Green electricity on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Low-carbon power is
Low-carbon power is
 During the late 20th and early 21st century significant findings regarding
During the late 20th and early 21st century significant findings regarding
 There are many options for lowering current levels of carbon emissions. Some options, such as wind power and solar power, produce low quantities of total life cycle carbon emissions, using entirely renewable sources. Other options, such as nuclear power, produce a comparable amount of carbon dioxide emissions as renewable technologies in total life cycle emissions, but consume non-renewable, but sustainable materials (
There are many options for lowering current levels of carbon emissions. Some options, such as wind power and solar power, produce low quantities of total life cycle carbon emissions, using entirely renewable sources. Other options, such as nuclear power, produce a comparable amount of carbon dioxide emissions as renewable technologies in total life cycle emissions, but consume non-renewable, but sustainable materials (

''Renewables in global energy supply: An IEA facts sheet''
(PDF), OECD, p. 3. However, there are typically low greenhouse gas emissions with
Nuclear ‘Renaissance’ Is Short on Largess
''

Geothermal Energy: International Market Update
May 2010, p. 4-6. while geothermal heating is in use in 70 countries. Current worldwide installed capacity is 10,715 megawatts (MW), with the largest capacity in the
Geothermal Energy: International Market Update
May 2010, p. 7.
/ref>
European Union hopes to sign a law
mandating net-zero greenhouse gas emissions in the coming year for all 27 countries in the union.
electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as describe ...
produced with substantially lower greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and ...
than conventional fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels ma ...
power generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery ( transmission, distribution, etc.) to end users or its stor ...
. The energy transition
The energy transition is the process of downshifting fossil fuels and re-developing whole systems to operate on low carbon energy sources. More generally, an energy transition is a significant structural change in an energy system regarding ...
to low-carbon power is one of the most important actions required to limit climate change. Power sector emissions may have peaked in 2018. During the first six months of 2020, scientists observed an 8.8% decrease in global CO2 emissions relative to 2019 due to COVID-19 lockdown measures. The two main sources of the decrease in emissions included ground transportation (40%) and the power sector (22%). This event is the largest absolute decrease in CO2 emissions in history, but emphasizes that low-carbon power "must be based on structural and transformational changes in energy-production systems".
Low carbon power generation sources include wind power
Wind power or wind energy is mostly the use of wind turbines to generate electricity. Wind power is a popular, sustainable, renewable energy source that has a much smaller impact on the environment than burning fossil fuels. Historically ...
, solar power
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovolta ...
, nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced b ...
and most hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of ...
. The term largely excludes conventional fossil fuel plant sources, and is only used to describe a particular subset of operating fossil fuel power systems, specifically, those that are successfully coupled with a flue gas
Flue gas is the gas exiting to the atmosphere via a flue, which is a pipe or channel for conveying exhaust gases from a fireplace, oven, furnace, boiler or steam generator. Quite often, the flue gas refers to the combustion exhaust gas produc ...
carbon capture and storage (CCS) system.https://www.gov.uk/innovation-funding-for-low-carbon-technologies-opportunities-for-bidders Innovation funding for low-carbon technologies: opportunities for bidders. "Meeting the energy challenge and government programme names nuclear power in the future energy mix, alongside other low-carbon sources, renewables and carbon capture and storage (CCS)." Globally almost 40% of electricity generation came from low-carbon sources in 2020: about 10% being nuclear power, almost 10% wind and solar, and around 20% hydropower and other renewables.
History
 During the late 20th and early 21st century significant findings regarding
During the late 20th and early 21st century significant findings regarding global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
highlighted the need to curb carbon emissions. From this, the idea for low-carbon power was born. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to advance scientific knowledge about climate change caused by human activities. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) ...
(IPCC), established by the World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology and geophysics.
The WMO originated from the Inter ...
(WMO) and the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) in 1988, set the scientific precedence for the introduction of low-carbon power. The IPCC has continued to provide scientific, technical and socio-economic advice to the world community, through its periodic assessment reports and special reports.
Internationally, the most prominent early step in the direction of low carbon power was the signing of the Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that (part ...
, which came into force on 16 February 2005, under which most industrialized countries committed to reduce their carbon emissions. The historical event set the political precedence for introduction of low-carbon power technology.
