Green Line B branch on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The B branch, also called the Commonwealth Avenue branch or Boston College branch, is a branch of the
 The first sections of what is now the B branch to open were built for what became the Watertown Line and Beacon Street Line. In 1889, the
The first sections of what is now the B branch to open were built for what became the Watertown Line and Beacon Street Line. In 1889, the
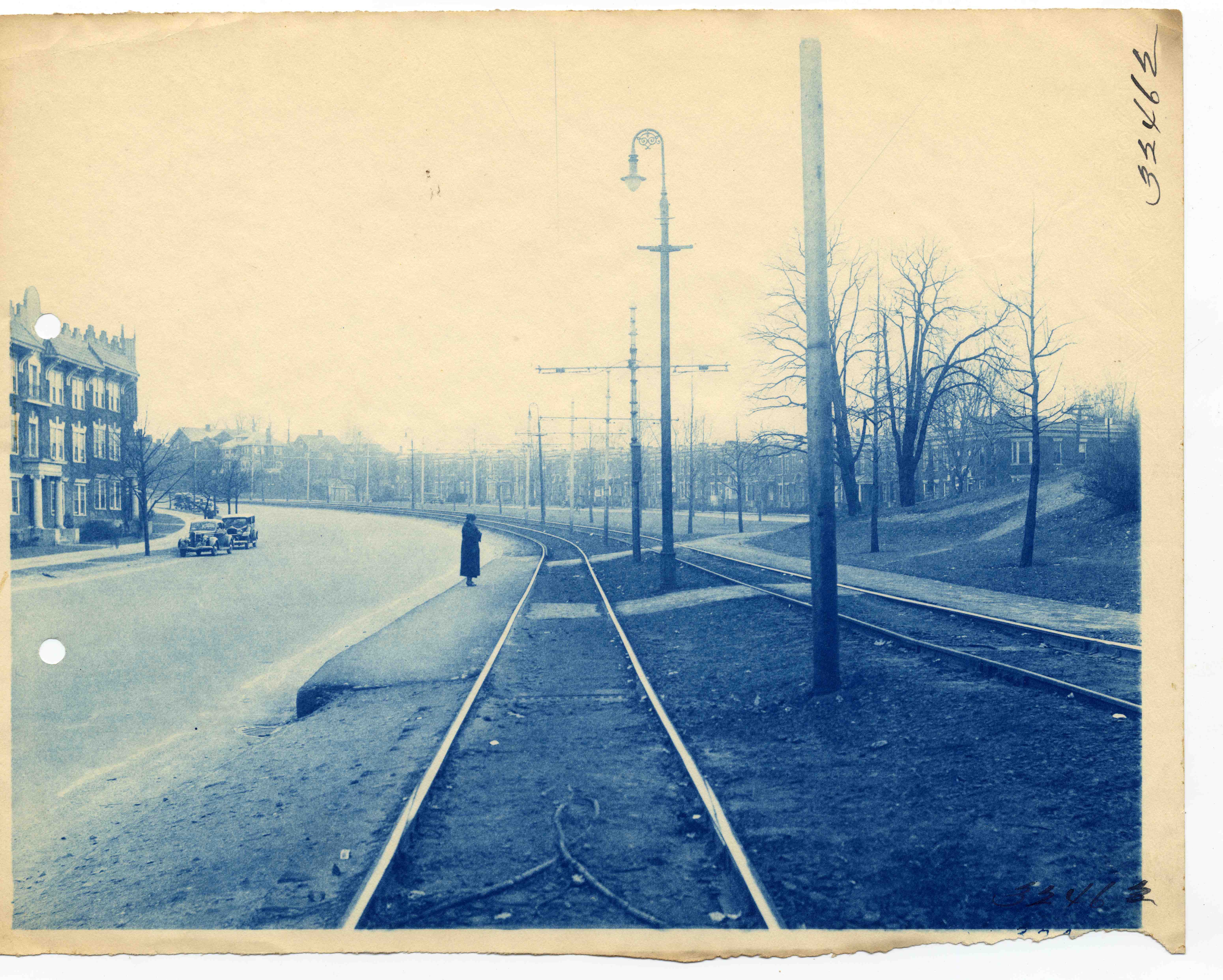 The Commonwealth Avenue Street Railway opened the popular Norumbega Park on June 17, 1897. (That line merged into the Newton and Boston Street Railway (N&B) in 1904 and the Middlesex and Boston Street Railway (M&B) in 1909.) Through service between Norumbega Park and Park Street station, operated by BERy east of Lake Street, begun on January 17, 1903. The Newton Street Railway (also merged into the N&B in 1904) began through service between Park Street and via the Watertown Line on February 23, 1903. When the Cambridge Tunnel opened in April 1912, the Waltham service was rerouted to Central Square station in Cambridge instead. On May 1, 1912, the M&B began a second through service over the Commonwealth Avenue route – this one running to Newton Highlands. The next month, two men were charged with a planned "conspiracy to blow up the tracks of the Elevated Company in Commonwealth av" using ten sticks of stolen dynamite.
