Henry Hudson on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and
/ref> He may have been born in London and it is possible that his father was an
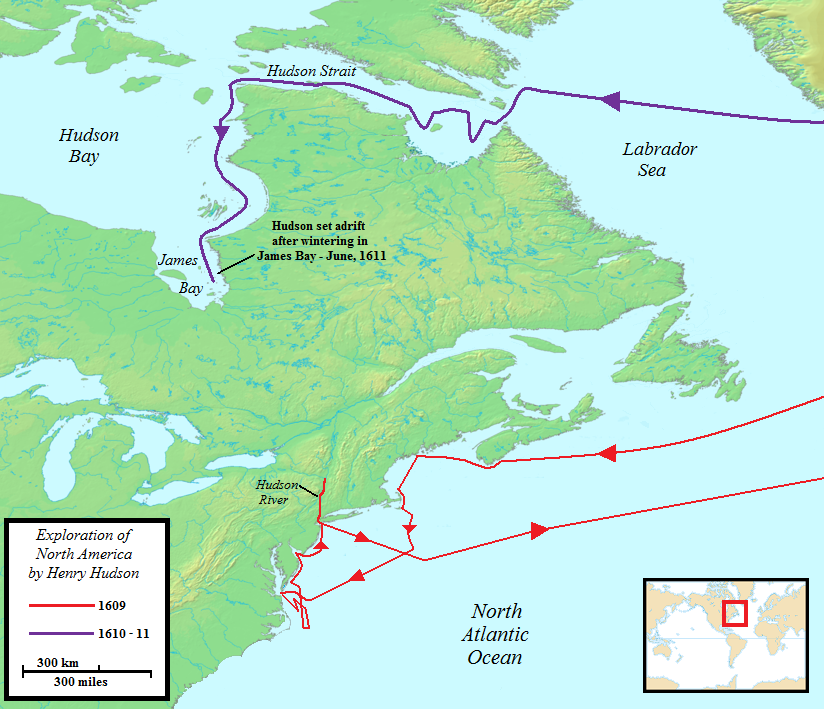 In 1609, Hudson was chosen by merchants of the
In 1609, Hudson was chosen by merchants of the  On 4 August, the ship was at
On 4 August, the ship was at
 After the mutiny, Hudson's shallop broke out oars and tried to keep pace with the ''Discovery'' for some time. Pricket recalled that the mutineers finally tired of the pursuit and unfurled additional sails aboard the ''Discovery'', enabling the larger vessel to leave the tiny open boat behind. Hudson and the other seven aboard the shallop were never seen by Europeans again. Despite subsequent searches, including those conducted by Thomas Button in 1612 and by Zachariah Gillam in 1668–1670, their fate is unknown.
After the mutiny, Hudson's shallop broke out oars and tried to keep pace with the ''Discovery'' for some time. Pricket recalled that the mutineers finally tired of the pursuit and unfurled additional sails aboard the ''Discovery'', enabling the larger vessel to leave the tiny open boat behind. Hudson and the other seven aboard the shallop were never seen by Europeans again. Despite subsequent searches, including those conducted by Thomas Button in 1612 and by Zachariah Gillam in 1668–1670, their fate is unknown.
navigator
A navigator is the person on board a ship or aircraft responsible for its navigation.Grierson, MikeAviation History—Demise of the Flight Navigator FrancoFlyers.org website, October 14, 2008. Retrieved August 31, 2014. The navigator's prim ...
during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the Northeastern United States.
In 1607 and 1608, Hudson made two attempts on behalf of English merchants to find a rumoured Northeast Passage to Cathay via a route above the Arctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the northernmost of the five major circle of latitude, circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth at about 66° 34' N. Its southern counterpart is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circl ...
. In 1609, he landed in North America on behalf of the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States Ge ...
and explored the region around the modern New York metropolitan area
The New York metropolitan area, also called the Tri-State area and sometimes referred to as Greater New York, is the List of cities by GDP, largest metropolitan economy in the world, with a List of U.S. metropolitan areas by GDP, gross metropo ...
