Human Parasites on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Human parasites are divided into endoparasites, which cause infection inside the body, and ectoparasites, which cause infection superficially within the skin. Parasites in general are hosts-dependent organisms that obtain nutrients while potentially harming their host in the process.
Parasitic infections cause global health concerns because they impact billions of people throughout the world at different disease severity. These infections split into the three main categories of protozoa and helminths (parasitic worms) alongside ectoparasites. Over 30% of global human population is affected by the roundworm "Ascaris lumbricoides". The incidence of certain parasitic diseases including malaria and schistosomiasis continue to rise year after year. The AIDS epidemic has worsened the situation by causing elevated rates of parasitic opportunistic infections to affect mainly weak-immune people through conditions such as cryptosporidiosis, Pneumocystis pneumonia and strongyloidiasis. Refugees and infected people moving between high-prevalence regions cause an increase in parasitic diseases to appear in places that were previously free from these infections. Public health system must develop improved strategies, as parasitic diseases continue to pose a persistent challenge to global health.
The cysts and eggs of endoparasites may be found in
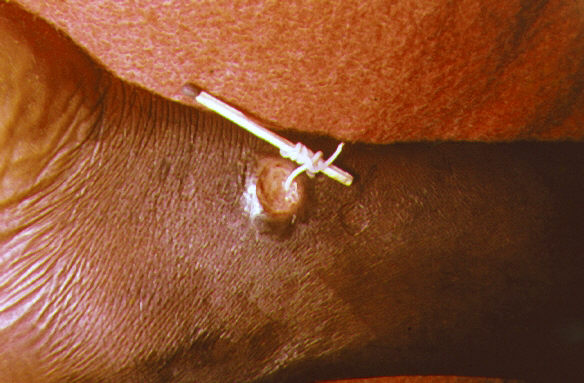 * ''
* ''
feces
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the ...
, which aids in the detection of the parasite in the human host while also providing the means for the parasitic species to exit the current host and enter other hosts. Although there are a number of ways in which humans can contract parasitic infections, observing basic hygiene and cleanliness tips can reduce its probability.
The most accurate diagnosis is by qPcr DNA antigen assay, not generally available by primary care physicians in the USA: most labs offer research only service.
History
Archaeological evidence
It was assumed that early human ancestors generally had parasites, but until recently there was no evidence to support this claim. Generally, the discovery of parasites in ancient humans relies on the study of feces and otherfossilized
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
material. The earliest known parasite in a human was eggs of the lung fluke found in fossilized feces in northern Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
and is estimated to be from around 5900 BC. There are also claims of hookworm
Hookworms are Gastrointestinal tract, intestinal, Hematophagy, blood-feeding, parasitic Nematode, roundworms that cause types of infection known as helminthiases. Hookworm infection is found in many parts of the world, and is common in areas with ...
eggs from around 5000 BC in Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
and large roundworm
The nematodes ( or ; ; ), roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. Species in the phylum inhabit a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but many are parasitic. Parasitic worms (hel ...
eggs from around 2330 BC in Peru. Tapeworm
Eucestoda, commonly referred to as tapeworms, is the larger of the two subclasses of flatworms in the class Cestoda (the other subclass being Cestodaria). Larvae have six posterior hooks on the scolex (head), in contrast to the ten-hooked Ce ...
eggs have also been found present in Egyptian
''Egyptian'' describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of year ...
mummies
A mummy is a dead human or an animal whose soft tissues and Organ (biology), organs have been preserved by either intentional or accidental exposure to Chemical substance, chemicals, extreme cold, very low humidity, or lack of air, so that the ...
dating from around 2000 BC, 1250 BC, and 1000 BC along with a well preserved and calcified female worm inside of a mummy.Cox, Francis E. G. "History of human parasitic diseases." ''Infectious Disease Clinics of North America'' June 2004
Written evidence
The first written records of parasites date from 3000 to 400 BC in Egyptianpapyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can a ...
records. They identify parasites such as roundworms, Guinea worm
''Dracunculus medinensis'' (Guinea worm, dragon worm, fiery serpent) is a nematode that causes dracunculiasis, also known as Guinea worm disease. The disease is caused by the female which, at around in length, is among the longest nematodes ...
s, threadworms, and some tapeworms of unknown varieties. In ancient Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
, Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; ; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician and philosopher of the Classical Greece, classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally referr ...
and Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
documented several parasites in his collection of works Corpus Hippocraticus. In this book, they documented the presence of worms and other parasites inside of fish, domesticated animals, and humans. The bladder worm is well documented in its presence in pigs along with the larval stages of a tapeworm (''Taenia solium
''Taenia solium'', the pork tapeworm, belongs to the cyclophyllid cestode family Taeniidae. It is found throughout the world and is most common in countries where pork is eaten. It is a tapeworm that uses humans (''Homo sapiens'') as its definit ...
