Glans penis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In 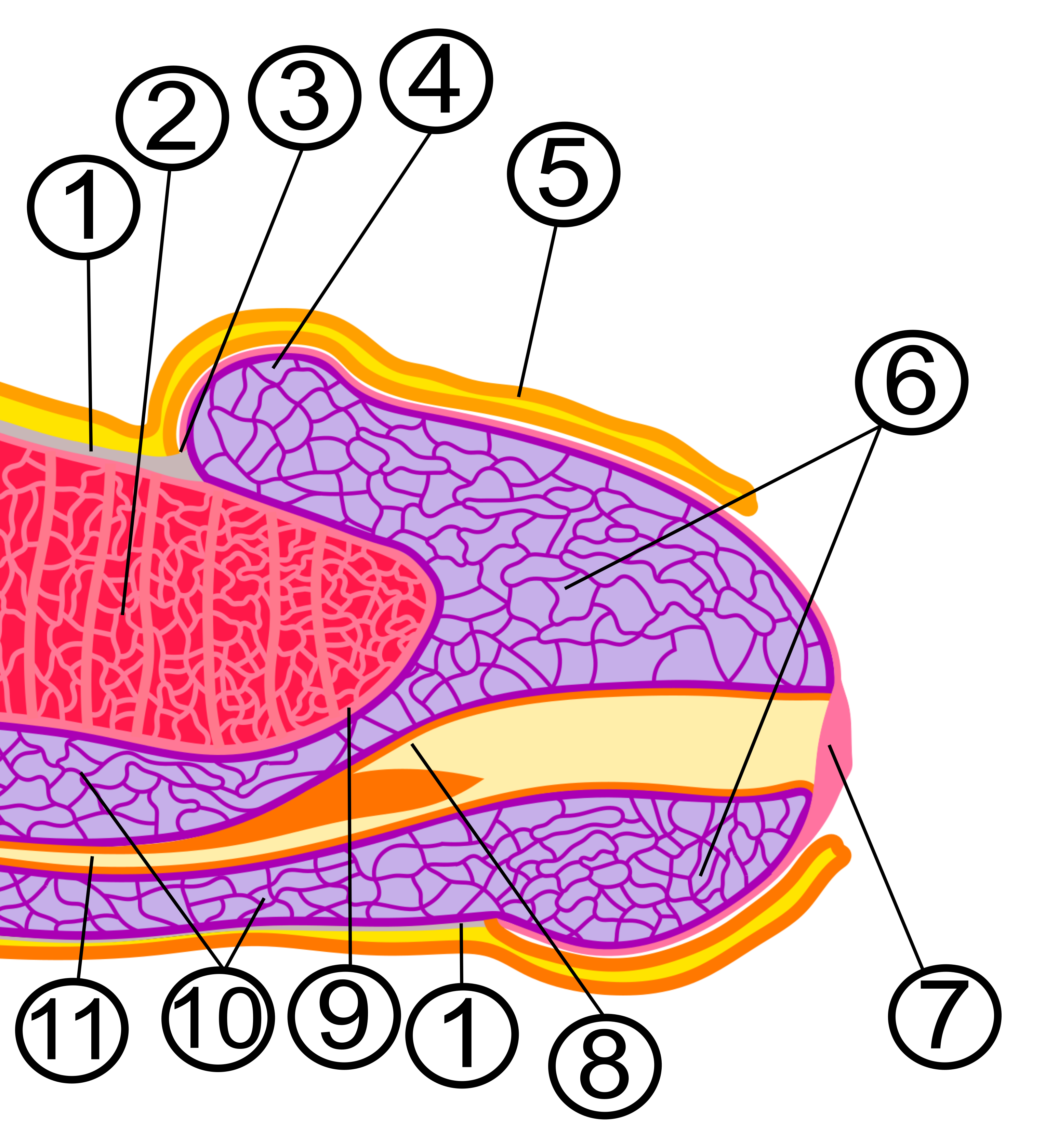

 The glans penis is a body of spongy erectile tissue that is moulded on the rounded ends of the two corpora cavernosa penis, extending farther on their upper than on their lower surfaces. It is the expanded cap of the corpus spongiosum, a sponge-like region that surrounds the male urethra within the penis maintaining it as a viable channel for
The glans penis is a body of spongy erectile tissue that is moulded on the rounded ends of the two corpora cavernosa penis, extending farther on their upper than on their lower surfaces. It is the expanded cap of the corpus spongiosum, a sponge-like region that surrounds the male urethra within the penis maintaining it as a viable channel for
 The glans develops as the terminal end of a phallic structure, called the genital tubercle, which forms in the embryo regardless of sex during the early weeks of
The glans develops as the terminal end of a phallic structure, called the genital tubercle, which forms in the embryo regardless of sex during the early weeks of
male
Male (Planet symbols, symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or Egg cell, ovum, in the process of fertilisation. A male organism cannot sexual repro ...