The Boylston Street subway opened on October 3, 1914, acting as an extension of the Tremont Street subway to just east of Governors Square, with intermediate stops at Copley Square and Massachusetts Avenue. (A third station, , was not built until 1921.) Lake Street service via Washington Street was cut back to except at rush hours. The Newton Highlands through service was cut back to Lake Street, where it connected with BERy streetcar service. Norumbega Park through service continued to use the surface route, as the older M&B streetcars could not match the speed of the newer BERy streetcars in the subway. It took was split at Lake Street on November 1, with a connecting BERy line using the surface route; that was cut to a Kenmore–Park Street route on November 21.
On November 21, rush hour Washington Street service was cut back to Reservoir, leaving only Beacon Street cars using the Chestnut Hill Avenue tracks. Beacon Street service was cut to Reservoir on November 6, 1915, with Washington Street service extended back to Lake Street. Beginning on February 6, 1922, all Washington Street service was operated as a Brookline Village–Lake Street shuttle as part of service changes on the Huntington Avenue line. The Washington Street shuttle was converted to bus on April 24, 1926. It was redirected to Brighton Center on June 23, 1928, and eventually became route 65.
The Commonwealth Avenue Street Railway opened the popular Norumbega Park on June 17, 1897. (That line merged into the Newton and Boston Street Railway (N&B) in 1904 and the Middlesex and Boston Street Railway (M&B) in 1909.) Through service between Norumbega Park and Park Street station, operated by BERy east of Lake Street, begun on January 17, 1903. The Newton Street Railway (also merged into the N&B in 1904) began through service between Park Street and via the Watertown Line on February 23, 1903. When the Cambridge Tunnel opened in April 1912, the Waltham service was rerouted to Central Square station in Cambridge instead. On May 1, 1912, the M&B began a second through service over the Commonwealth Avenue route – this one running to Newton Highlands. The next month, two men were charged with a planned "conspiracy to blow up the tracks of the Elevated Company in Commonwealth av" using ten sticks of stolen dynamite.
The Boylston Street subway opened on October 3, 1914, acting as an extension of the Tremont Street subway to just east of Governors Square, with intermediate stops at Copley Square and Massachusetts Avenue. (A third station, , was not built until 1921.) Lake Street service via Washington Street was cut back to except at rush hours. The Newton Highlands through service was cut back to Lake Street, where it connected with BERy streetcar service. Norumbega Park through service continued to use the surface route, as the older M&B streetcars could not match the speed of the newer BERy streetcars in the subway. It took was split at Lake Street on November 1, with a connecting BERy line using the surface route; that was cut to a Kenmore–Park Street route on November 21.
On November 21, rush hour Washington Street service was cut back to Reservoir, leaving only Beacon Street cars using the Chestnut Hill Avenue tracks. Beacon Street service was cut to Reservoir on November 6, 1915, with Washington Street service extended back to Lake Street. Beginning on February 6, 1922, all Washington Street service was operated as a Brookline Village–Lake Street shuttle as part of service changes on the Huntington Avenue line. The Washington Street shuttle was converted to bus on April 24, 1926. It was redirected to Brighton Center on June 23, 1928, and eventually became route 65.
 The Commonwealth Avenue line served two major baseball stadiums:
The Commonwealth Avenue line served two major baseball stadiums:
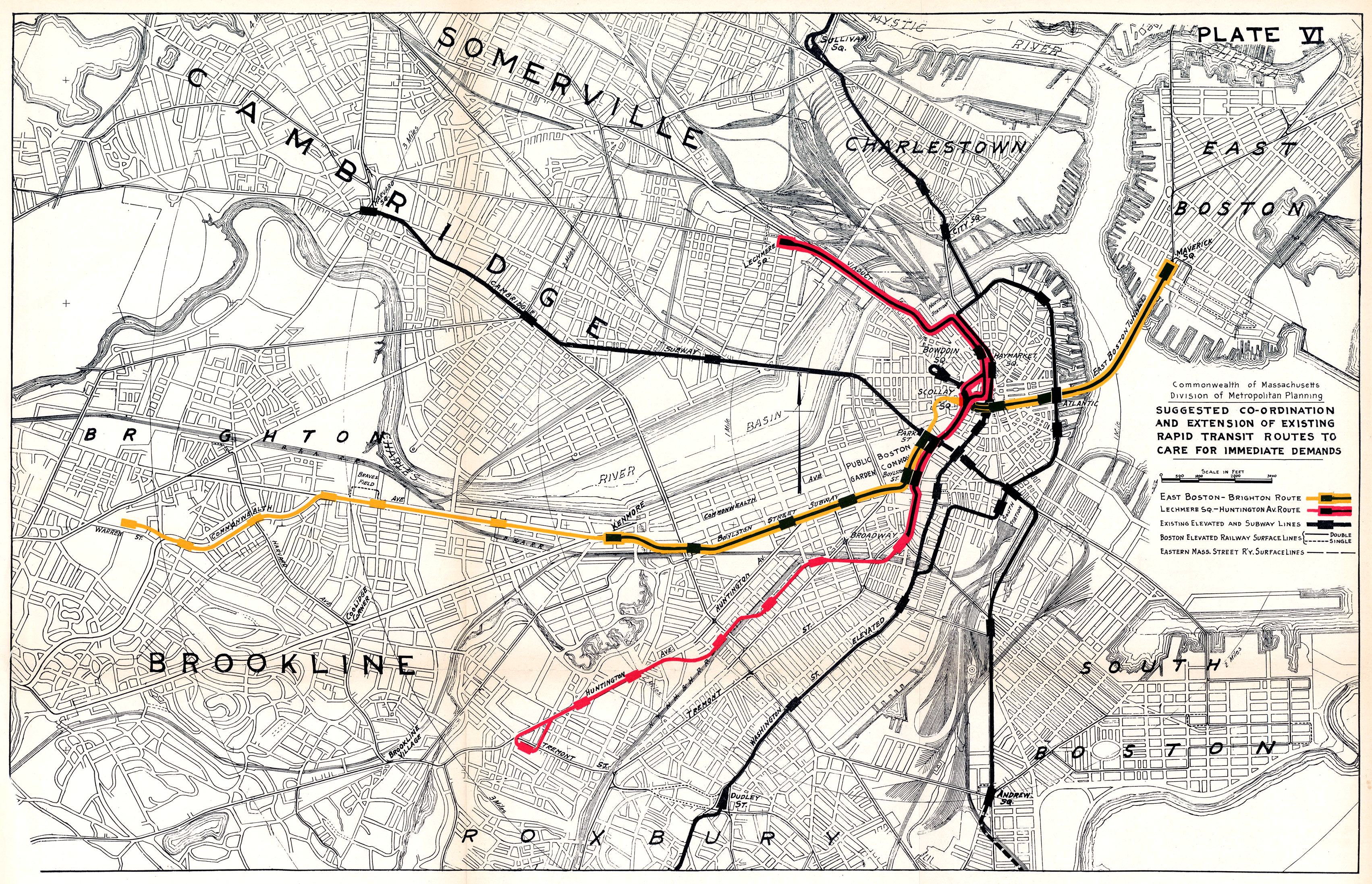 In June 1922, the BERy proposed to operate the inner part of the Commonwealth Avenue line as a rapid transit service. Three-car trains of recently acquired center-entrance cars, which had higher capacity and shorter dwell times than older streetcars, would run on headways as low as two minutes at rush hour and four minutes at other times. A terminal stations would be built at Linden Street (near ) in Allston, where passengers would transfer between the subway trains and surface streetcar lines. The