''). These tapeworms were mentioned in a play by Aristophanes
Aristophanes (; ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Ancient Greek comedy, comic playwright from Classical Athens, Athens. He wrote in total forty plays, of which eleven survive virtually complete today. The majority of his surviving play ...
as "hailstones" with Aristotle in the section about pig diseases in his book ''History of Animals
''History of Animals'' (, ''Ton peri ta zoia historion'', "Inquiries on Animals"; , "History of Animals") is one of the major texts on biology by the ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle. It was written in sometime between the mid-fourth centur ...
''. The cysts of the ''Echinococcus granulosus
''Echinococcus granulosus'', also called the hydatid worm or dog tapeworm, is a cyclophyllid cestode that dwells in the small intestine of canids as an adult, but which has important intermediate hosts such as livestock and humans, where it caus ...
'' tapeworm were also well known in ancient cultures mainly because of their presence in slaughtered and sacrificed animals.
The major parasitic disease that has been documented in early records is dracunculiasis
Dracunculiasis, also called Guinea-worm disease, is a parasitic infection by the Guinea worm ('' Dracunculus medinensis).'' A person becomes infected by drinking water contaminated with Guinea-worm larvae that reside inside copepods (a typ ...
. This disease is caused by the Guinea worm and is characterized by the female worm emerging from the leg. This symptom is so specific to the disease that it is mentioned in many texts and plays that predate 1000 AD.
Greece and Rome
In Greece, Hippocrates and Aristotle created considerable medical documentation about parasites in the Corpus Hippocraticus. In this work, they documented the presence of parasitic worms in many animals ranging from fish to domesticated animals and humans. Among the most extensively documented was the Bladder Worm (Taenia solium). This condition was called "measly pork" when present in pigs and was characterized by the presence of thelarval
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase ...
stages of the Bladder Worm in muscle tissue. This disease was also mentioned by the playwright Aristophanes when he referred to "hailstones" in one of his plays. This naming convention is also reflected by Aristotle when he refers to "bladders that are like hailstones."
Another worm that was commonly written about in ancient Greek texts was the tapeworm ''Echinococccus granulosus''. This worm was distinguished by the presence of "massive cysts" in the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
of animals. This condition was documented so well mainly because of its presence in slaughtered and sacrificed animals. It was documented by several different cultures of the time other than the Greeks including the Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
, Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
, and Babylonians
Babylonia (; , ) was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as an Akkadian-populated but Amorite-ru ...
.
Not many parasitic diseases were identified in ancient Greek and Roman texts mainly because the symptoms for parasitic diseases are shared with many other illnesses such as the flu
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
, the common cold
The common cold, or the cold, is a virus, viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract that primarily affects the Respiratory epithelium, respiratory mucosa of the human nose, nose, throat, Paranasal sinuses, sinuses, and larynx. ...
, and dysentery
Dysentery ( , ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications may include dehyd ...
. However, several diseases such as Dracunculiasis
Dracunculiasis, also called Guinea-worm disease, is a parasitic infection by the Guinea worm ('' Dracunculus medinensis).'' A person becomes infected by drinking water contaminated with Guinea-worm larvae that reside inside copepods (a typ ...
(Guinea worm disease), Hookworm, Elephantiasis
Elephantiasis, often incorrectly called elephantitis, is the enlargement and hardening of limbs or body parts due to tissue swelling (edema). It is characterised by edema, hypertrophy, and fibrosis of skin and subcutaneous tissues, due to obstru ...
, Schistosomiasis
Schistosomiasis, also known as snail fever, bilharzia, and Katayama fever is a neglected tropical helminthiasis, disease caused by parasitism, parasitic Schistosoma, flatworms called schistosomes. It affects both humans and animals. It affects ...
, Malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
, and Amebiasis
Amoebiasis, or amoebic dysentery, is an infection of the intestines caused by a parasitic amoeba ''Entamoeba histolytica''. Amoebiasis can be present with no, mild, or severe symptoms. Symptoms may include lethargy, loss of weight, colonic ulc ...
cause unique and specific symptoms and are well documented because of this. The most documented by far was Guinea worm disease mainly because the grown female worm emerges from the skin, which causes considerable irritation, and which cannot really be ignored. This particular disease is widely accepted to also be the "fiery serpents" written about in the Old Testament of the Bible
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) originally writt ...
