Human–robot interaction (HRI) is the study of interactions between humans and robots. Human–robot interaction is a multidisciplinary field with contributions from
human–computer interaction
Human–computer interaction (HCI) is the process through which people operate and engage with computer systems. Research in HCI covers the design and the use of computer technology, which focuses on the interfaces between people (users) and comp ...
,
artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
,
robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
,
natural language processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related ...
,
design
A design is the concept or proposal for an object, process, or system. The word ''design'' refers to something that is or has been intentionally created by a thinking agent, and is sometimes used to refer to the inherent nature of something ...
,
psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ...
and
philosophy
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
. A subfield known as physical human–robot interaction (pHRI) has tended to focus on device design to enable people to safely interact with robotic systems.
Origins
Human–robot interaction has been a topic of both science fiction and academic speculation even before any robots existed. Because much of active HRI development depends on
natural language processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related ...
, many aspects of HRI are continuations of
human communication
Human communication, or anthroposemiotics, is a field of study dedicated to understanding how humans Communication, communicate. Humans' ability to communicate with one another would not be possible without an understanding of what we are refere ...
s, a field of research which is much older than robotics.
The origin of HRI as a discrete problem was stated by 20th-century author
Isaac Asimov
Isaac Asimov ( ; – April 6, 1992) was an Russian-born American writer and professor of biochemistry at Boston University. During his lifetime, Asimov was considered one of the "Big Three" science fiction writers, along with Robert A. H ...
in 1941, in his novel ''I, Robot''. Asimov coined
Three Laws of Robotics
The Three Laws of Robotics (often shortened to The Three Laws or Asimov's Laws) are a set of rules devised by science fiction author Isaac Asimov, which were to be followed by robots in several of his stories. The rules were introduced in his 194 ...
, namely:
# A robot may not injure a human being or, through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm.
# A robot must obey the orders by human beings except where such orders would conflict with the First Law.
# A robot must protect its own existence as long as such protection does not conflict with the First or Second Laws.
These three laws provide an overview of the goals engineers and researchers hold for safety in the HRI field, although the fields of
robot ethics
Robot ethics, sometimes known as "roboethics", concerns ethical problems that occur with robots, such as whether robots pose a threat to humans in the long or short run, whether some ''uses'' of robots are problematic (such as in healthcare or as ...
and
machine ethics
Machine ethics (or machine morality, computational morality, or computational ethics) is a part of the ethics of artificial intelligence concerned with adding or ensuring moral behaviors of man-made machines that use artificial intelligence, otherw ...
are more complex than these three principles. However, generally human–robot interaction prioritizes the safety of humans that interact with potentially dangerous robotics equipment. Solutions to this problem range from the philosophical approach of treating robots as ethical agents (individuals with
moral agency
Moral agency is an individual's ability to make morality, moral choices based on some notion of ethics, right and wrong and to be held accountable for these actions. A moral agent is "a being who is capable of acting with reference to right and wro ...
), to the practical approach of creating safety zones. These safety zones use technologies such as
lidar
Lidar (, also LIDAR, an acronym of "light detection and ranging" or "laser imaging, detection, and ranging") is a method for determining ranging, ranges by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected li ...
to detect human presence or physical barriers to protect humans by preventing any contact between machine and operator.
Although initially robots in the human–robot interaction field required some human intervention to function, research has expanded this to the extent that fully autonomous systems are now far more common than in the early 2000s.
Autonomous systems include from
simultaneous localization and mapping
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) is the computational problem of constructing or updating a map of an unknown environment while simultaneously keeping track of an Intelligent agent, agent's location within it. While this initially ap ...
systems which provide intelligent robot movement to
natural-language processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related ...
and
natural-language generation
Natural language generation (NLG) is a software process that produces natural language output. A widely cited survey of NLG methods describes NLG as "the subfield of artificial intelligence and computational linguistics that is concerned with the ...
systems which allow for natural, human-esque interaction which meet well-defined psychological benchmarks.
Anthropomorphic
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human entities. It is considered to be an innate tendency of human psychology. Personification is the related attribution of human form and characteristics to ...
robots (machines which imitate human body structure) are better described by the
biomimetic
Biomimetics or biomimicry is the emulation of the models, systems, and elements of nature for the purpose of solving complex human problems. The terms "biomimetics" and "biomimicry" are derived from (''bios''), life, and μίμησις ('' mīm ...
s field, but overlap with HRI in many research applications. Examples of robots which demonstrate this trend include
Willow Garage
Willow Garage was a robotics research lab and technology incubator devoted to developing hardware and open source software for personal robotics applications. The company was best known for its open source software suite Robot Operating Syste ...
's
PR2 robot, the
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
Robonaut
A robonaut is a humanoid robot, part of a development project conducted by the Dexterous Robotics Laboratory at NASA's Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center (JSC) in Houston, Texas. Robonaut differs from other current space-faring robots in that, while ...
, and
Honda
commonly known as just Honda, is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate automotive manufacturer headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Founded in October 1946 by Soichiro Honda, Honda has bee ...
ASIMO
ASIMO (Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility) is a humanoid robot created by Honda in 2000.
In 2002, there were 20 units of the first ASIMO model produced; three different ASIMO models subsequently followed. As of February 2009, there were over ...
. However, robots in the human–robot interaction field are not limited to human-like robots:
Paro and
Kismet are both robots designed to elicit emotional response from humans, and so fall into the category of human–robot interaction.
Goals in HRI range from industrial manufacturing through
Cobot
A cobot, or collaborative robot, also known as a companion robot, is a robot intended for direct human-robot interaction within a shared space, or where humans and robots are in close proximity. Cobot applications contrast with traditional industr ...
s, medical technology through rehabilitation, autism intervention, and elder care devices, entertainment, human augmentation, and human convenience. Future research therefore covers a wide range of fields, much of which focuses on assistive robotics, robot-assisted search-and-rescue, and space exploration.
