The history of the
graphical user interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such ...
, understood as the use of graphic
icons
An icon () is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, in the cultures of the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, Catholic, and Lutheran churches. The most common subjects include Jesus, Mary, saints, and angels. Although especially ...
and a pointing device to control a
computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
, covers a five-decade span of incremental refinements, built on some constant core principles. Several vendors have created their own windowing systems based on independent
code
In communications and information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes shortened or secret, for communication through a communicati ...
, but with basic elements in common that define the
WIMP
WiMP is a music streaming service available on mobile devices, tablets, network players and computers. WiMP, standing for "Wireless Music Player," was a music streaming service that emphasized high-quality audio. WiMP offered music and podcast ...
"window, icon, menu and pointing device" paradigm.
There have been important technological achievements, and enhancements to the general interaction in small steps over previous systems. There have been a few significant breakthroughs in terms of use, but the same organizational
metaphors
A metaphor is a figure of speech that, for rhetorical effect, directly refers to one thing by mentioning another. It may provide, or obscure, clarity or identify hidden similarities between two different ideas. Metaphors are usually meant to cr ...
and interaction
idioms
An idiom is a phrase or expression that largely or exclusively carries a figurative or non-literal meaning, rather than making any literal sense. Categorized as formulaic language, an idiomatic expression's meaning is different from the lit ...
are still in use.
Desktop computers are often controlled by computer mice and/or keyboards while laptops often have a
pointing stick or
touchpad
A touchpad or trackpad is a type of pointing device. Its largest component is a tactile sensor: an electronic device with a flat surface, that detects the motion and position of a user's fingers, and translates them to 2D motion, to control a Cu ...
, and smartphones and tablet computers have a
touchscreen
A touchscreen (or touch screen) is a type of electronic visual display, display that can detect touch input from a user. It consists of both an input device (a touch panel) and an output device (a visual display). The touch panel is typically l ...
. The influence of game computers and
joystick
A joystick, sometimes called a flight stick, is an input device consisting of a stick that pivots on a base and reports its angle or direction to the device it is controlling. Also known as the control column, it is the principal control devic ...
operation has been omitted.
Early research and developments

Early dynamic information devices such as
radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
displays, where input devices were used for direct control of computer-created data, set the basis for later improvements of graphical interfaces. Some early
cathode-ray-tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms on an oscilloscope, ...
(CRT) screens used a
light pen
A light pen is a computer input device in the form of a light-sensitive wand used in conjunction with a computer's cathode-ray tube (CRT) display.
It allows the user to point to displayed objects or draw on the screen in a similar way to a to ...
, rather than a mouse, as the pointing device.
The concept of a multi-panel windowing system was introduced by the first real-time graphic display systems for computers: the
SAGE Project and
Ivan Sutherland
Ivan Edward Sutherland (born May 16, 1938) is an American computer scientist and Internet pioneer, widely regarded as a pioneer of computer graphics. His early work in computer graphics as well as his teaching with David C. Evans in that subje ...
's
Sketchpad
Sketchpad (a.k.a. Robot Draftsman) is a computer program written by Ivan Sutherland in 1963 in the course of his PhD thesis, for which he received the Turing Award in 1988, and the Kyoto Prize in 2012. It pioneered human–computer interaction ...
.
Augmentation of Human Intellect (NLS)
In the 1960s,
Douglas Engelbart
Douglas Carl Engelbart (January 30, 1925 – July 2, 2013) was an American engineer, inventor, and a pioneer in many aspects of computer science. He is best known for his work on founding the field of human–computer interaction, particularly ...
's
Augmentation of Human Intellect project at the
Augmentation Research Center
SRI International's Augmentation Research Center (ARC) was founded in the 1960s by electrical engineer Douglas Engelbart to develop and experiment with new tools and techniques for collaboration and information processing.
The main product to ...
at
SRI International
SRI International (SRI) is a nonprofit organization, nonprofit scientific research, scientific research institute and organization headquartered in Menlo Park, California, United States. It was established in 1946 by trustees of Stanford Univer ...
in
Menlo Park, California
Menlo Park ( ) is a city at the eastern edge of San Mateo County, California, San Mateo County in the San Francisco Bay Area of California, United States. It is bordered by San Francisco Bay on the north and east; East Palo Alto, California, Eas ...
developed the
oN-Line System (NLS). This computer incorporated a mouse-driven cursor and multiple windows used to work on
hypertext
Hypertext is E-text, text displayed on a computer display or other electronic devices with references (hyperlinks) to other text that the reader can immediately access. Hypertext documents are interconnected by hyperlinks, which are typic ...
. Engelbart had been inspired, in part, by the
memex
A memex (from "memory expansion") is a hypothetical electromechanical device for interacting with microform documents and described in Vannevar Bush's 1945 article " As We May Think". Bush envisioned the memex as a device in which individuals w ...
desk-based information machine suggested by
Vannevar Bush
Vannevar Bush ( ; March 11, 1890 – June 28, 1974) was an American engineer, inventor and science administrator, who during World War II, World War II headed the U.S. Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD), through which almo ...
in 1945.
Much of the early research was based on how young children learn. So, the design was based on the childlike characteristics of
hand–eye coordination, rather than use of
command language
A command language is a language for job control in computing. It is a domain-specific and interpreted language; common examples of a command language are shell or batch programming languages.
These languages can be used directly at the ...
s, user-defined
macro procedures, or automated transformation of data as later used by adult professionals.
Engelbart publicly demonstrated this work at the
Association for Computing Machinery
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) is a US-based international learned society for computing. It was founded in 1947 and is the world's largest scientific and educational computing society. The ACM is a non-profit professional membe ...
/
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an American 501(c)(3) public charity professional organization for electrical engineering, electronics engineering, and other related disciplines.
The IEEE has a corporate office ...
(ACM/IEEE)—Computer Society's
Fall Joint Computer Conference in
San Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
on December 9, 1968. It was so-called
The Mother of All Demos
"The Mother of All Demos" was a landmark computer demonstration, named retroactively, of developments by Stanford Research Institute's Augmentation Research Center. It was presented at the Association for Computing Machinery / Institute of Ele ...
.

The development of computers having multiple overlapping and resizable windows on a "desktop" is commonly, and incorrectly, attributed to
Xerox PARC
Future Concepts division (formerly Palo Alto Research Center, PARC and Xerox PARC) is a research and development company in Palo Alto, California. It was founded in 1969 by Jacob E. "Jack" Goldman, chief scientist of Xerox Corporation, as a div ...
and its
Alto
The musical term alto, meaning "high" in Italian (Latin: '' altus''), historically refers to the contrapuntal part higher than the tenor and its associated vocal range. In four-part voice leading alto is the second-highest part, sung in ch ...
. The Xerox Alto's windowing system was inspired by the DNLS (Display NLS)'s overlapping multi-windowing system, which was operational by early 1973 and used at several
ARPA locations.
In the DNLS, overlapping windows were referred to as "display areas" and could store multiple lines of strings.
In 1971, the screen could only be split into two display areas, vertically or horizontally; by early 1973, the full overlapping windowing system was implemented, and was capable of displaying on an
Imlac PDS-1.
The Xerox Alto greatly improved upon this system by adding the capability to display bitmapped images, buttons, and other graphics in these windows, as opposed to the DNLS's overlapping display areas which could only display strings of text.
Xerox PARC
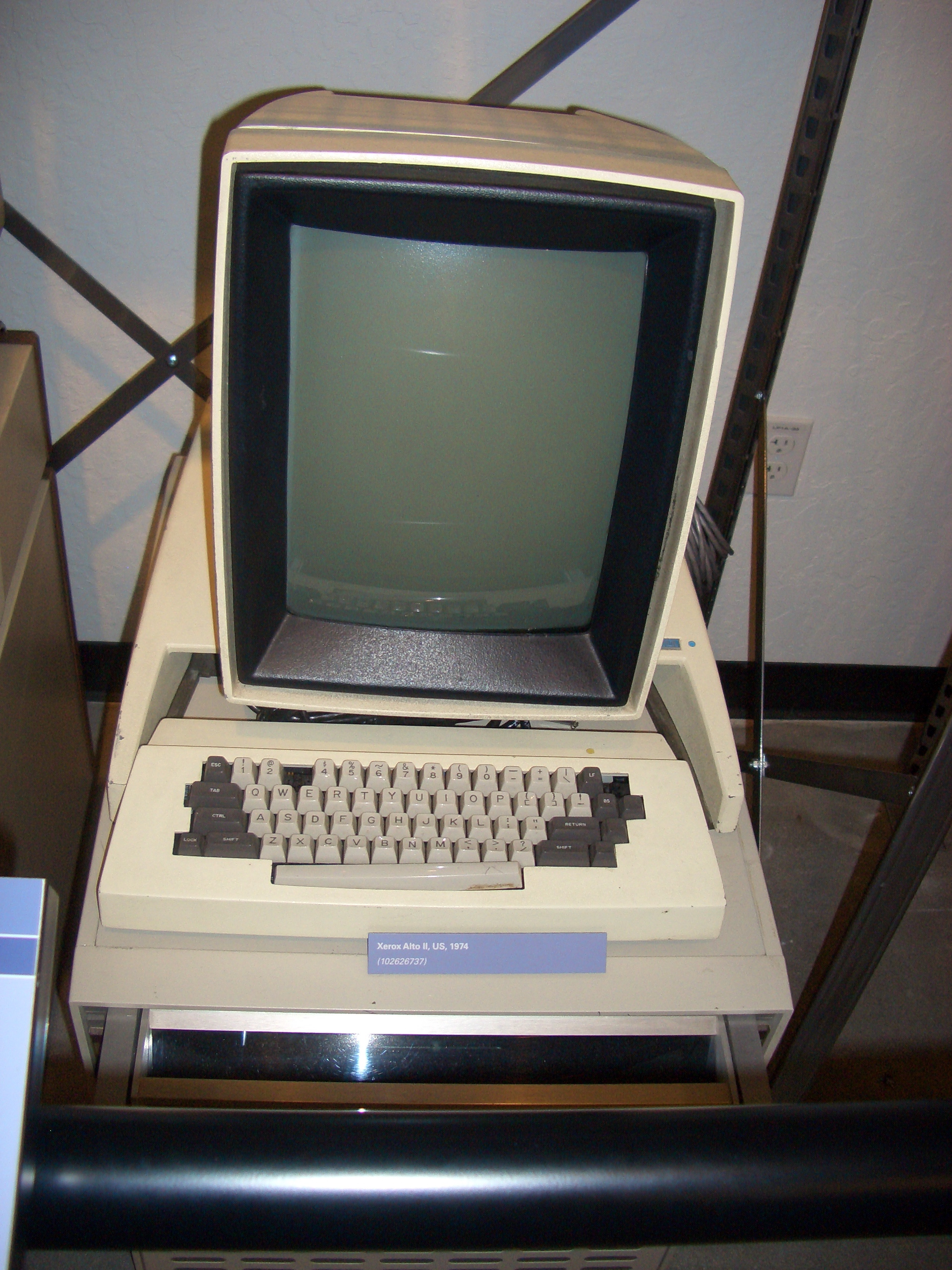

led to the advances at
Xerox PARC
Future Concepts division (formerly Palo Alto Research Center, PARC and Xerox PARC) is a research and development company in Palo Alto, California. It was founded in 1969 by Jacob E. "Jack" Goldman, chief scientist of Xerox Corporation, as a div ...
