HR 8799 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
HR 8799 is a roughly 30 million-year-old
 The star HR 8799 is a member of the Lambda Boötis ( Boo) class, a group of
The star HR 8799 is a member of the Lambda Boötis ( Boo) class, a group of

 On 13 November 2008, Christian Marois of the National Research Council of Canada's Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics and his team announced they had directly observed three
On 13 November 2008, Christian Marois of the National Research Council of Canada's Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics and his team announced they had directly observed three
 In January 2009 the
In January 2009 the
 Up until the year 2010,
Up until the year 2010,
main-sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a classification of stars which appear on plots of stellar color versus brightness as a continuous and distinctive band. Stars on this band are known as main-sequence stars or dwarf stars, and positions of star ...
star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
located away from Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
in the constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
of Pegasus
Pegasus (; ) is a winged horse in Greek mythology, usually depicted as a white stallion. He was sired by Poseidon, in his role as horse-god, and foaled by the Gorgon Medusa. Pegasus was the brother of Chrysaor, both born from Medusa's blood w ...
. It has roughly 1.5 times the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
's mass and 4.9 times its luminosity. It is part of a system that also contains a debris disk
A debris disk (American English), or debris disc ( Commonwealth English), is a circumstellar disk of dust and debris in orbit around a star. Sometimes these disks contain prominent rings, as seen in the image of Fomalhaut on the right. Debris ...
and at least four massive planets. These planets were the first exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first confirmed detection of an exoplanet was in 1992 around a pulsar, and the first detection around a main-sequence star was in 1995. A different planet, first det ...
s whose orbital motion was confirmed by direct imaging. The star is a Gamma Doradus variable: its luminosity
Luminosity is an absolute measure of radiated electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic energy per unit time, and is synonymous with the radiant power emitted by a light-emitting object. In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of electroma ...
changes because of non-radial pulsations of its surface. The star is also classified as a Lambda Boötis star, which means its surface layers are depleted in iron peak