The goal of friendly human–robot interactions
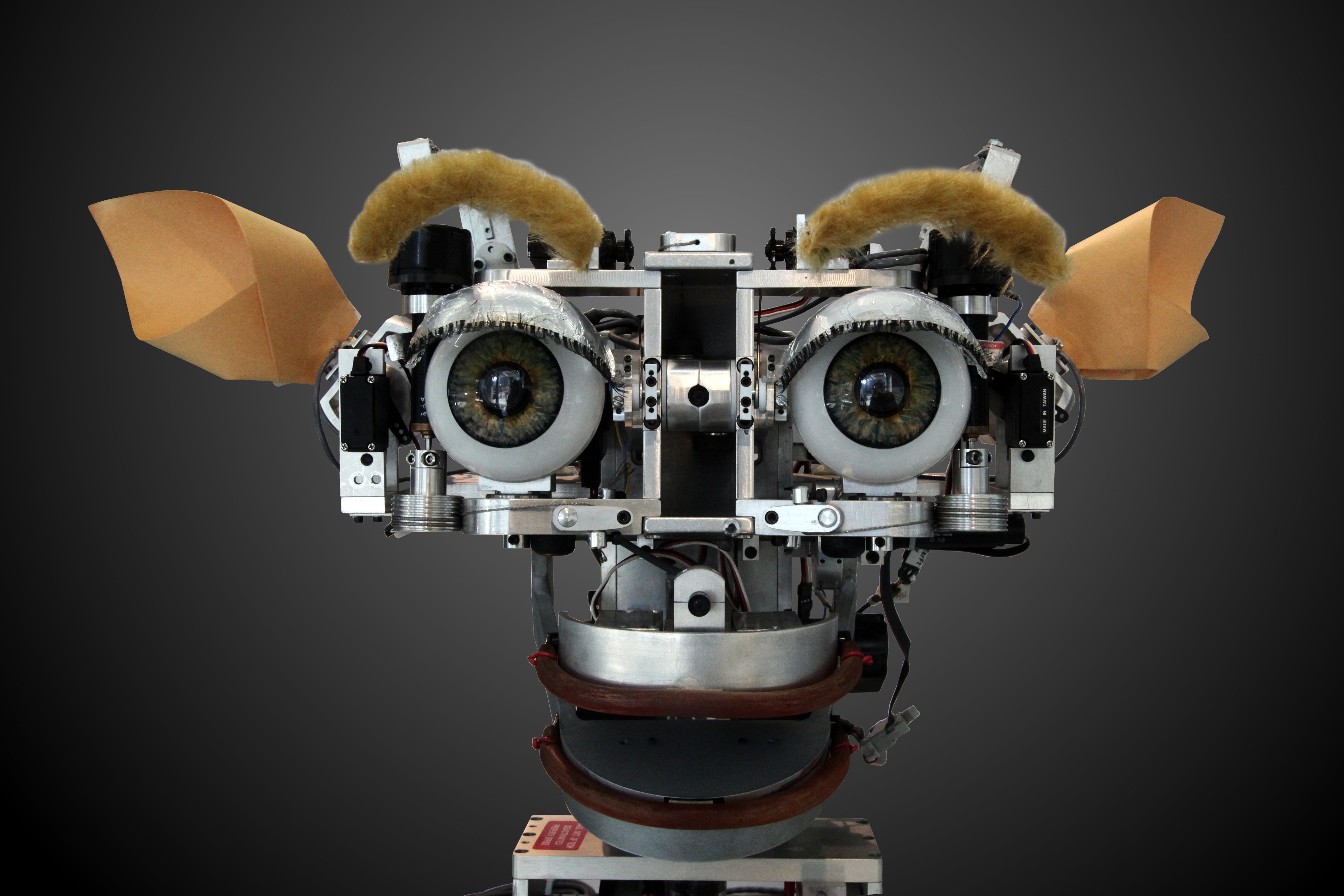
Robots are
artificial agents
In artificial intelligence, an intelligent agent is an entity that perceives its environment, takes actions autonomously to achieve goals, and may improve its performance through machine learning or by acquiring knowledge. Leading AI textbook ...
with capacities of perception and action in the physical world often referred by researchers as workspace. Their use has been generalized in factories but nowadays they tend to be found in the most technologically advanced societies in such critical domains as search and rescue, military battle, mine and bomb detection, scientific exploration, law enforcement, entertainment and hospital care.
These new domains of applications imply a closer interaction with the user. The concept of closeness is to be taken in its full meaning, robots and humans share the workspace but also share goals in terms of task achievement. This close interaction needs new theoretical models, on one hand for the robotics scientists who work to improve the robots utility and safety and on the other hand to evaluate the risks and benefits of this new "friend" for our modern society. The subfield of physical human–robot interaction (pHRI) has largely focused on device design to enable people to safely interact with robotic systems, but is increasingly developing algorithmic approaches in an attempt to support fluent and expressive interactions between humans and robotic systems.
With the advance in
AI, the research is focusing on one part towards the safest physical interaction but also on a socially correct interaction, dependent on cultural criteria. The goal is to build an intuitive, and easy communication with the robot through speech, gestures, and facial expressions.
Kerstin Dautenhahn
Kerstin Dautenhahn (born 1964) is a German computer scientist specializing in social robotics and human–robot interaction. She is a professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Waterloo, where she holds the Canada 150 ...
refers to friendly Human–robot interaction as "Robotiquette" defining it as the "social rules for robot behaviour (a 'robotiquette') that is comfortable and acceptable to humans" The robot has to adapt itself to our way of expressing desires and orders and not the contrary. But every day environments such as homes have much more complex social rules than those implied by factories or even military environments. Thus, the robot needs perceiving and understanding capacities to build dynamic models of its surroundings. It needs to
categorize objects, recognize and locate humans and further
recognize their emotions. The need for dynamic capacities pushes forward every sub-field of robotics.
Furthermore, by understanding and perceiving social cues, robots can enable collaborative scenarios with humans. For example, with the rapid rise of personal fabrication machines such as desktop
3D printers
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer ...
,
laser cutters, etc., entering our homes, scenarios may arise where robots can collaboratively share control, co-ordinate and achieve tasks together.
Industrial robots
An industrial robot is a robot system used for manufacturing. Industrial robots are automated, programmable and capable of movement on three or more axes.
Typical applications of robots include robot welding, welding, painting, assembly, Circu ...
have already been integrated into industrial assembly lines and are collaboratively working with humans. The social impact of such robots have been studied and has indicated that workers still treat robots and social entities, rely on social cues to understand and work together.
