granite on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive
igneous rock
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma o ...
composed mostly of quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical ...
, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
and alkali metal oxide
The alkali metals react with oxygen to form several different compounds: suboxides, oxides, peroxides, sesquioxides, superoxides, and ozonides. They all react violently with water.
Alkali metal suboxides
* Hexarubidium monoxide (Rb6O) h
* No ...
s that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called '' sial'' be ...
of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers.
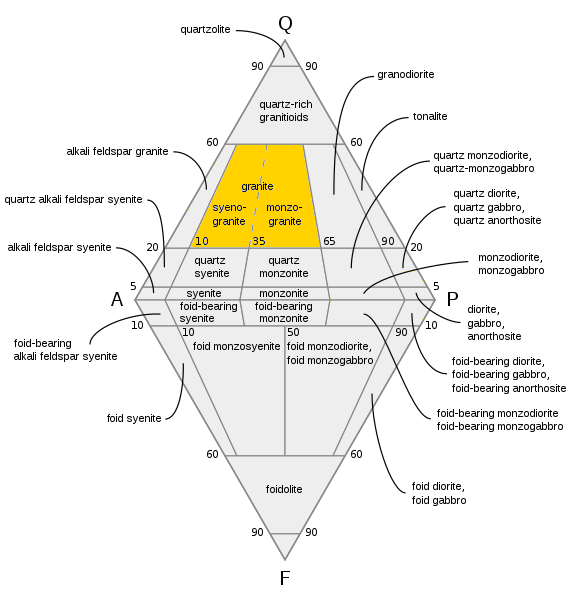
Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or '' granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranite
Leucogranite is a light-colored, granitic, igneous rock containing almost no dark minerals. Alaskite is a synonym.
Granite is nearly always massive (lacking any internal structures), hard, and tough. These properties have made granite a widespread construction stone throughout human history.
 The word "granite" comes from the
The word "granite" comes from the
Description

Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''granum'', a grain, in reference to the coarse-grained structure of such a completely crystalline rock. Granitic rocks mainly consist of feldspar, quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical ...
, mica, and amphibole mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
s, which form an interlocking, somewhat equigranular matrix of feldspar and quartz with scattered darker biotite mica and amphibole (often hornblende
Hornblende is a complex inosilicate series of minerals. It is not a recognized mineral in its own right, but the name is used as a general or field term, to refer to a dark amphibole. Hornblende minerals are common in igneous and metamorphic rock ...
) peppering the lighter color minerals. Occasionally some individual crystals (phenocryst
300px, feldspathic phenocrysts. This granite, from the Switzerland">Swiss side of the Mont Blanc massif, has large white plagioclase phenocrysts, triclinic minerals that give trapezoid shapes when cut through). 1 euro coins, 1 euro coin (diameter ...
s) are larger than the groundmass, in which case the texture is known as porphyritic. A granitic rock with a porphyritic texture is known as a granite porphyry. Granitoid is a general, descriptive field term for lighter-colored, coarse-grained igneous rocks. Petrographic
Petrography is a branch of petrology that focuses on detailed descriptions of rocks. Someone who studies petrography is called a petrographer. The mineral content and the textural relationships within the rock are described in detail. The class ...
examination is required for identification of specific types of granitoids. Granites can be predominantly white, pink, or gray in color, depending on their mineralogy.
The alkali feldspar in granites is typically orthoclase
Orthoclase, or orthoclase feldspar ( endmember formula K Al Si3 O8), is an important tectosilicate mineral which forms igneous rock. The name is from the Ancient Greek for "straight fracture," because its two cleavage planes are at right angles ...
or microcline and is often perthitic
Perthite is used to describe an intergrowth of two feldspars: a host grain of potassium-rich alkali feldspar (near K-feldspar, KAlSi3O8, in composition) includes exsolved lamellae or irregular intergrowths of sodic alkali feldspar (near albite, Na ...
. The plagioclase is typically sodium-rich oligoclase. Phenocrysts are usually alkali feldspar.
Granitic rocks are classified according to the QAPF diagram for coarse grained plutonic rocks and are named according to the percentage of quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical ...
, alkali feldspar (orthoclase
Orthoclase, or orthoclase feldspar ( endmember formula K Al Si3 O8), is an important tectosilicate mineral which forms igneous rock. The name is from the Ancient Greek for "straight fracture," because its two cleavage planes are at right angles ...
, sanidine, or microcline) and plagioclase feldspar on the A-Q-P half of the diagram. True granite (according to modern petrologic
Petrology () is the branch of geology that studies rocks and the conditions under which they form. Petrology has three subdivisions: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary petrology. Igneous and metamorphic petrology are commonly taught together ...
convention) contains between 20% and 60% quartz by volume, with 35% to 90% of the total feldspar consisting of alkali feldspar. Granitic rocks poorer in quartz are classified as syenites or monzonite
Monzonite is an igneous intrusive rock, formed by slow cooling of underground magma that has a moderate silica content and is enriched in alkali metal oxides. Monzonite is composed mostly of plagioclase and alkali feldspar.
Syenodiorite is an o ...
s, while granitic rocks dominated by plagioclase are classified as granodiorite
Granodiorite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock similar to granite, but containing more plagioclase feldspar than orthoclase feldspar.
The term banatite is sometimes used informally for various rocks ranging from gr ...
s or tonalite
Tonalite is an igneous, plutonic ( intrusive) rock, of felsic composition, with phaneritic (coarse-grained) texture. Feldspar is present as plagioclase (typically oligoclase or andesine) with alkali feldspar making up less than 10% of the total ...
s. Granitic rocks with over 90% alkali feldspar are classified as alkali feldspar granites. Granitic rock with more than 60% quartz, which is uncommon, is classified simply as quartz-rich granitoid or, if composed almost entirely of quartz, as quartzolite.