. Looking for a Northwest Passage to Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
on his ship '' Halve Maen'' ("Half Moon"), he sailed up the Hudson River
The Hudson River, historically the North River, is a river that flows from north to south largely through eastern New York (state), New York state. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains at Henderson Lake (New York), Henderson Lake in the ...
, which was later named after him, and thereby laid the foundation for Dutch colonization of the region. His contributions to the exploration of the New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
were significant and lasting. His voyages helped to establish European contact with the native peoples of North America and contributed to the development of trade and commerce.
On his final expedition, while still searching for the Northwest Passage, Hudson became the first European to see Hudson Strait and the immense Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay, sometimes called Hudson's Bay (usually historically), is a large body of Saline water, saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of . It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba, and southeast o ...
. In 1611, after wintering on the shore of James Bay
James Bay (, ; ) is a large body of water located on the southern end of Hudson Bay in Canada. It borders the provinces of Quebec and Ontario, and is politically part of Nunavut. Its largest island is Akimiski Island.
Numerous waterways of the ...
, Hudson wanted to press on to the west, but most of his crew mutinied. The mutineers cast Hudson, his son, and six others adrift; what then happened to the Hudsons and their companions is unknown.
Early life
Virtually nothing of Hudson's early life is known for certain. His year of birth is variously estimated between 1560 and 1570.Henry Hudson's entry in ''Encyclopædia Britannica''/ref> He may have been born in London and it is possible that his father was an
alderman
An alderman is a member of a Municipal government, municipal assembly or council in many jurisdictions founded upon English law with similar officials existing in the Netherlands (wethouder) and Belgium (schepen). The term may be titular, denotin ...
of that city. When Hudson first entered the historical record in 1607, he was already an experienced mariner with sufficient credentials to be commissioned the leader of an expedition charged with a search for a trade route across the North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's rotation, Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distingu ...
.
Exploration
Expeditions of 1607 and 1608
In 1607, theMuscovy Company
The Muscovy Company (also called the Russia Company or the Muscovy Trading Company; ) was an English trading company chartered in 1555. It was the first major Chartered company, chartered joint-stock company, the precursor of the type of business ...
of England hired Hudson to find a northerly route to the Pacific coast of Asia. At the time, the English were engaged in an economic battle with the Dutch for control of northwest routes. It was thought that, because the sun shone for three months in the northern latitudes in the summer, the ice would melt, and a ship could make it across the "top of the world".
On 1 May 1607, Hudson sailed with a crew of ten men and a boy on the 80-ton ''Hopewell''. They reached the east coast of Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ...
on 13 May, coasting northward until 22 May. Here the party named a headland "Young's Cape", a "very high mount, like a round castle" near it "Mount of God's Mercy" and land at 73° north latitude " Hold with Hope". After turning east, they sighted "Newland" (Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian language, Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipel ...
) on 27 May near the mouth of the great bay Hudson later simply named the "Great Indraught" ( Isfjorden).
On 13 July, Hudson and his crew estimated that they had sailed as far north as 80° 23′ N, but had more likely only reached 79° 23′ N. The following day they entered what Hudson later in the voyage named "Whales Bay" ( Krossfjorden and Kongsfjorden), naming its northwestern point "Collins Cape" (Kapp Mitra) after his boatswain
A boatswain ( , ), bo's'n, bos'n, or bosun, also known as a deck boss, or a qualified member of the deck department, or the third hand on a fishing vessel, is the most senior Naval rating, rate of the deck department and is responsible for the ...
, William Collins. They sailed north the following two days. On 16 July, they reached as far north as Hakluyt's Headland (which Thomas Edge says Hudson named on this voyage) at 79° 49′ N, thinking they saw the land continue to 82° N (Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), previously known as Spitsbergen or Spitzbergen, is a Norway, Norwegian archipelago that lies at the convergence of the Arctic Ocean with the Atlantic Ocean. North of continental Europe, mainland Europe, it lies about midway be ...