On the other end of HRI research the
cognitive model
A cognitive model is a representation of one or more cognitive processes in humans or other animals for the purposes of comprehension and prediction. There are many types of cognitive models, and they can range from box-and-arrow diagrams to a se ...
ling of the "relationship" between human and the robots benefits the psychologists and robotic researchers the user study are often of interests on both sides. This research endeavours part of human society. For effective ''human – humanoid robot'' interaction numerous communication skills and related features should be implemented in the design of such artificial agents/systems.
General HRI research
HRI research spans a wide range of fields, some general to the nature of HRI.
Methods for perceiving humans
Methods for perceiving humans in the environment are based on sensor information. Research on sensing components and software led by Microsoft provide useful results for extracting the human kinematics (see
Kinect
Kinect is a discontinued line of motion sensing input devices produced by Microsoft and first released in 2010. The devices generally contain RGB color model, RGB cameras, and Thermographic camera, infrared projectors and detectors that map dep ...
). An example of older technique is to use colour information for example the fact that for light skinned people the hands are lighter than the clothes worn. In any case a human modelled a priori can then be fitted to the sensor data. The robot builds or has (depending on the level of autonomy the robot has) a 3D
mapping of its surroundings to which is assigned the humans locations.
Most methods intend to
build a 3D model through
vision
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to:
Perception Optical perception
* Visual perception, the sense of sight
* Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight
* Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain und ...
of the environment. The
proprioception
Proprioception ( ) is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position.
Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, a type of sensory receptor, located within muscles, tendons, and joints. Most animals possess multiple subtypes of propri ...
sensors permit the robot to have information over its own state. This information is relative to a reference. Theories of
proxemics
Proxemics is the study of human use of space and the effects that population density has on behavior, communication, and social interaction. Proxemics is one among several subcategories in the study of nonverbal communication, including Haptic co ...
may be used to perceive and plan around a person's personal space.
A speech recognition system is used to interpret human desires or commands. By combining the information inferred by proprioception, sensor and speech the human position and state (standing, seated). In this matter,
natural-language processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related ...
is concerned with the interactions between computers and human (natural) languages, in particular how to program computers to process and analyze large amounts of
natural-language data. For instance, neural-network architectures and learning algorithms that can be applied to various natural-language processing tasks including part-of-speech tagging, chunking,
named-entity recognition
Named-entity recognition (NER) (also known as (named) entity identification, entity chunking, and entity extraction) is a subtask of information extraction that seeks to locate and classify named entities mentioned in unstructured text into pr ...
, and
semantic role labeling
In natural language processing, semantic role labeling (also called shallow semantic parsing or slot-filling) is the process that assigns labels to words or phrases in a sentence that indicates their semantic role in the sentence, such as that of ...
.
Methods for motion planning
Motion planning
Motion planning, also path planning (also known as the navigation problem or the piano mover's problem) is a computational problem to find a sequence of valid configurations that moves the object from the source to destination. The term is used ...
in dynamic environments is a challenge that can at the moment only be achieved for robots with 3 to 10
degrees of freedom
In many scientific fields, the degrees of freedom of a system is the number of parameters of the system that may vary independently. For example, a point in the plane has two degrees of freedom for translation: its two coordinates; a non-infinite ...
. Humanoid robots or even 2 armed robots, which can have up to 40 degrees of freedom, are unsuited for dynamic environments with today's technology. However lower-dimensional robots can use the potential field method to compute trajectories which avoid collisions with humans.
Cognitive models and theory of mind
Humans exhibit negative social and emotional responses as well as decreased trust toward some robots that closely, but imperfectly, resemble humans; this phenomenon has been termed the "Uncanny Valley."
However recent research in telepresence robots has established that mimicking human body postures and expressive gestures has made the robots likeable and engaging in a remote setting. Further, the presence of a human operator was felt more strongly when tested with an android or humanoid telepresence robot than with normal video communication through a monitor.
While there is a growing body of research about users' perceptions and emotions towards robots, we are still far from a complete understanding. Only additional experiments will determine a more precise model.
Based on past research, we have some indications about current user sentiment and behavior around robots:
* During initial interactions, people are more uncertain, anticipate less social presence, and have fewer positive feelings when thinking about interacting with robots, and prefer to communicate with a human. This finding has been called the human-to-human interaction script.
* It has been observed that when the robot performs a proactive behaviour and does not respect a "safety distance" (by penetrating the user space) the user sometimes expresses fear. This fear response is person-dependent.
* It has also been shown that when a robot has no particular use, negative feelings are often expressed. The robot is perceived as useless and its presence becomes annoying.
* People have also been shown to attribute personality characteristics to the robot that were not implemented in software.
* People similarly infer the mental states of both humans and robots, except for when robots and humans use non-literal language (such as sarcasm or white lies).
* In line with the contact hypothesis, supervised exposure to a social robot can decrease uncertainty and increase willingness to interact with the robot, compared to pre-exposure attitudes toward robots as a class of agents.
* Interacting with a robot by looking at or touching the robot can reduce negative feelings that some people have about robots before interacting with them. Even imagined interaction can reduce negative feelings. However, in some cases, interacting with a robot can increase negative feelings for people with strong pre-existing negative sentiments towards robots.
Methods for human–robot coordination
A large body of work in the field of human–robot interaction has looked at how humans and robots may better collaborate. The primary social cue for humans while collaborating is the shared perception of an activity, to this end researchers have investigated anticipatory robot control through various methods including: monitoring the behaviors of human partners using
eye tracking
Eye tracking is the process of measuring either the point of gaze (where one is looking) or the motion of an eye relative to the head. An eye tracker is a device for measuring eye positions and eye movement. Eye trackers are used in research ...
, making inferences about human task intent, and proactive action on the part of the robot. The studies revealed that the anticipatory control helped users perform tasks faster than with reactive control alone.
A common approach to program social cues into robots is to first study human–human behaviors and then transfer the learning. For example, coordination mechanisms in human–robot collaboration are based on work in neuroscience which examined how to enable joint action in human–human configuration by studying perception and action in a social context rather than in isolation. These studies have revealed that maintaining a shared representation of the task is crucial for accomplishing tasks in groups. For example, the authors have examined the task of driving together by separating responsibilities of acceleration and braking i.e., one person is responsible for accelerating and the other for braking; the study revealed that pairs reached the same level of performance as individuals only when they received feedback about the timing of each other's actions. Similarly, researchers have studied the aspect of human–human handovers with household scenarios like passing dining plates in order to enable an adaptive control of the same in human–robot handovers. Another study in the domain of
Human Factors and Ergonomics
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are great apes characterized by their hairlessness, bipedalism, and high intellig ...
of human–human handovers in warehouses and supermarkets reveal that Givers and Receivers perceive handover tasks differently which has significant implications for designing user-centric
human–robot collaborative systems. Most recently, researchers have studied a system that automatically distributes assembly tasks among co-located workers to improve co-ordination.