The iron peak is a local maximum in the vicinity of Iron, Fe (Chromium, Cr, Manganese, Mn, Fe, Cobalt, Co and Nickel, Ni) on the graph of the abundances of the chemical elements.
For elements lighter than iron on the periodic table, nuclear fusio ...
elements. It is the only known star which is simultaneously a Gamma Doradus variable, a Lambda Boötis type, and a Vega
Vega is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Lyra. It has the Bayer designation α Lyrae, which is Latinised to Alpha Lyrae and abbreviated Alpha Lyr or α Lyr. This star is relatively close at only from the Sun, and ...
-like star (a star with excess infrared emission caused by a circumstellar disk
A Circumstellar disc (or circumstellar disk) is a torus, pancake or ring-shaped accretion disk of matter composed of gas, dust, planetesimals, asteroids, or collision fragments in orbit around a star. Around the youngest stars, they are the res ...
).
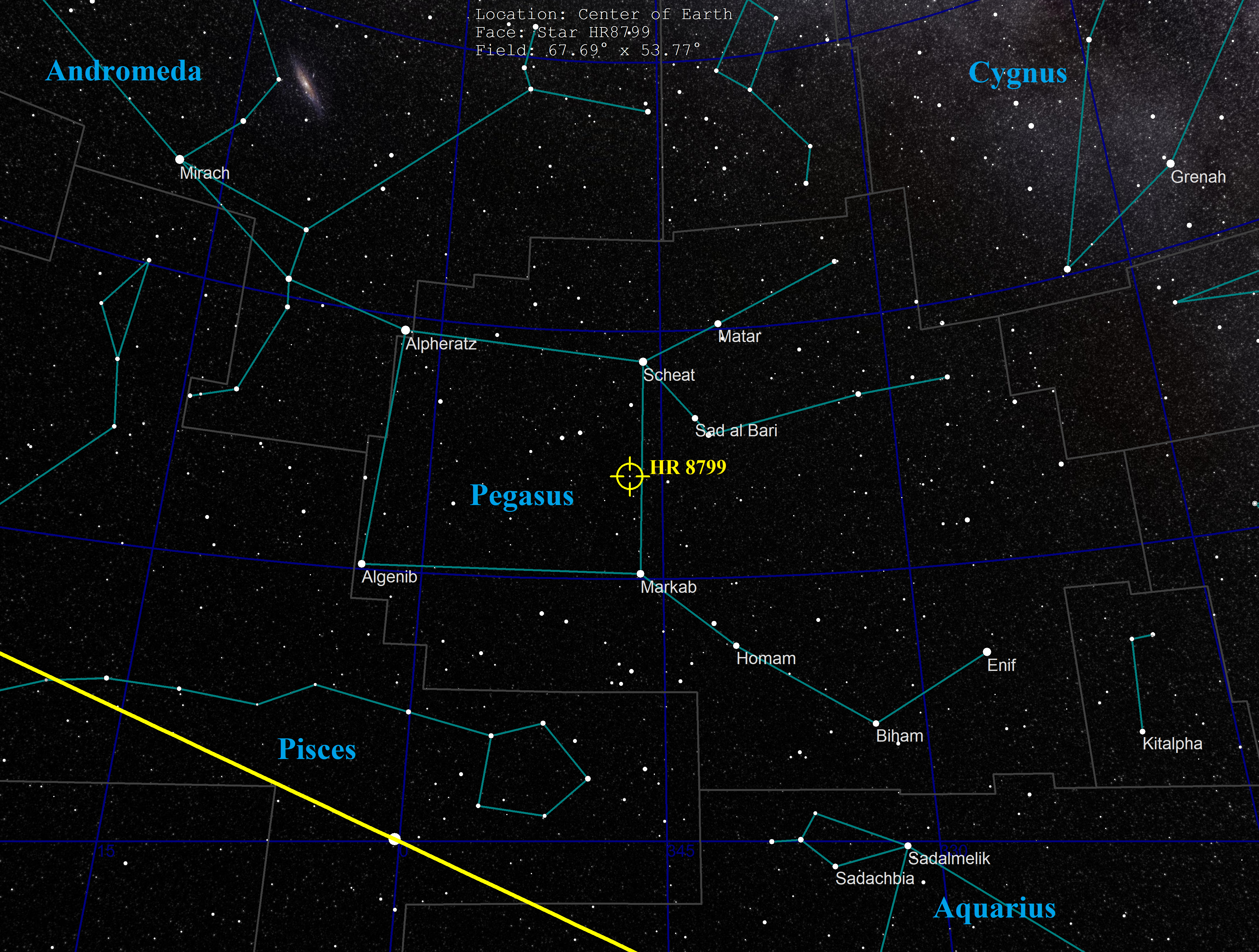
Location
HR 8799 is a star that is visible to the naked eye. It has a magnitude 5.96 and it is located inside the western edge of the great square of Pegasus almost exactly halfway betweenBeta
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; or ) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive . In Modern Greek, it represe ...
and Alpha Pegasi. The star's name of ''HR 8799'' is its line number in the Bright Star Catalogue
The Bright Star Catalogue, also known as the Yale Catalogue of Bright Stars, Yale Bright Star Catalogue, or just YBS, is a star catalogue that lists all stars of stellar magnitude 6.5 or brighter, which is roughly every star visible to the na ...
.

Stellar properties
 The star HR 8799 is a member of the Lambda Boötis ( Boo) class, a group of
The star HR 8799 is a member of the Lambda Boötis ( Boo) class, a group of peculiar star
In astrophysics, chemically peculiar stars (CP stars) are stars with distinctly unusual metal abundances, at least in their surface layers.
Classification
Chemically peculiar stars are common among hot main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) stars. These ...
s with an unusual lack of "metals" (elements heavier than hydrogen and helium) in their upper atmosphere. Because of this special status, stars like HR 8799 have a very complex spectral type. The luminosity profile of the Balmer lines
The Balmer series, or Balmer lines in atomic physics, is one of a set of six named series describing the spectral line emissions of the hydrogen atom. The Balmer series is calculated using the Balmer formula, an empirical equation discovered b ...
in the star's spectrum, as well as the star's effective temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature ...
