H-IIB F4 Launching HTV4 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
H-IIB (H2B) was an expendable space launch system jointly developed by the Japanese government's space agency
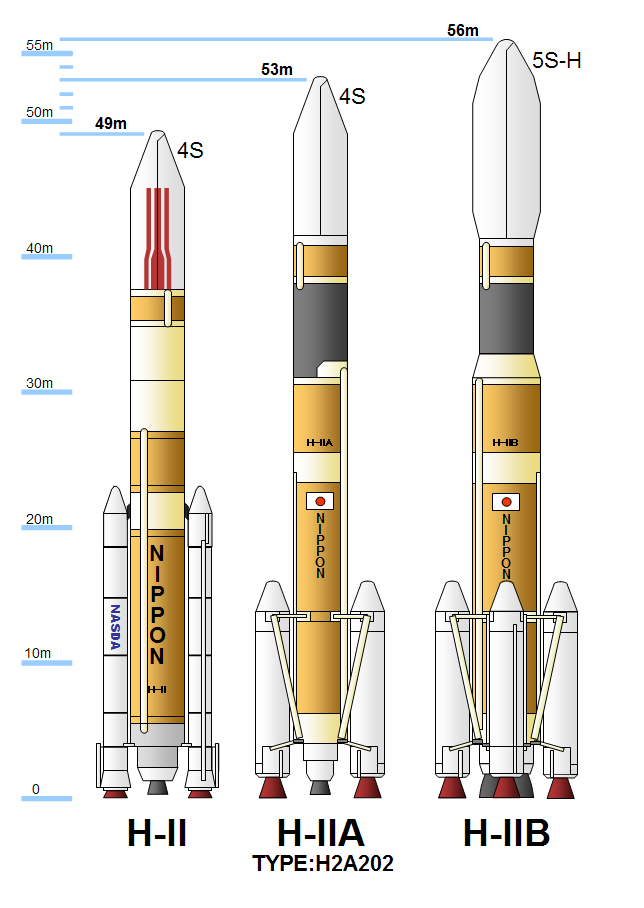 The H-IIB was a space launch vehicle jointly designed, manufactured and operated by
The H-IIB was a space launch vehicle jointly designed, manufactured and operated by
JAXA , H-IIB Launch Vehicle
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Technical Review Volume 45 Number 4
H-2B rocket 3D model
{{Expendable launch systems Mitsubishi Heavy Industries space launch vehicles Vehicles introduced in 2009 Expendable space launch systems
JAXA
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into o ...
and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational engineering, electrical equipment and electronics corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. MHI is one of the core companies of the Mitsubishi Group and its automobile division is the prede ...
. It was used to launch the H-II Transfer Vehicle
The H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV), also called , is an Expendable launch system, expendable Japanese Cargo spacecraft, automated cargo spacecraft designed for International Space Station (ISS) resupply missions, particularly the Kibo (ISS module ...
(HTV, or ''Kōnotori'') cargo spacecraft for the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
. The H-IIB was a liquid-fueled rocket, with solid-fuel strap-on boosters and was launched from the Tanegashima Space Center
The (TNSC) is Japan's primary spaceport, covering approximately about . It is located on the southeastern tip of Tanegashima, the easternmost of the Ōsumi Islands, approximately south of the major island of Kyushu.
The site was selected on ...
in southern Japan. H-IIB made its first flight in 2009, and had made a total of nine flights through 2020 with no failures.
H-IIB was able to carry a payload of up to to Geostationary transfer orbit
In space mission design, a geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) or geosynchronous transfer orbit is a highly elliptical type of geocentric orbit, usually with a perigee as low as low Earth orbit (LEO) and an apogee as high as geostationary orbit ...
(GTO), compared with the payload of 4000–6000 kg for the H-IIA
H-IIA (H-2A) is an active expendable launch system operated by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) for the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. These liquid fuel rockets have been used to launch satellites into geostationary orbit; lunar orbi ...
, a predecessor design. Its performance to low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an geocentric orbit, orbit around Earth with a orbital period, period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an orbital eccentricity, eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial object ...
(LEO) was sufficient for the H-II Transfer Vehicle
The H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV), also called , is an Expendable launch system, expendable Japanese Cargo spacecraft, automated cargo spacecraft designed for International Space Station (ISS) resupply missions, particularly the Kibo (ISS module ...
(HTV). The first H-IIB was launched in September 2009 and the last H-IIB was launched in May 2020.
Development
 The H-IIB was a space launch vehicle jointly designed, manufactured and operated by
The H-IIB was a space launch vehicle jointly designed, manufactured and operated by JAXA
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into o ...
and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational engineering, electrical equipment and electronics corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. MHI is one of the core companies of the Mitsubishi Group and its automobile division is the prede ...
to launch the H-II Transfer Vehicle
The H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV), also called , is an Expendable launch system, expendable Japanese Cargo spacecraft, automated cargo spacecraft designed for International Space Station (ISS) resupply missions, particularly the Kibo (ISS module ...
