Geography of Greece on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
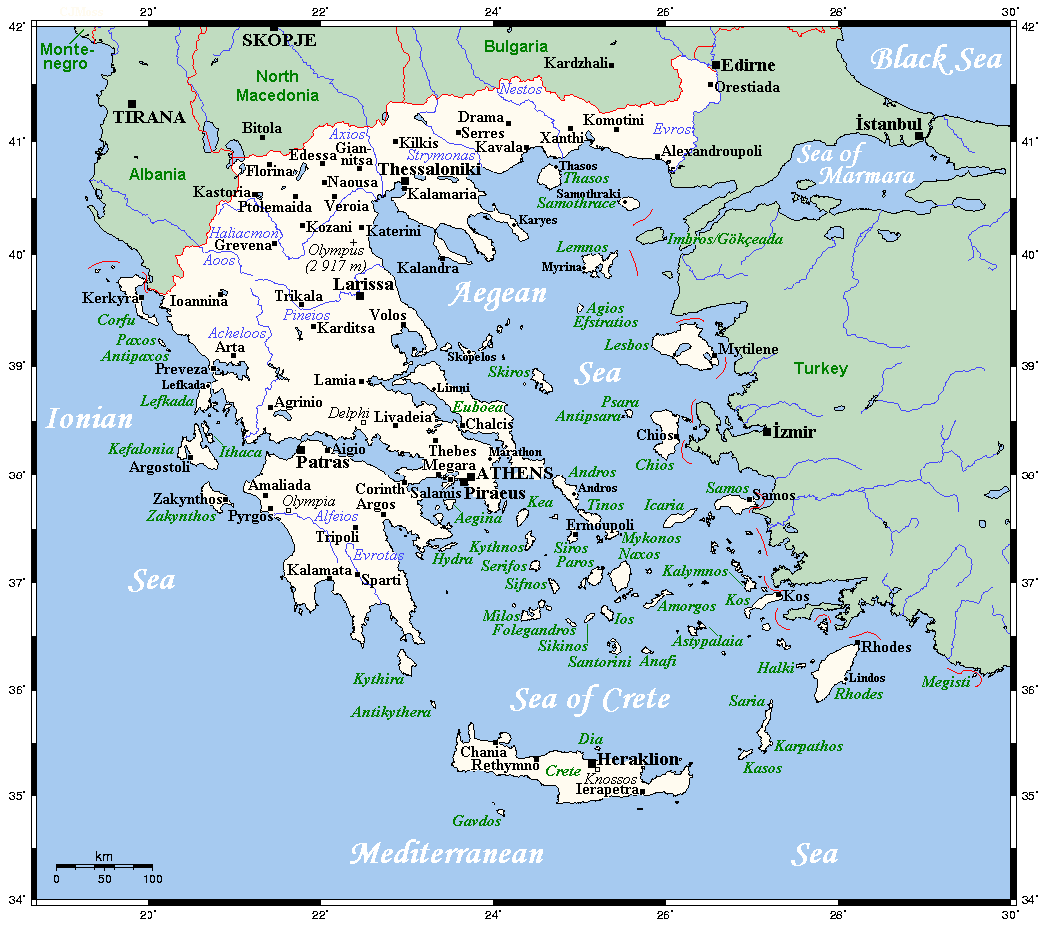
 Greece is located in South Eastern Europe, bordering the Ionian Sea and the
Greece is located in South Eastern Europe, bordering the Ionian Sea and the
/ref> It has an
File:Island of Crete, Greece.JPG, Crete (
 Greece is a mostly mountainous country with a very long coastline, filled with peninsulas and islands.
The climate can range from cold semi-arid to cold climate mountain forests.
Greece's natural hazards include severe earthquakes, floods, droughts and wildfires. Current environmental issues in Greece include
Greece is a mostly mountainous country with a very long coastline, filled with peninsulas and islands.
The climate can range from cold semi-arid to cold climate mountain forests.
Greece's natural hazards include severe earthquakes, floods, droughts and wildfires. Current environmental issues in Greece include
File:Mytikas.jpg,
''A Geological Companion to Greece and the Aegean'' by Michael and Reynold Higgins, Cornell University Press, 1996
{{DEFAULTSORT:Geography Of Greece
Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
is a country in Southeastern Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe is a geographical sub-region of Europe, consisting primarily of the region of the Balkans, as well as adjacent regions and Archipelago, archipelagos. There are overlapping and conflicting definitions of t ...