. This disease was mentioned by Hippocrates in Greece along with Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
, Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus (; September 129 – AD), often Anglicization, anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Ancient Rome, Roman and Greeks, Greek physician, surgeon, and Philosophy, philosopher. Considered to be one o ...
, Aetius of Amida, and Paulus Aegineta
Paul of Aegina or Paulus Aegineta (; Aegina, ) was a 7th-century Byzantine Greek physician best known for writing the medical encyclopedia ''Medical Compendium in Seven Books.'' He is considered the “Father of Early Medical Writing”. For many ...
of Alexandria in Rome. Strangely, this disease was never present in Greece even though it was documented.
Northern Africa, the Middle East, and Mesopotamia
The medieval Persian doctorAvicenna
Ibn Sina ( – 22 June 1037), commonly known in the West as Avicenna ( ), was a preeminent philosopher and physician of the Muslim world, flourishing during the Islamic Golden Age, serving in the courts of various Iranian peoples, Iranian ...
records the presence of several parasites
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The en ...
in animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s and in his patient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by Health professional, healthcare professionals. The patient is most often Disease, ill or Major trauma, injured and in need of therapy, treatment by a physician, nurse, op ...
s including Guinea worm
''Dracunculus medinensis'' (Guinea worm, dragon worm, fiery serpent) is a nematode that causes dracunculiasis, also known as Guinea worm disease. The disease is caused by the female which, at around in length, is among the longest nematodes ...
, threadworms, tapeworms
Cestoda is a class of parasitic worms in the flatworm phylum (Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, commonly known as tapeworms. Their bodies con ...
, and the Ascaris worm. This followed a tradition of Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
medical writings spanning over 1000 years in the area near the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
. However, the Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
never made the connection between parasites
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The en ...
and the disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical condi ...
s they caused.
As with Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
and Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
texts, the Guinea worm
''Dracunculus medinensis'' (Guinea worm, dragon worm, fiery serpent) is a nematode that causes dracunculiasis, also known as Guinea worm disease. The disease is caused by the female which, at around in length, is among the longest nematodes ...
is very well documented in Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
ern medical texts. Several Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
n document
A document is a writing, written, drawing, drawn, presented, or memorialized representation of thought, often the manifestation of nonfiction, non-fictional, as well as fictional, content. The word originates from the Latin ', which denotes ...
s in the library
A library is a collection of Book, books, and possibly other Document, materials and Media (communication), media, that is accessible for use by its members and members of allied institutions. Libraries provide physical (hard copies) or electron ...
of King Ashurbanipal
Ashurbanipal (, meaning " Ashur is the creator of the heir")—or Osnappar ()—was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 669 BC to his death in 631. He is generally remembered as the last great king of Assyria. Ashurbanipal inherited the th ...
refer to an affliction that has been interpreted as Guinea worm disease
Dracunculiasis, also called Guinea-worm disease, is a parasitic infection by the Dracunculus medinensis, Guinea worm (''Dracunculus medinensis).'' A person becomes infected by drinking Water pollution, water contaminated with Guinea-worm larv ...
.
In Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, the Ebers Papyrus
The Ebers Papyrus, also known as Papyrus Ebers, is an Egyptian medical papyrus of herbal knowledge dating to (the late Second Intermediate Period or early New Kingdom). Among the oldest and most important medical papyri of Ancient Egypt, it ...
contains one of the few references to hookworm
Hookworms are Gastrointestinal tract, intestinal, Hematophagy, blood-feeding, parasitic Nematode, roundworms that cause types of infection known as helminthiases. Hookworm infection is found in many parts of the world, and is common in areas with ...
disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical condi ...
in ancient texts. This disease does not have very specific symptom
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition.
Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences.
A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature ...
s and was vaguely mentioned. However vague the reference, it is one of the few that connect the disease to the hookworm parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted str ...
. Another documented disease is elephantiasis. Symptoms of this disease are highly visible, since it causes extreme swelling in the limbs, breasts, and genitals
A sex organ, also known as a reproductive organ, is a part of an organism that is involved in sexual reproduction. Sex organs constitute the primary sex characteristics of an organism. Sex organs are responsible for producing and transporting ...