. Several people went from SRI to Xerox PARC in the early 1970s.
In 1973, Xerox PARC developed the
Alto
The musical term alto, meaning "high" in Italian (Latin: '' altus''), historically refers to the contrapuntal part higher than the tenor and its associated vocal range. In four-part voice leading alto is the second-highest part, sung in ch ...
personal computer. It had a
bitmapped screen, and was the first computer to demonstrate the
desktop metaphor
In computing, the desktop metaphor is an interface metaphor which is a set of unifying concepts used by graphical user interfaces to help users interact more easily with the computer. The desktop metaphor treats the computer monitor as if it is ...
and
graphical user interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such ...
(GUI). Several thousand units were built and were heavily used at PARC, as well as other XEROX offices, and at several universities for many years. The Alto greatly influenced the design of personal computers during the late 1970s and early 1980s, notably the
Three Rivers PERQ, the
Apple Lisa
Lisa is a desktop computer developed by Apple, produced from January 19, 1983, to August 1, 1986, and succeeded by Macintosh. It is generally considered the first mass-market personal computer operable through a graphical user interface (GUI). I ...
and
Macintosh
Mac is a brand of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 1984. The name is short for Macintosh (its official name until 1999), a reference to the McIntosh (apple), McIntosh apple. The current product lineup inclu ...
, and the first
Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
workstations.
The modern
WIMP
WiMP is a music streaming service available on mobile devices, tablets, network players and computers. WiMP, standing for "Wireless Music Player," was a music streaming service that emphasized high-quality audio. WiMP offered music and podcast ...
GUI was first developed at Xerox PARC by
Alan Kay
Alan Curtis Kay (born May 17, 1940) published by the Association for Computing Machinery 2012 is an American computer scientist who pioneered work on object-oriented programming and windowing graphical user interface (GUI) design. At Xerox ...
,
Larry Tesler
Lawrence Gordon Tesler (April 24, 1945 – February 16, 2020) was an American computer scientist who worked in the field of human–computer interaction. Tesler worked at Xerox PARC, Apple Inc., Apple, Amazon.com, Amazon, and Yahoo!.
While at PA ...
,
Dan Ingalls
Daniel Henry Holmes Ingalls Jr. (born 1944) is a pioneer of object-oriented computer programming and the principal architect, designer and implementer of five generations of Smalltalk environments. He designed the bytecoded virtual machine that m ...
,
David Smith,
Clarence Ellis and a number of other researchers. This was introduced in the
Smalltalk
Smalltalk is a purely object oriented programming language (OOP) that was originally created in the 1970s for educational use, specifically for constructionist learning, but later found use in business. It was created at Xerox PARC by Learni ...
programming environment. It used
windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
,
icons
An icon () is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, in the cultures of the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, Catholic, and Lutheran churches. The most common subjects include Jesus, Mary, saints, and angels. Although especially ...
, and
menus (including the first fixed drop-down menu) to support commands such as opening files, deleting files, moving files, etc. In 1974, work began at PARC on Gypsy, the first bitmap What-You-See-Is-What-You-Get (
WYSIWYG
In computing, WYSIWYG ( ), an acronym for what you see is what you get, refers to software that allows content to be edited in a form that resembles its appearance when printed or displayed as a finished product, such as a printed document, web ...
) cut and paste editor. In 1975, Xerox engineers demonstrated a graphical user interface "including icons and the first use of pop-up menus".
In 1981 Xerox introduced a pioneering product,
Star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
, a
workstation
A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or computational science, scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by a single user, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating syste ...
incorporating many of PARC's innovations. Although not commercially successful, Star greatly influenced future developments, for example at
Apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
,
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
and
Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc., often known as Sun for short, was an American technology company that existed from 1982 to 2010 which developed and sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services. Sun contributed sig ...
.
Quantel Paintbox
Released by digital imaging company
Quantel in 1981, the
Paintbox was a color graphical workstation with support for mouse input, but more oriented for
graphics tablet
A graphics tablet (also known as a digitizer, digital graphic tablet, pen tablet, drawing tablet, external drawing pad or digital art board) is a computer input device that enables a user to hand draw or paint images, animations and graphics, w ...
s; this model also was notable as one of the first systems to implement
pop-up menus.
Blit
The
Blit, a graphics terminal, was developed at Bell Labs in 1982.
Lisp machines, Symbolics
Lisp machines originally developed at
MIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of modern technology and sc ...
and later commercialized by
Symbolics
Symbolics, Inc., is a privately held American computer software maker that acquired the assets of the former manufacturing company of the identical name and continues to sell and maintain the Open Genera Lisp (programming language), Lisp sy ...
and other manufacturers, were early high-end single user computer workstations with advanced graphical user interfaces, windowing, and mouse as an input device. First workstations from Symbolics came to market in 1981, with more advanced designs in the subsequent years.
Lisa, Macintosh, and Apple II
Beginning in 1979, started by
Steve Jobs
Steven Paul Jobs (February 24, 1955 – October 5, 2011) was an American businessman, inventor, and investor best known for co-founding the technology company Apple Inc. Jobs was also the founder of NeXT and chairman and majority shareholder o ...
and led by
Jef Raskin
Jef Raskin (born Jeff Raskin; March 9, 1943 – February 26, 2005) was an American human–computer interface expert who conceived and began leading the Macintosh project at Apple in the late 1970s.
Early life and education
Jef Raskin was bo ...
, the
Apple Lisa
Lisa is a desktop computer developed by Apple, produced from January 19, 1983, to August 1, 1986, and succeeded by Macintosh. It is generally considered the first mass-market personal computer operable through a graphical user interface (GUI). I ...
and
Macintosh
Mac is a brand of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 1984. The name is short for Macintosh (its official name until 1999), a reference to the McIntosh (apple), McIntosh apple. The current product lineup inclu ...
teams at
Apple Computer
Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California, in Silicon Valley. It is best known for its consumer electronics, software, and services. Founded in 1976 as Apple Computer Co ...
(which included former members of the Xerox PARC group) continued to develop such ideas. The Lisa, released in 1983, featured a document-centric graphical interface atop an advanced hard disk based OS that featured such things as
preemptive multitasking
In computing, preemption is the act performed by an external scheduler — without assistance or cooperation from the task — of temporarily interrupting an executing task, with the intention of resuming it at a later time. This preemptive sc ...
and
graphically oriented inter-process communication
In computer science, interprocess communication (IPC) is the sharing of data between running Process (computing), processes in a computer system. Mechanisms for IPC may be provided by an operating system. Applications which use IPC are often cat ...
. The comparatively simplified Macintosh, released in 1984 and designed to be lower in cost, was the first commercially successful product to use a multi-panel window interface. A
desktop metaphor
In computing, the desktop metaphor is an interface metaphor which is a set of unifying concepts used by graphical user interfaces to help users interact more easily with the computer. The desktop metaphor treats the computer monitor as if it is ...
was used, in which files looked like pieces of paper, file directories looked like file folders, there were a set of
desk accessories like a calculator, notepad, and alarm clock that the user could place around the screen as desired, and the user could delete files and folders by dragging them to a
trash-can icon on the screen. The Macintosh, in contrast to the Lisa, used a program-centric rather than document-centric design. Apple revisited the document-centric design, in a limited manner, much later with
OpenDoc
OpenDoc is a defunct multi-platform software componentry framework standard created by Apple in the 1990s for compound documents, intended as an alternative to Microsoft's proprietary Object Linking and Embedding (OLE). It is one of Apple's ea ...
.
There is still some controversy over the amount of influence that Xerox's
PARC work, as opposed to previous academic research, had on the GUIs of the
Apple Lisa
Lisa is a desktop computer developed by Apple, produced from January 19, 1983, to August 1, 1986, and succeeded by Macintosh. It is generally considered the first mass-market personal computer operable through a graphical user interface (GUI). I ...
and Macintosh, but it is clear that the influence was extensive, because first versions of Lisa GUIs even lacked icons. These prototype GUIs are at least mouse-driven, but completely ignored the
WIMP
WiMP is a music streaming service available on mobile devices, tablets, network players and computers. WiMP, standing for "Wireless Music Player," was a music streaming service that emphasized high-quality audio. WiMP offered music and podcast ...
( "window, icon, menu, pointing device") concept. Screenshots of first GUIs of Apple Lisa prototypes show the early designs. Apple engineers visited the PARC facilities (Apple secured the rights for the visit by compensating Xerox with a pre-IPO purchase of Apple stock) and a number of PARC employees subsequently moved to Apple to work on the Lisa and Macintosh GUI. However, the Apple work extended PARC's considerably, adding manipulatable icons, and
drag and drop
In computer graphical user interfaces, drag and drop is a pointing device gesture in which the user (computing), user selects a virtual object by "grabbing" it and dragging it to a different location or onto another virtual object. In general, i ...
manipulation of objects in the file system (see
Macintosh Finder) for example. A list of the improvements made by Apple, beyond the PARC interface, can be read at Folklore.org. Jef Raskin warns that many of the reported facts in the history of the PARC and Macintosh development are inaccurate, distorted or even fabricated, due to the lack of usage by historians of direct primary sources.
In 1984, Apple released a television commercial which introduced the Apple Macintosh during the telecast of
Super Bowl XVIII
Super Bowl XVIII was an American football game played on January 22, 1984, at Tampa Stadium between the National Football Conference (NFC) champion and defending Super Bowl XVII champion 1983 Washington Redskins season, Washington Redskins and t ...
by
CBS, with allusions to
George Orwell
Eric Arthur Blair (25 June 1903 – 21 January 1950) was an English novelist, poet, essayist, journalist, and critic who wrote under the pen name of George Orwell. His work is characterised by lucid prose, social criticism, opposition to a ...
's noted novel, ''
Nineteen Eighty-Four
''Nineteen Eighty-Four'' (also published as ''1984'') is a dystopian novel and cautionary tale by the English writer George Orwell. It was published on 8 June 1949 by Secker & Warburg as Orwell's ninth and final completed book. Thematically ...