True granites are further classified by the percentage of their total feldspar that is alkali feldspar. Granites whose feldspar is 65% to 90% alkali feldspar are syenogranites, while the feldspar in monzogranite
Monzogranites are biotite granite rocks that are considered to be the final fractionation product of magma. Monzogranites are characteristically felsic (SiO2 > 73%, and FeO + MgO + TiO2 < 2.4), weakly A granite containing both muscovite and biotite micas is called a binary or ''two-mica'' granite. Two-mica granites are typically high in potassium and low in plagioclase, and are usually S-type granites or A-type granites, as described below.
Another aspect of granite classification is the ratios of metals that potentially form feldspars. Most granites have a composition such that almost all their aluminum and alkali metals (sodium and potassium) are combined as feldspar. This is the case when K2O + Na2O + CaO > Al2O3 > K2O + Na2O. Such granites are described as ''normal'' or ''metaluminous''. Granites in which there is not enough aluminum to combine with all the alkali oxides as feldspar (Al2O3 < K2O + Na2O) are described as ''peralkaline'', and they contain unusual sodium amphiboles such as



 Granitic rock is widely distributed throughout the
Granitic rock is widely distributed throughout the
 Granite and related marble industries are considered one of the oldest industries in the world, existing as far back as Ancient Egypt.
Major modern exporters of granite include China, India, Italy, Brazil, Canada, Germany, Sweden, Spain and the United States.
Granite and related marble industries are considered one of the oldest industries in the world, existing as far back as Ancient Egypt.
Major modern exporters of granite include China, India, Italy, Brazil, Canada, Germany, Sweden, Spain and the United States.
 The
The
 In some areas, granite is used for gravestones and memorials. Granite is a hard stone and requires skill to carve by hand. Until the early 18th century, in the Western world, granite could be carved only by hand tools with generally poor results.
A key breakthrough was the invention of steam-powered cutting and dressing tools by Alexander MacDonald of Aberdeen, inspired by seeing ancient Egyptian granite carvings. In 1832, the first polished tombstone of Aberdeen granite to be erected in an English cemetery was installed at
In some areas, granite is used for gravestones and memorials. Granite is a hard stone and requires skill to carve by hand. Until the early 18th century, in the Western world, granite could be carved only by hand tools with generally poor results.
A key breakthrough was the invention of steam-powered cutting and dressing tools by Alexander MacDonald of Aberdeen, inspired by seeing ancient Egyptian granite carvings. In 1832, the first polished tombstone of Aberdeen granite to be erected in an English cemetery was installed at
 Granite has been extensively used as a dimension stone and as flooring tiles in public and commercial buildings and monuments. Aberdeen in Scotland, which is constructed principally from local granite, is known as "The Granite City". Because of its abundance in New England, granite was commonly used to build foundations for homes there. The
Granite has been extensively used as a dimension stone and as flooring tiles in public and commercial buildings and monuments. Aberdeen in Scotland, which is constructed principally from local granite, is known as "The Granite City". Because of its abundance in New England, granite was commonly used to build foundations for homes there. The
 Curling stones are traditionally fashioned of Ailsa Craig granite. The first stones were made in the 1750s, the original source being
Curling stones are traditionally fashioned of Ailsa Craig granite. The first stones were made in the 1750s, the original source being
File:St. Louis wharf cobbles 20090121 1.jpg, Granite was used for setts on the
riebeckite
Riebeckite is a sodium-rich member of the amphibole group of silicate minerals, chemical formula Na2(Fe2+3Fe3+2)Si8O22(OH)2. It forms a solid solution series with magnesioriebeckite. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system, usually as long prisma ...
. Granites in which there is an excess of aluminum beyond what can be taken up in feldspars (Al2O3 > CaO + K2O + Na2O) are described as ''peraluminous'', and they contain aluminum-rich minerals such as muscovite
Muscovite (also known as common mica, isinglass, or potash mica) is a hydrated phyllosilicate mineral of aluminium and potassium with formula K Al2(Al Si3 O10)( F,O H)2, or ( KF)2( Al2O3)3( SiO2)6( H2O). It has a highly perfect basal cleavag ...
.
Physical properties
The average density of granite is between , its compressive strength usually lies above 200 MPa, and its viscosity nearSTP
STP may refer to:
Places
* São Tomé and Príncipe (ISO 3166-1 alpha-3 code, IOC country code, and FIFA country code STP)
* St Pancras railway station, London St Pancras (Domestic) railway station (National Rail code STP)
* St. Paul Downtown Air ...
is 3–6·1020 Pa·s.
The melting temperature of dry granite at ambient pressure is ; it is strongly reduced in the presence of water, down to 650 °C at a few hundred megapascals of pressure.
Granite has poor primary permeability overall, but strong secondary permeability through cracks and fractures if they are present.
Chemical composition
A worldwide average of the chemical composition of granite, by weight percent, based on 2485 analyses:Blatt and Tracy 1996, p.66 The medium-grained equivalent of granite is microgranite. Theextrusive
Extrusive rock refers to the mode of igneous volcanic rock formation in which hot magma from inside the Earth flows out (extrudes) onto the surface as lava or explodes violently into the atmosphere to fall back as pyroclastics or tuff. In contra ...
igneous rock equivalent of granite is rhyolite.
Occurrence



 Granitic rock is widely distributed throughout the
Granitic rock is widely distributed throughout the continental crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called '' sial'' be ...
. Much of it was intruded during the Precambrian age; it is the most abundant basement rock that underlies the relatively thin sedimentary veneer of the continents. Outcrop
An outcrop or rocky outcrop is a visible exposure of bedrock or ancient superficial deposits on the surface of the Earth.
