Hexadecimal time on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

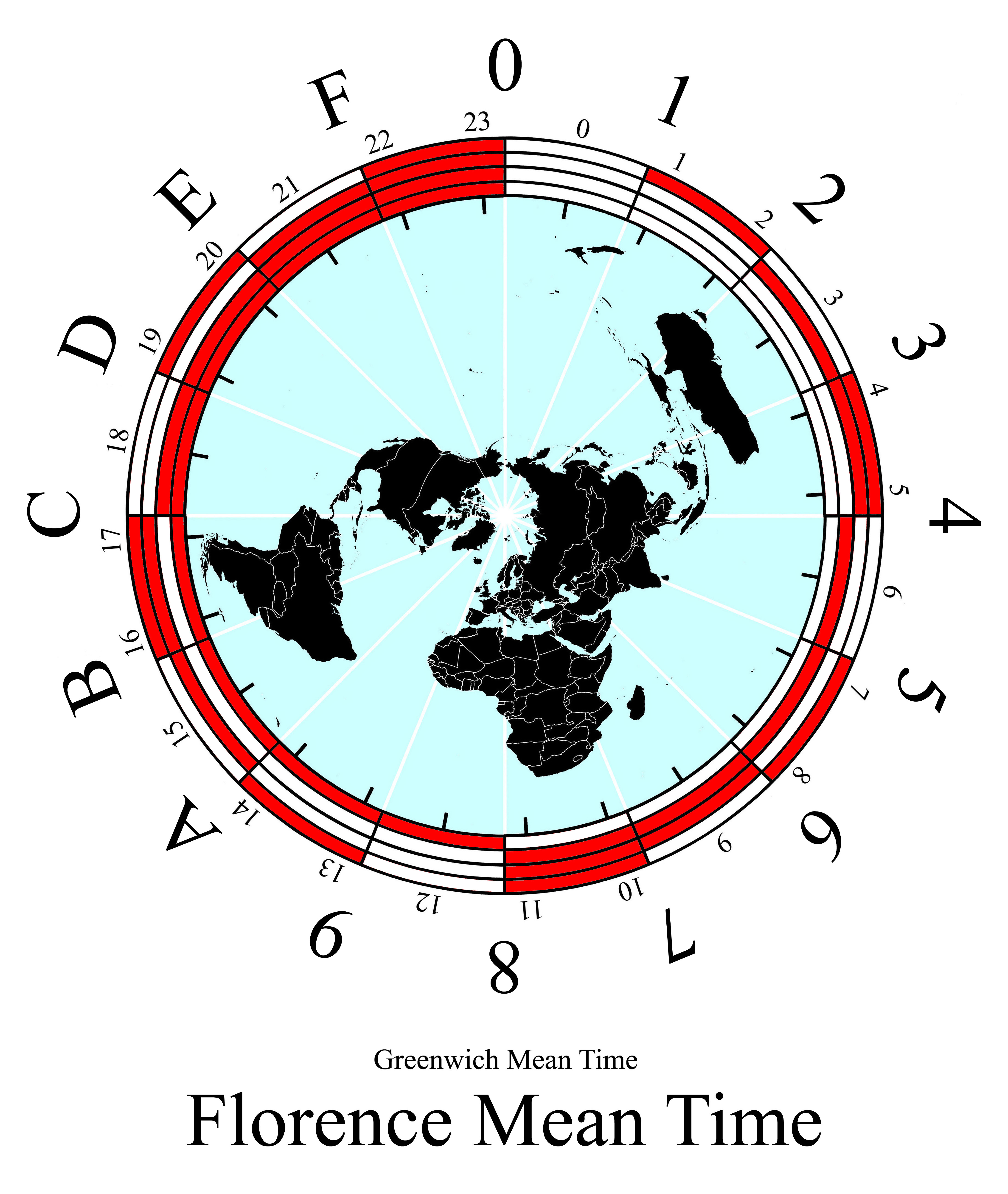 Hexadecimal time is the representation of the
Hexadecimal time is the representation of the
Hexadecimal Time Applet
- digital and analog
True Binary Time
- local time as a binary number
- Florence Mean Time {{Time Topics Time measurement systems Hexadecimal numeral system Clock designs

 Hexadecimal time is the representation of the
Hexadecimal time is the representation of the time
Time is the continuous progression of existence that occurs in an apparently irreversible process, irreversible succession from the past, through the present, and into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequ ...
of day
A day is the time rotation period, period of a full Earth's rotation, rotation of the Earth with respect to the Sun. On average, this is 24 hours (86,400 seconds). As a day passes at a given location it experiences morning, afternoon, evening, ...
as a hexadecimal
Hexadecimal (also known as base-16 or simply hex) is a Numeral system#Positional systems in detail, positional numeral system that represents numbers using a radix (base) of sixteen. Unlike the decimal system representing numbers using ten symbo ...
number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
in the interval [0, 1).
The day is divided into 1016 (1610) hexadecimal hours, each hour into 10016 (25610) hexadecimal minutes, and each minute into 1016 (1610) hexadecimal seconds.
History
This time format was proposed by the Swedish-American engineer John W. Nystrom in 1863 as part of his ''tonal system''. In 1997, the American Mark Vincent Rogers of Intuitor proposed a similar system of hexadecimal time and implemented it in JavaScript as the Hexclock.Implementation
A day is unity, or 1, and any fraction thereof can be shown with digits to the right of the hexadecimal separator. So the day begins at midnight with .0000 and one hexadecimal second after midnight is .0001. Noon is .8000 (one half), one hexadecimal second before was .7FFF and one hexadecimal second before next midnight will be .FFFF. Intuitor-hextime may also be formatted with an underscore separating hexadecimal hours, minutes and seconds. For example:Clock
Conversions
See also
* Binary time *Decimal time
Decimal time is the representation of the time of day using units which are decimally related. This term is often used specifically to refer to the French Republican calendar time system used in #France, France from 1794 to 1800, during the Fre ...
* Metric time
Metric time is the measure of time intervals using the metric system. The modern SI system defines the second as the base unit of time, and forms multiples and submultiples with metric prefixes such as kiloseconds and milliseconds. Other units ...
References
Further reading
*External links
Hexadecimal Time Applet
- digital and analog
True Binary Time
- local time as a binary number
- Florence Mean Time {{Time Topics Time measurement systems Hexadecimal numeral system Clock designs