Hypnogram on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A hypnogram is a form of
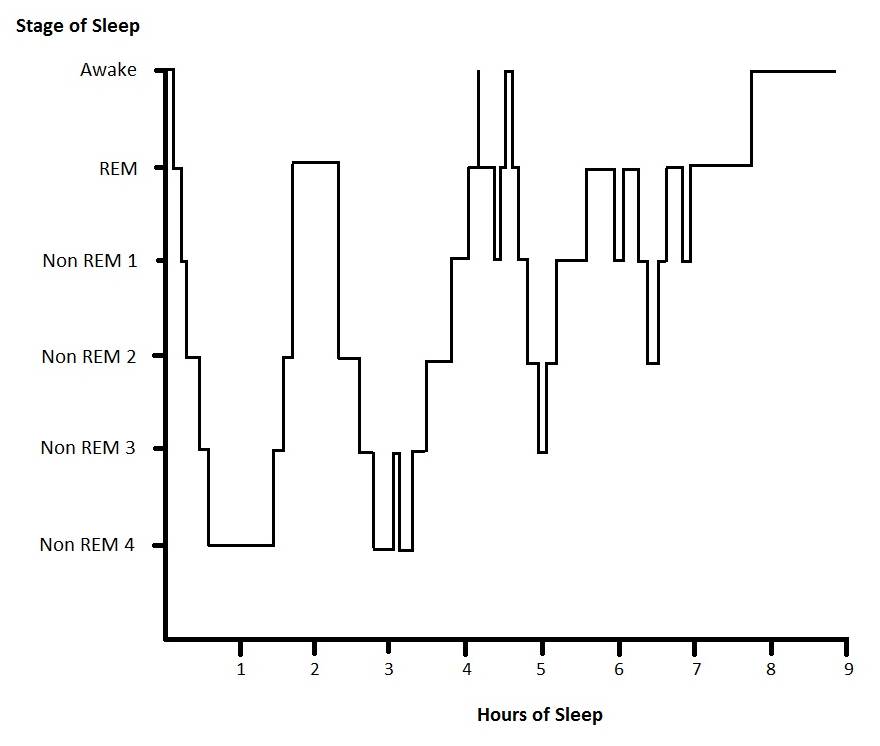
A hypnogram is a form of
American Academy of Sleep Medicine
{{Authority control Sleep medicine
 A hypnogram is a form of
A hypnogram is a form of polysomnography
Polysomnography (PSG) is a multi-parameter type of sleep study and a diagnostic tool in sleep medicine. The test result is called a polysomnogram, also abbreviated PSG. The name is derived from Greek and Latin roots: the Greek πολύς ('' ...
; it is a graph that represents the stages of sleep
Sleep is a state of reduced mental and physical activity in which consciousness is altered and certain sensory activity is inhibited. During sleep, there is a marked decrease in muscle activity and interactions with the surrounding environme ...
as a function of time. It was developed as an easy way to present the recordings of the brain wave activity from an electroencephalogram
Electroencephalography (EEG)
is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neoc ...
(EEG) during a period of sleep. It allows the different stages of sleep: rapid eye movement sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of sleep in mammals (including humans) and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes, accompanied by low muscle tone throughout the body, and the propensity of the s ...
(REM) and non-rapid eye movement sleep (NREM) to be identified during the sleep cycle. NREM sleep can be further classified into NREM stage 1, 2 and 3. The previously considered 4th stage of NREM sleep has been included within stage 3; this stage is also called slow wave sleep (SWS) and is the deepest stage of sleep.
Method
Hypnograms are usually obtained by visually scoring the recordings fromelectroencephalogram
Electroencephalography (EEG)
is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neoc ...
(EEGs), electrooculography
Electrooculography (EOG) is a technique for measuring the corneo-retinal standing potential that exists between the front and the back of the human eye. The resulting signal is called the electrooculogram. Primary applications are in ophthalmo ...
(EOGs) and electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyo ...
(EMGs).
The output from these three sources is recorded simultaneously on a graph by a monitor or computer as a hypnogram. Certain frequencies displayed by EEGs, EOGs and EMGs are characteristic and determine what stage of sleep or wake the subject is in. There is a protocol defined by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) is a United States professional society for the medical subspecialty of sleep medicine which includes disorders of circadian rhythms. It was established in 1975.
The organization's functions includ ...