. A number of surviving statue
A statue is a free-standing sculpture in which the realistic, full-length figures of persons or animals are carved or Casting (metalworking), cast in a durable material such as wood, metal or stone. Typical statues are life-sized or close to ...
s indicate that Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''wikt:pr ꜥꜣ, pr ꜥꜣ''; Meroitic language, Meroitic: 𐦲𐦤𐦧, ; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') was the title of the monarch of ancient Egypt from the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty ( ...
Mentuhotep II
Mentuhotep II (, meaning "Mentu is satisfied"), also known under his Prenomen (Ancient Egypt), prenomen Nebhepetre (, meaning "The Lord of the rudder is Ra"), was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh, the sixth ruler of the Eleventh Dynasty of Egypt, Elev ...
is likely to have suffered from elephantiasis. This disease was well known to Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
physician
A physician, medical practitioner (British English), medical doctor, or simply doctor is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the Medical education, study, Med ...
s and Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( – 22 June 1037), commonly known in the West as Avicenna ( ), was a preeminent philosopher and physician of the Muslim world, flourishing during the Islamic Golden Age, serving in the courts of various Iranian peoples, Iranian ...
, who noted specific differences between elephantiasis and leprosy
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease (HD), is a Chronic condition, long-term infection by the bacteria ''Mycobacterium leprae'' or ''Mycobacterium lepromatosis''. Infection can lead to damage of the Peripheral nervous system, nerves, respir ...
.
China
TheChinese
Chinese may refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people identified with China, through nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**Han Chinese, East Asian ethnic group native to China.
**'' Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic ...
mostly documented diseases rather than the parasites associated with them. Chinese texts contain one of the few references to hookworm disease found in ancient records, but no connection to the hookworm parasite is made. The Emperor Huang Ti recorded the earliest mentioning (2700 BC) of malaria in his text Nei Ching. He lists chills, headaches, and fevers as the main symptoms and distinguished between the different kinds of fevers.
India
InIndia
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, the Charaka Samhita
The ''Charaka Samhita'' () is a Sanskrit text on Ayurveda (Indian traditional medicine). Along with the '' Sushruta Samhita'', it is one of the two foundational texts of this field that have survived from ancient India. It is one of the three w ...
and Sushruta Samhita
The ''Sushruta Samhita'' (, ) is an ancient Sanskrit text on medicine and one of the most important such treatises on this subject to survive from the ancient world. The ''Compendium of Sushruta, Suśruta'' is one of the foundational texts of ...
document malaria. These documents list the main symptoms as fever and enlarged spleens. The Bhrigu Samhita
The ''Bhṛgu Saṃhitā'' is a Saṃskṛta astrological ( Jyotisha) treatise attributed in its introduction to Bhrigu, one of the " Saptarshis" ("seven sages") of the Vedic period. Its introductory chapter states that it was compiled by th ...
from 1000 BCE makes the earliest reference to Amebiasis. The symptoms were given as bloody and mucosal diarrhea.
Most common parasites
As of 2013, the parasites causing the most deaths globally were as follows:Commonly documented parasites
Endoparasites
Protozoa
* ''Plasmodium
''Plasmodium'' is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes that are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. The life cycles of ''Plasmodium'' species involve development in a Hematophagy, blood-feeding insect host (biology), host which then inj ...
'' spp.: causes malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
* ''Entamoeba
''Entamoeba'' is a genus of Amoebozoa found as internal parasites or commensals of animals. In 1875, Fedor Lösch described the first proven case of amoebic dysentery in St. Petersburg, Russia. He referred to the amoeba he observed microscopica ...
'': causes amoebiasis
Amoebiasis, or amoebic dysentery, is an infection of the intestines caused by a parasitic amoeba '' Entamoeba histolytica''. Amoebiasis can be present with no, mild, or severe symptoms. Symptoms may include lethargy, loss of weight, colon ...
* ''Giardia
''Giardia'' ( or ) is a genus of anaerobic flagellated protozoan parasites of the phylum Metamonada that colonise and reproduce in the small intestines of several vertebrates, causing the disease giardiasis. Their life cycle alternates be ...
'': causes giardiasis
Giardiasis is a parasitic disease caused by the protist enteropathogen ''Giardia duodenalis'' (also known as ''G. lamblia'' and ''G. intestinalis''), especially common in children and travellers. Infected individuals experience steatorrhea, a typ ...