, best match the typical properties of an F0 V star. However, the strength of the calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
II K absorption line
Absorption spectroscopy is spectroscopy that involves techniques that measure the absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of electromagnetic radiation, as a function of frequency or wavelength, due to its interaction with a sample. Th ...
and the other metallic lines are more like those of an A5 V star. The star's spectral type is therefore written as .
Age determination of this star shows some variation based on the method used. Statistically, for stars hosting a debris disk, the luminosity of this star suggests an age of about 20–150 million years. Comparison with stars having similar motion through space gives an age in the range 30–160 million years. Given the star's position on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram of luminosity versus temperature, it has an estimated age in the range of 30–1,128 million years. Boötis stars like this are generally young, with a mean age of a billion years. More accurately, asteroseismology
Asteroseismology is the study of oscillations in stars. Stars have many Resonance, resonant modes and frequencies, and the path of sound waves passing through a star depends on the local speed of sound, which in turn depends on local temperature a ...
also suggests an age of approximately a billion years. However, this is disputed because it would make the planets become brown dwarfs to fit into the cooling models. Brown dwarfs would not be stable in such a configuration. The best accepted value for an age of HR 8799 is 30 million years, consistent with being a member of the Columba association co-moving group of stars.
Earlier analysis of the star's spectrum reveals that it has a slight overabundance of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
and oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
compared to the Sun (by approximately 30% and 10% respectively). While some Lambda Boötis stars have sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
abundances similar to that of the Sun, this is not the case for HR 8799; the sulfur abundance is only around 35% of the solar level. The star is also poor in elements heavier than sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
: for example, the iron abundance is only 28% of the solar iron abundance. Asteroseismic observations of other pulsating Lambda Boötis stars suggest that the peculiar abundance patterns of these stars are confined to the surface only: the bulk composition is likely more normal. This may indicate that the observed element abundances are the result of the accretion of metal-poor gas from the environment around the star.
In 2020, spectral analysis utilizing multiple data sources have detected an inconsistency in prior data and concluded the star carbon and oxygen abundances are the same or slightly higher than solar. The iron abundance was updated to 30% of solar value.
Astroseismic analysis using spectroscopic data indicates that the rotational inclination of the star is constrained to be greater than or approximately equal to 40°. This contrasts with the planets' orbital inclinations, which are in roughly the same plane at an angle of about . Hence, there may be an unexplained misalignment between the rotation of the star and the orbits of its planets. Observation of this star with the Chandra X-ray Observatory
The Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), previously known as the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), is a Flagship-class space telescope launched aboard the during STS-93 by NASA on July 23, 1999. Chandra is sensitive to X-ray sources ...
indicates that it has a weak level of magnetic activity
A stellar magnetic field is a magnetic field generated by the motion of conductive Plasma (physics), plasma inside a star. This motion is created through convection, which is a form of energy transport involving the physical movement of material ...
, but the X-ray activity is much higher than that of an A‑type star like Altair
Altair is the brightest star in the constellation of Aquila (constellation), Aquila and the list of brightest stars, twelfth-brightest star in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation Alpha Aquilae, which is Latinisation of name ...
. This suggests that the internal structure of the star more closely resembles that of an F0 star. The temperature of the stellar corona
In astronomy, a corona (: coronas or coronae) is the outermost layer of a star's Stellar atmosphere, atmosphere. It is a hot but relatively luminosity, dim region of Plasma (physics), plasma populated by intermittent coronal structures such as so ...
is about 3.0 million K.
Planetary system

 On 13 November 2008, Christian Marois of the National Research Council of Canada's Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics and his team announced they had directly observed three
On 13 November 2008, Christian Marois of the National Research Council of Canada's Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics and his team announced they had directly observed three planets
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets by the most restrictive definition of the te ...
orbiting the star with the Keck and Gemini telescopes in Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
, in both cases employing adaptive optics
Adaptive optics (AO) is a technique of precisely deforming a mirror in order to compensate for light distortion. It is used in Astronomy, astronomical telescopes and laser communication systems to remove the effects of Astronomical seeing, atmo ...
to make observations in the infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
. A precovery
In astronomy, precovery (short for pre-discovery recovery) is the process of finding the image of a celestial object in images or photographic plates predating its discovery, typically for the purpose of calculating a more accurate orbit. This ha ...
observation of the outer 3 planets was later found in infrared images obtained in 1998 by the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most ...