In June 1922, the BERy proposed to operate the inner part of the Commonwealth Avenue line as a rapid transit service. Three-car trains of recently acquired center-entrance cars, which had higher capacity and shorter dwell times than older streetcars, would run on headways as low as two minutes at rush hour and four minutes at other times. A terminal stations would be built at Linden Street (near ) in Allston, where passengers would transfer between the subway trains and surface streetcar lines. The  The subway under Governors Square was projected to cost $5 million (equivalent to $ million in ). The BERy and the city objected to this cost and proposed a $1.4 million plan where flyover ramps would separate Beacon Street auto and streetcar traffic from other traffic in the square. The tunnel was eventually chosen but construction did not begin until 1930, after the legislature lowered the cost that the BERy would pay to rent the subway from the city.
The subway under Governors Square was projected to cost $5 million (equivalent to $ million in ). The BERy and the city objected to this cost and proposed a $1.4 million plan where flyover ramps would separate Beacon Street auto and streetcar traffic from other traffic in the square. The tunnel was eventually chosen but construction did not begin until 1930, after the legislature lowered the cost that the BERy would pay to rent the subway from the city.


MBTA – Green Line B branch
{{DEFAULTSORT:Green Line B branch Green Line (MBTA) Railway lines opened in 1932
MBTA
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (abbreviated MBTA and known colloquially as "the T") is the public agency responsible for operating most public transportation services in Greater Boston, Massachusetts. The MBTA transit network in ...
Green Line light rail system which operates on Commonwealth Avenue west of downtown Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- most p ...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
. One of four branches of the Green Line, the B branch runs from Boston College station down the median of Commonwealth Avenue to . There, it enters Blandford Street portal into Kenmore station
Kenmore station is a light rail station on the MBTA Green Line, located under Kenmore Square in the Fenway/Kenmore neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. The station opened on October 23, 1932 as a one-station extension of the Boylston Stre ...
, where it merges with the C and D branches. The combined services run into the Boylston Street subway and Tremont Street subway
The Tremont Street subway in Boston's MBTA subway system is the oldest subway tunnel in North America and the third oldest still in use worldwide to exclusively use electric traction (after the City and South London Railway in 1890, and the B ...
to downtown Boston. B branch service has terminated at since October 2021. Unlike the other branches, the B branch runs solely through the city limits of Boston. The Green Line Rivalry
The Green Line Rivalry, also known as the B-Line Rivalry, the Battle of Boston and Battle of Commonwealth Avenue, is the name for the sports rivalry between Boston College and Boston University. The rivalry is named after the Green Line, a lig ...
between Boston College
Boston College (BC) is a private Jesuit research university in Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts. Founded in 1863, the university has more than 9,300 full-time undergraduates and nearly 5,000 graduate students. Although Boston College is classifie ...
and Boston University
Boston University (BU) is a Private university, private research university in Boston, Massachusetts. The university is nonsectarian, but has a historical affiliation with the United Methodist Church. It was founded in 1839 by Methodists with ...
is named in reference to the B branch, which runs to both universities.