* ''Trypanosoma brucei
''Trypanosoma brucei'' is a species of parasitic Kinetoplastida, kinetoplastid belonging to the genus ''Trypanosoma'' that is present in sub-Saharan Africa. Unlike other protozoan parasites that normally infect blood and tissue cells, it is excl ...
'': causes African trypanosomiasis
African trypanosomiasis is an insect-borne parasitic infection of humans and other animals.
Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, is caused by the species ''Trypanosoma bru ...
* ''Toxoplasma gondii
''Toxoplasma gondii'' () is a species of parasitic alveolate that causes toxoplasmosis. Found worldwide, ''T. gondii'' is capable of infecting virtually all warm-blooded animals, but members of the cat family (felidae) are the only known d ...
'': causes toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by ''Toxoplasma gondii'', an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis are associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric and behavioral conditions. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or month ...
* ''Acanthamoeba
''Acanthamoeba'' is a genus of amoeboid, amoebae that are commonly recovered from soil, fresh water, and other habitat (ecology), habitats.
The genus ''Acanthamoeba'' has two stages in its life cycle, the metabolically active trophozoite stage a ...
'': causes acanthamoeba keratitis
''Acanthamoeba'' keratitis (AK) is a rare disease in which amoebae of the genus ''Acanthamoeba'' invade the clear portion of the front (cornea) of the human eye, eye. It affects roughly 100 people in the United States each year. ''Acanthamoeba'' ...
* ''Leishmania
''Leishmania'' () is a genus of parasitic protozoans, single-celled eukaryotic organisms of the trypanosomatid group that are responsible for the disease leishmaniasis. The parasites are transmitted by sandflies of the genus '' Phlebotomus'' ...
'': causes leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by protozoal parasites of the Trypanosomatida genus ''Leishmania''. It is generally spread through the bite of Phlebotominae, phlebotomine Sandfly, sandflies, ''Phlebotomus'' an ...
* ''Babesia
''Babesia'', also called ''Nuttallia'', is an apicomplexan parasite that infects red blood cells and is transmitted by ticks. Originally discovered by Romanian bacteriologist Victor Babeș in 1888; over 100 species of ''Babesia'' have since ...
'': causes babesiosis
Babesiosis or piroplasmosis is a malaria-like parasitic disease caused by infection with a eukaryotic parasite in the order Piroplasmida, typically a ''Babesia'' or '' Theileria'', in the phylum Apicomplexa. Human babesiosis transmission via ...
* ''Balamuthia mandrillaris
''Balamuthia mandrillaris'' is a free-living amoeba that causes the rare but deadly neurological condition granulomatous amoebic encephalitis (GAE). ''B. mandrillaris'' is a soil-dwelling amoeba and was first discovered in 1986 in the brain of ...
'': causes granulomatous amoebic encephalitis
Granulomatous amoebic encephalitis (GAE) is a rare, often fatal, subacute-to-chronic central nervous system disease caused by certain species of free-living amoebae of the genera ''Acanthamoeba'', ''Balamuthia mandrillaris, Balamuthia'' and ''Sa ...
* ''Cryptosporidium
''Cryptosporidium'', sometimes called crypto, is an apicomplexan genus of alveolates which are parasitism, parasites that can cause a respiratory and gastrointestinal illness (cryptosporidiosis) that primarily involves watery diarrhea (inte ...
'': causes cryptosporidiosis
Cryptosporidiosis, sometimes informally called crypto, is a parasitic disease caused by ''Cryptosporidium'', a genus of protozoan parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa. It affects the ileum, distal small intestine and can affect the respiratory tr ...
* ''Cyclospora
''Cyclospora'' is a genus of apicomplexan parasites. It includes the species ''Cyclospora cayetanensis'', the causative agent of cyclosporiasis. Members of ''Cyclospora'' are characterized as having oocysts with two sporocysts, each containing ...
'': causes cyclosporiasis
* ''Naegleria fowleri
''Naegleria fowleri'', also known as the brain-eating amoeba, is a species of the genus ''Naegleria''. It belongs to the phylum Percolozoa and is classified as an amoeboflagellate Excavata, excavate, an organism capable of behaving as both an ...
'': causes primary amoebic meningoencephalitis
Naegleriasis, also known as primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM), is an almost invariably fatal infection of the brain by the free-living protozoan '' Naegleria fowleri''. Symptoms include headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, a stiff neck, ...
