GRB 080319B on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
__NOTOC__
GRB 080319B was a
Hubble Pinpoints Record-Breaking Explosion
SkyWatch Show 165: Brightest Explosion Ever Seen
(mp3)
AAVSO Alert Notice 372 Possible naked-eye gamma-ray burst detected (GRB 080319B)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Grb 080319b 080319B Boötes 20080319 March 2008
gamma-ray burst
In gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are extremely energetic events occurring in distant Galaxy, galaxies which represent the brightest and most powerful class of explosion in the universe. These extreme Electromagnetic radiation, ele ...
(GRB) detected by the Swift
Swift or SWIFT most commonly refers to:
* SWIFT, an international organization facilitating transactions between banks
** SWIFT code
* Swift (programming language)
* Swift (bird), a family of birds
It may also refer to:
Organizations
* SWIF ...
satellite at 06:12 UTC on March 19, 2008. The burst set a new record for the farthest object that was observable with the naked eye
Naked eye, also called bare eye or unaided eye, is the practice of engaging in visual perception unaided by a magnification, magnifying, Optical telescope#Light-gathering power, light-collecting optical instrument, such as a telescope or microsc ...
: it had a peak visual apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the Irradiance, brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction (astronomy), ...
of 5.8 and remained visible to human eyes for approximately 30 seconds. The magnitude was brighter than 9.0 for approximately 60 seconds.
If viewed from 1 AU away, it would have had a peak apparent magnitude of −67.57 (21 quadrillion times brighter than the Sun seen from Earth). It had an absolute magnitude of −38.6, beaten by GRB 220101A with −39.4 in 2023.
Overview
The GRB'sredshift
In physics, a redshift is an increase in the wavelength, and corresponding decrease in the frequency and photon energy, of electromagnetic radiation (such as light). The opposite change, a decrease in wavelength and increase in frequency and e ...
was measured to be 0.937, which means that the explosion occurred about 7.5 billion () years ago (the lookback time), and it took the light that long to reach Earth. This is roughly half the time since the Big Bang
The Big Bang is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models based on the Big Bang concept explain a broad range of phenomena, including th ...
. The first scientific paper submitted on the event suggested that the GRB could have easily been seen to a redshift of 16 (essentially to the time in the universe when stars were just being formed, well into the age of reionization
In the fields of Big Bang theory and physical cosmology, cosmology, reionization is the process that caused electrically neutral atoms in the primordial universe to reionize after the lapse of the "Timeline of the Big Bang#Dark Ages, dark ages". ...
) from a sub-meter sized telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
equipped with near-infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
filters.
The afterglow of the burst set a new record for the "most intrinsically bright object ever observed by humans in the universe",
2.5 million times brighter than the brightest supernova to date, SN 2005ap.
Evidence suggests that the afterglow was particularly bright because its gamma jet pointed directly at Earth. This allowed an unprecedented examination of the jet structure, which appears to have consisted of a narrowly focused cone and a wider secondary one. If this is the norm for GRB jets, it follows that most GRB detections only capture the fainter wide cone, which means that most distant GRBs are too faint to detect with current telescopes. This would imply that GRBs are a far more common phenomenon than so far assumed.
A record for the number of observed bursts with the same satellite on one day, four, was also set. This burst was named with the suffix B since it was the second burst detected that day. There were five GRBs detected in a 24-hour period, including GRB 080320.
Until this gamma-ray burst event, the galaxy M83, at a distance of about 15 million light years, was the most distant object visible to the naked eye, albeit only under excellent conditions. The galaxy remains the most distant permanent object viewable without aid.
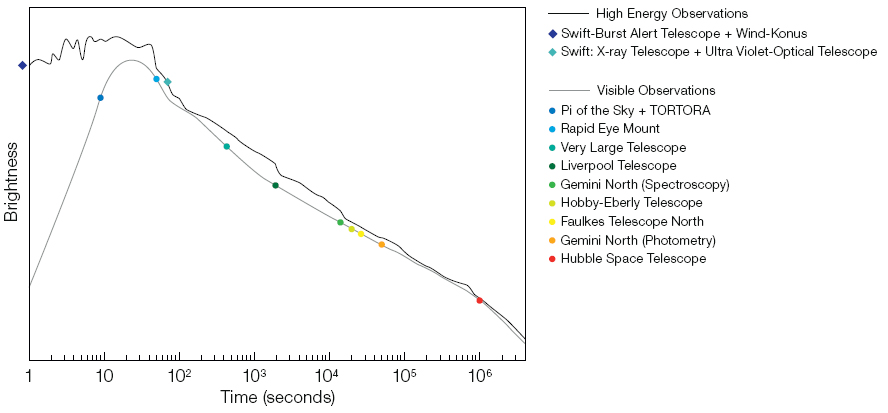
The plot below shows the brightness in both the optical wavelengths and at higher energy for the event. The first optical exposure started about 2 seconds before the source was first observed by the SWIFT telescope and lasted for 10 seconds. The emission in both curves then peaks at around 15–30 seconds before a long exponential decay.

See also
*GRB 080916C
GRB 080916C is a gamma-ray burst (GRB) that was recorded on September 16, 2008, in the Carina constellation and detected by NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope. The burst lasted for 23 minutes (1400 s). It is one of the most extreme gamma-ray ...
References
Citations
* *Database references
*External links
Hubble Pinpoints Record-Breaking Explosion
SkyWatch Show 165: Brightest Explosion Ever Seen
(mp3)
AAVSO Alert Notice 372 Possible naked-eye gamma-ray burst detected (GRB 080319B)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Grb 080319b 080319B Boötes 20080319 March 2008