On a social level, perhaps the biggest factor contributing to the general public's awareness of climate change and the need for new technologies, including low carbon power, came from the documentary '' An Inconvenient Truth'', which clarified and highlighted the problem of global warming.
Power sources by greenhouse gas emissions
Differentiating attributes of low-carbon power sources
 There are many options for lowering current levels of carbon emissions. Some options, such as wind power and solar power, produce low quantities of total life cycle carbon emissions, using entirely renewable sources. Other options, such as nuclear power, produce a comparable amount of carbon dioxide emissions as renewable technologies in total life cycle emissions, but consume non-renewable, but sustainable materials (
There are many options for lowering current levels of carbon emissions. Some options, such as wind power and solar power, produce low quantities of total life cycle carbon emissions, using entirely renewable sources. Other options, such as nuclear power, produce a comparable amount of carbon dioxide emissions as renewable technologies in total life cycle emissions, but consume non-renewable, but sustainable materials (uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
). The term ''low-carbon power'' can also include power that continues to utilize the world's natural resources, such as natural gas and coal, but only when they employ techniques that reduce carbon dioxide emissions from these sources when burning them for fuel, such as the, as of 2012, pilot plants performing Carbon capture and storage.
Because the cost of reducing emissions in the electricity sector appears to be lower than in other sectors such as transportation, the electricity sector may deliver the largest proportional carbon reductions under an economically efficient climate policy.
Technologies to produce electric power with low-carbon emissions are in use at various scales. Together, they accounted for almost 40% of global electricity in 2020, with wind and solar almost 10%.
Technologies
The 2014 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report identifies nuclear, wind, solar and hydroelectricity in suitable locations as technologies that can provide electricity with less than 5% of the lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions of coal power.Hydroelectric power

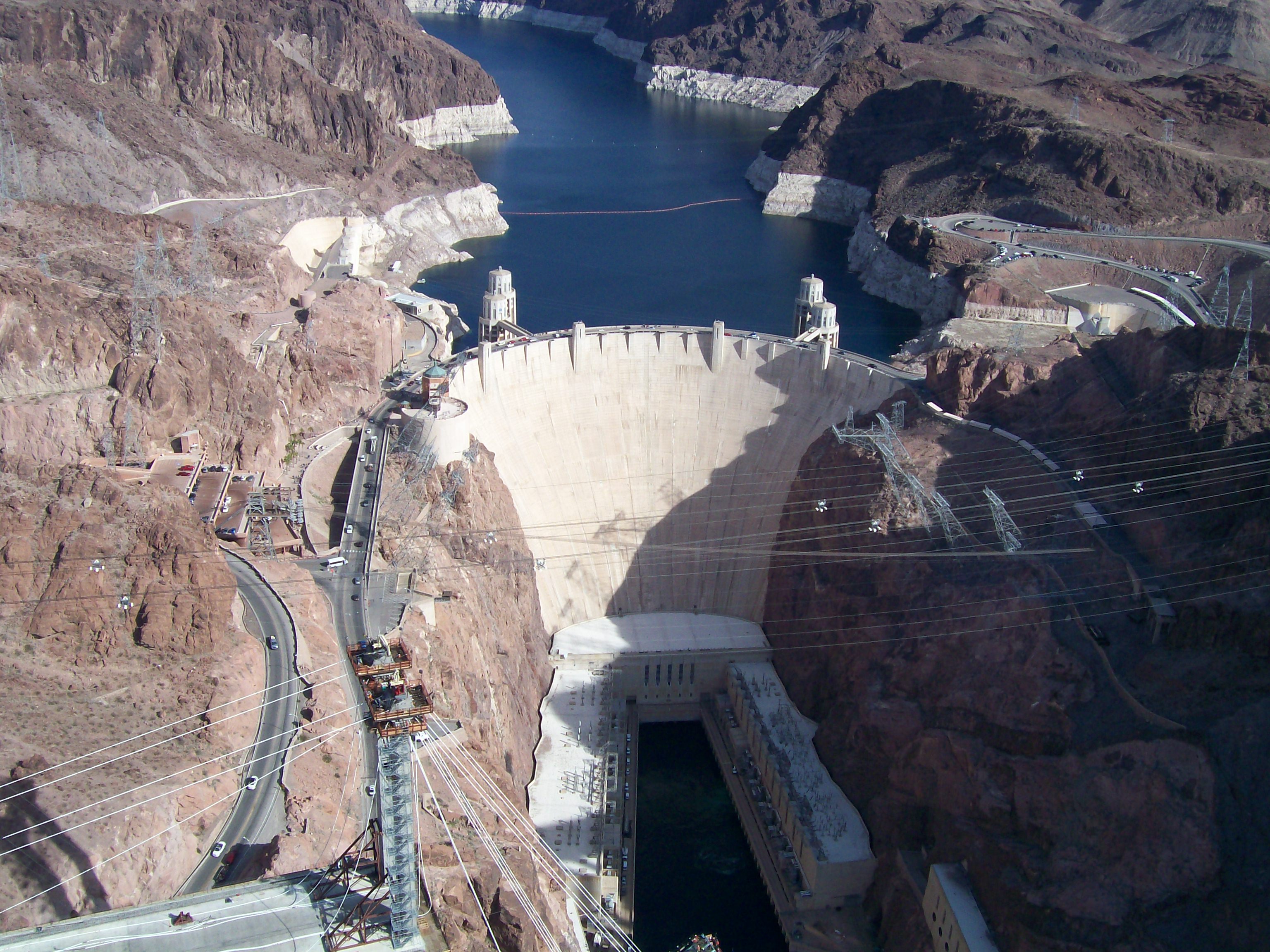
Hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined an ...
plants have the advantage of being long-lived and many existing plants have operated for more than 100 years. Hydropower is also an extremely flexible technology from the perspective of power grid operation. Large hydropower provides one of the lowest cost options in today's energy market, even compared to fossil fuels and there are no harmful emissions associated with plant operation.International Energy Agency (2007)''Renewables in global energy supply: An IEA facts sheet''
(PDF), OECD, p. 3. However, there are typically low greenhouse gas emissions with
reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.
Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including contr ...
s, and possibly high emissions in the tropics.