Parasitic worms (helminths)
 * ''
* ''Ascaris lumbricoides
''Ascaris lumbricoides'' is a large parasitic worm, parasitic Nematoda, roundworm of the genus ''Ascaris.'' It is the most common parasitic worm in humans. An estimated 807 million–1.2 billion people are infected with ''Ascaris lumbricoides'' ...
'': causes ascariasis
Ascariasis is a disease caused by the parasitic roundworm ''Ascaris lumbricoides''. Infections have no symptoms in more than 85% of cases, especially if the number of worms is small. Symptoms increase with the number of worms present and may in ...
* Pinworm: causes enterobiasis
Pinworm infection (threadworm infection in the UK), also known as enterobiasis, is a human parasitic disease caused by the pinworm (parasite), pinworm, ''Enterobius vermicularis''. The most common symptom is pruritus ani, or itching in the Human ...
* ''Strongyloides stercoralis
''Strongyloides stercoralis'' is a human pathogenic parasitic roundworm causing the disease strongyloidiasis. Its common name in the US is threadworm. In the UK and Australia, however, the term ''threadworm'' can also refer to nematodes of t ...
'': causes trongyloidiasis
* ''Toxocara
The Toxocaridae are a zoonotic family of parasitic nematodes that infect canids and felids and which cause toxocariasis in humans ( visceral larva migrans and ocular larva migrans). The worms are unable to reproduce in humans.
Notable species ...
'': causes toxocariasis
Toxocariasis is an illness of humans caused by the dog roundworm ('' Toxocara canis'') and, less frequently, the cat roundworm ('' Toxocara cati'').https://academic.oup.com/ajcp/article/142/suppl_1/A104/1771175 Eosinophilic Pseudoleukemia Due to ...
* Guinea worm
''Dracunculus medinensis'' (Guinea worm, dragon worm, fiery serpent) is a nematode that causes dracunculiasis, also known as Guinea worm disease. The disease is caused by the female which, at around in length, is among the longest nematodes ...
: causes dracunculiasis
Dracunculiasis, also called Guinea-worm disease, is a parasitic infection by the Guinea worm ('' Dracunculus medinensis).'' A person becomes infected by drinking water contaminated with Guinea-worm larvae that reside inside copepods (a typ ...
.Greenaway, C. "Dracunculiasis". ''Canadian Medical Association Journal'' (Feb 2004)
* Hookworm
Hookworms are Gastrointestinal tract, intestinal, Hematophagy, blood-feeding, parasitic Nematode, roundworms that cause types of infection known as helminthiases. Hookworm infection is found in many parts of the world, and is common in areas with ...
: causes helminthiasis
Helminthiasis, also known as worm infection, is any macroparasite, macroparasitic disease of humans and other animals in which a part of the body is infected with parasitism, parasitic worms, known as helminths. There are numerous species of the ...
* Tapeworm
Eucestoda, commonly referred to as tapeworms, is the larger of the two subclasses of flatworms in the class Cestoda (the other subclass being Cestodaria). Larvae have six posterior hooks on the scolex (head), in contrast to the ten-hooked Ce ...
(Eucestoda): causes cysticercosis
Cysticercosis is a tissue infection caused by the young form of the pork tapeworm. People may have few or no symptoms for years. In some cases, particularly in Asia, solid lumps of between one and two centimeters may develop under the skin. Af ...
, echinococcosis
Echinococcosis is a parasitic disease caused by tapeworms of the ''Echinococcus'' type. The two main types of the disease are ''cystic echinococcosis'' and ''alveolar echinococcosis''. Less common forms include ''polycystic echinococcosis'' an ...
, hymenolepiasis
Hymenolepiasis is infestation by one of two species of tapeworm: '' Hymenolepis nana'' or '' H. diminuta''. Alternative names are dwarf tapeworm infection and rat tapeworm infection. The disease is a type of helminthiasis which is classified as a ...
, diphyllobothriasis
Diphyllobothriasis is the infection caused by tapeworms of the genus '' Diphyllobothrium'' (commonly '' D. latum'' and ''D. nihonkaiense'').
Diphyllobothriasis mostly occurs in regions where raw fish is regularly consumed; those who consume raw f ...
and sparganosis
Sparganosis is a parasitic infection caused by the plerocercoid larvae of the genus '' Spirometra'' including '' S. mansoni'', '' S. ranarum'', '' S. mansonoides'' and '' S. erinacei''.John, D.T. and Petri, W.A. Markell and Voge's Medical Parasit ...