human anatomy
Human anatomy (gr. ἀνατομία, "dissection", from ἀνά, "up", and τέμνειν, "cut") is primarily the scientific study of the morphology of the human body. Anatomy is subdivided into gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. Gross ...
, the glans penis or penile glans, commonly referred to as the glans, (; from Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''glans'' meaning "acorn") is the bulbous structure at the distal end of the human penis
In Human body, human anatomy, the penis (; : penises or penes; from the Latin ''pēnis'', initially 'tail') is an external sex organ (intromittent organ) through which males urination, urinate and ejaculation, ejaculate, as Penis, on other anim ...
that is the human male's most sensitive erogenous zone and primary anatomical
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old scien ...
source of sexual pleasure. The glans penis is present in the male reproductive organs of human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s and most other mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s where it may appear smooth, spiny, elongated or divided. It is externally lined with mucosal tissue, which creates a smooth texture and glossy appearance. In humans, the glans is located over the distal ends of the corpora cavernosa and is a continuation of the corpus spongiosum of the penis. At the summit appears the urinary meatus and at the base forms the corona glandis. An elastic band of tissue, known as the frenulum, runs on its ventral surface. In men who are not circumcised, it is completely or partially covered by a fold of skin called the foreskin
In male Human body, human anatomy, the foreskin, also known as the prepuce (), is the double-layered fold of Human skin, skin, Mucous membrane, mucosal and Muscle tissue, muscular tissue at the distal end of the human penis that covers the glans ...
. In adults, the foreskin can generally be retracted over and past the glans manually or sometimes automatically during an erection
An erection (clinically: penile erection or penile tumescence) is a Physiology, physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, ...
.
The glans penis develops as the terminal end of the genital tubercle during the embryonic development of the male fetus. The tubercle is present in the embryos of both sexes as an outgrowth in the caudal region that later develops into a primordial phallus. Exposure to male hormones (androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
s) initiates the tubercle's development into a penis making the glans penis anatomically homologous to the clitoral glans in females.
The glans is more commonly known as the "head" or the "tip" of the penis, and colloquially referred to in British English
British English is the set of Variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United Kingdom, especially Great Britain. More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in England, or, more broadly, to ...
and Irish English as the "bellend".

Structure

 The glans penis is a body of spongy erectile tissue that is moulded on the rounded ends of the two corpora cavernosa penis, extending farther on their upper than on their lower surfaces. It is the expanded cap of the corpus spongiosum, a sponge-like region that surrounds the male urethra within the penis maintaining it as a viable channel for
The glans penis is a body of spongy erectile tissue that is moulded on the rounded ends of the two corpora cavernosa penis, extending farther on their upper than on their lower surfaces. It is the expanded cap of the corpus spongiosum, a sponge-like region that surrounds the male urethra within the penis maintaining it as a viable channel for ejaculation
Ejaculation is the discharge of semen (the ''ejaculate''; normally containing sperm) from the penis through the urethra. It is the final stage and natural objective of male sexual stimulation, and an essential component of natural conception. ...
. The glans is covered by a stratified squamous epithelium
A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural ...
and a dense layer of connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
equivalent to the dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (skin), epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis (anatomy), cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from s ...
of typical skin. The papillary layer of the dermis blends into the dense connective tissue forming the tunica albuginea of the corpus spongiosum behind the glans. The external lining with mucosal tissue is responsible for its typical smooth texture and appearance.