Hydroelectric power is the world's largest low carbon source of electricity, supplying 15.6% of total electricity in 2019. China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
is by far the world's largest producer of hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined an ...
in the world, followed by Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
.
However, there are several significant social and environmental disadvantages of large-scale hydroelectric power systems: dislocation, if people are living where the reservoirs are planned, release of significant amounts of carbon dioxide and methane during construction and flooding of the reservoir, and disruption of aquatic ecosystems and birdlife. There is a strong consensus now that countries should adopt an integrated approach towards managing water resources, which would involve planning hydropower development in co-operation with other water-using sectors.
Nuclear power

Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced b ...
, with a 10.6% share of world electricity production as of 2013, is the second largest low-carbon power source.
Nuclear power, in 2010, also provided two thirds of the twenty seven nation European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
's low-carbon energy, with some EU nations sourcing a large fraction of their electricity from nuclear power; for example France derives 79% of its electricity from nuclear. As of 2020 nuclear power provided 47% low-carbon power in the EU with countries largely based on nuclear power routinely achieving carbon intensity of 30-60 gCO2eq/kWh.
According to the IAEA
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 195 ...
and the European Nuclear Society, worldwide there were 68 civil nuclear power reactors under construction in 15 countries in 2013. China has 29 of these nuclear power reactors under construction, as of 2013, with plans to build many more, while in the US the licenses of almost half its reactors have been extended to 60 years, and plans to build another dozen are under serious consideration.Matthew L. Wald (7 December 2010)Nuclear ‘Renaissance’ Is Short on Largess
''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
''. There is also a considerable number of new reactors being built in South Korea, India, and Russia.
Nuclear power's capability to add significantly to future low carbon energy growth depends on several factors, including the economics of new reactor designs, such as Generation III reactor
Generation III reactors, or Gen III reactors, are a class of nuclear reactors designed to succeed Generation II reactors, incorporating evolutionary improvements in design. These include improved fuel technology, higher thermal efficiency, sign ...
s, public opinion and national and regional politics.
The 104 U.S. nuclear plants are undergoing a Light Water Reactor Sustainability Program, to sustainably extend the life span of the U.S. nuclear fleet by a further 20 years. With further US power plants under construction in 2013, such as the two AP1000s at Vogtle Electric Generating Plant. However the Economics of new nuclear power plants are still evolving and plans to add to those plants are mostly in flux.