, service operates on 7 to 7.5-minute headways at weekday peak hours and 8 to 12-minute headways at other times, using 10 to 16 trains (20 to 32 LRVs).
History
Initial construction
 The first sections of what is now the B branch to open were built for what became the Watertown Line and Beacon Street Line. In 1889, the
The first sections of what is now the B branch to open were built for what became the Watertown Line and Beacon Street Line. In 1889, the West End Street Railway
The West End Street Railway was a streetcar company that operated in Boston, Massachusetts and several surrounding communities in the late nineteenth century.
Originally an offshoot of a land development venture, the West End rose to prominence ...
opened the Beacon Street Line, including a branch that ran from Coolidge Corner
Coolidge Corner is a neighborhood of Brookline, Massachusetts, centered on the intersection of Beacon Street and Harvard Street. The neighborhood takes its name from the Coolidge & Brother general store that opened in 1857 at that intersecti ...
to Oak Square
Oak Square is a former station on the Green Line A branch
The A branch or Watertown Line was a streetcar line in the Boston, Massachusetts, area, operating as a branch of the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority Green Line. The line ...
along Harvard Avenue, Brighton Avenue, Cambridge Street, and Washington Street. While this route provided service to the fast-growing suburbs of Allston and Brighton, a more direct route was desirable. When Commonwealth Avenue was improved between Governors Square and the junction with Brighton Avenue in the mid-1890s, a -wide median was included for use by a streetcar line to support real estate development. Service began from Governors Square to Brighton Avenue, and along Brighton Avenue to connect with the older trackage at , on May 18, 1896. (That line was extended to near Nonantum Square on June 13, 1896.)
Further west, between and the Boston– Newton boundary at Lake Street, a -wide streetcar median was built. Service between Lake Street and downtown Boston began on August 15, 1896. Streetcars ran on Chestnut Hill Avenue, the existing Beacon Street line, Washington Street, and Huntington Avenue
Huntington Avenue is a secondary thoroughfare in the city of Boston, Massachusetts, beginning at Copley Square, and continuing west through the Back Bay, Fenway, Longwood, and Mission Hill neighborhoods. Huntington Avenue is signed as Route ...
. At Lake Street, the line connected with the Commonwealth Avenue Street Railway
The Middlesex and Boston Street Railway (M&B) was a streetcar and later bus company in the area west of Boston. Streetcars last ran in 1930, and in 1972 the company's operations were merged into the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBT ...
, which had opened to Auburndale on March 26, 1896.
East of Governors Square, the Beacon Street line originally ran on Beacon Street, Massachusetts Avenue, and Boylston Street to Park Square. By the time the Commonwealth Avenue segments opened, streetcars continued along heavily congested tracks on Tremont Street (electrified in 1891) to reach the northern railroad terminals. Both the Nonantum Square and Lake Street lines were rerouted into the Tremont Street subway
The Tremont Street subway in Boston's MBTA subway system is the oldest subway tunnel in North America and the third oldest still in use worldwide to exclusively use electric traction (after the City and South London Railway in 1890, and the B ...
to terminate at Park Street station soon after the tunnel's September 1, 1897 opening.
The Boston Elevated Railway
The Boston Elevated Railway (BERy) was a streetcar and rapid transit railroad operated on, above, and below, the streets of Boston, Massachusetts and surrounding communities. Founded in 1894, it eventually acquired the West End Street Railwa ...
(BERy) leased the West End Street Railway on October 1, 1897, and continued its system expansion. The BERy opened new tracks on Commonwealth Avenue from Chestnut Hill Avenue to Brighton Avenue on May 26, 1900, allowing direct service from Lake Street to downtown via Commonwealth Avenue. Even though much of the land surrounding Commonwealth Avenue in Brighton was not yet developed, the new line was heavily patronized. For most of its length, the 1900-built trackage was not in a center median, but in a reservation between the southbound travel lane and southbound carriage lane. Between and Wallingford Road, the reservation was significantly wider than the tracks.
Growing service
 The Commonwealth Avenue Street Railway opened the popular Norumbega Park on June 17, 1897. (That line merged into the Newton and Boston Street Railway (N&B) in 1904 and the Middlesex and Boston Street Railway (M&B) in 1909.) Through service between Norumbega Park and Park Street station, operated by BERy east of Lake Street, begun on January 17, 1903. The Newton Street Railway (also merged into the N&B in 1904) began through service between Park Street and via the Watertown Line on February 23, 1903. When the Cambridge Tunnel opened in April 1912, the Waltham service was rerouted to Central Square station in Cambridge instead. On May 1, 1912, the M&B began a second through service over the Commonwealth Avenue route – this one running to Newton Highlands. The next month, two men were charged with a planned "conspiracy to blow up the tracks of the Elevated Company in Commonwealth av" using ten sticks of stolen dynamite.