Features
Outcrops do not cover the majority of the Earth's land surface because in most places the bedrock or superficia ...
s of granite tend to form tors, domes or bornhardt
A bornhardt () is a dome-shaped, steep-sided, bald rock outcropping at least in height and several hundred metres in width. They are named after Wilhelm Bornhardt (1864–1946), a German geologist and explorer of German East Africa, who first d ...
s, and rounded massif
In geology, a massif ( or ) is a section of a planet's crust that is demarcated by faults or flexures. In the movement of the crust, a massif tends to retain its internal structure while being displaced as a whole. The term also refers to a ...
s. Granites sometimes occur in circular depressions surrounded by a range of hills, formed by the metamorphic aureole
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of che ...
or hornfels
Hornfels is the group name for a set of contact metamorphic rocks that have been baked and hardened by the heat of intrusive igneous masses and have been rendered massive, hard, splintery, and in some cases exceedingly tough and durable. These pro ...
. Granite often occurs as relatively small, less than 100 km2 stock masses ( stocks) and in batholiths that are often associated with orogenic
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted t ...
mountain ranges. Small dikes of granitic composition called aplite
Aplite () is an intrusive igneous rock in which the mineral composition is the same as granite, but in which the grains are much finer, under 1 mm across. Quartz and feldspar are the dominant minerals. The term ''aplite'' or ''aplitic'' ...
s are often associated with the margins of granitic intrusions. In some locations, very coarse-grained pegmatite masses occur with granite.
Origin
Granite forms from silica-rich ( felsic) magmas. Felsic magmas are thought to form by addition of heat or water vapor to rock of the lower crust, rather than by decompression of mantle rock, as is the case with basaltic magmas. It has also been suggested that some granites found at convergent boundaries between tectonic plates, where oceanic crust subducts below continental crust, were formed from sediments subducted with the oceanic plate. The melted sediments would have produced magma intermediate in its silica content, which became further enriched in silica as it rose through the overlying crust. Early fractional crystallisation serves to reduce a melt in magnesium and chromium, and enrich the melt in iron, sodium, potassium, aluminum, and silicon. Further fractionation reduces the content of iron, calcium, and titanium. This is reflected in the high content of alkali feldspar and quartz in granite. The presence of granitic rock inisland arc
Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle alon ...
s shows that fractional crystallization alone can convert a basaltic magma to a granitic magma, but the quantities produced are small. For example, granitic rock makes up just 4% of the exposures in the South Sandwich Islands
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type =
, song =
, image_map = South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands in United Kingdom.svg
, map_caption = Location of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands in the southern Atlantic Oce ...
. In continental arc settings, granitic rocks are the most common plutonic rocks, and batholiths composed of these rock types extend the entire length of the arc. There are no indication of magma chambers where basaltic magmas differentiate into granites, or of cumulates produced by mafic crystals settling out of the magma. Other processes must produce these great volumes of felsic magma. One such process is injection of basaltic magma into the lower crust, followed by differentiation, which leaves any cumulates in the mantle. Another is heating of the lower crust by underplating
Magmatic underplating occurs when basaltic magmas are trapped during their rise to the surface at the Mohorovičić discontinuity or within the Crust (geology), crust. Entrapment (or 'stalling out') of magmas within the crust occurs due to the dif ...
basaltic magma, which produces felsic magma directly from crustal rock. The two processes produce different kinds of granites, which may be reflected in the division between S-type (produced by underplating) and I-type (produced by injection and differentiation) granites, discussed below.
Alphabet classification system
The composition and origin of any magma that differentiates into granite leave certain petrological evidence as to what the granite's parental rock was. The final texture and composition of a granite are generally distinctive as to its parental rock. For instance, a granite that is derived from partial melting of metasedimentary rocks may have more alkali feldspar, whereas a granite derived from partial melting of metaigneous rocks may be richer in plagioclase. It is on this basis that the modern "alphabet" classification schemes are based. The letter-based Chappell & White classification system was proposed initially to divide granites into I-type (igneous source) granite and S-type (sedimentary sources). Both types are produced by partial melting of crustal rocks, either metaigneous rocks or metasedimentary rocks. I-type granites are characterized by a high content of sodium and calcium, and by a strontium isotope ratio, 87Sr/86Sr, of less than 0.708. 87Sr is produced by radioactive decay of 87Rb, and since rubidium is concentrated in the crust relative to the mantle, a low ratio suggests origin in the mantle. The elevated sodium and calcium favor crystallization of hornblende rather than biotite. I-type granites are known for theirporphyry copper
Porphyry copper deposits are copper ore bodies that are formed from hydrothermal fluids that originate from a voluminous magma chamber several kilometers below the deposit itself. Predating or associated with those fluids are vertical dikes of ...
deposits. I-type granites are orogenic (associated with mountain building) and usually metaluminous.
S-type granites are sodium-poor and aluminum-rich. As a result, they contain micas such as biotite and muscovite instead of hornblende. Their strontium isotope ratio is typically greater than 0.708, suggesting a crustal origin. They also commonly contain xenoliths of metamorphosed sedimentary rock, and host tin ores. Their magmas are water-rich, and they readily solidify as the water outgasses from the magma at lower pressure, so they less commonly make it to the surface than magmas of I-type granites, which are thus more common as volcanic rock (rhyolite). They are also orogenic but range from metaluminous to strongly peraluminous.
Although both I- and S-type granites are orogenic, I-type granites are more common close to the convergent boundary than S-type. This is attributed to thicker crust further from the boundary, which results in more crustal melting.
A-type granites show a peculiar mineralogy and geochemistry, with particularly high silicon and potassium at the expense of calcium and magnesium and a high content of high field strength cations (cations with a small radius and high electrical charge, such as zirconium, niobium, tantalum, and rare earth elements.) They are not orogenic, forming instead over hot spots and continental rifting, and are metaluminous to mildly peralkaline and iron-rich. These granites are produced by partial melting of refractory lithology such as granulites in the lower continental crust at high thermal gradients. This leads to significant extraction of hydrous felsic melts from granulite-facies resitites. A-type granites occur in the Koettlitz Glacier Alkaline Province in the Royal Society Range, Antarctica. The rhyolites of the Yellowstone Caldera are examples of volcanic equivalents of A-type granite.
M-type granite was later proposed to cover those granites that were clearly sourced from crystallized mafic magmas, generally sourced from the mantle. Although the fractional crystallisation of basaltic melts can yield small amounts of granites, which are sometimes found in island arcs, such granites must occur together with large amounts of basaltic rocks.