The increase of arterial flow during erection
An erection (clinically: penile erection or penile tumescence) is a Physiology, physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, ...
fills the erectile tissue with blood causing the glans to grow in size and sensitivity. While the penis is rigid when erect, the glans itself remains slightly softer. The soft cushiony texture of the glans absorbs impact during rigorous instances of copulation. The proportional size of the glans penis can vary among males. While the shape of the glans is typically acorn-like, in some men it might be wider in circumference than the shaft, giving the penis a mushroom-like appearance, while in others it might be narrower and more akin to a probe in shape.
The reason for the shape of the glans is uncertain. Some researchers have suggested that it evolved to become acorn-, mushroom- or cone-shaped so that, during copulation, it acts to remove any semen from previous sex partners. However, that is not supported when looking at primate
Primates is an order (biology), order of mammals, which is further divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include lemurs, galagos, and Lorisidae, lorisids; and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include Tarsiiformes, tarsiers a ...
relatives which have different mating behaviors.
At the summit of the glans is the slit-like vertical external urethral orifice, called the urinary meatus, through which urine, semen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is a bodily fluid that contains spermatozoon, spermatozoa which is secreted by the male gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphrodite, hermaphroditic animals. In humans and placen ...
and pre-ejaculatory fluid exit the penis. The circumference of the base of the glans forms a rounded projecting border, the corona glandis, overhanging a deep retroglandular groove known as the ''coronal sulcus''. Behind the corona is the neck of the penis, which separates the glans and the penile shaft. Ventrally, the two glans wings merge on the midline forming the septum glandis and a triangle or a V-shaped area under it. The frenulum is the highly vascularized elastic band of tissue located on the underside of the glans that connects the foreskin to the head of the penis. The frenulum is supple enough to allow the retraction of the foreskin over the glans and pull it back when the erection is gone. In flaccid state, it tightens to narrow the foreskin opening.
Innervation
The glans and the frenulum are innervated by the bilateral dorsal nerve of the penis and the perineal nerve, both divisions of the pudendal nerve. Branches of the dorsal nerve extend through the glans ventrolaterally displaying a three-dimensional innervation pattern. The main branches form smaller bundles of nerves that expand outwards into the tissue of the glans. The rich innervation of the glans penis reveals its function as a primary anatomical source of male sexual pleasure. Yang & Bradley argue; "the distinct pattern of innervation of the glans emphasizes its role as a sensory structure". While Yang & Bradley's (1998) report "showed no areas in the glans to be more densely innervated than others.", Halata & Munger (1986) report that the density of several nerve terminals is greatest in the corona glandis. Halata & Spathe (1997) reported: "The glans penis contains a predominance of free nerve endings, numerous genital end bulbs and rarely Pacinian and Ruffinian corpuscles. Merkel nerve endings and Meissner's corpuscles ( mechanoreceptors typically found in thick glabrous skin) are not present". The genital end bulbs, that are present throughout the glans, are most numerous in the corona and near the frenulum. Simple, Pacinian and Ruffinian corpuscles are identified predominantly in the corona glandis. The most numerous nerve terminals are free nerve endings present in almost every dermal papilla of the glans, as well as scattered throughout the deeperdermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (skin), epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis (anatomy), cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from s ...
.
Blood supply
The glans penis receives blood from the internal pudental artery through its branch, the dorsal artery of the penis, which also supplies the foreskin, and the penile shaft. Behind the corona, the terminal branches of the dorsal arteries anastomose with the axial arteries through perforating branches before they end in the glans. Branches of the dorsal artery curve around each side of the distal shaft to enter the glans and the frenulum ventrally. Venous drainage of the penis begins at the base of the glans. Small tributaries deriving from the corona form a venous plexus at the neck of the penis, known as the retro-coronal, or retro- balanic, plexus. Smaller paired venules run into the frenulum and the glans from its ventral surface. The deep dorsal vein, one of the two dorsal veins of the penis, serves as a common vessel receiving blood drained from the glans and the two corpora cavernosa through the circumflex veins that surround them.Foreskin
The glans is completely or partially covered by a double-layered fold of skin, known as theforeskin
In male Human body, human anatomy, the foreskin, also known as the prepuce (), is the double-layered fold of Human skin, skin, Mucous membrane, mucosal and Muscle tissue, muscular tissue at the distal end of the human penis that covers the glans ...