's NICMOS instrument, after a newly developed image-processing technique was applied. Further observations in 2009–2010 revealed the fourth giant planet orbiting inside the first three planets at a projected separation
This glossary of astronomy is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to astronomy and cosmology, their sub-disciplines, and related fields. Astronomy is concerned with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outs ...
just less than 15 , which has been confirmed by multiple studies.
The outer planet orbits are inside a dusty disk like the Solar Kuiper belt
The Kuiper belt ( ) is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times ...
. It is one of the most massive disks known around any star within 300 light years of Earth, and there is room in the inner system for terrestrial planet
A terrestrial planet, tellurian planet, telluric planet, or rocky planet, is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate, rocks or metals. Within the Solar System, the terrestrial planets accepted by the IAU are the inner planets closest to ...
s. There is an additional debris disk just inside the orbit of the innermost planet.
The orbital radii of planets e, d, c, and b are 2–3 times those of Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
, Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant, with an average radius of about 9 times that of Earth. It has an eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 tim ...
, Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It is a gaseous cyan-coloured ice giant. Most of the planet is made of water, ammonia, and methane in a Supercritical fluid, supercritical phase of matter, which astronomy calls "ice" or Volatile ( ...
, and Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun. It is the List of Solar System objects by size, fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 t ...
's orbits, respectively. Because of the inverse square law
In science, an inverse-square law is any scientific law stating that the observed "intensity" of a specified physical quantity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of that physical quantity. The fundamental cau ...
relating radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
intensity
Intensity may refer to:
In colloquial use
* Strength (disambiguation)
*Amplitude
* Level (disambiguation)
* Magnitude (disambiguation)
In physical sciences
Physics
*Intensity (physics), power per unit area (W/m2)
*Field strength of electric, m ...
to distance from the source, comparable radiation intensities are present at distances farther from HR 8799 than from the Sun, the upshot being that corresponding planets in the solar and HR 8799 systems receive similar amounts of stellar radiation.
These objects are near the upper mass limit for classification as planets; if they exceeded 13 Jupiter masses, they would be capable of deuterium
Deuterium (hydrogen-2, symbol H or D, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen; the other is protium, or hydrogen-1, H. The deuterium nucleus (deuteron) contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more c ...
fusion in their interiors and thus qualify as brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs are substellar objects that have more mass than the biggest gas giant planets, but less than the least massive main sequence, main-sequence stars. Their mass is approximately 13 to 80 Jupiter mass, times that of Jupiter ()not big en ...
s under the definition of these terms used by the IAU
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; , UAI) is an international non-governmental organization (INGO) with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and developmen ...
's Working Group on Extrasolar Planets. If the mass estimates are correct, the HR 8799 system is the first multiple-planet extrasolar system to be directly imaged. The orbital motion of the planets is in an anticlockwise direction and was confirmed via multiple observations dating back to 1998. The system is more likely to be stable if the planets e, d, and c are in a 4:2:1 resonance, which would imply that the orbit of the planet d has an eccentricity exceeding 0.04 in order to match the observational constraints. Planetary systems with the best-fit masses from evolutionary models would be stable if the outer three planets are in a 1:2:4 orbital resonance
In celestial mechanics, orbital resonance occurs when orbiting bodies exert regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually because their orbital periods are related by a ratio of small integers. Most commonly, this relation ...
(similar to the Laplace resonance between Jupiter's inner three Galilean satellites: Io, Europa, and Ganymede as well as three of the planets in the Gliese 876 system). However, it is disputed if planet b is in resonance with the other 3 planets. According to dynamical simulations, the HR 8799 planetary system may be even an extrasolar system with multiple resonance 1:2:4:8. The 4 young planets are still glowing red hot from the heat of their formation, and are larger than Jupiter and over time they will cool and shrink to the sizes of 0.8–1.0 Jupiter radii.