Robots used for research in HRI
Some research involved designing a new robot while others use available robots to conduct study. Some commonly used robots are
Nao, a humanoid and programmable robot,
Pepper
Pepper(s) may refer to:
Food and spice
* Piperaceae or the pepper family, a large family of flowering plants
** Black pepper
** Long pepper
** Kampot pepper
* ''Capsicum'' or pepper, a genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family Solanacea ...
and
Furhat
Furhat is a back-projected humanoid social robot developed by the Swedish company Furhat Robotics. It is used to facilitate face-to-face interaction between humans and AI by employing a combination of projection technology, speech capabilities, a ...
, two other social humanoid robots, an
Misty a programmable companion robot.

Color
The majority of robots are of a white color, stemming from a bias against robots of other colors.
Application areas
The application areas of human–robot interaction include robotic technologies that are used by humans for industry, medicine, and companionship, among other purposes.
Industrial robots

Major manufacturers lik
FANUCproduce a wide range of
industrial robot
An industrial robot is a robot system used for manufacturing. Industrial robots are automated, programmable and capable of movement on three or more axes.
Typical applications of robots include robot welding, welding, painting, assembly, Circu ...
s have been implemented to collaborate with humans to perform industrial manufacturing tasks. While humans have the flexibility and the intelligence to consider different approaches to solve the problem, choose the best option among all choices, and then command robots to perform assigned tasks, robots are able to be more precise and more consistent in performing repetitive and dangerous work.
Together, the collaboration of industrial robots and humans demonstrates that robots have the capabilities to ensure efficiency of
manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer ...
and assembling.
However, there are persistent concerns about the safety of human–robot collaboration, since industrial robots have the ability to move heavy objects and operate often dangerous and sharp tools, quickly and with force. As a result, this presents a potential threat to the people who work in the same workspace.
Therefore, the planning of safe and effective layouts for collaborative workplaces is one of the most challenging topics that research faces.
Medical robots
Rehabilitation

A
rehabilitation robot is an example of a robot-aided system implemented in
health care
Health care, or healthcare, is the improvement or maintenance of health via the preventive healthcare, prevention, diagnosis, therapy, treatment, wikt:amelioration, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other disability, physic ...
. This type of robot would aid
stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
survivors or individuals with neurological impairment to recover their hand and finger movements.
In the past few decades, the idea of how human and robot interact with each other is one factor that has been widely considered in the design of rehabilitation robots.
For instance, human–robot interaction plays an important role in designing
exoskeleton
An exoskeleton () . is a skeleton that is on the exterior of an animal in the form of hardened integument, which both supports the body's shape and protects the internal organs, in contrast to an internal endoskeleton (e.g. human skeleton, that ...
rehabilitation robots since the exoskeleton system makes direct contact with humans' body.
Elder care and companion robot
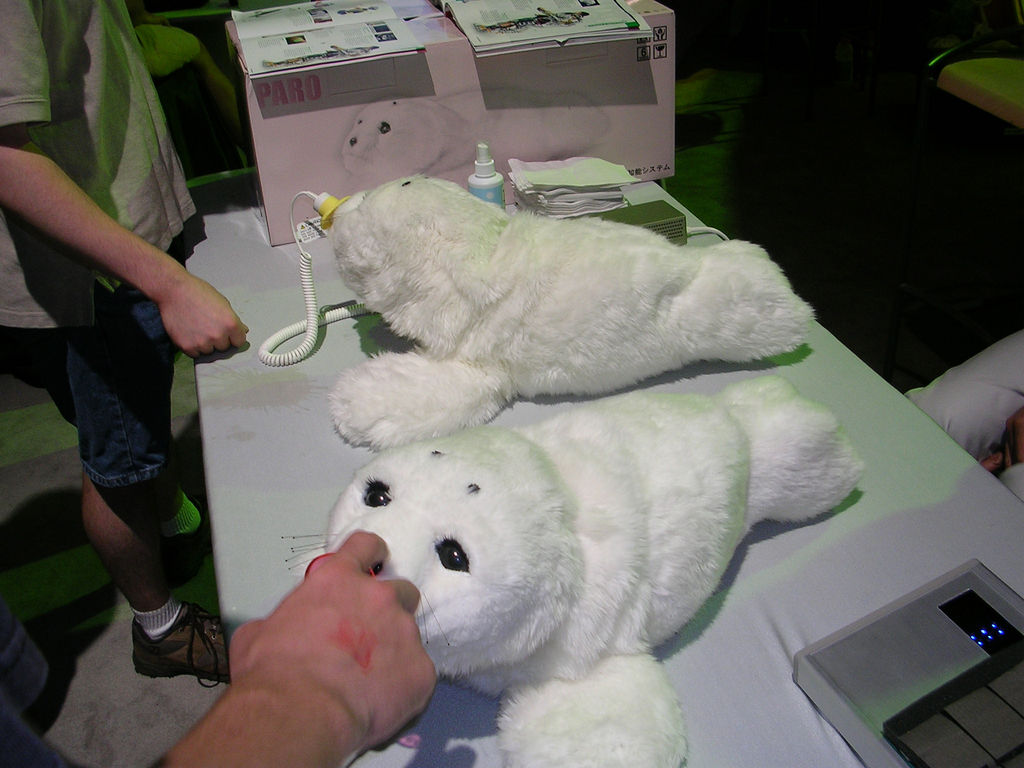

Nursing robots are aimed to provide assistance to
elderly
Old age is the range of ages for people nearing and surpassing life expectancy. People who are of old age are also referred to as: old people, elderly, elders, senior citizens, seniors or older adults. Old age is not a definite biological sta ...
people who may have faced a decline in physical and
cognitive
Cognition is the "mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, ...
function, and, consequently, developed
psychosocial
The psychosocial approach looks at individuals in the context of the combined influence that psychological factors and the surrounding social environment have on their physical and mental wellness and their ability to function. This approach is ...
issues.