's northernmost point is 80° 49′ N) when really it trended to the east. Encountering ice packed along the north coast, they were forced to turn back south. Hudson wanted to make his return "by the north of Greenland to Davis his Streights (Davis Strait
The Davis Strait (Danish language, Danish: ''Davisstrædet'') is a southern arm of the Arctic Ocean that lies north of the Labrador Sea. It lies between mid-western Greenland and Baffin Island in Nunavut, Canada. To the north is Baffin Bay. The ...
), and so for Kingdom of England", but ice conditions would have made this impossible. The expedition returned to Tilbury Hope on the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, s ...
on 15 September.
Hudson reported large numbers of whales in Spitsbergen waters during this voyage. Many authors credit his reports as the catalyst for several nations sending whaling
Whaling is the hunting of whales for their products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that was important in the Industrial Revolution. Whaling was practiced as an organized industry as early as 875 AD. By the 16t ...
expeditions to the islands. This claim is contentious; others have pointed to strong evidence that it was Jonas Poole's reports in 1610, that led to the establishment of English whaling, and voyages of Nicholas Woodcock and Willem Cornelisz van Muyden in 1612, which led to the establishment of Dutch, French and Spanish whaling. The whaling industry was built by neither Hudson nor Poole—both were dead by 1612.
In 1608, English merchants of the East India
East India is a region consisting of the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha
and West Bengal and also the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
The states of Bihar and West Bengal lie on the Indo-Gangetic plain. Jharkhan ...
and Muscovy Companies again sent Hudson in the ''Hopewell'' to attempt to locate a passage to the Indies, this time to the east around northern Russia. Leaving London on 22 April, the ship travelled almost , making it to Novaya Zemlya well above the Arctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the northernmost of the five major circle of latitude, circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth at about 66° 34' N. Its southern counterpart is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circl ...
in July, but even in the summer they found the ice impenetrable and turned back, arriving at Gravesend on 26 August.
Alleged discovery of Jan Mayen
According to Thomas Edge, "William Hudson" in 1608 discovered an island he named "Hudson's Tutches" (Touches) at 71° N, the latitude ofJan Mayen
Jan Mayen () is a Norway, Norwegian volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean with no permanent population. It is long (southwest-northeast) and in area, partly covered by glaciers (an area of around the Beerenberg volcano). It has two parts: la ...
. However, records of Hudson's voyages suggest that he could only have come across Jan Mayen in 1607 by making an illogical detour, and historians have pointed out that Hudson himself made no mention of it in his journal. There is also no cartographical proof of this supposed discovery.
Jonas Poole in 1611 and Robert Fotherby in 1615 both had possession of Hudson's journal while searching for his elusive Hold-with-Hope—which is now believed to have been on the east coast of Greenland—but neither had any knowledge of any discovery of Jan Mayen, an achievement which was only later attributed to Hudson. Fotherby eventually stumbled across Jan Mayen, thinking it a new discovery and naming it "Sir Thomas Smith's Island", though the first verifiable records of the discovery of the island had been made a year earlier, in 1614.
Expedition of 1609
 In 1609, Hudson was chosen by merchants of the
In 1609, Hudson was chosen by merchants of the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States Ge ...
in the Netherlands to find an easterly passage to Asia. While awaiting orders and supplies in Amsterdam, he heard rumours of a northwest route to the Pacific through North America. Hudson had been told to sail through the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five oceanic divisions. It spans an area of approximately and is the coldest of the world's oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, ...
north of Russia, into the Pacific and so to the Far East
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North Asia, North, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In mod ...
. Hudson departed Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , ; ; ) is the capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, largest city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It has a population of 933,680 in June 2024 within the city proper, 1,457,018 in the City Re ...
on 4 April, in command of the Dutch ship (English: Half Moon). He could not complete the specified (eastward) route because ice blocked the passage, as with all previous such voyages, and he turned the ship around in mid-May while somewhere east of Norway's North Cape. At that point, acting outside his instructions, Hudson pointed the ship west and decided to try to seek a westerly passage through North America.