. In adults, glans exposure can be easily achieved by manual retraction of the foreskin and sometimes automatically during erection
An erection (clinically: penile erection or penile tumescence) is a Physiology, physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, ...
. The degree of automatic foreskin retraction varies considerably depending on the foreskin length. The foreskin can be characterized as long when the preputial orifice extends beyond the glans during erection, or medium when the orifice is located around the meatus. The primary purpose of the foreskin is considered to be the covering of the glans and the urinary meatus, while also maintaining the mucosa in a moist environment.
Foreskin rectractability gradually increases with age. In infancy the foreskin is fused to the glans. It remains non-retractable in early childhood
A child () is a human being between the stages of childbirth, birth and puberty, or between the Development of the human body, developmental period of infancy and puberty. The term may also refer to an unborn human being. In English-speaking ...
and it continues to be tight during preadolescence. The skin begins to loosen up significantly during puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
allowing the glans to be completely exposed when needed. By the age of eighteen, most boys will have a fully retractable foreskin.
In some cases, for cultural
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
, medical
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
, or prophylactic reasons, some men undergo circumcision
Circumcision is a procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, after which the foreskin is excised. T ...
or were circumcised as infants, a procedure in which the foreskin is partially or completely removed from the penis. The glans of circumcised men remains fully exposed and dry. Several studies have suggested that, generally, the glans of both circumcised and uncircumcised penises are equally sensitive.
Development
 The glans develops as the terminal end of a phallic structure, called the genital tubercle, which forms in the embryo regardless of sex during the early weeks of
The glans develops as the terminal end of a phallic structure, called the genital tubercle, which forms in the embryo regardless of sex during the early weeks of pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
. Initially undifferentiated, the tubercle develops into a penis during the development of the reproductive system depending on the exposure to male hormones, such as androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
s. In mammals, sexual differentiation is determined by the sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
that carries either an X or a Y (male) chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
. The Y chromosome contains a sex-determining gene ( SRY) that encodes a transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
for the protein TDF (testis determining factor) and triggers the creation of testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
for the embryo's development into a male.
Although the sex of the infant is determined from the moment of conception, the complete external differentiation of the organs begins about eight or nine weeks after conception. Some sources state that the process will be completed by the twelfth week, while others state that it is clearly evident by the thirteenth week and that the sex organs are fully developed by the sixteenth week.
Both the penis and clitoris develop from the same tissues that become the glans and shaft of the penis and this shared embryonic origin makes these two organs homologous (different versions of the same structure). In the female
An organism's sex is female ( symbol: ♀) if it produces the ovum (egg cell), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete (sperm cell) during sexual reproduction.
A female has larger gametes than a male. Females and ...
fetus the absence of testosterone will stop the growth of the phallus causing the tubercle to shrink and form the clitoris. In the male
Male (Planet symbols, symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or Egg cell, ovum, in the process of fertilisation. A male organism cannot sexual repro ...
fetus the presence of a Y chromosome leads to the development of the testes, which secrete a large amount of hormones called androgens. These hormones will cause the masculinization of the phenotypically indifferent organs. When exposed to testosterone, the genital tubercle elongates to form the penis
A penis (; : penises or penes) is a sex organ through which male and hermaphrodite animals expel semen during copulation (zoology), copulation, and through which male placental mammals and marsupials also Urination, urinate.
The term ''pen ...
. By fusion of the urogenital folds—elongated spindle-shaped structures that contribute to the formation of the urethral groove on the belly aspect of the genital tubercle—the urogenital sinus
The urogenital sinus is a body part of a human or other Placentalia, placental only present in the development of the urinary system, development of the urinary and development of the reproductive organs, reproductive organs. It is the ventral p ...
closes completely to form the spongy urethra and the labioscrotal swellings unite to form the scrotum. The secretion of testosterone during this phase plays a decisive role in the final shaping of the penis. After birth, testosterone levels drop significantly until puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
.