, on the Balkan Peninsula
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
. It is bordered to the north by Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
, North Macedonia
North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the n ...
and Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
; to the east by Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, and is surrounded to the east by the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some . In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn con ...
, to the south by the Cretan and the Libyan seas, and to the west by the Ionian Sea which separates Greece from Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
.
The country consists of an extremely rough, mountainous, peninsular mainland jutting out into the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
at the southernmost tip of the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
, and two smaller peninsulas projecting from it:
the Chalkidiki and the Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridg ...
, which is joined to the mainland by the Isthmus of Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
. Greece also has many islands, of various sizes, the largest being Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
, Euboea, Lesvos, Rhodes
Rhodes (; ) is the largest of the Dodecanese islands of Greece and is their historical capital; it is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, ninth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Administratively, the island forms a separ ...
, Chios
Chios (; , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest Greece, Greek list of islands of Greece, island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea, and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, tenth largest island in the Medi ...
, Kefalonia
Kefalonia or Cephalonia (), formerly also known as Kefallinia or Kephallonia (), is the largest of the Ionian Islands in western Greece and the 6th-largest island in Greece after Crete, Euboea, Lesbos, Rhodes and Chios. It is also a separate regio ...
, and Corfu
Corfu ( , ) or Kerkyra (, ) is a Greece, Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands; including its Greek islands, small satellite islands, it forms the margin of Greece's northwestern frontier. The island is part of the Corfu (regio ...
; groups of smaller islands include the Dodecanese
The Dodecanese (, ; , ''Dodekánisa'' , ) are a group of 15 larger and 150 smaller Greek islands in the southeastern Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean, off the coast of Anatolia, of which 26 are inhabited. This island group generally define ...
and the Cyclades
The CYCLADES computer network () was a French research network created in the early 1970s. It was one of the pioneering networks experimenting with the concept of packet switching and, unlike the ARPANET, was explicitly designed to facilitate i ...
. According to the ''CIA World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the United States' Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print ve ...
'', Greece has of coast
A coast (coastline, shoreline, seashore) is the land next to the sea or the line that forms the boundary between the land and the ocean or a lake. Coasts are influenced by the topography of the surrounding landscape and by aquatic erosion, su ...
line, the largest in the Mediterranean Basin.
Greece's latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
ranges from 35°N to 42°N and its longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east- west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lett ...
from 19°E to 28°E. As a result of this and its physical geography, the country has considerable climatic variation.
Physical geography
 Greece is located in South Eastern Europe, bordering the Ionian Sea and the
Greece is located in South Eastern Europe, bordering the Ionian Sea and the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
. It is a peninsular country, with an archipelago of about 3,000 islands.
It has a total area of , of which land area is 130,647 km2 and internal waters (lakes and rivers) account for 1,310 km2. Land boundaries with Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
(212 km), North Macedonia
North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the n ...
(234 km), Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
(472 km) and Turkey (192 km) measure approximately 1,110 km in total. Of the country's total territory, 83.33% or is mainland territory and the rest 16.67% or is island territory.Artificial Structures and Shorelines/ref> It has an
exclusive economic zone
An exclusive economic zone (EEZ), as prescribed by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, is an area of the sea in which a sovereign state has exclusive rights regarding the exploration and use of marine natural resource, reso ...
of which is the 53rd largest.
Greece's coastline measures .
80% of Greece is mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher t ...
ous. The Pindus mountain range lies across the center of the country in a northwest-to-southeast direction, with a maximum elevation of 2,637 m. Extensions of the same mountain range stretch across the Peloponnese and underwater across the Aegean, forming many of the Aegean Islands including Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
, and joining with the Taurus Mountains of southern Turkey. Central and western Greece contain high and steep peaks intersected by many canyons and other karstic landscapes, including the Meteora
The Meteora (; , ) is a rock formation in the regional unit of Trikala, in Thessaly, in northwestern Greece, hosting one of the most prominent complexes of Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox monastery, monasteries, viewed locally as se ...
and the Vikos Gorges – the latter being the world's deepest canyon in proportion to its width, and the third deepest after the Copper Canyon in Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
and the Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon is a steep-sided canyon carved by the Colorado River in Arizona, United States. The Grand Canyon is long, up to wide and attains a depth of over a mile ().