By assisting in daily physical activities, physical assistance from the robots would allow the elderly to have a sense of
autonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy is the capacity to make an informed, uncoerced decision. Autonomous organizations or institutions are independent or self-governing. Autonomy can also be ...
and feel that they are still able to take care of themselves and stay in their own homes.
Long-term research on human-robot interaction could show that residents of care home are willing to interact with humanoid robots and benefit from cognitive and physical activation that is led by the robot Pepper. Another long-term study in a care home could show that people working in the care sector are willing to use robots in their daily work with the residents.
But it also revealed that even though that the robots are ready to be used, they do need human assistants, they cannot replace the human work force but they can assist them and give them new possibilities.
In addition to supporting care recipients, robots are also being studied as a source of support for their caregivers. A study found that informal caregivers who engaged in repeated self-disclosure to a social robot experienced reduced stress and loneliness, improved mood, and greater acceptance of their caregiving roles, suggesting potential benefits of social robots as emotional support tools for caregivers.
Social robots
Autism intervention
Over the past decade, human–robot interaction has shown promising outcomes in autism intervention.
Children with
autism spectrum disorders
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by differences or difficulties in social communication and interaction, a preference for predictability and routine, sensory processing di ...
(ASD) are more likely to connect with robots than humans, and using
social robot
A social robot is an autonomous robot that interacts and Human–robot interaction, communicates with humans or other autonomous physical Intelligent agent, agents by following social behaviors and rules attached to its role. Like other robots, ...
s is considered to be a beneficial approach to help these children with ASD.
However, social robots that are used to intervene in children's ASD are not viewed as viable treatment by clinical communities because the study of using social robots in ASD intervention, often, does not follow standard research protocol.
In addition, the outcome of the research could not demonstrate a consistent positive effect that could be considered as
evidence-based practice
Evidence-based practice is the idea that occupational practices ought to be based on scientific evidence. The movement towards evidence-based practices attempts to encourage and, in some instances, require professionals and other decision-makers ...
(EBP) based on the clinical systematic evaluation.
As a result, the researchers have started to establish guidelines which suggest how to conduct studies with robot-mediated intervention and hence produce reliable data that could be treated as EBP that would allow clinicians to choose to use robots in ASD intervention.
Education robots
Robots can become tutors or peers in the classroom. When acting as a tutor, the robot can provide instruction, information and also individual attention to student. When acting as a peer learner, the robot can enable "learning by teaching" for students.
Rehabilitation
Robots can be configured as collaborative robot and can be used for rehabilitation of users with motor impairment. Using various interactive technologies like automatic
speech recognition
Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers. It is also ...
, eye gaze tracking and so on, users with motor impairment can control robotic agents and use it for rehabilitation activities like powered wheelchair control, object manipulation and so on.
Automatic driving
A specific example of human–robot interaction is the human-vehicle interaction in automated driving. The goal of human-vehicle cooperation is to ensure safety, security, and comfort in
automated driving system
Vehicular automation is using technology to assist or replace the operator of a vehicle such as a car, truck, aircraft, rocket, military vehicle, or boat. Assisted vehicles are ''semi-autonomous'', whereas vehicles that can travel without a ...
s.
The continued improvement in this system and the progress in advancements towards highly and fully automated vehicles aim to make the driving experience safer and more efficient in which humans do not need to intervene in the driving process when there is an unexpected driving condition such as a pedestrian walking across the street when it is not supposed to.

Search and rescue
Unmanned aerial vehicles
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) or unmanned aircraft system (UAS), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft with no human pilot, crew, or passengers onboard, but rather is controlled remotely or is autonomous.De Gruyter Handbook of Dron ...
(UAV) and
unmanned underwater vehicles
An uncrewed vehicle or unmanned vehicle is a vehicle without a person on board. Uncrewed vehicles can either be under telerobotic control—remote controlled or remote guided vehicles—or they can be autonomously controlled—autonomous vehicl ...
(UUV) have the potential to assist search and rescue work in
wilderness area
Wilderness or wildlands (usually in the plural) are Earth's natural environments that have not been significantly modified by human activity, or any nonurbanized land not under extensive agricultural cultivation. The term has traditionally ...
s, such as locating a missing person remotely from the evidence that they left in surrounding areas.
The system integrates autonomy and information, such as
coverage map
Coverage maps are designed to indicate the service areas of radiocommunication transmitting stations. Typically these may be produced for radio or television
Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images a ...
s, GPS information and quality search video, to support humans performing the
search and rescue
Search and rescue (SAR) is the search for and provision of aid to people who are in distress or imminent danger. The general field of search and rescue includes many specialty sub-fields, typically determined by the type of terrain the search ...
work efficiently in the given limited time.

Space exploration
Humans have been working on achieving the next breakthrough in space exploration, such as a crewed mission to Mars.
This challenge identified the need for developing planetary rovers that are able to assist astronauts and support their operations during their mission.
The collaboration between rovers, UAVs, and humans enables leveraging capabilities from all sides and optimizes task performance.
Agricultural robots
Human labor has been greatly used in agriculture but
Agricultural robots like milking robots have been adopted in large-scale farming. Hygiene is the main issue in the agri-food sector and the invention of this technology has widely impacted agriculture. Robots can also be used in tasks that might be hazardous to human health like in the application of chemicals to plants.
See also
Robotics
*
Autonomous robot
An autonomous robot is a robot that acts without recourse to human control. Historic examples include space probes. Modern examples include self-driving Robotic vacuum cleaner, vacuums and Self-driving car, cars.
Industrial robot, Industrial robot ...
s
*
Cobot
A cobot, or collaborative robot, also known as a companion robot, is a robot intended for direct human-robot interaction within a shared space, or where humans and robots are in close proximity. Cobot applications contrast with traditional industr ...
s
*
Gesture recognition
Gesture recognition is an area of research and development in computer science and language technology concerned with the recognition and interpretation of human gestures. A subdiscipline of computer vision, it employs mathematical algorithms to ...
*
Humanoid robot
A humanoid robot is a robot resembling the human body in shape. The design may be for functional purposes, such as interacting with human tools and environments and working alongside humans, for experimental purposes, such as the study of bipeda ...
s
*
Human–robot collaboration Human-Robot Collaboration is the study of collaborative processes in human and robot agents work together to achieve shared goals. Many new applications for robots require them to work alongside people as capable members of human-robot teams. These ...