''. The commercial was aimed at making people think about computers, identifying the user-friendly interface as a personal computer which departed from previous business-oriented systems,
and becoming a signature representation of Apple products.
In 1986, the
Apple II
Apple II ("apple Roman numerals, two", stylized as Apple ][) is a series of microcomputers manufactured by Apple Computer, Inc. from 1977 to 1993. The Apple II (original), original Apple II model, which gave the series its name, was designed ...
was launched with 16-bit CPU and significantly improved graphics and audio. It shipped with a new operating system, Apple GS/OS, with a Finder (software), Finder-like GUI similar to the Macintosh series.
Agat
The Soviet Union-produced Agat (computer), Agat PC featured a graphical interface and a mouse device and was released in 1983.
SGI 1000 series and MEX
Founded 1982,
SGI introduced the
IRIS 1000 Series in 1983.
The first graphical terminals (IRIS 1000) shipped in late 1983, and the corresponding workstation model (IRIS 1400) was released in mid-1984. The machines used an early version of the
MEX windowing system on top of the GL2 Release 1 operating environment. Examples of the MEX user interface can be seen in a 1988 article in the journal "Computer Graphics", while earlier screenshots can not be found. The first commercial GUI-based systems, these did not find widespread use as to their (discounted) academic list price of $22,500 and $35,700 for the IRIS 1000 and IRIS 1400, respectively.
However, these systems were commercially successful enough to start SGI's business as one of the main graphical workstation vendors. In later revisions of graphical workstations, SGI switched to the
X window system
The X Window System (X11, or simply X) is a windowing system for bitmap displays, common on Unix-like operating systems.
X originated as part of Project Athena at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1984. The X protocol has been at ...
, which had been developed starting at
MIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of modern technology and sc ...
since 1984 and which became the standard for UNIX workstations.
Visi On
VisiCorp
VisiCorp, originally Personal Software, was an early personal computer software publisher. Its most famous products were Microchess, Visi On and VisiCalc.
History
Personal Software was founded in 1977 by Dan Fylstra. In 1978, it merged with ...
's
Visi On
Visi On (also known as VisiOn) is an operating environment for IBM PCs and compatibles running DOS, developed by VisiCorp and released in December 1983. Visi On was the first piece of software with a graphical user interface (GUI) for the ...
was a GUI designed to run on DOS for IBM PCs. It was released in December 1983. Visi On had many features of a modern GUI, and included a few that did not become common until many years later. It was fully mouse-driven, used a bit-mapped display for both text and graphics, included on-line help, and allowed the user to open a number of programs at once, each in its own window, and switch between them to multitask. Visi On did not, however, include a graphical file manager. Visi On also demanded a hard drive in order to implement its virtual memory system used for "fast switching", at a time when hard drives were very expensive.
GEM (Graphics Environment Manager)

Digital Research
Digital Research, Inc. (DR or DRI) was a privately held American software company created by Gary Kildall to market and develop his CP/M operating system and related 8-bit, 16-bit and 32-bit systems like MP/M, Concurrent DOS, FlexOS, Multiuser ...
(DRI) created GEM as an add-on program for personal computers. GEM was developed to work with existing
CP/M
CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/Intel 8085, 85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Dig ...
and
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few op ...
compatible operating systems on business computers such as
IBM PC compatible
An IBM PC compatible is any personal computer that is hardware- and software-compatible with the IBM Personal Computer (IBM PC) and its subsequent models. Like the original IBM PC, an IBM PC–compatible computer uses an x86-based central p ...
s. It was developed from DRI software, known as GSX, designed by a former
PARC employee. Its similarity to the
Macintosh
Mac is a brand of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 1984. The name is short for Macintosh (its official name until 1999), a reference to the McIntosh (apple), McIntosh apple. The current product lineup inclu ...
desktop led to a copyright lawsuit from
Apple Computer
Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California, in Silicon Valley. It is best known for its consumer electronics, software, and services. Founded in 1976 as Apple Computer Co ...
, and a settlement which involved some changes to GEM. This was to be the first of a series of "
look and feel
In software design, the look and feel of a graphical user interface comprises aspects of its design, including elements such as colors, shapes, layout, and typefaces (the "look"), as well as the behavior of dynamic elements such as buttons, boxes ...
" lawsuits related to GUI design in the 1980s.
GEM received widespread use in the consumer market from 1985, when it was made the default user interface built into the
Atari TOS
TOS (The Operating System) is the operating system of the Atari ST range of computers. This range includes the 520ST and 1040ST, their STF/M/FM and STE variants and the Mega ST/STE. Later, 32-bit machines ( TT, Falcon030) were developed using a ...
operating system of the
Atari ST
Atari ST is a line of personal computers from Atari Corporation and the successor to the company's Atari 8-bit computers, 8-bit computers. The initial model, the Atari 520ST, had limited release in April–June 1985, and was widely available i ...
line of personal computers. It was also bundled by other computer manufacturers and distributors, such as
Amstrad
Amstrad plc was a British consumer electronics company, founded in 1968 by Alan Sugar. During the 1980s, the company was known for its Home computer, home computers beginning with the Amstrad CPC and later also the ZX Spectrum range after the ...
. Later, it was distributed with the best-sold Digital Research version of DOS for IBM PC compatibles, the
DR-DOS
DR-DOS is a disk operating system for IBM PC compatibles, originally developed by Gary A. Kildall's Digital Research, Inc. and derived from Concurrent PC DOS 6.0, which was an advanced successor of CP/M-86. Upon its introduction in 198 ...
6.0. The GEM desktop faded from the market with the withdrawal of the Atari ST line in 1992 and with the popularity of the
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
Windows 3.0 in the PC front around the same period of time. The Falcon030, released in 1993 was the last computer from Atari to use GEM.
DeskMate
Tandy's DeskMate appeared in the early 1980s on its
TRS-80
The TRS-80 Micro Computer System (TRS-80, later renamed the Model I to distinguish it from successors) is a desktop microcomputer developed by American company Tandy Corporation and sold through their Radio Shack stores. Launched in 1977, it is ...
machines and was ported to its
Tandy 1000
The Tandy 1000 was the first in a series of IBM PC compatible home computers produced by the Tandy Corporation, sold through its Radio Shack and Radio Shack Computer Center stores. Introduced in 1984, the Tandy 1000 line was designed to offer af ...
range in 1984. Like most PC GUIs of the time, it depended on a
disk operating system
A disk operating system (DOS) is a computer operating system that requires a disk or other direct-access storage device as secondary storage. A DOS provides a file system and a means for loading and running computer program, programs stored on th ...
such as
TRSDOS
TRSDOS (which stands for the Tandy Radio Shack Disk Operating System) is the operating system for the Tandy TRS-80 line of eight-bit Zilog Z80 microcomputers that were sold through Radio Shack from 1977 through 1991. Tandy's manuals recommended ...
or
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few op ...
. The application was popular at the time and included a number of programs like Draw, Text and Calendar, as well as attracting outside investment such as
Lotus 1-2-3
Lotus 1-2-3 is a discontinued spreadsheet program from Lotus Software (later part of IBM). It was the first killer application of the IBM PC, was hugely popular in the 1980s, and significantly contributed to the success of IBM PC-compatibles ...
for DeskMate.
MSX-View

MSX-View was developed for
MSX
MSX is a standardized home computer architecture, announced by ASCII Corporation on June 16, 1983. It was initially conceived by Microsoft as a product for the Eastern sector, and jointly marketed by Kazuhiko Nishi, the director at ASCII Corpo ...
computers by
ASCII Corporation
was a Japanese publishing company based in Chiyoda, Tokyo. It became a subsidiary of Kadokawa Group Holdings in 2004, and merged with another Kadokawa subsidiary MediaWorks on April 1, 2008, becoming ASCII Media Works. The company published ' ...
and
HAL Laboratory
formerly shortened as HALKEN, is a Japanese video game developer based in Chiyoda, Tokyo. It was founded on February 21, 1980 by Mitsuhiro Ikeda. The company started out developing games for home computers of the era, but has since establishe ...
. MSX-View contains software such as Page Edit, Page View, Page Link, VShell, VTed, VPaint and VDraw. An external version of the built-in MSX View of the Panasonic FS-A1GT was released as an add-on for the Panasonic FS-A1ST on disk instead of 512 KB ROM DISK.
Amiga Intuition and the Workbench
The
Amiga
Amiga is a family of personal computers produced by Commodore International, Commodore from 1985 until the company's bankruptcy in 1994, with production by others afterward. The original model is one of a number of mid-1980s computers with 16-b ...
computer was launched by
Commodore in 1985 with a GUI called
Workbench
A workbench is a sturdy table at which manual work is done. They range from simple flat surfaces to very complex designs that may be considered tools in themselves. Workbenches vary in size from tiny jewellers benches to the huge benches used by ...
. Workbench was based on an internal engine developed mostly by
RJ Mical
Robert J. Mical (born 26 January 1956) is an American computer programmer and hardware designer who has primarily worked in video games. He is best known for creating the user interface, Intuition, for Commodore's Amiga personal computer (1985) ...
, called
Intuition
Intuition is the ability to acquire knowledge without recourse to conscious reasoning or needing an explanation. Different fields use the word "intuition" in very different ways, including but not limited to: direct access to unconscious knowledg ...
, which drove all the input events. The first versions used a blue/orange/white/black default palette, which was selected for high contrast on televisions and
composite monitor
A composite monitor or composite video monitor is any analog video display that receives input in the form of an analog composite video signal to a defined specification. A composite video signal encodes all information on a single conductor; a ...
s. Workbench presented directories as drawers to fit in with the "
workbench
A workbench is a sturdy table at which manual work is done. They range from simple flat surfaces to very complex designs that may be considered tools in themselves. Workbenches vary in size from tiny jewellers benches to the huge benches used by ...
" theme. Intuition was the
widget and graphics library that made the GUI work. It was driven by user events through the mouse, keyboard, and other input devices.
Due to a mistake made by the Commodore sales department, the first floppies of
AmigaOS
AmigaOS is a family of proprietary native operating systems of the Amiga and AmigaOne personal computers. It was developed first by Commodore International and introduced with the launch of the first Amiga, the Amiga 1000, in 1985. Early versions ...
(released with the Amiga1000) named the whole OS "Workbench". Since then, users and CBM itself referred to "Workbench" as the nickname for the whole
AmigaOS
AmigaOS is a family of proprietary native operating systems of the Amiga and AmigaOne personal computers. It was developed first by Commodore International and introduced with the launch of the first Amiga, the Amiga 1000, in 1985. Early versions ...