The Boylston Street subway opened on October 3, 1914, acting as an extension of the Tremont Street subway to just east of Governors Square, with intermediate stops at Copley Square and Massachusetts Avenue. (A third station, , was not built until 1921.) Lake Street service via Washington Street was cut back to except at rush hours. The Newton Highlands through service was cut back to Lake Street, where it connected with BERy streetcar service. Norumbega Park through service continued to use the surface route, as the older M&B streetcars could not match the speed of the newer BERy streetcars in the subway. It took was split at Lake Street on November 1, with a connecting BERy line using the surface route; that was cut to a Kenmore–Park Street route on November 21.
On November 21, rush hour Washington Street service was cut back to Reservoir, leaving only Beacon Street cars using the Chestnut Hill Avenue tracks. Beacon Street service was cut to Reservoir on November 6, 1915, with Washington Street service extended back to Lake Street. Beginning on February 6, 1922, all Washington Street service was operated as a Brookline Village–Lake Street shuttle as part of service changes on the Huntington Avenue line. The Washington Street shuttle was converted to bus on April 24, 1926. It was redirected to Brighton Center on June 23, 1928, and eventually became route 65.
The Commonwealth Avenue Street Railway opened the popular Norumbega Park on June 17, 1897. (That line merged into the Newton and Boston Street Railway (N&B) in 1904 and the Middlesex and Boston Street Railway (M&B) in 1909.) Through service between Norumbega Park and Park Street station, operated by BERy east of Lake Street, begun on January 17, 1903. The Newton Street Railway (also merged into the N&B in 1904) began through service between Park Street and via the Watertown Line on February 23, 1903. When the Cambridge Tunnel opened in April 1912, the Waltham service was rerouted to Central Square station in Cambridge instead. On May 1, 1912, the M&B began a second through service over the Commonwealth Avenue route – this one running to Newton Highlands. The next month, two men were charged with a planned "conspiracy to blow up the tracks of the Elevated Company in Commonwealth av" using ten sticks of stolen dynamite.
The Boylston Street subway opened on October 3, 1914, acting as an extension of the Tremont Street subway to just east of Governors Square, with intermediate stops at Copley Square and Massachusetts Avenue. (A third station, , was not built until 1921.) Lake Street service via Washington Street was cut back to except at rush hours. The Newton Highlands through service was cut back to Lake Street, where it connected with BERy streetcar service. Norumbega Park through service continued to use the surface route, as the older M&B streetcars could not match the speed of the newer BERy streetcars in the subway. It took was split at Lake Street on November 1, with a connecting BERy line using the surface route; that was cut to a Kenmore–Park Street route on November 21.
On November 21, rush hour Washington Street service was cut back to Reservoir, leaving only Beacon Street cars using the Chestnut Hill Avenue tracks. Beacon Street service was cut to Reservoir on November 6, 1915, with Washington Street service extended back to Lake Street. Beginning on February 6, 1922, all Washington Street service was operated as a Brookline Village–Lake Street shuttle as part of service changes on the Huntington Avenue line. The Washington Street shuttle was converted to bus on April 24, 1926. It was redirected to Brighton Center on June 23, 1928, and eventually became route 65.
 The Commonwealth Avenue line served two major baseball stadiums:
The Commonwealth Avenue line served two major baseball stadiums: Fenway Park
Fenway Park is a baseball stadium located in Boston, Massachusetts, United States, near Kenmore Square. Since 1912, it has been the home of the Boston Red Sox, the city's American League baseball team, and since 1953, its only Major League Base ...
(opened 1912) near Governors Square, and Braves Field
Braves Field was a baseball park located in Boston, Massachusetts. Today the site is home to Nickerson Field on the campus of Boston University. The stadium was home of the Boston Braves of the National League from 1915 to 1952, prior to the Br ...
(opened 1915) in Allston. The BERy opened a prepayment surface station (where riders paid their fares at the stop, rather than on board the streetcar) at Kenmore Street in Governors Square in 1915. The new Braves Field opened on August 18, 1915; it included a loop track between Gaffney Street and Babcock Street with a prepayment station to allow streetcars to directly serve the ballpark. The loop was also used to turn trains for Red Sox games at Fenway Park, and for rush-hour short turn
In public transport, a short turn, short working or turn-back is an earlier terminus on a bus or rail line that is used on some scheduled trips that do not operate along the full length of the route.
Short turns are practical in scheduling when ...
s; after November 1945, these short turns also operated during midday and on Saturdays. The loop was heavily used during games; for the 1948 World Series
The 1948 World Series was the championship series in Major League Baseball for the 1948 season. The 45th edition of the World Series, it matched the American League (AL) champion Cleveland Indians and the National League (NL) champion Boston Br ...
, streetcars ran between Park Street and Braves Field on 45-second headways.