*
Mobile robot
A mobile robot is an automatic machine that is capable of locomotion.Hu, J.; Bhowmick, P.; Lanzon, A.,Group Coordinated Control of Networked Mobile Robots with Applications to Object Transportation IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 202 ...
s
*
Motion planning
Motion planning, also path planning (also known as the navigation problem or the piano mover's problem) is a computational problem to find a sequence of valid configurations that moves the object from the source to destination. The term is used ...
*
Personal robot
A personal robot is one whose human interface and design make it useful for individuals. This is by contrast to industrial robots which are generally configured and operated by robotics specialists. A personal robot is one that enables an indivi ...
*
Robot simulations
*
Robot teams
*
Social robot
A social robot is an autonomous robot that interacts and Human–robot interaction, communicates with humans or other autonomous physical Intelligent agent, agents by following social behaviors and rules attached to its role. Like other robots, ...
Technology
*
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
*
CAPTCHA
Completely Automated Public Turing Test to tell Computers and Humans Apart (CAPTCHA) ( ) is a type of challenge–response authentication, challenge–response turing test used in computing to determine whether the user is human in order to de ...
*
Computer supported collaborative work
*
Dialog management
*
Face detection
Face detection is a computer technology being used in a variety of applications that identifies human faces in digital images. Face detection also refers to the psychological process by which humans locate and attend to faces in a visual scene ...
*
Haptic technology
Haptic technology (also kinaesthetic communication or 3D touch) is technology that can create an experience of touch by applying forces, vibrations, or motions to the user. These technologies can be used to create virtual objects in a computer s ...
*
Human–computer interaction
Human–computer interaction (HCI) is the process through which people operate and engage with computer systems. Research in HCI covers the design and the use of computer technology, which focuses on the interfaces between people (users) and comp ...
*
Interactive Systems Engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering and engineering management that focuses on how to design, integrate, and manage complex systems over their life cycles. At its core, systems engineering utilizes systems thinking ...
*
Multimodal interaction
Multimodal interaction provides the user with multiple modes of interacting with a system. A multimodal interface provides several distinct tools for input and output of data.
Multimodal human-computer interaction involves natural communicati ...
*
Natural-language understanding
Natural language understanding (NLU) or natural language interpretation (NLI) is a subset of natural language processing in artificial intelligence that deals with machine reading comprehension. NLU has been considered an AI-hard problem.
The ...
*
Telematics
Telematics is an interdisciplinary field encompassing telecommunications, vehicular technologies (road transport, road safety, etc.), electrical engineering (sensors, instrumentation, wireless communications, etc.), and computer science (multimedia ...
*
Face recognition
A facial recognition system is a technology potentially capable of matching a human face from a digital image or a Film frame, video frame against a database of faces. Such a system is typically employed to authenticate users through ID verif ...
*
Human sensing
Human sensing (also called human detection or human presence detection) encompasses a range of technologies for detecting the presence of a human body in an area of space, typically without the intentional participation of the detected person. Com ...
Psychology
* Anthropomorphism and the
uncanny valley
The effect is a hypothesized psychological and aesthetic relation between an object's degree of resemblance to a human being and the emotional response to the object. The uncanny valley hypothesis predicts that an entity appearing almost huma ...
Properties
Bartneck and Okada suggest that a robotic user interface can be described by the following four properties:
; Tool – toy scale
* Is the system designed to solve a problem effectively or is it just for entertainment?
;
Remote control
A remote control, also known colloquially as a remote or clicker, is an consumer electronics, electronic device used to operate another device from a distance, usually wirelessly. In consumer electronics, a remote control can be used to operat ...
– autonomous scale
* Does the robot require remote control or is it capable of action without direct human influence?
; Reactive – dialogue scale
* Does the robot rely on a fixed interaction pattern or is it able to have dialogue — exchange of information — with a human?
; Anthropomorphism scale
* Does it have the shape or properties of a human?
Conferences
ACE – International Conference on Future Applications of AI, Sensors, and Robotics in Society
The International Conference on Future Applications of AI, Sensors, and Robotics in Society explore the state of the art research, highlighting the future challenges as well as the hidden potential behind the technologies. The accepted contributions to this conference will be published annually in the special edition of the Journal of Future Robot Life.
International Conference on Social Robotics
The International Conference on Social Robotics is a conference for scientists, researchers, and practitioners to report and discuss the latest progress of their forefront research and findings in social robotics, as well as interactions with human beings and integration into our society.
* ICSR2009, Incheon, Korea in collaboration with the FIRA RoboWorld Congress
* ICSR2010, Singapore
* ICSR2011, Amsterdam, Netherlands
International Conference on Human–Robot Personal Relationships
* HRPR2008, Maastricht
* HRPR 2009, Tilburg. Keynote speaker was
Hiroshi Ishiguro
is a Japanese roboticist and engineer. He is the director of the Intelligent Robotics Laboratory, part of the Department of Systems Innovation in the Graduate School of Engineering Science at Osaka University, Japan. A notable development of the ...
.
* HRPR2010, Leiden. Keynote speaker was
Kerstin Dautenhahn
Kerstin Dautenhahn (born 1964) is a German computer scientist specializing in social robotics and human–robot interaction. She is a professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Waterloo, where she holds the Canada 150 ...
.
International Congress on Love and Sex with Robots
The International Congress on Love and Sex with Robots is an annual congress that invites and encourages a broad range of topics, such as AI, Philosophy, Ethics, Sociology, Engineering, Computer Science, Bioethics.
The earliest academic papers on the subject were presented at the 2006 E.C. Euron Roboethics Atelier, organized by the School of Robotics in Genoa, followed a year later by the first book – "Love and Sex with Robots" – published by Harper Collins in New York. Since that initial flurry of academic activity in this field the subject has grown significantly in breadth and worldwide interest. Three conferences on Human–Robot Personal Relationships were held in the Netherlands during the period 2008–2010, in each case the proceedings were published by respected academic publishers, including Springer-Verlag. After a gap until 2014 the conferences were renamed as the "International Congress on Love and Sex with Robots", which have previously taken place at the University of Madeira in 2014; in London in 2016 and 2017; and in Brussels in 2019. Additionally, the Springer-Verlag "International Journal of Social Robotics", had, by 2016, published articles mentioning the subject, and an open access journal called "Lovotics" was launched in 2012, devoted entirely to the subject. The past few years have also witnessed a strong upsurge of interest by way of increased coverage of the subject in the print media, TV documentaries and feature films, as well as within the academic community.