The canyon and adjacent rim are contained within Grand Canyon Nati ...
in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, plunging vertically for more than 1,100 metres.
Mount Olympus
Mount Olympus (, , ) is an extensive massif near the Thermaic Gulf of the Aegean Sea, located on the border between Thessaly and Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia, between the regional units of Larissa (regional unit), Larissa and Pieria (regional ...
is the highest point in Greece, the 7th highest and the 9th most prominent mountain in mainland Europe (together with Gerlachovský štít and including Großglockner as a separate mountain), rising to 2,917 m above sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an mean, average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal Body of water, bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical ...
. The Rhodope Mountains form the border between Greece and Bulgaria; that area is covered with vast and thick forests.
Plains are found in eastern Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
, in central Macedonia and in Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
.
Elevation extremes
* Highest point:Mount Olympus
Mount Olympus (, , ) is an extensive massif near the Thermaic Gulf of the Aegean Sea, located on the border between Thessaly and Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia, between the regional units of Larissa (regional unit), Larissa and Pieria (regional ...
:
* Lowest point: Epitalio:
Extremities of Greece
The extreme points of Greece are *North: Ormenio village (42°00′41″ N, 26°13′15″ E) *South: Gavdos island (35°48′11″ N, 24°07′25″ E) *East: Strongyli island (36°06′17″ N, 29°38′39″ E) *West: Othonoi island (40°51′11″ N, 19°22′41″ E)Natural resources
Greece has notable deposits ofpetroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil or simply oil, is a naturally occurring, yellowish-black liquid chemical mixture found in geological formations, consisting mainly of hydrocarbons. The term ''petroleum'' refers both to naturally occurring un ...
, magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula . It is one of the iron oxide, oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetism, ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetization, magnetized to become a ...
, lignite, bauxite
Bauxite () is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)), and diaspore (α-AlO(OH) ...
, hydropower
Hydropower (from Ancient Greek -, "water"), also known as water power or water energy, is the use of falling or fast-running water to Electricity generation, produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by energy transformation, ...
, marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is ty ...
, limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
Ancient Greeks used limestone as a durable building material in many buildings such as the Parthenon
The Parthenon (; ; ) is a former Ancient Greek temple, temple on the Acropolis of Athens, Athenian Acropolis, Greece, that was dedicated to the Greek gods, goddess Athena. Its decorative sculptures are considered some of the high points of c ...
. Greece has substantial marine life
Marine life, sea life or ocean life is the collective ecological communities that encompass all aquatic animals, aquatic plant, plants, algae, marine fungi, fungi, marine protists, protists, single-celled marine microorganisms, microorganisms ...
with plentiful fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
in its EEZ.
Land use
*''Arable land:'' 19.71% *''Permanent crops:'' 8.95% *''Other:'' 71.37% (2012 est.) ''Irrigated land:'' 15,550 km2 (2007)
Mainland
Mainland Greece forms the southernmost part of theBalkan peninsula
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
with two additional smaller peninsulas projecting from it: the Chalkidiki and the Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridg ...
. The north of the country includes the regions of Macedonia and Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
. To the south the mainland narrows and includes the regions of Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
, Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
and Central Greece, where the region of Attica
Attica (, ''Attikḗ'' (Ancient Greek) or , or ), or the Attic Peninsula, is a historical region that encompasses the entire Athens metropolitan area, which consists of the city of Athens, the capital city, capital of Greece and the core cit ...
and the capital city Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
are located. Further south, the smaller peninsula of Peloponnese is separated from the rest of the Greek mainland by the Corinthian and Saronic Gulfs, but joined by the Isthmus of Corinth
The Isthmus of Corinth ( Greek: Ισθμός της Κορίνθου) is the narrow land bridge which connects the Peloponnese peninsula with the rest of the mainland of Greece, near the city of Corinth. The wide Isthmus was known in the a ...
.
Mainland Greece covers about 80% of the total territory and is largely mountainous. The largest mountain range of Greece is the Pindus range, the southern extension of the Dinaric Alps
The Dinaric Alps (), also Dinarides, are a mountain range in Southern Europe, Southern and Southcentral Europe, separating the continental Balkan Peninsula from the Adriatic Sea. They stretch from Italy in the northwest through Slovenia, Croatia ...