In 2021 United Nations Economic Commission for Europe
The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (ECE or UNECE) is one of the five regional commissions under the jurisdiction of the United Nations Economic and Social Council. It was established in order to promote economic cooperation and ...
(UNECE) described nuclear power as important tool to mitigate climate change that has prevented 74 Gt of emissions over the last half century, providing 20% of energy in Europe and 43% of low-carbon energy.
Wind power

Solar power
Solar power is the conversion ofsunlight
Sunlight is a portion of the electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun, in particular infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light. On Earth, sunlight is scattered and filtered through Earth's atmosphere, and is obvious as daylight when ...
into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially ...
(PV), or indirectly using concentrated solar power
Concentrated solar power (CSP, also known as concentrating solar power, concentrated solar thermal) systems generate solar power by using mirrors or lenses to concentrate a large area of sunlight into a receiver. Electricity is generated when ...
(CSP). Concentrated solar power systems use lenses or mirrors and tracking systems to focus a large area of sunlight into a small beam. Photovoltaics convert light into electric current using the photoelectric effect
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation, such as light, hits a material. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons. The phenomenon is studied in condensed matter physics, and solid sta ...
.
Commercial concentrated solar power plants were first developed in the 1980s. The 354 MW SEGS CSP installation is the largest solar power plant in the world, located in the Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert ( ; mov, Hayikwiir Mat'aar; es, Desierto de Mojave) is a desert in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada mountains in the Southwestern United States. It is named for the indigenous Mojave people. It is located primarily ...
of California. Other large CSP plants include the Solnova Solar Power Station (150 MW) and the Andasol solar power station (150 MW), both in Spain. The over 200 MW Agua Caliente Solar Project in the United States, and the 214 MW Charanka Solar Park
Gujarat Solar Park-1 (also called Charanka Solar Park) is a solar power plant near Charanka village in Patan district of Gujarat, India. It is spread over an area of 2,000 hectares(4,900 acres). It has installed generation capacity of about 6 ...
in India, are the world's largest photovoltaic plant
A photovoltaic power station, also known as a solar park, solar farm, or solar power plant, is a large-scale grid-connected photovoltaic power system (PV system) designed for the supply of merchant power. They are different from most building- ...
s. Solar power's share of worldwide electricity usage at the end of 2014 was 1%.http://www.ren21.net/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/REN12-GSR2015_Onlinebook_low1.pdf pg31
Geothermal power
Geothermal electricity is electricity generated from geothermal energy. Technologies in use include dry steam power plants, flash steam power plants and binary cycle power plants. Geothermal electricity generation is used in 24 countriesGeothermal Energy AssociationGeothermal Energy: International Market Update
May 2010, p. 4-6. while geothermal heating is in use in 70 countries. Current worldwide installed capacity is 10,715 megawatts (MW), with the largest capacity in the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
(3,086 MW),Geothermal Energy AssociationGeothermal Energy: International Market Update
May 2010, p. 7.
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
. Estimates of the electricity generating potential of geothermal energy vary from 35 to 2000 GW.
Geothermal power is considered to be sustainable
Specific definitions of sustainability are difficult to agree on and have varied in the literature and over time. The concept of sustainability can be used to guide decisions at the global, national, and individual levels (e.g. sustainable livi ...
because the heat extraction is small compared to the Earth's heat content. The emission intensity of existing geothermal electric plants is on average 122 kg of per megawatt-hour (MW·h) of electricity, a small fraction of that of conventional fossil fuel plants.
Tidal power
Tidal power
Tidal power or tidal energy is harnessed by converting energy from tides into useful forms of power, mainly electricity using various methods.
Although not yet widely used, tidal energy has the potential for future electricity generation. ...
is a form of hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of ...
that converts the energy of tides into electricity or other useful forms of power. The first large-scale tidal power plant (the Rance Tidal Power Station) started operation in 1966. Although not yet widely used, tidal power has potential for future electricity generation. Tides are more predictable than wind energy and solar power.