(including Amiga DOS, Extras, etc.). This common consent ended with release of version
2.0 of AmigaOS, which re-introduced proper names to the installation floppies of
AmigaDOS
AmigaDOS is the disk operating system of the AmigaOS, which includes file systems, file and directory manipulation, the command-line interface, and file Redirection (computing), redirection.
In AmigaOS 1.x, AmigaDOS is based on a TRIPOS port by ...
, Workbench, Extras, etc.
Starting with Workbench 1.0,
AmigaOS
AmigaOS is a family of proprietary native operating systems of the Amiga and AmigaOne personal computers. It was developed first by Commodore International and introduced with the launch of the first Amiga, the Amiga 1000, in 1985. Early versions ...
treated the Workbench as a backdrop, borderless window sitting atop a blank screen. With the introduction of
AmigaOS
AmigaOS is a family of proprietary native operating systems of the Amiga and AmigaOne personal computers. It was developed first by Commodore International and introduced with the launch of the first Amiga, the Amiga 1000, in 1985. Early versions ...
2.0, however, the user was free to select whether the main Workbench window appeared as a normally layered window, complete with a border and scrollbars, through a menu item.
Amiga users were able to boot their computer into a
command-line interface
A command-line interface (CLI) is a means of interacting with software via command (computing), commands each formatted as a line of text. Command-line interfaces emerged in the mid-1960s, on computer terminals, as an interactive and more user ...
(also known as the CLI or Amiga Shell). This was a keyboard-based environment without the Workbench GUI. Later they could invoke it with the CLI/SHELL command "LoadWB" which loaded Workbench GUI.
One major difference between other OS's of the time (and for some time after) was the Amiga's fully
multi-tasking operating system, a powerful built-in animation system using a hardware
blitter
A blitter is a circuit, sometimes as a coprocessor or a logic block on a microprocessor, dedicated to the rapid movement and modification of data within a computer's memory. A blitter can copy large quantities of data from one memory area to a ...
and
copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
and four channels of 26 kHz 8-bit sampled sound. This made the Amiga the first multi-media computer years before other OS's.
Like most GUIs of the day, Amiga's Intuition followed Xerox's, and sometimes Apple's, lead. But a
CLI CLI may refer to:
Computing
* Call Level Interface, an SQL database management API
* Command-line interface, of a computer program
* Command-line interpreter or command language interpreter; see List of command-line interpreters
* CLI (x86 instruc ...
was included which dramatically extended the functionality of the platform. However, the CLI/Shell of Amiga is not just a simple
text-based
In computing, text-based user interfaces (TUI) (alternately terminal user interfaces, to reflect a dependence upon the properties of computer terminals and not just text), is a retronym describing a type of user interface (UI) common as an ear ...
interface like in
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few op ...
, but another graphic process driven by Intuition, and with the same gadgets included in Amiga's graphics.library. The CLI/Shell interface integrates itself with the Workbench, sharing privileges with the GUI.
The Amiga Workbench evolved over the 1990s, even after Commodore's 1994 bankruptcy.
Acorn BBC Master Compact
Acorn's 8-bit BBC Master Compact shipped with Acorn's first public
GUI interface in 1986. Little commercial software, beyond that included on the Welcome disk, was ever made available for the system, despite the claim by Acorn at the time that "the major software houses have worked with Acorn to make over 100 titles available on compilation discs at launch". The most avid supporter of the Master Compact appeared to be
Superior Software, who produced and specifically labelled their games as 'Master Compact' compatible.
Arthur / RISC OS
RISC OS is a series of
graphical user interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such ...
-based computer
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s (OSes) designed for
ARM architecture
ARM (stylised in lowercase as arm, formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a family of reduced instruction set computer, RISC instruction set architectures (ISAs) for central processing unit, com ...
systems. It takes its name from the RISC (
reduced instruction set computer
In electronics and computer science, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer architecture designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a com ...
) architecture supported. The OS was originally developed by
Acorn Computers
Acorn Computers Ltd. was a British computer company established in Cambridge, England in 1978 by Hermann Hauser, Christopher Curry (businessman), Chris Curry and Andy Hopper. The company produced a number of computers during the 1980s with asso ...
for use with their 1987 range of
Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse ( ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Greek mathematics, mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and Invention, inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse, Sicily, Syracuse in History of Greek and Hellenis ...
personal computers using the
Acorn RISC Machine (ARM) processors. It comprises a
command-line interface
A command-line interface (CLI) is a means of interacting with software via command (computing), commands each formatted as a line of text. Command-line interfaces emerged in the mid-1960s, on computer terminals, as an interactive and more user ...
and
desktop environment
In computing, a desktop environment (DE) is an implementation of the desktop metaphor made of a bundle of programs running on top of a computer operating system that share a common graphical user interface (GUI), sometimes described as a graphi ...
with a
windowing system.
Originally branded as the ''Arthur 1.20'' the subsequent ''Arthur 2'' release was shipped under the name RISC OS 2.
Desktop
The
WIMP
WiMP is a music streaming service available on mobile devices, tablets, network players and computers. WiMP, standing for "Wireless Music Player," was a music streaming service that emphasized high-quality audio. WiMP offered music and podcast ...
interface incorporates three
mouse buttons (named ''Select'', ''Menu'' and ''Adjust''),
context-sensitive menus, window stack control (i.e. send to back) and dynamic window
focus
Focus (: foci or focuses) may refer to:
Arts
* Focus or Focus Festival, former name of the Adelaide Fringe arts festival in East Australia Film
*Focus (2001 film), ''Focus'' (2001 film), a 2001 film based on the Arthur Miller novel
*Focus (2015 ...
(a window can have input focus at any position on the stack). The
Icon bar (
Dock
The word dock () in American English refers to one or a group of human-made structures that are involved in the handling of boats or ships (usually on or near a shore). In British English, the term is not used the same way as in American Engl ...
) holds icons which represent mounted disc drives, RAM discs, network directories, running applications, system utilities and docked: Files, Directories or inactive Applications. These icons and open windows have context-sensitive menus and support
drag-and-drop
In computer graphical user interfaces, drag and drop is a pointing device gesture in which the user selects a virtual object by "grabbing" it and dragging it to a different location or onto another virtual object. In general, it can be used to ...
behaviour. They represent the running application as a whole, irrespective of whether it has open windows.
The application has control of the context-sensitive menus, inapplicable menu choices can be 'greyed out' to make them unavailable. Menus have their own titles and may be moved around the desktop by the user. Any menu can have further sub-menus or a new window for complicated choices.
The GUI is centered around the concept of files. The Filer displays the contents of a disc. Applications are run from the Filer view and files can be dragged to the Filer view from applications to perform saves. The opposite can perform a load. With their co-operation data can be copied or moved directly between applications by saving (dragging) to another application.
Application directories are used to store applications. The OS differentiates them from normal directories through the use of a
pling (exclamation mark, also called shriek) prefix. Double-clicking on such a directory launches the application rather than opening the directory. The application's executable files and resources are contained within the directory, but normally they remain hidden from the user. Because applications are self-contained, this allows drag-and-drop installation and removal.
Files are normally typed. RISC OS has some predefined types. Applications can supplement the set of known types. Double-clicking a file with a known type will launch the appropriate application to load the file.
The ''Style Guide'' encourages a consistent look and feel across applications. This was introduced in and specifies application appearance and behaviour. Acorn's own main
bundled applications were not updated to comply with the guide until 's ''Select'' release in 2001.
Font manager
The
outline font
A computer font is implemented as a digital data file containing a set of graphically related glyphs. A computer font is designed and created using a font editor. A computer font specifically designed for the computer screen, and not for print ...
s manager provides
spatial anti-aliasing
In digital signal processing, spatial anti-aliasing is a technique for minimizing the distortion artifacts (aliasing) when representing a high-resolution image at a lower resolution. Anti-aliasing is used in digital photography, computer graphics ...
of fonts, the OS being the first operating system to include such a feature, having included it since before January 1989.
Since 1994, in RISC OS 3.5, it has been possible to use an outline anti-aliased font in the WindowManager for UI elements, rather than the
bitmap system font from previous versions.
MS-DOS file managers and utility suites
Because most of the very early
IBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the List of IBM Personal Computer models, IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible ''de facto'' standard. Released on ...
and compatibles lacked any common true graphical capability (they used the 80-column basic
text mode
Text mode is a computer display mode in which content is internally represented on a computer screen in terms of characters rather than individual pixels. Typically, the screen consists of a uniform rectangular grid of ''character cells'', ea ...
compatible with the original
MDA display adapter), a series of
file manager
A file manager or file browser is a computer program that provides a user interface to manage computer files, files and folder (computing), folders. The most common Computer file#Operations, operations performed on files or groups of files incl ...
s arose, including
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
's
DOS Shell
DOS Shell is a file manager that debuted in MS-DOS and PC DOS version 4.0, released in June 1988. It was no longer included in MS-DOS version 6, but remained part of the Supplemental Disk. The Supplemental Disk could be ordered or could b ...
, which features typical GUI elements as menus, push buttons, lists with scrollbars and mouse pointer. The name
text-based user interface
In computing, text-based user interfaces (TUI) (alternately terminal user interfaces, to reflect a dependence upon the properties of computer terminals and not just text), is a retronym describing a type of user interface (UI) common as an ear ...
was later invented to name this kind of interface. Many MS-DOS text mode applications, like the default text editor for MS-DOS 5.0 (and related tools, like
QBasic
QBasic is an integrated development environment (IDE) and BASIC interpreter, interpreter for a variety of dialects of BASIC which are based on QuickBASIC. Code entered into the IDE is compiled into an intermediate representation (IR), and this ...
), also used the same philosophy. The IBM DOS Shell included with IBM DOS 5.0 (circa 1992) supported both text display modes and actual graphics display modes, making it both a TUI and a GUI, depending on the chosen mode.
Advanced file managers for
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few op ...
were able to redefine character shapes with
EGA and better display adapters, giving some basic low resolution icons and graphical interface elements, including an arrow (instead of a coloured cell block) for the mouse pointer. When the display adapter lacks the ability to change the character's shapes, they default to the
CP437 character set found in the adapter's
ROM
Rom, or ROM may refer to:
Biomechanics and medicine
* Risk of mortality, a medical classification to estimate the likelihood of death for a patient
* Rupture of membranes, a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac
* ...
. Some popular utility suites for MS-DOS, as
Norton Utilities
Norton Utilities is a utility software suite designed to help analyze, configure, optimize and maintain a computer. The latest version of the original series of Norton Utilities is Norton Utilities 16 for Windows XP/Vista/7/8, released 26 Octob ...