, which forms the spine of the Greek mainland, separating Epirus from Thessaly and Macedonia. The country's tallest mountain is Mount Olympus
Mount Olympus (, , ) is an extensive massif near the Thermaic Gulf of the Aegean Sea, located on the border between Thessaly and Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia, between the regional units of Larissa (regional unit), Larissa and Pieria (regional ...
, which also separates Thessaly from Macedonia. Its highest peak rises to 2,918 m above sea level, making it the second highest of the Balkan peninsula after Musala in the Rila Mountain.
The number of islands vary between 1,200 and 6,000. A figure frequently cited in travel guides is 1,425 islands, of which 166 are said to be inhabited. The Greek Tourism Organization reports a figure of 6,000, with 227 of them inhabited. Paris Match, however, raises this number to 9,841 islands, of which only 169 have a recorded continuous human presence.
The Greek islands account for about 20% of the country's total territory, and vary greatly in size as well as in climate. The country's largest island is Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
, with Euboea being second largest. Other large Greek islands include Rhodes
Rhodes (; ) is the largest of the Dodecanese islands of Greece and is their historical capital; it is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, ninth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Administratively, the island forms a separ ...
and Lesbos in the Aegean Sea, and Corfu
Corfu ( , ) or Kerkyra (, ) is a Greece, Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands; including its Greek islands, small satellite islands, it forms the margin of Greece's northwestern frontier. The island is part of the Corfu (regio ...
and Cephalonia
Kefalonia or Cephalonia (), formerly also known as Kefallinia or Kephallonia (), is the largest of the Ionian Islands in western Greece and the 6th-largest island in Greece after Crete, Euboea, Lesbos, Rhodes and Chios. It is also a separate regio ...
in the Ionian Sea. Many of the smaller Greek islands form groups or chains, often called archipelagos, with notable examples being the Cyclades
The CYCLADES computer network () was a French research network created in the early 1970s. It was one of the pioneering networks experimenting with the concept of packet switching and, unlike the ARPANET, was explicitly designed to facilitate i ...
and the Sporades in the south and central Aegean Sea respectively.
Aegean
The islands of the Aegean Sea are situated between mainland Greece to the west and north,Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
to the east and the island of Crete to the south. Traditionally, the islands are classified into seven groups, from north to south:
* North Aegean Islands
* Sporades
* Euboea
* Saronic Islands
* Cyclades
The CYCLADES computer network () was a French research network created in the early 1970s. It was one of the pioneering networks experimenting with the concept of packet switching and, unlike the ARPANET, was explicitly designed to facilitate i ...
* Dodecanese
The Dodecanese (, ; , ''Dodekánisa'' , ) are a group of 15 larger and 150 smaller Greek islands in the southeastern Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean, off the coast of Anatolia, of which 26 are inhabited. This island group generally define ...
(Southern Sporades)
* Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
Ionian Islands
The Ionian Islands are a group of seven islands. The six northern islands lie off the western coast of Greece, in the Ionian Sea. The other island, Kythira, lies off the southern tip of thePeloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridg ...
. Kythira is part of the modern administrative region of Attica
Attica (, ''Attikḗ'' (Ancient Greek) or , or ), or the Attic Peninsula, is a historical region that encompasses the entire Athens metropolitan area, which consists of the city of Athens, the capital city, capital of Greece and the core cit ...
, not the Ionian Islands (''Ionioi Nisoi''). The Ionian Islands are distinct from the historical region of Ionia, which is today part of western Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
.
Crete
Crete is the largest island of Greece and the second largest in theEastern Mediterranean
The Eastern Mediterranean is a loosely delimited region comprising the easternmost portion of the Mediterranean Sea, and well as the adjoining land—often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea. It includes the southern half of Turkey ...
, after Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
. The island spans 260 km from east to west and 60 km from north to south at its widest. The island narrows in the region close to Ierapetra, where it is only 12 km wide. Crete covers an area of , with a coastline of 1046 km. It is surrounded to the north by the Sea of Crete; to the south by the Libyan Sea; to the west by the Myrtoan Sea; and to the east by the Karpathion Sea. It lies about 160 km south of the Greek mainland.