* Whipworm
''Trichuris trichiura, Trichocephalus trichiuris'' or whipworm, is a parasitic roundworm (a type of helminth) that causes trichuriasis (a type of helminthiasis which is one of the neglected tropical diseases) when it infects a human large intest ...
(''Trichuris trichiura''): causes trichuriasis
Trichuriasis, also known as whipworm infection, is an infection by the parasitic worm '' Trichuris trichiura'' (whipworm). If the infection is only with a few worms, there are often no symptoms. In those who are infected with many worms, there ...
Parasitic flukes
* ''Schistosoma
''Schistosoma'' is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are Parasitism, parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed ''schistosomiasis'', which is considered by the World H ...
'': causes schistosomiasis
Schistosomiasis, also known as snail fever, bilharzia, and Katayama fever is a neglected tropical helminthiasis, disease caused by parasitism, parasitic Schistosoma, flatworms called schistosomes. It affects both humans and animals. It affects ...
* ''Gnathostoma
''Gnathostoma'' is a genus of parasitic nematode
The nematodes ( or ; ; ), roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. Species in the phylum inhabit a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microor ...
'': causes gnathostomiasis
* '' Paragonimus'': causes paragonimiasis
Paragonimiasis is a food-borne parasitic disease caused by several species of lung flukes belonging to genus '' Paragonimus''. Infection is acquired by eating crustaceans such as crabs and crayfishes which host the infective forms called metacerc ...
* ''Fasciola hepatica
''Fasciola hepatica'', also known as the common liver fluke or sheep liver fluke, is a parasitism, parasitic trematode (fluke (flatworm), fluke or flatworm, a type of helminth) of the class (biology), class Trematoda, phylum Platyhelminthes. It ...
'': causes fascioliasis
Fasciolosis is a parasitic worm infection caused by the common liver fluke ''Fasciola hepatica'' as well as by '' Fasciola gigantica''. The disease is a plant-borne trematode zoonosis, and is classified as a neglected tropical disease (NTD). I ...
* ''Trichobilharzia regenti
''Trichobilharzia regenti'' is a neuropathogenic parasitic flatworm of birds which also causes cercarial dermatitis in humans. The species was originally described in 1998 in the Czech Republic and afterwards it was detected also in other Europ ...
'': causes cercarial dermatitis
Swimmer's itch, cercarial dermatitis or schistosome dermatitis is a short-term allergic contact dermatitis occurring in the skin of humans that have been infected by water-borne schistosomes, a type of flatworm. It is common in freshwater, brac ...
Other organisms
*New World screwworm
''Cochliomyia'' is a genus in the family Calliphoridae, known as blowflies, in the order Diptera. ''Cochliomyia'' is commonly referred to as the New World screwworm flies, as distinct from Old World screwworm flies. Four species are in this ge ...
(''Cochliomyia''): causes myiasis
Ectoparasites
*Head louse
The head louse (''Pediculus humanus capitis'') is an obligate parasite, obligate parasitism, ectoparasite of humans. Head lice are wingless insects that spend their entire lives on the human scalp and feed exclusively on human blood. Humans are ...
(''Pediculus humanus capitis'') causes pediculosis
Pediculosis is an infestation of lice from the sub-order Anoplura, family Pediculidae. Accordingly, the infestation with head lice is named pediculosis capitis, while this with body lice, pediculosis corporis. Although ''pediculosis'' in humans ...
*Body louse
The body louse (''Pediculus humanus humanus'', also known as ''Pediculus humanus corporis'') or the cootie is a hematophagic ectoparasite louse that infests humans. It is one of three lice which infest humans, the other two being the head lo ...
(''Pediculus humanus humanus''): causes pediculosis
*Crab louse
The crab louse or pubic louse (''Pthirus pubis'') is an insect that is an obligate parasite, obligate Parasitism#Basic concepts, ectoparasite of humans, feeding exclusively on blood. The crab louse usually is found in the person's pubic hair. A ...
(''Pthirus pubis):'' causes phthiriasis
''Pediculosis pubis'' (also known as "crabs" and "pubic lice") is an infestation by the pubic louse, ''Pthirus pubis'', a wingless insect which feeds on blood and lays its eggs (nits) on mainly pubic hair. Less commonly, hair near the anus, ...
* Human botfly maggot (''Dermatobia hominis''): causes myiasis
Myiasis ( ), also known as flystrike or fly strike, is the parasitic infestation of the body of a live animal by fly larvae (maggots) that grow inside the host while feeding on its Biological tissue, tissue. Although flies are most commonly attr ...