H-type granites were suggested for hybrid granites, which were hypothesized to form by mixing between mafic and felsic from different sources, such as M-type and S-type. However, the big difference in rheology between mafic and felsic magmas makes this process problematic in nature.
Granitization
Granitization is an old, and largely discounted, hypothesis that granite is formed in place through extrememetasomatism
Metasomatism (from the Greek μετά ''metá'' "change" and σῶμα ''sôma'' "body") is the chemical alteration of a rock by hydrothermal and other fluids. It is the replacement of one rock by another of different mineralogical and chemical co ...
. The idea behind granitization was that fluids would supposedly bring in elements such as potassium, and remove others, such as calcium, to transform a metamorphic rock into granite. This was supposed to occur across a migrating front. However, experimental work had established by the 1960s that granites were of igneous origin. The mineralogical and chemical features of granite can be explained only by crystal-liquid phase relations, showing that there must have been at least enough melting to mobilize the magma.
However, at sufficiently deep crustal levels, the distinction between metamorphism and crustal melting itself becomes vague. Conditions for crystallization of liquid magma are close enough to those of high-grade metamorphism that the rocks often bear a close resemblance. Under these conditions, granitic melts can be produced in place through the partial melting of metamorphic rocks by extracting melt-mobile elements such as potassium and silicon into the melts but leaving others such as calcium and iron in granulite residues. This may be the origin of ''migmatite
Migmatite is a composite rock found in medium and high-grade metamorphic environments, commonly within Precambrian cratonic blocks. It consists of two or more constituents often layered repetitively: one layer is an older metamorphic rock th ...
s''. A migmatite consists of dark, refractory rock (the ''melanosome'') that is permeated by sheets and channels of light granitic rock (the ''leucosome''). The leucosome is interpreted as partial melt of a parent rock that has begun to separate from the remaining solid residue (the melanosome). If enough partial melt is produced, it will separate from the source rock, become more highly evolved through fractional crystallization during its ascent toward the surface, and become the magmatic parent of granitic rock. The residue of the source rock becomes a granulite
Granulites are a class of high-grade metamorphic rocks of the granulite facies that have experienced high-temperature and moderate-pressure metamorphism. They are medium to coarse–grained and mainly composed of feldspars sometimes associated ...
.
The partial melting of solid rocks requires high temperatures and the addition of water or other volatiles which lower the solidus temperature (temperature at which partial melting commences) of these rocks. It was long debated whether crustal thickening in orogens (mountain belts along convergent boundaries) was sufficient to produce granite melts by radiogenic heating
A radiogenic nuclide is a nuclide that is produced by a process of radioactive decay. It may itself be radioactive (a radionuclide) or stable (a stable nuclide).
Radiogenic nuclides (more commonly referred to as radiogenic isotopes) form some of ...
, but recent work suggests that this is not a viable mechanism. In-situ granitization requires heating by the asthenospheric mantle or by underplating with mantle-derived magmas.
Ascent and emplacement
Granite magmas have a density of 2.4 Mg/m3, much less than the 2.8 Mg/m3 of high-grade metamorphic rock. This gives them tremendous buoyancy, so that ascent of the magma is inevitable once enough magma has accumulated. However, the question of precisely how such large quantities of magma are able to shove aside country rock to make room for themselves (the ''room problem'') is still a matter of research. Two main mechanisms are thought to be important: *Stokes diapir * Fracture propagation Of these two mechanisms, Stokes diapirism has been favoured for many years in the absence of a reasonable alternative. The basic idea is that magma will rise through the crust as a single mass through buoyancy. As it rises, it heats the wall rocks, causing them to behave as apower-law fluid
__NOTOC__
In continuum mechanics, a power-law fluid, or the Ostwald–de Waele relationship, is a type of generalized Newtonian fluid (time-independent non-Newtonian fluid) for which the shear stress, , is given by
:\tau = K \left( \frac \right ...
and thus flow around the intrusion allowing it to pass without major heat loss. This is entirely feasible in the warm, ductile
Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to drawing (e.g. into wire). In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stres ...
lower crust where rocks are easily deformed, but runs into problems in the upper crust which is far colder and more brittle. Rocks there do not deform so easily: for magma to rise as a diapir it would expend far too much energy in heating wall rocks, thus cooling and solidifying before reaching higher levels within the crust.
Fracture propagation is the mechanism preferred by many geologists as it largely eliminates the major problems of moving a huge mass of magma through cold brittle crust. Magma rises instead in small channels along self-propagating dykes which form along new or pre-existing fracture or fault systems and networks of active shear zones. As these narrow conduits open, the first magma to enter solidifies and provides a form of insulation for later magma.
These mechanisms can operate in tandem. For example, diapirs may continue to rise through the brittle upper crust through stoping, where the granite cracks the roof rocks, removing blocks of the overlying crust which then sink to the bottom of the diapir while the magma rises to take their place. This can occur as piecemeal stopping (stoping of small blocks of chamber roof), as cauldron subsidence (collapse of large blocks of chamber roof), or as roof foundering (complete collapse of the roof of a shallow magma chamber accompanied by a caldera eruption.) There is evidence for cauldron subsidence at the Mt. Ascutney intrusion in eastern Vermont. Evidence for piecemeal stoping is found in intrusions that are rimmed with ''igneous breccia'' containing fragments of country rock.
Assimilation is another mechanism of ascent, where the granite melts its way up into the crust and removes overlying material in this way. This is limited by the amount of thermal energy available, which must be replenished by crystallization of higher-melting minerals in the magma. Thus, the magma is melting crustal rock at its roof while simultaneously crystallizing at its base. This results in steady contamination with crustal material as the magma rises. This may not be evident in the major and minor element chemistry, since the minerals most likely to crystallize at the base of the chamber are the same ones that would crystallize anyway, but crustal assimilation is detectable in isotope ratios. Heat loss to the country rock means that ascent by assimilation is limited to distance similar to the height of the magma chamber.