They reached the Grand Banks of Newfoundland on 2 July, and in mid-July made landfall near the LaHave area of Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
. Here they encountered Indigenous people
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
who were accustomed to trading with the French; they were willing to trade beaver pelts, but apparently no trades occurred. The ship stayed in the area about ten days, the crew replacing a broken mast and fishing for food. On the 25 July, a dozen men from the ''Halve Maen'', using muskets and small cannon, went ashore and assaulted the village near their anchorage. They drove the people from the settlement and took their boat and other property—probably pelts and trade goods.
 On 4 August, the ship was at
On 4 August, the ship was at Cape Cod
Cape Cod is a peninsula extending into the Atlantic Ocean from the southeastern corner of Massachusetts, in the northeastern United States. Its historic, maritime character and ample beaches attract heavy tourism during the summer months. The ...
, from which Hudson sailed south to the entrance of the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Ea ...
. Rather than entering the Chesapeake he explored the coast to the north, finding Delaware Bay but continuing on north. On 3 September, he reached the estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime enviro ...
of the river that initially was called the "North River" or "Mauritius" and now carries his name. He was not the first European to discover the estuary, though, as it had been known since the voyage of Giovanni da Verrazzano in 1524.
On 6 September 1609, John Colman of his crew was killed by natives with an arrow to his neck. Hudson sailed into the Upper New York Bay
New York Harbor is a bay that covers all of the Upper Bay. It is at the mouth of the Hudson River near the East River tidal estuary on the East Coast of the United States.
New York Harbor is generally synonymous with Upper New York Bay ...
on 11 September, and the following day encountered a group of 28 Lenape canoes, buying oysters and beans from the Native Americans, and then began a journey up what is now known as the Hudson River. Over the next ten days his ship ascended the river, reaching a point near Stuyvesant Landing (Old Kinderhook), and the ship's boat with five crew members ventured to the vicinity of present-day Albany.
On 23 September, Hudson decided to return to Europe. He put in at Dartmouth, England on 7 November, and was detained by authorities who wanted access to his log. He managed to pass the log to the Dutch ambassador to England, who sent it, along with his report, to Amsterdam.
While exploring the river, Hudson had traded with several native groups, mainly obtaining furs. His voyage was used to establish Dutch claims to the region and to the fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal ecosystem, boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals h ...
that prospered there when a trading post was established at Albany in 1614. New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam (, ) was a 17th-century Dutch Empire, Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''Factory (trading post), fac ...
on Manhattan Island
Manhattan ( ) is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. Coextensive with New York County, Manhattan is the smallest county by area in the U.S. state of New York. Located almost entire ...
became the capital of New Netherland in 1625.
Expedition of 1610–1611
In 1610, Hudson obtained backing for another voyage, this time under the English flag. The funding came from theVirginia Company
The Virginia Company was an English trading company chartered by King James I on 10 April 1606 with the objective of colonizing the eastern coast of America. The coast was named Virginia, after Elizabeth I, and it stretched from present-day ...
and the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
. At the helm of his new ship, the , he stayed to the north (some claim he had deliberately stayed too far south on his Dutch-funded voyage), reached Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ...
on 11 May, the south of Greenland on 4 June, and rounded the southern tip of Greenland.
On 25 June, the explorers reached what is now the Hudson Strait at the northern tip of Labrador
Labrador () is a geographic and cultural region within the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is the primarily continental portion of the province and constitutes 71% of the province's area but is home to only 6% of its populatio ...
. Following the southern coast of the strait on 2 August, the ship entered Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay, sometimes called Hudson's Bay (usually historically), is a large body of Saline water, saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of . It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba, and southeast o ...
