Hair Follicle Receptors on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
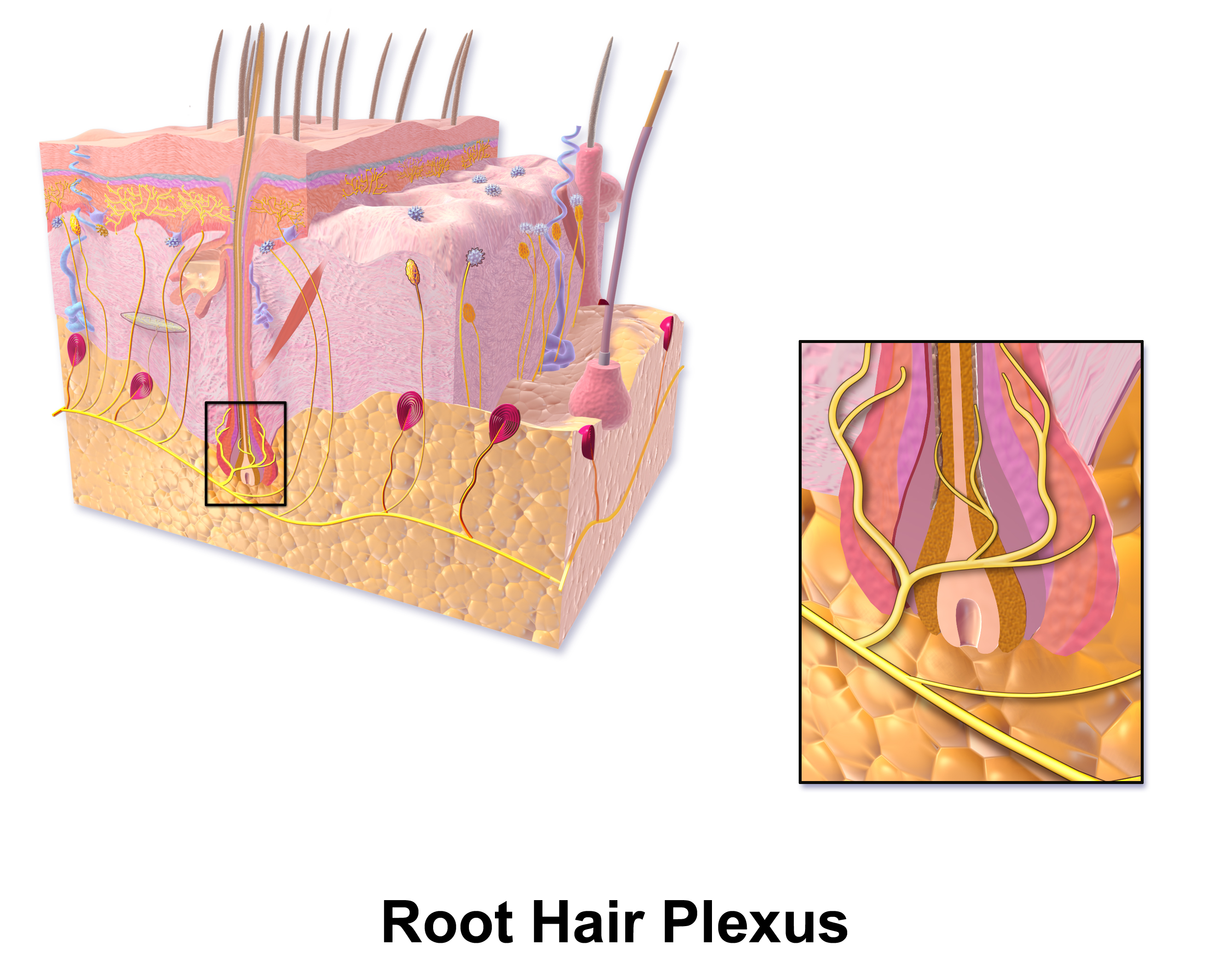 A hair plexus or root hair plexus is a special group of
A hair plexus or root hair plexus is a special group of
 A hair plexus or root hair plexus is a special group of
A hair plexus or root hair plexus is a special group of nerve fiber
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis) or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences) is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action pot ...
endings and serves as a very sensitive mechanoreceptor
A mechanoreceptor, also called mechanoceptor, is a sensory receptor that responds to mechanical pressure or distortion. Mechanoreceptors are located on sensory neurons that convert mechanical pressure into action potential, electrical signals tha ...
for touch sensation. Hair contains a number of different types of nerve endings. They are specialized for the detection of different kinds of stimuli and thus different types of neuron innervate these structures within the skin. In particular there are neurons innervating the hair that detect, deflection of the hair (i.e. to detect stroking), and pulling of the hair (i.e. noxious stimuli). The hair follicles are innervated by at least 5 classes of low threshold mechanical receptors.
They are mechanoreceptor
A mechanoreceptor, also called mechanoceptor, is a sensory receptor that responds to mechanical pressure or distortion. Mechanoreceptors are located on sensory neurons that convert mechanical pressure into action potential, electrical signals tha ...
s conveying touch sensation with cell bodies located inside of either dorsal root ganglia
A dorsal root ganglion (or spinal ganglion; also known as a posterior root ganglion) is a cluster of neurons (a ganglion) in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the dors ...
or trigeminal root ganglia. For most of the body (excluding the head and neck), crude touch and noxious stimuli from these receptors are further conveyed by the spinothalamic tract
The spinothalamic tract is a nerve tract in the anterolateral system in the spinal cord. This tract is an ascending sensory pathway to the thalamus. From the ventral posterolateral nucleus in the thalamus, sensory information is relayed upwar ...
whereas discriminative and light touch are conveyed to via the dorsal column medial lemniscus pathway. The head and neck use pathways involving the spinal trigeminal nucleus
The spinal trigeminal nucleus is a nucleus in the medulla that receives information about deep/crude touch, pain, and temperature from the ipsilateral face. In addition to the trigeminal nerve (CN V), the facial (CN VII), glossopharyngeal (CN ...
.
References