. The system was designed to adopt methods and components that have already been verified by flights on the H-IIA
H-IIA (H-2A) is an active expendable launch system operated by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) for the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. These liquid fuel rockets have been used to launch satellites into geostationary orbit; lunar orbi ...
, so that manufacturing the new launch vehicle would be more cost-effective, with less risk, in a shorter period of time. JAXA was in charge of preliminary design, readiness of the ground facility, and the development of new technologies for the H-IIB, in which the private sector has limited competencies, while the Mitsubishi Heavy Industries was responsible for manufacturing. JAXA successfully conducted eight firing tests of the new cluster design with the simulated first-stage propulsion system, called Battleship Firing Tests, since March 2008, at MHI's Tashiro Test Facility in Ōdate, Akita Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Tōhoku region of Honshu.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Provinces and prefectures" in ; "Tōhoku" in . Its population is estimated 915,691 as of 1 August 2023 and its geographi ...
.
Before launch, two Captive Firing Tests were conducted on the H-IIB. The first test, which consisted of firing the first stage for ten seconds, was originally scheduled to occur at 02:30 UTC
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is the primary time standard globally used to regulate clocks and time. It establishes a reference for the current time, forming the basis for civil time and time zones. UTC facilitates international communica ...
on 27 March 2009, however it was cancelled after the launch pad's coolant system failed to activate. This was later discovered to have been due to a manual supply valve not being open. The test was rescheduled for 1 April 2009, but then postponed again due to a leak in a pipe associated with the launch facility's fire suppression system. The test was rescheduled for 2 April 2009, when it was successfully conducted at 05:00 UTC. Following this, the second test, which involved a 150-second burn of the first stage, was scheduled for 20 April. This was successfully conducted at 04:00 UTC on 22 April 2009, following a two-day delay due to unfavorable weather conditions. A ground test, using a battleship
A battleship is a large, heavily naval armour, armored warship with a main battery consisting of large naval gun, guns, designed to serve as a capital ship. From their advent in the late 1880s, battleships were among the largest and most form ...
mockup of the rocket was subsequently conducted on 11 July 2009.
By 2009, the development program of the H-IIB had cost approximately 27 billion yen.
Vehicle description
The H-IIB launch vehicle was a two-stage rocket. The first stage usedliquid oxygen
Liquid oxygen, sometimes abbreviated as LOX or LOXygen, is a clear cyan liquid form of dioxygen . It was used as the oxidizer in the first liquid-fueled rocket invented in 1926 by Robert H. Goddard, an application which is ongoing.
Physical ...
and liquid hydrogen
Liquid hydrogen () is the liquid state of the element hydrogen. Hydrogen is found naturally in the molecule, molecular H2 form.
To exist as a liquid, H2 must be cooled below its critical point (thermodynamics), critical point of 33 Kelvins, ...
as propellants and had four strap-on solid rocket
A solid-propellant rocket or solid rocket is a rocket with a rocket engine that uses solid propellants (fuel/ oxidizer). The earliest rockets were solid-fuel rockets powered by gunpowder. The inception of gunpowder rockets in warfare can be cr ...
boosters ( SRB-A3) powered by polybutadiene
Polybutadiene utadiene rubber, BRis a synthetic rubber. It offers high elasticity, high resistance to wear, good strength even without fillers, and excellent abrasion resistance when filled and vulcanized. "Polybutadiene" is a collective name fo ...
. The first stage was powered by two LE-7A engines, instead of one for the H-IIA
H-IIA (H-2A) is an active expendable launch system operated by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) for the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. These liquid fuel rockets have been used to launch satellites into geostationary orbit; lunar orbi ...
. It had four SRB-As attached to the body, while the standard version of H-IIA had two SRB-As. In addition, the first-stage body of the H-IIB was 5.2 m in diameter compared with 4 m for the H-IIA. The total length of the first stage was extended by 1 m from that of H-IIA. As a result, the H-IIB first stage held 70% more propellant than that of the H-IIA. The second stage was powered by a single LE-5B engine, which was also propelled by a hydrogen/oxygen fuel and oxidizer.
Launch history
The first launch of the H-IIB occurred on 10 September 2009 at 17:01:46 UTC. It successfully launched the HTV-1, which was on a mission to resupply the International Space Station (ISS).See also
*Comparison of orbital launchers families
This article compares different orbital launcher families (launchers which are significantly different from other members of the same 'family' have separate entries). The article is organized into two tables: the first contains a list of currentl ...
* Comparison of orbital launch systems
This comparison of orbital launch systems lists the attributes of all current and future individual rocket configurations designed to reach orbit. A first list contains rockets that are operational or have attempted an orbital flight attempt as o ...
References
External links
JAXA , H-IIB Launch Vehicle
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Technical Review Volume 45 Number 4
H-2B rocket 3D model
{{Expendable launch systems Mitsubishi Heavy Industries space launch vehicles Vehicles introduced in 2009 Expendable space launch systems