Weathering
Physical weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs ''in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement), ...
occurs on a large scale in the form of exfoliation joint
Exfoliation joints or sheet joints are surface-parallel fracture systems in rock, and often leading to erosion of concentric slabs. ''(See Joint (geology)).''
General characteristics of exfoliation joints
* Commonly follow topography.
* Divi ...
s, which are the result of granite's expanding and fracturing as pressure is relieved when overlying material is removed by erosion or other processes.
Chemical weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs ''in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement ...
of granite occurs when dilute carbonic acid, and other acids present in rain and soil waters, alter feldspar in a process called hydrolysis. As demonstrated in the following reaction, this causes potassium feldspar to form kaolinite, with potassium ions, bicarbonate, and silica in solution as byproducts. An end product of granite weathering is grus, which is often made up of coarse-grained fragments of disintegrated granite.
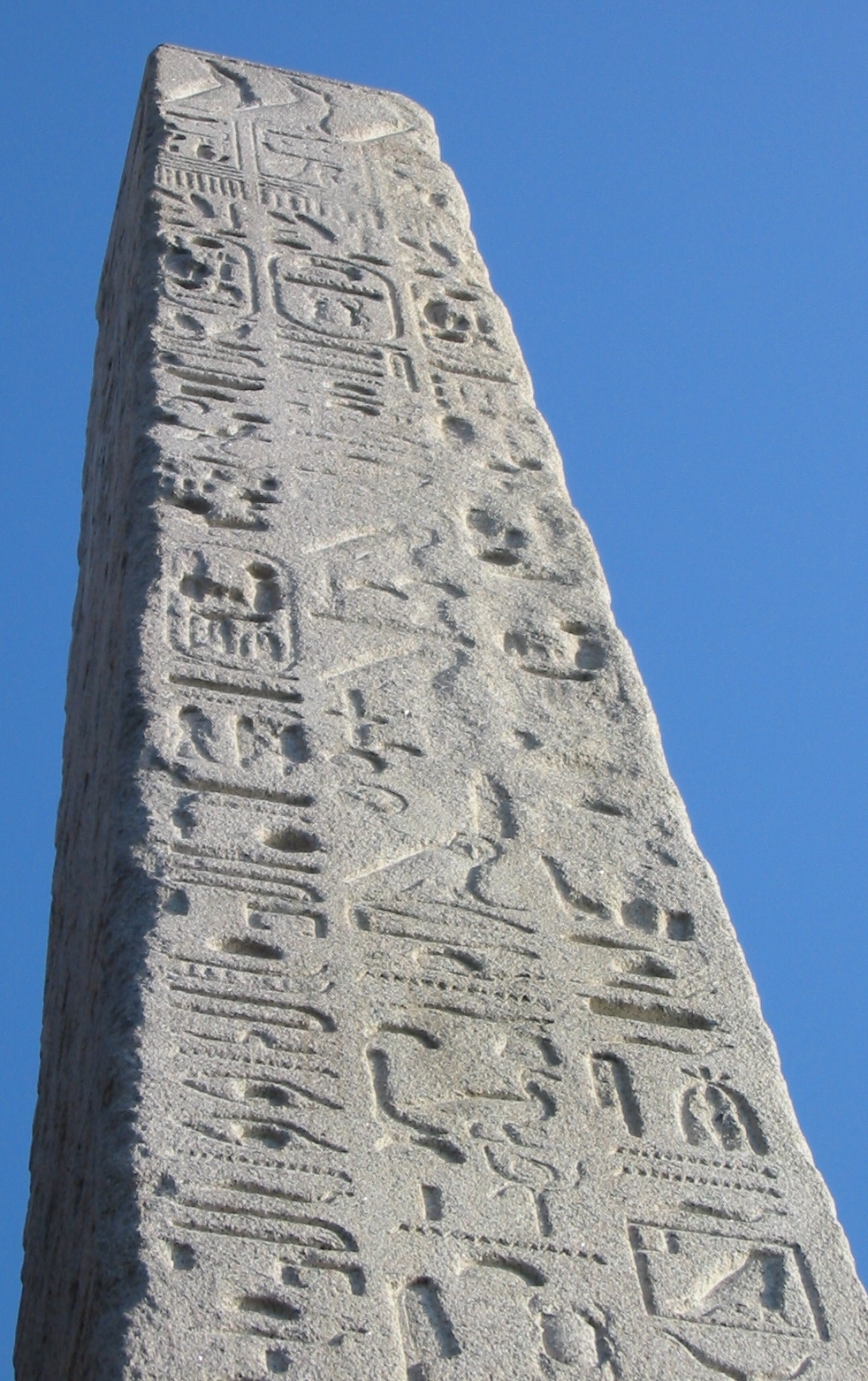
Climatic variations also influence the weathering rate of granites. For about two thousand years, the relief engravings on Cleopatra's Needle obelisk had survived the arid conditions of its origin before its transfer to London. Within two hundred years, the red granite has drastically deteriorated in the damp and polluted air there.
Soil development on granite reflects the rock's high quartz content and dearth of available bases, with the base-poor status predisposing the soil to acidification and podzol
In soil science, podzols are the typical soils of coniferous or boreal forests and also the typical soils of eucalypt forests and heathlands in southern Australia. In Western Europe, podzols develop on heathland, which is often a construct of ...
ization in cool humid climates as the weather-resistant quartz yields much sand. Feldspars also weather slowly in cool climes, allowing sand to dominate the fine-earth fraction. In warm humid regions, the weathering of feldspar as described above is accelerated so as to allow a much higher proportion of clay with the Cecil soil series a prime example of the consequent Ultisol great soil group.
Natural radiation
Granite is a natural source of radiation, like most natural stones.Potassium-40
Potassium-40 (40K) is a radioactive isotope of potassium which has a long half-life of 1.25 billion years. It makes up about 0.012% (120 ppm) of the total amount of potassium found in nature.