(AASM) for sleep scoring, whereby the sleep or wake state is recorded in 30-second epochs. Prior to this the Rechtschaffen and Kales (RK) rules were used to classify sleep stages.
Output
Normal sleep
Cycles of REM and non-REM stages make up sleep. A normal healthy adult requires 7–9 hours of sleep per night. The number of hours of sleep is variable, however the proportion of sleep spent in a particular stage remains mostly consistent; healthy adults normally spend 20–25% of their sleep in REM sleep. During rest following a sleep-deprived state, there is a period of rebound sleep which has longer and deeper episodes of SWS to make up for the lack of sleep. On a hypnogram, a sleep cycle is usually around 90 minutes and there are four to six cycles of REM/NREM stages that occur during a major period of sleep. Most SWS occurs in the first one or two cycles; this is the deepest period of sleep. The second half of the sleeping period contains most REM sleep and little or no SWS and may contain brief periods ofwakefulness
Wakefulness is a daily recurring brain state and state of consciousness in which an individual is conscious and engages in coherent cognition, cognitive and behavioral responses to the external world.
Being awake is the opposite of being asleep, ...
which can be recorded but are not usually perceived. The stage that occurs before waking is normally REM sleep.
Hypnograms for healthy persons vary slightly according to age, emotional state, and environmental factors.
Disrupted sleep
Sleep architecture can be evaluated using hypnograms, demonstrating irregular sleeping patterns associated with sleep disorders. Disruptions or irregularities to the normal sleep cycle or sleep stage transitions can be detected; for example a hypnogram can show that inobstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-related breathing disorder and is characterized by recurrent episodes of complete or partial airway obstruction, obstruction of the respiratory tract#Upper respiratory tract, upper airway lea ...
(OSA) the stability of transition between REM and NREM stages is disrupted.
The effects of certain medications on sleep architecture can be visualised on a hypnogram. For example, the anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs, antiseizure drugs, or anti-seizure medications (ASM)) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also used in the treatme ...
Phenytoin
Phenytoin (PHT), sold under the brand name Dilantin among others, is an anticonvulsant, anti-seizure medication. It is useful for the prevention of tonic-clonic seizures (also known as grand mal seizures) and focal seizures, but not absence se ...
(PHT) can be seen to disrupt sleep by increasing the duration of NREM stage 1 and decreasing the duration of SWS; whereas the drug Gabapentin
Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropath ...
is seen to revive sleep by increasing the duration of SWS.
Analysis
The main use of a hypnogram is as a qualitative method to visualise the time period of each stage of sleep, as well as the number of transitions between stages. Hypnograms are rarely used to providequantitative
Quantitative may refer to:
* Quantitative research, scientific investigation of quantitative properties
* Quantitative analysis (disambiguation)
* Quantitative verse, a metrical system in poetry
* Statistics, also known as quantitative analysis
...
data, however it has been suggested that statistical evaluation can be carried out using multistate survival analysis and log-linear model
A log-linear model is a mathematical model that takes the form of a function whose logarithm equals a linear combination of the parameters of the model, which makes it possible to apply (possibly multivariate) linear regression. That is, it has ...
s to provide numerical significance.
Limitations
The restrictions of measuring sleep at short 30-second epochs limits the ability to record events shorter than 30 seconds; hence, the macrostructure of sleep can be evaluated while the microstructure is not. The sleep process is smoothened out in hypnogram results unlike it occurs naturally. Also some specific features of sleep such assleep spindles
Sleep spindles are bursts of neural oscillatory activity that are generated by interplay of the thalamic reticular nucleus (TRN) and other thalamic nuclei during stage 2 NREM sleep in a frequency range of ~11 to 16 Hz (usually 12–14&nbs ...
and K complexes may not be defined in the hypnogram; this is particularly true for sleep scoring that is automated.
The method of obtaining the data used in a hypnogram is restricted to the input from an EEG, EOG or EMG. The interval of recording may include features from several stages, in which case it is recorded as the stage whose features occupy the recording for the longest duration. For this reason, the stage of sleep may be misrepresented on the hypnogram.
Research directions
Suggestions to improve the automated output of hypnograms to provide more reliable and accurate results include increasing the measures of sleep, for example by additionally measuring sleep with an electrocardiogram (ECG). Another advancement involves combining hypnograms with color density spectral arrays to improve the quality of sleep analysis.References
External links
American Academy of Sleep Medicine
{{Authority control Sleep medicine