. Excitement was very high due to the expectation that the ship had finally found the Northwest Passage through the continent. Hudson spent the following months mapping and exploring its eastern shores, but he and his crew did not find a passage to Asia. In November, the ship became trapped in the ice in James Bay
James Bay (, ; ) is a large body of water located on the southern end of Hudson Bay in Canada. It borders the provinces of Quebec and Ontario, and is politically part of Nunavut. Its largest island is Akimiski Island.
Numerous waterways of the ...
, and the crew moved ashore for the winter.
Mutiny
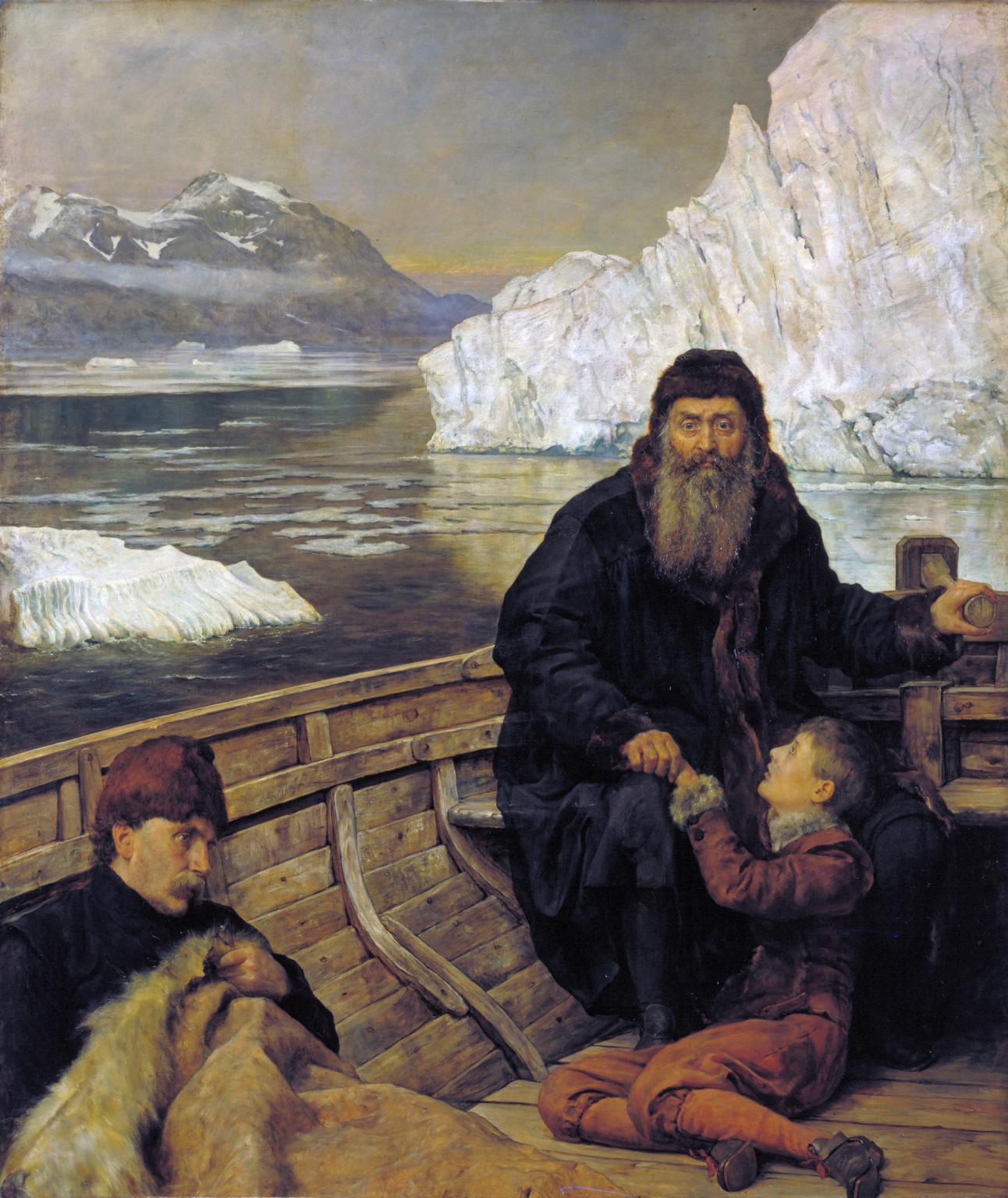
When the ice cleared in the spring of 1611, Hudson planned to use his ''Discovery'' to further explore Hudson Bay with the continuing goal of discovering the Passage; however, most of the members of his crew ardently desired to return home. Matters came to a head and much of the crew mutinied in June. Descriptions of the successful mutiny are one-sided, because the only survivors who could tell their story were the mutineers and those who went along with the mutiny. In the latter class was ship's navigator, Abacuk Pricket, a survivor who kept a journal that was to become one of the sources for the narrative of the mutiny. According to Pricket, the leaders of the mutiny were Henry Greene and Robert Juet. The latter, a navigator, had accompanied Hudson on the 1609 expedition, and his account is said to be "the best contemporary record of the voyage". Pricket's narrative tells how the mutineers set Hudson, his teenage son John, and seven crewmen—men who were either sick and infirm or loyal to Hudson—adrift from the ''Discovery'' in a small shallop, an open boat, effectively marooning them in Hudson Bay. The Pricket journal reports that the mutineers provided the castaways with clothing, powder and shot, some pikes, an iron pot, some food, and other miscellaneous items.Disappearance
 After the mutiny, Hudson's shallop broke out oars and tried to keep pace with the ''Discovery'' for some time. Pricket recalled that the mutineers finally tired of the pursuit and unfurled additional sails aboard the ''Discovery'', enabling the larger vessel to leave the tiny open boat behind. Hudson and the other seven aboard the shallop were never seen by Europeans again. Despite subsequent searches, including those conducted by Thomas Button in 1612 and by Zachariah Gillam in 1668–1670, their fate is unknown.