Carbon capture and storage
Carbon capture and storage captures carbon dioxide from theflue gas
Flue gas is the gas exiting to the atmosphere via a flue, which is a pipe or channel for conveying exhaust gases from a fireplace, oven, furnace, boiler or steam generator. Quite often, the flue gas refers to the combustion exhaust gas produc ...
of power plants or other industry, transporting it to an appropriate location where it can be buried securely in an underground reservoir. While the technologies involved are all in use, and carbon capture and storage is occurring in other industries (e.g., at the Sleipner gas field), no large scale integrated project has yet become operational within the power industry.
Improvements to current carbon capture and storage technologies could reduce CO2 capture costs by at least 20-30% over approximately the next decade, while new technologies under development promise more substantial cost reduction.The National Energy Technology Laboratory Web site “Tracking New Coal Fired Power Plants”/ref>
Outlook and requirements
Emissions
TheIntergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to advance scientific knowledge about climate change caused by human activities. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) ...
stated in its first working group report that “most of the observed increase in globally averaged temperatures since the mid-20th century is very likely due to the observed increase in anthropogenic
Anthropogenic ("human" + "generating") is an adjective that may refer to:
* Anthropogeny, the study of the origins of humanity
Counterintuitively, anthropogenic may also refer to things that have been generated by humans, as follows:
* Human i ...
greenhouse gas concentrations, contribute to climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
.
As a percentage of all anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and ...
, carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
(CO2) accounts for 72 percent (see Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (), carbon dioxide (), methane ...
), and has increased in concentration in the atmosphere from 315 parts per million (ppm) in 1958 to more than 375 ppm in 2005.
Emissions from energy make up more than 61.4 percent of all greenhouse gas emissions. Power generation from traditional coal fuel sources accounts for 18.8 percent of all world greenhouse gas emissions, nearly double that emitted by road transportation.
Estimates state that by 2020 the world will be producing around twice as much carbon emissions as it was in 2000.
ThEuropean Union hopes to sign a law
mandating net-zero greenhouse gas emissions in the coming year for all 27 countries in the union.
Electricity usage
World energy consumption is predicted to increase from in 2003 to in 2030. Coal consumption is predicted to nearly double in that same time. The fastest growth is seen in non-OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate ...
Asian countries, especially China and India, where economic growth drives increased energy use. By implementing low-carbon power options, world electricity demand could continue to grow while maintaining stable carbon emission levels.
In the transportation sector there are moves away from fossil fuels and towards electric vehicles, such as mass transit
Public transport (also known as public transportation, public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) is a system of transport for passengers by group travel systems available for use by the general public unlike private transport, typical ...
and the electric car
An electric car, battery electric car, or all-electric car is an automobile that is propelled by one or more electric motors, using only energy stored in batteries. Compared to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, electric cars are quiet ...
. These trends are small, but may eventually add a large demand to the electrical grid.
Domestic and industrial heat and hot water have largely been supplied by burning fossil fuels such as fuel oil or natural gas at the consumers' premises. Some countries have begun heat pump rebates to encourage switching to electricity, potentially adding a large demand to the grid.
Energy infrastructure
Coal-fired power plants are losing market share compared to low carbon power, and any built in the 2020s risk becoming stranded assets orstranded costs In discussions of electric power generation deregulation, stranded costs represent a public utility's existing infrastructure investments that may become redundant after substantial changes in regulatory or market conditions. An incumbent electric ...
, partly because their capacity factors will decline.
Investment
Investment in low-carbon power sources and technologies is increasing at a rapid rate. Zero-carbon power sources produce about 2% of the world's energy, but account for about 18% of world investment in power generation, attracting $100 billion of investment capital in 2006.See also
* Carbon capture and storage * Carbon sink *Climate Change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
* Emissions trading
Emissions trading is a market-based approach to controlling pollution by providing economic incentives for reducing the emissions of pollutants. The concept is also known as cap and trade (CAT) or emissions trading scheme (ETS). Carbon emissi ...
* Energy development
Energy development is the field of activities focused on obtaining sources of energy from natural resources. These activities include production of renewable, nuclear, and fossil fuel derived sources of energy, and for the recovery and reuse ...
* Energy portal
* Global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
* Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (), carbon dioxide (), methane ...
es
* List of renewable energy organizations
* Renewable energy commercialization
References
{{reflist Sustainable energy Energy development Low-carbon economy