(pictured) and
PC Tools used these techniques as well.
DESQview
DESQview (DV) is a text mode multitasking operating environment developed by Quarterdeck Office Systems which enjoyed modest popularity in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Running on top of DOS, it allows users to run multiple programs concurr ...
was a text mode multitasking program introduced in July 1985. Running on top of
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few op ...
, it allowed users to run multiple DOS programs concurrently in windows. It was the first program to bring multitasking and windowing capabilities to a DOS environment in which existing DOS programs could be used. DESQview was not a true GUI but offered certain components of one, such as resizable, overlapping windows and mouse pointing.
Applications under MS-DOS with proprietary GUIs
Before the
MS-Windows age, and with the lack of a true common GUI under MS-DOS, most graphical applications which worked with
EGA,
VGA and better graphic cards had proprietary built-in GUIs. One of the best known such graphical applications was
Deluxe Paint, a popular painting software with a typical WIMP interface.
The original
Adobe Acrobat
Adobe Acrobat is a family of application software and web services developed by Adobe Inc. to view, create, manipulate, print and manage Portable Document Format (PDF) files.
The family comprises Acrobat Reader (formerly Reader), Acrobat (former ...
Reader executable file for MS-DOS was able to run on both the standard Windows 3.x GUI and the standard DOS command prompt. When it was launched from the command prompt, on a machine with a
VGA graphics card, it provided its own GUI.
Microsoft Windows (16-bit versions)
Windows 1.0, a GUI for the
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few op ...
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
, was released in 1985.
The market's response was less than stellar.
followed, but it wasn't until the 1990 launch of
Windows 3.0, based on
Common User Access that its popularity truly exploded. The GUI has seen minor redesigns since, mainly the
networking enabled
Windows 3.11 and its
Win32s
Win32s is a 32-bit application runtime environment for the Microsoft Windows 3.1 and 3.11 operating systems. It allowed some 32-bit applications to run on the 16-bit operating system using call thunks. A beta version of Win32s was available in ...
32-bit patch. The
16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two ...
line of MS Windows were discontinued with the introduction of
Windows 95
Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented operating system developed by Microsoft and the first of its Windows 9x family of operating systems, released to manufacturing on July 14, 1995, and generally to retail on August 24, 1995. Windows 95 merged ...
and
Windows NT
Windows NT is a Proprietary software, proprietary Graphical user interface, graphical operating system produced by Microsoft as part of its Windows product line, the first version of which, Windows NT 3.1, was released on July 27, 1993. Original ...
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in a maximum of 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform la ...
based architecture in the 1990s.
The main window of a given application can occupy the full screen in ''maximized'' status. The users must then to switch between maximized applications using the Alt+Tab keyboard shortcut; no alternative with the
mouse
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus'' ...
except for de-maximize. When none of the running application windows are maximized, switching can be done by clicking on a partially visible window, as is the common way in other GUIs.
In 1988,
Apple sued Microsoft for copyright infringement of the
Lisa
Lisa or LISA may refer to:
People
People with the mononym
* Lisa (Japanese musician, born 1974), stylized "LISA"
* Lisa, stagename of Japanese singer Lisa Komine (born 1978)
* Lisa (South Korean singer) (born 1980)
* Lisa (Japanese musician, b ...
and
Apple Macintosh
Mac is a brand of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 1984. The name is short for Macintosh (its official name until 1999), a reference to the McIntosh (apple), McIntosh apple. The current product lineup inclu ...
GUI. The court case lasted 4 years before almost all of Apple's claims were denied on a contractual technicality. Subsequent appeals by Apple were also denied. Microsoft and Apple apparently entered a final, private settlement of the matter in 1997.
GEOS
GEOS was launched in 1986, originally written for the 8-bit home computer
Commodore 64
The Commodore 64, also known as the C64, is an 8-bit computing, 8-bit home computer introduced in January 1982 by Commodore International (first shown at the Consumer Electronics Show, January 7–10, 1982, in Las Vegas). It has been listed in ...
, and shortly after, the
Apple II
Apple II ("apple Roman numerals, two", stylized as Apple ][) is a series of microcomputers manufactured by Apple Computer, Inc. from 1977 to 1993. The Apple II (original), original Apple II model, which gave the series its name, was designed ...
. The name was later used by the company as PC/Geos for IBM PC systems, then Geoworks Ensemble. It came with several application programs like a calendar and word processor. A cut-down version served as the basis for AOL, America Online's MS-DOS client. Compared to the competing Windows 3.0 GUI, it could run reasonably well on simpler hardware, but its developer had a restrictive policy towards third-party developers that prevented it from becoming a serious competitor. Additionally, it was targeted at
8-bit
In computer architecture, 8-bit integers or other data units are those that are 8 bits wide (1 octet). Also, 8-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers or data bu ...
machines, whilst the
16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two ...
computer age was dawning.
The X Window System

The standard windowing system in the
Unix
Unix (, ; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, a ...
world is the
X Window System
The X Window System (X11, or simply X) is a windowing system for bitmap displays, common on Unix-like operating systems.
X originated as part of Project Athena at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1984. The X protocol has been at ...
(commonly X11 or X), first released in the mid-1980s. The
W Window System
The W Window System, or simply W, is a discontinued windowing system and precursor, in name and concept, to the modern X Window System.
W was originally developed at Stanford University by Paul Asente and Brian Reid for the V operating system. ...
(1983) was the precursor to X; X was developed at MIT as
Project Athena
Project Athena was a joint project of MIT, Digital Equipment Corporation, and IBM to produce a campus-wide distributed computing environment for educational use. It was launched in 1983, and research and development ran until June 30, 1991. , At ...
. Its original purpose was to allow users of the newly emerging graphic terminals to access remote graphics
workstation
A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or computational science, scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by a single user, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating syste ...
s without regard to the workstation's operating system or the hardware. Due largely to the availability of the source code used to write X, it has become the standard layer for management of graphical and input/output devices and for the building of both local and remote graphical interfaces on virtually all Unix,
Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
and other
Unix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X, *nix or *NIX) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Uni ...
operating systems, with the notable exceptions of
macOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
and
Android.
X allows a graphical terminal user to make use of remote resources on the network as if they were all located locally to the user by running a single module of software called the X server. The software running on the remote machine is called the client application. X's network transparency protocols allow the display and input portions of any application to be separated from the remainder of the application and 'served up' to any of a large number of remote users. X is available today as
free software
Free software, libre software, libreware sometimes known as freedom-respecting software is computer software distributed open-source license, under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, distribut ...
.
NeWS

The
PostScript
PostScript (PS) is a page description language and dynamically typed, stack-based programming language. It is most commonly used in the electronic publishing and desktop publishing realm, but as a Turing complete programming language, it c ...
-based
NeWS
News is information about current events. This may be provided through many different Media (communication), media: word of mouth, printing, Mail, postal systems, broadcasting, Telecommunications, electronic communication, or through the te ...
(Network extensible Window System) was developed by
Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc., often known as Sun for short, was an American technology company that existed from 1982 to 2010 which developed and sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services. Sun contributed sig ...
in the mid-1980s. For several years
SunOS
SunOS is a Unix-branded operating system developed by Sun Microsystems for their workstation and server computer systems from 1982 until the mid-1990s. The ''SunOS'' name is usually only used to refer to versions 1.0 to 4.1.4, which were based ...
included a window system combining NeWS and the
X Window System
The X Window System (X11, or simply X) is a windowing system for bitmap displays, common on Unix-like operating systems.
X originated as part of Project Athena at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1984. The X protocol has been at ...
. Although NeWS was considered technically elegant by some commentators, Sun eventually dropped the product. Unlike X, NeWS was always
proprietary software
Proprietary software is computer software, software that grants its creator, publisher, or other rightsholder or rightsholder partner a legal monopoly by modern copyright and intellectual property law to exclude the recipient from freely sharing t ...
.
The 1990s: Mainstream usage of the desktop
The widespread adoption of the PC platform in homes and small businesses popularized computers among people with no formal training. This created a fast-growing market, opening an opportunity for commercial exploitation and of easy-to-use interfaces and making economically viable the incremental refinement of the existing GUIs for home systems.
Also, the spreading of
high-color and
true-color capabilities of
display adapter
A graphics card (also called a video card, display card, graphics accelerator, graphics adapter, VGA card/VGA, video adapter, display adapter, or colloquially GPU) is a computer expansion card that generates a feed of graphics output to a displa ...
s providing
thousands and
millions of colors, along with faster
CPUs and accelerated graphic cards, cheaper
RAM
Ram, ram, or RAM most commonly refers to:
* A male sheep
* Random-access memory, computer memory
* Ram Trucks, US, since 2009
** List of vehicles named Dodge Ram, trucks and vans
** Ram Pickup, produced by Ram Trucks
Ram, ram, or RAM may also ref ...
,
storage devices orders of magnitude larger (from
megabyte
The megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Its recommended unit symbol is MB. The unit prefix ''mega'' is a multiplier of (106) in the International System of Units (SI). Therefore, one megabyte is one million bytes ...
s to
gigabyte
The gigabyte () is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. The SI prefix, prefix ''giga-, giga'' means 109 in the International System of Units (SI). Therefore, one gigabyte is one billion bytes. The unit symbol for the gigabyte i ...
s) and larger
bandwidth
Bandwidth commonly refers to:
* Bandwidth (signal processing) or ''analog bandwidth'', ''frequency bandwidth'', or ''radio bandwidth'', a measure of the width of a frequency range
* Bandwidth (computing), the rate of data transfer, bit rate or thr ...
for telecom
networking at lower cost helped to create an environment in which the common user was able to run complicated GUIs which began to favor aesthetics.
Windows 95 and "a computer in every home"

After Windows 3.11, Microsoft started development on a new consumer-oriented version of the operating system. Windows 95 was intended to integrate Microsoft's formerly separate MS-DOS and Windows products and included an enhanced version of DOS, often referred to as MS-DOS 7.0. It also featured a significant redesign of the GUI, dubbed "Cairo". While Cairo never really materialized, parts of Cairo found their way into subsequent versions of the operating system starting with Windows 95. Both Win95 and WinNT could run 32-bit applications, and could exploit the abilities of the
Intel 80386
The Intel 386, originally released as the 80386 and later renamed i386, is the third-generation x86 architecture microprocessor from Intel. It was the first 32-bit computing, 32-bit processor in the line, making it a significant evolution in ...