Potassium-40 undergoes three types of radioactive d ...
is a radioactive isotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferr ...
of weak emission, and a constituent of alkali feldspar, which in turn is a common component of granitic rocks, more abundant in alkali feldspar granite and syenites.
Some granites contain around 10 to 20 parts per million
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo-units to describe small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction. Since these fractions are quantity-per-quantity measures, th ...
(ppm) of uranium. By contrast, more mafic rocks, such as tonalite, gabbro and diorite, have 1 to 5 ppm uranium, and limestones and sedimentary rocks usually have equally low amounts. Many large granite plutons are sources for palaeochannel-hosted or roll front uranium ore deposits
Uranium ore deposits are economically recoverable concentrations of uranium within the Earth's crust. Uranium is one of the more common elements in the Earth's crust, being 40 times more common than silver and 500 times more common than gold. It ...
, where the uranium washes into the sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sa ...
s from the granite uplands and associated, often highly radioactive pegmatites. Cellars and basements built into soils over granite can become a trap for radon gas, which is formed by the decay of uranium. Radon gas poses significant health concerns and is the number two cause of lung cancer in the US behind smoking.
Thorium occurs in all granites. Conway granite has been noted for its relatively high thorium concentration of 56±6 ppm.
There is some concern that some granite sold as countertops or building material may be hazardous to health. Dan Steck of St. Johns University has stated
that approximately 5% of all granite is of concern, with the caveat that only a tiny percentage of the tens of thousands of granite slab types have been tested. Resources from national geological survey organizations are accessible online to assist in assessing the risk factors in granite country and design rules relating, in particular, to preventing accumulation of radon gas in enclosed basements and dwellings.
A study of granite countertops was done (initiated and paid for by the Marble Institute of America) in November 2008 by National Health and Engineering Inc. of USA. In this test, all of the 39 full-size granite slabs that were measured for the study showed radiation levels well below the European Union safety standards (section 4.1.1.1 of the National Health and Engineering study) and radon emission levels well below the average outdoor radon concentrations in the US.
Industry
 Granite and related marble industries are considered one of the oldest industries in the world, existing as far back as Ancient Egypt.
Major modern exporters of granite include China, India, Italy, Brazil, Canada, Germany, Sweden, Spain and the United States.
Granite and related marble industries are considered one of the oldest industries in the world, existing as far back as Ancient Egypt.
Major modern exporters of granite include China, India, Italy, Brazil, Canada, Germany, Sweden, Spain and the United States.
Uses
Antiquity
 The
The Red Pyramid
The Red Pyramid, also called the North Pyramid, is the largest of the pyramids located at the Dahshur necropolis in Cairo, Egypt. Named for the rusty reddish hue of its red limestone stones, it is also the third largest Egyptian pyramid, after t ...
of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
(circa 2590 BC), named for the light crimson hue of its exposed limestone surfaces, is the third largest of Egyptian pyramids. Pyramid of Menkaure, likely dating 2510 BC, was constructed of limestone and granite blocks. The Great Pyramid of Giza (c. 2580 BC) contains a huge granite sarcophagus fashioned of "Red Aswan
Aswan (, also ; ar, أسوان, ʾAswān ; cop, Ⲥⲟⲩⲁⲛ ) is a city in Southern Egypt, and is the capital of the Aswan Governorate.
Aswan is a busy market and tourist centre located just north of the Aswan Dam on the east bank of the ...
Granite". The mostly ruined Black Pyramid dating from the reign of Amenemhat III once had a polished granite pyramidion or capstone, which is now on display in the main hall of the Egyptian Museum
The Museum of Egyptian Antiquities, known commonly as the Egyptian Museum or the Cairo Museum, in Cairo, Egypt, is home to an extensive collection of ancient Egyptian antiquities. It has 120,000 items, with a representative amount on display a ...
in Cairo (see Dahshur
DahshurAlso transliterated ''Dahshour'' (in English often called ''Dashur'' ar, دهشور ' , ''Dahchur'') is a royal necropolis located in the desert on the west bank of the Nile approximately south of Cairo. It is known chiefly for several p ...
). Other uses in Ancient Egypt include columns, door lintels, sills, jamb
A jamb (from French ''jambe'', "leg"), in architecture, is the side-post or lining of a doorway or other aperture. The jambs of a window outside the frame are called “reveals.” Small shafts to doors and windows with caps and bases are known ...
s, and wall and floor veneer. How the Egyptians worked the solid granite is still a matter of debate. Patrick Hunt has postulated that the Egyptians used emery, which has greater hardness on the Mohs scale.
The Seokguram
The Seokguram Grotto is a hermitage and part of the Bulguksa temple complex. It lies four kilometers east of the temple on Mt. Tohamsan, in Gyeongju, South Korea. It is classified as ''National Treasure No. 24'' by the South Korean government ...
Grotto in Korea is a Buddhist shrine and part of the Bulguksa
Bulguksa is located on the slopes of Mount Toham (Jinheon-dong, Gyeongju city, North Gyeongsang province, South Korea). It is a head temple of the Jogye Order of Korean Buddhism and encompasses six National treasures of South Korea, including th ...
temple complex. Completed in 774 AD, it is an artificial grotto constructed entirely of granite. The main Buddha of the grotto is a highly regarded piece of Buddhist art
Buddhist art is visual art produced in the context of Buddhism. It includes depictions of Gautama Buddha and other Buddhas and bodhisattvas, notable Buddhist figures both historical and mythical, narrative scenes from their lives, mandalas, an ...
, and along with the temple complex to which it belongs, Seokguram was added to the UNESCO World Heritage List
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
in 1995.
Rajaraja Chola I of the Chola Dynasty in South India built the world's first temple entirely of granite in the 11th century AD in Tanjore, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. The Brihadeeswarar Temple dedicated to Lord Shiva was built in 1010. The massive Gopuram (ornate, upper section of shrine) is believed to have a mass of around 81 tonnes. It was the tallest temple in south India.