After the mutiny, Hudson's shallop broke out oars and tried to keep pace with the ''Discovery'' for some time. Pricket recalled that the mutineers finally tired of the pursuit and unfurled additional sails aboard the ''Discovery'', enabling the larger vessel to leave the tiny open boat behind. Hudson and the other seven aboard the shallop were never seen by Europeans again. Despite subsequent searches, including those conducted by Thomas Button in 1612 and by Zachariah Gillam in 1668–1670, their fate is unknown.
Pricket's reliability
While Pricket's account is one of the few surviving records of the voyage, its reliability has been questioned by some historians. Pricket's journal and testimony have been severely criticized for bias, on two grounds. Firstly, prior to the mutiny the alleged leaders of the uprising, Greene and Juet, had been friends and loyal seamen of Hudson. Secondly, Greene and Juet did not survive the return voyage to England (Juet, who had been the navigator on the return journey, died of starvation a few days before the company reached Ireland). Pricket knew he and the other survivors of the mutiny would be tried in England forpiracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and valuable goods, or taking hostages. Those who conduct acts of piracy are call ...
, and it would have been in his interest, and the interest of the other survivors, to put together a narrative that would place the blame for the mutiny upon men who were no longer alive to defend themselves.
The Pricket narrative became the controlling story of the expedition's disastrous end. Only eight of the thirteen mutinous crewmen survived the return voyage to Europe. They were arrested in England, and some were put on trial, but no punishment was imposed for the mutiny. One theory holds that the survivors were considered too valuable as sources of information to execute, as they had travelled to the New World and could describe sailing routes and conditions.
Later developments
In 1612, Nicolas de Vignau claimed he saw wreckage of an English ship on the shores ofJames Bay
James Bay (, ; ) is a large body of water located on the southern end of Hudson Bay in Canada. It borders the provinces of Quebec and Ontario, and is politically part of Nunavut. Its largest island is Akimiski Island.
Numerous waterways of the ...