Further changes
Around 1916, the BERy built a storage yard for streetcars north of Commonwealth Avenue at Lake Street. Remaining M&B service to Lake Street was replaced by buses in 1930; the BERy replaced the old transfer station in the median with a new platform and waiting room in the yard on September 12, 1930. An expansion of Reservoir Yard (south of Beacon Street near Chestnut Hill Avenue), completed in May 1940, supplemented Lake Street Yard and eliminated the need to base some Commonwealth Avenue streetcars at Bennett Street Carhouse in Cambridge. In June 1922, the BERy proposed to operate the inner part of the Commonwealth Avenue line as a rapid transit service. Three-car trains of recently acquired center-entrance cars, which had higher capacity and shorter dwell times than older streetcars, would run on headways as low as two minutes at rush hour and four minutes at other times. A terminal stations would be built at Linden Street (near ) in Allston, where passengers would transfer between the subway trains and surface streetcar lines. The
In June 1922, the BERy proposed to operate the inner part of the Commonwealth Avenue line as a rapid transit service. Three-car trains of recently acquired center-entrance cars, which had higher capacity and shorter dwell times than older streetcars, would run on headways as low as two minutes at rush hour and four minutes at other times. A terminal stations would be built at Linden Street (near ) in Allston, where passengers would transfer between the subway trains and surface streetcar lines. The Lechmere Square
Lechmere Square ( ) is located at the intersection of Cambridge Street and First Street in East Cambridge, Massachusetts. It was originally named for the Colonial-era landowner Richard Lechmere, a Loyalist who returned to England at the beginning ...
in East Cambridge (already under construction) opened that July, but local opposition to the forced transfer caused the Linden Street terminal plan to be scrapped.
The congestion at busy Governors Square caused numerous delays to the streetcar lines. In May 1924, the state legislature directed the Metropolitan District Commission to plan an expanded rapid transit system in Boston, including an extension of the Boylston street Subway under Governors Square. The report, released in December 1926, called for the existing streetcar tunnels in Boston to be reorganized into two rapid transit lines with high-floor rolling stock. One line was to run from East Boston
East Boston, nicknamed Eastie, is a neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts annexed by the city of Boston in 1637. Neighboring communities include Winthrop, Revere, and Chelsea. It is separated from the Boston neighborhood of Charlestown and d ...
to Brighton, with the East Boston Tunnel
The Blue Line is a rapid transit line in the Greater Boston metropolitan area, one of four rapid transit lines operated by the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA). It runs from Bowdoin station in downtown Boston under Boston Har ...
(which had been converted from streetcars to rapid transit in 1924) realigned to connect with the Tremont Street subway near Park Street station. The Boylston Street subway would have been extended to Commonwealth Avenue, with a new station under Governors Square. A transfer station between the rapid transit line and the truncated Watertown and Lake Street surface lines was to be located at Warren Street between Commonwealth Avenue and Cambridge Street, near Brighton Center. Intermediate surface stops were to be located at St. Marys Street, Gaffney Street, , , and . Several busy grade crossings also were to be eliminated, and the report noted that the then-rapid growth along Commonwealth Avenue in Brighton might later justify extension of rapid transit to Lake Street.
 The subway under Governors Square was projected to cost $5 million (equivalent to $ million in ). The BERy and the city objected to this cost and proposed a $1.4 million plan where flyover ramps would separate Beacon Street auto and streetcar traffic from other traffic in the square. The tunnel was eventually chosen but construction did not begin until 1930, after the legislature lowered the cost that the BERy would pay to rent the subway from the city.
The subway under Governors Square was projected to cost $5 million (equivalent to $ million in ). The BERy and the city objected to this cost and proposed a $1.4 million plan where flyover ramps would separate Beacon Street auto and streetcar traffic from other traffic in the square. The tunnel was eventually chosen but construction did not begin until 1930, after the legislature lowered the cost that the BERy would pay to rent the subway from the city. Kenmore station
Kenmore station is a light rail station on the MBTA Green Line, located under Kenmore Square in the Fenway/Kenmore neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. The station opened on October 23, 1932 as a one-station extension of the Boylston Stre ...
and the new subway, which split to separate portals at on Beacon Street and on Commonwealth Avenue, opened on October 23, 1932. The extension was built to support future rapid transit conversion of the Commonwealth Avenue line, including extension of the underground section further west.
Interest in converting the Commonwealth Avenue line to rapid transit declined as focus shifted to expanding the subway to further suburbs. The 1945 and 1947 Coolidge Commission reports (the next major planning effort after the 1926 report) instead recommended a parallel rapid transit line along the Boston and Albany Railroad
The Boston and Albany Railroad was a railroad connecting Boston, Massachusetts to Albany, New York, later becoming part of the New York Central Railroad system, Conrail, and CSX Transportation. The line is currently used by CSX for freight. Pass ...
corridor, with local streetcar service retained on Commonwealth Avenue. However, several smaller improvements were made to the line. A siding was opened at on October 27, 1926, allowing trains to be short turn
In public transport, a short turn, short working or turn-back is an earlier terminus on a bus or rail line that is used on some scheduled trips that do not operate along the full length of the route.