The International Congress on Love and Sex with Robots provides an excellent opportunity for academics and industry professionals to present and discuss their innovative work and ideas in an academic symposium.
* 2020, Berlin, Germany
* 2019, Brussels, Belgium
* 2017, London, United Kingdom
* 2016, London, United Kingdom
* 2014, Madeira, Portugal
International Symposium on New Frontiers in Human–Robot Interaction
This symposium is organized in collaboration with the Annual Convention of the Society for the Study of Artificial Intelligence and Simulation of Behaviour.
* 2015, Canterbury, United Kingdom
* 2014, London, United Kingdom
* 2010, Leicester, United Kingdom
* 2009, Edinburgh, United Kingdom
IEEE International Symposium in Robot and Human Interactive Communication
The IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication ( RO-MAN ) was founded in 1992 by Profs. Toshio Fukuda, Hisato Kobayashi, Hiroshi Harashima and Fumio Hara. Early workshop participants were mostly Japanese, and the first seven workshops were held in Japan. Since 1999, workshops have been held in Europe and the United States as well as Japan, and participation has been of international scope.
ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human–Robot Interaction
This conference is amongst the best conferences in the field of HRI and has a very selective reviewing process. The average acceptance rate is 26% and the average attendance is 187. Around 65% of the contributions to the conference come from the US and the high level of quality of the submissions to the conference becomes visible by the average of 10 citations that the HRI papers attracted so far.
* HRI 2006 in
Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City, often shortened to Salt Lake or SLC, is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Utah. It is the county seat of Salt Lake County, the most populous county in the state. The city is the core of the Salt Lake Ci ...
, Utah, USA, Acceptance Rate: 0.29
* HRI 2007 in
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
, USA, Acceptance Rate: 0.23
* HRI 2008 in
Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , ; ; ) is the capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, largest city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It has a population of 933,680 in June 2024 within the city proper, 1,457,018 in the City Re ...
, Netherlands, Acceptance Rate: 0.36 (0.18 for oral presentations)
* HRI 2009 in
San Diego
San Diego ( , ) is a city on the Pacific coast of Southern California, adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a population of over 1.4 million, it is the List of United States cities by population, eighth-most populous city in t ...
, CA, USA, Acceptance Rate: 0.19
* HRI 2010 in
Osaka
is a Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the List of cities in Japan, third-most populous city in J ...
, Japan, Acceptance Rate: 0.21
* HRI 2011 in
Lausanne
Lausanne ( , ; ; ) is the capital and largest List of towns in Switzerland, city of the Swiss French-speaking Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Vaud, in Switzerland. It is a hilly city situated on the shores of Lake Geneva, about halfway bet ...
, Switzerland, Acceptance Rate: 0.22 for full papers
* HRI 2012 in
Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, Massachusetts, USA, Acceptance Rate: 0.25 for full papers
* HRI 2013 in
Tokyo
Tokyo, officially the Tokyo Metropolis, is the capital of Japan, capital and List of cities in Japan, most populous city in Japan. With a population of over 14 million in the city proper in 2023, it is List of largest cities, one of the most ...
, Japan, Acceptance Rate: 0.24 for full papers
* HRI 2014 in
Bielefeld
Bielefeld () is a city in the Ostwestfalen-Lippe Region in the north-east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population of 341,755, it is also the most populous city in the administrative region () of Detmold (region), Detmold and the L ...
, Germany, Acceptance Rate: 0.24 for full papers
* HRI 2015 in
Portland, Oregon
Portland ( ) is the List of cities in Oregon, most populous city in the U.S. state of Oregon, located in the Pacific Northwest region. Situated close to northwest Oregon at the confluence of the Willamette River, Willamette and Columbia River, ...
, USA, Acceptance Rate: 0.25 for full papers
* HRI 2016 in
Christchurch
Christchurch (; ) is the largest city in the South Island and the List of cities in New Zealand, second-largest city by urban area population in New Zealand. Christchurch has an urban population of , and a metropolitan population of over hal ...
, New Zealand, Acceptance Rate: 0.25 for full papers
* HRI 2017 in
Vienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. ...
, Austria, Acceptance Rate: 0.24 for full papers
* HRI 2018 in
Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
, USA, Acceptance Rate: 0.24 for full papers
* HRI 2021 in
Boulder
In geology, a boulder (or rarely bowlder) is a rock fragment with size greater than in diameter. Smaller pieces are called cobbles and pebbles. While a boulder may be small enough to move or roll manually, others are extremely massive. In ...
, USA, Acceptance Rate: 0.23 for full papers
International Conference on Human–Agent Interaction
* HAI 2013 in
Sapporo
is a Cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, designated city in Hokkaido, Japan. Located in the southwest of Hokkaido, it lies within the alluvial fan of the Toyohira River, a tributary of the Ishikari River. Sapporo is the capital ...
, Japan
* HAI 2014 in
Tsukuba
is a city located in Ibaraki Prefecture, Japan. As of January 1, 2024, the city had an estimated population of 256,526 in 121,001 households and a population density of 900 persons per km2. The percentage of the population aged over 65 wa ...
, Japan
* HAI 2015 in
Daegu
Daegu (; ), formerly spelled Taegu and officially Daegu Metropolitan City (), is a city in southeastern South Korea. It is the third-largest urban agglomeration in South Korea after Seoul and Busan; the fourth-largest List of provincial-level ci ...
, Korea
* HAI 2016 in Singapore
* HAI 2017 in
Bielefeld
Bielefeld () is a city in the Ostwestfalen-Lippe Region in the north-east of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population of 341,755, it is also the most populous city in the administrative region () of Detmold (region), Detmold and the L ...
, Germany
Related conferences
There are many conferences that are not exclusively HRI, but deal with broad aspects of HRI, and often have HRI papers presented.
* IEEE-RAS/RSJ International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids)
* Ubiquitous Computing (UbiComp)
* IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)
* Intelligent User Interfaces (IUI)
* Computer Human Interaction (CHI)
* American Association for Artificial Intelligence (AAAI)
* INTERACT
Journals
There are currently two dedicated HRI Journals
* ''ACM Transactions on Human–Robot Interaction'' (Originally Journal of Human–Robot Interaction)
* ''International Journal of Social Robotics''
and there are several more general journals in which one will find HRI articles.