The broadband photometry of planets b, c and d has shown that there may be significant clouds in their atmospheres, while the infrared spectroscopy of planets b and c points to non-equilibrium / chemistry. Near-infrared observations with the Project 1640 integral field spectrograph on the Palomar Observatory have shown that compositions between the four planets vary significantly. This is a surprise since the planets presumably formed in the same way from the same disk and have similar luminosities.
An additional planet candidate was found in cycle 1 with NIRCam, 5 arcseconds
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a degree. Since one degree is of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is of a tu ...
south of HR 8799. Follow-up observations with NIRCam are planned to confirm or reject this candidate.
Planet spectra
A number of studies have used the spectra of HR 8799's planets to determine their chemical compositions and constrain their formation scenarios. The first spectroscopic study of planet b (performed at near-infrared wavelengths) detected strong water absorption and hints of methane absorption. Subsequently, weak methane and carbon monoxide absorption in this planet's atmosphere was also detected, indicating efficient vertical mixing of the atmosphere and a disequilibrium / ratio at the photosphere. Compared to models of planetary atmospheres, this first spectrum of planet b is best matched by a model of enhancedmetallicity
In astronomy, metallicity is the Abundance of the chemical elements, abundance of Chemical element, elements present in an object that are heavier than hydrogen and helium. Most of the normal currently detectable (i.e. non-Dark matter, dark) matt ...
(about 10 times the metallicity of the Sun), which may support the notion that this planet formed through core-accretion.
The first simultaneous spectra of all four known planets in the HR 8799 system were obtained in 2012 using the Project 1640 instrument at Palomar Observatory. The near-infrared spectra from this instrument confirmed the red colors of all four planets and are best matched by models of planetary atmospheres that include clouds. Though these spectra do not directly correspond to any known astrophysical objects, some of the planet spectra demonstrate similarities with L- and T-type brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs are substellar objects that have more mass than the biggest gas giant planets, but less than the least massive main sequence, main-sequence stars. Their mass is approximately 13 to 80 Jupiter mass, times that of Jupiter ()not big en ...
s and the night-side spectrum of Saturn. The implications of the simultaneous spectra of all four planets obtained with Project 1640 are summarized as follows: Planet b contains ammonia and/or acetylene as well as carbon dioxide, but has little methane; planet c contains ammonia, perhaps some acetylene but neither carbon dioxide nor substantial methane; planet d contains acetylene, methane, and carbon dioxide but ammonia is not definitively detected; planet e contains methane and acetylene but no ammonia or carbon dioxide. The spectrum of planet e is similar to a reddened spectrum of Saturn.
Moderate-resolution near-infrared spectroscopy, obtained with the Keck telescope, definitively detected carbon monoxide and water absorption lines in the atmosphere of planet c. The carbon-to-oxygen ratio, which is thought to be a good indicator of the formation history for giant planets, for planet c was measured to be slightly greater than that of the host star HR 8799. The enhanced carbon-to-oxygen ratio and depleted levels of carbon and oxygen in planet c favor a history in which the planet formed through core accretion. However, it is important to note that conclusions about the formation history of a planet based solely on its composition may be inaccurate if the planet has undergone significant migration, chemical evolution, or core dredging. Later, in November 2018, researchers confirmed the existence of water and the absence of methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
in the atmosphere of using high-resolution spectroscopy and near-infrared adaptive optics ( NIRSPAO) at the Keck Observatory.
The red colors of the planets may be explained by the presence of iron and silicate atmospheric clouds, while their low surface gravities might explain the strong disequilibrium concentrations of carbon monoxide and the lack of strong methane absorption.
Debris disk
 In January 2009 the
In January 2009 the Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), was an infrared space telescope launched in 2003, that was deactivated when operations ended on 30 January 2020. Spitzer was the third space telescope dedicate ...
obtained images of the debris disk around HR 8799. Three components of the debris disk were distinguished:
# Warm dust ( ≈ 150 K) orbiting within the innermost planet (e). The inner and outer edges of this belt are close to 4:1 and 2:1 resonances with the planet.