Imperial Roman granite was quarried mainly in Egypt, and also in Turkey, and on the islands of Elba
Elba ( it, isola d'Elba, ; la, Ilva) is a Mediterranean island in Tuscany, Italy, from the coastal town of Piombino on the Italian mainland, and the largest island of the Tuscan Archipelago. It is also part of the Arcipelago Toscano Nationa ...
and Giglio. Granite became "an integral part of the Roman language of monumental architecture". The quarrying ceased around the third century AD. Beginning in Late Antiquity the granite was reused, which since at least the early 16th century became known as spolia. Through the process of case-hardening
Case-hardening or surface hardening is the process of hardening the surface of a metal object while allowing the metal deeper underneath to remain soft, thus forming a thin layer of harder metal at the surface. For iron or steel with low carbon ...
, granite becomes harder with age. The technology required to make tempered metal chisels was largely forgotten during the Middle Ages. As a result, Medieval stoneworkers were forced to use saws or emery to shorten ancient columns or hack them into discs. Giorgio Vasari
Giorgio Vasari (, also , ; 30 July 1511 – 27 June 1574) was an Italian Renaissance Master, who worked as a painter, architect, engineer, writer, and historian, who is best known for his work '' The Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculp ...
noted in the 16th century that granite in quarries was "far softer and easier to work than after it has lain exposed" while ancient columns, because of their "hardness and solidity have nothing to fear from fire or sword, and time itself, that drives everything to ruin, not only has not destroyed them but has not even altered their colour."
Modern
Sculpture and memorials
 In some areas, granite is used for gravestones and memorials. Granite is a hard stone and requires skill to carve by hand. Until the early 18th century, in the Western world, granite could be carved only by hand tools with generally poor results.
A key breakthrough was the invention of steam-powered cutting and dressing tools by Alexander MacDonald of Aberdeen, inspired by seeing ancient Egyptian granite carvings. In 1832, the first polished tombstone of Aberdeen granite to be erected in an English cemetery was installed at
In some areas, granite is used for gravestones and memorials. Granite is a hard stone and requires skill to carve by hand. Until the early 18th century, in the Western world, granite could be carved only by hand tools with generally poor results.
A key breakthrough was the invention of steam-powered cutting and dressing tools by Alexander MacDonald of Aberdeen, inspired by seeing ancient Egyptian granite carvings. In 1832, the first polished tombstone of Aberdeen granite to be erected in an English cemetery was installed at Kensal Green Cemetery
Kensal Green Cemetery is a cemetery in the Kensal Green area of Queens Park in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea in London, England. Inspired by Père Lachaise Cemetery in Paris, it was founded by the barrister George Frederick ...
. It caused a sensation in the London monumental trade and for some years all polished granite ordered came from MacDonald's. As a result of the work of sculptor William Leslie, and later Sidney Field, granite memorials became a major status symbol in Victorian Britain. The royal sarcophagus at Frogmore
Frogmore is an estate within the Home Park, adjoining Windsor Castle, in Berkshire, England. It comprises , of primarily private gardens managed by the Crown Estate. It is the location of Frogmore House, a royal retreat, and Frogmore Cottage. ...
was probably the pinnacle of its work, and at 30 tons one of the largest. It was not until the 1880s that rival machinery and works could compete with the MacDonald works.
Modern methods of carving include using computer-controlled rotary bits and sandblasting
Sandblasting, sometimes known as abrasive blasting, is the operation of forcibly propelling a stream of abrasive material against a surface under high pressure to smooth a rough surface, roughen a smooth surface, shape a surface or remove s ...
over a rubber stencil. Leaving the letters, numbers, and emblems exposed and the remainder of the stone covered with rubber, the blaster can create virtually any kind of artwork or epitaph.
The stone known as "black granite" is usually gabbro, which has a completely different chemical composition.
Buildings
 Granite has been extensively used as a dimension stone and as flooring tiles in public and commercial buildings and monuments. Aberdeen in Scotland, which is constructed principally from local granite, is known as "The Granite City". Because of its abundance in New England, granite was commonly used to build foundations for homes there. The
Granite has been extensively used as a dimension stone and as flooring tiles in public and commercial buildings and monuments. Aberdeen in Scotland, which is constructed principally from local granite, is known as "The Granite City". Because of its abundance in New England, granite was commonly used to build foundations for homes there. The Granite Railway
The Granite Railway was one of the first railroads in the United States, built to carry granite from Quincy, Massachusetts, to a dock on the Neponset River in Milton. From there boats carried the heavy stone to Charlestown for construction o ...
, America's first railroad, was built to haul granite from the quarries in Quincy, Massachusetts, to the Neponset River in the 1820s.
Engineering
Engineers have traditionally used polished granitesurface plate
A surface plate is a solid, flat plate used as the main horizontal reference plane for precision inspection, marking out (layout), and tooling setup. The surface plate is often used as the baseline for all measurements to a workpiece, theref ...
s to establish a plane of reference, since they are relatively impervious, inflexible, and maintain good dimensional stability. Sandblasted concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most wid ...
with a heavy aggregate content has an appearance similar to rough granite, and is often used as a substitute when use of real granite is impractical. Granite tables are used extensively as bases or even as the entire structural body of optical instruments, CMMs, and very high precision CNC machines because of granite's rigidity, high dimensional stability, and excellent vibration characteristics. A most unusual use of granite was as the material of the tracks of the Haytor Granite Tramway, Devon, England, in 1820. Granite block is usually processed into slabs, which can be cut and shaped by a cutting center. In military engineering, Finland planted granite boulders along its Mannerheim Line to block invasion by Russian tanks in the Winter War of 1939–40.