* ''
International Journal of Humanoid Robotics
The ''International Journal of Humanoid Robotics'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed
Peer review is the evaluation of work by one or more people with similar competencies as the producers of the work ( peers). It functions as a form of self-regulat ...
''
* ‘Entertainment robotics’ section of the ''Entertainment Computing Journal''
* ''Interaction Studies Journal''
*
''Artificial Intelligence''
* ''Systems, Man and Cybernetics''
Books
There are several books available that specialise on Human–Robot Interaction. While there are several edited books, only a few dedicated texts are available:
*
– free PDF available online
*
* – chapter in an extensive handbook.
Courses
Many universities offer courses in Human–Robot Interaction.
University Courses and Degrees
*
Tufts University
Tufts University is a private research university in Medford and Somerville, Massachusetts, United States, with additional facilities in Boston and Grafton, as well as Talloires, France. Tufts also has several Doctor of Physical Therapy p ...
, Medford, MA, USA, MS and PhD programs in Human–Robot Interaction
*
University of Waterloo
The University of Waterloo (UWaterloo, UW, or Waterloo) is a Public university, public research university located in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. The main campus is on of land adjacent to uptown Waterloo and Waterloo Park. The university also op ...
, Canada, Kerstin Dautenhahn, Social Robotics – Foundations, Technology and Applications of Human-Centered Robotics
*
National Taipei University
National Taipei University (NTPU; ), founded in 1949, is a national university in Taiwan. Before 2000, the university was named the College of Law and Business, National Chung Hsing University (). The university's main campus is in Sanxia Distr ...
in Taiwan, Taiwan, Hooman Samani, M5226 Advanced Robotics
*
Ontario Tech University
The University of Ontario Institute of Technology, branded as Ontario Tech University or Ontario Tech, is a public university, public research university located in Oshawa, Ontario, Canada. The university's main campus is located on approximately ...
, Canada, Patrick C. K. Hung, BUSI4590U Topics in Technology Management & INFR 4599U Service Robots Innovation for Commerce
* The
Colorado School of Mines
The Colorado School of Mines (Mines) is a public research university in Golden, Colorado, United States. Founded in 1874, the school offers both undergraduate and graduate degrees in engineering, science, and mathematics, with a focus on ener ...
, USA, Tom Williams, CSCI 436 / 536: Human–Robot Interaction
*
Heriot-Watt University
Heriot-Watt University () is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. It was established in 1821 as the School of Arts of Edinburgh, the world's first mechanics' institute, and was subsequently granted university status by roya ...
, UK, Lynne Baillie, F21HR Human Robot Interaction
*
Uppsala University
Uppsala University (UU) () is a public university, public research university in Uppsala, Sweden. Founded in 1477, it is the List of universities in Sweden, oldest university in Sweden and the Nordic countries still in operation.
Initially fou ...
, Sweden, Filip Malmberg, UU-61611 Social Robotics and Human–Robot Interaction
*
Skövde University
Skövde () is a locality and urban centre in Skövde Municipality and Västra Götaland County, in the Västergötland (Western Gothland region) in central southern Sweden.
Skövde is situated around 150 km northeast of Gothenburg, between Swe ...
, Sweden, MSc Human–Robot Interaction program
*
Indiana University
Indiana University (IU) is a state university system, system of Public university, public universities in the U.S. state of Indiana. The system has two core campuses, five regional campuses, and two regional centers under the administration o ...
, Bloomington, USA, Selma Sabanovic, INFO-I 440 Human–Robot Interaction
*
Ghent University
Ghent University (, abbreviated as UGent) is a Public university, public research university located in Ghent, in the East Flanders province of Belgium.
Located in Flanders, Ghent University is the second largest Belgian university, consisting o ...
, Belgium, Tony Belpaeme, E019370A Robotics module
*
Bielefeld University
Bielefeld University () is a public university in Bielefeld, Germany. Founded in 1969, it is one of the country's newer universities, and considers itself a "reform" university, following a different style of organization and teaching than the e ...
, Germany, Frederike Eyssel, 270037 Sozialpsychologische Aspekte der Mensch-Maschine Interaktion
*
Kyoto University
, or , is a National university, national research university in Kyoto, Japan. Founded in 1897, it is one of the former Imperial Universities and the second oldest university in Japan.
The university has ten undergraduate faculties, eighteen gra ...
, Japan, Takayuki Kanda, 3218000 Human–Robot Interaction (ヒューマンロボットインタラクション)
*
KTH Royal Institute of Technology
KTH Royal Institute of Technology (), abbreviated KTH, is a Public university, public research university in Stockholm, Sweden. KTH conducts research and education in Institute of technology, engineering and technology and is Sweden's largest te ...
, Sweden, Iolanda Leite, DD2413 Social Robotics
*
Chalmers University of Technology
Chalmers University of Technology (, commonly referred to as Chalmers) is a private university, private research university located in Gothenburg, Sweden. Chalmers focuses on engineering and science, but more broadly it also conducts research ...
, Sweden, Mohammad Obaid, DAT545 Human-Robot Interaction Design
Online Courses and Degrees
There are also online courses available such as
Mooc
A massive open online course (MOOC ) or an open online course is an online course aimed at unlimited participation and open access via the World Wide Web, Web. In addition to traditional course materials, such as filmed lectures, readings, and p ...
:
*
University of Canterbury
The University of Canterbury (UC; ; postnominal abbreviation ''Cantuar.'' or ''Cant.'' for ''Cantuariensis'', the Latin name for Canterbury) is a public research university based in Christchurch, New Zealand. It was founded in 1873 as Canterbur ...
(UCx) – edX program
** Professional Certificate in Human–Robot Interaction
** Introduction to Human–Robot Interaction
** Methods and Application in Human–Robot Interaction
Footnotes
References
External resources
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Human-Robot Interaction
Human communication
Multimodal interaction
Robotics
Robotics engineering
 Robots are
Robots are 
 Major manufacturers lik
Major manufacturers lik A rehabilitation robot is an example of a robot-aided system implemented in
A rehabilitation robot is an example of a robot-aided system implemented in  Nursing robots are aimed to provide assistance to
Nursing robots are aimed to provide assistance to 