, located on the southern end of Hudson Bay—while this was discounted at the time by Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain (; 13 August 1574#Fichier]For a detailed analysis of his baptismal record, see #Ritch, RitchThe baptism act does not contain information about the age of Samuel, neither his birth date nor his place of birth. – 25 December ...
, historians believe it may have credence.
British-born Canadian author Dorothy Harley Eber (1925–2022) collected Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwe ...
testimonies that she thought made reference to Hudson and his son after the mutiny. According to these, an old man with a long white beard and a young boy arrived in a small wooden boat. The Inuit had never seen a white person before, but they took them to an encampment and fed them. After the old man died, the Inuit tethered the boy to one of their houses so he would not run away. Despite the long time passed, the story might be given some credence after long-ignored Inuit testimonies proved reliable enough to lead to the discovery of the wrecks of the two ships of Franklin's lost expedition of 1845, and , in the 2010s. Charles Francis Hall, who searched for Franklin in the mid-19th century, also collected Inuit stories that he interpreted as references to the even earlier expedition of Martin Frobisher, who explored the area and mined fool's gold
The mineral pyrite ( ), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic Lustre (mineralogy), lu ...
in 1578.Roobol, M.J. (2019) ''Franklin's Fate: An investigation into what happened to the lost 1845 expedition of Sir John Frankin.'' Conrad Press, 368 pp.
In the late 1950s, a stone near Deep River, Ontario, which is approximately south of James Bay, was found to have carving on it with Hudson's initials (H. H.), the year 1612, and the word "captive". While lettering on the stone was consistent with English maps of the 17th century, the Geological Survey of Canada
The Geological Survey of Canada (GSC; , CGC) is a Canadian federal government agency responsible for performing geological surveys of the country developing Canada's natural resources and protecting the environment. A branch of the Earth Science ...
was unable to determine when the carving was made.
Legacy
The bay visited by and named after Hudson is three times the size of theBaltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
, and its many large estuaries afford access to otherwise landlocked parts of Western Canada
Western Canada, also referred to as the Western provinces, Canadian West, or Western provinces of Canada, and commonly known within Canada as the West, is a list of regions of Canada, Canadian region that includes the four western provinces and t ...
and the Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
. This allowed the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), originally the Governor and Company of Adventurers of England Trading Into Hudson’s Bay, is a Canadian holding company of department stores, and the oldest corporation in North America. It was the owner of the ...
to exploit a lucrative fur trade along its shores for more than two centuries, growing powerful enough to influence the history and present international boundaries of western North America.
Along with Hudson Bay and Hudson Strait in Canada, many other topographical features and landmarks are named for Hudson. The Hudson River
The Hudson River, historically the North River, is a river that flows from north to south largely through eastern New York (state), New York state. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains at Henderson Lake (New York), Henderson Lake in the ...
in New York and New Jersey is named after him, as are Hudson County, New Jersey, the Henry Hudson Bridge, the Henry Hudson Parkway, and the city of Hudson, New York
Hudson is a Administrative divisions of New York#City, city in and the county seat of Columbia County, New York, United States. At the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census, it had a population of 5,894. On the east side of the Hudson River, f ...
.
See also
*Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (), also known as the Age of Exploration, was part of the early modern period and overlapped with the Age of Sail. It was a period from approximately the 15th to the 17th century, during which Seamanship, seafarers fro ...
* List of people who disappeared before 1910
* List of people who disappeared mysteriously at sea
References
Notes
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * Volumes XIII and XIV (Reprint 1906 J. Maclehose and sons). * * * Wordie, J.M. (1922). "Jan Mayen Island", ''The Geographical Journal''. Vol 59 (3).External links
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Hudson, Henry 16th-century English explorers 17th-century English explorers 1560s births 1610s deaths 1610s missing person cases Dutch East India Company people English explorers of North America English navigators Sailors from London Explorers of Canada Explorers of Svalbard British explorers of the Arctic Explorers of the United States Lost explorers Persons of National Historic Significance (Canada) Sailors on ships of the Dutch East India Company Muscovy Company