfish – BBC
(0:39)
Vancouver Aquarium Hagfish Slime
{{Authority control Scavengers Taxa named by Constantine Samuel Rafinesque