Crete is characterized by a mountain range crossing from west to east, formed by three different subranges:
*The White Mountains or Lefka Ori (2,452 m);
*The Idi Range ( Psiloritis () 2,456 m);
*The Dikti Mountains (2,148 m)
These encompass fertile plateaus, such as Lasithi, Omalos and Nidha; caves such as Diktaion and Idaion; and gorges such as the Samariá Gorge. The protected area of the Samariá Gorge is the home of the Cretan goat, or kri-kri, while the endangered Bearded vulture or lammergeyer lives in the Cretan mountains and gorges.
Crete's rivers include the Ieropotamos River in the southern part of the island.
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
photograph)
Environment
air pollution
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the Atmosphere of Earth, air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be Gas, gases like Ground-level ozone, ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles li ...
and water pollution.
Climate
The climate of Greece is mild. AMediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate ( ), also called a dry summer climate, described by Köppen and Trewartha as ''Cs'', is a temperate climate type that occurs in the lower mid-latitudes (normally 30 to 44 north and south latitude). Such climates typic ...
prevails on the coast and islands, and a strong Continental climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm to hot summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in central and eastern parts of the three northern-tier continents (North America, Europe, and Asia), typi ...
prevails in all of the mountainous regions of the interior. Summers are hot and dry and winters are cold and humid. Summer is rainless and the almost cloudless season lasts about three months. In July and August, the temperature usually rises to around 30–35 °C and even above 40 °C. In the eastern part of the country and especially in the archipelago, a cooling Etesian wind blows in the summer, but in big cities like Athens it can get sweltering hot. The wind can be very strong at times, which makes sailing difficult.
A special feature of Greek weather is the high amount of sunshine. It is available for six hours even in winter, and up to 12–13 hours a day in summer. The rains mostly occur in winter. Snow can be found everywhere in Greece, but it is rare in the archipelago. In low-lying areas, snow hardly ever stays on the ground more than 1 day. On the tops of the highest mountains, snow remains well into the summer. Spring and autumn are short in-between seasons when the weather is variable.
Extensive forest fires A forest fire
A wildfire, forest fire, or a bushfire is an unplanned and uncontrolled fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a bushfire ( in Au ...
cause problems almost every year in late summer. Sometimes they lead to widespread evacuations and even deaths.
Gallery
Mount Olympus
Mount Olympus (, , ) is an extensive massif near the Thermaic Gulf of the Aegean Sea, located on the border between Thessaly and Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia, between the regional units of Larissa (regional unit), Larissa and Pieria (regional ...
File:010607-0930-17 - Nea Kameni - Krater.jpg, Volcanic crater, Santorini
File:Acheloos river narrows 02.jpg, Achelous River
File:Taygetos Ilias 1.jpg, Taygetus (Mountain Range)
File:Mountains to the North.jpg, Pindus National Park
File:Zagori Vikos gorge Oxia towards Vikos.jpg, Vikos–Aoös National Park
File:Samaria Gorge 09.jpg, Samariá Gorge
File:Kremasta Lake 03.JPG, Kremasta (lake)
File:Pilion with monastery pau.JPG, Mount Pelion
File:Kanal von Potidea.jpg, Potidea Kanal, Chalkidiki
File:Manganari2.jpg, Manganari beach, Ios (island)
File:Stymfalia-north 2006.jpg, Landscape of Stymfalia with Mount Kyllini
File:Vai R05.jpg, Palm beach of Vai (Crete)
File:Navagio 01.jpg, Navagio, Zakynthos
Zakynthos (also spelled Zakinthos; ; ) or Zante (, , ; ; from the Venetian language, Venetian form, traditionally Latinized as Zacynthus) is a Greece, Greek island in the Ionian Sea. It is the third largest of the Ionian Islands, with an are ...
File:Parnassos1.jpg, Mount Parnassus
See also
* Geography of Europe * Greek names of mountains * List of earthquakes in Greece * List of islands of Greece * National parks of Greece * Wildlife of GreeceReferences
Further reading
''A Geological Companion to Greece and the Aegean'' by Michael and Reynold Higgins, Cornell University Press, 1996
{{DEFAULTSORT:Geography Of Greece