Short turns are practical in scheduling when ...
ed when necessary. On February 7, 1931, the Beacon Street and Commonwealth Avenue lines were extended to Lechmere, replacing shuttle services between Lechmere and various points in the subway. On June 30, 1931, the existing crossover west of Blandford Street was replaced by a pocket track, allowing temporary storage of streetcars there. It replaced the former surface cutback at Kenmore for subway short turn
In public transport, a short turn, short working or turn-back is an earlier terminus on a bus or rail line that is used on some scheduled trips that do not operate along the full length of the route.
Short turns are practical in scheduling when ...
s, which began on September 24, 1934. Around 1940, the Lake Street line was assigned route number 62 as part of a systemwide renumbering. On May 6, 1940, the line was reassigned from Bennett Street Carhouse (near Harvard Square) to Reservoir Carhouse, eliminating the need for deadhead moves on Cambridge Street.
Postwar years
In the early 1940s, the BERy began replacing its older streetcars with thePCC streetcar
The PCC (Presidents' Conference Committee) is a streetcar (tram) design that was first built in the United States in the 1930s. The design proved successful in its native country, and after World War II it was licensed for use elsewhere in the ...
. PCCs were first used on the Lake Street line in May 1944, and they fully replaced center-entrance cars on the line in regular service on December 10, 1945. The short length of trackage on Chestnut Hill Avenue – which had not been used in revenue service
A revenue service, revenue agency or taxation authority is a government agency responsible for the intake of government revenue, including taxes and sometimes non-tax revenue. Depending on the jurisdiction, revenue services may be charged with ...
since 1926 – was modified as part of trackwork related to the introduction of the PCCs. A connecting track from Commonwealth Avenue westbound to Chestnut Hill Avenue southbound was opened on May 31, 1947, completing the wye between the two avenues. On May 21, 1947, in recognition of the expansion of Boston College
Boston College (BC) is a private Jesuit research university in Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts. Founded in 1863, the university has more than 9,300 full-time undergraduates and nearly 5,000 graduate students. Although Boston College is classifie ...
, the BERy changed the "Lake Street" designation to "Boston College". On August 29, 1947, the privately owned BERy was succeeded by the publicly owned Metropolitan Transit Authority (MTA).
The little-used siding at Washington Street was removed in January 1953, leaving only a crossover. In April 1959, all Boston and Albany Railroad
The Boston and Albany Railroad was a railroad connecting Boston, Massachusetts to Albany, New York, later becoming part of the New York Central Railroad system, Conrail, and CSX Transportation. The line is currently used by CSX for freight. Pass ...
Worcester Line
The Framingham/Worcester Line of the MBTA Commuter Rail system runs west from Boston, Massachusetts to Worcester, Massachusetts through the MetroWest region, serving 17 station stops in Boston, Newton, Wellesley, Natick, Framingham, Ashlan ...
stops between and were closed for the construction of the Turnpike Extension, leaving the Watertown and Boston College lines as the only rail transit serving Allston and Brighton. Boston University
Boston University (BU) is a Private university, private research university in Boston, Massachusetts. The university is nonsectarian, but has a historical affiliation with the United Methodist Church. It was founded in 1839 by Methodists with ...
purchased Braves Field in 1953 when the Braves moved to Milwaukee, and soon wished to use the loop area for other purposes. After several years of requests, the MTA abandoned the loop on January 15, 1962.
In 1960, the wide streetcar reservation between Warren Street and Wallingford Road was narrowed to add additional travel lanes to Commonwealth Avenue, leaving the streetcar tracks in a relocated median between the travel lanes. On November 25, 1961, the Boston College was cut back to Park Street station, while the 1959-opened Riverside Line was extended to Lechmere in its stead. In 1963–65, the Commonwealth Avenue bridge over the Boston and Albany Railroad was rebuilt to accommodate the Turnpike Extension. Streetcar service was maintained using a temporary parallel bridge.
MBTA era
In August 1964, theMassachusetts Bay Transportation Authority
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (abbreviated MBTA and known colloquially as "the T") is the public agency responsible for operating most public transportation services in Greater Boston, Massachusetts. The MBTA transit network in ...
(MBTA) replaced the MTA. As part of systemwide rebranding efforts, the remaining streetcar routes feeding the Tremont Street subway became the Green Line on August 26, 1965. In 1967, the five branches were given letters to distinguish them; the Boston College line became the B branch. (The Watertown line became the A branch, while the Beacon Street line became the C branch.) The MBTA experimented with changing the downtown terminals of the Green Line branches (unlike its predecessors, which had changed the downtown terminal of the Boston College line just twice.) The B branch was extended to the new loop at opened on November 18, 1964 – the first service to regularly use the loop. Over the next two decades, the downtown termini were frequently changed; the B branch variously terminated at Park Street, Government Center, , North Station
North Station is a commuter rail and intercity rail terminal station in Boston, Massachusetts. It is served by four MBTA Commuter Rail lines – the Fitchburg Line, Haverhill Line, Lowell Line, and Newburyport/Rockport Line – and the Amtrak ...
, and Lechmere. On July 30, 1983, the terminus was finally changed to Government Center station, where it would stay until 2004.