CPU, as the
preemptive multitasking and up to 4 GiB of
linear address memory space. Windows 95 was touted as a 32-bit based operating system but it was actually based on a hybrid kernel (VWIN32.VXD) with the 16-bit user interface (USER.EXE) and graphic device interface (GDI.EXE) of Windows for Workgroups (3.11), which had 16-bit kernel components with a 32-bit subsystem (USER32.DLL and GDI32.DLL) that allowed it to run native 16-bit applications as well as 32-bit applications. In the marketplace, Windows 95 was an unqualified success, promoting a general upgrade to 32-bit technology, and within a year or two of its release had become the most successful operating system ever produced.
Accompanied by
an extensive marketing campaign,
Windows 95 was a major success in the marketplace at launch and shortly became the most popular desktop operating system.
Windows 95 saw the beginning of the
browser wars
A browser war is a competition for dominance in the usage share of web browsers. The "first browser war" (1995–2001) occurred between proponents of Internet Explorer and Netscape Navigator, and the "second browser war" (2004–2017) between tho ...
, when the World Wide Web began receiving a great deal of attention in popular culture and mass media. Microsoft at first did not see potential in the Web, and Windows 95 was shipped with Microsoft's own online service called
The Microsoft Network, which was dial-up only and was used primarily for its own content, not internet access. As versions of
Netscape Navigator
The 1990s releases of the Netscape (web browser), Netscape line referred to as Netscape Navigator were a series of now discontinued web browsers. from versions 1 to 4.08. It was the Core product, flagship product of the Netscape, Netscape Comm ...
and
Internet Explorer
Internet Explorer (formerly Microsoft Internet Explorer and Windows Internet Explorer, commonly abbreviated as IE or MSIE) is a deprecation, retired series of graphical user interface, graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft that were u ...
were released at a rapid pace over the following few years, Microsoft used its desktop dominance to push its browser and shape the ecology of the web mainly as a
monoculture
In agriculture, monoculture is the practice of growing one crop species in a field at a time. Monocultures increase ease and efficiency in planting, managing, and harvesting crops short-term, often with the help of machinery. However, monocultur ...
.
Windows 95 evolved through the years into
Windows 98
Windows 98 is a consumer-oriented operating system developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows 9x family of Microsoft Windows operating systems. It was the second operating system in the 9x line, as the successor to Windows 95. It was Software ...
and
Windows ME
Windows Me (Millennium Edition) is an operating system developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows 9x family of Microsoft Windows operating systems. It was the successor to Windows 98, and was released to manufacturing on June 19, 2000, and t ...
. Windows ME was the last in the line of the Windows 3.x-based operating systems from Microsoft. Windows underwent a parallel 32-bit evolutionary path, where Windows NT 3.1 was released in 1993. Windows NT (for New Technology) was a native 32-bit operating system with a new driver model, was unicode-based, and provided for true separation between applications. Windows NT also supported 16-bit applications in an NTVDM, but it did not support VxD based drivers. Windows 95 was supposed to be released before 1993 as the predecessor to Windows NT. The idea was to promote the development of 32-bit applications with backward compatibility – leading the way for more successful NT release. After multiple delays, Windows 95 was released without unicode and used the VxD driver model. Windows NT 3.1 evolved to Windows NT 3.5, 3.51 and then 4.0 when it finally shared a similar interface with its Windows 9x desktop counterpart and included a Start button. The evolution continued with Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, then Windows 7. Windows XP and higher were also made available in 64-bit modes. Windows server products branched off with the introduction of Windows Server 2003 (available in 32-bit and 64-bit IA64 or x64), then Windows Server 2008 and then Windows Server 2008 R2. Windows 2000 and XP shared the same basic GUI although XP introduced Visual Styles. With Windows 98, the
Active Desktop
Active Desktop was a feature of Microsoft Internet Explorer 4, Internet Explorer 4.0's optional Windows Desktop Update that allowed users to add Hypertext Markup Language, HTML content to the desktop metaphor, desktop, along with some other featu ...
theme was introduced, allowing an
HTML
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It defines the content and structure of web content. It is often assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets ( ...
approach for the desktop, but this feature was coldly received by customers, who frequently disabled it. At the end, Windows Vista definitively discontinued it, but put a new
SideBar on the desktop.
Macintosh
The Macintosh's GUI has been revised multiple times since 1984, with major updates including
System 7 and
Mac OS 8
Mac OS 8 is the eighth major release of the classic Mac OS operating system for Macintosh computers, released by Apple Computer on July 26, 1997. It includes the largest overhaul of the classic Mac OS experience since the release of System 7 ...
. It underwent its largest revision to date with the introduction of the "
Aqua" interface in 2001's
Mac OS X
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
. It was a new operating system built primarily on technology from
NeXTSTEP
NeXTSTEP is a discontinued object-oriented, multitasking operating system based on the Mach kernel and the UNIX-derived BSD. It was developed by NeXT, founded by Steve Jobs, in the late 1980s and early 1990s and was initially used for its ...
with UI elements of the original Mac OS grafted on.
macOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
uses a technology known as
Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The Atom, atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tet ...
, for graphics rendering and drawing on-screen. Some interface features of macOS are inherited from NeXTSTEP (such as the
Dock
The word dock () in American English refers to one or a group of human-made structures that are involved in the handling of boats or ships (usually on or near a shore). In British English, the term is not used the same way as in American Engl ...
, the automatic wait cursor, or double-buffered windows giving a solid appearance and flicker-free window redraws), while others are inherited from the old Mac OS operating system (the single system-wide menu-bar).
Mac OS X 10.3 introduced features to improve usability including
Exposé, which is designed to make finding open windows easier.
With
Mac OS X 10.4 released in April 2005, new features were added, including
Dashboard
A dashboard (also called dash, instrument panel or IP, or fascia) is a control panel (engineering), control panel set within the central console of a vehicle, boat, or cockpit of an aircraft or spacecraft. Usually located directly ahead of the ...
(a virtual alternate desktop for mini specific-purpose applications) and a search tool called
Spotlight, which provides users with an option for searching through files instead of browsing through folders.
With
Mac OS X 10.7 released in July 2011, included support for
full screen apps and
Mac OS X 10.11 (El Capitan) released in September 2015 support creating a full screen split view by pressing the green button on left upper corner of the window or Control+Cmd+F keyboard shortcut.
GUIs built on the X Window System


of X Window development, Sun Microsystems and AT&T attempted to push for a GUI standard called
OPEN LOOK in competition with
Motif. OPEN LOOK was developed from scratch in conjunction with
Xerox
Xerox Holdings Corporation (, ) is an American corporation that sells print and electronic document, digital document products and services in more than 160 countries. Xerox was the pioneer of the photocopier market, beginning with the introduc ...
, while Motif was a collective effort. Motif eventually gained prominence and became the basis for
Hewlett-Packard
The Hewlett-Packard Company, commonly shortened to Hewlett-Packard ( ) or HP, was an American multinational information technology company. It was founded by Bill Hewlett and David Packard in 1939 in a one-car garage in Palo Alto, California ...
's
Visual User Environment (VUE), which later became the
Common Desktop Environment
The Common Desktop Environment (CDE) is a desktop environment for Unix and OpenVMS, based on the Motif (software), Motif widget toolkit. It was part of the UNIX 98, UNIX 98 Workstation Product Standard, and was for a long time the Unix desktop a ...
(CDE).
In the late 1990s, there was significant growth in the Unix world, especially among the
free software community
The free software movement is a social movement with the goal of obtaining and guaranteeing certain freedoms for software users, namely the freedoms to run, study, modify, and share copies of software. Software which meets these requirements, ...
. New graphical desktop movements grew up around Linux and similar operating systems, based on the X Window System. A new emphasis on providing an integrated and uniform interface to the user brought about new desktop environments, such as
KDE Plasma 5
KDE Plasma 5 is the fifth generation of the KDE Plasma graphical workspaces environment, created by KDE primarily for Linux systems. KDE Plasma 5 is the successor of KDE Plasma 4 and was first released on 15 July 2014. It was succeeded by KDE Pl ...
,
GNOME
A gnome () is a mythological creature and diminutive spirit in Renaissance magic and alchemy, introduced by Paracelsus in the 16th century and widely adopted by authors, including those of modern fantasy literature. They are typically depict ...
and
Xfce
Xfce or XFCE (pronounced as four individual letters, ) is a Free and open-source software, free and open-source desktop environment for Linux and other Unix-like operating systems.
Xfce aims to be fast and Lightweight software, lightweight whil ...
which have supplanted CDE in popularity on both Unix and Unix-like operating systems. The Xfce, KDE and GNOME look and feel each tend to undergo more rapid change and less codification than the earlier OPEN LOOK and Motif environments.
Amiga
Later releases added improvements over the original Workbench, like support for high-color Workbench screens, context menus, and embossed 2D icons with pseudo-3D aspect. Some Amiga users preferred alternative interfaces to standard Workbench, such as
Directory Opus Magellan.
The use of improved, third-party GUI engines became common amongst users who preferred more attractive interfaces – such as
Magic User Interface (MUI), and
ReAction
Reaction may refer to a process or to a response to an action, event, or exposure.
Physics and chemistry
*Chemical reaction
*Nuclear reaction
*Reaction (physics), as defined by Newton's third law
* Chain reaction (disambiguation)
Biology and ...
. These object-oriented graphic engines driven by user interface classes and methods were then standardized into the Amiga environment and changed Amiga Workbench to a complete and modern guided interface, with new standard gadgets, animated buttons, true 24-bit-color icons, increased use of wallpapers for screens and windows, alpha channel, transparencies and shadows as any modern GUI provides.
Modern derivatives of Workbench are
Ambient for
MorphOS
MorphOS is an AmigaOS-like operating system designed for Power and PowerPC based computers. The core, based on the Quark microkernel, is proprietary, although several libraries and other parts are open source, such as the Ambient desktop.
The p ...
, Scalos, Workbench for
AmigaOS 4
AmigaOS 4 (abbreviated as OS4 or AOS4) is a line of Amiga operating systems which runs on PowerPC microprocessors. It is mainly based on AmigaOS 3.1 source code developed by Commodore International, Commodore, and partially on version 3.9 develop ...
and
Wanderer
Wanderer, Wanderers, or The Wanderer may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film, television, and theater
* The Wanderer (1913 film), ''The Wanderer'' (1913 film), a silent film
* The Wanderer (1925 film), ''The Wanderer'' (1925 film), a silen ...
for
AROS.
There is a brief article on Ambient and descriptions of MUI icons, menus and gadgets a
aps.fr and images of
Zune stay at mai
AROS site
Use of
object oriented
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of '' objects''. Objects can contain data (called fields, attributes or properties) and have actions they can perform (called procedures or methods and impleme ...
graphic engines dramatically changes the look and feel of a GUI to match actual styleguides.