*Flea
Flea, the common name for the order (biology), order Siphonaptera, includes 2,500 species of small flightless insects that live as external parasites of mammals and birds. Fleas live by hematophagy, ingesting the blood of their hosts. Adult f ...
(Siphonaptera): causes papular urticaria
* Chigoe flea (''Tunga penetrans''): causes tungiasis
Tungiasis is an inflammatory skin disease caused by infection with the female ectoparasitic ''Tunga penetrans'', a flea also known as the chigoe, chigo, chigoe flea, chigo flea, jigger, nigua, sand flea, or burrowing flea (and not to be confused ...
*Mosquito
Mosquitoes, the Culicidae, are a Family (biology), family of small Diptera, flies consisting of 3,600 species. The word ''mosquito'' (formed by ''Musca (fly), mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish and Portuguese for ''little fly''. Mos ...
(Culicidae): causes papular urticaria
*Bed bug (''Cimex lectularius
''Cimex lectularius'', or the common bed bug, is a species of Cimicidae. Its primary hosts are humans, and it is one of the world's major "nuisance pests."
Although bed bugs can be infected with at least 28 human pathogens, no studies have fou ...
''): causes papular urticaria
*Tick
Ticks are parasitic arachnids of the order Ixodida. They are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, and species, but can become larger when engorged. Ticks a ...
( Ixodoidea): causes papular urticaria
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a kind of skin rash with red or flesh-colored, raised, itchy bumps. Hives may burn or sting. The patches of rash may appear on different body parts, with variable duration from minutes to days, and typically ...
*Chiggers
''Trombicula'', known as chiggers, red bugs, scrub-itch mites, or berry bugs, are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods) in the Trombiculidae family. In their larval stage, they attach to various animals and humans, then feed on skin, often ...
(Trombiculidae): causes trombiculosis
Trombiculosis is a rash caused by trombiculid mites, especially those of the genus '' Trombicula'' (chiggers). The rash is also often known as chigger bites.
__NOTOC__
Chiggers are commonly found on the tip of blades of grasses to catch a host ...
*Scabies mite
''Sarcoptes scabiei'' (/sɑː''r''ˈkɒptiːz skeɪˈbiːaɪ/ Traditional English pronunciation of Latin) or the itch mite is a parasitic mite found in all parts of the world that burrows into skin and causes scabies. Humans become infested by ...
(''Sarcoptes scabiei)'': causes scabies
Scabies (; also sometimes known as the seven-year itch) is a contagious human skin infestation by the tiny (0.2–0.45 mm) mite ''Sarcoptes scabiei'', variety ''hominis''. The word is from . The most common symptoms are severe itchiness a ...
* Red mite (''Dermanyssus gallinae''): causes gamasoidosis
Gamasoidosis, also known as dermanyssosis, is a frequently unrecognized form of zoonotic dermatitis, following human infestation with avian mites of the genera ''Dermanyssus'' or ''Ornithonyssus''. It is characterized by pruritic erythematous pa ...
* Tropical fowl mite (''Ornithonyssus bursa''): causes gamasoidosis
* Northern fowl mite (''Ornithonyssus sylviarum''): causes gamasoidosis
*Tropical rat mite (''Ornithonyssus bacoti
''Ornithonyssus bacoti'' (also known as the tropical rat mite and formerly called Liponyssus bacoti) is a hematophagous parasite. It feeds on blood and serum from many hosts. ''O. bacoti'' can be found and cause disease on rats and wild rodents m ...
''): causes rodent mite dermatitis
*Spiny rat mite ('' Laelaps echidnina''): causes rodent mite dermatitis
*House mouse mite (''Liponyssoides sanguineus
''Liponyssoides sanguineus'' is a species of mite that infests the house mouse (''Mus musculus'').
It can transmit human disease, is associated with causing rodent mite dermatitis in humans and is noted for carrying '' Rickettsia akari'', which ...
''): causes rodent mite dermatitis
*Demodex mite
''Demodex'' is a genus of tiny mites that live in or near hair follicles of mammals. Around 65 species of ''Demodex'' are known. Two species live on humans: '' Demodex folliculorum'' and '' Demodex brevis'', both frequently referred to as eyela ...
: associated with acne vulgaris
Acne ( ), also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, ...
and rosacea
Rosacea is a long-term skin condition that typically affects the face. It results in redness, pimples, swelling, and small and superficial dilated blood vessels. Often, the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin are most involved. A red, en ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Human Parasites