# A broad zone of cold dust ( ≈ 45 K) with a sharp inner edge orbiting just outside the outermost planet (b). The inner edge of this belt is approximately in 3:2 resonance with said planet, similar to Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun. It is the List of Solar System objects by size, fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 t ...
and the Kuiper belt
The Kuiper belt ( ) is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times ...
.
# A dramatic halo of small grains originating in the cold dust component.
The halo is unusual and implies a high level of dynamic activity which is likely due to gravitational stirring by the massive planets. The Spitzer team says that collisions are likely occurring among bodies similar to those in the Kuiper Belt and that the three large planets may not yet have settled into their final, stable orbits.
In the photo, the bright, yellow-white portions of the dust cloud come from the outer cold disk. The huge extended dust halo, seen in orange-red, has a diameter of ≈ 2,000 . The diameter of Pluto's orbit (≈ 80 ) is shown for reference as a dot in the centre.
This disk is so thick that it threatens the young system's stability.
The disk was first resolved with ALMA in 2016 and was later imaged again in 2018. These later observations were more detailed and were studied by a team of astronomers. The disk has according to this team a smooth inner edge and a smooth outer edge. These also observed a possible inner dust belt. This inner belt was confirmed with MIRI
Miri () is a coastal city in north-eastern Sarawak, Malaysia, located near the border of Brunei, on the island of Borneo. The city covers an area of , located northeast of Kuching and southwest of Kota Kinabalu. Miri is the second largest ...
observations, which measured a radius of 15 au of the inner disk.
Vortex Coronagraph: Testbed for high-contrast imaging technology
 Up until the year 2010,
Up until the year 2010, telescopes
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
could only directly image exoplanets under exceptional circumstances. Specifically, it is easier to obtain images when the planet is especially large (considerably larger than Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
), widely separated from its parent star, and hot so that it emits intense infrared radiation. However, in 2010 a team from NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
s Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) in La Cañada Flintridge, California, Crescenta Valley, United States. Founded in 1936 by Cali ...
demonstrated that a vortex coronagraph could enable small telescopes to directly image planets. They did this by imaging the previously imaged HR 8799 planets using just a 1.5 m portion of the Hale Telescope
The Hale Telescope is a , 3.3 reflecting telescope at the Palomar Observatory in San Diego County, California, US, named after astronomer George Ellery Hale. With funding from the Rockefeller Foundation in 1928, he orchestrated the planning, de ...
.
NICMOS images
In 2009, an old NICMOS image was processed to show a predicted exoplanet around HR 8799. In 2011, three furtherexoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first confirmed detection of an exoplanet was in 1992 around a pulsar, and the first detection around a main-sequence star was in 1995. A different planet, first det ...
s were rendered viewable in a NICMOS image taken in 1998, using advanced data processing. The image allows the planets' orbits to be better characterised, since they take many decades to orbit their host star.
Search for radio emissions
Starting in 2010, astronomers searched for radio emissions from theexoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first confirmed detection of an exoplanet was in 1992 around a pulsar, and the first detection around a main-sequence star was in 1995. A different planet, first det ...
s orbiting HR 8799 using the radio telescope at Arecibo Observatory
The Arecibo Observatory, also known as the National Astronomy and Ionosphere Center (NAIC) and formerly known as the Arecibo Ionosphere Observatory, is an observatory in Barrio Esperanza, Arecibo, Puerto Rico owned by the US National Science F ...
. Despite the large masses, warm temperatures, and brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs are substellar objects that have more mass than the biggest gas giant planets, but less than the least massive main sequence, main-sequence stars. Their mass is approximately 13 to 80 Jupiter mass, times that of Jupiter ()not big en ...
-like luminosities, they failed to detect any emissions at 5 GHz down to a flux density detection threshold of 1.0 mJy.
See also
* List of exoplanets * Direct imaging of extrasolar planetsNotes
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:HR 8799 A-type main-sequence stars Gamma Doradus variables Pegasus (constellation) 218396 114189 8799 Pegasi, V342 Planetary systems with four confirmed planets Lambda Boötis stars Circumstellar disks Durchmusterung objects