Clinical significance
Theepithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
of the glans penis consists of mucosal tissue. Birley ''et al.'' report that excessive washing with soap may dry the mucous membrane which covers the glans penis and cause non-specific dermatitis
Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened ...
. The condition is described as an inflammation of the skin, often caused by an irritating substance or a contact allergy. Sensitivity to chemicals in certain products can cause an allergic reaction, including irritation, itching and rash.
Inflammation of the glans penis is known as balanitis. It is a treatable condition that occurs in about 3–11% of males (up to 35% of diabetic males). Edwards reported that it is generally more common in males who have poor hygiene
Hygiene is a set of practices performed to preserve health.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene refers to conditions and practices that help to maintain health and prevent the spread of diseases." Personal hygiene refer ...
habits or have not been circumcised. It has many causes, including irritation or infection with a wide variety of pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
s. Symptoms of balanitis may appear suddenly or develop gradually. They might include pain, irritation, redness or red patches on the glans penis. Careful identification of the cause with the aid of patient history, physical examination, swabs and cultures, and biopsy are essential in order to determine the proper treatment.
The meatus (opening) of the urethra located at the tip of the glans might become subject to meatal stenosis, a condition mostly seen as a late complication of circumcision. It occurs in about 2–20% of circumcised boys and it is rarely seen in uncircumcised men. It is characterized by a narrowing of the meatus, which might cause sudden or often urges to urinate and burning during the process.
For some individuals who experience difficulty in achieving full glanular engorgement of glans penis, they may be diagnosed with soft glans syndrome ( glans insufficiency syndrome). It is often undiagnosed in the general population due to the lack of a standardized nomenclature.
Other animals
Mammals
Carnivores
Malefelid
Felidae ( ) is the Family (biology), family of mammals in the Order (biology), order Carnivora colloquially referred to as cats. A member of this family is also called a felid ( ).
The 41 extant taxon, extant Felidae species exhibit the gre ...
s are able to urinate backwards by curving the tip of the glans penis backward. In cats, the glans penis is covered with spines. Penile spines also occur on the glans of male and female spotted hyenas. In male dogs the glans penis is smooth and consists of two parts called the '' bulbus glandis'' and ''pars longa glandis''. The glans of a fossa's penis extends about halfway down the shaft and is spiny except at the tip. In comparison, the glans of felids is short and spiny, while that of viverrids is smooth and long.
Rodents
The glans penis of the marsh rice rat is long and robust,Hooper and Musser, 1964, p. 13 averaging long and broad.Winkelmann's mouse
Winkelmann's mouse (''Peromyscus winkelmanni'') is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae, It is a species of the genus '' Peromyscus'', a closely related group of New World mice often called "deermice". It is endemic to Mexico, and is na ...
can most readily be distinguished from its close relatives by its partially corrugated glans penis. In '' Thomasomys ucucha'', the glans penis is rounded, short, and small and is superficially divided into left and right halves by a trough at the top and a ridge at the bottom. Most of the glans is covered with spines, except for an area near the tip. The glans penis of a male cape ground squirrel is large with a prominent baculum
The baculum (: bacula), also known as the penis bone, penile bone, ''os penis'', ''os genitale'', or ''os priapi'', is a bone in the penis of many placental mammals. It is not present in humans, but is present in the penises of some primates, ...
.Skurski, D., J. Waterman. 2005. "Xerus inauris", ''Mammalian Species'' 781:1-4.
Perissodactyls
When erect, the glans of a horse's penis increases by 3 to . The urethra opens within the urethral fossa, a small pouch at the distal end of the glans. Unlike the human glans, the glans of a horse's penis extends backwards on its shaft.Marsupials, monotremes and bats
The shape of the glans varies among differentmarsupial
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a r ...
species. In most marsupials, the glans is divided, but male macropods have an undivided glans penis.
The glans penis is also divided into two parts in platypuses and echidnas.
Males of Racey's pipistrelle bat have a narrow, egg-shaped glans penis.Bates et al., 2006, pp. 306–307
See also
* Corona of glans penis * Pearly penile papulesReferences
External links
{{Authority control Mammal male reproductive system Human penis Human penis anatomy Human male reproductive system