On June 21, 1969, the A branch was replaced with Watertown–Kenmore buses, halving streetcar service on Commonwealth Avenue east of Packard's Corner. In 1970, the median was moved slightly south between Chestnut Hill Avenue and Lake Street. The westbound roadway was lowered several feet below the median between South Street and Greycliff Road, with the Foster Street stop moved west to the grade crossing. Around 1975, the stop at University Road was discontinued, while the stop at Alcorn Street was moved 500 feet east to .
The downtown terminus was extended to North Station on June 25, 2004, but cut back to Government Center on January 1, 2005. It was cut back further to Park Street on March 22, 2014, when Government Center closed for reconstruction. When the station reopened in 2016, Park Street remained the B branch terminus. The B branch was re-extended to Government Center on October 24, 2021, as part of changes in preparation for the opening of the Green Line Extension
The Green Line Extension (GLX) was a construction project to extend the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) Green Line light rail system northwest into Somerville and Medford, two inner suburbs of Boston, Massachusetts. The p ...
the next year. The B branch extension was intended to improve access to the Blue Line and better distribute downtown service. B branch service was replaced by buses from June 20 to July 1, 2022, to allow for trackwork and installation of train protection system equipment.
Accessibility and stop consolidation
The introduction of low-floor LRVs in 2000 allowed foraccessible
Accessibility is the design of products, devices, services, vehicles, or environments so as to be usable by people with disabilities. The concept of accessible design and practice of accessible development ensures both "direct access" (i.e ...
service on the Green Line. In the early 2000s, the MBTA modified key surface stops with raised platforms as part of the Light Rail Accessibility Program. Portable lifts were installed at and around 2000. Four surface stops – , Boston University Central, , and – were modified with raised platforms in 2002–03; Boston College was similarly modified in 2009.
The B branch is frequently criticized by riders for its slow service, with a high number of stops and level crossings. Until 2004, the line had 22 stops on the surface section, while the C and D branches had 13 each and the E branch just 9. In late 2003, the MBTA proposed eliminating five surface stops (Greycliff Road, , Mount Hood Road, Summit Avenue, and ) as part of a project to improve the line. The five stops were chosen because they had low ridership and were located very close to other stations. No stops east of Packards Corner were chosen, although they would affect the largest number of riders; despite their close spacing, they had higher ridership, and their proximity to traffic lights lowered the travel time savings from elimination. After a public comment period, Chiswick Road was removed from the proposal, as it served a nearby elderly housing community. On April 20, 2004, the other four stops were closed as a 6-to-8-month pilot program. On March 15, 2005, after a survey showed that 73% of 1,142 riders surveyed approved of the closures, the MBTA board voted to make the closures permanent.
In 2014, the MBTA began planning to consolidate four stops – , , , and – located near Boston University
Boston University (BU) is a Private university, private research university in Boston, Massachusetts. The university is nonsectarian, but has a historical affiliation with the United Methodist Church. It was founded in 1839 by Methodists with ...
's West Campus. The four stops, which were not accessible
Accessibility is the design of products, devices, services, vehicles, or environments so as to be usable by people with disabilities. The concept of accessible design and practice of accessible development ensures both "direct access" (i.e ...
, were replaced by two fully accessible stops as part of a reconstruction of Commonwealth Avenue between the BU Bridge and Packard's Corner. The MBTA awarded a $17.8 million construction contract on March 23, 2020. Construction was to last from February 2021 to early 2022, with night and weekend bustitution
A rail replacement bus service uses buses to replace a passenger train service on a temporary or permanent basis. The train service that is replaced may be of any type such as light rail, tram, streetcar, commuter rail, regional rail or heavy r ...
for much of 2021. Stop names of "Babcock Street" and "Amory Street" were announced in February 2021. Buses replaced rail service between Washington Street and Kenmore from April 17–May 9 and May 17–June 13, 2021, for construction of the platforms and canopy steelwork. Track replacement was also conducted between Blandford Street and BU Central during the closure. The two new stations, Babcock Street and , opened on November 15, 2021.
Track work in 2018–19, which included replacement of platform edges at several stops, triggered requirements for accessibility modifications at those stops. By December 2022, design for , , Chiswick Road, , and was 30% complete, with construction expected to last from fall 2023 to mid-2024. The short-term accessibility modifications at 14 B and C branch stops is expected to cost $57.5 million. In 2021, the MBTA indicated that a future project may replace side platform
A side platform (also known as a marginal platform or a single-face platform) is a platform positioned to the side of one or more railway tracks or guideways at a railway station, tram stop, or transitway. A station having dual side platfor ...
s with wider island platform
An island platform (also center platform, centre platform) is a station layout arrangement where a single platform is positioned between two tracks within a railway station, tram stop or transitway interchange. Island platforms are popular o ...
s at some or all surface stops. The full project of station consolidation and renovations, as well as track realignment and traction power improvements, is expected to cost $221 million. A $29.3 million reconstruction and expansion of Lake Street Yard to support new Type 10 LRVs is planned for the late 2020s.
Station listing
References
External links
MBTA – Green Line B branch
{{DEFAULTSORT:Green Line B branch Green Line (MBTA) Railway lines opened in 1932