Paving
Granite is used as a pavement material. This is because it is extremely durable, permeable and requires little maintenance. For example, in Sydney, Australia black granite stone is used for the paving and kerbs throughout the Central Business District.Curling stones
 Curling stones are traditionally fashioned of Ailsa Craig granite. The first stones were made in the 1750s, the original source being
Curling stones are traditionally fashioned of Ailsa Craig granite. The first stones were made in the 1750s, the original source being Ailsa Craig
Ailsa Craig (; sco, Ailsae Craig; gd, Creag Ealasaid) is an island of in the outer Firth of Clyde, west of mainland Scotland, upon which microgranite has long been quarried to make curling stones. The now-uninhabited island comprises the ...
in Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a Anglo-Scottish border, border with England to the southeast ...
. Because of the rarity of this granite, the best stones can cost as much as US$1,500. Between 60 and 70 percent of the stones used today are made from Ailsa Craig granite, although the island is now a wildlife reserve and is still used for quarrying under license for Ailsa granite by Kays of Scotland
Kays of Scotland is the only remaining UK manufacturer and supplier of curling stones. Founded in 1851, it retains exclusive rights to harvest granite from Ailsa Craig, granted by the Marquess of Ailsa. Kays of Scotland produces the only stone ...
for curling stones.
Rock climbing
Granite is one of the rocks most prized by climbers, for its steepness, soundness, crack systems, and friction. Well-known venues for granite climbing include the Yosemite Valley, the Bugaboos, theMont Blanc
Mont Blanc (french: Mont Blanc ; it, Monte Bianco , both meaning "white mountain") is the highest mountain in the Alps and Western Europe, rising above sea level. It is the second-most prominent mountain in Europe, after Mount Elbrus, and ...
massif (and peaks such as the Aiguille du Dru, the Mourne Mountains, the Adamello-Presanella Alps
The Adamello-Presanella Alps Alpine group is a mountain range in the Southern Limestone Alps mountain group of the Eastern Alps. It is located in northern Italy, in the provinces of Trentino and Brescia. The name stems from its highest peaks: Ada ...
, the Aiguille du Midi
The Aiguille du Midi () is a mountain in the Mont Blanc massif within the French Alps. It is a popular tourist destination and can be directly accessed by cable car from Chamonix that takes visitors close to Mont Blanc.
Cable car
The idea fo ...
and the Grandes Jorasses), the Bregaglia
Bregaglia (Italian and rm, ) is a municipality in the Maloja Region in the canton of Grisons in Switzerland. It was formed by the 2010 merger of the municipalities of Bondo, Castasegna, Soglio, Stampa and Vicosoprano, all located in the Val ...
, Corsica, parts of the Karakoram (especially the Trango Towers
__NOTOC__
The Trango Towers ( ur, ) are a family of rock towers situated in Gilgit-Baltistan, in the north of Pakistan. The Towers offer some of the largest cliffs and most challenging rock climbing in the world, and every year a number of expedi ...
), the Fitzroy Massif, Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and g ...
, Baffin Island, Ogawayama
is a 2,418m tall mountain on the border of Nagano and Yamanashi prefectures in Japan. It is a famous rock climbing
Rock climbing is a sport in which participants climb up, across, or down natural rock formations. The goal is to reach the ...
, the Cornish coast, the Cairngorms
The Cairngorms ( gd, Am Monadh Ruadh) are a mountain range in the eastern Highlands of Scotland closely associated with the mountain Cairn Gorm. The Cairngorms became part of Scotland's second national park (the Cairngorms National Park) on 1 S ...
, Sugarloaf Mountain
Sugarloaf Mountain ( pt, Pão de Açúcar, ) is a peak situated in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, at the mouth of Guanabara Bay on a peninsula that juts out into the Atlantic Ocean. Rising above the harbor, the peak is named for its resemblance to ...
in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, and the Stawamus Chief
The Stawamus Chief, officially Stawamus Chief Mountain (often referred to as simply The Chief, or less commonly Squamish Chief), is a granitic dome located adjacent to the town of Squamish, British Columbia, Canada. It towers over above the wa ...
, British Columbia, Canada.
Gallery
St. Louis
St. Louis () is the second-largest city in Missouri, United States. It sits near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri Rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a population of 301,578, while the bi-state metropolitan area, which e ...
riverfront
A riverfront is a region along a river. Often in larger cities that are traversed or bordered by one or more rivers, the riverfront is lined with marinas, docks, cafes, museums, parks, or minor attractions. Today many riverfronts are a staple of ...
and for the piers of the Eads Bridge
The Eads Bridge is a combined road and railway bridge over the Mississippi River connecting the cities of St. Louis, Missouri and East St. Louis, Illinois. It is located on the St. Louis riverfront between Laclede's Landing, to the north, and ...
(background)
File:Torres del Paine, Patagonia (2004).jpg, The granite peaks of the Cordillera Paine in the Chilean Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and g ...
File:Yosemite 20 bg 090404.jpg, alt=Half Dome, Yosemeite National Park, Half Dome, Yosemite National Park, is actually a granite arête
An arête ( ) is a narrow ridge of rock which separates two valleys. It is typically formed when two glaciers erode parallel U-shaped valleys. Arêtes can also form when two glacial cirques erode headwards towards one another, although frequ ...
and is a popular rock climbing destination
File:Rixö granitbrott 4.jpg, Rixö red granite quarry in Lysekil, Sweden
File:Auyuittuq National Park, Baffin Island, Nunavut -c.jpg, Granite in Auyuittuq National Park
Auyuittuq National Park ( iu, ᐊᐅᔪᐃᑦᑐᖅ, , "the land that never melts") is a national park located on Baffin Island's Cumberland Peninsula, in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, the largest political subdivision of Canada. The park was ...
on Baffin Island, Canada
File:Paarl Mountain04.jpg, Granite in Paarl
Paarl (; Afrikaans: ; derived from ''Parel'', meaning "pearl" in Dutch) is a town with 112,045 inhabitants in the Western Cape province of South Africa. It is the third-oldest city and European settlement in the Republic of South Africa (after ...
, South Africa
See also
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * ,Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
*
*
* ,
*
*
References
; CitationsFurther reading
* * *External links
{{Authority control Felsic rocks National symbols of Finland Plutonic rocks Sculpture materials Symbols of Wisconsin Industrial minerals