OS/2
Originally collaboratively developed by Microsoft and IBM to replace DOS,
OS/2
OS/2 is a Proprietary software, proprietary computer operating system for x86 and PowerPC based personal computers. It was created and initially developed jointly by IBM and Microsoft, under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci, ...
version 1.0 (released in 1987) had no GUI at all. Version 1.1 (released 1988) included Presentation Manager (PM), an implementation of
IBM Common User Access, which looked a lot like the later Windows 3.1 UI. After the split with Microsoft, IBM developed the
Workplace Shell (WPS) for version 2.0 (released in 1992), a quite radical, object-oriented approach to GUIs. Microsoft later imitated much of this look in Windows 95.
NeXTSTEP

The
NeXTSTEP
NeXTSTEP is a discontinued object-oriented, multitasking operating system based on the Mach kernel and the UNIX-derived BSD. It was developed by NeXT, founded by Steve Jobs, in the late 1980s and early 1990s and was initially used for its ...
user interface was used in the
NeXT
NeXT, Inc. (later NeXT Computer, Inc. and NeXT Software, Inc.) was an American technology company headquartered in Redwood City, California that specialized in computer workstations for higher education and business markets, and later develope ...
line of computers. NeXTSTEP's first major version was released in 1989. It used
Display PostScript for its graphical underpinning. The NeXTSTEP interface's most significant feature was the
Dock
The word dock () in American English refers to one or a group of human-made structures that are involved in the handling of boats or ships (usually on or near a shore). In British English, the term is not used the same way as in American Engl ...
, carried with some modification into
Mac OS X
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
, and had other minor interface details that some found made it easier and more intuitive to use than previous GUIs. NeXTSTEP's GUI was the first to feature opaque dragging of windows in its user interface, on a comparatively weak machine by today's standards, ideally aided b
high performance graphics hardware
BeOS
BeOS
BeOS is a discontinued operating system for personal computers that was developed by Be Inc. It was conceived for the company's BeBox personal computer which was released in 1995. BeOS was designed for multitasking, multithreading, and a graph ...
was developed on custom
AT&T Hobbit-based computers before switching to
PowerPC
PowerPC (with the backronym Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC – Performance Computing, sometimes abbreviated as PPC) is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple Inc., App ...
hardware by a team led by former Apple executive
Jean-Louis Gassée
Jean-Louis Gassée (born 24 March 1944) is a business executive. He is best known as a former executive at Apple Computer, where he worked from 1981 to 1990. He also founded Be Inc., creators of the BeOS computer operating system. After leavin ...
as an alternative to Mac OS. BeOS was later ported to Intel hardware. It used an object-oriented kernel written by Be, and did not use the
X Window System
The X Window System (X11, or simply X) is a windowing system for bitmap displays, common on Unix-like operating systems.
X originated as part of Project Athena at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1984. The X protocol has been at ...
, but a different
GUI written from scratch. Much effort was spent by the developers to make it an efficient platform for multimedia applications. Be Inc. was acquired by
PalmSource, Inc. (Palm Inc. at the time) in 2001. The BeOS GUI still lives in
Haiku
is a type of short form poetry that originated in Japan. Traditional Japanese haiku consist of three phrases composed of 17 Mora (linguistics), morae (called ''On (Japanese prosody), on'' in Japanese) in a 5, 7, 5 pattern; that include a ''kire ...
, an
open-source software
Open-source software (OSS) is Software, computer software that is released under a Open-source license, license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to use, study, change, and Software distribution, distribute the software an ...
reimplementation of the BeOS.
Current trends
Mobile devices
General Magic
General Magic was an American software and electronics company co-founded by Bill Atkinson, Andy Hertzfeld, and Marc Porat. Based in Mountain View, California, the company developed precursors to "USB, software modems, small touchscreens, to ...
is the apparent parent of all modern smartphone GUI, i.e. touch-screen based including the iPhone et al. In 2007, with the
iPhone
The iPhone is a line of smartphones developed and marketed by Apple that run iOS, the company's own mobile operating system. The first-generation iPhone was announced by then–Apple CEO and co-founder Steve Jobs on January 9, 2007, at ...
and later in 2010 with the introduction of the
iPad
The iPad is a brand of tablet computers developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple that run the company's mobile operating systems iOS and later iPadOS. The IPad (1st generation), first-generation iPad was introduced on January 27, 2010. ...
, Apple popularized the
post-WIMP
In computing, post-WIMP ("windows, icons, menus, pointer") comprises work on user interfaces, mostly graphical user interfaces, which attempt to go beyond the paradigm of windows, icons, menus and a pointing device, i.e. WIMP interfaces.
The reas ...
style of interaction for
multi-touch
In computing, multi-touch is technology that enables a surface (a touchpad or touchscreen) to recognize the presence of more than one somatosensory system, point of contact with the surface at the same time. The origins of multitouch began at CE ...
screens, with those devices considered to be milestones in the development of
mobile device
A mobile device or handheld device is a computer small enough to hold and operate in hand. Mobile devices are typically battery-powered and possess a flat-panel display and one or more built-in input devices, such as a touchscreen or keypad. ...
s.
Other portable devices such as
MP3 player
A portable media player (PMP) or digital audio player (DAP) is a portable consumer electronics device capable of storing and playing digital media such as audio, images, and video files. Normally they refer to small, battery-powered devices ...
s and
cell phones
A mobile phone or cell phone is a portable telephone that allows users to make and receive Telephone call, calls over a radio frequency link while moving within a designated telephone service area, unlike fixed-location phones (landline phone ...
have been a burgeoning area of deployment for GUIs in recent years. Since the mid-2000s, a vast majority of portable devices have advanced to having high-screen resolutions and sizes. (The
Galaxy Note 4's 2,560 × 1,440 pixel display is an example). Because of this, these devices have their own famed user interfaces and
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s that have large
homebrew communities dedicated to creating their own visual elements, such as icons, menus, wallpapers, and more. Post-WIMP interfaces are often used in these mobile devices, where the traditional pointing devices required by the desktop metaphor are not practical.
As high-powered graphics hardware draws considerable power and generates significant heat, many of the 3D effects developed between 2000 and 2010 are not practical on this class of device. This has led to the development of
simpler interfaces making a design feature of two dimensionality such as exhibited by the
Metro (Modern) UI first used in
Windows 8
Windows 8 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on August 1, 2012, made available for download via Microsoft ...
and the 2012
Gmail
Gmail is the email service provided by Google. it had 1.5 billion active user (computing), users worldwide, making it the largest email service in the world. It also provides a webmail interface, accessible through a web browser, and is also ...
redesign.
3D user interface
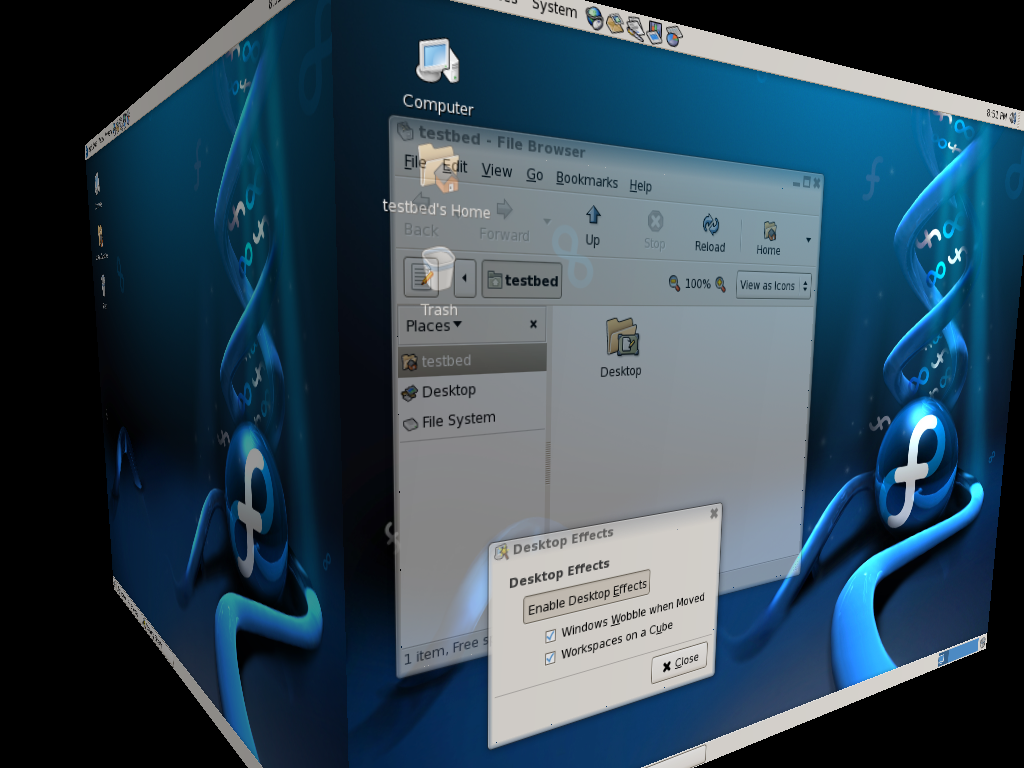
In the first decade of the 21st century, the rapid development of
GPUs led to a trend for the inclusion of 3D effects in window management. It is based in experimental research in
user interface design
User interface (UI) design or user interface engineering is the design of user interfaces for machines and software, such as computers, home appliances, mobile devices, and other electronic devices, with the focus on maximizing usability and the ...
trying to expand the expressive power of the existing toolkits in order to enhance the physical cues that allow for
direct manipulation. New effects common to several projects are scale resizing and zooming, several windows transformations and animations (wobbly windows, smooth minimization to system tray...), composition of images (used for window drop shadows and transparency) and enhancing the global organization of open windows (
zooming to
virtual desktop
In computing, a virtual desktop is a term used with respect to user interfaces, usually within the WIMP (computing), WIMP paradigm, to describe ways in which the virtual space of a computer's desktop environment is expanded beyond the physical ...
s,
desktop cube,
Exposé, etc.) The proof-of-concept
BumpTop desktop combines a physical representation of documents with tools for
document classification
Document classification or document categorization is a problem in library science, information science and computer science. The task is to assign a document to one or more Class (philosophy), classes or Categorization, categories. This may be do ...
possible only in the simulated environment, like instant reordering and automated grouping of related documents.
These effects are popularized thanks to the widespread use of 3D video cards (mainly due to gaming) which allow for complex visual processing with low CPU use, using the 3D acceleration in most modern graphics cards to render the application clients in a 3D scene. The application window is drawn off-screen in a pixel buffer, and the graphics card renders it into the 3D scene.
This can have the advantage of moving some of the window rendering to the
GPU on the graphics card and thus reducing the load on the main
CPU, but the facilities that allow this must be available on the graphics card to be able to take advantage of this.
Examples of 3D user-interface software include
Xgl and
Compiz
Compiz () is a compositing window manager for the X Window System, using 3D graphics hardware to create fast compositing desktop effects for window management. Effects, such as a minimization animation or a cube workspace, are implemented as loa ...
from
Novell
Novell, Inc. () was an American software and services company headquartered in Provo, Utah, that existed from 1980 until 2014. Its most significant product was the multi-platform network operating system known as NetWare. Novell technolog ...
, and
AIGLX bundled with
Red Hat
Red Hat, Inc. (formerly Red Hat Software, Inc.) is an American software company that provides open source software products to enterprises and is a subsidiary of IBM. Founded in 1993, Red Hat has its corporate headquarters in Raleigh, North ...
/
Fedora.
Quartz Extreme for
macOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
and
Windows 7
Windows 7 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009, and became generally available on October 22, ...
and
Vista's
Aero
Aero is a Greek prefix relating to flight and air. In British English, it is used as an adjective related to flight (e.g., as a shortened substitute for aeroplane).
Aero, Ærø, or Aeros may refer to:
Aeronautics Airlines and companies
* Aero (A ...
interface use 3D rendering for
shading
Shading refers to the depiction of depth perception in 3D models (within the field of 3D computer graphics) or illustrations (in visual art) by varying the level of darkness. Shading tries to approximate local behavior of light on the object's ...
and transparency effects as well as
Exposé and
Windows Flip and Flip 3D, respectively.
Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, released five years earlier, which was then the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft W ...
uses
Direct3D
Direct3D is a graphics application programming interface (API) for Microsoft Windows. Part of DirectX, Direct3D is used to render three-dimensional graphics in applications where performance is important, such as games. Direct3D uses hardware ...
to accomplish this, whereas the other interfaces use
OpenGL
OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a Language-independent specification, cross-language, cross-platform application programming interface (API) for rendering 2D computer graphics, 2D and 3D computer graphics, 3D vector graphics. The API is typic ...
.
Notebook interface
The
notebook interface
A notebook interface or computational notebook is a virtual notebook environment used for literate programming, a method of writing computer programs. Some notebooks are WYSIWYG environments including executable calculations embedded in formatte ...
is widely used in
data science
Data science is an interdisciplinary academic field that uses statistics, scientific computing, scientific methods, processing, scientific visualization, algorithms and systems to extract or extrapolate knowledge from potentially noisy, stru ...
and other areas of research. Notebooks allow users to mix text, calculations, and graphs in the same interface which was previously impossible with a
command-line interface
A command-line interface (CLI) is a means of interacting with software via command (computing), commands each formatted as a line of text. Command-line interfaces emerged in the mid-1960s, on computer terminals, as an interactive and more user ...
.
Virtual reality and presence
Virtual reality
Virtual reality (VR) is a Simulation, simulated experience that employs 3D near-eye displays and pose tracking to give the user an immersive feel of a virtual world. Applications of virtual reality include entertainment (particularly video gam ...
devices such as the
Oculus Rift
Oculus Rift is a discontinued line of virtual reality headsets, virtual reality headsets developed and manufactured by Oculus VR, a virtual reality company founded by Palmer Luckey that is widely credited with reviving the virtual reality indust ...
and Sony's
PlayStation VR
The PlayStation VR (PS VR) is a virtual reality headset developed by Sony Interactive Entertainment, which was released in October 2016. The headset works with the company's PlayStation 4 video game console and is forward compatible with PlaySta ...
(formerly Project Morpheus)
aim to provide users with
presence, a perception of full immersion into a virtual environment.
See also
*
Windowing system
*
Bill Atkinson
*
The Blit (graphics terminal by
Rob Pike
Robert Pike (born 1956) is a Canadian programmer and author.
He is best known for his work on the Go programming language while working at Google
and the Plan 9 operating system while working at Bell Labs, where he was a member of the Unix t ...
, 1982)
*
Direct manipulation interface
*
Douglas Engelbart
Douglas Carl Engelbart (January 30, 1925 – July 2, 2013) was an American engineer, inventor, and a pioneer in many aspects of computer science. He is best known for his work on founding the field of human–computer interaction, particularly ...
's
On-Line System
*
Graphical user interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such ...
*
Text-based user interface
In computing, text-based user interfaces (TUI) (alternately terminal user interfaces, to reflect a dependence upon the properties of computer terminals and not just text), is a retronym describing a type of user interface (UI) common as an ear ...
*
History of computing hardware
The history of computing hardware spans the developments from early devices used for simple calculations to today's complex computers, encompassing advancements in both analog and digital technology.
The first aids to computation were purely mec ...
*
History of computer icons
*
Ivan Sutherland
Ivan Edward Sutherland (born May 16, 1938) is an American computer scientist and Internet pioneer, widely regarded as a pioneer of computer graphics. His early work in computer graphics as well as his teaching with David C. Evans in that subje ...
's
Sketchpad
Sketchpad (a.k.a. Robot Draftsman) is a computer program written by Ivan Sutherland in 1963 in the course of his PhD thesis, for which he received the Turing Award in 1988, and the Kyoto Prize in 2012. It pioneered human–computer interaction ...
*
Jef Raskin
Jef Raskin (born Jeff Raskin; March 9, 1943 – February 26, 2005) was an American human–computer interface expert who conceived and began leading the Macintosh project at Apple in the late 1970s.
Early life and education
Jef Raskin was bo ...
*
Office of the future
The office of the future is a collection of ideas for redesigning the office. As technology and society have evolved, the definition of the office of the future has changed. Current concepts, dating from the 1940s, are now known as the "paperless ...
*
ETH Oberon
*
Xgl
*
AIGLX
*
DirectFB
*
Tiling window manager
In computing, a tiling window manager is a window manager with the organization of the screen often dependant on mathematical formulas to organise the windows into a non-overlapping frame. This is opposed to the more common approach used by stac ...
*
Macro command language
A command language is a language for job control in computing. It is a domain-specific and interpreted language; common examples of a command language are shell or batch programming languages.
These languages can be used directly at the ...
*
Texting
Text messaging, or texting, is the act of composing and sending electronic messages, typically consisting of alphabetic and numeric characters, between two or more users of mobile phones, tablet computers, smartwatches, desktops/laptops, or ...
*
Skeuomorph
*
Apple v. Microsoft
*
IBM Common User Access
*
The Mother of All Demos
"The Mother of All Demos" was a landmark computer demonstration, named retroactively, of developments by Stanford Research Institute's Augmentation Research Center. It was presented at the Association for Computing Machinery / Institute of Ele ...
References
{{reflist, colwidth=30em
External links
Raj Lal "User Interface evolution in last 50 years" Digital Design and Innovation Summit, San Francisco, Sept 20, 2013
Jeremy Reimer. "A History of the GUI"Ars Technica
''Ars Technica'' is a website covering news and opinions in technology, science, politics, and society, created by Ken Fisher and Jon Stokes in 1998. It publishes news, reviews, and guides on issues such as computer hardware and software, sci ...
. May 5, 2005.
"User Interface Timeline" George Mason UniversityNathan Lineback. "The Graphical User Interface Gallery". Nathan's Toasty Technology Page.Oral history interview with Marvin L. Minsky Charles Babbage Institute
The IT History Society (ITHS) is an organization that supports the history and scholarship of information technology by encouraging, fostering, and facilitating archival and historical research. Formerly known as the Charles Babbage Foundation, ...
, University of Minnesota. Minsky describes artificial intelligence (AI) research at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), including research in the areas of graphics, word processing, and time-sharing.
Oral history interview with Ivan Sutherland Charles Babbage Institute
The IT History Society (ITHS) is an organization that supports the history and scholarship of information technology by encouraging, fostering, and facilitating archival and historical research. Formerly known as the Charles Babbage Foundation, ...
, University of Minnesota. Sutherland describes his tenure as head of ARPA's Information Processing Techniques Office (IPTO) from 1963 to 1965, including new projects in graphics and networking.
Oral history interview with Charles A. Csuri Charles Babbage Institute
The IT History Society (ITHS) is an organization that supports the history and scholarship of information technology by encouraging, fostering, and facilitating archival and historical research. Formerly known as the Charles Babbage Foundation, ...
, University of Minnesota. Csuri recounts his art education and explains his transition to computer graphics in the mid-1960s, after receiving a National Science Foundation grant for research in graphics.
GUIdebook: Graphical User Interface galleryAnecdotes about the development of the Macintosh Hardware & GUIFirsts: The Demo – Doug Engelbart Institute
History of human–computer interaction
History of computing
 Early dynamic information devices such as
Early dynamic information devices such as  The development of computers having multiple overlapping and resizable windows on a "desktop" is commonly, and incorrectly, attributed to
The development of computers having multiple overlapping and resizable windows on a "desktop" is commonly, and incorrectly, attributed to  led to the advances at
led to the advances at 
 MSX-View was developed for
MSX-View was developed for  The standard windowing system in the
The standard windowing system in the  The
The  After Windows 3.11, Microsoft started development on a new consumer-oriented version of the operating system. Windows 95 was intended to integrate Microsoft's formerly separate MS-DOS and Windows products and included an enhanced version of DOS, often referred to as MS-DOS 7.0. It also featured a significant redesign of the GUI, dubbed "Cairo". While Cairo never really materialized, parts of Cairo found their way into subsequent versions of the operating system starting with Windows 95. Both Win95 and WinNT could run 32-bit applications, and could exploit the abilities of the
After Windows 3.11, Microsoft started development on a new consumer-oriented version of the operating system. Windows 95 was intended to integrate Microsoft's formerly separate MS-DOS and Windows products and included an enhanced version of DOS, often referred to as MS-DOS 7.0. It also featured a significant redesign of the GUI, dubbed "Cairo". While Cairo never really materialized, parts of Cairo found their way into subsequent versions of the operating system starting with Windows 95. Both Win95 and WinNT could run 32-bit applications, and could exploit the abilities of the 
 of X Window development, Sun Microsystems and AT&T attempted to push for a GUI standard called OPEN LOOK in competition with Motif. OPEN LOOK was developed from scratch in conjunction with
of X Window development, Sun Microsystems and AT&T attempted to push for a GUI standard called OPEN LOOK in competition with Motif. OPEN LOOK was developed from scratch in conjunction with  The
The  In the first decade of the 21st century, the rapid development of GPUs led to a trend for the inclusion of 3D effects in window management. It is based in experimental research in
In the first decade of the 21st century, the rapid development of GPUs led to a trend for the inclusion of 3D effects in window management. It is based in experimental research in